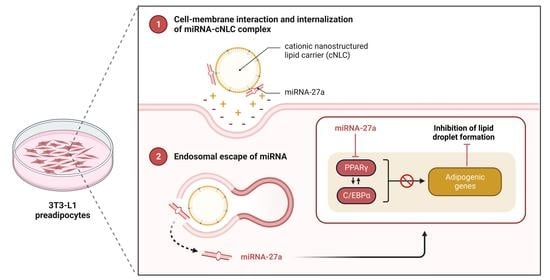
Development and Characterization of Cationic Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Drug Delivery Systems for miRNA-27a
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Development of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers by High-Pressure Homogenization
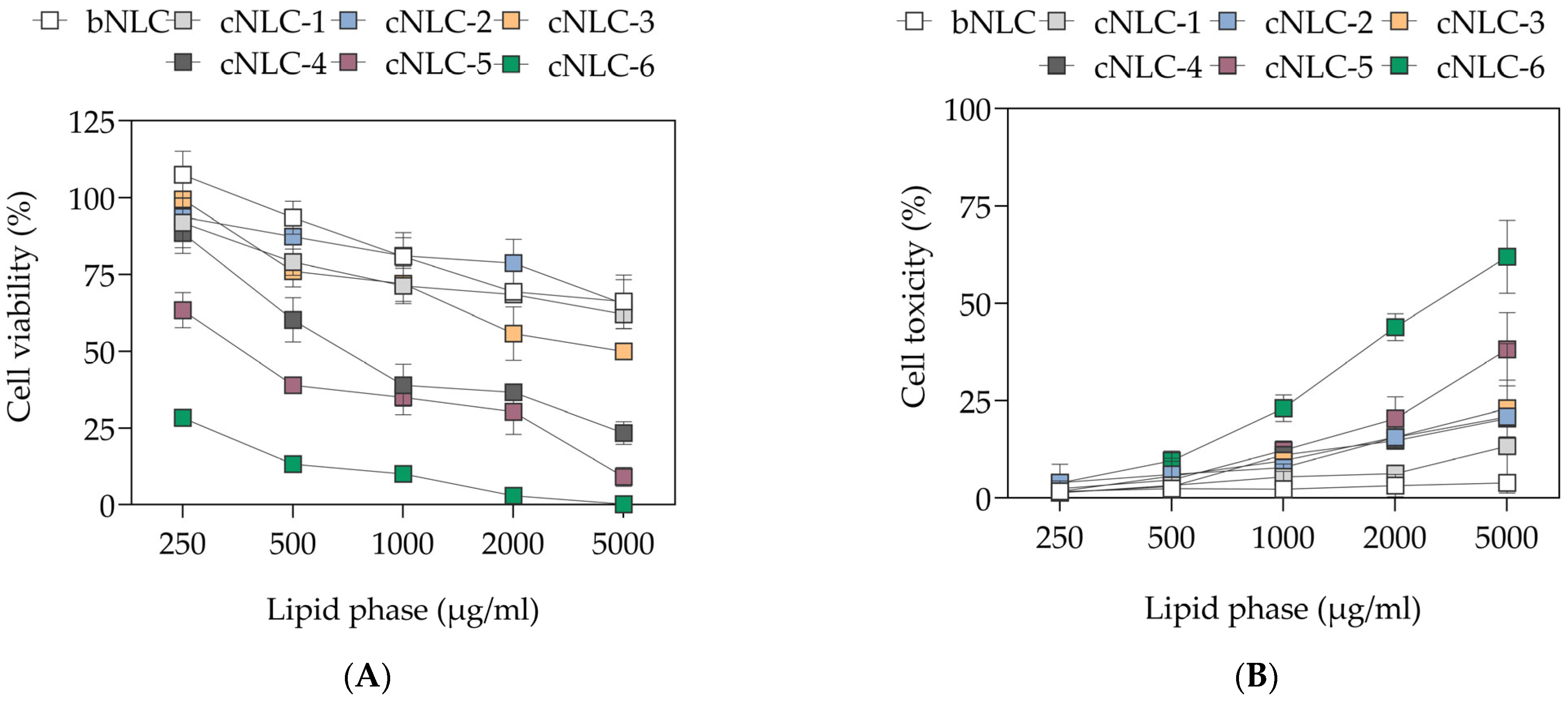
2.2. Cytotoxicity of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers
2.3. Stability Studies of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers
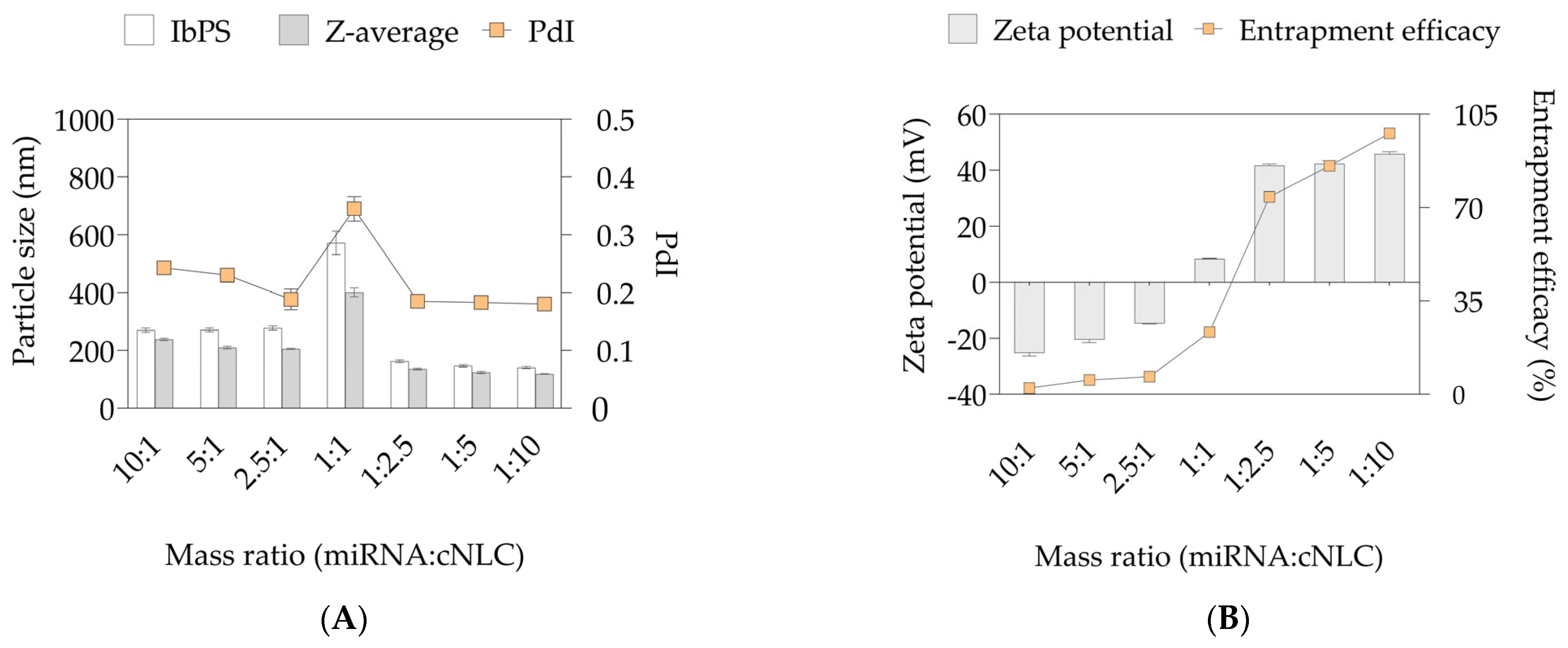
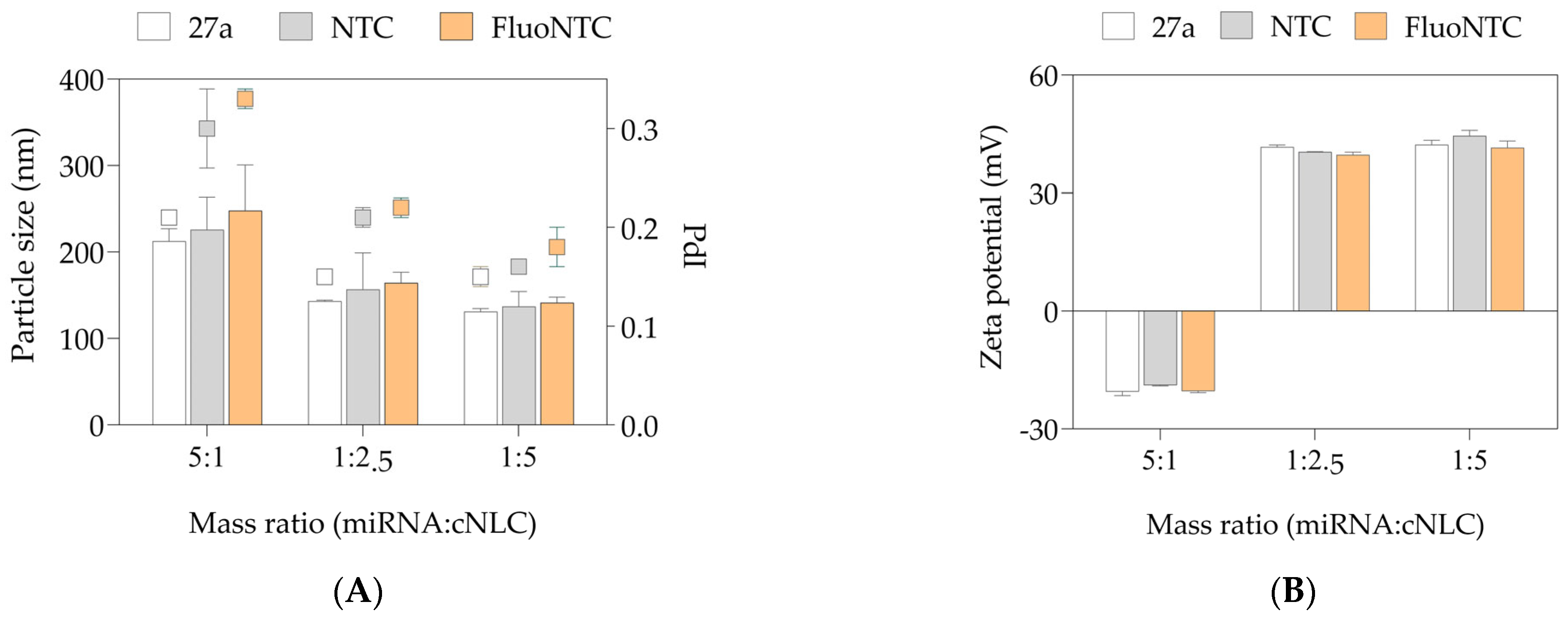
2.4. Preparation of miRNA/cNLC Complexes
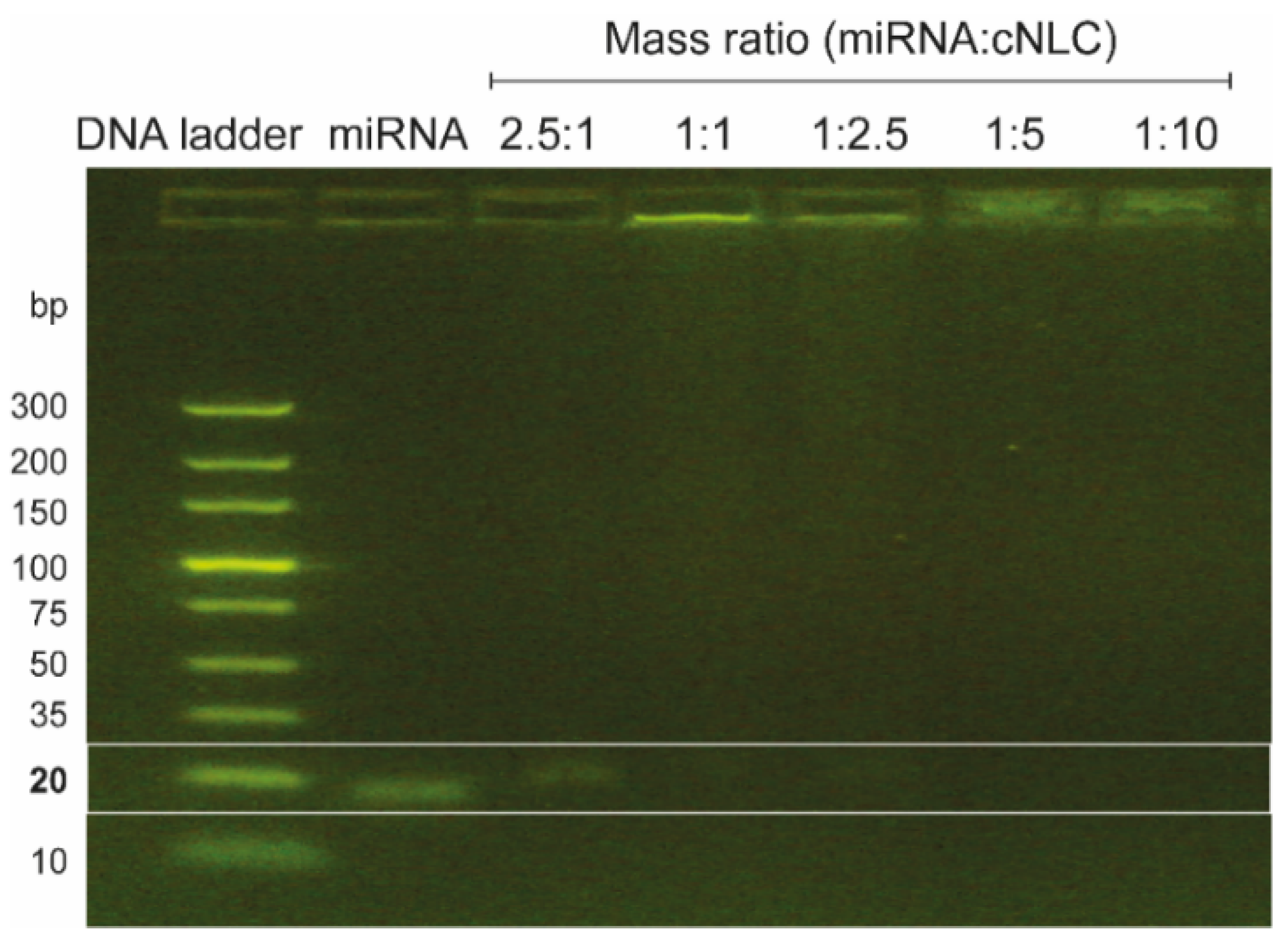
2.5. Complexation with Different Types of miRNAs
2.6. Morphology and Topographic Studies
2.7. Stability Studies of miRNA/cNLC Complex
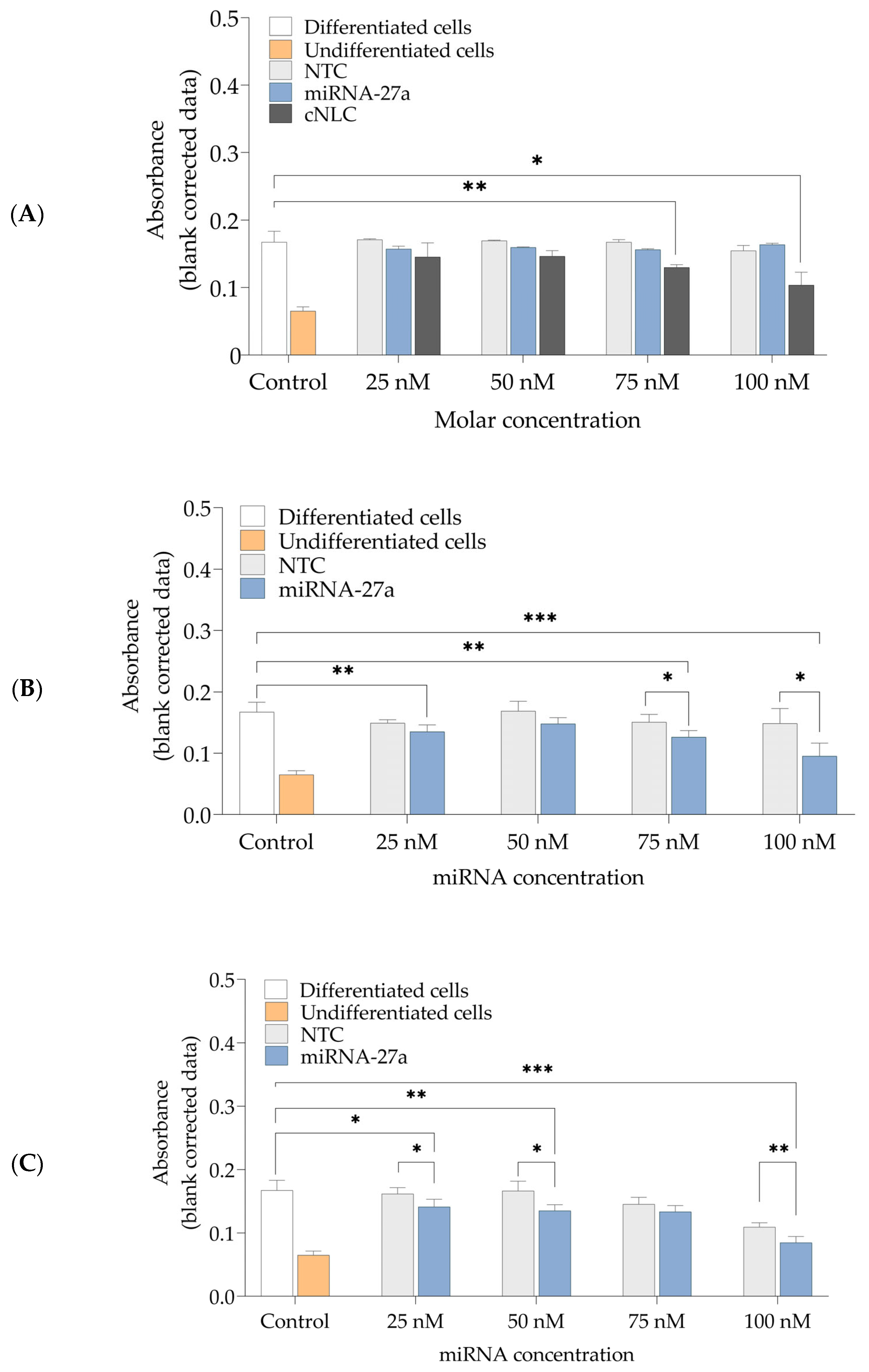
2.8. Cytotoxicity Study
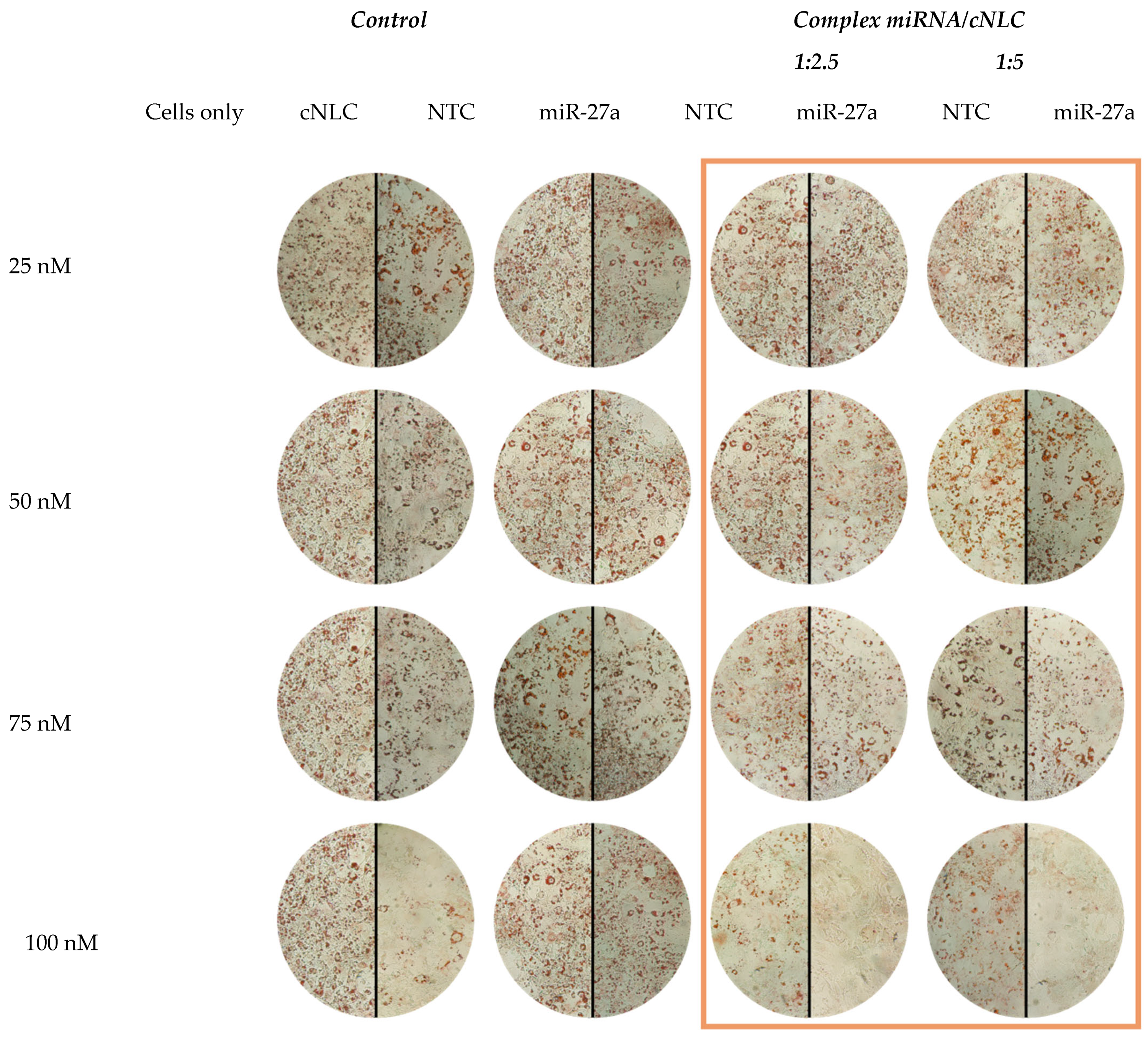
2.9. In Vitro Transfection and Differentiation of 3T3-L1 Cells
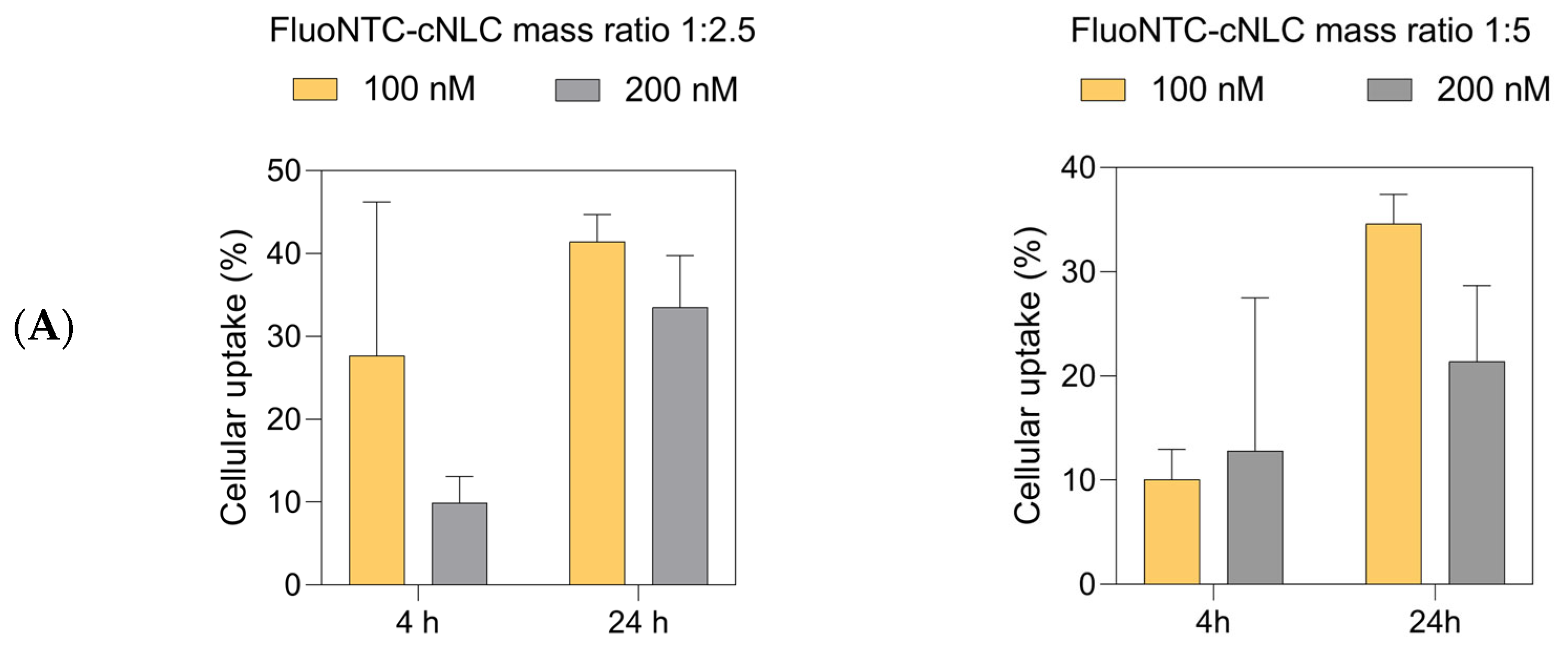
2.10. Cellular Uptake Studies
2.11. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
- double-stranded miRNA mimic mmu-miR-27a-3p (miRNA-27a) with the sequence UUC ACA GUG GCU AAG UUC CGC (MW 13,454 g/mol);
- miRNA mimic negative control (miRNA-NTC) with the sequence UCA CAA CCU CCU AGA AAG AGU AGA (MW 15,384.3 g/mol);
- miRNA mimic transfection control with fluorescence-labeled Cy3 group (FluoNTC) and the sequence UCA CAA CCU CCU AGA AAG AGU AGA (MW 15,891.5 g/mol).
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. High-Pressure Homogenization
4.2.2. Preparation of miRNA/cNLC Complexes
4.2.3. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Analysis
4.2.4. pH Measurements
4.2.5. Stability Studies
4.2.6. Entrapment Efficiency (EE%)
4.2.7. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
4.2.8. Morphology and Topography Studies
4.2.9. Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Studies (MTS and LDH Assay)
4.2.10. In Vitro Transfection and Differentiation Studies
Preparation of ORO Working Solution
4.2.11. Cellular Uptake Studies
4.2.12. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (cLSM)
4.2.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abarca-Goómez, L.; Abdeen, Z.A.; Hamid, Z.A.; Abu-Rmeileh, N.M.; Acosta-Cazares, B.; Acuin, C.; Adams, R.J.; Aekplakorn, W.; Afsana, K.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; et al. Worldwide Trends in Body-Mass Index, Underweight, Overweight, and Obesity from 1975 to 2016: A Pooled Analysis of 2416 Population-Based Measurement Studies in 128·9 Million Children, Adolescents, and Adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacomino, G.; Siani, A. Role of MicroRNAs in Obesity and Obesity-Related Diseases. Genes Nutr. 2017, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunney, P.E.; Zink, A.N.; Holm, A.A.; Billington, C.J.; Kotz, C.M. Orexin Activation Counteracts Decreases in Nonexercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT) Caused by High-Fat Diet. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 176, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, J.; Kiefer, K.; Kimpfler, A.; Garidel, P.; Peschka-Süss, R. Large-Scale Production of Lipoplexes with Long Shelf-Life. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 59, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, M.; Laux, M.; Zandoná, B.; Santos, G.R.; dos Santos Giuberti, C.; de Oliveira, M.C.; Matte, U.; Teixeira, H.F. Optimization of Stearylamine-Based Nanoemulsions Obtained by Spontaneous Emulsification Process as Nucleic Acids Delivery Systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2008, 18, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krützfeldt, J.; Stoffel, M. MicroRNAs: A New Class of Regulatory Genes Affecting Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carthew, R.W.; Sontheimer, E.J. Origins and Mechanisms of MiRNAs and SiRNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, N.; Tanaka, T. Role of MiRNAs in the Pathogenesis and Susceptibility of Diabetes Mellitus. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 62, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, J.A.; Zamore, P.D. MicroRNA Therapeutics. Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, A.Y.; Lee, H.W.; Son, Y.H.; Lee, G.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, J.B. MiR-27a Is a Negative Regulator of Adipocyte Differentiation via Suppressing PPARγ Expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 392, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheideler, M.; Vidakovic, I.; Prassl, R. Lipid Nanocarriers for MicroRNA Delivery. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2020, 226, 104837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Jia, L.; Chu, F.; Zhou, Y.; He, Z.; Guo, M.; Chen, C.; Xu, L. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for MicroRNA Delivery in Tumor Gene Therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gemeinhart, R.A. Progress in MicroRNA Delivery. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 962–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reischl, D.; Zimmer, A. Drug Delivery of SiRNA Therapeutics: Potentials and Limits of Nanosystems. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2009, 5, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Wei, J.; Yu, C.; Han, X.; Qin, X.; Zhang, C.; Liao, W.; Li, L.; Huang, W. Non-Viral Nanocarriers for Intracellular Delivery of MicroRNA Therapeutics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 1209–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmali, P.P.; Chaudhuri, A. Cationic Liposomes as Non-Viral Carriers of Gene Medicines: Resolved Issues, Open Questions, and Future Promises. Med. Res. Rev. 2007, 27, 696–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botto, C.; Mauro, N.; Amore, E.; Martorana, E.; Giammona, G.; Bondì, M.L. Surfactant Effect on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Cationic Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 516, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Shegokar, R.; Keck, C.M. 20 Years of Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN & NLC): Present State of Development & Industrial Applications. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2011, 8, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloqui, A.; Solinís, M.Á.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Almeida, A.J.; Préat, V. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: Promising Drug Delivery Systems for Future Clinics. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapeinos, C.; Battaglini, M.; Ciofani, G. Advances in the Design of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Targeting Brain Diseases. J. Control. Release 2017, 264, 306–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamjidi, F.; Shahedi, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Nasirpour, A. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC): A Potential Delivery System for Bioactive Food Molecules. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 19, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenning, V.; Thünemann, A.F.; Gohla, S.H. Characterisation of a Novel Solid Lipid Nanoparticle Carrier System Based on Binary Mixtures of Liquid and Solid Lipids. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 199, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmowafy, M.; Al-Sanea, M.M. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs) as Drug Delivery Platform: Advances in Formulation and Delivery Strategies. Saudi Pharm. J. 2021, 29, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, H.F.; Bruxel, F.; Fraga, M.; Schuh, R.S.; Zorzi, G.K.; Matte, U.; Fattal, E. Cationic Nanoemulsions as Nucleic Acids Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 534, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jesus, M.B.; Zuhorn, I.S. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Nucleic Acid Delivery System: Properties and Molecular Mechanisms. J. Control. Release 2015, 201, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietwyk, S.; Peer, D. Next-Generation Lipids in RNA Interference Therapeutics. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7572–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.K.K.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Chen, S.; Hafez, I.M.; Cullis, P.R. Microfluidic Mixing: A General Method for Encapsulating Macromolecules in Lipid Nanoparticle Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 8698–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.; Mukundan Geetha, K. Lipid Nanoparticles in the Development of MRNA Vaccines for COVID-19. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 74, 103553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadea, A.; Jackman, M.; Cui, L.; Pereira, S.; Lawrence, M.J.; Campbell, R.A.; Ashford, M. Nucleic Acid-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticle Interactions with Model Endosomal Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 30371–30384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schachner-Nedherer, A.; Werzer, O.; Zimmer, A. A Protocol to Characterize Peptide-Based Drug Delivery Systems for MiRNAs. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 7014–7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.M. Getting MiRNA Therapeutics into the Target Cells for Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Mini-Review. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, B.; Ren, W.; Mo, X.; Zhou, C.; He, H.; Jia, H.; Wang, L.; Jacob, S.T.; Lee, R.J.; et al. Enhanced Hepatic Delivery of SiRNA and MicroRNA Using Oleic Acid Based Lipid Nanoparticle Formulations. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Huang, L. Nanoparticles Modified with Tumor-Targeting ScFv Deliver SiRNA and MiRNA for Cancer Therapy. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, L.; Zhang, M.; Datta, J.; Xie, X.; Su, T.; Li, H.; Teknos, T.N.; Pan, Q. Lipid-Based Nanoparticle Delivery of Pre-MiR-107 Inhibits the Tumorigenicity of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, M.W.; Oh, S.G.; Kim, Y.C. Effects of Amine and Amine Oxide Compounds on the Zeta-Potential of Emulsion Droplets Stabilized by Phosphatidylcholine. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 181, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, H.; Dubernet, C.; Chacun, H.; Rabinovich, L.; Boutet, V.; Deverre, J.R.; Benita, S.; Couvreur, P. Cationic Emulsions Improves the Delivery of Oligonucleotides to Leukemic P388/ADR Cells in Ascite. J. Control. Release 2003, 89, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonça, M.C.P.; Kont, A.; Kowalski, P.S.; O’Driscoll, C.M. Design of Lipid-Based Nanoparticles for Delivery of Therapeutic Nucleic Acids. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, É.; Fattal, E.; de Oliveira, M.C.; Teixeira, H. Effect of Cationic Lipid Composition on Properties of Oligonucleotide/Emulsion Complexes: Physico-Chemical and Release Studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 352, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romøren, K.; Thu, B.J.; Bols, N.C.; Evensen, Ø. Transfection Efficiency and Cytotoxicity of Cationic Liposomes in Salmonid Cell Lines of Hepatocyte and Macrophage Origin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2004, 1663, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Zaks, T.; Langer, R.; Dong, Y. Lipid Nanoparticles for MRNA Delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1078–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schachner-Nedherer, A.; Werzer, O.; Kornmueller, K.; Prassl, R.; Zimmer, A. Biological Activity of MiRNA-27a Using Peptide-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 7795–7808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyn, G.S.; Correa, L.H.; Magalhães, K.G. The Impact of Adipose Tissue—Derived MiRNAs in Metabolic Syndrome, Obesity, and Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 563816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucak, A.; Sirbubalo, M.; Zimmer, A.; Vranić, E. Cationic Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (CNLCs) as Drug Delivery Systems for MiRNA: Investigations of Formulation and Process Parameters. In Proceedings of the II. Symposium of Young Researchers on Pharmaceutical Technology, Biotechnology and Regulatory Science, Szeged, Hungary, 23–24 January 2020; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- McClements, D.J.; Rao, J. Food-Grade Nanoemulsions: Formulation, Fabrication, Properties, Performance, Biological Fate, and Potential Toxicity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 285–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, H.; Rosilio, V.; Laigle, A.; Lepault, J.; Erk, I.; Scherman, D.; Benita, S.; Couvreur, P.; Dubernet, C. Characterization of Oligonucleotide/Lipid Interactions in Submicron Cationic Emulsions: Influence of the Cationic Lipid Structure and the Presence of PEG-Lipids. Biophys. Chem. 2001, 92, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagigit, T.; Nassar, T.; Behar-Cohen, F.; Lambert, G.; Benita, S. The Influence of Cationic Lipid Type on In-Vitro Release Kinetic Profiles of Antisense Oligonucleotide from Cationic Nanoemulsions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesnoy, S.; Durand, D.; Doucet, J.; Stolz, D.B.; Huang, L. Improved DNA/Emulsion Complex Stabilized by Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Conjugated Phospholipid. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 1480–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, M.; De Carvalho, T.G.; Da Silva Diel, D.; Bruxel, F.; Filho, N.A.K.; Teixeira, H.F.; Matte, U. Cationic Nanoemulsions as a Gene Delivery System: Proof of Concept in the Mucopolysaccharidosis I Murine Model. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.H.; Yu, S.Y. Cationic Nanoemulsions as Non-Viral Vectors for Plasmid DNA Delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 79, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shegokar, R.; Shaal, L.A.L.; Mishra, P.R. SiRNA Delivery: Challenges and Role of Carrier Systems. Pharmazie 2011, 66, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severino, P.; Szymanski, M.; Favaro, M.; Azzoni, A.R.; Chaud, M.V.; Santana, M.H.A.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Development and Characterization of a Cationic Lipid Nanocarrier as Non-Viral Vector for Gene Therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 66, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montana, G.; Bondì, M.L.; Carrotta, R.; Picone, P.; Craparo, E.F.; San Biagio, P.L.; Giammona, G.; Di Carlo, M. Employment of Cationic Solid-Lipid Nanoparticles as RNA Carriers. Bioconjugate Chem. 2007, 18, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.L.; Marcelino, H.R.; Veríssimo, L.M.; Araujo, I.B.; Agnez-Lima, L.F.; Do Egito, E.S.T. Stearylamine-Containing Cationic Nanoemulsion as a Promising Carrier for Gene Delivery. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukovski, B.J.; Bračko, A.; Šare, M.; Pepić, I.; Lovrić, J. In Vitro Evaluation of Stearylamine Cationic Nanoemulsions for Improved Ocular Drug Delivery. Acta Pharm. 2019, 69, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, M.L.; Craparo, E.F. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Applications in Gene Therapy: A Review of the State of the Art. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doktorovova, S.; Shegokar, R.; Rakovsky, E.; Gonzalez-Mira, E.; Lopes, C.M.; Silva, A.M.; Martins-Lopes, P.; Müller, R.H.; Souto, E.B. Cationic Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (CSLN): Structure, Stability and DNA Binding Capacity Correlation Studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajavinia, A.; Varshosaz, J.; Dehkordi, A.J. Targeting Etoposide to Acute Myelogenous Leukaemia Cells Using Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Coated with Transferrin. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 405101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardeike, J.; Weber, S.; Zarfl, H.P.; Pagitz, M.; Zimmer, A. Itraconazole-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) for Pulmonary Treatment of Aspergillosis in Falcons. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.K.; Chun, S.K.; Choi, W.J.; Kim, J.K.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, A.; Oungbho, K.; Park, J.S.; Ahn, W.S.; Kim, C.K. The Use of Chitosan as a Condensing Agent to Enhance Emulsion-Mediated Gene Transfer. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2147–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponti, F.; Campolungo, M.; Melchiori, C.; Bono, N.; Candiani, G. Cationic Lipids for Gene Delivery: Many Players, One Goal. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2021, 235, 105032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçüktürkmen, B.; Bozkır, A. Development and Characterization of Cationic Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Co-Delivery of Pemetrexed and MiR-21 Antisense Oligonucleotide to Glioblastoma Cells. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Fantin, M.; Marti, M.; Drechsler, M.; Paccamiccio, L.; Mariani, P.; Sivieri, E.; Lain, F.; Menegatti, E.; Morari, M.; et al. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Delivery Systems for Bromocriptine. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jores, K.; Mehnert, W.; Drechsler, M.; Bunjes, H.; Johann, C.; Mäder, K. Investigations on the Structure of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) and Oil-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles by Photon Correlation Spectroscopy, Field-Flow Fractionation and Transmission Electron Microscopy. J. Control. Release 2004, 95, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.Q.; Wanunu, M.; Wang, M.X.; McReynolds, L.; Wang, Y. Detection of MiRNAs with a Nanopore Single-Molecule Counter. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 12, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, M.; Bruxel, F.; Lagranha, V.L.; Teixeira, H.F.; Matte, U. Influence of Phospholipid Composition on Cationic Emulsions/DNA Complexes: Physicochemical Properties, Cytotoxicity, and Transfection on Hep G2 Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isar, S.; Akbaba, H.; Erel-Akbaba, G.; Başpinar, Y. Development and Characterization of Cationic Nanoemulsions as Non-Viral Vectors for Plasmid DNA Delivery. J. Res. Pharm. 2020, 24, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, T.C.; Lane, M.D. Adipose Development: From Stem Cell to Adipocyte. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 40, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbal-Chaloin, S.; Gondeau, C.; Aldrian-Herrada, G.; Heitz, F.; Gauthier-Rouvière, C.; Divita, G. First Step of the Cell-Penetrating Peptide Mechanism Involves Rac1 GTPase-Dependent Actin-Network Remodelling. Biol. Cell 2007, 99, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaksonen, M.; Roux, A. Mechanisms of Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strachan, J.B.; Dyett, B.P.; Nasa, Z.; Valery, C.; Conn, C.E. Toxicity and Cellular Uptake of Lipid Nanoparticles of Different Structure and Composition. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 576, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucak, A.; Sirbubalo, M.; Hadžiabdić, J.; Rahić, O.; Ruseska, I.; Zimmer, A.; Vranić, E. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Drug Delivery Systems for MiRNA. Maced. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 66, 235–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. ICH Topic Q 1 A (R2): Stability Testing of New Drug Substances and Products; Current Step 4; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; p. 24.
- Karn-Orachai, K.; Smith, S.M.; Phunpee, S.; Treethong, A.; Puttipipatkhachorn, S.; Pratontep, S.; Ruktanonchai, U.R. The Effect of Surfactant Composition on the Chemical and Structural Properties of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. J. Microencapsul. 2014, 31, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Formulation | PCS Data | LD Data (µm) | ELS Data | pH | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z-ave (nm) | PdI | d(0.5) | d(0.9) | d(0.99) | ZP (mV) | ||
| bNLC | 105.6 ± 1.8 | 0.180 ± 0.003 | 0.128 ± 0.001 | 0.189 ± 0.002 | 0.240 ± 0.001 | −18.2 ± 1.2 | 4.998 ± 0.039 |
| cNLC–1 | 112.9 ± 1.7 | 0.185 ± 0.009 | 0.127 ± 0.001 | 0.188 ± 0.001 | 0.250 ± 0.002 | 14.6 ± 0.5 | 6.706 ± 0.047 |
| cNLC–2 | 109.4 ± 1.4 | 0.213 ± 0.015 | 0.123 ± 0.001 | 0.187 ± 0.002 | 0.250 ± 0.001 | 33.9 ± 1.0 | 8.390 ± 0.081 |
| cNLC–3 | 113.2 ± 0.8 | 0.213 ± 0.007 | 0.126 ± 0.004 | 0.184 ± 0.003 | 0.240 ± 0.013 | 39.6 ± 2.1 | 8.861 ± 0.053 |
| cNLC–4 | 114.9 ± 1.7 | 0.207 ± 0.006 | 0.129 ± 0.001 | 0.188 ± 0.002 | 0.240 ± 0.003 | 40.6 ± 0.4 | 9.114 ± 0.021 |
| cNLC–5 | 116.4 ± 2.8 | 0.217 ± 0.016 | 0.126 ± 0.002 | 0.186 ± 0.002 | 0.250 ± 0.004 | 43.0 ± 2.5 | 9.323 ± 0.001 |
| cNLC–6 | 116.2 ± 3.7 | 0.218 ± 0.013 | 0.132 ± 0.002 | 0.183 ± 0.001 | 0.250 ± 0.009 | 46.8 ± 2.1 | 9.617 ± 0.014 |
| Percentage of Reduction of Lipid Accumulation in Cells | miRNA/cNLC Complex | Control | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:2.5 | 1:5 | NTC | 27a | cNLC | Undif. Cells | ||||
| NTC | 27a | NTC | 27a | ||||||
| miRNA concentration | 25 nM | 10.77 ± 1.31% | 19.16 ± 1.56% | 3.11 ± 1.13% | 15.45 ± 1.36% | 0.77 ± 0.14% | 5.98 ± 0.42% | 12.87 ± 2.07% | 61.08 ± 3.75% |
| 50 nM | 1.01 ± 0.81% | 11.49 ± 1.52% | 1.53 ± 1.71% | 19.04 ± 0.86% | 1.17 ± 0.07% | 4.49 ± 0.07% | 12.39 ± 0.81% | ||
| 75 nM | 9.71 ± 0.58% | 20.20 ± 1.03% | 12.87 ± 1.21% | 24.37 ± 1.03% | 1.0 ± 0.35% | 6.58 ± 0.14% | 22.35± 0.51% | ||
| 100 nM | 11.08 ± 3.67% | 42.87 ± 2.11% | 34.71 ± 1.38% | 49.40 ± 0.97% | 7.48 ± 0.78% | 2.09 ± 0.21% | 37.9 ± 1.87% | ||
| Formulation | Lipid Phase (%, w/w) | Water Phase (%, w/w) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA | Precirol® ATO 5 | Miglyol® 812 | Tween® 80 | Pluronic® F68 | MQ Water | |
| bNLC | 0 | 4.50 | 0.50 | 1.33 | 0.67 | 93 |
| cNLC–1 | 0.05 | 4.455 | 0.495 | 1.33 | 0.67 | 93 |
| cNLC–2 | 0.10 | 4.41 | 0.490 | 1.33 | 0.67 | 93 |
| cNLC–3 | 0.15 | 4.365 | 0.485 | 1.33 | 0.67 | 93 |
| cNLC–4 | 0.20 | 4.32 | 0.480 | 1.33 | 0.67 | 93 |
| cNLC–5 | 0.25 | 4.275 | 0.475 | 1.33 | 0.67 | 93 |
| cNLC–6 | 0.50 | 4.05 | 0.450 | 1.33 | 0.67 | 93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tucak-Smajić, A.; Ruseska, I.; Letofsky-Papst, I.; Vranić, E.; Zimmer, A. Development and Characterization of Cationic Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Drug Delivery Systems for miRNA-27a. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071007
Tucak-Smajić A, Ruseska I, Letofsky-Papst I, Vranić E, Zimmer A. Development and Characterization of Cationic Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Drug Delivery Systems for miRNA-27a. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(7):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071007
Chicago/Turabian StyleTucak-Smajić, Amina, Ivana Ruseska, Ilse Letofsky-Papst, Edina Vranić, and Andreas Zimmer. 2023. "Development and Characterization of Cationic Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Drug Delivery Systems for miRNA-27a" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 7: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071007
APA StyleTucak-Smajić, A., Ruseska, I., Letofsky-Papst, I., Vranić, E., & Zimmer, A. (2023). Development and Characterization of Cationic Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Drug Delivery Systems for miRNA-27a. Pharmaceuticals, 16(7), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071007