Dalbavancin in Bone and Joint Infections: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.3. Selection and Data Collection Process
2.4. Data Items
3. Results
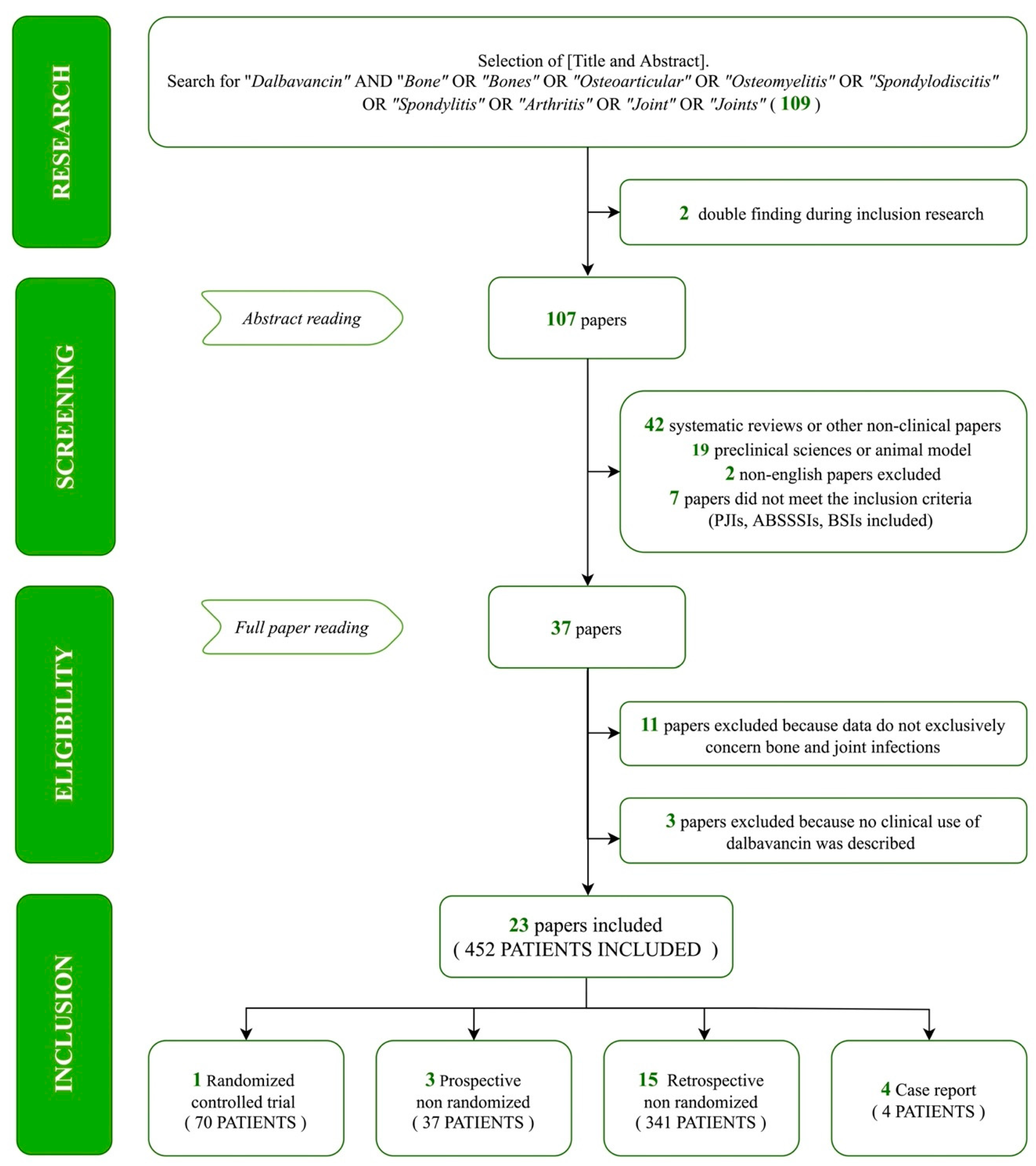
3.1. Study Selection and Search Results
3.2. Results of Synthesis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Approval
References
- De Vito, A.; Fiore, V.; Colpani, A.; Zauli, B.; Fanelli, C.; Tiseo, G.; Occhineri, S.; Babudieri, S.; Falcone, M.; Madeddu, G. The current and future off-label uses of dalbavancin: A narrative review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 1222–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Andreoni, M.; Bassetti, M.; Corrao, S.; De Rosa, F.G.; Esposito, V.; Falcone, M.; Grossi, P.; Pea, F.; Petrosillo, N.; Tascini, C.; et al. The role of dalbavancin for Gram positive infections in the COVID-19 era: State of the art and future perspectives. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, M.W.; Puttagunta, S.; Sprenger, C.R.; Rubino, C.; Van Wart, S.; Baldassarre, J. Extended-duration dosing and distribution of dalbavancin into bone and articular tissue. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangour, T.A.; Alhifany, A.A. Dalbavancin for the management of osteomyelitis: A major step forward? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 2717–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neudorfer, K.; Schmidt-Malan, S.M.; Patel, R. Dalbavancin is active in vitro against biofilms formed by dalbavancin-susceptible enterococci. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 90, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.N.; Sader, H.S.; Flamm, R.K. Update of dalbavancin spectrum and potency in the USA: Report from the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (2011). Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 75, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, K.C.; Miller, M.A.; Mueller, S.W.; Van Matre, E.T.; Krsak, M.; Kiser, T.H. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Dalbavancin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2022, 61, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, M.; Andreoni, M.; Pea, F.; Viale, P. Real-World Use of Dalbavancin in the Era of Empowerment of Outpatient Antimicrobial Treatment: A Careful Appraisal Beyond Approved Indications Focusing on Unmet Clinical Needs. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 3349–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andes, D.; Craig, W.A. In vivo pharmacodynamic activity of the glycopeptide dalbavancin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krsak, M.; Morrisette, T.; Miller, M.; Molina, K.; Huang, M.; Damioli, L.; Pisney, L.; Wong, M.; Poeschla, E. Advantages of Outpatient Treatment with Long-Acting Lipoglycopeptides for Serious Gram-Positive Infections: A Review. Pharmacotherapy 2020, 40, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojutti, P.G.; Rinaldi, M.; Zamparini, E.; Rossi, N.; Tedeschi, S.; Conti, M.; Pea, F.; Viale, P. Population pharmacokinetics of dalbavancin and dosing consideration for optimal treatment of adult patients with staphylococcal osteoarticular infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2023, 65, e02260-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantoni, M.; Taccari, F.; Giovannenze, F. Systemic antibiotic treatment of chronic osteomyelitis in adults. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23 (Suppl. 2), 258–270. [Google Scholar]
- Thabit, A.K.; Fatani, D.F.; Bamakhrama, M.S.; Barnawi, O.A.; Basudan, L.O.; Alhejaili, S.F. Antibiotic penetration into bone and joints: An updated review. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 81, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, S.K. Osteomyelitis. Infect. Dis. Clin. North. Am. 2017, 31, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappo, U.; Puttagunta, S.; Shevchenko, V.; Shevchenko, A.; Jandourek, A.; Gonzalez, P.L.; Suen, A.; Mas Casullo, V.; Melnick, D.; Miceli, R.; et al. Dalbavancin for the Treatment of Osteomyelitis in Adult Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial of Efficacy and Safety. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 6, ofy331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morata, L.; Cobo, J.; Fernández-Sampedro, M.; Guisado Vasco, P.; Ruano, E.; Lora-Tamayo, J.; Sánchez Somolinos, M.; González Ruano, P.; Rico Nieto, A.; Arnaiz, A.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Prolonged Use of Dalbavancin in Bone and Joint Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e02280-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, A.; Duran, C.; Pavese, P.; Khatchatourian, L.; Monnin, B.; Bleibtreu, A.; Denis, E.; Etienne, C.; Rouanes, N.; Mahieu, R.; et al. French national cohort of first use of dalbavancin: A high proportion of off-label use. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, A.R.; Bremmer, D.N.; Carr, D.R.; Buchanan, C.; Jacobs, M.; Walsh, T.L.; Moffa, M.A.; Shively, N.R.; Trienski, T.L. Effectiveness of Dalbavancin Compared With Standard of Care for the Treatment of Osteomyelitis: A Real-world Analysis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 9, ofab589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangour, T.A.; Perry, G.K.; Terriff, C.M.; Alhifany, A.A.; Kaye, K.S. Dalbavancin for the management of gram-positive osteomyelitis: Effectiveness and potential utility. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 93, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroffolini, G.; De Nicolò, A.; Gaviraghi, A.; Mula, J.; Cariti, G.; Scabini, S.; Manca, A.; Cusato, J.; Corcione, S.; Bonora, S.; et al. Clinical Effectiveness and Pharmacokinetics of Dalbavancin in Treatment-Experienced Patients with Skin, Osteoarticular, or Vascular Infections. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadan, M.S.; Gallo, R.; Lugarà, M.; Gambardella, M.; Oliva, G.; Bertolino, L.; Andini, R.; Coppola, N.; Zampino, R.; Durante-Mangoni, E. Dalbavancin treatment for spondylodiscitis: Multi-center clinical experience and literature review. J. Chemother. 2022, 34, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brescini, L.; Della Martera, F.; Morroni, G.; Mazzanti, S.; Di Pietrantonio, M.; Mantini, P.; Candelaresi, B.; Pallotta, F.; Olivieri, S.; Iencinella, V.; et al. Use of Dalbavancin in Skin, Bone and Joint Infections: A Real-Life Experience in an Italian Center. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nicolò, A.; Stroffolini, G.; Antonucci, M.; Mula, J.; De Vivo, E.D.; Cusato, J.; Palermiti, A.; Cariti, G.; Di Perri, G.; Corcione, S.; et al. Long-Term Pharmacokinetics of Dalbavancin in ABSSSI and Osteoarticular Settings: A Real-Life Outpatient Context. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Jiménez, G.; Fuentes-Santos, C.; Moreno-Núñez, L.; Alfayate-García, J.; Campelo-Gutierrez, C.; Sanz-Márquez, S.; Pérez-Fernández, E.; Velasco-Arribas, M.; Hervás-Gómez, R.; Martín-Segarra, O.; et al. Experience in the use of dalbavancin in diabetic foot infection. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2021, 40, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobudic, S.; Forstner, C.; Burgmann, H.; Lagler, H.; Steininger, C.; Traby, L.; Vossen, M.G.; Winkler, S.; Thalhammer, F. Real-world experience with dalbavancin therapy in gram-positive skin and soft tissue infection, bone and joint infection. Infection 2019, 47, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojutti, P.G.; Tedeschi, S.; Gatti, M.; Zamparini, E.; Meschiari, M.; Siega, P.D.; Mazzitelli, M.; Soavi, L.; Binazzi, R.; Erne, E.M.; et al. Population Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Analysis of Dalbavancin for Long-Term Treatment of Subacute and/or Chronic Infectious Diseases: The Major Role of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueking, R.; Wei, W.; Mang, N.S.; Ortwine, J.K.; Meisner, J. Evaluation of Dalbavancin Use on Clinical Outcomes, Cost-Savings, and Adherence at a Large Safety Net Hospital. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0238522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, J.J.; Kayani, J.; Fisher, A.; Kotansky, B.; Dembry, L.M.; Datta, R. Clinical outcomes following dalbavancin administration in patients with barriers to outpatient parenteral antimicrobial therapy. Antimicrob. Steward. Healthc. Epidemiol. 2022, 2, e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzitelli, M.; Gatti, M.; Scaglione, V.; Mengato, D.; Trevenzoli, M.; Sattin, A.; Pea, F.; Cattelan, A.M. Off-Label Use of Dalbavancin for Sequential Treatment of Spondylodiscitis by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A Retrospective Single-Centre Experience. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangour, T.A.; Perry, G.K.; Alhifany, A.A. Dalbavancin versus standard of care for the treatment of osteomyelitis in adults: A retrospective matched cohort study. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loupa, C.V.; Lykoudi, E.; Meimeti, E.; Moisoglou, I.; Voyatzoglou, E.D.; Kalantzi, S.; Konsta, E. Successful Treatment of Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis with Dalbavancin. Med. Arch. 2020, 74, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bork, J.T.; Heil, E.L.; Berry, S.; Lopes, E.; Davé, R.; Gilliam, B.L.; Amoroso, A. Dalbavancin Use in Vulnerable Patients Receiving Outpatient Parenteral Antibiotic Therapy for Invasive Gram-Positive Infections. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2019, 8, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, H.; Aggarwal, A.; Schimmel, J.; Lorenzo, M.P. Clinical failure of dalbavancin for MRSA bacteremia in patient with severe obesity and history of IVDU. J. Infect. Chemother. 2022, 28, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangour, T.A.; Fletcher, V.; Alessa, M.; Alhifany, A.A.; Tabb, D. Multiple Weekly Dalbavancin Dosing for the Treatment of Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis Caused by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: A Case Report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2017, 18, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina Collada, J.; Rico Nieto, A.; Díaz de Bustamante Ussia, M.; Balsa Criado, A. Septic arthritis in a native knee due to Corynebacterium striatum. Reumatol. Clin. 2018, 14, 301–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryson-Cahn, C.; Beieler, A.M.; Chan, J.D.; Harrington, R.D.; Dhanireddy, S. Dalbavancin as Secondary Therapy for Serious Staphylococcus aureus Infections in a Vulnerable Patient Population. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, ofz028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.; Gomez Villegas, S.; Aitken, S.L.; Butler-Wu, S.M.; Soriano, A.; Werth, B.J.; Munita, J.M. New Perspectives on Antimicrobial Agents: Long-Acting Lipoglycopeptides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0261420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsch, S.; Krause, R.; Valentin, T.; Prattes, J.; Janata, O.; Lenger, A.; Bellmann-Weiler, R.; Weiss, G.; Zollner-Schwetz, I. Multicenter clinical experience of real life Dalbavancin use in gram-positive infections. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 81, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliseno, M.; Bavaro, D.F.; Brindicci, G.; Luzzi, G.; Carretta, D.M.; Spinarelli, A.; Messina, R.; Miolla, M.P.; Achille, T.I.; Dibartolomeo, M.R.; et al. Dalbavancin Efficacy and Impact on Hospital Length-of-Stay and Treatment Costs in Different Gram-Positive Bacterial Infections. Clin. Drug Investig. 2021, 41, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerio, M.; Veintimilla, C.; Rodríguez, C.; de la Villa, S.; Sánchez-Somolinos, M.; Cerezales, M.; Crespo, C.; Rodríguez, S.; Adán, I.; Chamorro, E.; et al. Cost analysis of disease including treatment with dalbavancin in a Spanish hospital: ECODAL ANALYSIS. J. Med. Econ. 2023, 26, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béraud, G.; Maupetit, J.C.; Darras, A.; Vimont, A.; Blachier, M. Dalbavancin in Real Life: Economic Impact of Prescription Timing in French Hospitals. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2022, 11, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veve, M.P.; Patel, N.; Smith, Z.A.; Yeager, S.D.; Wright, L.R.; Shorman, M.A. Comparison of dalbavancin to standard-of-care for outpatient treatment of invasive Gram-positive infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jame, W.; Basgut, B.; Abdi, A. Efficacy and safety of novel glycopeptides versus vancomycin for the treatment of gram-positive bacterial infections including methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanyam, K.N.; Mundargi, A.V.; Prabhu, M.V.; Gopakumar, K.U.; Gowda, D.S.A.; Reddy, D.R. Surgical management of chronic osteomyelitis: Organisms, recurrence and treatment outcome. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pablo-Miró, M.; Pujol-Ruiz, S.; Iftimie, S.; Arenas-Miras, M.D.M.; López-Montesinos, I.; Duran-Jordà, X.; Anglès, A.; Grau, S.; Horcajada, J.P. Comparative Analysis of Dalbavancin versus Other Antimicrobial Options for Gram-Positive Cocci Infections: Effectiveness, Hospital Stay and Mortality. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacopardo, B.; Cattaneo, D.; Cortese, F.; Di Luca, M.; Falcone, M.; Marchetti, G.; Tascini, C.; Tiseo, G.; Venditti, M. Role of dalbavancin as combination therapy: Evidence from the literature and clinical scenarios. Expert. Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2022, 20, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.; Henao-Martínez, A.F.; Franco-Paredes, C.; Chastain, D.B. Treatment of osteoarticular, cardiovascular, intravascular-catheter-related and other complicated infections with dalbavancin and oritavancin: A systematic review. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.L.; Oliveira, P.R.; Carvalho, V.C.; Cimerman, S.; Savio, E.; Diretrizes Panamericanas para el Tratamiento de las Osteomielitis e Infecciones de Tejidos Blandos Group. Recommendations for the treatment of osteomyelitis. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 18, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cierny, G., 3rd. Surgical treatment of osteomyelitis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127 (Suppl. 1), 190S–204S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, G.; Derbentli, S. In vitro activity of daptomycin combined with dalbavancin and linezolid, and dalbavancin with linezolid against MRSA strains. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 441–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldoni, D.; Furustrand Tafin, U.; Aeppli, S.; Angevaare, E.; Oliva, A.; Haschke, M.; Zimmerli, W.; Trampuz, A. Activity of dalbavancin, alone and in combination with rifampicin, against meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a foreign-body infection model. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 42, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xhemali, X.; Smith, J.R.; Kebriaei, R.; Rice, S.A.; Stamper, K.C.; Compton, M.; Singh, N.B.; Jahanbakhsh, S.; Rybak, M.J. Evaluation of dalbavancin alone and in combination with β-lactam antibiotics against resistant phenotypes of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pilato, V.; Ceccherini, F.; Sennati, S.; D’Agostino, F.; Arena, F.; D’Atanasio, N.; Di Giorgio, F.P.; Tongiani, S.; Pallecchi, L.; Rossolini, G.M. In vitro time-kill kinetics of dalbavancin against Staphylococcus spp. biofilms over prolonged exposure times. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 114901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Patel, R. In vitro activity of dalbavancin against biofilms of staphylococci isolated from prosthetic joint infections. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 85, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marbury, T.; Dowell, J.A.; Seltzer, E.; Buckwalter, M. Pharmacokinetics of dalbavancin in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 49, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarini, L.; Lipsky, B.A.; Mader, J.T. Antibiotic treatment of osteomyelitis: What have we learned from 30 years of clinical trials? Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 9, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbari, E.F.; Kanj, S.S.; Kowalski, T.J.; Darouiche, R.O.; Widmer, A.F.; Schmitt, S.K.; Hendershot, E.F.; Holtom, P.D.; Huddleston, P.M., 3rd; Petermann, G.W.; et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2015 Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis in Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, e26–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| First Author | Ref. | N. of Patients | Type of the Study | Type of Infection (n) | Aetiology (n) | Outcome (n) | DBV Dosage (n) | N. Administrations (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rappo U, et al. | [15] | 70 | Randomized controlled trial | Osteomyelitis (70) | S. aureus (42) CoNS (14) Enterococcus spp. (8) Streptococcus spp. (3) Other Gram-positive (13) Gram-negative and fungi (3) | Clinical cure (63) Clinical cure after different therapy (1) Lost to FU (2) Unrelated death (1) NA (3) | 1500 mg (70) | 1 dose (3) 2 doses, 1 week apart (67) |
| Morata L, et al. | [16] | 19 | Retrospective | Osteomyelitis (12) Arthritis or spondylodiscitis (7) | S. aureus (10) CoNS (4) Enterococcus spp. (2) Streptococcus spp. (3) Other Gram+ (2) | Clinical cure (17) Clinical failure (1) Relapse (1) | NA | NA |
| Almangour TA, et al. | [20] | 27 | Retrospective | Osteomyelitis (16) Spondylodiscitis (14) | S. aureus (27) CoNS (1) Streptococcus spp. (2) Gram-negative and fungi (1) | Clinical cure (24) Clinical failure (1) NA (2) | 1500 mg (11) 1000 + 500 mg (15) 2000 + 500 mg (1) | 1 dose (6) 2 doses, 1 week apart (6) 3 doses > 1 week apart (1) 3 doses, 1 week apart (2) 4 doses,1 week apart (4) 4 doses > 1 week apart (19) >4 doses (7) |
| Stroffolini G, et al. | [21] | 25 | Prospective | Osteomyelitis (9) Spondylodiscitis (6) Arthritis (3) | NA | Clinical cure (9) NA (16) | 1500 mg (25) | 1 dose (3) 2 doses, 1 week apart (9) NA (13) |
| Ramadan MS, et al. | [22] | 13 | Retrospective | Spondylodiscitis (13) | S. aureus (6) CoNS (4) Other Gram-positive (1) Gram-negative and fungi (2) | Clinical cure (8) Relapse (5) | 1500 mg (12) 1000 + 500 mgfor 5 times (1) | 2 doses, 1 week apart (12) >4 doses (1) |
| Brescini L, et al. | [23] | 13 | Retrospective | Osteomyelitis (8) Arthritis (5) | NA | NA (13) | NA | NA |
| De Nicolò A, et al. | [24] | 10 | Prospective | Osteomyelitis (4) Spondylodiscitis (3) Arthritis (3) | S. aureus (7) CoNS (2) Streptococcus spp. (1) | NA (10) | 1500 mg (10) | 1 dose (3) 2 doses, 1 week apart (7) |
| Navarro-Jiménez G, et al. | [25] | 23 | Retrospective | Osteomyelitis (23) | S. aureus (12) Other Gram-positive (7) CoNS (3) Enterococcus spp. (1) | Clinical cure (20) Clinical failure (3) | 1000 + 500 mg for 5 times (8) 1000 + 500 + 500 + 500 mg (1) 1000 + 500 mg for 9 times (1) 1500 mg (9) 1000 mg (1) 750 mg (1) 1500 + 500 mg (2) | 1 dose (5) 2 doses, 1 week apart (5) 3 doses, 1 week apart (2) 4 doses, 1 week apart (1) >4 doses (10) |
| Tobudic S, et al. | [26] | 38 | Retrospective | Osteomyelitis (20) Spondylodiscitis (14) Septic arthritis (4) | NA | Clinical cure (19) Clinical failure (7) Clinical cure after different therapy (8) NA (4) | 1000 + 500 (6) 1500 + 1000 mg (28) 1500 + 1500 mg (4) | NA |
| Cain AR, et al. | [18] | 42 | Retrospective | Osteomyelitis (42) | S. aureus (23) NA (19) | Clinical cure (20) Relapse (13) Clinical failure (9) | 1500 mg (42) | 2 doses, 1 week apart (42) |
| Cojutti PG, et al. | [27] | 27 | Retrospective | Osteomyelitis (16) Spondylodiscitis (9) Arthritis (2) | NA | NA (27) | 1000 mg (NA) 1500 mg (NA) | NA |
| Cojutti PG, et al. | [11] | 2 | Prospective | Spondylodiscitis (1) Arthritis (1) | S. aureus (1) NA (1) | Clinical cure (1) Relapse (1) | 1500 mg (2) | 2 doses, 1 week apart (2) |
| Lueking R, et al. | [28] | 19 | Retrospective | Osteomyelitis (15) Arthritis (4) | MSSA (1) NA (18) | Clinical cure (18) Relapse (1) | 1500 + 1500 (1) NA (18) | 2 doses, 1 week apart (1) NA (14) |
| Tuan JJ, et al. | [29] | 23 | Retrospective | Osteomyelitis (21) Arthritis (2) | NA | Clinical cure (21) Clinical failure (1) Death from BJIs (1) | NA | NA |
| Mazzitelli M, et al. | [30] | 14 | Retrospective | Spondylodiscitis (14) | S. aureus (14) | Clinical cure (14) | 1500 mg (14) | 3 doses >1 week apart (7) 4 doses > 1 week apart (5) |
| Almangour TA, et al. | [31] | 9 | Retrospective | Osteomyelitis (6) Spondylodiscitis (3) | S. aureus (9) | Clinical cure (9) | NA (9) | NA |
| Dinh A, et al. | [17] | 48 | Retrospective | NA | NA | Clinical cure (35) Clinical failure (11) NA (2) | 1000 mg (2) 1500 mg (37) 1500 + 1000 mg (1) 1500 + 500 mg (2) 1000 + 500 + 500 + 500 mg (6) | 1 dose (5) 2 doses > 1 week apart (4) 2 doses, 1 week apart (30) 3 doses, 1 week apart (1) 4 doses > 1 week apart (3) >4 doses (5) |
| Loupa CV, et al. | [32] | 1 | Case report | Osteomyelitis (1) | Enterococcus spp. (1) | Lost at FU (1) | 1500 mg (1) | 2 doses > 1 week apart (1) |
| Bork JT, et al. | [33] | 14 | Retrospective | Osteomyelitis (13) Arthritis (1) | NA | Clinical cure (6) Clinical failure (4) Lost to FU (3) Unrelated death (1) | NA | NA |
| Ritchie H, et al. | [34] | 1 | Case report | Spondylodiscitis (1) | S. aureus (1) | Clinical cure after different therapy (1) | 1500 mg (1) | 1 dose (1) |
| Almangour TA, et al. | [35] | 1 | Case report | Spondylodiscitis (1) | S. aureus (1) | Clinical cure (1) | 1000 + 1000 + 500 mg for 6 times (1) | >4 doses (1) |
| Molina Collada J, et al. | [36] | 1 | Case report | Septic arthritis (1) | Other Gram-positive (1) | Clinical cure (1) | 1500 mg (1) | 1 dose (1) |
| Bryson-Cagn C, et al. | [37] | 10 | Retrospective | Osteomyelitis (4) Septic arthritis (3) Spondylodiscitis (3) | S. aureus (10) | Clinical cure (6) Clinical failure (3) NA (1) | 1000 mg (5) 1500 + 1000 + 500 + 500 + 500 mg (1) 1000 + 500 mg (3) 1000 + 500 + 500 mg (1) | 1 dose (5) 2 doses, 1 week apart (3) 3 doses, 1 week apart (1) >4 doses (1) |
| Type of osteoarticular infections | |
| N. of patients included | 388 (86.2%) |
| Osteomyelitis (n, %) | 280 (72.2%) |
| Spondylodiscitis (n, %) | 79 (20.4%) |
| Septic arthritis (n, %) | 29 (7.5%) |
| Site of infection | |
| N. of patients included | 178 (39.6%) |
| Osteomyelitis (total) | 148 |
| Lower extremities (n, %) | 123 (83.1%) |
| Upper extremities (n, %) | 18 (12.1%) |
| Other (n, %) | 7 (4.7%) |
| Spondylodiscitis | 30 |
| Lumbo-sacral (n, %) | 21 (70%) |
| Cervical-thoracic (n, %) | 8 (26.7%) |
| Both (n, %) | 1 (3.3%) |
| Isolated pathogens | |
| N. of isolated included | 243 |
| S. aureus * (n, %) | 164 (67.5%) |
| Other Gram-positive (n, %) | 24 (9.9%) |
| CoNS ** (n, %) | 28 (11.5%) |
| Enterococcus spp. *** (n, %) | 12 (4.9%) |
| Streptococcus spp. (n, %) | 9 (3.7%) |
| Gram-negative and fungi (n, %) | 6 (2.5%) |
| Sample type | |
| N. of patients included | 130 (28.9%) |
| Bone biopsy or deep tissues (n, %) | 110 (84.6%) |
| Blood (n, %) | 19 (14.6%) |
| Bone biopsy or deep tissues and blood (n, %) | 1 (0.8%) |
| Surgery before DBV | |
| N. of patients included | 159 (35.3%) |
| Patients who underwent surgery before DBV* (n,%) | 110 (69.2%) |
| Patients who did not undergo surgery before DBV (n,%) | 49 (30.8%) |
| Antibiotics pre-DBV | |
| N. of patients included | 239 (53.1%) |
| None (n,%) | 83 (34.7%) |
| Unspecified molecule (n,%) | 64 (26.8%) |
| Anti-MRSA IV (n,%) | 47 (19.7%) |
| Anti-MRSA AND anti-Gram-negative po (n,%) | 16 (6.7%) |
| Anti-MRSA AND anti-Gram-negative IV (n,%) | 14 (5.9%) |
| Anti-MRSA po (n,%) | 8 (3.4%) |
| Anti-Gram-positive (n,%) | 7 (2.9%) |
| Reason to switch to DBV | |
| N. of patients included | 96 (21.3%) |
| Failure of the previous antimicrobial regimen (n,%) | 45 (46.9%) |
| Simplification (n,%) | 19 (19.8%) |
| Adverse reaction (n,%) | 14 (14.6%) |
| Other (n,%) | 18 (18.8%) |
| Adverse reactions to DBV | |
| N. of patients included | 285 (63.3%) |
| No adverse reactions (n,%) | 255 (89.5%) |
| Adverse reaction (n,%): | 30 (10.5%) |
| ➢ Unspecified (n,%) | 13 (4.6%) |
| ➢ Cutaneous (n,%) | 7 (2.5%) |
| ➢ Nausea (n,%) | 6 (2.1%) |
| ➢ Diarrhoea (n,%) | 2 (0.7%) |
| ➢ INR abnormalities (n,%) | 1 (0.4%) |
| ➢ Acute kidney injuries (n,%) | 1 (0.4%) |
| Antibiotics co-administered | |
| N. of patients included | 238 (52.9%) |
| None (n,%) | 182 (76.5%) |
| Unspecified molecule (n,%) | 22 (9.2%) |
| Anti-MRSA AND anti-Gram-negative IV (n,%) | 10 (4.2%) |
| Anti-MRSA AND anti-Gram-negative po (n,%) | 13 (5.5%) |
| Anti-MRSA po (n,%) | 11 (4.6%) |
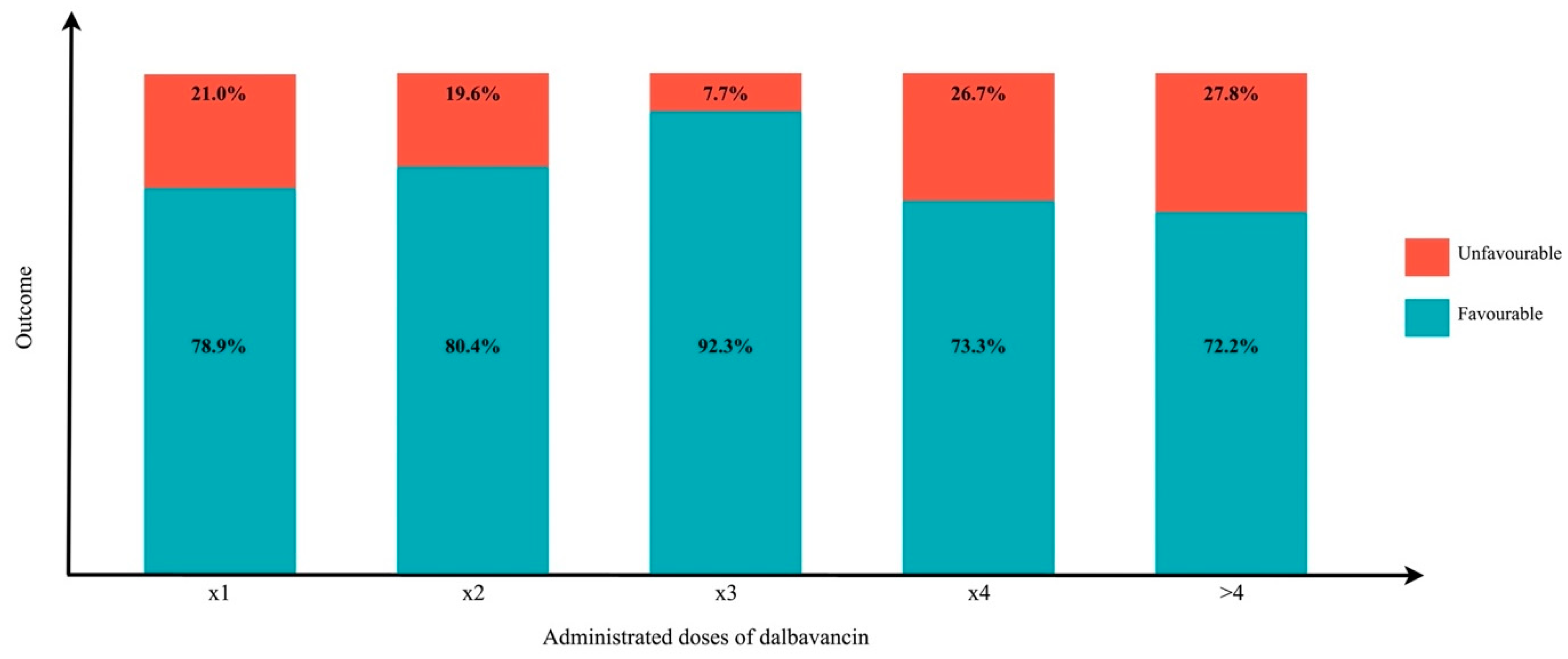
| DBV Scheme of Administration | n | 1500 + 1500 * n | 1500 + 1000 * n | 1500 + 500 * n | 1000 + 500 * n | 750 + 750 * n | Total (320 Patients) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 dose | 0 | 26 | 6 | 0 | 32 (10.0%) | ||
| 2 doses, More than 1 week apart | 1 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 13 (4.1%) |
| 2 doses, 1 week apart | 1 | 177 | 0 | 2 | 5 *** | 0 | 184 (57.5%) |
| 3 doses, More than 1 week apart | 2 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 8 (2.5%) |
| 3 doses, 1 week apart | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 7 (2.2%) |
| 4 doses, More than 1 week apart | 3 | 10 | 17 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 30 (9.4%) |
| 4 doses, 1 week apart | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 * | 4 | 0 | 5 (1.6%) |
| > 4 doses | x | 3 | 9 | 4 ** | 24 **** | 1 | 41 (12.8%) |
| Outcome at last visit | ||
| N. of patients included | 401 (89.1%) | |
| Success (n,%) | 318 (79.3%) | |
| Failure for persistent infection (n,%) | 44 (11.0%) | |
| Failure for relapse (n,%) | 21 (5.2%) | |
| Failure for need to switch therapy (n,%) | 10 (2.5%) | |
| Lost-to-follow-up (n,%) | 5 (1.2%) | |
| Infection-related death (n,%) | 1 (0.2%) | |
| Unrelated death (n,%) | 2 (0.5%) | |
| Outcome within and after 4 weeks since the end of treatment | ||
| N. of patients included | 12; 274 (60.9%) | |
| Outcome within 4 weeks | Outcome after 4 weeks | |
| Success (n,%) | 231 (84.3%) | 212 (77.4%) |
| Failure-persistent infection (n,%) | 37 (13.5%) | 25 (9.1%) |
| Failure-relapse (n,%) | 2 (0.7%) | 20 (7.3%) |
| Failure-switch therapy (n,%) | 0 (0.0%) | 10 (3.6%) |
| Lost-to-follow-up (n,%) | 4 (1.5%) | 5 (1.8%) |
| Infection-related death (n,%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Unrelated death (n,%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (0.7%) |
| Favourable Outcome | Unfavourable Outcome | |
| N. of patients included | 318 | 76 |
| Surgery before DBV | ||
| Patients with available data | 112 | 16 |
| Subjected to surgery before DBV (n,%) | 90 (80.4%) | 4 (25%) |
| Did not undergo surgery before DBV (n,%) | 22 (19.6%) | 12 (75%) |
| Isolated pathogens | ||
| Patients with available data | 68 | 10 |
| MRSA (n,%) | 39 (57.4%) | 8 (80%) |
| MSSA (n,%) | 14 (20.6%) | 2 (20%) |
| Other Gram-positive (n,%) | 6 (8.8%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| CoNS (n,%) | 6 (8.8%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Enterococcus spp. (n,%) | 2 (2.9%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Streptococcus spp. (n,%) | 1 (1.5%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Type of osteoarticular infections | ||
| Patients with available data | 242 | 59 |
| Osteomyelitis | 180 (74.4%) | 41 (70.7%) |
| Spondylodiscitis | 45 (18.6%) | 14 (23.7%) |
| Septic arthritis | 17 (7%) | 4 (6.8%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lovatti, S.; Tiecco, G.; Mulé, A.; Rossi, L.; Sforza, A.; Salvi, M.; Signorini, L.; Castelli, F.; Quiros-Roldan, E. Dalbavancin in Bone and Joint Infections: A Systematic Review. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071005
Lovatti S, Tiecco G, Mulé A, Rossi L, Sforza A, Salvi M, Signorini L, Castelli F, Quiros-Roldan E. Dalbavancin in Bone and Joint Infections: A Systematic Review. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(7):1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071005
Chicago/Turabian StyleLovatti, Sofia, Giorgio Tiecco, Alice Mulé, Luca Rossi, Anita Sforza, Martina Salvi, Liana Signorini, Francesco Castelli, and Eugenia Quiros-Roldan. 2023. "Dalbavancin in Bone and Joint Infections: A Systematic Review" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 7: 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071005
APA StyleLovatti, S., Tiecco, G., Mulé, A., Rossi, L., Sforza, A., Salvi, M., Signorini, L., Castelli, F., & Quiros-Roldan, E. (2023). Dalbavancin in Bone and Joint Infections: A Systematic Review. Pharmaceuticals, 16(7), 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071005







