Beneficial Effects of Zoledronic Acid on Tendons of the Osteogenesis Imperfecta Mouse (Oim)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
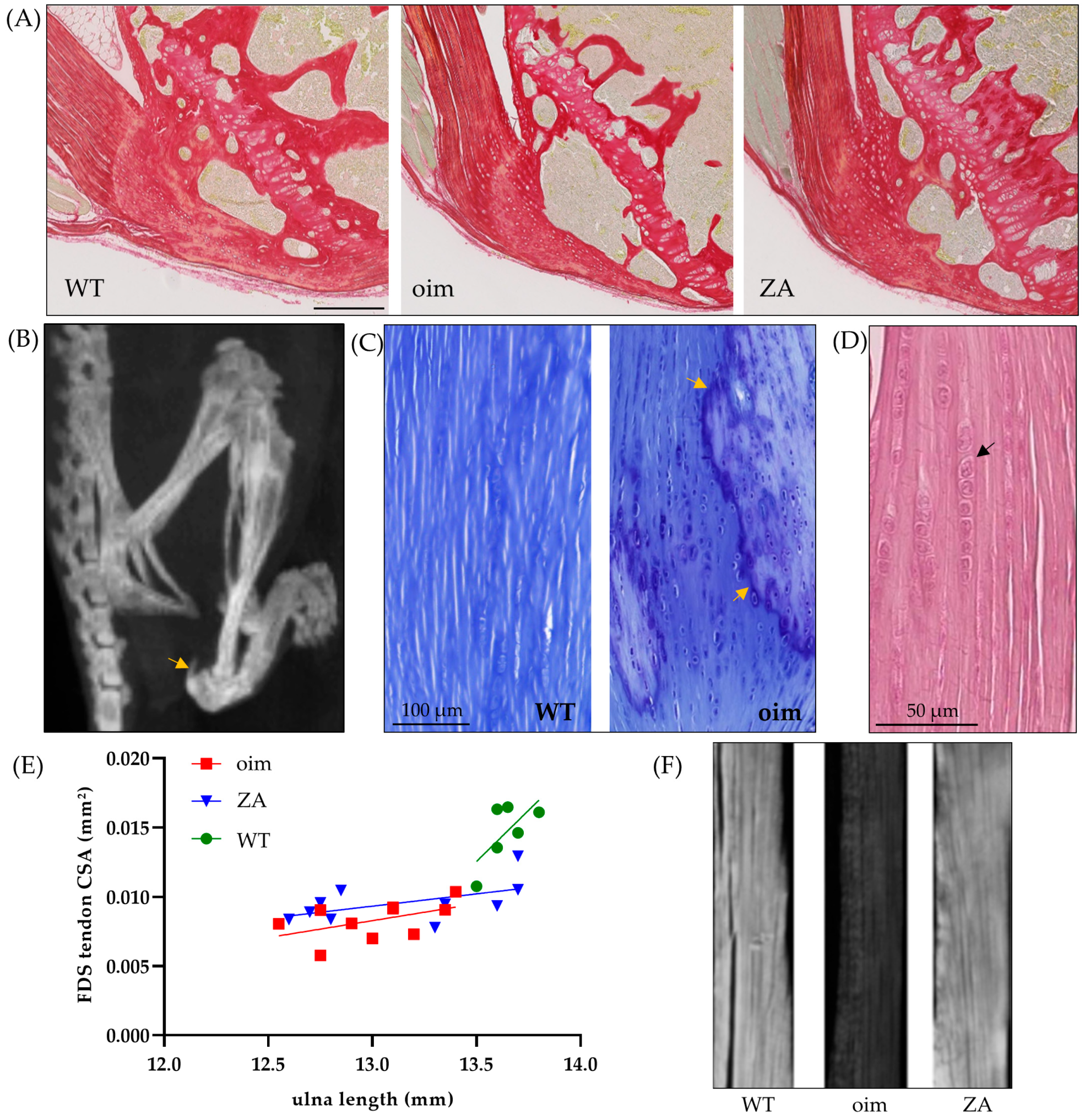
2.1. Macro- to Microscopic Analysis of Bone and Tendon
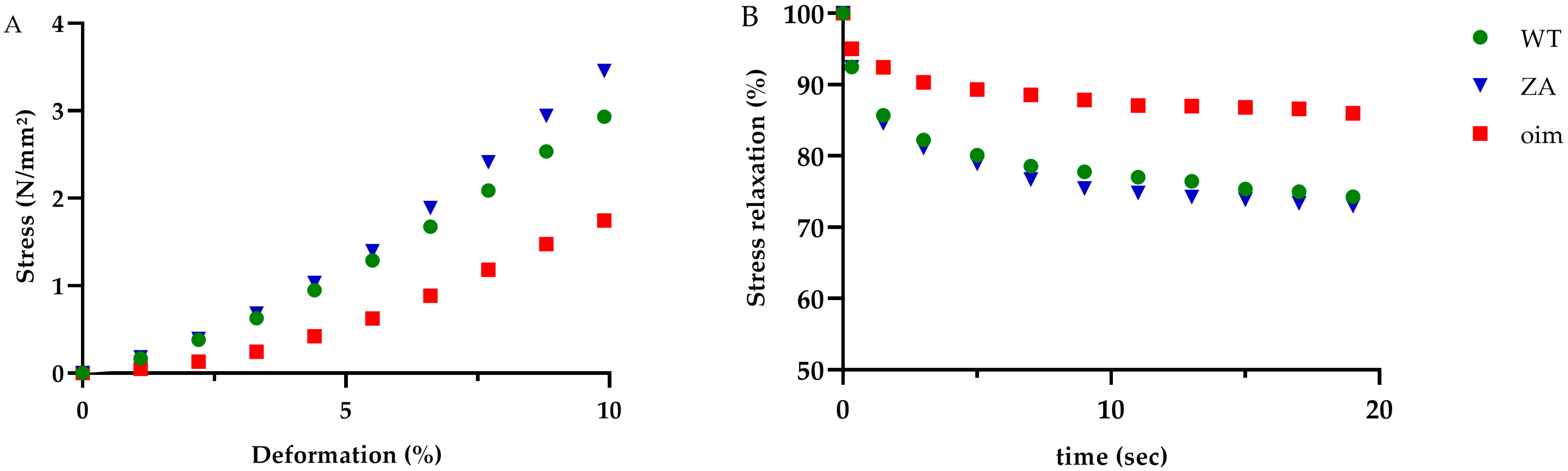
2.2. Mechanical Tests
2.3. Tissue Composition and Material Properties
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Procedures
4.3. Histology
4.4. Mechanical Test
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Raman Spectroscopy
4.7. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Theocharis, A.D.; Skandalis, S.S.; Gialeli, C.; Karamanos, N.K. Extracellular matrix structure. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 97, 4–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, F.; Glorieux, F.H. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Lancet 2004, 363, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baujat, G.; Lebre, A.S.; Cormier-Daire, V.; Le Merrer, M. Ostéogenèse imparfaite, annonce du diagnostic (classification clinique et génétique). Arch. Pédiatrie 2008, 15, 789–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaripova, A.R.; Khusainova, R.I. Modern classification and molecular-genetic aspects of osteogenesis imperfecta. Vavilovskii Zhurnal Genet Sel. 2020, 24, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Garcia, J.; Heymann, D.; Giurgea, I.; Legendre, M.; Amselem, S.; Castañeda, B.; Lézot, F.; William Vargas-Franco, J. Pharmacological options in the treatment of osteogenesis imperfecta: A comprehensive review of clinical and potential alternatives. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 213, 115584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. Bisphosphonates pathway. Pharm. Genom. 2011, 21, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sánchez, L.M.; Cabrera-Pedroza, A.U.; Palacios-Saucedo, G.; de la Fuente-Cortez, B. Zoledronic acid (zoledronate) in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. Gac. Med. Mex. 2015, 151, 164–168. [Google Scholar]
- Biggin, A.; Munns, C.F. Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Diagnosis and Treatment. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2014, 12, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournis, S.; Dede, A.D. Osteogenesis imperfecta—A clinical update. Metabolism 2018, 80, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasra, M.H.; Dijanic, C.; Sudah, S.; Michel, C.R.; Cohen, J. Simultaneous Bilateral Patellar Tendon Rupture in a Patient With Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Cureus 2021, 13, e15466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.; Mahajan, U. Tibial-tubercle avulsion and patellar-tendon rupture in pre-pubertal child with osteogenesis imperfecta(OI): Case report and review of current treatment in OI. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 11, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Yousef, M.A.; Rosenfeld, S. Acute traumatic rupture of the patellar tendon in pediatric population: Case series and review of the literature. Injury 2017, 48, 2515–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.A.; Haddad, F.S. Distal patellar tendon avulsion fracture in a football player with osteogenesis imperfecta. Knee Surg. Sport. Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2012, 20, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grol, M.W.; Haelterman, N.A.; Lim, J.; Munivez, E.M.; Archer, M.; Hudson, D.M.; Tufa, S.F.; Keene, D.R.; Lei, K.; Park, D.; et al. Tendon and motor phenotypes in the Crtap(-/-) mouse model of recessive osteogenesis imperfecta. eLife 2021, 10, e63488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkam, L.; Boraschi-Diaz, I.; Svensson, R.B.; Kjaer, M.; Komarova, S.V.; Bergeron, R.; Rauch, F.; Veilleux, L.N. Tendon properties in a mouse model of severe osteogenesis imperfecta. Connect. Tissue Res. 2022, 64, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J.R.; McBride, D.J., Jr.; Fedarko, N.S. OIM and related animal models of osteogenesis imperfecta. Connect. Tissue Res. 1995, 31, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinal, M.; Dessain, A.; Roels, T.; Lafont, S.; Ominsky, M.S.; Devogelaer, J.P.; Chappard, D.; Mabilleau, G.; Ammann, P.; Nyssen-Behets, C.; et al. Sclerostin-Antibody Treatment Decreases Fracture Rates in Axial Skeleton and Improves the Skeletal Phenotype in Growing oim/oim Mice. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2020, 106, 494–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chretien, A.; Couchot, M.; Mabilleau, G.; Behets, C. Biomechanical, Microstructural and Material Properties of Tendon and Bone in the Young Oim Mice Model of Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukunami, C.; Yoshimoto, Y.; Takimoto, A.; Yamashita, H.; Hiraki, Y. Molecular characterization and function of tenomodulin, a marker of tendons and ligaments that integrate musculoskeletal components. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2016, 52, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Marumo, K. Collagen cross-links as a determinant of bone quality: A possible explanation for bone fragility in aging, osteoporosis, and diabetes mellitus. Osteoporos. Int. 2010, 21, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, M.; Akkus, O. Raman spectral classification of mineral- and collagen-bound water’s associations to elastic and post-yield mechanical properties of cortical bone. Bone 2015, 81, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killian, M.L. Growth and mechanobiology of the tendon-bone enthesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 123, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, A.G.; Organ, J.M.; Allen, M.R.; Wallace, J.M. Muscle contraction induces osteogenic levels of cortical bone strain despite muscle weakness in a mouse model of Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Bone 2020, 132, 115061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.Q.; Wang, J.H. Creating an Animal Model of Tendinopathy by Inducing Chondrogenic Differentiation with Kartogenin. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.H. The effects of mechanical loading on tendons--an in vivo and in vitro model study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, S.; Otsuru, S.; Candela, M.E.; Cantley, L.; Uchibe, K.; Hofmann, T.J.; Zhang, K.; Wapner, K.L.; Soslowsky, L.J.; Horwitz, E.M.; et al. Tendon progenitor cells in injured tendons have strong chondrogenic potential: The CD105-negative subpopulation induces chondrogenic degeneration. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 3266–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suydam, S.M.; Soulas, E.M.; Elliott, D.M.; Silbernagel, K.G.; Buchanan, T.S.; Cortes, D.H. Viscoelastic properties of healthy achilles tendon are independent of isometric plantar flexion strength and cross-sectional area. J. Orthop. Res. 2015, 33, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappu, P.; Salo, A.M.; Myllyharju, J.; Heino, J. Role of prolyl hydroxylation in the molecular interactions of collagens. Essays Biochem. 2019, 63, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Marumo, K. Effects of Collagen Crosslinking on Bone Material Properties in Health and Disease. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 97, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautieri, A.; Redaelli, A.; Buehler, M.J.; Vesentini, S. Age- and diabetes-related nonenzymatic crosslinks in collagen fibrils: Candidate amino acids involved in Advanced Glycation End-products. Matrix Biol. 2014, 34, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.; Khan, M.A.; Sadaf, A.; Younus, H. A structural study on the protection of glycation of superoxide dismutase by thymoquinone. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 69, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.; Khan, S.; Almatroudi, A.; Khan, A.A.; Alsahli, M.A.; Almatroodi, S.A.; Rahmani, A.H. A review on mechanism of inhibition of advanced glycation end products formation by plant derived polyphenolic compounds. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 787–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wouters, S.; Detrembleur, C.; Durnez, A.; Mahaudens, P.; Henry, B.; Schrooyen, J.; Docquier, P.L. Quantitative gait analysis in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: Relationship between gait deviations and clinical features. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2022, 88, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.I.; Lee, J.S.; Kang, K.T.; Shim, Y.B.; Kim, Y.S.; Jang, J.W.; Moon, S.H.; D’Lima, D.D. In Vitro and In Vivo Performance of Tissue-Engineered Tendons for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2018, 46, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Song, G.; Ju, Y.; Li, X.; Song, Y.; Watanabe, S. RhoA/ROCK, cytoskeletal dynamics, and focal adhesion kinase are required for mechanical stretch-induced tenogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 2722–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Xu, J.; Fei, Y.; Heng, B.C.; Jiang, X.; Chen, W.; Shen, W. Tendon Stem/Progenitor Cell Subpopulations and Their Implications in Tendon Biology. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 631272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Thampatty, B.P.; Wang, J.H. Tendon Stem/Progenitor Cells and Their Interactions with Extracellular Matrix and Mechanical Loading. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 3674647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiesz, E.M.; Thorpe, C.T.; Thurner, P.J.; Screen, H.R.C. Structure and collagen crimp patterns of functionally distinct equine tendons, revealed by quantitative polarised light microscopy (qPLM). Acta Biomater. 2018, 70, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazon, J.; de Aro, A.A.; Simões, P.W.; Pimentel, E.R. Effect of different resistance-training protocols on the extracellular matrix of the calcaneal tendon of rats. Ann. Anat.-Anat. Anz. 2018, 216, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Deng, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Fu, W. Exercise Effects on the Biomechanical Properties of the Achilles Tendon—A Narrative Review. Biology 2022, 11, 172. [Google Scholar]
- Masic, A.; Bertinetti, L.; Schuetz, R.; Chang, S.-W.; Metzger, T.H.; Buehler, M.J.; Fratzl, P. Osmotic pressure induced tensile forces in tendon collagen. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, H.; Wagermaier, W.; Horbelt, N.; Scoppola, E.; Li, C.; Werner, P.; Fu, Z.; Fratzl, P. Mineralization generates megapascal contractile stresses in collagen fibrils. Science 2022, 376, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanvetyanon, T.; Stiff, P.J. Management of the adverse effects associated with intravenous bisphosphonates. Ann. Oncol. 2006, 17, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjorthaug, G.A.; Søreide, E.; Nordsletten, L.; Madsen, J.E.; Reinholt, F.P.; Niratisairak, S.; Dimmen, S. Negative effect of zoledronic acid on tendon-to-bone healing. Acta Orthop. 2018, 89, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besio, R.; Iula, G.; Garibaldi, N.; Cipolla, L.; Sabbioneda, S.; Biggiogera, M.; Marini, J.C.; Rossi, A.; Forlino, A. 4-PBA ameliorates cellular homeostasis in fibroblasts from osteogenesis imperfecta patients by enhancing autophagy and stimulating protein secretion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864 Pt A, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutkowska-Skolimowska, J.; Brańska-Januszewska, J.; Strawa, J.W.; Ostrowska, H.; Botor, M.; Gawron, K.; Galicka, A. Rosemary Extract-Induced Autophagy and Decrease in Accumulation of Collagen Type I in Osteogenesis Imperfecta Skin Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, B.L.; Lewis, G.S.; Brown, J.L. Multiscale Poly-(ϵ-caprolactone) Scaffold Mimicking Nonlinearity in Tendon Tissue Mechanics. Regen. Eng. Transl. Med. 2016, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| WT | Oim | ZA | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative bone surface (BV/TV) | 0.65 ± 0.05 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 0.51 ± 0.03 | p < 0.001; a **; b,c * |
| Mean grey level (birefringence) | 89.5 ± 10.2 | 40.6 ± 4.1 | 95.0 ± 10.8 | p < 0.01; a,b ** |
| WT | Oim | ZA | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultimate stress (N/mm2) | 14.0 ± 1.7 | 9.8 ± 1.1 | 13.0 ± 1.9 | 0.16 |
| Ultimate strain (%) | 46.1 ± 3.6 | 49.9 ± 2.8 | 42.7 ± 3.1 | 0.30 |
| Toughness (N/mm2) | 313 ± 67 | 215 ± 29 | 274 ± 47 | 0.51 |
| Elastic Modulus (N/mm2) | 0.31 ± 0.06 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 0.32 ± 0.04 | 0.09 |
| Stress toe region (N/mm2) | 0.63 ± 0.11 | 0.32 ± 0.06 | 0.58 ±0.07 | p < 0.05 a,b * |
| Stress relaxation (%) | 27.4 ± 2.3 | 13.5 ± 1.7 | 27.9 ± 2.3 | p < 0.001 a,b ** |
| Raman Spectroscopy 700–1800 cm−1 | WT | Oim | ZA | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzymatic Collagen Cross-link IR 1670/1690 | 1.41 ± 0.32 | 1.24 ± 0.10 | 1.31 ± 0.25 | 0.15 |
| Pentosidine (AGE) IR 1345/920 | 1.91 ± 0.45 | 2.03 ± 0.20 | 2.55 ± 0.56 | p < 0.05 c * |
| Hydroxyproline IR 872/920 | 0.73 ± 0.16 | 0.57 ± 0.11 | 0.88 ± 0.21 | p < 0.05 b * |
| Glycosaminoglycan IR 1380/920 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.90 |
| Porosity IR 1380/920 | 7.1 ± 1.9 | 9.6 ± 3.4 | 11.6 ± 3.0 | p < 0.05 c * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chretien, A.; Mabilleau, G.; Lebacq, J.; Docquier, P.-L.; Behets, C. Beneficial Effects of Zoledronic Acid on Tendons of the Osteogenesis Imperfecta Mouse (Oim). Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060832
Chretien A, Mabilleau G, Lebacq J, Docquier P-L, Behets C. Beneficial Effects of Zoledronic Acid on Tendons of the Osteogenesis Imperfecta Mouse (Oim). Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(6):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060832
Chicago/Turabian StyleChretien, Antoine, Guillaume Mabilleau, Jean Lebacq, Pierre-Louis Docquier, and Catherine Behets. 2023. "Beneficial Effects of Zoledronic Acid on Tendons of the Osteogenesis Imperfecta Mouse (Oim)" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 6: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060832
APA StyleChretien, A., Mabilleau, G., Lebacq, J., Docquier, P.-L., & Behets, C. (2023). Beneficial Effects of Zoledronic Acid on Tendons of the Osteogenesis Imperfecta Mouse (Oim). Pharmaceuticals, 16(6), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060832





