Preparation and Characterization of Amorphous Solid Dispersions for the Solubilization of Fenretinide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
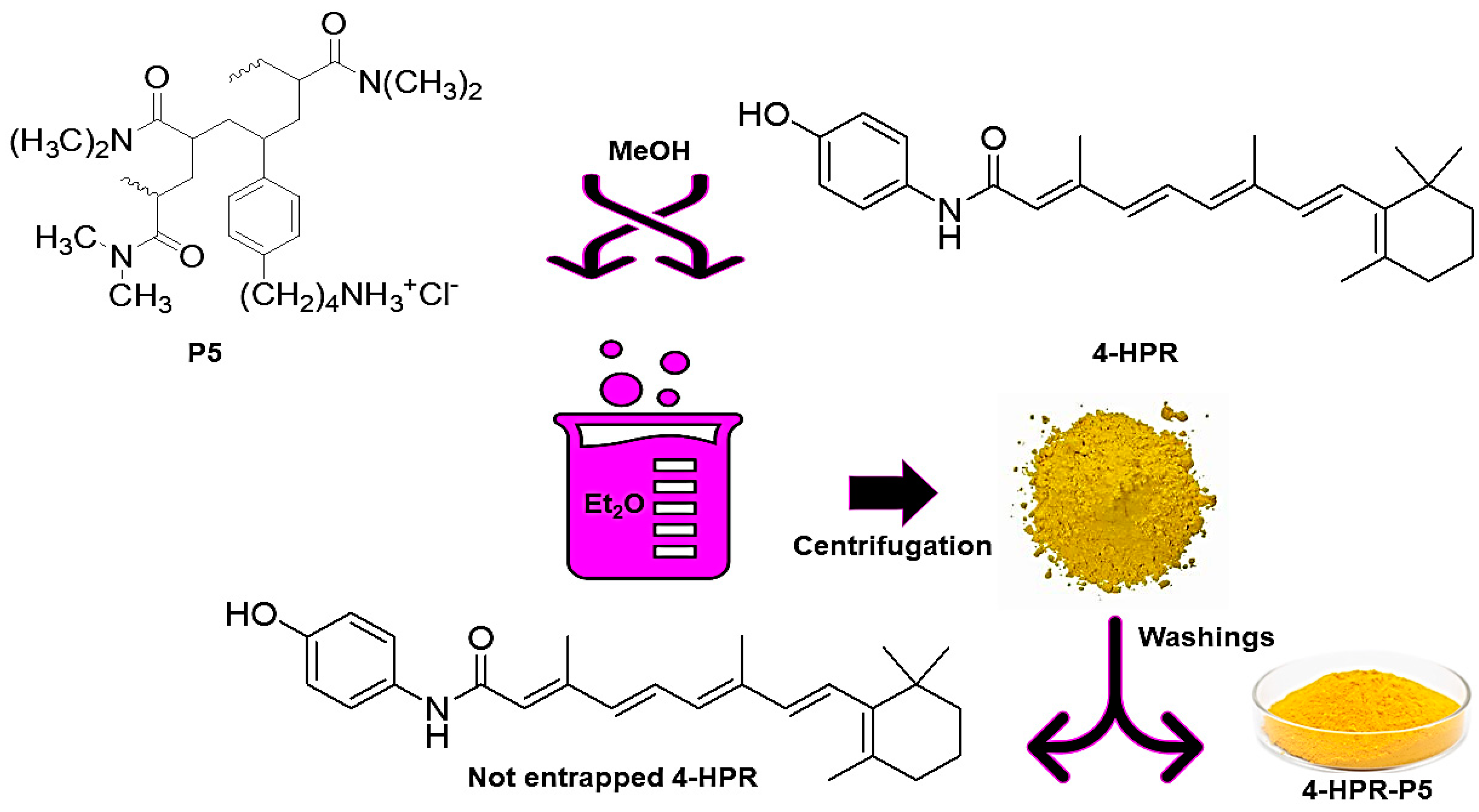
2.1. Preparation of 4-HPR-P5 NPs
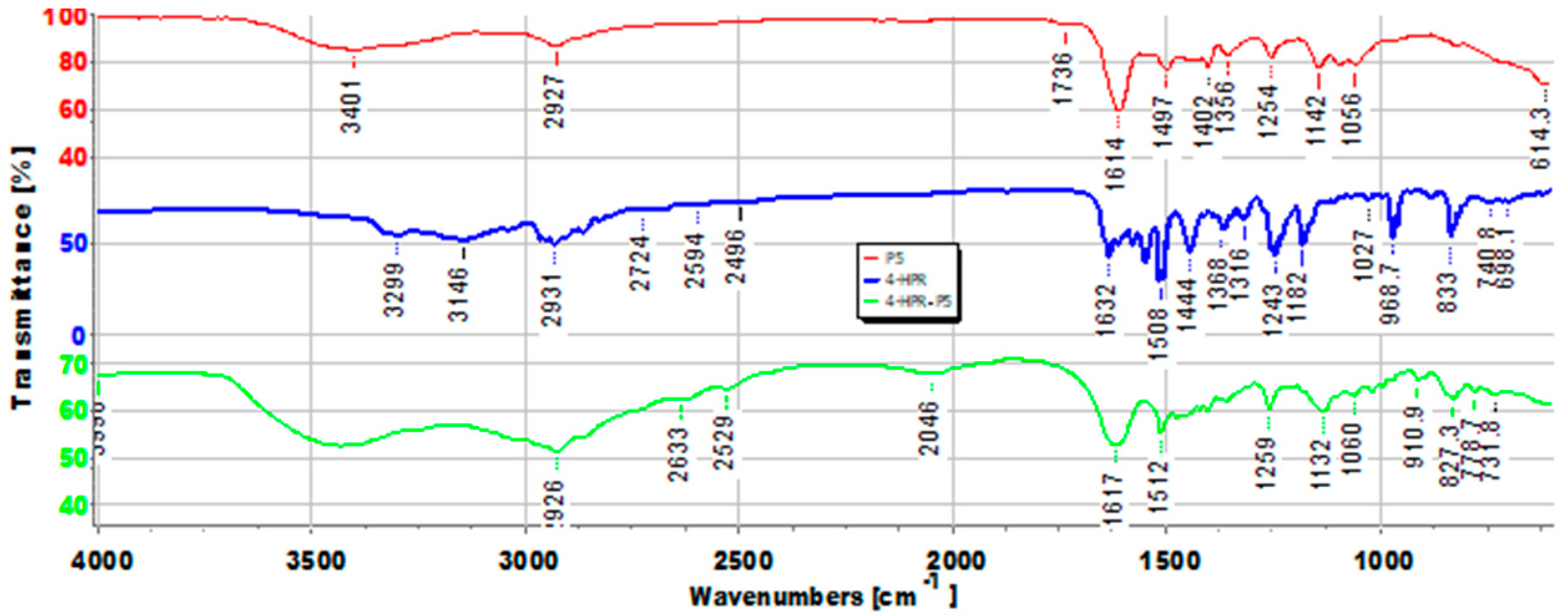
2.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of ATR-FTIR Data
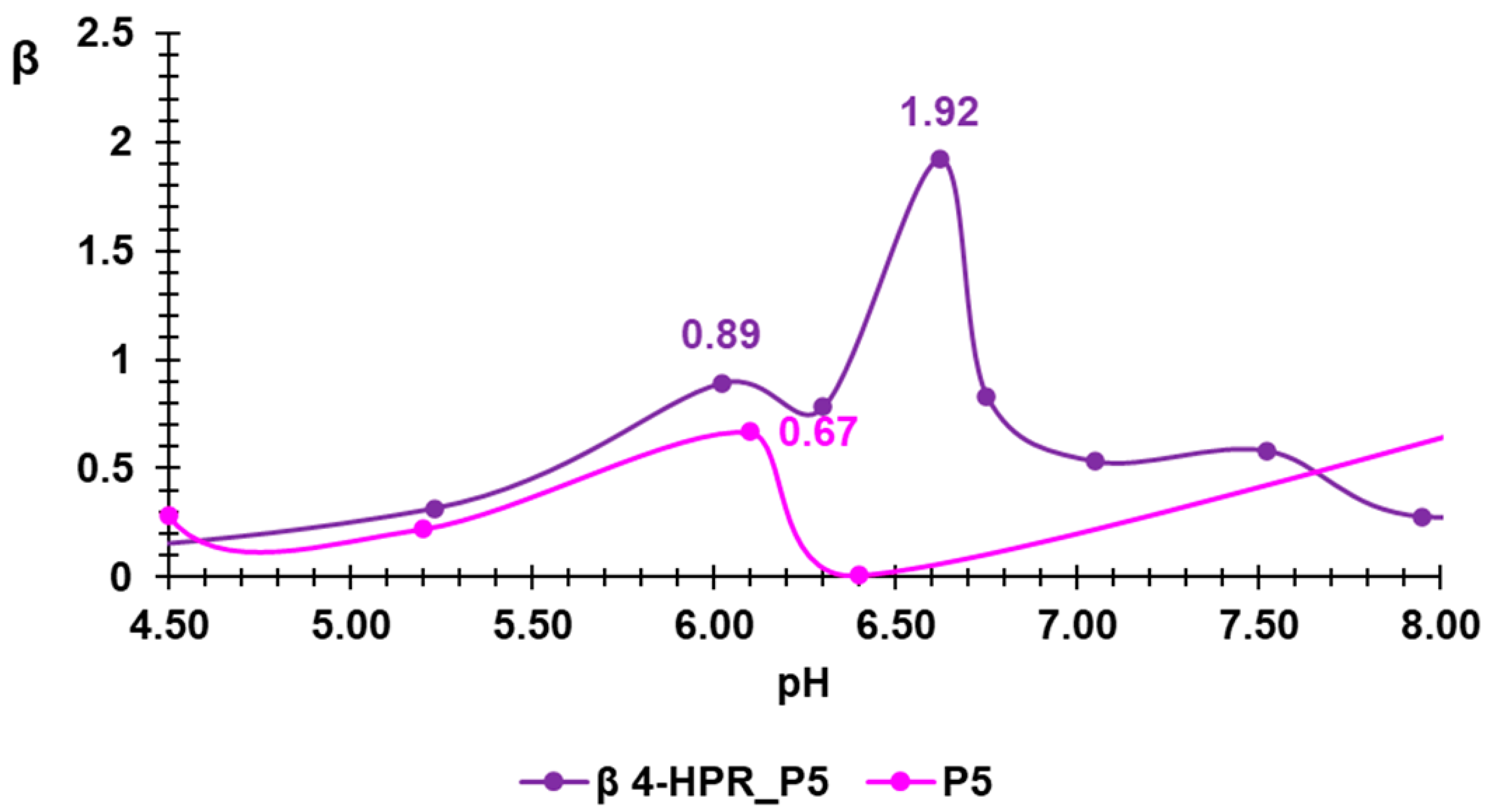
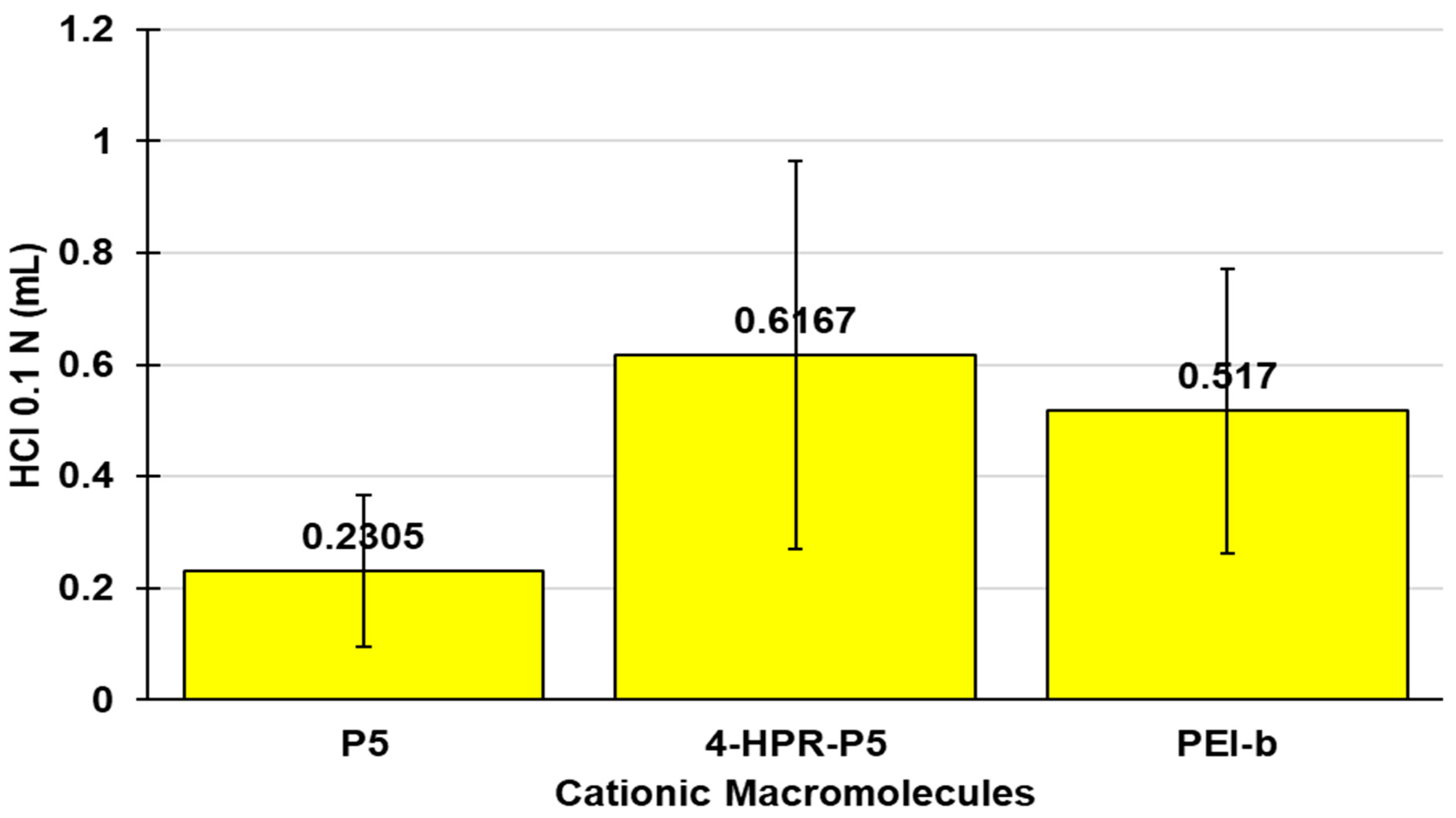
2.3. Potentiometric Titrations of 4-HPR-P5 NPs
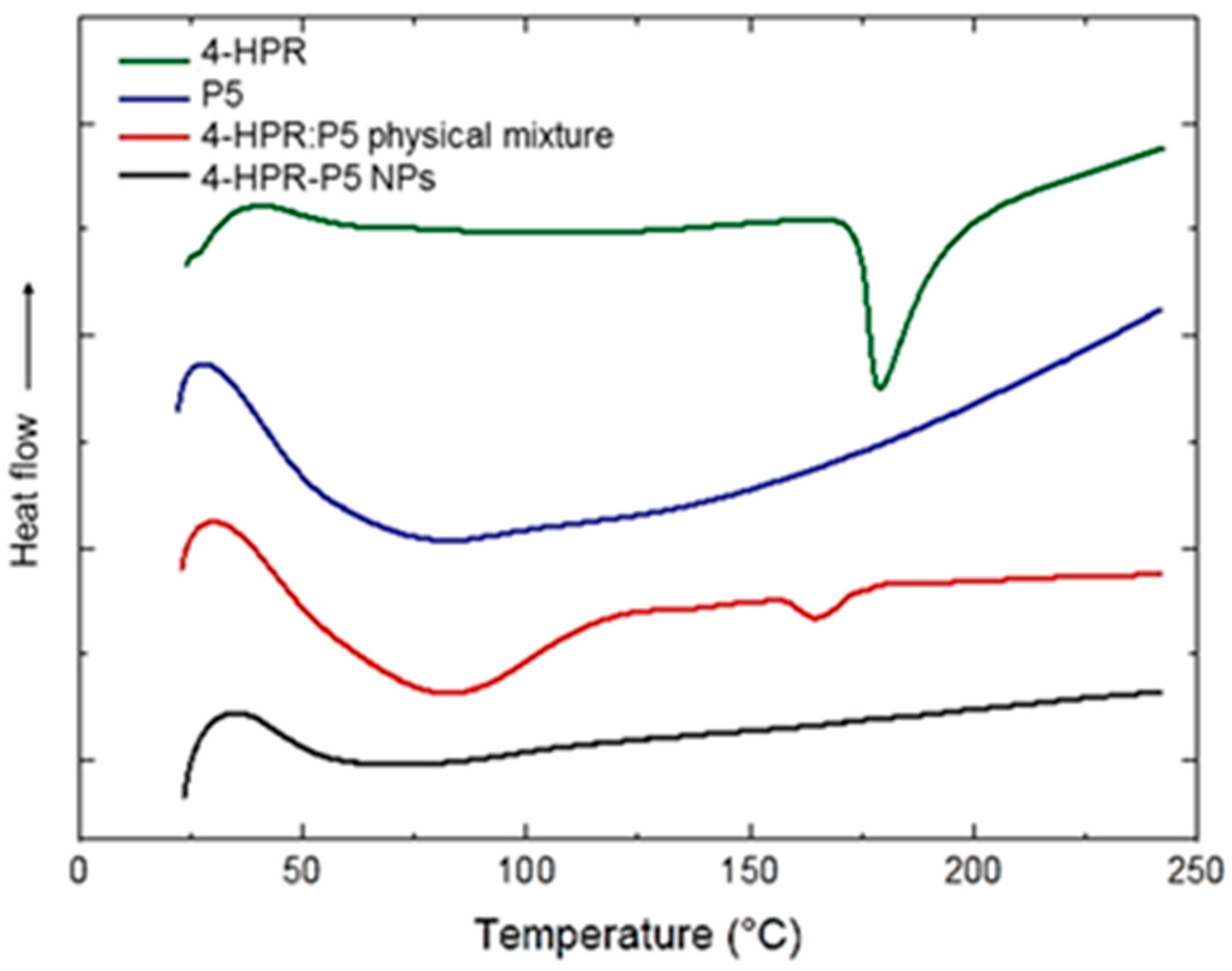
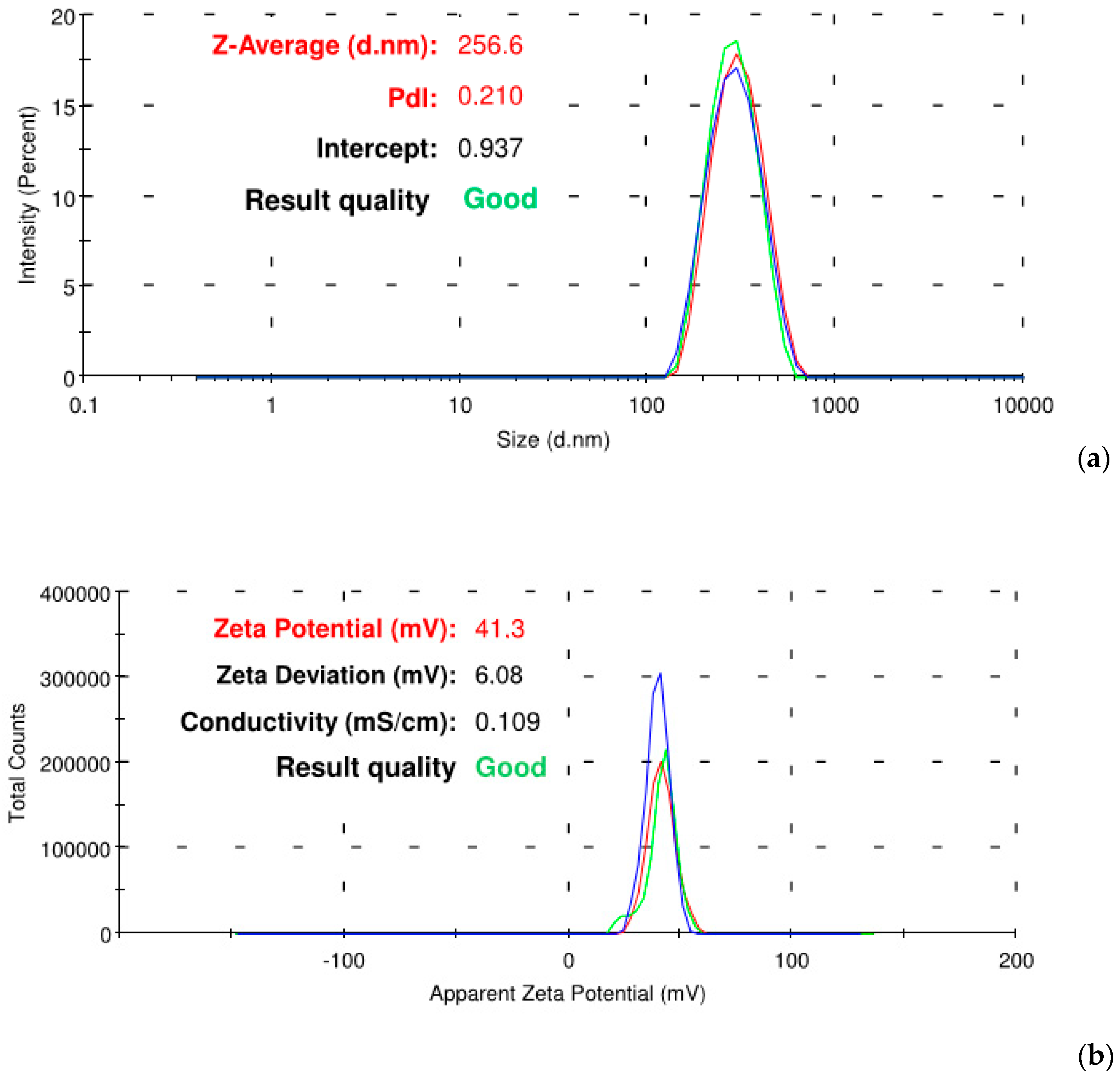
2.4. 4-HPR-P5 NPs Characterization
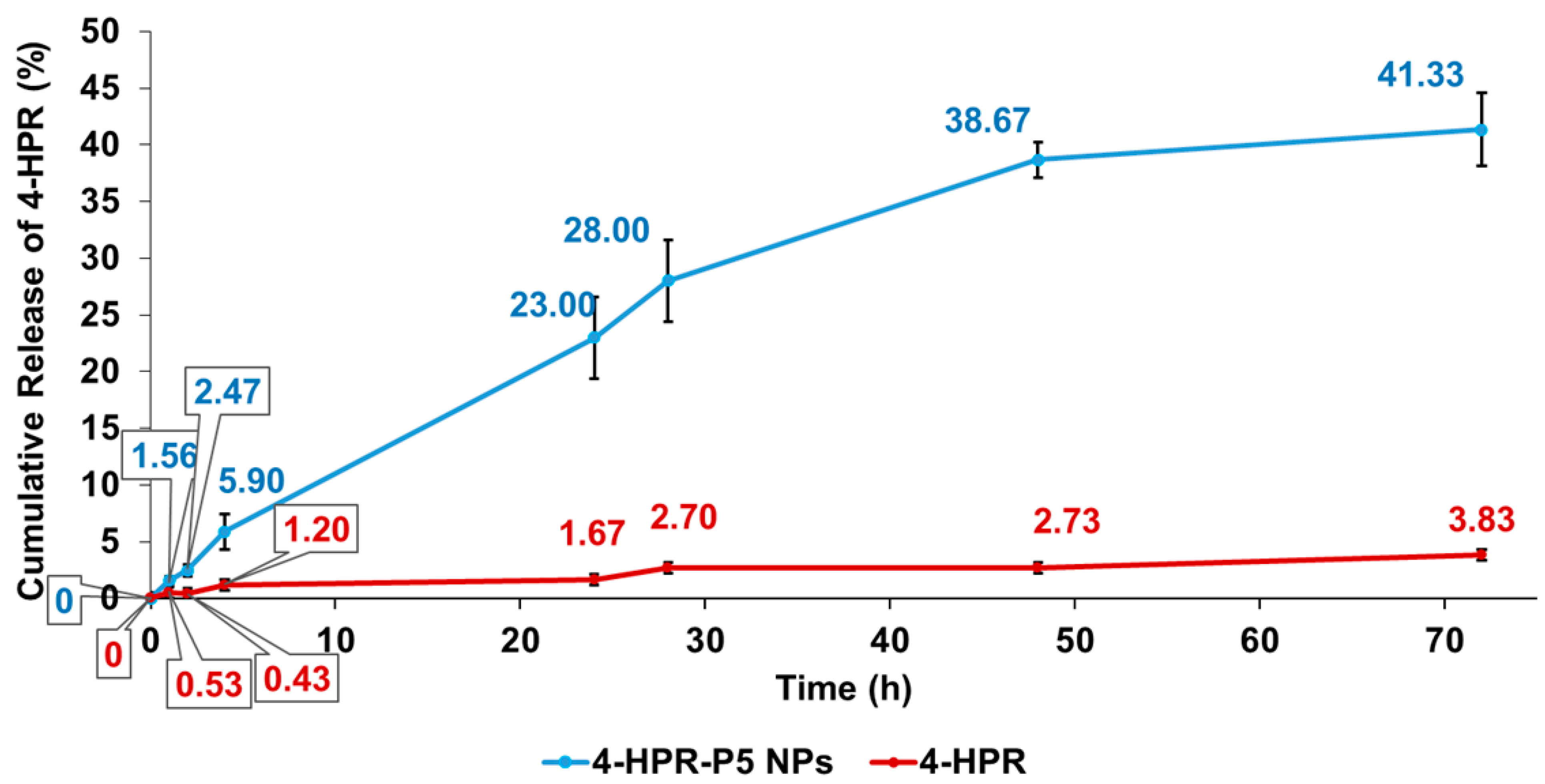
2.5. In Vitro Release Profile of 4-HPR from 4-HPR-P5 NPs
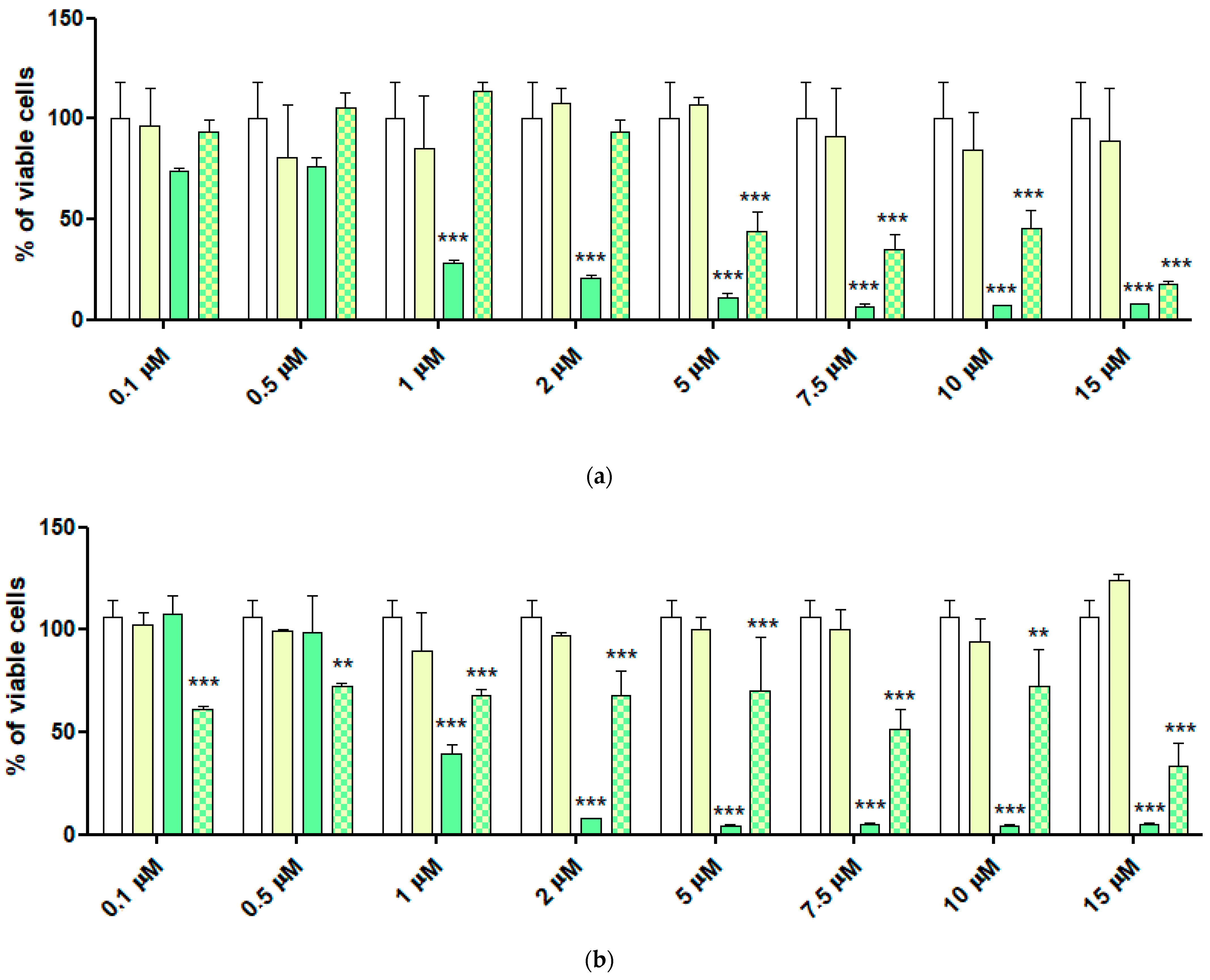
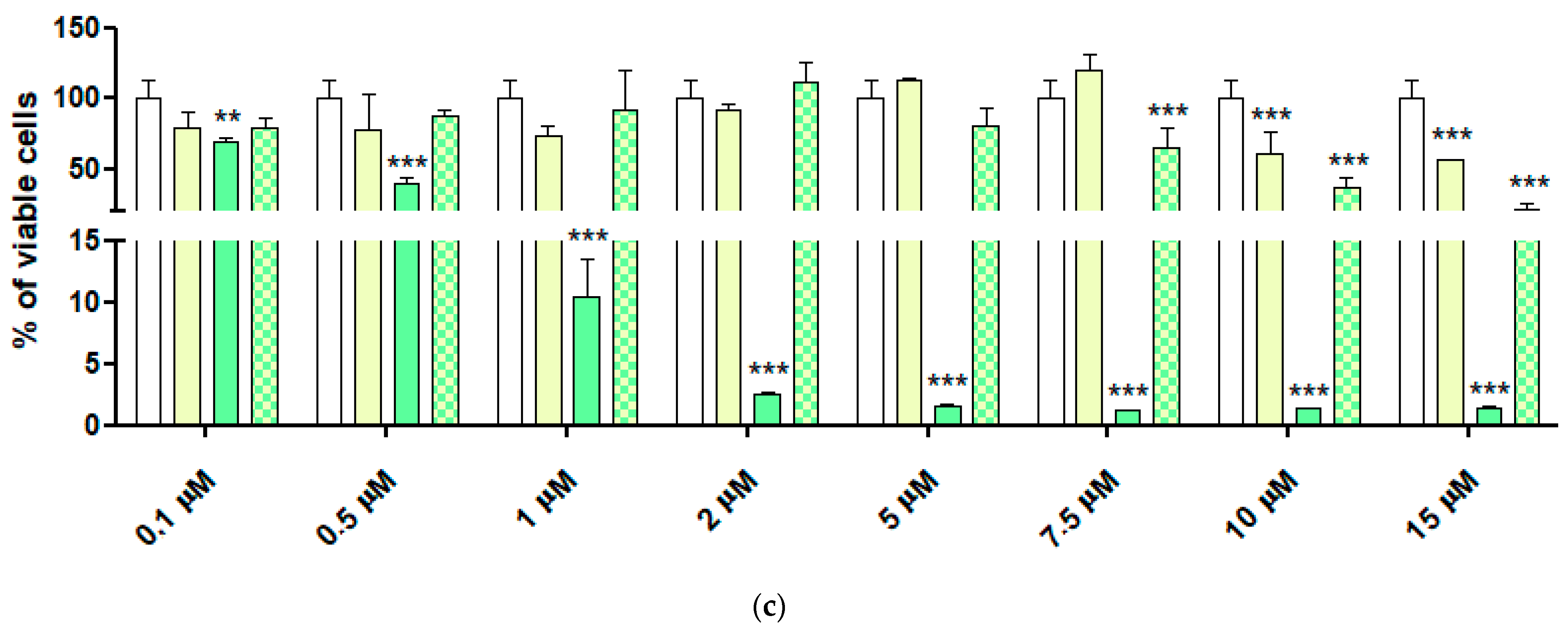
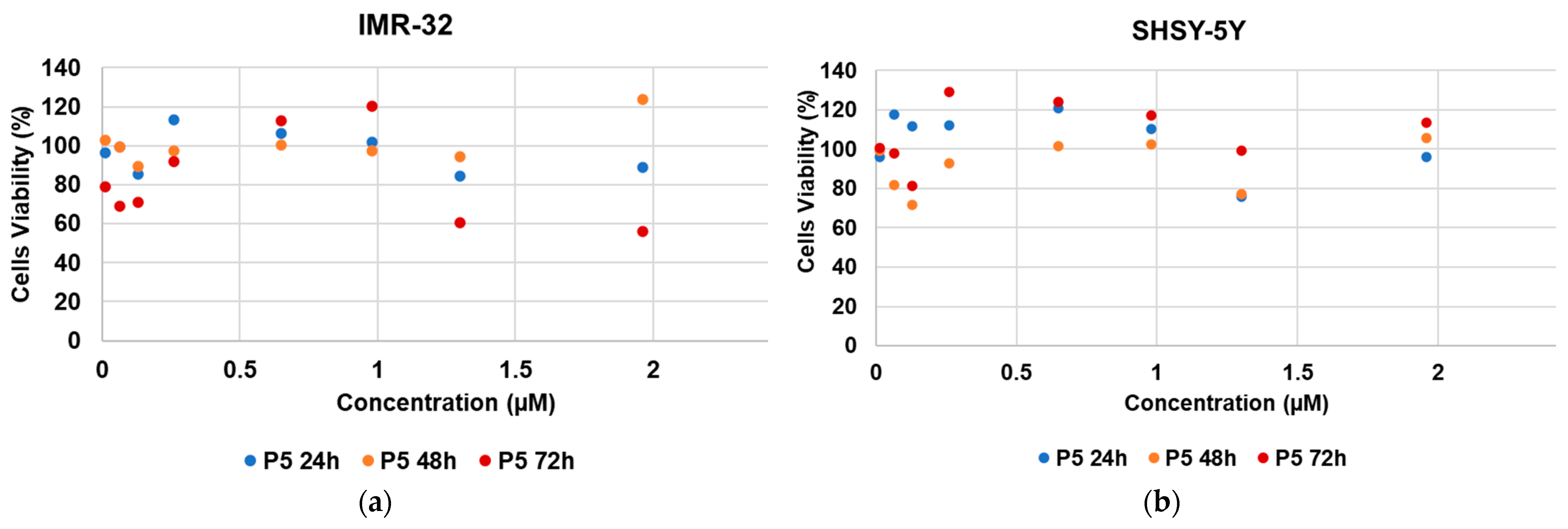
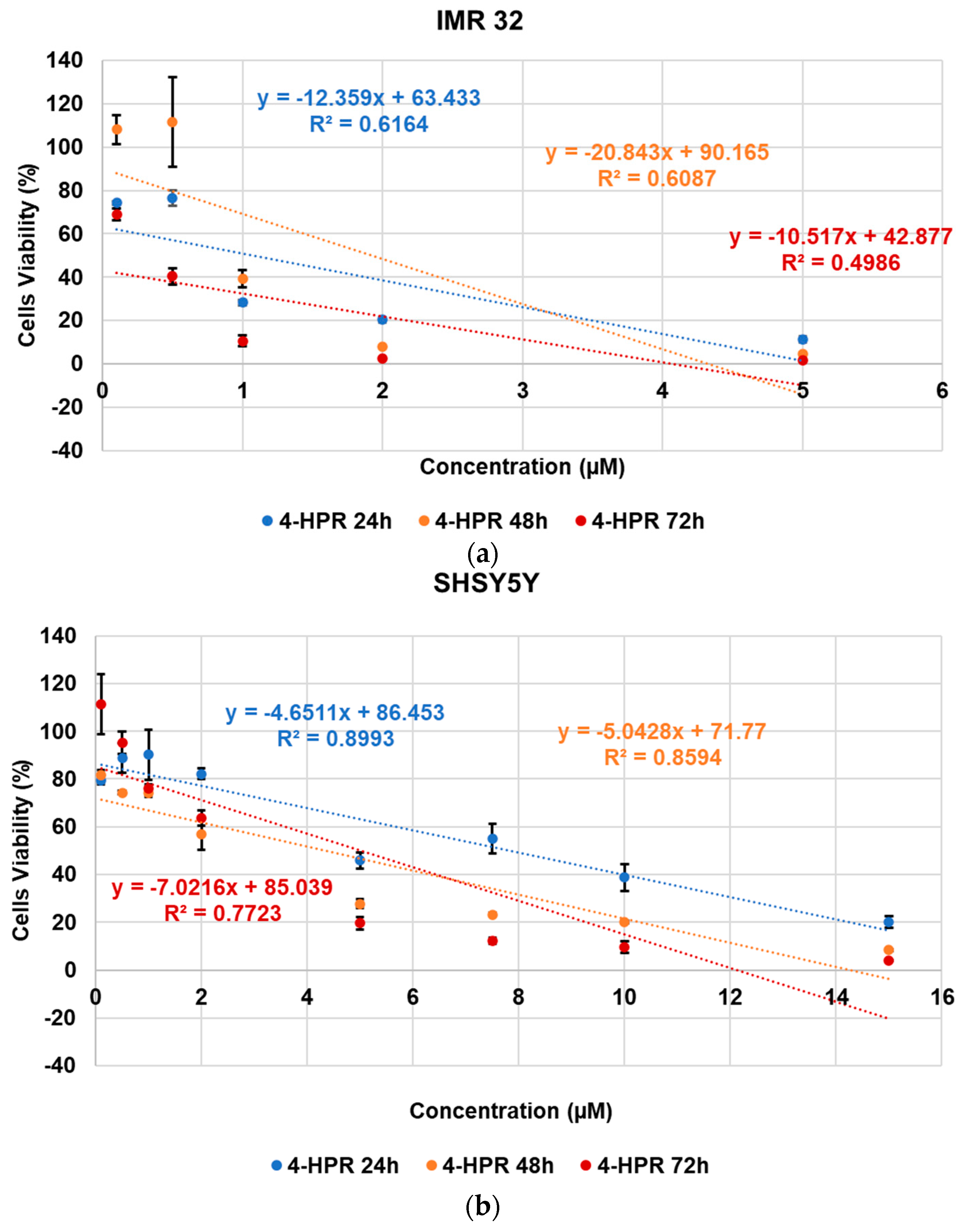
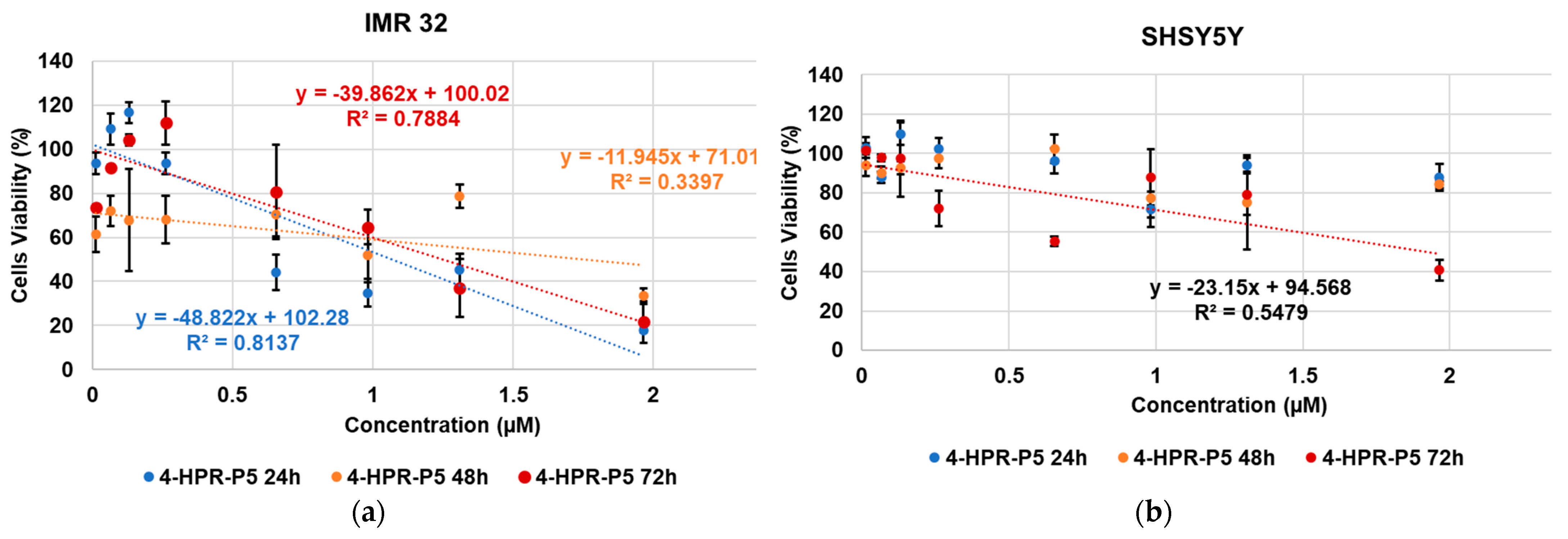
2.6. Cytotoxic Activity of 4-HPR and 4-HPR-P5 NPs on Neuroblastoma Cell Lines
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental Procedure to Prepare 4-HPR-Loaded P5-Based NPs
3.2. Chemometric-Assisted ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
3.3. Potentiometric Titration of 4-HPR-P5 NPs
3.4. Characterization of 4-HPR-P5 NPs: Drug Loading, Solubility, and Stability
3.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.6. Determination of Size, Polydispersity Index, and Zeta Potential
3.7. In Vitro Release Studies
3.8. Cell Viability Studies
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sporn, M.B.; Dunlop, N.M.; Newton, D.L.; Henderson, W.R. Relationships between Structure and Activity of Retinoids. Nature 1976, 263, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.P.; Reynolds, C.P.; Cho, H.; Kang, M.H. Clinical Development of Fenretinide as an Antineoplastic Drug: Pharmacology Perspectives. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazzaniga, M.; Varricchio, C.; Montefrancesco, C.; Feroce, I.; Guerrieri-Gonzaga, A. Fenretinide (4-HPR): A Preventive Chance for Women at Genetic and Familial Risk? J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 172897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villablanca, J.G.; London, W.B.; Naranjo, A.; McGrady, P.; Ames, M.M.; Reid, J.M.; McGovern, R.M.; Buhrow, S.A.; Jackson, H.; Stranzinger, E.; et al. Phase II Study of Oral Capsular 4-Hydroxyphenylretinamide (4-HPR/Fenretinide) in Pediatric Patients with Refractory or Recurrent Neuroblastoma: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6858–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, B.J.; Kang, M.H.; Villablanca, J.G.; Janeba, J.; Groshen, S.; Matthay, K.K.; Sondel, P.M.; Maris, J.M.; Jackson, H.A.; Goodarzian, F.; et al. Phase I Trial of Fenretinide Delivered Orally in a Novel Organized Lipid Complex in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Neuroblastoma: A Report from the New Approaches to Neuroblastoma Therapy (NANT) Consortium: Phase I Trial of Fenretinide/LXS Powder. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.S.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Maurer, B.J.; Groshen, S.; Pinski, J.K.; Cobos, E.; Gandara, D.R.; Lenz, H.J.; Kang, M.H.; Reynolds, C.P.; et al. A phase I study of intravenous fenretinide (4-HPR) for patients with malignant solid tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orienti, I.; Zuccari, G.; Carosio, R.; Montaldo, P.G. Improvement of Aqueous Solubility of Fenretinide and Other Hydrophobic Anti-Tumor Drugs by Complexation with Amphiphilic Dextrins. Drug Deliv. 2009, 16, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orienti, I.; Zuccari, G.; Falconi, M.; Teti, G.; Illingworth, N.A.; Veal, G.J. Novel Micelles Based on Amphiphilic Branched PEG as Carriers for Fenretinide. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orienti, I.; Zuccari, G.; Bergamante, V.; Carosio, R.; Gotti, R.; Cilli, M. Montaldo Fenretinide-Polyvinylalcohol Conjugates: New Systems Allowing Fenretinide Intravenous Administration. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3258–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wischke, C.; Mittal, S.; Mitra, A.; Schwendeman, S.P. Design of Controlled Release PLGA Microspheres for Hydrophobic Fenretinide. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 2622–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paolo, D.; Pastorino, F.; Zuccari, G.; Caffa, I.; Loi, M.; Marimpietri, D.; Brignole, C.; Perri, P.; Cilli, M.; Nico, B.; et al. Enhanced Anti-Tumor and Anti-Angiogenic Efficacy of a Novel Liposomal Fenretinide on Human Neuroblastoma. J. Control. Release 2013, 170, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orienti, I.; Salvati, V.; Sette, G.; Zucchetti, M.; Bongiorno-Borbone, L.; Peschiaroli, A.; Zolla, L.; Francescangeli, F.; Ferrari, M.; Matteo, C.; et al. A Novel Oral Micellar Fenretinide Formulation with Enhanced Bioavailability and Antitumour Activity against Multiple Tumours from Cancer Stem Cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghel, S.; Cathcart, H.; O’Reilly, N.J. Polymeric amorphous solid dispersions: A review of amorphization, crystallization, stabilization, solid-state characterization, and aqueous solubilization of biopharmaceutical classification system class II drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vemula, V.R.; Lagishetty, V.; Lingala, S. Solubility enhancement techniques. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2010, 5, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, K.J.; Rosenblatt, K.M.; Westedt, U.; Hölig, P.; Rosenberg, J.; Mägerlein, M.; Fricker, G.; Brandl, M. Amorphous solid dispersion enhances permeation of poorly soluble ABT-102: True supersaturation vs. apparent solubility enhancement. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 437, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhujbal, S.V.; Pathak, V.; Zemlyanov, D.Y.; Taylor, L.S.; Zhou, Q. Physical Stability and Dissolution of Lumefantrine Amorphous Solid Dispersions Produced by Spray Anti-Solvent Precipitation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 2423–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.; Schenck, L.; Koynov, A.; Su, Y.; Li, Y.; Variankaval, N. Optimizing Solvent Selection and Processing Conditions to Generate High Bulk-Density, Co-Precipitated Amorphous Dispersions of Posaconazole. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jermain, S.V.; Brough, C.; Williams, R.O., III. Amorphous solid dispersions and nanocrystal technologies for poorly water-soluble drug delivery—An update. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Ho, C. Amorphous solid dispersions: Utilization and challenges in drug discovery and development. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 3237–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudie, D.M.; Buchanan, S.; Stewart, A.M.; Smith, A.; Shepard, K.B.; Biswas, N.; Marshall, D.; Ekdahl, A.; Pluntze, A.; Craig, C.D. A novel architecture for achieving high drug loading in amorphous spray dried dispersion tablets. Int. J. Pharm. X 2020, 2, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitenbach, J. Melt extrusion: From process to drug delivery technology. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2002, 54, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshman, J.P.; Cao, Y.; Kowalski, J.; Serajuddin, A.T. Application of melt extrusion in the development of a physically and chemically stable high-energy amorphous solid dispersion of a poorly water-soluble drug. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Sarmento, B.; Costa, P. Solid dispersions as strategy to improve oral bioavailability of poor water soluble drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Piatti, G.; Caviglia, D.; Schito, A.M. Synthesis, Characterization, and Bactericidal Activity of a 4-Ammoniumbuthylstyrene-Based Random Copolymer. Polymers 2021, 13, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Marengo, B.; Valenti, G.; Domenicotti, C. Synthesis of Polystyrene-Based Cationic Nanomaterials with Pro-Oxidant Cytotoxic Activity on Etoposide-Resistant Neuroblastoma Cells. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Zuccari, G.; Caviglia, D.; Brullo, C. Synthesis and Characterization of Pyrazole-Enriched Cationic Nanoparticles as New Promising Antibacterial Agent by Mutual Cooperation. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Zeng, Z. The Antisolvent Coprecipitation Method for Enhanced Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 626, 122043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Qi, J.; Wu, W.; Yin, Z.; Li, T.; Lu, Y. Development of Carrier-Free Nanocrystals of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs by Exploring Metastable Zone of Nucleation. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Schito, A.M.; Zuccari, G. Considerable Improvement of Ursolic Acid Water Solubility by Its Encapsulation in Dendrimer Nanoparticles: Design, Synthesis and Physicochemical Characterization. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Oliveri, P.; Malegori, C. Assessment of the Efficiency of a Nanospherical Gallic Acid Dendrimer for Long-Term Preservation of Essential Oils: An Integrated Chemometric-Assisted FTIR Study. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 8891–8901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Castellaro, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Polyester-Based Dendrimers Containing Peripheral Arginine or Mixed Amino Acids as Potential Vectors for Gene and Drug Delivery. Macromol. Res. 2017, 25, 1172–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Castellaro, S.; Taptue, G.B. Synthesis and NMR Characterization of Dendrimers Based on 2, 2-Bis-(Hydroxymethyl)-Propanoic Acid (Bis-HMPA) Containing Peripheral Amino Acid Residues for Gene Transfection. Org. Commun. 2017, 10, 144–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Seel, F. Grundlagen der Analytischen Chemie, 5th ed.; Geier, G., Ed.; Verlag Chemie: Weinheim, Germany, 1970; Volume 82, p. 962. [Google Scholar]
- Aravindan, L.; Bicknell, K.A.; Brooks, G.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V.; Williams, A.C. Effect of Acyl Chain Length on Transfection Efficiency and Toxicity of Polyethylenimine. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 378, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orienti, I.; Zuccari, G.; Bergamante, V.; Mileo, E.; Lucarini, M.; Carosio, R.; Montaldo, P.G. Amphiphilic Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Derivatives as Complexing Agents for Fenretinide. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3157–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledet, G.A.; Graves, R.A.; Glotser, E.Y.; Mandal, T.K.; Bostanian, L.A. Preparation and in Vitro Evaluation of Hydrophilic Fenretinide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 479, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccari, G.; Baldassari, S.; Alfei, S.; Marengo, B.; Valenti, G.E.; Domenicotti, C.; Ailuno, G.; Villa, C.; Marchitto, L.; Caviglioli, G. D-α-Tocopherol-Based Micelles for Successful Encapsulation of Retinoic Acid. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanaik, M.; Bhaumik, S.K. Adsorption Behaviour of Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone on Oxide Surfaces. Mater. Lett. 2000, 44, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Otte, A.; Park, K. Evolution of Drug Delivery Systems: From 1950 to 2020 and Beyond. J. Control. Release 2022, 342, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mircioiu, C.; Voicu, V.; Anuta, V.; Tudose, A.; Celia, C.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M.; Sandulovici, R.; Mircioiu, I. Mathematical Modeling of Release Kinetics from Supramolecular Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Spallarossa, A.; Lusardi, M.; Zuccari, G. Successful Dendrimer and Liposome-Based Strategies to Solubilize an Antiproliferative Pyrazole Otherwise Not Clinically Applicable. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhujbal, S.V.; Mitra, B.; Jain, U.; Gong, Y.; Agrawal, A.; Karki, S.; Taylor, L.S.; Kumar, S.; (Tony) Zhou, Q. Pharmaceutical Amorphous Solid Dispersion: A Review of Manufacturing Strategies. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2505–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.J.; Pygall, S.R.; Cooper, V.B.; Mann, J.C. Overcoming sink limitations in dissolution testing: A review of traditional methods and the potential utility of biphasic systems. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, G. Papers Presented Before the Industrial Pharmacy Section. In Proceedings of the American Pharmaceutical Association Annual Meeting, Dallas, TX, USA, 25–28 April 1966; pp. 233–252. [Google Scholar]





| Entry | β (pH Value) | βAVE * (mL/pH) |
|---|---|---|
| P5 | 0.667 (6.10) | 0.2305 ± 0.1354 |
| 4-HPR-P5 NPs | 1.92 (6.62) | 0.6167 ± 0.3468 |
| PEI-b | 0.08261 (7.33) 0.0760 (6.81) | 0.517 ± 0.2541 |
| Samples | Concentrations (µM) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPR | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 7.5 | 10 | 15 |
| HPR-P5 | 0.0132 | 0.0655 | 0.1310 | 0.2620 | 0.6551 | 0.9827 | 1.3100 | 1.9654 |
| P5 | 0.0130 | 0.0650 | 0.1300 | 0.2600 | 0.6500 | 0.9803 | 1.3000 | 1.9606 |
| Cells | Times (h) | 4-HPR (µM) | P5 (µM) | 4-HPR-P5 NPs (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMR-32 | 24 | 1.08 | N.D. | 1.07 |
| 48 | 1.93 | N.D. | 1.76 | |
| 72 | 0.68 | N.D. | 1.25 | |
| SH-SY5Y | 24 | 7.84 | N.D. | N.D. |
| 48 | 4.32 | N.D. | N.D. | |
| 72 | 4.99 | N.D. | 1.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuccari, G.; Russo, E.; Villa, C.; Zorzoli, A.; Marimpietri, D.; Marchitto, L.; Alfei, S. Preparation and Characterization of Amorphous Solid Dispersions for the Solubilization of Fenretinide. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030388
Zuccari G, Russo E, Villa C, Zorzoli A, Marimpietri D, Marchitto L, Alfei S. Preparation and Characterization of Amorphous Solid Dispersions for the Solubilization of Fenretinide. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(3):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030388
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuccari, Guendalina, Eleonora Russo, Carla Villa, Alessia Zorzoli, Danilo Marimpietri, Leonardo Marchitto, and Silvana Alfei. 2023. "Preparation and Characterization of Amorphous Solid Dispersions for the Solubilization of Fenretinide" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 3: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030388
APA StyleZuccari, G., Russo, E., Villa, C., Zorzoli, A., Marimpietri, D., Marchitto, L., & Alfei, S. (2023). Preparation and Characterization of Amorphous Solid Dispersions for the Solubilization of Fenretinide. Pharmaceuticals, 16(3), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030388










