Evaluation of the Relationship between Baseline Autonomic Tone and Haemodynamic Effects of Dexmedetomidine
Abstract
1. Introduction
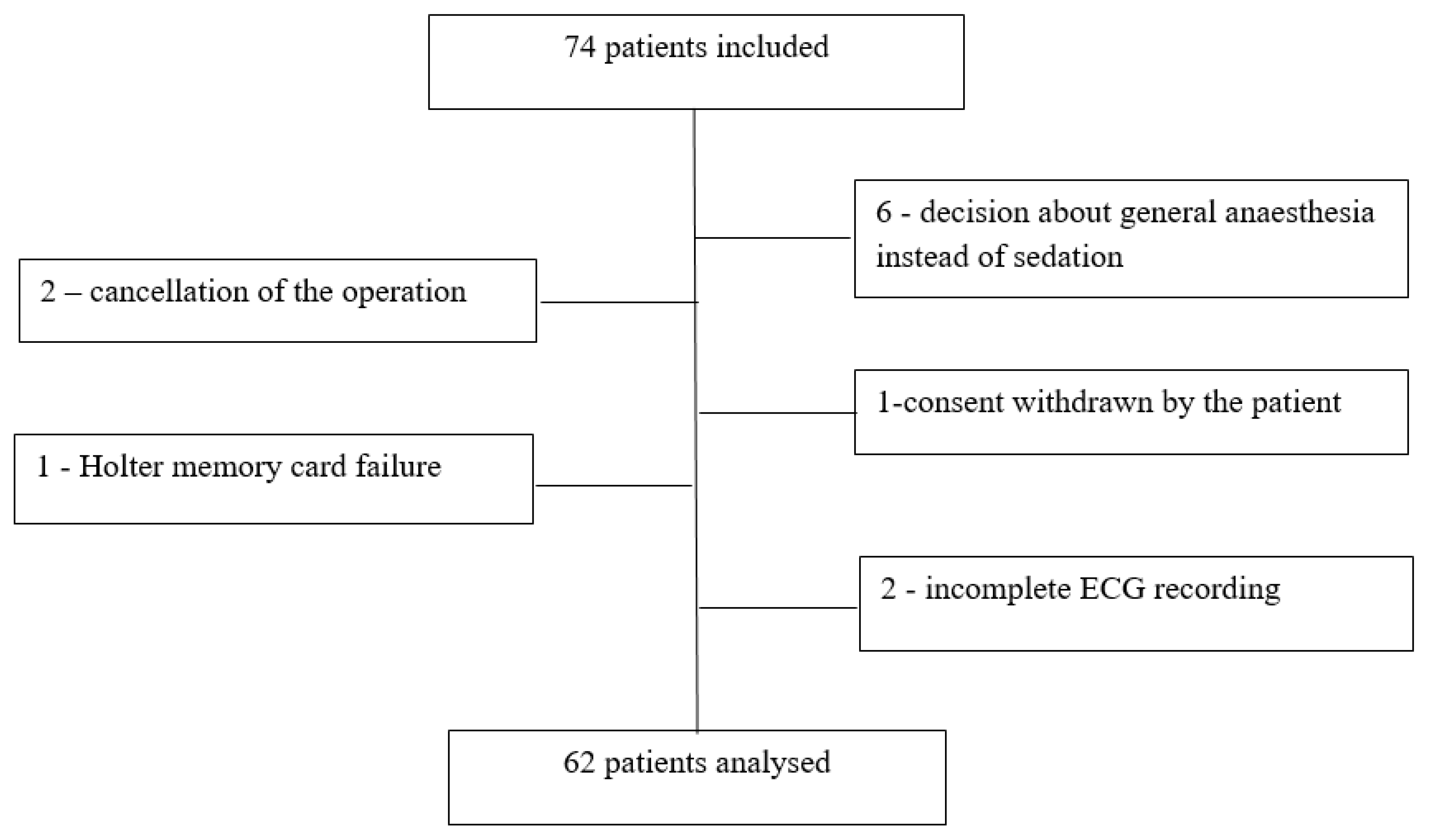
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reade, M.C.; Finfer, S. Sedation and delirium in the intensive care unit. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drug Approval Package: Precedex (Dexmedetomidine Hydrochloride) NDA# 21-038. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/99/21-038_Precedex.cfm (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Weerink, M.A.S.; Struys, M.M.R.F.; Hannivoort, L.N.; Barends, C.R.M.; Absalom, A.R.; Colin, P. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Dexmedetomidine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 893–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reel, B.; Maani, C.V. Dexmedetomidine. 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513303/ (accessed on 27 July 2022).
- Kirksey, M.A.; Haskins, S.C.; Cheng, J.; Liu, S.S. Local anesthetic peripheral nerve block adjuvants for prolongation of analgesia: A systematic qualitative review. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, J.W.; Mallow-Corbett, S.; Riker, R.R. Adverse drug events associated with the use of analgesics, sedatives, and antipsychotics in the intensive care unit. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38 (Suppl. S6), S231–S243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naaz, S.; Ozair, E. Dexmedetomidine in current anaesthesia practice—A review. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, GE01–GE04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Jeong, J.S.; Ko, J.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, S.J.; Cha, S.; Lee, J.J. Intraoperative dexmedetomidine attenuates norepinephrine levels in patients undergoing transsphenoidal surgery: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020, 20, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Bae, S.J.; Jo, M.; Cho, J.S. Intraoperative dexmedetomidine attenuates stress responses in patients undergoing major spine surgery. Minerva Anestesiol. 2019, 85, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarvainen, M.P.; Georgiadis, S.; Laitio, T.; Lipponen, J.A.; Karjalainen, P.A.; Kaskinoro, K.; Scheinin, H. Heart rate variability dynamics during low-dose propofol and dexmedetomidine anesthesia. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 1802–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.C.; Fontana, D.J.; Hedley, L.R.; Jasper, J.R.; Lewis, R.; Link, R.E.; Secchi., R.; Sutton, J.; Eglen, R.M. Assessment of the role of alpha2-adrenoceptor subtypes in the antinociceptive, sedative and hypothermic action of dexmedetomidine in transgenic mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 122, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertler, R.; Brown, H.C.; Mitchell, D.H.; Silvius, E.N. Dexmedetomidine: A novel sedative-analgesic agent. Proc. (Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent.) 2001, 14, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grape, S.; Kirkham, K.R.; Frauenknecht, J.; Albrecht, E. Intra-operative analgesia with remifentanil vs. dexmedetomidine: A systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. Anaesthesia 2019, 74, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, J. Comparison of dexmedetomidine and sufentanil as adjuvants to local anesthetic for epidural labor analgesia: A randomized controlled trial. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2019, 13, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Li, J.; Cao, R.; Hu, L.; Lu, S. Efficacy and safety of dexmedetomidine-ropivacaine versus sufentanil-ropivacaine for epidural labor analgesia: A randomized controlled trial. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2022, 11, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguerreche, C.; Cadier, G.; Beurton, A.; Imbault, J.; Leuillet, S.; Remy, A.; Zaouter, C.; Ouattara, A. Feasibility and postoperative opioid sparing effect of an opioid-free anaesthesia in adult cardiac surgery: A retrospective study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2021, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, T.L.; Chi, P. The opioid-sparing effect of perioperative dexmedetomidine combined with Oxycodone infusion during open hepatectomy: A randomized controlled trial. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 8, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannitti, J.; Thoms, S.M.; Crawford, J.J. Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonists: A review of current clinical applications. Anesth. Prog. 2015, 62, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tang, J.; Dong, J.; Zheng, J. Alpha2-adrenoceptor-independent inhibition of acetylcholine receptor channel and sodium channel by dexmedetomidine in rat superior cervical ganglion neurons. Neuroscience 2015, 289, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frandsen, M.N.; Mehlsen, J.; Foss, N.B.; Kehlet, H. Preoperative heart rate variability as a predictor of perioperative outcomes: A systematic review without meta-analysis. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2022, 36, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frandsen, M.N.; Mehlsen, J.; Bang Foss, N.; Kehlet, H. Pre-operative autonomic nervous system function—A missing link for post-induction hypotension? Anaesthesia 2022, 77, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenwright, D.A.; Bernjak, A.; Draegni, T.; Dzeroski, S.; Entwistle, M.; Horvat, M.; Kvandal, P.; Landsverk, S.A.; McClintock, P.E.V.; Musizza, B.; et al. The discriminatory value of cardiorespiratory interactions in distinguishing awake from anaesthetised states: A randomised observational study. Anaesthesia 2015, 70, 1356–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Kurokawa, S.; Asakura, Y.; Wakao, Y.; Nishiwaki, K.; Komatsu, T. Correlation between heart rate variability and haemodynamic fluctuation during induction of general anaesthesia: Comparison between linear and non-linear analysis. Anaesthesia 2007, 62, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, Y.; Morita, K.; Ozaki, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Okayama, A.; Oya, N.; Hiraoka, T.; Takeda, J. The Efficacy and Safety of Dexmedetomidine for Procedural Sedation in Patients Receiving Local Anesthesia Outside the Intensive Care Unit: A Prospective, Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Phase III Trial in Japan. Yonago Acta Med. 2000, 65, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Fu, Y.; Deng, F.; Shao, Y.; Lu, Y.G.; Song, J.C. Median Effective Dose of Dexmedetomidine Inducing Bradycardia in Elderly Patients Determined by Up-and-Down Sequential Allocation Method. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 19, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikaterini, A.; Ioannis, D.; Dimitrios, G.; Konstantinos, S.; Vasilios, G.; George, P. Bradycardia Leading to Asystole Following Dexmedetomidine Infusion during Cataract Surgery: Dexmedetomidine-Induced Asystole for Cataract Surgery. Case Rep. Anesthesiol. 2018, 2896032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogue, C.W.; Talke, P.; Stein, P.K.; Richardson, C.; Domitrovich, P.P.; Sessler, D.I. Autonomic nervous system responses during sedative infusions of dexmedetomidine. Anesthesiology 2002, 97, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.S.; Kim, H.I.; Lee, K.Y.; An, J.Y.; Bai, S.J.; Cho, J.Y.; Yoo, Y.C. Effect of Intraoperative Dexmedetomidine Infusion on Postoperative Bowel Movements in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Gastrectomy A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. Medicine 2015, 94, e959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, J.W.; Skrobik, Y.; Gélinas, C.; Needham, D.M.; Slooter, A.J.C.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Watson, P.L.; Weinhouse, G.L.; Nunnally, M.E.; Rochwerg, B.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Pain, Agitation/Sedation, Delirium, Immobility, and Sleep Disruption in Adult Patients in the ICU. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, E825–E873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahraini, A.; Banerjee, O.; Ra, J. Bradycardia resulting in cardiac arrest in a critically ill patient receiving dexmedetomidine. Trauma Case Rep. 2021, 36, 100548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.J.; Kuok, C.H.; Kuo, T.B.J.; Hsu, Y.W.; Tsai, P.S. Pre-operative measurement of heart rate variability predicts hypotension during general anesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2006, 50, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padley, J.R.; Ben-Menachem, E. Low pre-operative heart rate variability and complexity are associated with hypotension after anesthesia induction in major abdominal surgery. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2018, 32, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokhal, S.; Rath, G.P.; Sokhal, N.; Chouhan, R.S. Severe Hypertension with Dexmedetomidine Infusion during Awake Craniotomy. J. Neuroanaesth. Crit. Care 2018, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, X.F.; Poblete, M.I.; Boric, M.P.; Mendizábal, V.E.; Adler-Graschinsky, E.; Huidobro-Toro, J.P. Clonidine-induced nitric oxide-dependent vasorelaxation mediated by endothelial alpha(2)-adrenoceptor activation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajwa, S.J.S.; Kaur, J.; Kulshrestha, A.; Haldar, R.; Sethi, R.; Singh, A. Nitroglycerine, esmolol and dexmedetomidine for induced hypotension during functional endoscopic sinus surgery: A comparative evaluation. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 32, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouybar, R.; Nemati, M.; Asmarian, N. Comparison of the effects of remifentanil and dexmedetomidine on surgeon satisfaction with surgical field visualization and intraoperative bleeding during rhinoplasty. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, B.; Zhang, L.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, F.S.; Chen, S. Comparison of effects and safety in providing controlled hypotension during surgery between dexmedetomidine and magnesium sulphate: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexopoulou, C.; Kondili, E.; Diamantaki, E.; Kokkini, S.; Bolaki, M.; Georgopoulos, D. Effects of dexmedetomidine on sleep quality in critically Ill patients: A pilot study. Anesthesiology 2014, 121, 801–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalabalik, J. Use of dexmedetomidine in the management of alcohol withdrawal syndrome in critically ill patients. Int. J. Crit. Care Emerg. Med. 2015, 1, 002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, A.D.; Chernobylsky, D.J.; Thakur, P.; Siddaiah, H.; Kaye, R.J.; Eng, L.K.; Harbell, M.W.; Lajaunie, J.; Cornett, E.M. Dexmedetomidine in Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) Protocols for Postoperative Pain. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2020, 24, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, A.T.; Blais, D.M.; Jones, G.M.; Burcham, P.K.; Stawicki, S.P.; Cook, C.H.; Murphy, C.V. Predictors of dexmedetomidine-associated hypotension in critically ill patients. Int. J. Crit. Illn. Inj. Sci. 2016, 6, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.; Hoth, L.; Kimmons, L.; Jones, M.; Parish, T.; Swiggart, B. 153: Predictors odof dexmedetomidine-associated hypotension in cardiovascular intensive care unit patients. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioccari, L.; Luethi, N.; Bailey, M.; Shehabi, Y.; Howe, B.; Messmer, A.S.; Proimos, H.K.; Peck, L.; Young, H.; Eastwood, G.M.; et al. The effect of dexmedetomidine on vasopressor requirements in patients with septic shock: A subgroup analysis of the Sedation Practice in Intensive Care Evaluation [SPICE III] Trial. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruickshank, M.; Henderson, L.; MacLennan, G.; Fraser, C.; Campbell, M.; Blackwood, B.; Gordon, A.; Brazzelli, M. Alpha-2 agonists for sedation of mechanically ventilated adults in intensive care units: A systematic review. Health Technol. Assess. 2016, 20, 1–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, M.; Mason, K.P. Dexmedetomidine: Review, update, and future considerations of paediatric perioperative and periprocedural applications and limitations. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 115, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dexmedetomidine: Increased Risk of Mortality in Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Patients ≤65 Years | European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/dhpc/dexmedetomidine-increased-risk-mortality-intensive-care-unit-icu-patients-65-years (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Szczepańska, A.J.; Pluta, M.P.; Krzych, Ł.J. Clinical practice in intraoperative haemodynamic monitoring in Poland: A point prevalence study in 31 Polish hospitals. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2020, 52, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarracino, F.; Bertini, P. Perioperative hypotension: Causes and remedies. J. Anesth. Analg. Crit. Care 2022, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.M.; Tablin, F.; Schelegle, E.S. Comparison of nonparametric and parametric methods for time-frequency heart rate variability analysis in a rodent model of cardiovascular disease. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichon, A.; Roulaud, M.; Antoine-Jonville, S.; de Bisschop, C.; Denjean, A. Spectral analysis of heart rate variability: Interchangeability between autoregressive analysis and fast Fourier transform. J. Electrocardiol. 2006, 39, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnod, T.; Yang, C.C.; Hsin, Y.L.; Shieh, K.R.; Wang, P.J.; Kuo, T.B. Heart rate variability in children with refractory generalized epilepsy. Seizure 2008, 17, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutschman, C.S.; Harris, A.P.; Fleisher, L.A. Changes in heart rate variability under propofol anesthesia: A possible explanation for propofol-induced bradycardia. Anaesth. Analg. 1994, 79, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanss, R.; Bein, B.; Weseloh, H.; Bauer, M.; Cavus, E.; Steinfath, M.; Tonner, P.H. Heart rate variability predicts severe hypotension after spinal anesthesia. Anesthesiology 2006, 104, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztajzel, J. Heart rate variability: A noninvasive electrocardiographic method to measure the autonomic nervous system. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2004, 134, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eckberg, D.L. Sympathovagal balance: A critical appraisal. Circulation 1997, 96, 3224–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, F. Chaos theory, heart rate variability, and arrhythmic mortality. Circulation 2000, 101, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Female sex | 31 |
| Age; years | 54 (42–60 [25–65]) |
| Height; cm | 171.4 (95% CI: 168.8–174.0) |
| Body mass; kg | 77.8 (95% CI: 73.5–82.2) |
| ASA physical status 1 | 50 |
| Systolic Arterial Pressure; mmHg | 137 (95% CI: 133–141) |
| Diastolic arterial pressure; mmHg | 81 (95% CI: 79–84) |
| Mean arterial pressure; mmHg | 100 (95% CI: 97–102) |
| Heart rate; beats min−1 | 69 (95% CI: 66–72) |
| Low frequency; ms2 | 1206 (324–1617 [56–5093]) |
| High frequency; ms2 | 421 (89–578 [8–2626]) |
| Low frequency/high frequency ratio | 4.59 (2.19–5.91 [0.11–19.65]) |
| LI 0 | LI 5 | LI 10 | MI 5 | MI 10 | MI 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart rate; beats min−1 | 69 (67–72) | 63 * (60–67) | 59 * (56–62) | 60 * (58–63) | 60 * (58–63) | 59 * (57–62) |
| SAP; mmHg | 137 (133–141) | 133 (129–136) | 131 ** (127–135) | 128 *** (124–132) | 124 *** (120–128) | 123 *** (119–127) |
| DAP; mmHg | 81 (79–84) | 79 (76–81) | 77 † (74–80) | 76 †† (73–78) | 74 †† (71–76) | 74 †† (71–77) |
| MAP; mmHg | 100 (91–102) | 97 (94–99) | 95 ‡ (92–98) | 90 ‡‡ (85–95) | 91 ‡‡ (88–94) | 90 ‡‡ (87–93) |
| Variable | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Low frequency | 0.999 (0.998–1.000) | 0.2233 |
| High frequency | 1.001 (0.999–1.004) | 0.2215 |
| Low frequency/high frequency ratio | 1.050 (0.887–1.266) | 0.5720 |
| Heart rate | 1.064 (1.005–1.134) | 0.0385 * |
| Mean arterial pressure | 0.942 (0.877–1.005) | 0.0788 |
| Male sex | 0.930 (0.211–4.043) | 0.9216 |
| Age | 0.981 (0.926–1.039) | 0.5148 |
| Variable | Decrease MAP >15% from the Pre-Drug Value | MAP Decrease >15% from the Pre-Drug Value, Observed at More Than One Consecutive Time Point | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Low frequency | 1.000 (0.999–1.001) | 0.6691 | 1.000 (0.999–1.000) | 0.1504 |
| High frequency | 0.998 (0.995–0.999) | 0.0245 * | 0.997 (0.994–0.999) | 0.0388 * |
| Low frequency/high frequency ratio | 1.186 (1.022–1.429) | 0.0433 * | 0.920 (0.682–0.999) | 0.4932 |
| Heart rate | 0.995 (0.930–1.060) | 0.8714 | 1.018 (0.970–1.069) | 0.468 |
| Systolic arterial pressure | 1.065 (1.024–1.115) | 0.0033 * | 1.057 (1.015–1.106) | 0.0107 * |
| Diastolic arterial pressure | 1.046 (0.991–1.111) | 0.1173 | 1.017 (0.961–1.080) | 0.5528 |
| Mean arterial pressure | 1.079 (1.020–1.154) | 0.0140 * | 1.052 (0.994–1.122) | 0.0926 |
| Male sex | 0.9295 (0.2105–4.043) | 0.9216 | 0.924 (0.845–0.998) | 0.974 |
| Age | 0.9814 (0.926–1.039) | 0.5149 | 0.993 (0.944–1.046) | 0.7956 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wujtewicz, M.; Twardowski, P.; Jasiński, T.; Michalska-Małecka, K.; Owczuk, R. Evaluation of the Relationship between Baseline Autonomic Tone and Haemodynamic Effects of Dexmedetomidine. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030354
Wujtewicz M, Twardowski P, Jasiński T, Michalska-Małecka K, Owczuk R. Evaluation of the Relationship between Baseline Autonomic Tone and Haemodynamic Effects of Dexmedetomidine. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(3):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030354
Chicago/Turabian StyleWujtewicz, Magdalena, Paweł Twardowski, Tomasz Jasiński, Katarzyna Michalska-Małecka, and Radosław Owczuk. 2023. "Evaluation of the Relationship between Baseline Autonomic Tone and Haemodynamic Effects of Dexmedetomidine" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 3: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030354
APA StyleWujtewicz, M., Twardowski, P., Jasiński, T., Michalska-Małecka, K., & Owczuk, R. (2023). Evaluation of the Relationship between Baseline Autonomic Tone and Haemodynamic Effects of Dexmedetomidine. Pharmaceuticals, 16(3), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030354







