Skin Wound Healing and Anti-Wrinkle-Promoting In Vitro Biological Activities of Caragana sinica Flower Absolute and Its Chemical Composition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
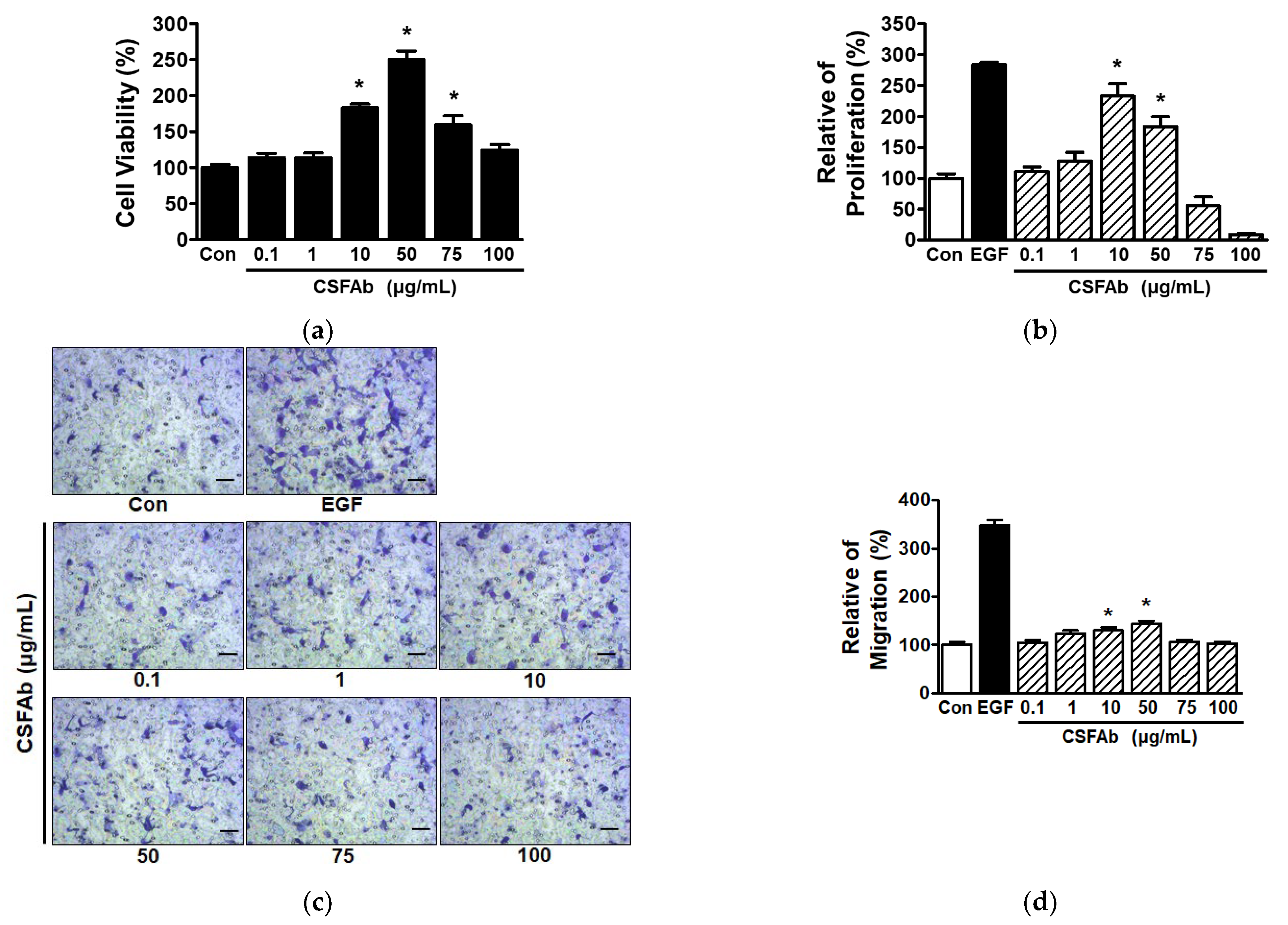
2.1. CS Flower Absolute-Induced Changes in the Proliferative and Migratory Activities of HaCaT Cells
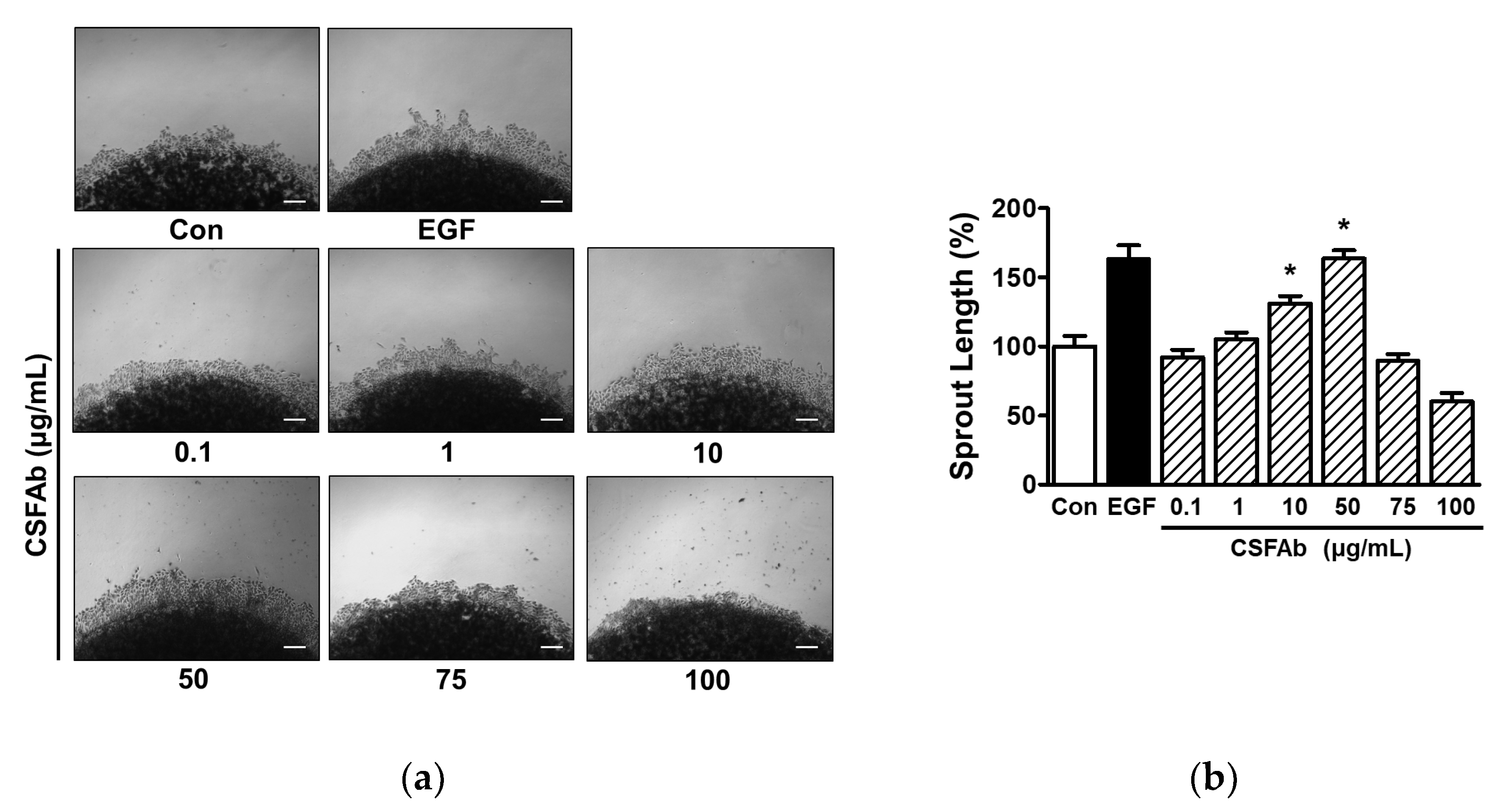
2.2. Changes in Sprout Outgrowth of HaCaT Cells Exposed to CS Flower Absolute
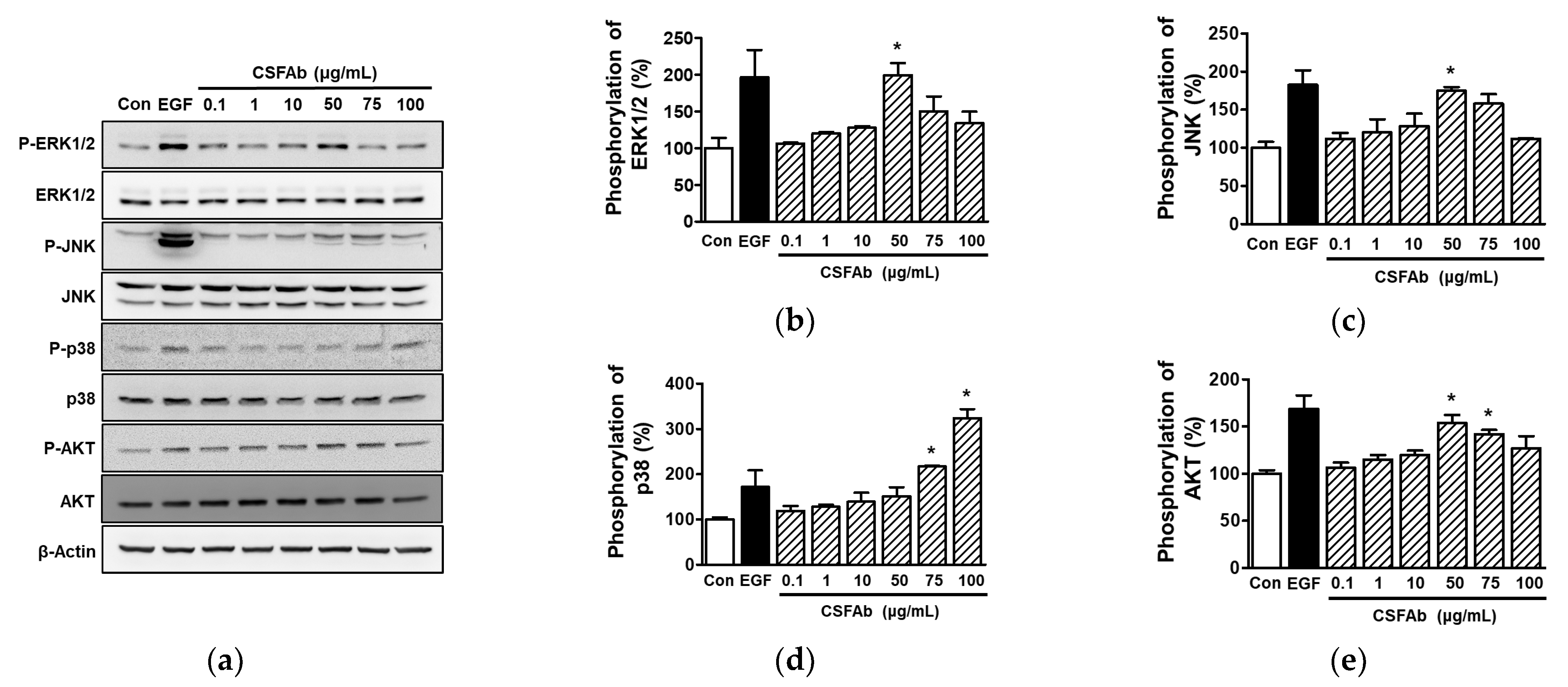
2.3. Effects of CS Flower Absolute on Intracellular Signal Proteins in HaCaT Cells
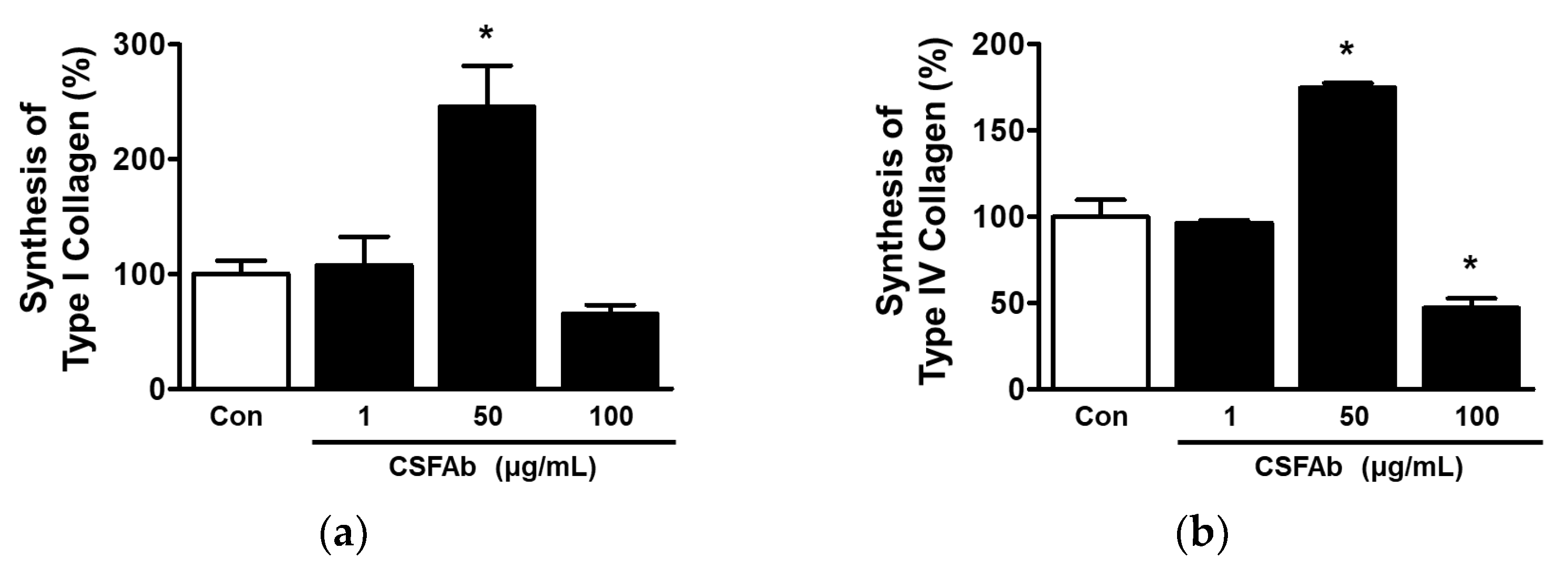
2.4. Collagen Synthesis by HaCaT Cells Exposed to CS Flower Absolute
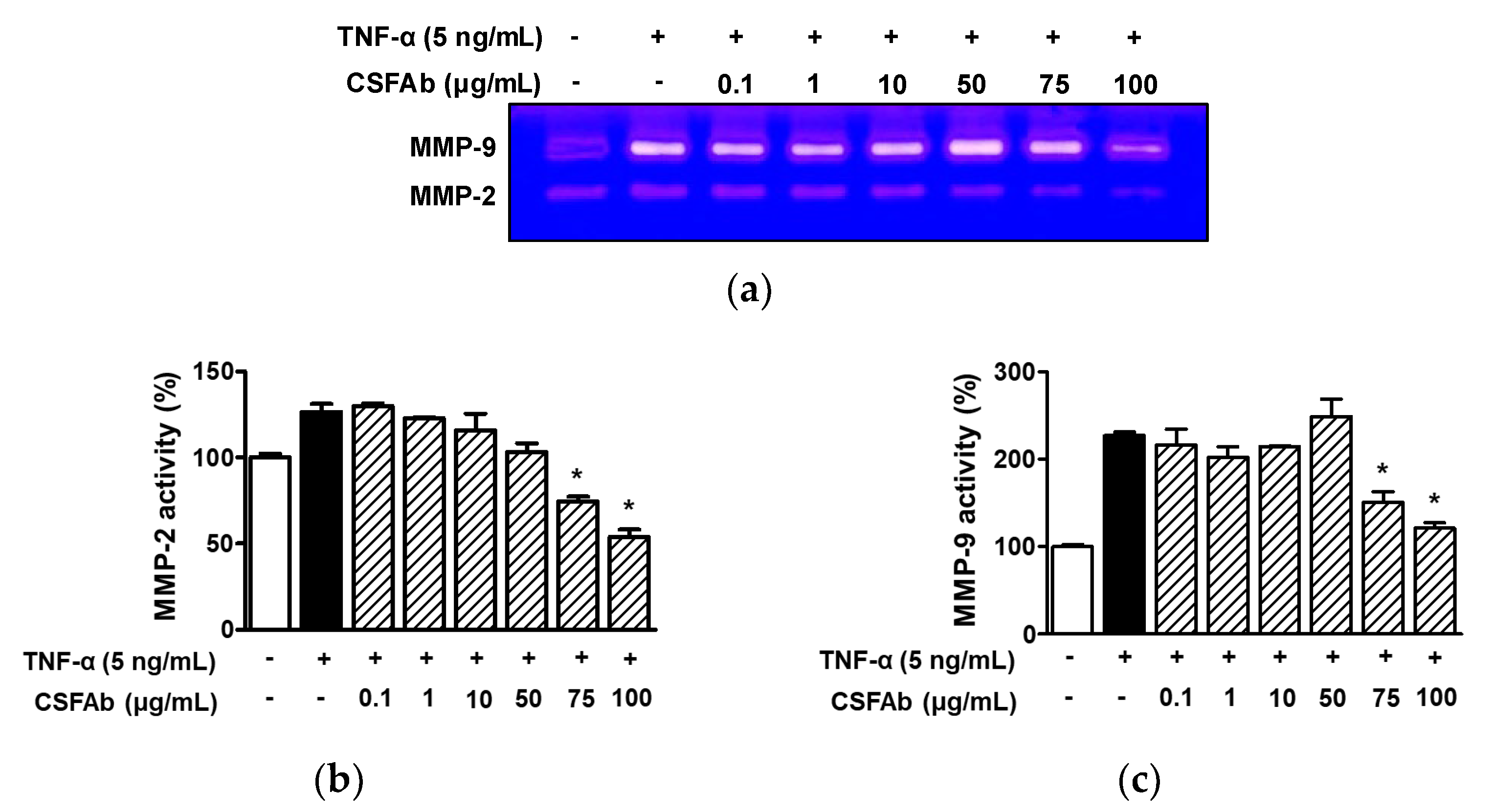
2.5. Effect of CS Flower Absolute on MMP-2 and MMP-9 Activities in HaCaT Cells
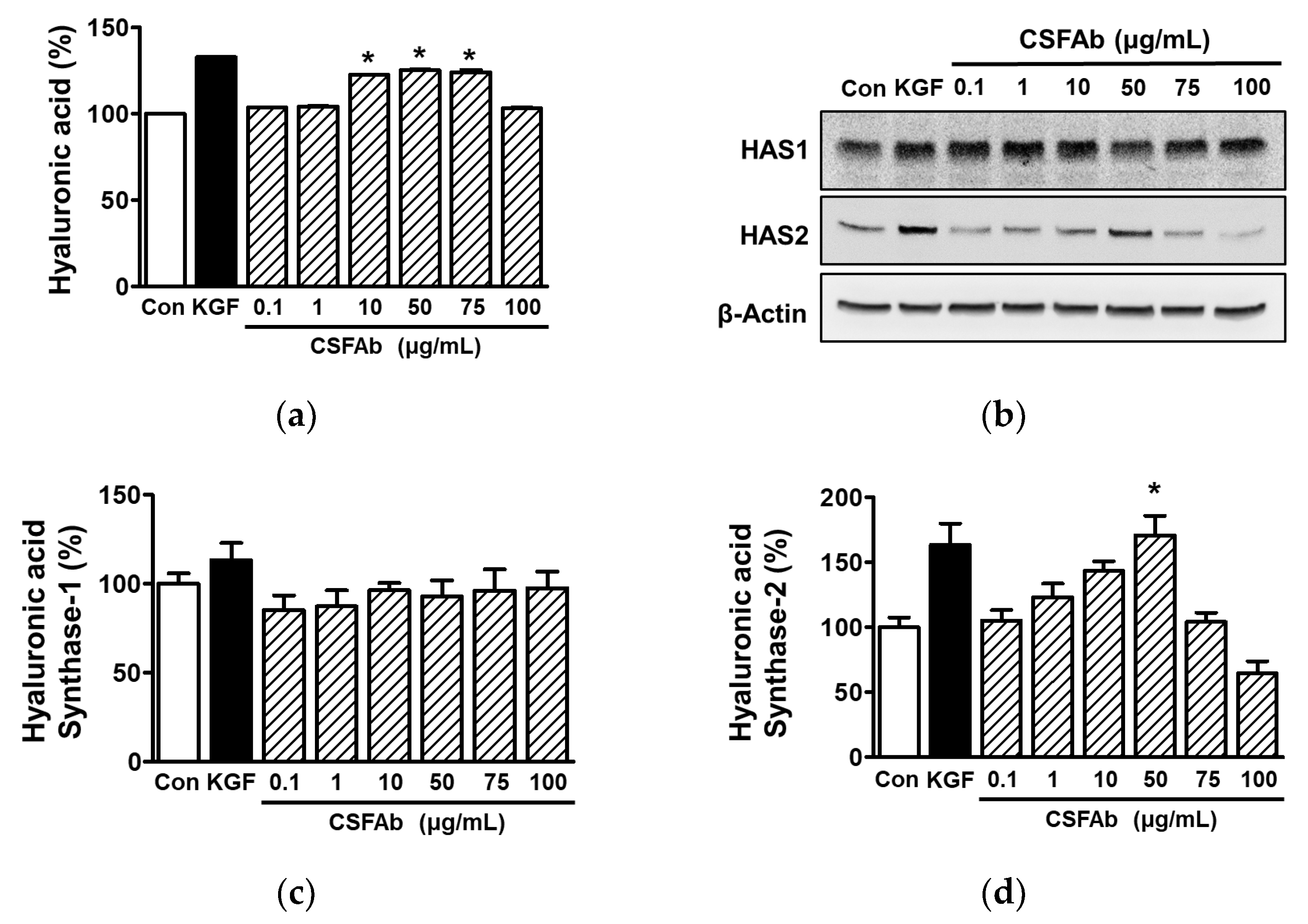
2.6. Effect of CS Flower Absolute on Hyaluronic Acid in HaCaT Cells
2.7. Chemical Composition of ITMFAb
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Caragana Sinica Flower Absolute
3.3. Analysis and Identification of Compounds from Caragana sinica Flower Absolute
3.4. Cell Culture
3.5. Cell Viability Assays
3.6. Proliferation Assays
3.7. Migration Assay
3.8. Collagen Sprout Outgrowth Assay
3.9. Collagen Synthesis Assay
3.10. Immunoblotting
3.11. Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis Assay
3.12. Gelatin Zymography Assay
3.13. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sorg, H.; Tilkorn, D.J.; Hager, S.; Hauser, J.; Mirastschijski, U. Skin wound healing: An update on the current knowledge and concepts. Eur. Surg. Res. 2017, 58, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgonc, R.; Gruber, J. Age-related aspects of cutaneous wound healing: A mini-review. Gerontology 2013, 59, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Kirsner, R. Pathophysiology of acute wound healing. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPersio, C.M.; Zheng, R.; Kenney, J.; Van De Water, L. Integrin-mediated regulation of epidermal wound functions. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 365, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.M.; Gaudino, G. Cellular and molecular facets of keratinocyte reepithelization during wound healing. Exp. Cell Res. 2005, 304, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswamy, V.R.; Korrapati, P.S. Role of dermatopontin in re-epithelialization: Implications on keratinocyte migration and proliferation. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, M.J. Estrogens and aging skin. Derm. -Endocrinol. 2013, 5, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaar, M.; Gilchrest, B.A. Photoageing: Mechanism, prevention and therapy. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 157, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.W.; Kwon, S.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Na, J.I.; Huh, C.H.; Choi, H.R.; Park, K.C. Molecular mechanisms of dermal aging and antiaging approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, E.A. Extracellular matrix and keratinocyte migration. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2001, 26, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousselle, P.; Montmasson, M.; Garnier, C. Extracellular matrix contribution to skin wound re-epithelialization. Matrix Biol. 2019, 75–76, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura-Hachiya, Y.; Arai, K.Y.; Muraguchi, T.; Sasaki, T.; Nishiyama, T. Type IV collagen aggregates promote keratinocyte proliferation and formation of epidermal layer in human skin equivalents. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page-McCaw, A.; Ewald, A.J.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittayapruek, P.; Meephansan, J.; Prapapan, O.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in photoaging and photocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juncan, A.M.; Moisă, D.G.; Santini, A.; Morgovan, C.; Rus, L.L.; Vonica-Țincu, A.L.; Loghin, F. Advantages of hyaluronic acid and its combination with other bioactive ingredients in cosmeceuticals. Molecules 2021, 26, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weindl, G.; Schaller, M.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Korting, H.C. Hyaluronic acid in the treatment and prevention of skin diseases: Molecular biological, pharmaceutical and clinical aspects. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2004, 17, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, G.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Datta, S.C.; Varani, J.; Kang, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Pathophysiology of premature skin aging induced by ultraviolet light. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, R.; Maibach, H.I. Hyaluronan in skin: Aspects of aging and its pharmacologic modulation. Clin. Dermatol. 2008, 26, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvinen, S.; Pasonen-Seppänen, S.; Hyttinen, J.M.; Pienimäki, J.P.; Törrönen, K.; Jokela, T.A.; Tammi, M.I.; Tammi, R.l. Keratinocyte growth factor stimulates migration and hyaluronan synthesis in the epidermis by activation of keratinocyte hyaluronan synthases 2 and 3. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 49495–49504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, E.; Roth, M.; Karakiulakis, G. Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging. Dermatoendocrinology 2012, 4, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Vijayakumar, M.; Govindarajan, R.; Pushpangadan, P. Ethnopharmacological approaches to wound healing–exploring medicinal plants of India. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 114, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Ma, Q.; Ye, L.; Piao, G. The traditional medicine and modern medicine from natural products. Molecules 2016, 21, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, P.S.; Shin, M.K. Hyangyak Daesageon; Younglim Press: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 1990; pp. 669–670. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Niu, Y.; Niu, X.; Roubin, R.H.; Hanrahan, J.R. Ethnobotany, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of the genus Caragana used in traditional Chinese medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 124, 350–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.R.; Kwak, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Pyo, S. Neuroprotective effects of kobophenol A against the withdrawal of tropic support, nitrosative stress, and mitochondrial damage in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 1879–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastar, I.; Stojadinovic, O.; Yin, N.C.; Ramirez, H.; Nusbaum, A.G.; Sawaya, A.; Patel, S.B.; Khalid, L.; Isseroff, R.R.; Tomic-Canic, M. Epithelialization in wound healing: A comprehensive review. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.Y.; Won, K.J.; Kim, H.B.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Won, Y.R.; Lee, H.M. Chemical composition of Salix koreensis Anderss flower absolute and its skin wound healing activities in vitro. Plants 2022, 11, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Chen, W.; Xia, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, B.; Chen, B.; Sun, W.; Song, X.; Xiang, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Extracellular matrix secreted by senescent fibroblasts induced by UVB promotes cell proliferation in HaCaT cells through PI3K/AKT and ERK signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 21, 777–784. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, D.; Jia, J.; Lv, Y.; Yuan, H.; Song, H.; Xiang, F.; et al. Microtubule-associated protein 4 phosphorylation regulates epidermal keratinocyte migration and proliferation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 1962–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Liu, J.Q.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.Y.; Han, S.C.; Zhou, Q.; Guan, H.; Li, C.; Su, L.L.; et al. Human amniotic epithelial stem cells promote wound healing by facilitating migration and proliferation of keratinocytes via ERK, JNK and AKT signaling pathways. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 365, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Jacobson, K.; Schaller, M.D. MAP kinases and cell migration. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 4619–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.E.; Cho, H.; Ishihara, A.; Kim, B.; Kim, O. Cell proliferation and migration mechanism of caffeoylserotonin and serotonin via serotonin 2B receptor in human keratinocyte HaCaT cells. BMB Rep. 2018, 51, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazel, A.; Nijhawan, R.I.; Walsh, R.; Blumenberg, M. Transcriptional profiling defines the roles of ERK and p38 kinases in epidermal keratinocytes. J. Cell Physiol. 2008, 215, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Eun, H.C.; Cho, K.H.; Chung, J.H. All-trans retinoic acid antagonizes UV-induced VEGF production and angiogenesis via the inhibition of ERK activation in human skin keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.; Fu, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Bai, X.; Hu, D. Loss of CAR promotes migration and proliferation of HaCaT cells, and accelerates wound healing in rats via Src-p38 MAPK pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19735–19741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.M.; Li, W.; Man, X.Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.Q.; Cai, S.Q.; Zheng, M. Pigment epithelium-derived factor plays an inhibitory role in proliferation and migration of HaCaT cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 2099–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, T.F. PI3K/Akt: Getting it right matters. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6473–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüppel, M.; Kürschner, U.; Kleuser, U.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Kleuser, B. Sphingosine 1-phosphate restrains insulin-mediated keratinocyte proliferation via inhibition of Akt through the S1P2 receptor subtype. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, E.; Steinbauer, J.; Landthaler, M.; Szeimies, R.M. Skin ageing. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imokawa, G. Mechanism of UVB-induced wrinkling of the skin: Paracrine cytokine linkage between keratinocytes and fibroblasts leading to the stimulation of elastase. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2009, 14, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.O.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, E.; Na, J.; Yoo, K.H.; Park, S.J.; Kim, B.J. Effect of A. polygama APEE (Actinidia polygama ethanol extract) or APWE (Actinidia polygama water extract) on wrinkle formation in UVB-irradiated hairless mice. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, S.; Matsunaga, Y.; Amano, S.; Takada, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Tsunenaga, M.; Nishiyama, T.; Kohno, Y.; Fukuda, M. Possible involvement of gelatinases in basement membrane damage and wrinkle formation in chronically ultraviolet B-exposed hairless mouse. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, A.R.; Hartzler, J.L.; Pelina, M.D.; Thorgeirsson, U.P. Studies on the ability of 65-kDa and 92-kDa tumor cell gelatinases to degrade type IV collagen. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 21929–21934. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mäkelä, M.; Larjava, H.; Pirilä, E.; Maisi, P.; Salo, T.; Sorsa, T.; Uitto, V.J. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (gelatinase A) is related to migration of keratinocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 1999, 251, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.K.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, H.Y.; Oh, M.H.; Byun, S.; Lim, S.H.; Heo, Y.S.; Kang, N.J.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z.; et al. Myricetin suppresses UVB-induced wrinkle formation and MMP-9 expression by inhibiting Raf. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Agrahari, G.; Lee, M.J.; Tak, L.-J.; Ham, W.-K.; Kim, T.-Y. Low-temperature argon plasma regulates skin moisturizing and melanogenesis-regulating markers through Yes-associated protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavicic, T.; Gauglitz, G.G.; Lersch, P.; Schwach-Abdellaoui, K.; Malle, B.; Korting, H.C.; Farwick, M. Efficacy of cream-based novel formulations of hyaluronic acid of different molecular weights in anti-wrinkle treatment. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2011, 10, 990–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Kang, W.; Choi, D.; Son, B.; Park, T. Nonanal stimulates growth factors via cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) signaling in human hair follicle dermal papilla cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Beserra, F.; Xue, M.; Maia, G.L.A.; Leite Rozza, A.; Helena Pellizzon, C.; Jackson, C.J. Lupeol, a pentacyclic triterpene, promotes migration, wound closure, and contractile effect in Vitro: Possible involvement of PI3K/Akt and p38/ERK/MAPK pathways. Molecules 2018, 23, 2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Beserra, F.; Sérgio Gushiken, L.F.; Vieira, A.J.; Augusto Bérgamo, D.; Luísa Bérgamo, P.; Oliveira de Souza, M.; Alberto Hussni, C.; Kiomi Takahira, R.; Henrique Nóbrega, R.; Monteiro Martinez, E.R.; et al. From inflammation to cutaneous repair: Topical application of lupeol improves skin wound healing in rats by modulating the cytokine levels, NF-κB, Ki-67, growth factor expression, and distribution of collagen fibers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okur, M.E.; Karadağ, A.E.; Üstündağ Okur, N.; Özhan, Y.; Sipahi, H.; Ayla, Ş.; Daylan, B.; Demirci, B.; Demirci, F. In vivo wound healing and in vitro anti-inflammatory activity evaluation of Phlomis russeliana extract gel formulations. Molecules 2020, 25, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, C.P.; Mendes, N.F.; Prado, T.P.D.; de Araújo, E.P. Bioactive fatty acids in the resolution of chronic inflammation in skin wounds. Adv. Wound Care 2020, 9, 472–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCusker, M.M.; Grant-Kels, J.M. Healing fats of the skin: The structural and immunologic roles of the omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. Clin. Dermatol. 2010, 28, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelenko, C., 3rd; McKinley, J.C. Studies in burns: XV. Use of a topical lipid in treating human burns. Am. Surg. 1976, 42, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dieamant, G.; Pereda Mdel, C.; Nogueira, C.; Eberlin, S.; Facchini, G.; Checon, J.T.; Cesar, C.K.; Mussi, L.; Polezel, M.A.; Martins-Oliveira, D., Jr.; et al. Antiageing mechanisms of a standardized supercritical CO2 preparation of black jack (Bidens pilosa L.) in human fibroblasts and skin fragments. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 280529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.J.; Song, B.R.; Kim, J.E.; Bae, S.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, S.J.; Gong, J.E.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, C.Y.; Kim, B.H.; et al. Therapeutic effects of cold-pressed perilla oil mainly consisting of linolenic acid, oleic acid and linoleic acid on UV-induced photoaging in NHDF cells and SKH-1 hairless mice. Molecules 2020, 25, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.; Lee, D.G.; Park, S.H.; Oh, M.S.; Kim, S.Y. Coriander leaf extract exerts antioxidant activity and protects against UVB-induced photoaging of skin by regulation of procollagen type I and MMP-1 expression. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soimee, W.; Nakyai, W.; Charoensit, P.; Grandmottet, F.; Worasakwutiphong, S.; Phimnuan, P.; Viyoch, J. Evaluation of moisturizing and irritation potential of sacha inchi oil. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, Y.R.; Won, K.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Hong, B.S.; Lee, H.M. Chemical composition of Impatiens textori Miq. flower absolute and its potential wound repair and anti-melanogenesis-promoting activities in skin cells. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Lee, Y.; Eun, H.C.; Chung, J.H. Eicosapentaenoic acid inhibits TNF-alpha-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in human keratinocytes, HaCaT cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 368, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, A.; Stellavato, A.; Busico, T.; Papa, A.; Tirino, V.; Papaccio, G.; La Gatta, A.; De Rosa, M.; Schiraldi, C. In vitro analysis of the effects on wound healing of high- and low-molecular weight chains of hyaluronan and their hybrid H-HA/L-HA complexes. BMC Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
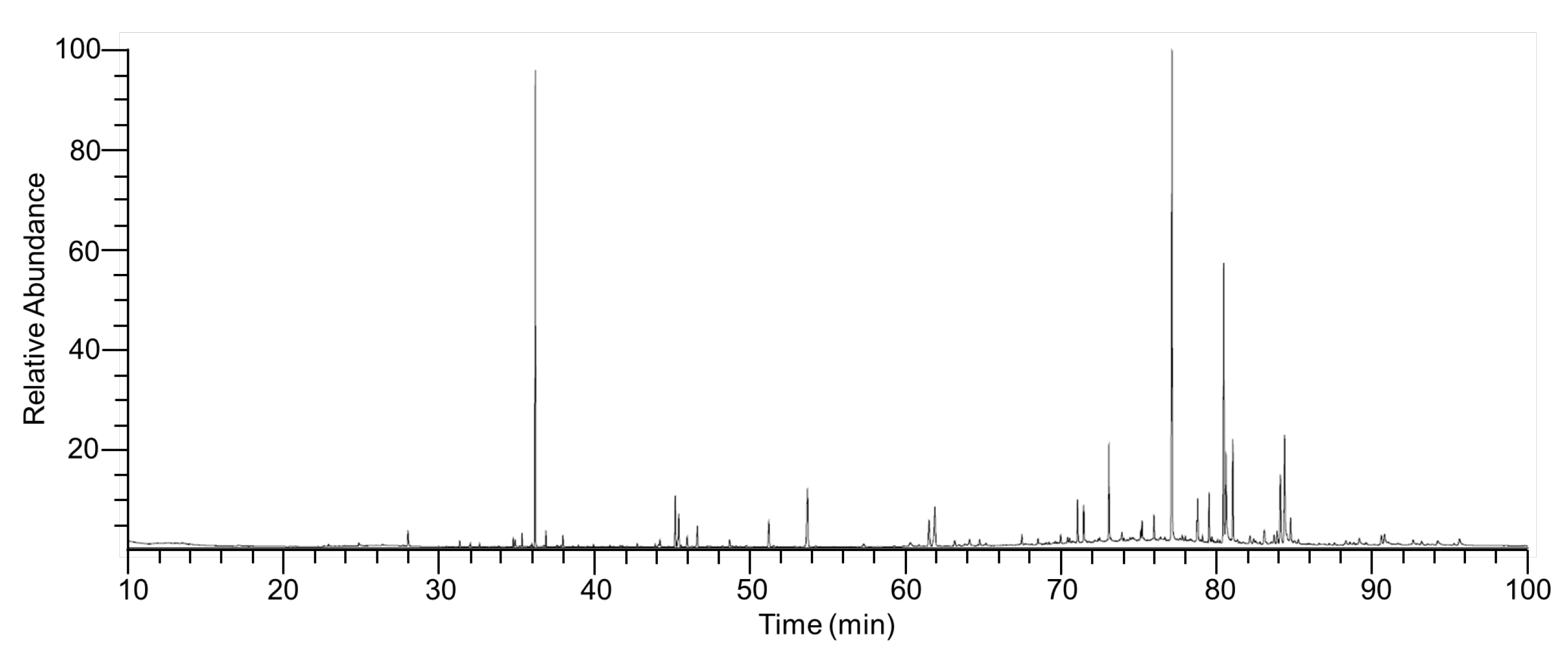
| No | Component Name | RT 1 | RI 2 | Area (%) | CAS No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cyclopentanone, 2-sec-butyl- | 24.8 | 1237 | 0.18 | 6376-92-7 |
| 2 | Nonanal | 27.96 | 1257 | 0.63 | 124-19-6 |
| 3 | Trimethylsilyl nonanoate | 34.73 | 1300 | 0.21 | 82326-11-2 |
| 4 | 2,2,4-Trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate | 34.86 | 1301 | 0.24 | 6846-50-0 |
| 5 | Propanoic acid, 2-methyl-, 3-hydroxy-2,2,4-trimethylpentyl ester | 35.3 | 1305 | 0.36 | 77-68-9 |
| 6 | Methyl undecanoate | 36.16 | 1312 | 12.88 | 1731-86-8 |
| 7 | Farnesane | 36.84 | 1318 | 0.48 | 3891-98-3 |
| 8 | 2-Allyl-5-t-butylhydroquinone | 37.94 | 1327 | 0.42 | 73685-60-6 |
| 9 | 2-Nonadecanone | 44.18 | 1380 | 0.45 | 629-66-3 |
| 10 | Neophytadiene | 45.16 | 1388 | 3.33 | 504-96-1 |
| 11 | 3,7,11,15-Tetramethyl-2-hexadecen-1-ol | 45.92 | 1395 | 0.51 | 102608-53-7 |
| 12 | Phytol | 46.58 | 1401 | 0.75 | 150-86-7 |
| 13 | Ethyl palmitate | 51.18 | 1469 | 1.38 | 628-97-7 |
| 14 | Palmitic Acid, TMS derivative | 53.67 | 1506 | 3.63 | 55520-89-3 |
| 15 | Heneicosane | 57.28 | 1551 | 0.30 | 629-94-7 |
| 16 | Linolenic acid | 60.29 | 1589 | 0.45 | 463-40-1 |
| 17 | Ethyl linoleate | 61.48 | 1607 | 1.53 | 544-35-4 |
| 18 | Ethyl linolenate | 61.87 | 1614 | 2.64 | 1191-41-9 |
| 19 | Ethyl stearate | 63.14 | 1639 | 0.30 | 111-61-5 |
| 20 | α-Linolenic acid, TMS derivative | 64.1 | 1658 | 0.69 | 97844-13-8 |
| 21 | 1,2-Epoxyhexadecane | 64.75 | 1671 | 0.36 | 7320-37-8 |
| 22 | Pentatriacontane | 67.47 | 1732 | 0.48 | 630-07-9 |
| 23 | 2,2-Dideutero octadecanal | 68.51 | 1760 | 0.24 | 56555-07-8 |
| 24 | 1-Heptatriacontanol | 69.96 | 1799 | 0.36 | 105794-58-9 |
| 25 | Ethyl arachidate | 70.4 | 1813 | 0.39 | 18281-05-5 |
| 26 | 2,2′-Methylenebis(4-methyl-6-tert-butylphenol) | 71.05 | 1835 | 1.56 | 119-47-1 |
| 27 | Octadecanal | 71.44 | 1848 | 1.44 | 638-66-4 |
| 28 | Octacosane | 73.06 | 1902 | 3.48 | 630-02-4 |
| 29 | Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | 73.9 | 1934 | 0.45 | 117-81-7 |
| 30 | Heptacosane | 75.19 | 1984 | 1.11 | 593-49-7 |
| 31 | Tetracosanal | 75.96 | 2013 | 0.84 | 57866-08-7 |
| 32 | Hexatriacontane | 77.13 | 2058 | 18.73 | 630-06-8 |
| 33 | 1,3-bis[(4′-Oct-7′-en-1′-yl)phenyl]-prop-2-yn-1-ol | 77.78 | 2082 | 0.21 | None |
| 34 | Icosanal | 79.51 | 2140 | 1.65 | 2400-66-0 |
| 35 | Nonacosane | 80.46 | 2169 | 19.12 | 630-03-5 |
| 36 | Dotriacontane | 82.14 | 2217 | 0.39 | 544-85-4 |
| 37 | 4-[4′-Acetylphenyl]-2-methyl-6-(1′-hydroxy-1′-methylpropyl)pyrido[3,4-c]thiazole | 83.05 | 2240 | 0.81 | None |
| 38 | 17-Pentatriacontene | 83.69 | 2256 | 0.33 | 6971-40-0 |
| 39 | 15-Nonacosanol | 84.37 | 2272 | 11.77 | 2764-81-0 |
| 40 | Ethyl iso-allocholate | 88.31 | 2413 | 0.63 | None |
| 41 | HAHNFETT | 89.17 | 2470 | 0.90 | None |
| 42 | Clionasterol | 90.8 | 2606 | 1.71 | 83-47-6 |
| 43 | beta-Amyrin | 92.64 | 2918 | 0.39 | 559-70-6 |
| 44 | Lupenone | 93.18 | 3014 | 0.18 | 1617-70-5 |
| 45 | Lupeol | 94.22 | 3191 | 0.42 | 545-47-1 |
| 46 | 24-Methylenecycloartanol | 95.61 | 3641 | 0.66 | 1449-09-8 |
| Total Identified (%) | 100.00 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.J.; Won, K.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Won, Y.R.; Kim, N.Y.; Lee, D.K.; Hong, B.S.; Lee, H.M. Skin Wound Healing and Anti-Wrinkle-Promoting In Vitro Biological Activities of Caragana sinica Flower Absolute and Its Chemical Composition. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020235
Kim MJ, Won KJ, Kim DY, Won YR, Kim NY, Lee DK, Hong BS, Lee HM. Skin Wound Healing and Anti-Wrinkle-Promoting In Vitro Biological Activities of Caragana sinica Flower Absolute and Its Chemical Composition. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(2):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020235
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Mi Jung, Kyung Jong Won, Do Yoon Kim, Yu Rim Won, Nan Young Kim, Da Kyoung Lee, Bok Sil Hong, and Hwan Myung Lee. 2023. "Skin Wound Healing and Anti-Wrinkle-Promoting In Vitro Biological Activities of Caragana sinica Flower Absolute and Its Chemical Composition" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 2: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020235
APA StyleKim, M. J., Won, K. J., Kim, D. Y., Won, Y. R., Kim, N. Y., Lee, D. K., Hong, B. S., & Lee, H. M. (2023). Skin Wound Healing and Anti-Wrinkle-Promoting In Vitro Biological Activities of Caragana sinica Flower Absolute and Its Chemical Composition. Pharmaceuticals, 16(2), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020235






