Ganetespib with Methotrexate Acts Synergistically to Impede NF-κB/p65 Signaling in Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
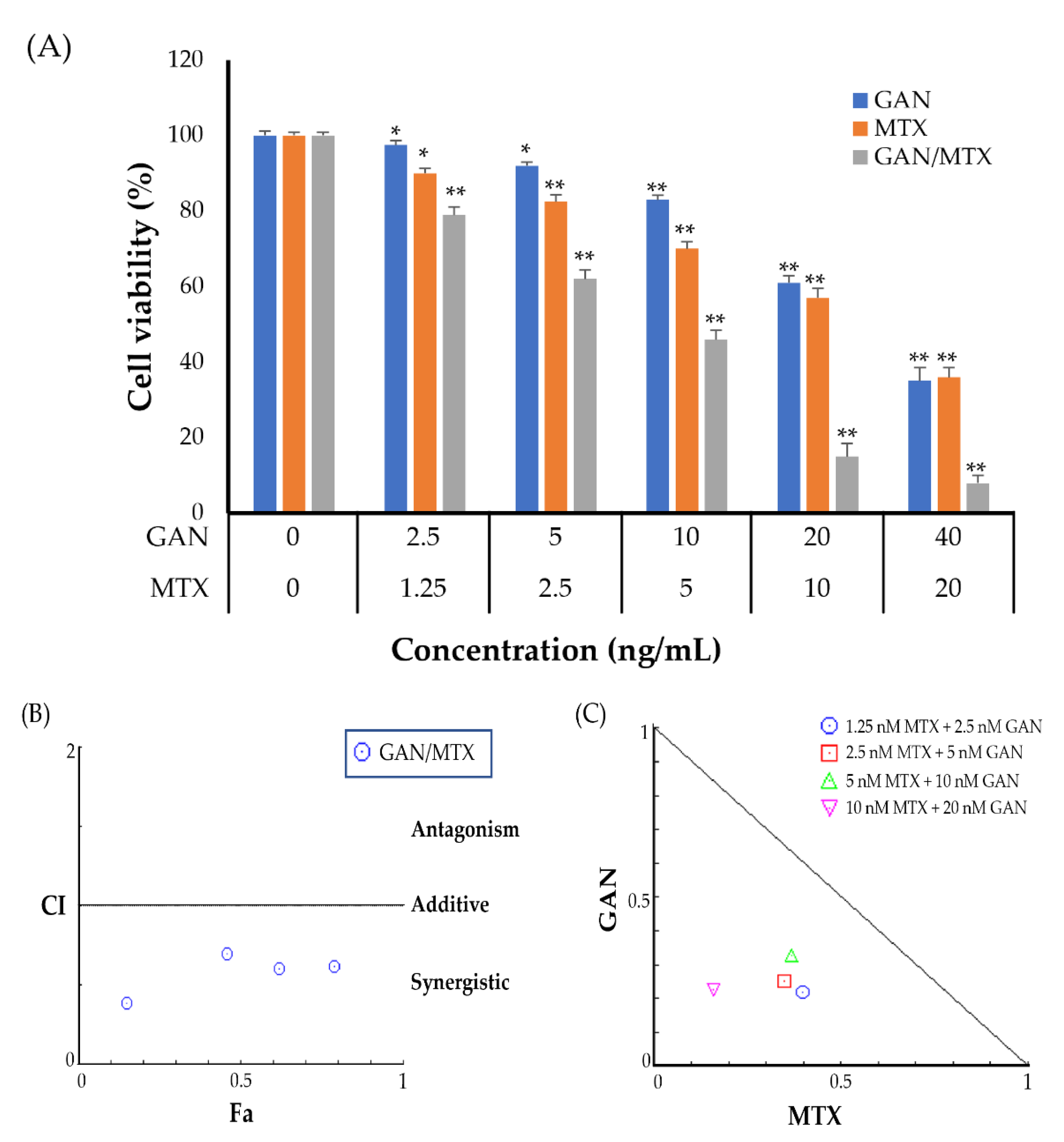
2.1. Combination of GAN and MTX Exhibits Synergistic Effect against the Proliferation of Lung Cancer Cells
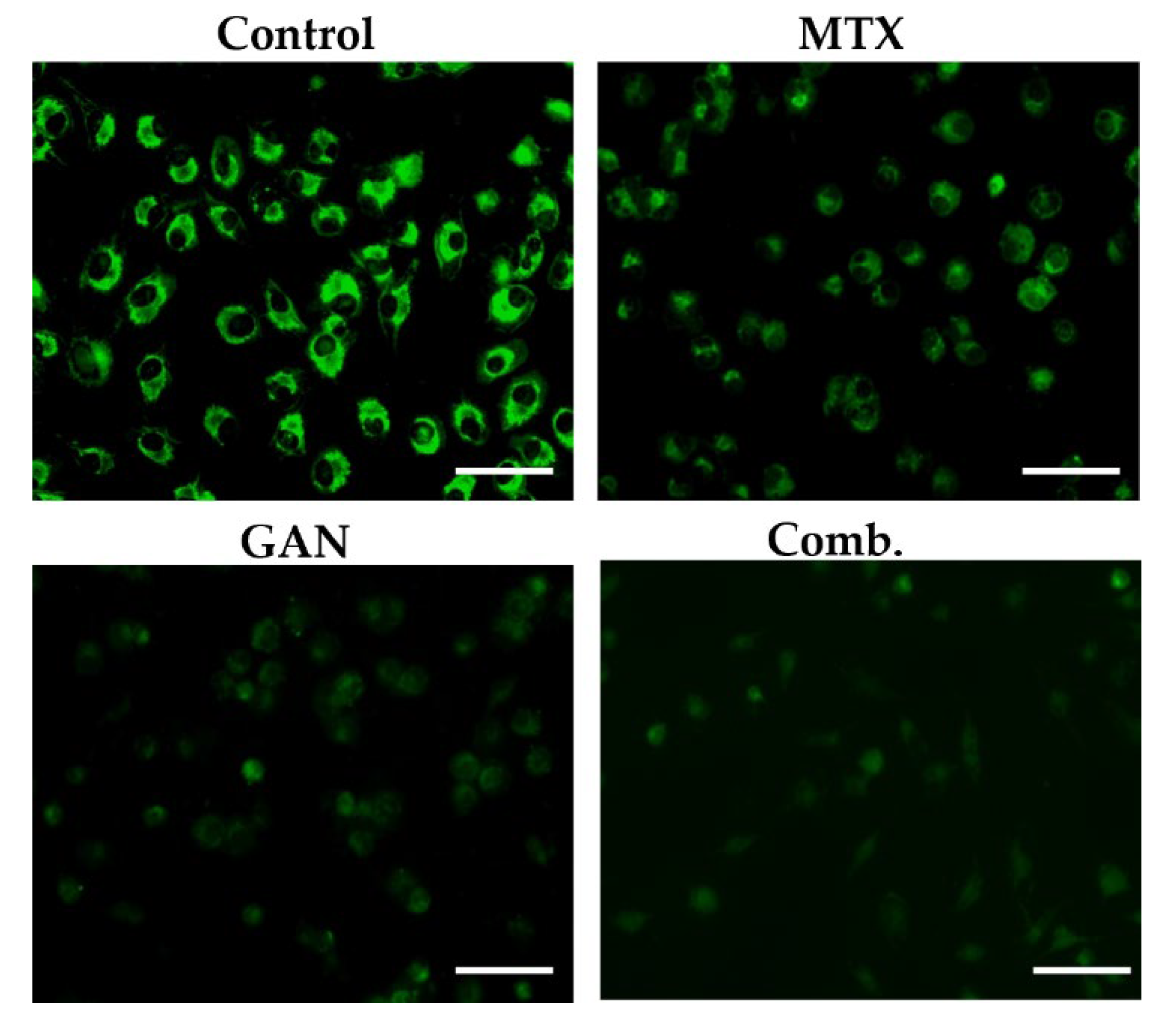
2.2. Combination of GAN and MTX Exhibits Synergistic Effect in Augmenting ROS Production in Lung Cancer Cells
2.3. Combination of GAN and MTX Exhibits Synergistic Effect in Inducing Nuclear Condensation and Fragmentation in Lung Cancer Cells
2.4. Combination of GAN and MTX Induces Caspase Activation in Lung Cancer A549 Cells
2.5. Combination of GAN and MTX Exhibits Synergistic Effect in Dissipating Mitochondrial Membrane Potential in Lung Cancer Cells
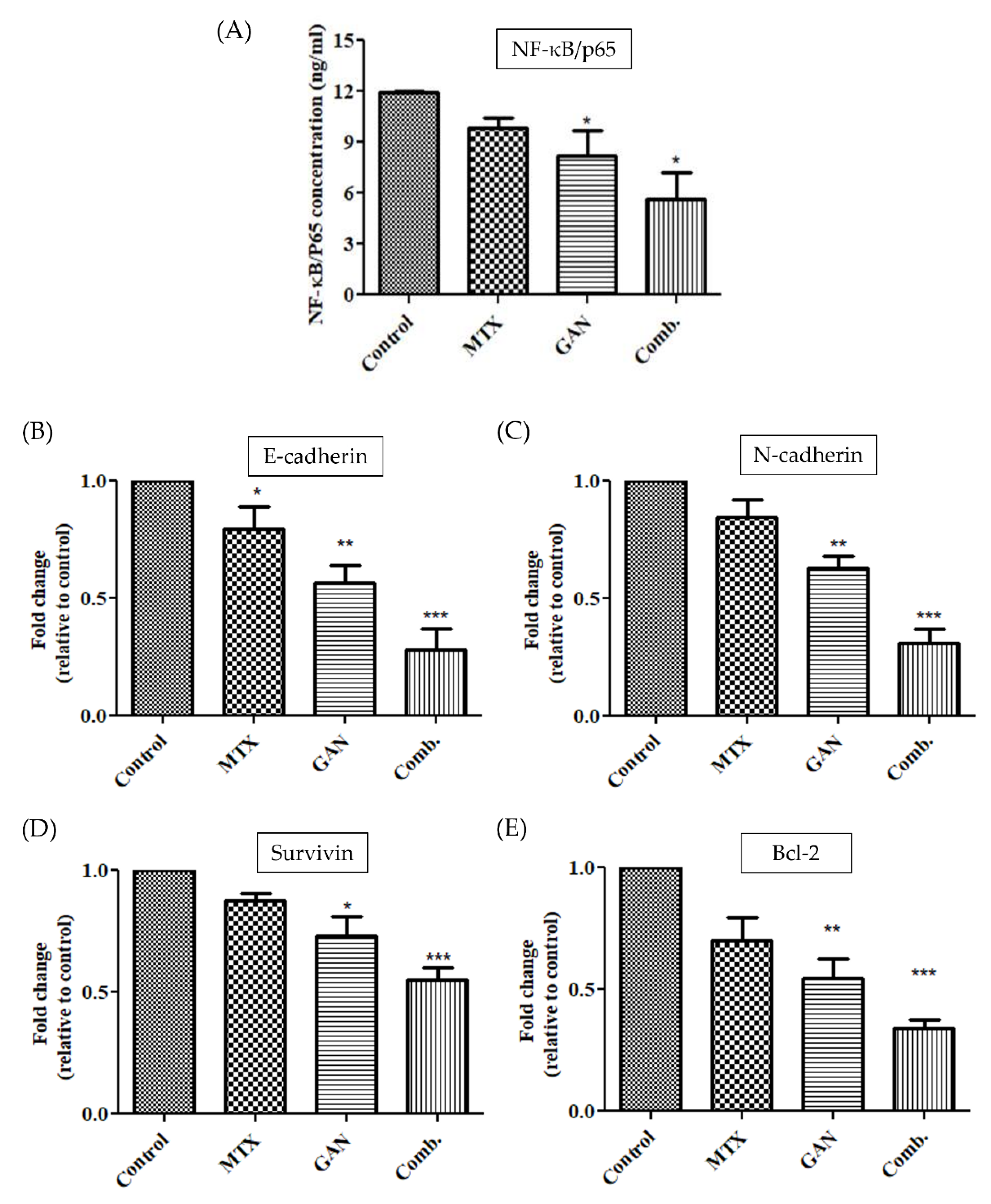
2.6. Combination of GAN and MTX Inhibits the NF-kB Signaling Pathway
2.7. Molecular Docking Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture Maintenance
4.3. Molecular Docking Studies
4.3.1. Preparation of Ligands’ 3D Structure
4.3.2. Retrieval of Targets’ 3D Structure
4.3.3. Visualization of Docked Complex
4.4. Cytotoxicity Assessment
4.5. Morphological Assessment of A549 Cells
4.6. Assessment of Nuclear Morphology
4.7. Caspase-3 Activity
4.8. Evaluation of Intracellular ROS
4.9. Assessment of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
4.10. Assessment of NF-κB Levels
4.11. qRT-PCR Based Assessment of Gene Expression
4.12. Statistical Assessments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldawsari, M.F.; Alalaiwe, A.; Khafagy, E.S.; Al Saqr, A.; Alshahrani, S.M.; Alsulays, B.B.; Alshehri, S.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Danish Rizvi, S.M.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Efficacy of SPG-ODN 1826 Nanovehicles in Inducing M1 Phenotype through TLR-9 Activation in Murine Alveolar J774A.1 Cells: Plausible Nano-Immunotherapy for Lung Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockswold, G.L.; Ramsey, H.E.; Buker, G.D. The results of treatment of lung cancer by surgery, radiation and chemotherapy at a USPHS hospital. Mil. Med. 1970, 135, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Camacho, E.; Trilla-Fuertes, L.; Gámez-Pozo, A.; Dapía, I.; López-Vacas, R.; Zapater-Moros, A.; Lumbreras-Herrera, M.I.; Arias, P.; Zamora, P.; Vara, J.Á.F.; et al. Synergistic effect of antimetabolic and chemotherapy drugs in triple-negative breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbo, B.; Madu, E.E.; Madu, C.O.; Jain, A.; Lu, Y. Role of HSP90 in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, Y.; Nakamoto, H.; Neckers, L. The therapeutic target Hsp90 and cancer hallmarks. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienstmann, R.; Martinez, P.; Felip, E. Personalizing therapy with targeted agents in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2011, 2, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solit, D.B.; Chiosis, G. Development and application of Hsp90 inhibitors. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, T.; Perera, S.A.; Foley, K.P.; Sang, J.; Rodig, S.J.; Inoue, T.; Chen, L.; Li, D.; Carretero, J.; Li, Y.C.; et al. Ganetespib (STA-9090), a nongeldanamycin HSP90 inhibitor, has potent antitumor activity in in vitro and in vivo models of non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4973–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.; Goss, G.; Rosell, R.; Schmid-Bindert, G.; Zaric, B.; Andric, Z.; Bondarenko, I.; Komov, D.; Ceric, T.; Khuri, F.; et al. A randomized phase II study of ganetespib, a heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, in combination with docetaxel in second-line therapy of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (GALAXY-1). Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhaveri, K.; Wang, R.; Teplinsky, E.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Solit, D.; Cadoo, K.; Speyer, J.; D’Andrea, G.; Adams, S.; Patil, S.; et al. A phase I trial of ganetespib in combination with paclitaxel and trastuzumab in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)-positive metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallu, J.; Banerjee, T.; Sulthana, S.; Darji, S.; Higginbotham, R.; Fletcher, C.; Gerasimchuk, N.N.; Santra, S. Nanomedicine-Assisted Combination Therapy of NSCLC: New Platinum-Based Anticancer Drug Synergizes the Therapeutic Efficacy of Ganetespib. Nanotheranostics 2019, 3, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhaveri, K.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Lake, D.; Gilewski, T.; Robson, M.; Goldfarb, S.; Drullinsky, P.; Sugarman, S.; Wasserheit-Leiblich, C.; Fasano, J.; et al. A phase II open-label study of ganetespib, a novel heat shock protein 90 inhibitor for patients with metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2014, 14, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proia, D.A.; Foley, K.P.; Korbut, T.; Sang, J.; Smith, D.; Bates, R.C.; Liu, Y.; Rosenberg, A.F.; Zhou, D.; Koya, K.; et al. Multifaceted intervention by the Hsp90 inhibitor ganetespib (STA-9090) in cancer cells with activated JAK/STAT signaling. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Carnero, A.; Paz-Ares, L. Inhibition of HSP90 molecular chaperones: Moving into the clinic. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, e358–e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.S., Jr. The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996, 14, 649–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Lin, A. NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Bai, L.; Lin, Y. NF-kappaB in lung cancer, a carcinogenesis mediator and a prevention and therapy target. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2011, 16, 1172–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ju, W.; Renouard, J.; Aden, J.; Belinsky, S.A.; Lin, Y. 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin synergistically potentiates tumor necrosis factor-induced lung cancer cell death by blocking the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Lin, Y. Sensitization of TNF-induced cytotoxicity in lung cancer cells by concurrent suppression of the NF-kappaB and Akt pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 355, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyrd-Hansen, M.; Meier, P. IAPs: From caspase inhibitors to modulators of NF-kappaB, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kani, K.; Momota, Y.; Harada, M.; Yamamura, Y.; Aota, K.; Yamanoi, T.; Takano, H.; Motegi, K.; Azuma, M. γ-tocotrienol enhances the chemosensitivity of human oral cancer cells to docetaxel through the downregulation of the expression of NF-κB-regulated anti-apoptotic gene products. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Methotrexate suppresses NF-kappaB activation through inhibition of IkappaBalpha phosphorylation and degradation. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 2911–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangjam, G.S.; Birmpas, C.; Barabutis, N.; Gregory, B.W.; Clemens, M.A.; Newton, J.R.; Fulton, D.; Catravas, J.D. Hsp90 inhibition suppresses NF-κB transcriptional activation via Sirt-2 in human lung microvascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2016, 310, L964–L974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kifer, D.; Jakšić, D.; Šegvić Klarić, M. Assessing the Effect of Mycotoxin Combinations: Which Mathematical Model Is (the Most) Appropriate? Toxins 2020, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Saqr, A.; Khafagy, E.S.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Almansour, K.; Abu Lila, A.S. Screening of Apoptosis Pathway-Mediated Anti-Proliferative Activity of the Phytochemical Compound Furanodienone against Human Non-Small Lung Cancer A-549 Cells. Life 2022, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, B.S.; Annunziata, C.M. NF-κB Signaling in Ovarian Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, I.S.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, J.M.; Cheong, J.H.; Ryu, J.I.; Han, M.H. Correlation of survivin and B-cell lymphoma 2 expression with pathological malignancy and anti-apoptotic properties of glial cell tumors. Biomed. Rep. 2017, 6, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Che, S.; Hui, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H. Combination Therapy of Lung Cancer Using Layer-by-Layer Cisplatin Prodrug and Curcumin Co-Encapsulated Nanomedicine. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 2263–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Bear, M.; Du, Z.; Foley, K.P.; Ying, W.; Barsoum, J.; London, C. The novel HSP90 inhibitor STA-9090 exhibits activity against Kit-dependent and -independent malignant mast cell tumors. Exp. Hematol. 2008, 36, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhaveri, K.; Modi, S. Ganetespib: Research and clinical development. Oncotargets Ther. 2015, 8, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.U.; Haj-Yehia, A.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction. Apoptosis 2000, 5, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, J.V.; Piazza, R.D.; Dos Santos, C.C.; Vega-Chacón, J.; Amantéa, B.E.; Pinto, G.C.; Magnani, M.; Piva, H.L.; Tedesco, A.C.; Primo, F.L.; et al. Synthesis and colloidal characterization of folic acid-modified PEG-b-PCL Micelles for methotrexate delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 177, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Shen, S.; Verma, I.M. NF-κB, an active player in human cancers. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, B.H.; Funkhouser, W.K.; Calvo, B.F.; Meyers, M.O.; Kim, H.J.; Goldberg, R.M.; Bernard, S.A.; Caskey, L.; Deal, A.M.; Wright, F.; et al. Nuclear factor κ-light chain-enhancer of activated B cells is activated by radiotherapy and is prognostic for overall survival in patients with rectal cancer treated with preoperative fluorouracil-based chemoradiotheraphy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.Y.; Chai, J.Y.; Tang, T.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chong, P.P.; Looi, C.Y. The E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Signaling, Therapeutic Implications, and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brayshaw, L.L.; Smith, R.C.G.; Badaoui, M.; Irving, J.A.; Price, S.R. Lanthanides compete with calcium for binding to cadherins and inhibit cadherin-mediated cell adhesion. Metallomics 2019, 11, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cailliez, F.; Lavery, R. Cadherin Mechanics and Complexation: The Importance of Calcium Binding. Biophys. J. 2005, 89, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alattia, J.-R.; Ames, J.B.; Porumb, T.; Tong, K.I.; Heng, Y.M.; Ottensmeyer, P.; Kay, C.M.; Ikura, M. Lateral self-assembly of E-cadherin directed by cooperative calcium binding. FEBS Lett. 1997, 417, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungles, J.M.; Dukes, M.P.; Vunnam, N.; Pedigo, S. Impact of pH on the structure and function of neural cadherin. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 7436–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iswanti, F.C.; Purba, H.H.; Prijanti, A.R.; Fadilah, F.; Herlina, L.; Paramita, R. Modulation of the NF-κB Activation Pathway by Phycocyanobilin from Spirulina platensis: An in Silico Study. Makara J. Sci. 2022, 26, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Alanazi, J.; Unnisa, A.; Alanazi, M.; Alharby, T.N.; Moin, A.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Hussain, T.; Awadelkareem, A.M.; Elkhalifa, A.O.; Faiyaz, S.S.M.; et al. 3-Methoxy Carbazole Impedes the Growth of Human Breast Cancer Cells by Suppressing NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, W.L.; Ballou, C.E. Sporulation in D-glucosamine auxotrophs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Meiosis with defective ascospore wall formation. J. Bacteriol. 1975, 124, 1545–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moin, A.; Wani, S.U.D.; Osmani, R.A.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Khafagy, E.S.; Arab, H.H.; Gangadharappa, H.V.; Allam, A.N. Formulation, characterization, and cellular toxicity assessment of tamoxifen-loaded silk fibroin nanoparticles in breast cancer. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1626–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Tiwari, R.K.; Saeed, M.; Ahmad, I.; Ansari, I.A. Glycyrrhizin Mediates Downregulation of Notch Pathway Resulting in Initiation of Apoptosis and Disruption in the Cell Cycle Progression in Cervical Cancer Cells. Nutr. Cancer 2022, 74, 622–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khafagy, E.-S.; Al Saqr, A.; Alotaibi, H.F.; Abu Lila, A.S. Cytotoxic and Apoptotic Effect of Rubus chingii Leaf Extract against Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma A549 Cells. Processes 2022, 10, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alafnan, A.; Alamri, A.; Hussain, T.; Rizvi, S.M.D. Cucurbitacin-B Exerts Anticancer Effects through Instigation of Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest within Human Prostate Cancer PC3 Cells via Downregulating JAK/STAT Signaling Cascade. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


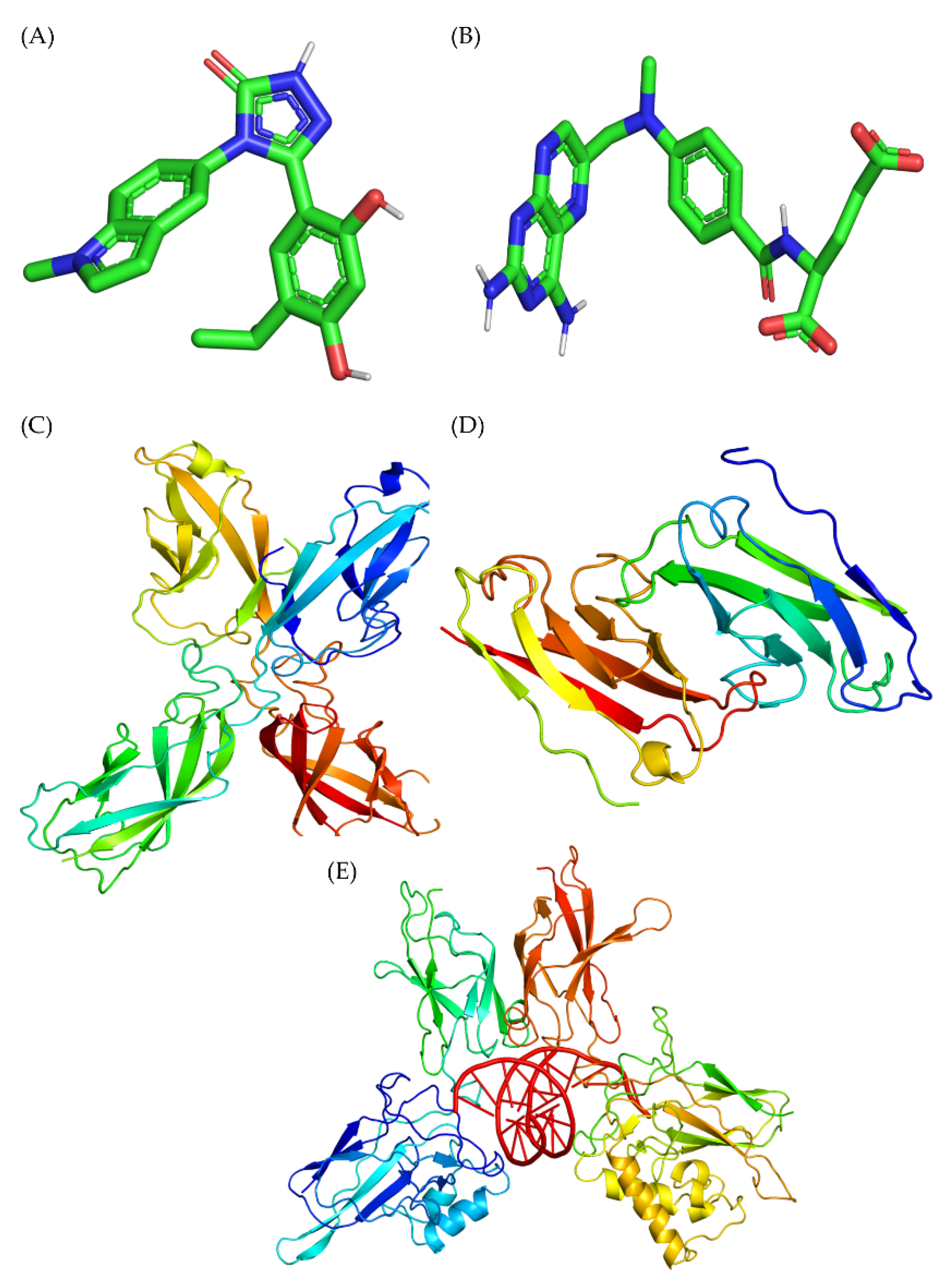
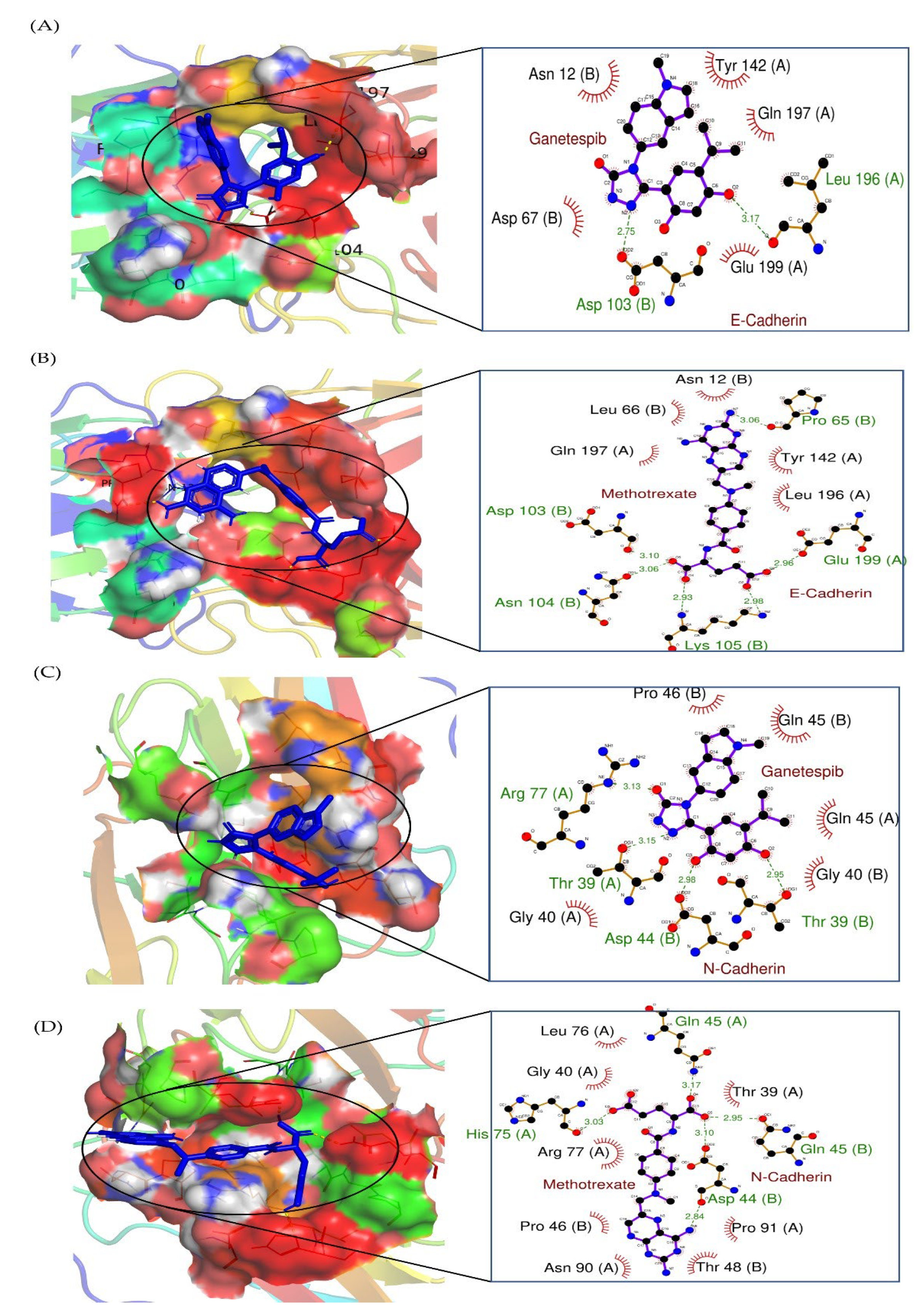

| Compound | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Hydrogen Bonds | Hydrophobic Interactions | pKi (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ganetespib-E-cadherin | −6.76 ± 0.02 | Leu 196 (A) (bond length 3.17) and Asp 103 (B) (bond length 2.75) residues were involved in hydrogen bonding. | Tyr 142 (A), Gln 197 (A), Glu 199 (A), Asp 67 (B), and Asn 12 (B) | −11.41 |
| Methotrexate-E-cadherin | −6.63 ± 0.02 | Glu 199 (A) (bond length 2.96), Lys 105 (B) (bond length 2.98 and 2.93), Asn 104 (B) (bond length 3.06), Asp 103 (B) (bond length 3.10), and Pro 65 (B) (bond length 3.06) amino acids engaged in hydrogen bonding. | Tyr 142 (A), Gln 197 (A), Glu 199 (A), Asp 67 (B), and Asn 12 (B) | −11.19 |
| Gantespib-N-cadherin | −6.23 ± 0.02 | Thr 39 (B) (bond length 2.95), Asp 44 (B) (bond length 2.98), Thr 39 (A) (bond length 3.15), and Arg 77 (A) (bond length 3.13) were involved in hydrogen bonding. | Pro 46 (B), Gln 45 (B), Gln 45 (A), Gly 40 (B), and Gly 40 (A) | −10.51 |
| Methotrexate-N-cadherin | −6.56 ± 0.02 | Gln 45 (A) (bond length 3.17), Gln 45 (B) (bond length 2.95), Asp 44 (B) (bond length 3.10 and 2.84), and His 75 (A) (bond length 3.03) residues were involved in hydrogen bonding. | Thr 39 (A), Pro 91 (A), Thr 48 (B), Asn 90 (A), Pro 46 (B), Arg 77 (A), Gly 40 (A), and Leu 76 (A) | −11.07 |
| Gantespib-NF-κB p65 | −6.36 ± 0.02 | Asp 185 (A) (bond length 2.86) engaged in hydrogen bonding. | Leu 154 (A), Cys 120 (A), His 88 (A), Arg 187 (A), Tyr 36 (A), Pro 189 (A), Asn 155 (A), Ala 188 (A), Asn 190 (A), andLys 123 (A) | −10.73 |
| Methotrexate-NF-κB p65 | −7.33 ± 0.05 | Leu 154 (A) (bond length 3.01), Asp 185 (A) (bond length 3.10), Arg 187 (A) (bond length 2.92 and 2.88), Tyr 36 (A) (bond length 3.16), and Val 121 (A) (bond length 2.78) engaged in hydrogen bonding. | His 88 (A), Cys 120 (A), Ala 188 (A), Arg 605 (B), Lys 218 (A), Asn 186 (A),Asn 155 (A), Lys 122 (A), and Lys 123 (A) | −12.37 |
| Gene Name | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | CGACCACTTTGTCAAGCTCA | CCCCTCTTCAAGGGGTCTAC |
| Bcl2 | ATTGGGAAGTTTCAAATCAGC | TGCATTCTTGGACGAGGG |
| Survivin | ACCGCATCTCTACATTCAAG | CAAGTCTGGCTCGTTCTC |
| E-cadherin | CAGGTCTCCTCATGGCTTTGC | CTTCCGAAAAGAAGGCTGTCC |
| N-cadherin | TCACCAACTGGGACGACAT | CACAGCCTGGATAGCAACG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Subaiea, G.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Yadav, H.K.S.; Al Hagbani, T.; Abdallah, M.H.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Gangadharappa, H.V.; Hussain, T.; Abu Lila, A.S. Ganetespib with Methotrexate Acts Synergistically to Impede NF-κB/p65 Signaling in Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020230
Subaiea G, Rizvi SMD, Yadav HKS, Al Hagbani T, Abdallah MH, Khafagy E-S, Gangadharappa HV, Hussain T, Abu Lila AS. Ganetespib with Methotrexate Acts Synergistically to Impede NF-κB/p65 Signaling in Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(2):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020230
Chicago/Turabian StyleSubaiea, Gehad, Syed Mohd Danish Rizvi, Hemant Kumar Singh Yadav, Turki Al Hagbani, Marwa Helmy Abdallah, El-Sayed Khafagy, Hosahalli Veerabhadrappa Gangadharappa, Talib Hussain, and Amr Selim Abu Lila. 2023. "Ganetespib with Methotrexate Acts Synergistically to Impede NF-κB/p65 Signaling in Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 2: 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020230
APA StyleSubaiea, G., Rizvi, S. M. D., Yadav, H. K. S., Al Hagbani, T., Abdallah, M. H., Khafagy, E.-S., Gangadharappa, H. V., Hussain, T., & Abu Lila, A. S. (2023). Ganetespib with Methotrexate Acts Synergistically to Impede NF-κB/p65 Signaling in Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 16(2), 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020230








