Identification of Potential JNK3 Inhibitors: A Combined Approach Using Molecular Docking and Deep Learning-Based Virtual Screening
Abstract
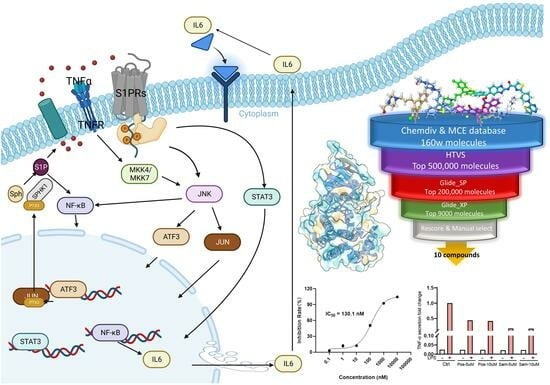
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Data Collection and “in-House” Database Construction
2.2. The Preparation of Protein and the Binding Pocket Determination
2.3. The Hybrid Virtual Screening Workflow
2.4. Inhibitory Activity Assay
2.5. Pro-Inflammatory Factor Release Inhibition Assay for Compound 6
2.6. Elucidating the Initial Binding Conformation of JNK3 and Compound 6 through Binding Pose Metadynamics
2.7. Structural Insight into the Precision Binding Mode between JNK3 and Compound 6 through Molecular Dynamics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Protein Preparation
4.2. Database Preparation
4.3. Receptor Grid Generation
4.4. The Hybrid Virtual Screening Workflow
4.5. IC50 Assay
4.6. Pro-Inflammatory Factor Release Inhibition Assay in LPS-Induced RAW264.7
4.7. Binding Pose Metadynamics
4.8. Molecular Dynamics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagy, M.A.; Hilgraf, R.; Mortensen, D.S.; Elsner, J.; Norris, S.; Tikhe, J.; Yoon, W.; Paisner, D.; Delgado, M.; Erdman, P.; et al. Discovery of the c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Inhibitor CC-90001. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 18193–18208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.M.; Shuai, W.; Zhao, M.; Pan, X.L.; Pei, J.P.; Wu, Y.Y.; Bu, F.Q.; Wang, A.X.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, G. Unraveling the Design and Discovery of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Inhibitors and Their Therapeutic Potential in Human Diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 3758–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawler, S.; Fleming, Y.; Goedert, M.; Cohen, P. Synergistic activation of SAPK1/JNK1 by two MAP kinase kinases in vitro. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 1387–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, T.; Kawasaki, H.; Nishina, H. Diverse Roles of JNK and MKK Pathways in the Brain. J. Recept. Sig. Transd. 2012, 2012, 459265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muth, F.; El-Gokha, A.; Ansideri, F.; Eitel, M.; Doring, E.; Sievers-Engler, A.; Lange, A.; Boeckler, F.M.; Lammerhofer, M.; Koch, P.; et al. Tri- and Tetrasubstituted Pyridinylimidazoles as Covalent Inhibitors of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase 3. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z.G. The functional contrariety of JNK. Mol. Carcinog. 2007, 46, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morfini, G.A.; You, Y.M.; Pollema, S.L.; Kaminska, A.; Liu, K.; Yoshioka, K.; Bjorkblom, B.; Coffey, E.T.; Bagnato, C.; Han, D.; et al. Pathogenic huntingtin inhibits fast axonal transport by activating JNK3 and phosphorylating kinesin. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambhore, N.; Mohire, S.; Kalidhindi, R.S.; Mulukutla, S.; Murthy, V.; Elango, K. H-3 Receptor Antagonist and JNK-3 Inhibitor: A new therapeutic approach to treat Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2016, 22, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, X.; Falconi, M.; Di Marino, D.; Borsello, T. JNK3 as a Therapeutic Target for Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011, 24, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfinogenova, N.D.; Quinn, M.T.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Atochin, D.N. Alarmins and c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Signaling in Neuroinflammation. Cells 2020, 9, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.; Moon, H.; Yang, S.; Lee, J.; Baek, J.; Kim, H.; Cho, H.; Hwang, K.; Ahn, S.; Kim, Y.; et al. Carbamate JNK3 Inhibitors Show Promise as Effective Treatments for Alzheimer’s Disease: In Vivo Studies on Mouse Models. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 6372–6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Kovrizhina, A.R.; Stankevich, K.S.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Quinn, M.T.; Cook, M.J. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel O-substituted tryptanthrin oxime derivatives as c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 958687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, J.; Yang, S.; Lee, J.; Moon, H.; Kim, J.; Jung, H.; Im, D.; Oh, Y.; Jang, M.; Cho, H.; et al. Discovery of novel imidazole chemotypes as isoform-selective JNK3 inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 245 Pt 1, 114894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graczyk, P.P. JNK inhibitors as anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective agents. Future Med. Chem. 2013, 5, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, P.; Gehringer, M.; Laufer, S.A. Inhibitors of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinases: An Update. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 72–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboni, S.; Hiver, A.; Szyndralewiez, C.; Gaillard, P.; Gotteland, J.-P.; Vitte, P.-A. AS601245 (1,3-Benzothiazol-2-yl (2-{[2-(3-pyridinyl) ethyl] amino}-4 pyrimidinyl) Acetonitrile): A c-Jun NH2-Terminal Protein Kinase Inhibitor with Neuroprotective Properties. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 310, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halazy, S. Designing heterocyclic selective kinase inhibitors: From concept to new drug candidates. Arkivoc 2006, 7, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messoussi, A.; Feneyrolles, C.; Bros, A.; Deroide, A.; Dayde-Cazals, B.; Cheve, G.; Van Hijfte, N.; Fauvel, B.; Bougrin, K.; Yasri, A. Recent Progress in the Design, Study, and Development of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Inhibitors as Anticancer Agents. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilevskaya, I.A.; Selvakumaran, M.; Hierro, L.C.; Goldstein, S.R.; Winkler, J.D.; O’Dwyer, P.J. Inhibition of JNK Sensitizes Hypoxic Colon Cancer Cells to DNA-Damaging Agents. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2015, 21, 4143–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Velden, J.L.J.; Ye, Y.; Nolin, J.D.; Hoffman, S.M.; Chapman, D.G.; Lahue, K.G.; Abdalla, S.; Chen, P.; Liu, Y.; Bennett, B.; et al. JNK inhibition reduces lung remodeling and pulmonary fibrotic systemic markers. Clin. Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenitsky, V.P.; Nadolny, L.; Delgado, M.; Ayala, L.; Clareen, S.; Hilgraf, R.; Albers, R.; Hegde, S.; D’Sidocky, N.; Sapienza, J.; et al. Discovery of CC-930, an orally active anti-fibrotic JNK inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, M.T.H.; Ahn, H.C. Fragment-Based and Structural Investigation for Discovery of JNK3 Inhibitors. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, J.X.; Feng, R.W.; Gao, J.; Yu, H.Y.; Weng, Q.J.; He, Q.J.; Dong, X.W.; Wu, J.; Yang, B. Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence in Participating Structure-Based Virtual Screening for Identifying Novel Interleukin-1 Receptor Associated Kinase-1 Inhibitors. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Kang, X.; Zhao, D.; Zou, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C. Machine Learning Models Combined with Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking to Predict Human Topoisomerase I Inhibitors. Molecules 2019, 24, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Lucio, O.; Ahmad, M.; del Rio-Chanona, E.A.; Wegner, J.K. A Geometric Deep Learning Approach to Predict Binding Conformations of Bioactive Molecules. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2021, 3, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cai, H.; Ren, L.; Yang, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Tan, W.; et al. Sphingosine Kinase 1 Promotes Growth of Glioblastoma by Increasing Inflammation Mediated by the NF-ΚB /IL-6/STAT3 and JNK/PTX3 Pathways. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 4390–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LigPrep; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2021.
- Feng, Y.B.; Park, H.; Ryu, J.C.; Yoon, S.O. N-Aromatic-Substituted Indazole Derivatives as Brain-Penetrant and Orally Bioavailable JNK3 Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainza, P.; Sverrisson, F.; Monti, F.; Rodola, E.; Boscaini, D.; Bronstein, M.M.; Correia, B.E. Deciphering interaction fingerprints from protein molecular surfaces using geometric deep learning. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.F.; Zhao, Y.S.; Zeng, X.; Chen, X.T.; Meng, Q.Q.; Ding, Z.; Zhao, W.S.; Qi, Y.M.; Gao, Y.F.; Du, J.F. Identification of Phelligridin-Based Compounds as Novel Human CD73 Inhibitors. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Maxwell, D.S.; Tirado-Rives, J. Development and testing of the OPLS all-atom force field on conformational energetics and properties of organic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11225–11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vass, M.; Tarcsay, A.; Keseru, G.M. Multiple ligand docking by Glide: Implications for virtual second-site screening. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2012, 26, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra precision glide: Docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 2. Enrichment factors in database screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glide; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2021.
- Sandor, M.; Kiss, R.; Keseru, G.M. Virtual Fragment Docking by Glide: A Validation Study on 190 Protein-Fragment Complexes. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, G.M.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and ligand preparation: Parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protein Preparation Wizard; Epik, Impact, Prime; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2021.
- Castoldi, R.E.; Pennella, G.; Saturno, G.S.; Grossi, P.; Brughera, M.; Venturi, M. Assessing and managing toxicities induced by kinase inhibitors. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 2007, 10, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Man, V.H.; Yang, W.; Lee, T.S.; Wang, J. A fast and high-quality charge model for the next generation general AMBER force field. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 114502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Ben-Shalom, I.Y.; Brozell, S.R.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cheatham, T.E., III.; Cruzeiro, V.W.D.; Darden, T.A.; Duke, R.E.; Ghoreishi, D.; Giambasu, G.; et al. AMBER 2019; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]






| Entry | Docking Score (HTVS) (kcal/mol) | Docking Score (SP) (kcal/mol) | Docking Score (XP) (kcal/mol) | MM-GBSA dG Bind (kcal/mol) | Deepdockscore | pIC50 Predicted | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound 1 | −11.107 | −11.896 | −13.871 | −86.10 | −185.12 | 6.25 | 17.50 ± 0.55 |
| Compound 2 | −9.373 | −10.870 | −11.918 | −80.93 | −169.34 | 5.89 | 43.24 ± 5.36 |
| Compound 3 | −9.190 | −8.696 | −10.808 | −85.84 | −154.42 | 6.84 | 5.70 ± 1.02 |
| Compound 4 | −9.023 | −10.094 | −8.959 | −76.28 | −90.94 | 5.34 | 7.77 ± 0.43 |
| Compound 5 | −8.941 | −9.200 | −8.537 | −83.07 | −140.73 | 5.35 | 16.58 ± 0.34 |
| Compound 6 | −8.401 | −11.535 | −13.065 | −82.05 | −173.73 | 5.82 | 99.73 ± 0.44 |
| Compound 7 | −8.147 | −10.439 | −10.690 | −78.60 | −172.77 | 6.20 | 26.88 ± 3.29 |
| Compound 8 | −7.853 | −10.406 | −8.840 | −80.03 | −116.72 | 5.30 | 16.76 ± 0.56 |
| Compound 9 | −6.757 | −11.754 | −13.694 | −87.01 | −183.26 | 6.34 | 34.81 ± 0.23 |
| Compound 10 | −8.571 | −9.496 | −9.765 | −75.76 | −97.41 | 5.33 | 43.76 ± 1.92 |
| Entry | Molecular Weight | XLogP3-AA | Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | Rotatable Bond Count | Heavy Atom Count | Topological Polar Surface Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound 1 | 468.6 | 5.3 | 2 | 6 | 9 | 35 | 59.1 |
| Compound 2 | 476.0 | 5.3 | 2 | 7 | 7 | 34 | 83.4 |
| Compound 3 | 435.5 | 2.1 | 2 | 7 | 7 | 32 | 94.3 |
| Compound 4 | 461.0 | 4.6 | 2 | 6 | 8 | 31 | 108.0 |
| Compound 5 | 453.6 | 4.60 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 34 | 69.2 |
| Compound 6 | 399.5 | 5.6 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 29 | 83.1 |
| Compound 7 | 442.5 | 3.1 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 33 | 82.6 |
| Compound 8 | 495.5 | 5.6 | 0 | 6 | 4 | 36 | 132.0 |
| Compound 9 | 568.7 | 5.9 | 1 | 9 | 9 | 42 | 92.3 |
| Compound 10 | 401.0 | 4.3 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 27 | 52.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, C.; Shen, Z.; Shen, L.; Kadier, K.; Zhao, J.; Guo, Y.; Xu, L.; Cao, J.; Dong, X.; Yang, B. Identification of Potential JNK3 Inhibitors: A Combined Approach Using Molecular Docking and Deep Learning-Based Virtual Screening. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101459
Yao C, Shen Z, Shen L, Kadier K, Zhao J, Guo Y, Xu L, Cao J, Dong X, Yang B. Identification of Potential JNK3 Inhibitors: A Combined Approach Using Molecular Docking and Deep Learning-Based Virtual Screening. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(10):1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101459
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Chenpeng, Zheyuan Shen, Liteng Shen, Kailibinuer Kadier, Jingyi Zhao, Yu Guo, Lei Xu, Ji Cao, Xiaowu Dong, and Bo Yang. 2023. "Identification of Potential JNK3 Inhibitors: A Combined Approach Using Molecular Docking and Deep Learning-Based Virtual Screening" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 10: 1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101459
APA StyleYao, C., Shen, Z., Shen, L., Kadier, K., Zhao, J., Guo, Y., Xu, L., Cao, J., Dong, X., & Yang, B. (2023). Identification of Potential JNK3 Inhibitors: A Combined Approach Using Molecular Docking and Deep Learning-Based Virtual Screening. Pharmaceuticals, 16(10), 1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101459