An Examination of the Complex Pharmacological Properties of the Non-Selective Opioid Modulator Buprenorphine
Abstract
1. Introduction and History
2. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
3. Misuse Potential
4. Toxicology
5. Buprenorphine: Human/Clinical Use
6. Prenatal Correlates and Consequences
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, M.P.; Pasternak, G.; Behm, B. Treating Chronic Pain: An overview of clinical studies centered on the buprenorphine option. Drugs 2018, 78, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, N.D.; Lovell, A.M. The history of the development of buprenorphine as an addiction therapeutic: Campbell & Lovell. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1248, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasinski, D.R. Human pharmacology and abuse potential of the analgesic buprenorphine: A potential agent for treating narcotic addiction. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1978, 35, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, B.M.; Christie, M.J.; Devi, L.; Toll, L.; Traynor, J.R. Challenges for opioid receptor nomenclature: IUPHAR Review 9: Challenges for opioid receptor nomenclature. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.Z.; Cunningham, A.M.; Joshi, A.; Oei, J.L.; Ward, M.C. Expression of kappa opioid receptors in developing rat brain—Implications for perinatal buprenorphine exposure. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 78, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschenroeder, A.C.; Vestal-Laborde, A.A.; Sanchez, E.S.; Robinson, S.E.; Sato-Bigbee, C. Oligodendrocyte responses to buprenorphine uncover novel and opposing roles of μ-opioid- and nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptors in cell development: Implications for drug addiction treatment during pregnancy. Glia 2012, 60, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, L.; Hellyer, P.; Rishniw, M.; Schoenfeld-Tacher, R. The US opioid epidemic and its impact on US general practice veterinarians. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, B.J.; McCall, K.L.; Kogan, L.R.; Hellyer, P. Assessment of controlled substance distribution to U.S. veterinary teaching institutions from 2006 to 2019. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 615646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudin, J.; Fudin, J. A Narrative pharmacological review of buprenorphine: A unique opioid for the treatment of chronic pain. Pain Ther. 2020, 9, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfy, K.; Cowan, A. Buprenorphine: A unique drug with complex pharmacology. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2004, 2, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.E. Buprenorphine: An analgesic with an expanding role in the treatment of opioid addiction. CNS Drug Rev. 2006, 8, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampman, K.; Jarvis, M. American society of addiction medicine (ASAM) national practice guideline for the use of medications in the treatment of addiction involving opioid use. J. Addict. Med. 2015, 9, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provider Clinical Support System. Available online: https://pcssnow.org (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Stahl, S.M. Stahl’s Essential Psychopharmacology: Neuroscientific Basis and Practical Application, 4th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-107-02598-1. [Google Scholar]
- Brunton, L.L.; Knollmann, B.C.; Hilal-Dandan, R. (Eds.) Goodman & Gilman’s the Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 13th ed.; McGraw Hill Medical: New York, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-259-58473-2. [Google Scholar]
- Emery, M.A.; Eitan, S. Members of the same pharmacological family are not alike: Different Opioids, different consequences, hope for the opioid crisis? Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 92, 428–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mégarbane, B.; Hreiche, R.; Pirnay, S.; Marie, N.; Baud, F.J. Does high-dose buprenorphine cause respiratory depression? Possible mechanisms and therapeutic consequences. Toxicol. Rev. 2006, 25, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.P. Buprenorphine in cancer pain. Support. Care Cancer 2005, 13, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iribarne, C.; Picart, D.; Dréano, Y.; Bail, J.-P.; Berthou, F. Involvement of cytochrome P450 3A4 in N-dealkylation of buprenorphine in human liver microsomes. Life Sci. 1997, 60, 1953–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Chiba, K.; Tani, M.; Shimada, N.; Ishizaki, T.; Kuroiwa, Y. Human buprenorphine N-dealkylation is catalyzed by cytochrome P450 3A4. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 1998, 26, 818–821. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elkader, A.; Sproule, B. Buprenorphine: Clinical pharmacokinetics in the treatment of opioid dependence. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2005, 44, 661–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, B.A.; Caperton, C.O.; Russell, L.N.; Cabanlong, C.V.; Wilson, C.D.; Urquhart, K.R.; Martins, B.S.; Zita, M.D.; Patton, A.L.; Alund, A.W.; et al. In utero exposure to norbuprenorphine, a major metabolite of buprenorphine, induces fetal opioid dependence and leads to neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.L.; Foster, D.; Upton, R.; Grant, C.; Martinez, A.; Somogyi, A. Comparison of cerebral pharmacokinetics of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine in an in vivo sheep model. Xenobiotica 2007, 37, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, V.A.; Rainey, P.M.; Moody, D.E.; Morse, G.D.; Ma, Q.; Prathikanti, S.; Pade, P.A.; Alvanzo, A.A.H.; McCance-Katz, E.F. Interactions between buprenorphine and the protease inhibitors darunavir-ritonavir and fosamprenavir-ritonavir. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, R.C.; Perez, M. How do I interpret and use quantitative buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine urine levels? Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2022, 89, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacinko, S.; Jones, H.; Johnson, R.; Choo, R.; Huestis, M. Correlations of maternal buprenorphine dose, buprenorphine, and metabolite concentrations in meconium with neonatal outcomes. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 84, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, R.S.; Wilkins, D.G.; Averin, O.; Choo, R.E.; Schroeder, J.R.; Jasinski, D.R.; Johnson, R.E.; Jones, H.E.; Huestis, M.A. Buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine in hair of pregnant women and their infants after controlled buprenorphine administration. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 2136–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, M. Basic pharmacology of buprenorphine. Eur. J. Pain Suppl. 2007, 1, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierke, C.; Marxen, B.; Boettcher, M.; Hiemke, C.; Havemann-Reinecke, U. Buprenorphine-cannabis interaction in patients undergoing opioid maintenance therapy. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 271, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Board on Population Health and Public Health Practice; Committee on the Health Effects of Marijuana: An Evidence Review and Research Agenda. The Health Effects of Cannabis and Cannabinoids: The Current State of Evidence and Recommendations for Research; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-309-45304-2.
- Lexicomp. Lexicomp Drug Interactions; Lexicomp®: Hudson, OH, USA. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/drug-interactions/?source=responsive_home#di-druglist (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Belbuca [Package Insert], Food and Drug Administration, Reference ID: 3837517. Revised: 10/2015. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2015/207932s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Butrans [Package Insert], Food and Drug Administration, Reference ID: 3534876. Revised: 06/2014. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/021306s015s019lbl.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Sublocade [Package Insert], Food and Drug Administration, Reference ID: 4188740. Revised: 11/2017. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/209819s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Subutex [Package Insert], Food and Drug Administration, Reference ID: 4215177. Revised: 02/2018. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/020732s018lbl.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- McCance-Katz, E.F.; Sullivan, L.E.; Nallani, S. Drug interactions of clinical importance among the opioids, methadone and buprenorphine, and other frequently prescribed medications: A review. Am. J. Addict. 2010, 19, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaud, M.; Petit, G.; Potard, D.; Courty, P. Six deaths linked to concomitant use of buprenorphine and benzodiazepines. Addict. Abingdon Engl. 1998, 93, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, M.A.; Lofwall, M.R.; Walsh, S.L. Buprenorphine pharmacology review: Update on transmucosal and long-acting formulations. J. Addict. Med. 2019, 13, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oifa, S.; Sydoruk, T.; White, I.; Ekstein, M.P.; Marouani, N.; Chazan, S.; Skornick, Y.; Weinbroum, A.A. Effects of intravenous patient-controlled analgesia with buprenorphine and morphine alone and in combination during the first 12 postoperative hours: A randomized, double-blind, four-arm trial in adults undergoing abdominal surgery. Clin. Ther. 2009, 31, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercadante, S.; Villari, P.; Ferrera, P.; Porzio, G.; Aielli, F.; Verna, L.; Casuccio, A. Safety and effectiveness of intravenous morphine for episodic breakthrough pain in patients receiving transdermal buprenorphine. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2006, 32, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxtable, C.A.; Macintyre, P.E. An alternative way of managing acute pain in patients who are in buprenorphine opioid substitution therapy programs. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2013, 30, 717–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, M.; Kotaki, H.; Uchino, K.; Sawada, Y.; Iga, T. Pharmacokinetic analysis of enterohepatic circulation of buprenorphine and its active metabolite, norbuprenorphine, in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 1994, 22, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khroyan, T.V.; Wu, J.; Polgar, W.E.; Cami-Kobeci, G.; Fotaki, N.; Husbands, S.M.; Toll, L. BU08073 a buprenorphine analogue with partial agonist activity at μ-receptors in vitro but long-lasting opioid antagonist activity in vivo in mice: BU08073 a long-lasting opiate antagonist. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, A.; Magiera, J.; Rethwan, N.; Andersson, Å.; Leen Lam, A.; Wyse, B.; Meutermans, W.; Lewis, R.; Smith, M. In vitro profiling of opioid ligands using the cAMP formation inhibition assay and the β-arrestin2 recruitment assay: No two ligands have the same profile. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 872, 172947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, T.P. The history and pharmacology of buprenorphine: New advances in cats. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 45, S1–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, S.A. Does potency predict clinical efficacy? Illustration through an antihistamine model. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002, 89, 7–11; quiz 11–12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Available online: https://medicaid.utah.gov/Documents/files/Opioid-Morphine-EQ-Conversion-Factors.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Piper, B.J.; Shah, D.T.; Simoyan, O.M.; McCall, K.L.; Nichols, S.D. Trends in medical use of opioids in the U.S., 2006–2016. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 54, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliwoda, S.; Noor, N.; Jenkins, J.S.; Stark, C.W.; Steib, M.; Hasoon, J.; Varrassi, G.; Urits, I.; Viswanath, O.; Kaye, A.M.; et al. Buprenorphine and its formulations: A comprehensive review. Health Psychol. Res. 2022, 10, 37517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Wang, H.; Li, D.; Lang, L.; Gray, F.; Liu, Y.; Laffont, C.M.; Young, M.; Jiang, J.; Liu, Z.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of sublingual buprenorphine tablets following single and multiple doses in Chinese participants with and without opioid use disorder. Drugs RD 2019, 19, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlman, J.J.; Lalani, S.; Magluilo, J.; Levine, B.; Darwin, W.D.; Johnson, R.E.; Cone, E.J. Human pharmacokinetics of intravenous, sublingual, and buccal buprenorphine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 1996, 20, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seligman, N.S.; Cleary, B.J.; Berghella, V. Methadone and Buprenorphine Pharmacotherapy of Opioid Use Disorder During Pregnancy. Available online: https://www.medilib.ir/uptodate/show/87238 (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- Nath, R.P.; Upton, R.A.; Everhart, E.T.; Cheung, P.; Shwonek, P.; Jones, R.T.; Mendelson, J.E. Buprenorphine pharmacokinetics: Relative bioavailability of sublingual tablet and liquid formulations. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 39, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuh, K.J.; Johanson, C.-E. Pharmacokinetic comparison of the buprenorphine sublingual liquid and tablet. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1999, 56, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhardt, K.; Ravn, C.; Gizurarson, S.; Bechgaard, E. Intranasal absorption of buprenorphine—In vivo bioavailability study in sheep. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 205, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongstorp, M.; Bogen, I.L.; Stiris, T.; Andersen, J.M. High accumulation of methadone compared with buprenorphine in fetal rat brain after maternal exposure. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 371, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.W.; Gao, C.; Mao, Q. An update on expression and function of P-Gp/ABCB1 and BCRP/ABCG2 in the placenta and fetus. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auvity, S.; Breuil, L.; Goislard, M.; Bottlaender, M.; Kuhnast, B.; Tournier, N.; Caillé, F. An original radio-biomimetic approach to synthesize radiometabolites for PET imaging. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2020, 90–91, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, M.Z.; Gao, C.; Shireman, L.M.; Phillips, B.; Risler, L.J.; Neradugomma, N.K.; Choudhari, P.; Prasad, B.; Shen, D.D.; Mao, Q. P-gp/ABCB1 exerts differential impacts on brain and fetal exposure to norbuprenorphine. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 119, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindemalm, S.; Nydert, P.; Svensson, J.-O.; Stahle, L.; Sarman, I. Transfer of buprenorphine into breast milk and calculation of infant drug dose. J. Hum. Lact. 2009, 25, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzung, B.G. (Ed.) Basic & Clinical Pharmacology, 14th ed.; A Lange medical book; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA; Chicago, IL, USA; San Francisco, CA, USA; Athens, Greece; London, UK; Madrid, Spain; Mexico City, Mexico; Milan, Italy; New Delhi, India; Singapore; Sydney, Australia; Toronto, Japan, 2018; ISBN 978-1-259-64115-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kenakin, T. Principles: Receptor theory in pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dum, J.E.; Herz, A. In vivo receptor binding of the opiate partial agonist, buprenorphine, correlated with its agonistic and antagonistic actions. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1981, 74, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lean, A.; Stadel, J.M.; Lefkowitz, R.J. A ternary complex model explains the agonist-specific binding properties of the adenylate cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 7108–7117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejwani, G.A.; Rattan, A.K. The role of spinal opioid receptors in antinociceptive effects produced by intrathecal administration of hydromorphone and buprenorphine in the rat. Anesth. Analg. 2002, 94, 1542–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Raffa, R.B. Identification of an additional supraspinal component to the analgesic mechanism of action of buprenorphine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galandrin, S.; Oligny-Longpré, G.; Bouvier, M. The evasive nature of drug efficacy: Implications for drug discovery. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 28, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, R. (Ed.) Principles of Rehabilitation Medicine; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-0-07-179333-9. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.M.; Holtzman, M.; Kim, T.; Kharasch, E.D. Buprenorphine metabolites, buprenorphine-3-glucuronide and norbuprenorphine-3-glucuronide, are biologically active. Anesthesiology 2011, 115, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Kehner, G.B.; Cowan, A.; Liu-Chen, L.Y. Comparison of pharmacological activities of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine: Norbuprenorphine is a potent opioid agonist. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 297, 688–695. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, S. Buprenorphine—Clinically useful but often misunderstood. Scand. J. Pain 2013, 4, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, M.; Kotaki, H.; Nishitateno, K.; Sawada, Y.; Iga, T. Kinetics of respiratory depression in rats induced by buprenorphine and its metabolite, norbuprenorphine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 281, 428–433. [Google Scholar]
- Dahan, A.; Yassen, A.; Bijl, H.; Romberg, R.; Sarton, E.; Teppema, L.; Olofsen, E.; Danhof, M. Comparison of the respiratory effects of intravenous buprenorphine and fentanyl in humans and rats. Br. J. Anaesth. 2005, 94, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahan, A. Opioid-induced respiratory effects: New data on buprenorphine. Palliat. Med. 2006, 20, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, M.; Kotaki, H.; Sawada, Y.; Iga, T. Comparative analysis of buprenorphine- and norbuprenorphine-induced analgesic effects based on pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 272, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coller, J.K.; Christrup, L.L.; Somogyi, A.A. Role of active metabolites in the use of opioids. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 65, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, N.; Cresteil, T.; Djebli, N.; Marquet, P. In vitro metabolism study of buprenorphine: Evidence for new metabolic pathways. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005, 33, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfy, K.; Eitan, S.; Bryant, C.D.; Yang, Y.C.; Saliminejad, N.; Walwyn, W.; Kieffer, B.L.; Takeshima, H.; Carroll, F.I.; Maidment, N.T.; et al. Buprenorphine-induced antinociception is mediated by μ-opioid receptors and compromised by concomitant activation of opioid receptor-like receptors. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10331–10337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfy, K.; Hossain, S.M.; Khaliq, I.; Maidment, N.T. Orphanin FQ/nociceptin attenuates the development of morphine tolerance in rats: Orphanin FQ/nociceptin and morphine tolerance. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pergolizzi, J.; Böger, R.H.; Budd, K.; Dahan, A.; Erdine, S.; Hans, G.; Kress, H.-G.; Langford, R.; Likar, R.; Raffa, R.B.; et al. Opioids and the management of chronic severe pain in the elderly: Consensus statement of an international expert panel with focus on the six clinically most often used world health organization step iii opioids (buprenorphine, fentanyl, hydromorphone, methadone, morphine, oxycodone). Pain Pract. 2008, 8, 287–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, M.; Garofoli, M.; Raffa, R.B. Benefit-risk analysis of buprenorphine for pain management. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremeans, C.M.; Gruley, E.; Kyle, D.J.; Ko, M.-C. Roles of μ-opioid receptors and nociceptin/orphanin fq peptide receptors in buprenorphine-induced physiological responses in primates. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 343, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kögel, B.; Christoph, T.; Straβburger, W.; Friderichs, E. Interaction of μ-opioid receptor agonists and antagonists with the analgesic effect of buprenorphine in mice. Eur. J. Pain 2005, 9, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassen, A.; Kan, J.; Olofsen, E.; Suidgeest, E.; Dahan, A.; Danhof, M. Mechanism-based pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling of the respiratory-depressant effect of buprenorphine and fentanyl in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 319, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, S.L.; Preston, K.L.; Stitzer, M.L.; Cone, E.J.; Bigelow, G.E. Clinical pharmacology of buprenorphine: Ceiling effects at high doses. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1994, 55, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoph, T.; Kögel, B.; Schiene, K.; Méen, M.; De Vry, J.; Friderichs, E. Broad analgesic profile of buprenorphine in rodent models of acute and chronic pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 507, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillarisetti, S.; Khanna, I. Buprenorphine—An attractive opioid with underutilized potential in treatment of chronic pain. J. Pain Res. 2015, 8, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukas, S.E.; Griffiths, R.R.; Brady, J.V. Buprenorphine self-administration by the baboon: Comparison with other opioids. NIDA Res. Monogr. 1983, 43, 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Sorge, J.; Sittl, R. Transdermal buprenorphine in the treatment of chronic pain: Results of a phase III, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin. Ther. 2004, 26, 1808–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.E.; Fudala, P.J.; Payne, R. Buprenorphine: Considerations for pain management. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2005, 29, 297–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kress, H.G. Clinical update on the pharmacology, efficacy and safety of transdermal buprenorphine. Eur. J. Pain 2009, 13, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likar, R. Transdermal buprenorphine in the management of persistent pain—Safety aspects. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2006, 2, 115–125. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, A.; Callaghan, D.; Spink, D.; Cloutier, C.; Dzongowski, P.; O’Mahony, W.; Sinclair, D.; Rashiq, S.; Buckley, N.; Cohen, G. Buprenorphine transdermal system in adults with chronic low back pain: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study, followed by an open-label extension phase. Clin. Ther. 2010, 32, 844–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, D.; Munera, C.; Hale, M.; Ripa, S.; Landau, C. Efficacy and safety of buprenorphine transdermal system (BTDS) for chronic moderate to severe low back pain: A randomized, double-blind study. J. Pain 2011, 12, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, M.C. Buprenorphine in long-term control of chronic pain in cancer patients. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Radbruch, L.; Vielvoye-Kerkmeer, A. Buprenorphine TDS: The clinical development rationale and results. Int. J. Clin. Pract. Suppl. 2003, 133, 15–18; discussion 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sittl, R.; Likar, R.; Nautrup, B.P. Equipotent doses of transdermal fentanyl and transdermal buprenorphine in patients with cancer and noncancer pain: Results of a retrospective cohort study. Clin. Ther. 2005, 27, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauck, R.L.; Potts, J.; Xiang, Q.; Tzanis, E.; Finn, A. Efficacy and tolerability of buccal buprenorphine in opioid-naive patients with moderate to severe chronic low back pain. Postgrad. Med. 2016, 128, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimbel, J.; Spierings, E.L.H.; Katz, N.; Xiang, Q.; Tzanis, E.; Finn, A. Efficacy and tolerability of buccal buprenorphine in opioid-experienced patients with moderate to severe chronic low back pain: Results of a phase 3, enriched enrollment, randomized withdrawal study. Pain 2016, 157, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, M.; Urdaneta, V.; Kirby, T.; Xiang, Q.; Rauck, R. Long-term safety and analgesic efficacy of buprenorphine buccal film in patients with moderate-to-severe chronic pain requiring around-the-clock opioids. J. Pain Res. 2017, 10, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergolizzi Jr, J.V.; Raffa, R.B. Safety and efficacy of the unique opioid buprenorphine for the treatment of chronic pain. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 3299–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenstein, S.L.; Kaiko, R.F.; Rogers, A.G.; Houde, R.W. Crossover trials in clinical analgesic assays: Studies of buprenorphine and morphine. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 1986, 6, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, W.G.; Cooper, G.M.; Morgan, M. Analgesic effects of sublingual buprenorphine. Anaesthesia 1979, 34, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risbo, A.; Jøosrgensen, B.C.; Kolby, P.; Pedersen, J.; Schmidt, J.F. Sublingual buprenorphine for premedication and postoperative pain relief in orthopaedic surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1985, 29, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullingham, R.; McQuay, H.; Moore, R.; Weir, L. An oral buprenorphine and paracetamol combination compared with paracetamol alone: A single dose double-blind postoperative study. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1981, 12, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, R.I.H.; Johnson, R.P.; Robinson, N.; Waite, E. The study of analgesics following single and repeated doses. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1981, 21, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tigerstedt, I.; Tammisto, T. Double-blind, multiple-dose comparison of buprenorphine and morphine in postoperative pain. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1980, 24, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, M.S.; Lippmann, M.; Steen, S.N. Multidose/observational, comparative clinical analgetic evaluation of buprenorphine. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1981, 21, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Hansen, M.; Bromham, N.; Taubert, M.; Arnold, S.; Hilgart, J.S. Buprenorphine for treating cancer pain. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2018, CD009596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, S.R.; Anderson, B.J.; Bailey, G.L.; Stein, M.D. Buprenorphine treatment formulations: Preferences among persons in opioid withdrawal management. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 2018, 94, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, A.; Doxey, J.C.; Harry, E.J.R. The animal pharmacology of buprenorphine, an oripavine analgesic agent. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1977, 60, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tröster, A.; Ihmsen, H.; Singler, B.; Filitz, J.; Koppert, W. Interaction of fentanyl and buprenorphine in an experimental model of pain and central sensitization in human volunteers. Clin. J. Pain 2012, 28, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrutti, D.; Niv, D.; Ben-Abraham, R.; Di Santo, S.; Weinbroum, A.A. Late antinociception and lower untoward effects of concomitant intrathecal morphine and intravenous buprenorphine in humans. J. Clin. Anesth. 2002, 14, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaveriaux-Ruff, C.; Nozaki, C.; Nadal, X.; Hever, X.C.; Weibel, R.; Matifas, A.; Reiss, D.; Filliol, D.; Nassar, M.A.; Wood, J.N.; et al. Genetic ablation of delta opioid receptors in nociceptive sensory neurons increases chronic pain and abolishes opioid analgesia. Pain 2011, 152, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, F. Transdermal buprenorphine in pain management—Experiences from clinical practice: Five case studies: Transdermal buprenorphine in pain management. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2006, 60, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Luo, L.Y.; Li, J.G.; Chen, C.; Liu-Chen, L.Y. Activation of the cloned human kappa opioid receptor by agonists enhances [35S]GTPgammaS binding to membranes: Determination of potencies and efficacies of ligands. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 282, 676–684. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, D.V.; Partilla, J.S.; Zheng, Q.-X.; Heyliger, S.O.; Ni, Q.; Rice, K.C.; Lai, J.; Rothman, R.B. Opioid peptide receptor studies. 12. buprenorphine is a potent and selective mu antagonist in the [35S]-GTP-gamma-S functional binding assay. Synapse 1999, 34, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toll, L.; Berzetei-Gurske, I.P.; Polgar, W.E.; Brandt, S.R.; Adapa, I.D.; Rodriguez, L.; Schwartz, R.W.; Haggart, D.; O’Brien, A.; White, A.; et al. Standard binding and functional assays related to medications development division testing for potential cocaine and opiate narcotic treatment medications. NIDA Res. Monogr. 1998, 178, 440–466. [Google Scholar]
- Rozenfeld, R.; Devi, L.A. Exploring a role for heteromerization in GPCR signalling specificity. Biochem. J. 2011, 433, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yekkirala, A.S.; Banks, M.L.; Lunzer, M.M.; Negus, S.S.; Rice, K.C.; Portoghese, P.S. Clinically employed opioid analgesics produce antinociception via μ-δ opioid receptor heteromers in rhesus monkeys. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2012, 3, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastlack, S.C.; Cornett, E.M.; Kaye, A.D. Kratom—Pharmacology, clinical implications, and outlook: A comprehensive review. Pain Ther. 2020, 9, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broyan, V.R.; Brar, J.K.; Allgaier, T.; Allgaier, J.T. Long-term buprenorphine treatment for kratom use disorder: A case series. Subst. Abuse 2022, 43, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.W.; Larochelle, M.R.; Saitz, R.; Wang, N.; Bernson, D.; Walley, A.Y. Associations between prescribed benzodiazepines, overdose death and buprenorphine discontinuation among people receiving buprenorphine. Addiction 2020, 115, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, N.K.; Bree, M.P.; Mendelson, J.H. Buprenorphine self-administration by rhesus monkey. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1981, 15, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubner, C.B.; Kornetsky, C. The reinforcing properties of the mixed agonist-antagonist buprenorphine as assessed by brain-stimulation reward. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1988, 30, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, C.L.; Vendruscolo, L.F.; Schlosburg, J.E.; Hernandez, D.O.; Koob, G.F. Compulsive-like responding for opioid analgesics in rats with extended access. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaiardi, M.; Bartoletti, M.; Bacchi, A.; Gubellini, C.; Babbini, M. Motivational properties of buprenorphine as assessed by place and taste conditioning in rats. Psychopharmacology 1997, 130, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, P.; Baliram, R.; Kieffer, B.L.; Lutfy, K. The mu opioid receptor is involved in buprenorphine-induced locomotor stimulation and conditioned place preference. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.-L.; Freret, T.; Lange, M.; Bourgine, J.; Coquerel, A.; Lelong-Boulouard, V. Benzodiazepines increase the reward effects of buprenorphine in a conditioned place preference test in the mouse. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 28, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs, D.P.; Leman, R.P.; Everett, T.J.; Lopez-Beltran, H.; Hamilton, L.R.; Oleson, E.B. Buprenorphine is a weak dopamine releaser relative to heroin, but its pretreatment attenuates heroin-evoked dopamine release in rats. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2020, 40, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintz, P. Deaths involving buprenorphine: A compendium of French cases. Forensic Sci. Int. 2001, 121, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rege, S.V.; Ngo, D.A.; Ait-Daoud, N.; Holstege, C.P. Epidemiology of severe buprenorphine exposures reported to the U.S. Poison Centers. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019, 202, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, L.D. Bupenorphine in wisconsin drivers: Concerns for impairment? J. Anal. Toxicol. 2019, 43, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zess Quite Nice, When I Don’t Have Anything Else Buprenorphine with Naloxone (Suboxone). Available online: https://www.erowid.org/experiences/exp.php?ID=86906 (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- Bunn Little Bit Goes a Long Way Buprenorphine. Available online: https://www.erowid.org/experiences/exp.php?ID=84031 (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- Blazes, C.K.; Morrow, J.D. Reconsidering the Usefulness of Adding Naloxone to Buprenorphine. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 549272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hswen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Brownstein, J.S. Leveraging black-market street buprenorphine pricing to increase capacity to treat opioid addiction, 2010–2018. Prev. Med. 2020, 137, 106105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, N.; Freifeld, C.; Brownstein, J.S.; Menone, C.M.; Surratt, H.L.; Poppish, L.; Green, J.L.; Lavonas, E.J.; Dart, R.C. Crowdsourcing black market prices for prescription opioids. J. Med. Internet Res. 2013, 15, e178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, K.J.; Moran, M.T.; Foster, M.L.; Shah, D.T.; Chung, D.Y.; Nichols, S.D.; McCall, K.L.; Piper, B.J. Descriptive, observational study of pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical arrests, use, and overdoses in Maine. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e027117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Placenza, F.M.; Rajabi, H.; Stewart, J. Effects of chronic buprenorphine treatment on levels of nucleus accumbens glutamate and on the expression of cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in rats. Psychopharmacology 2008, 200, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouche, S.; Le Marec, T.; Coquerel, A.; Noble, F.; Marie, N. Striatal dopamine D1 and D2 receptors are differentially regulated following buprenorphine or methadone treatment. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orwin, J.M.; Orwin, J.; Price, M. A double blind comparison of buprenorphine and morphine in conscious subjects following administration by the intramuscular route. Acta Anaesthesiol. Belg. 1976, 27, 171–181. [Google Scholar]
- Budd, K. High dose buprenorphine for postoperative analgesia. Anaesthesia 1981, 36, 900–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, T.; Clark, B.; Hickman, M.; Grebely, J.; Campbell, G.; Sordo, L.; Chen, A.; Tran, L.T.; Bharat, C.; Padmanathan, P.; et al. Association of opioid agonist treatment with all-cause mortality and specific causes of death among people with opioid dependence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsen, E.; Algera, M.H.; Moss, L.; Dobbins, R.L.; Groeneveld, G.J.; van Velzen, M.; Niesters, M.; Dahan, A.; Laffont, C.M. Modeling buprenorphine reduction of fentanyl-induced respiratory depression. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e156973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, L.R.; Cater, J.; Smith, T. Pharmacokinetics of buprenorphine buccal film and orally-administered oxycodone in a respiratory study: An analysis of secondary outcomes from a randomized controlled trial. Pain Ther. 2022, 11, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueye, P.N. Buprenorphine and midazolam act in combination to depress respiration in rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 65, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, S.; Tzeng, T.-B.; Cowan, A. Characterization of the pharmacokinetics of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine in rats after intravenous bolus administration of buprenorphine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 15, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintz, P. A new series of 13 buprenorphine-related deaths. Clin. Biochem. 2002, 35, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariottini, C.; Kriikku, P.; Ojanperä, I. Concomitant drugs with buprenorphine user deaths. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021, 218, 108345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wightman, R.S.; Perrone, J.; Scagos, R.; Krieger, M.; Nelson, L.S.; Marshall, B.D.L. Opioid Overdose Deaths with Buprenorphine Detected in Postmortem Toxicology: A Retrospective Analysis. J. Med. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedapati, E.V.; Bateman, S.T. Toddlers requiring pediatric intensive care unit admission following at-home exposure to buprenorphine/naloxone. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 12, e102–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, B.D.; Klein-Schwartz, W.; Doyon, S. Toxicity of buprenorphine overdoses in children. Pediatrics 2008, 121, e782–e786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, G.; Nachmani, A. Drugs that can kill a toddler with one tablet or teaspoonful: A 2018 updated list. Clin. Drug Investig. 2019, 39, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Smiddy, M.; Hoffman, R.S.; Nelson, L.S. Buprenorphine may not be as safe as you think: A pediatric fatality from unintentional exposure. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e1700–e1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, S.; Spiller, H.A.; Casavant, M.J.; Chounthirath, T.; Smith, G.A. Buprenorphine exposures among children and adolescents reported to US poison control centers. Pediatrics 2018, 142, e20173652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkkola, K.; Leijala, M.; Maunuksela, E.-L. Paediatric ventilatory effects of morphine and buprenorphine revisited. Pediatr. Anesth. 1995, 5, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, L.; Mercurio-Zappala, M.; Howland, M.A.; Hoffman, R.S.; Su, M.K. Unintentional methadone and buprenorphine exposures in children: Developing prevention messages. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2017, 57, S83–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hampp, C.; Lovegrove, M.C.; Budnitz, D.S.; Mathew, J.; Ho, A.; McAninch, J. The role of unit-dose child-resistant packaging in unintentional childhood exposures to buprenorphine–naloxone tablets. Drug Saf. 2020, 43, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UpToDate. Buprenorphine drug information. In UpToDate; Post, T.W., Ed.; UpToDate: Waltham, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Vadivelu, N.; Hines, R.L. Management of chronic pain in the elderly: Focus on transdermal buprenorphine. Clin. Interv. Aging 2008, 3, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böger, R.H. Renal impairment: A challenge for opioid treatment? The role of buprenorphine. Palliat. Med. 2006, 20 (Suppl. S1), s17–s23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, A.A.; Kullgren, J.; Anwar, S.; Pedraza, S.; Davis, M.P. Treating chronic pain with buprenorphine-the practical guide. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2021, 22, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeeck, R.K. Pharmacokinetics and dosage adjustment in patients with hepatic dysfunction. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 64, 1147–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buprenorphine for Chronic Pain: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness; CADTH Rapid Response Reports; Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2017.
- Chang, K.-Y.; Chang, W.-K.; Chang, W.-L.; Lin, S.-M.; Chan, K.-H.; Sung, C.-S.; Tsou, M.-Y. Comparison of intravenous patient-controlled analgesia with buprenorphine versus morphine after lumbar spinal fusion—A prospective randomized clinical trial. Acta Anaesthesiol. Taiwanica Off. J. Taiwan Soc. Anesthesiol. 2006, 44, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Huhn, A.S.; Dunn, K.E. Why aren’t physicians prescribing more buprenorphine? J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 2017, 78, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahan, A.; Yassen, A.; Romberg, R.; Sarton, E.; Teppema, L.; Olofsen, E.; Danhof, M. Buprenorphine Induces Ceiling in Respiratory Depression but Not in Analgesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2006, 96, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee Opinion No. 711: Opioid use and opioid use disorder in pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 130, e81–e94. [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.Z.; Gao, C.; Phillips, B.R.; Neradugomma, N.K.; Han, L.W.; Bhatt, D.K.; Prasad, B.; Shen, D.D.; Mao, Q. Pregnancy increases norbuprenorphine clearance in mice by induction of hepatic glucuronidation. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2018, 46, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastian, J.R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Rothenberger, S.; Tarter, R.; English, D.; Venkataramanan, R.; Caritis, S.N. Dose-adjusted plasma concentrations of sublingual buprenorphine are lower during than after pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 216, 64.e1–64.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.M.; Campbell, S.D.; Crafford, A.; Regina, K.J.; Holtzman, M.J.; Kharasch, E.D. P-Glycoprotein is a major determinant of norbuprenorphine brain exposure and antinociception. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 343, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlatter, J.; Chiadmi, F. Buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine determination in mice plasma and brain by gas chromatography—Mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. Insights 2014, 9, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudeck, J.; Vogl, S.; Heinl, C.; Steinfath, M.; Fritzwanker, S.; Kliewer, A.; Schulz, S.; Schönfelder, G.; Bert, B. Analgesic treatment with buprenorphine should be adapted to the mouse strain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 191, 172877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, B.J.; Meyer, J.S. Developmental Neurotoxicity of Abused Drugs. In Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 413–429. ISBN 978-0-12-804239-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kongstorp, M.; Bogen, I.L.; Stiris, T.; Andersen, J.M. Prenatal exposure to methadone or buprenorphine impairs cognitive performance in young adult rats. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020, 212, 108008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.S.; Bigbee, J.W.; Fobbs, W.; Robinson, S.E.; Sato-Bigbee, C. Opioid addiction and pregnancy: Perinatal exposure to buprenorphine affects myelination in the developing brain. Glia 2008, 56, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-J.; Wu, C.-C.; Chen, W.-Y.; Chang, C.-Y.; Kuan, Y.-H.; Pan, H.-C.; Liao, S.-L.; Chen, C.-J. Depression-like effect of prenatal buprenorphine exposure in rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-C.; Hung, C.-J.; Shen, C.-H.; Chen, W.-Y.; Chang, C.-Y.; Pan, H.-C.; Liao, S.-L.; Chen, C.-J. Prenatal buprenorphine exposure decreases neurogenesis in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 225, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcheva, M.M.; Dawn, S.; Barg, J.; McHale, R.J.; Ho, M.T.; Ignatova, E.; Coscia, C.J. Transient down-regulation of neonatal rat brain μ-opioid receptors upon in utero exposure to buprenorphine. Dev. Brain Res. 1994, 80, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Bastian, J.R.; Zhao, W.; Chen, H.; Shaik, I.H.; Chaphekar, N.; Caritis, S.N.; Venkataramanan, R. Pregnancy alters CYP- and UGT-mediated metabolism of buprenorphine. Ther. Drug Monit. 2020, 42, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.M.; Høiseth, G.; Nygaard, E. Prenatal exposure to methadone or buprenorphine and long-term outcomes: A meta-analysis. Early Hum. Dev. 2020, 143, 104997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-C.; Hung, C.-J.; Lin, S.-Y.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Chang, C.-Y.; Chen, W.-Y.; Liao, S.-L.; Raung, S.-L.; Yang, C.-P.; Chen, C.-J. Treadmill exercise alleviated prenatal buprenorphine exposure-induced depression in rats. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 110, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, C.M.; Bowen, S.E.; Roberge, C.L.; Richardson, L.M.; Brummelte, S. Gestational buprenorphine exposure: Effects on pregnancy, development, neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, and behavior in a translational rodent model. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019, 205, 107625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, V.W.; Mo, Q.; Yabe, T.; Schwartz, J.P.; Robinson, S.E. Perinatal opioids reduce striatal nerve growth factor content in rat striatum. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 414, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minozzi, S.; Amato, L.; Jahanfar, S.; Bellisario, C.; Ferri, M.; Davoli, M. Maintenance agonist treatments for opiate-dependent pregnant women. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 11, CD006318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konijnenberg, C.; Melinder, A. Prenatal exposure to methadone and buprenorphine: A review of the potential effects on cognitive development. Child Neuropsychol. 2011, 17, 495–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashmineh Azar, A.R.; Cruz-Mullane, A.; Podd, J.C.; Lam, W.S.; Kaleem, S.H.; Lockard, L.B.; Mandel, M.R.; Chung, D.Y.; Simoyan, O.M.; Davis, C.S.; et al. Rise and regional disparities in buprenorphine utilization in the United States. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2020, 29, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobacyk, J.; Parks, B.J.; Salazar, P.; Coward, L.U.; Berquist, M.D.; Gorman, G.S.; Brents, L.K. Interaction between buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2023, 249, 110832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
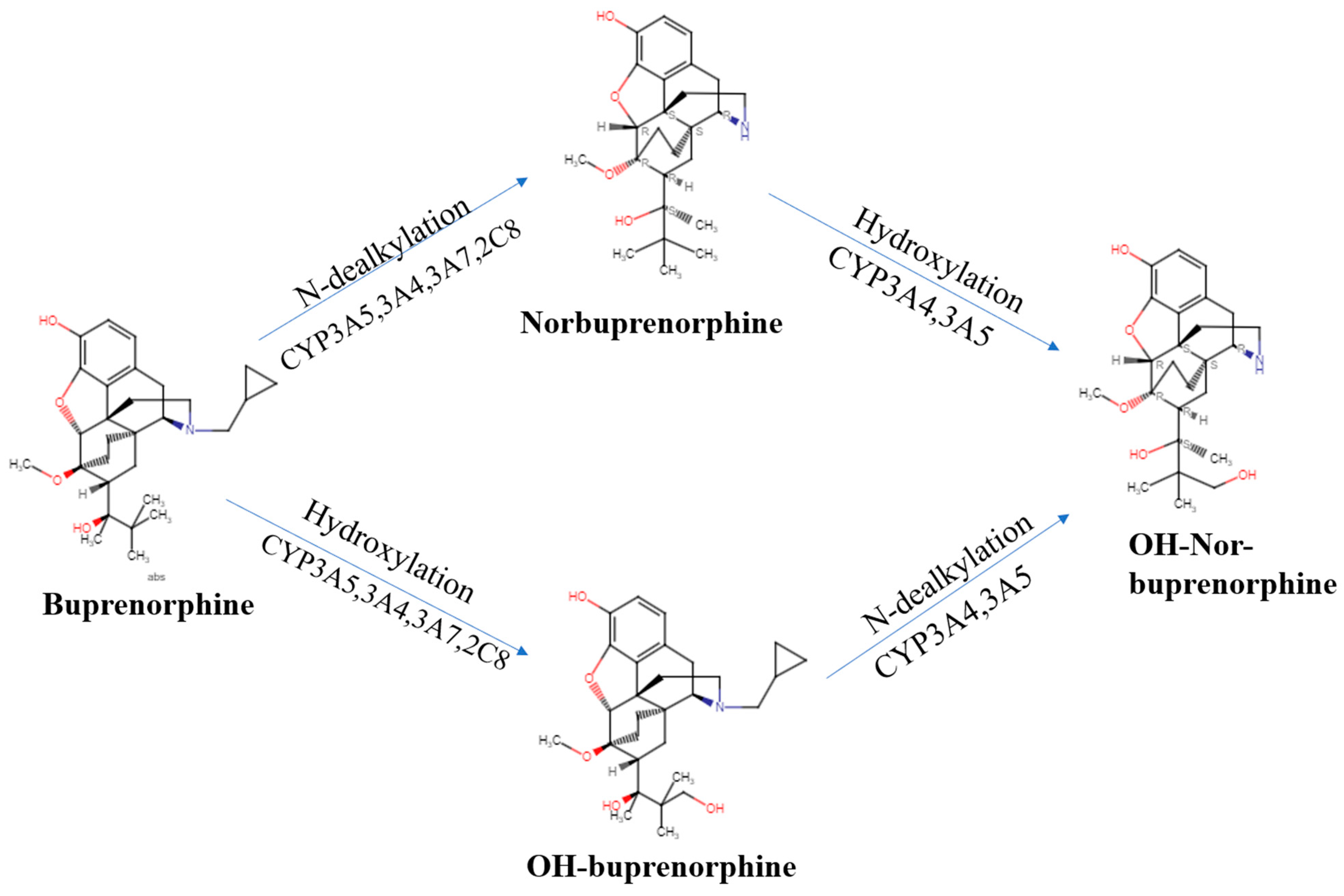
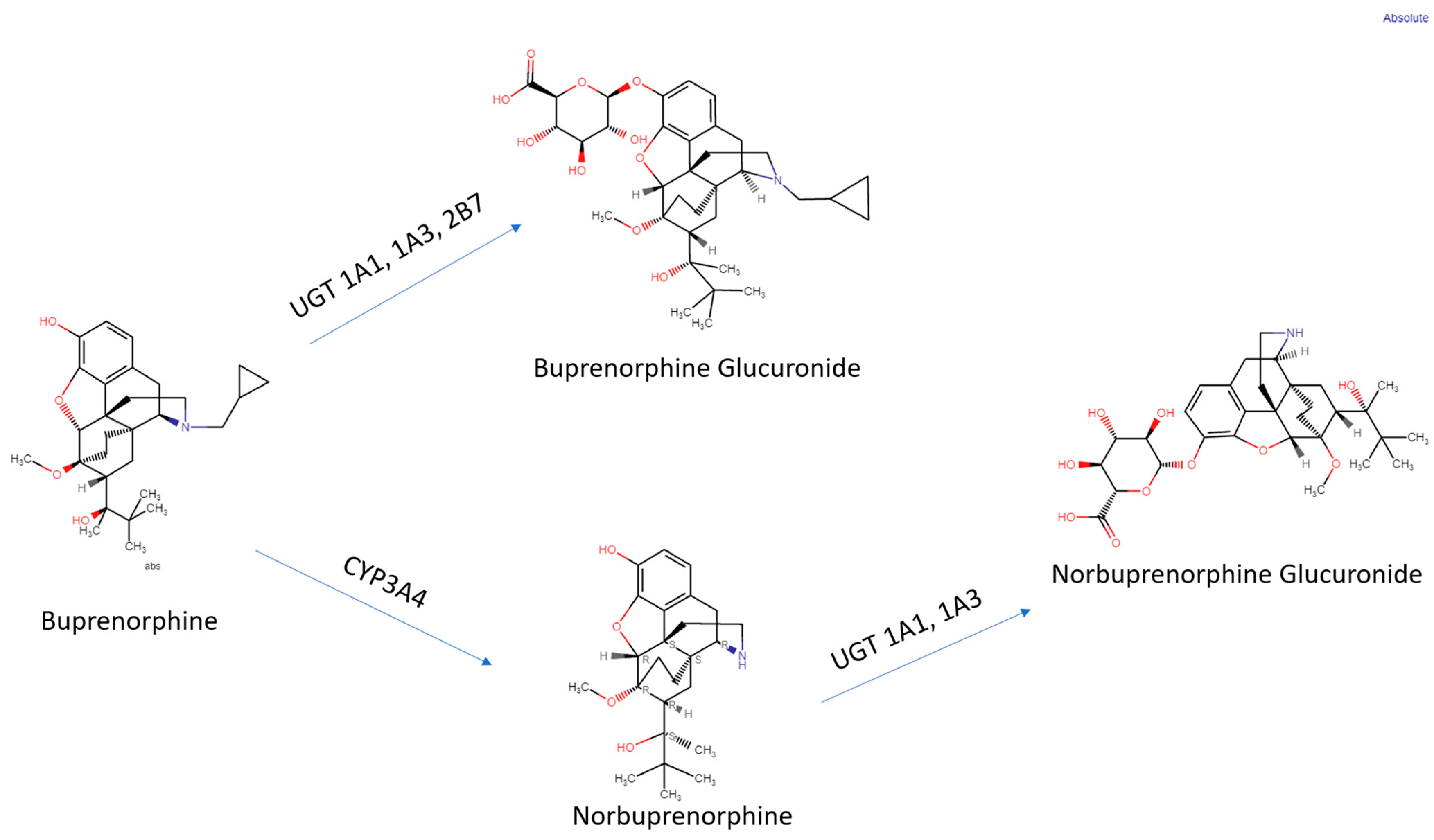
| Route of Administration | Brand Name | T1/2 | Tmax (h) | Cmax (ng/mL) | AUC (h × ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sublingual (2 mg) | Subutex | 31.7 B 39.3 NB | 1.8 B 2.4 NB | 1.3 B 0.3 NB | 10.9 B 12.4 NB |
| Buccal film | Belbuca | 27.6 ± 11.2 | 3.0 | 0.17 ± 0.30 | 0.46 ± 0.22 |
| Transdermal (at 10 mcg/h, steady state) | Butrans | 26 | - | 0.224 | 27.543 |
| Injectable ER (300 mg) | Sublocade | Days 1032–1440 | - | 10.12 | 3006 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pande, L.J.; Arnet, R.E.; Piper, B.J. An Examination of the Complex Pharmacological Properties of the Non-Selective Opioid Modulator Buprenorphine. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101397
Pande LJ, Arnet RE, Piper BJ. An Examination of the Complex Pharmacological Properties of the Non-Selective Opioid Modulator Buprenorphine. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(10):1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101397
Chicago/Turabian StylePande, Leana J., Rhudjerry E. Arnet, and Brian J. Piper. 2023. "An Examination of the Complex Pharmacological Properties of the Non-Selective Opioid Modulator Buprenorphine" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 10: 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101397
APA StylePande, L. J., Arnet, R. E., & Piper, B. J. (2023). An Examination of the Complex Pharmacological Properties of the Non-Selective Opioid Modulator Buprenorphine. Pharmaceuticals, 16(10), 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101397







