Magnesium Isoglycyrrhizinate Attenuates Anti-Tuberculosis Drug-Induced Liver Injury by Enhancing Intestinal Barrier Function and Inhibiting the LPS/TLRs/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
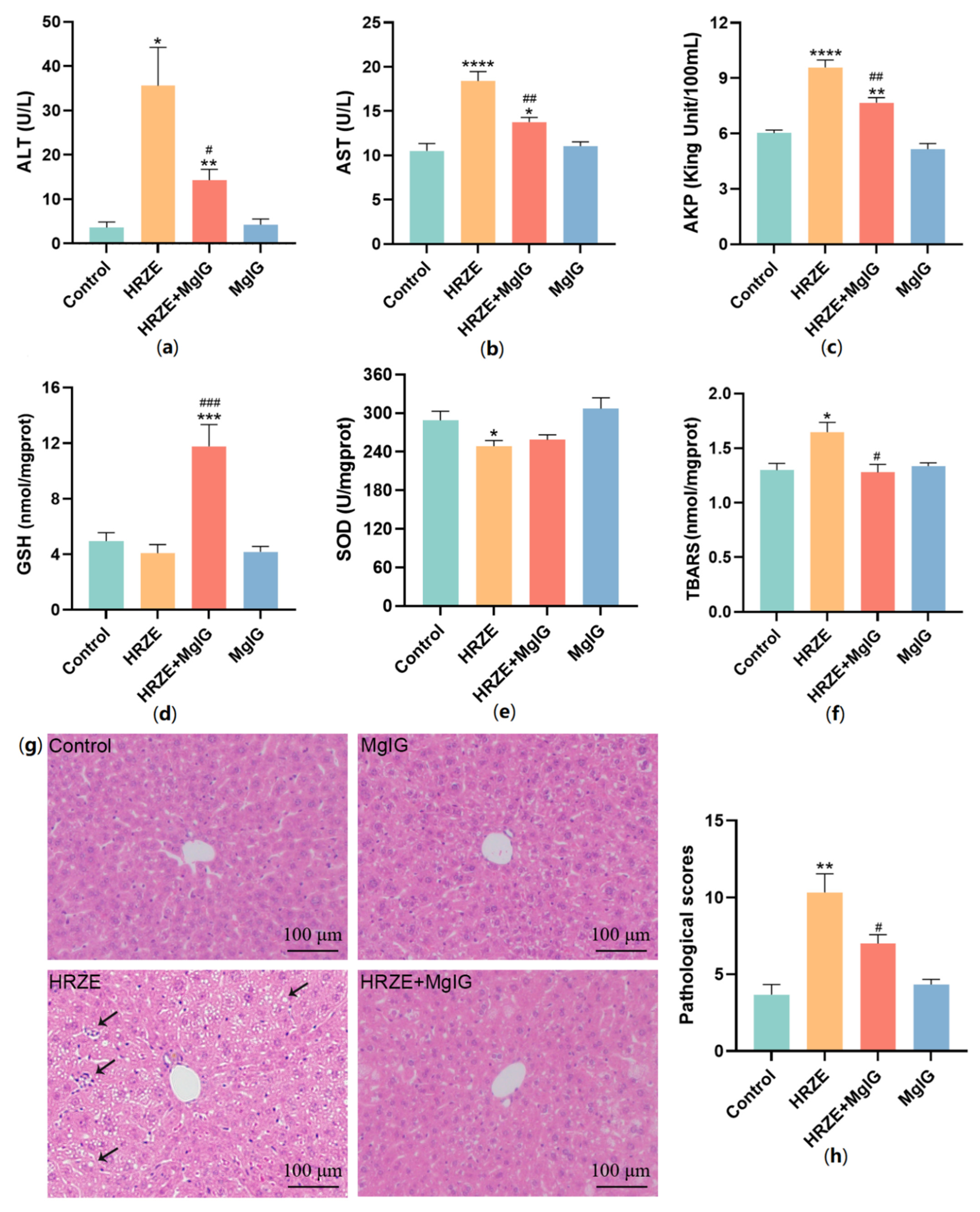
2.1. MgIG Ameliorates HRZE-Induced Liver Injury
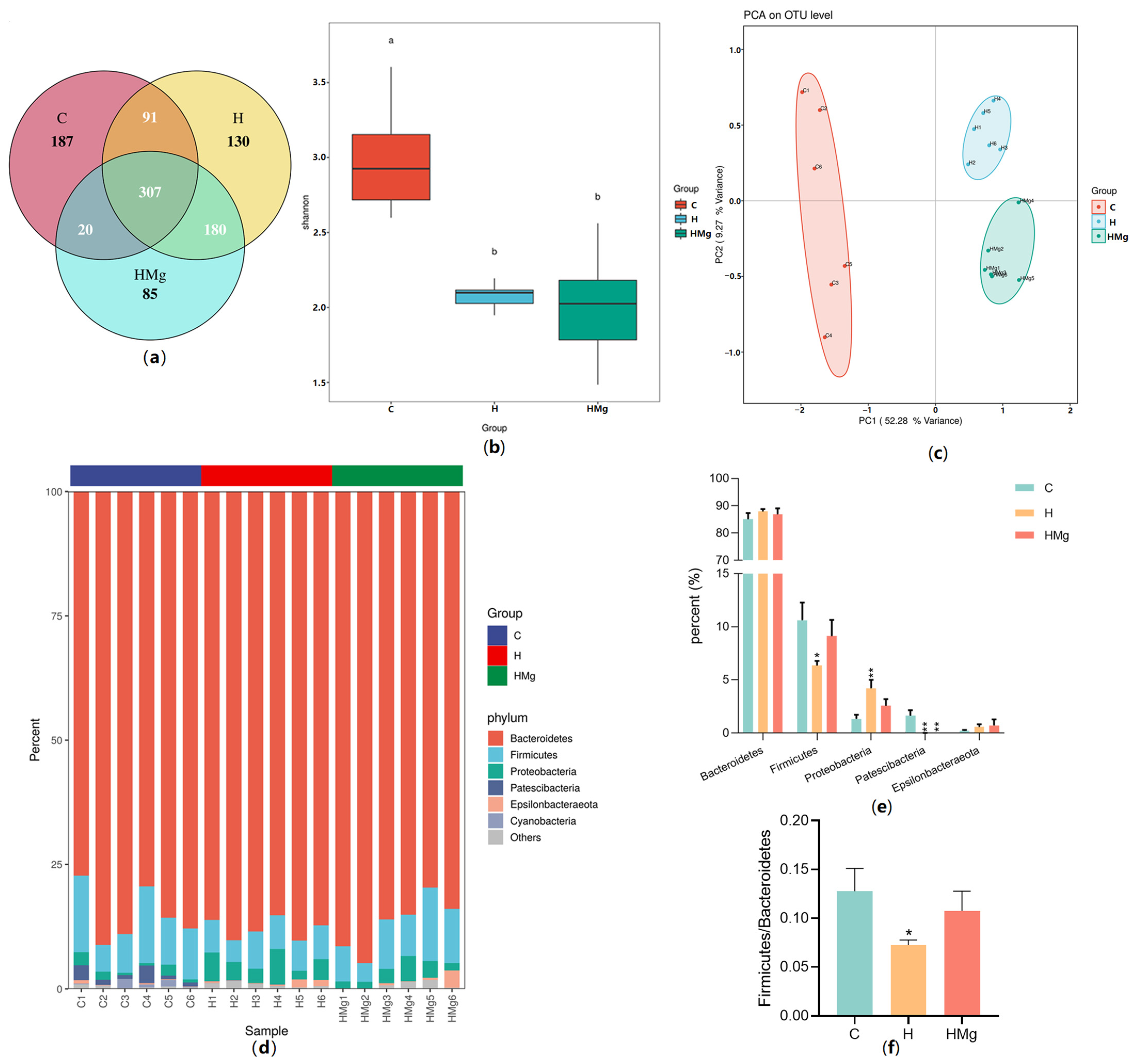
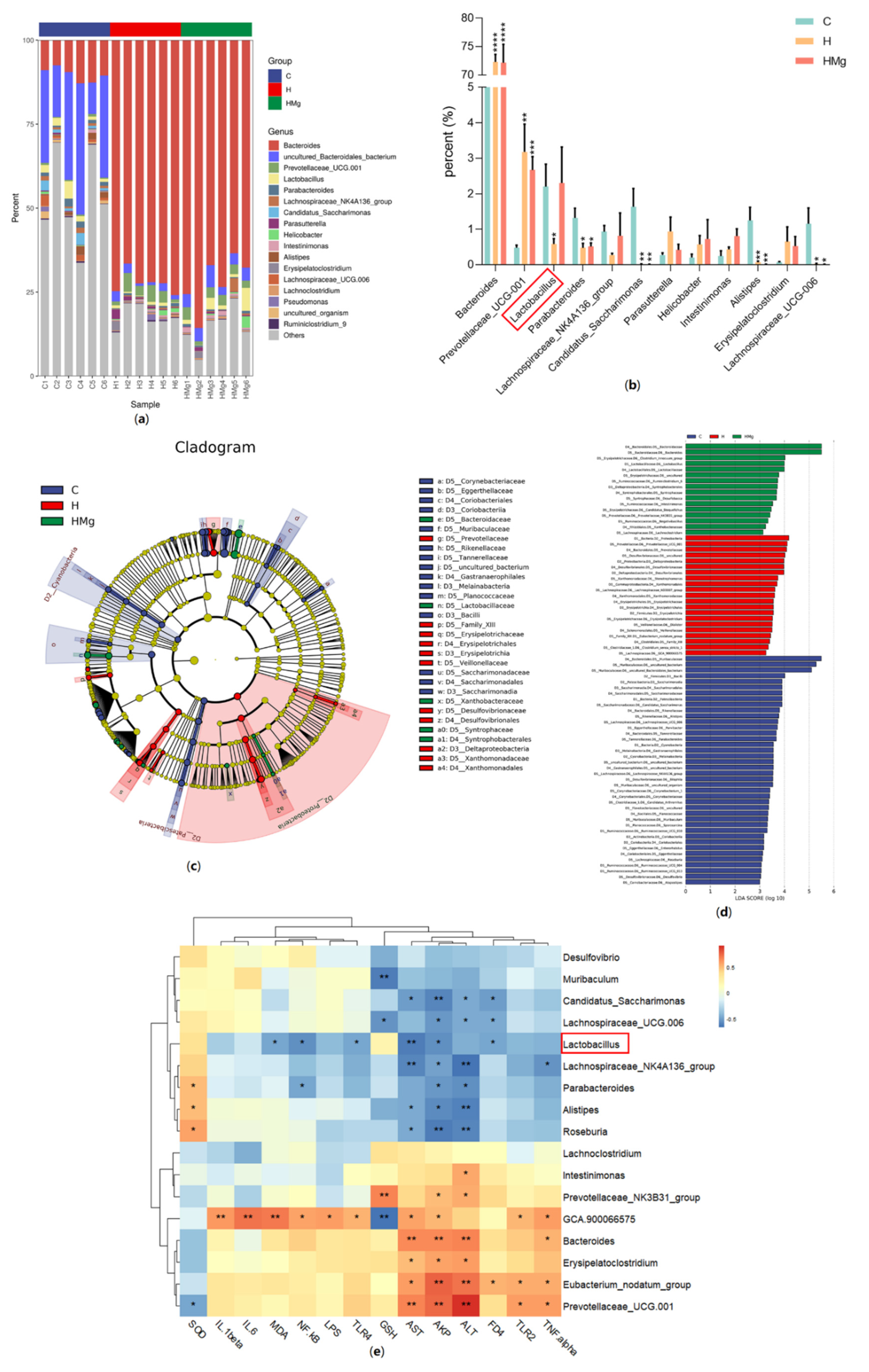
2.2. MgIG Modifies HRZE-Induced Gut Microbiota Composition
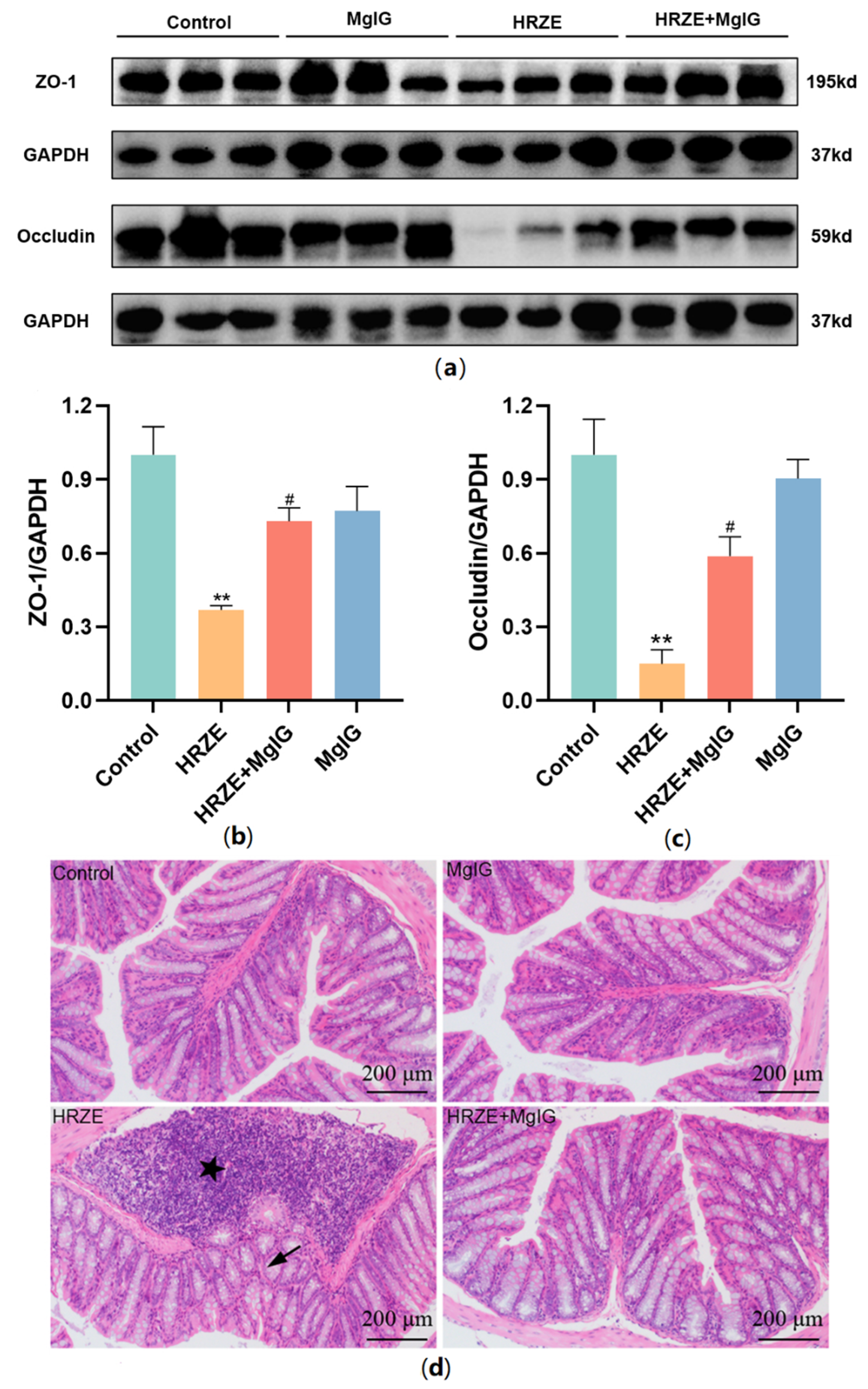
2.3. MgIG Improves HRZE-Induced Intestinal Barrier Disruption
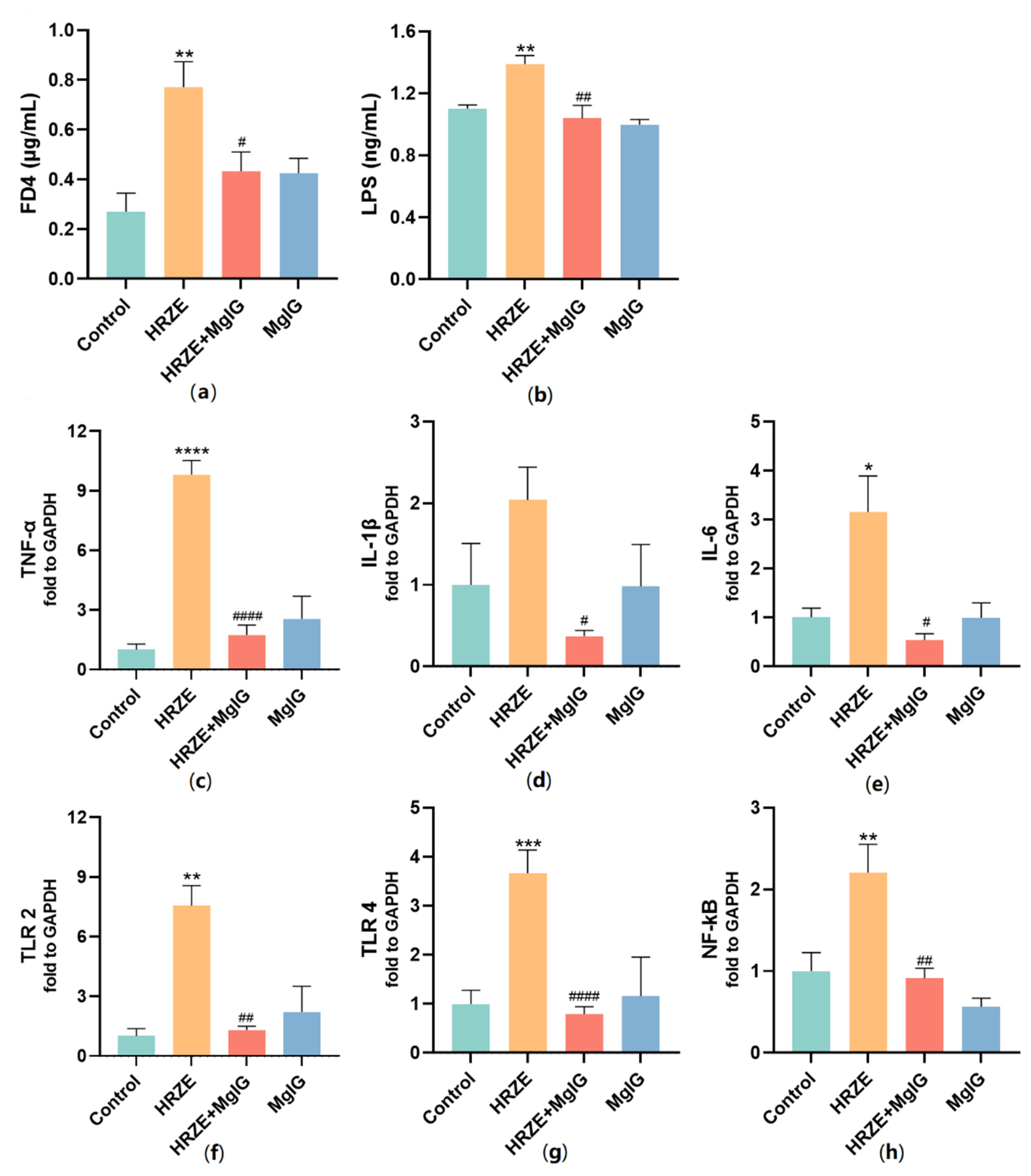
2.4. MgIG Decreases HRZE-Induced Intestinal Permeability and Inhibits HRZE-Induced LPS/TLRs/NF-κB Pathway Activation
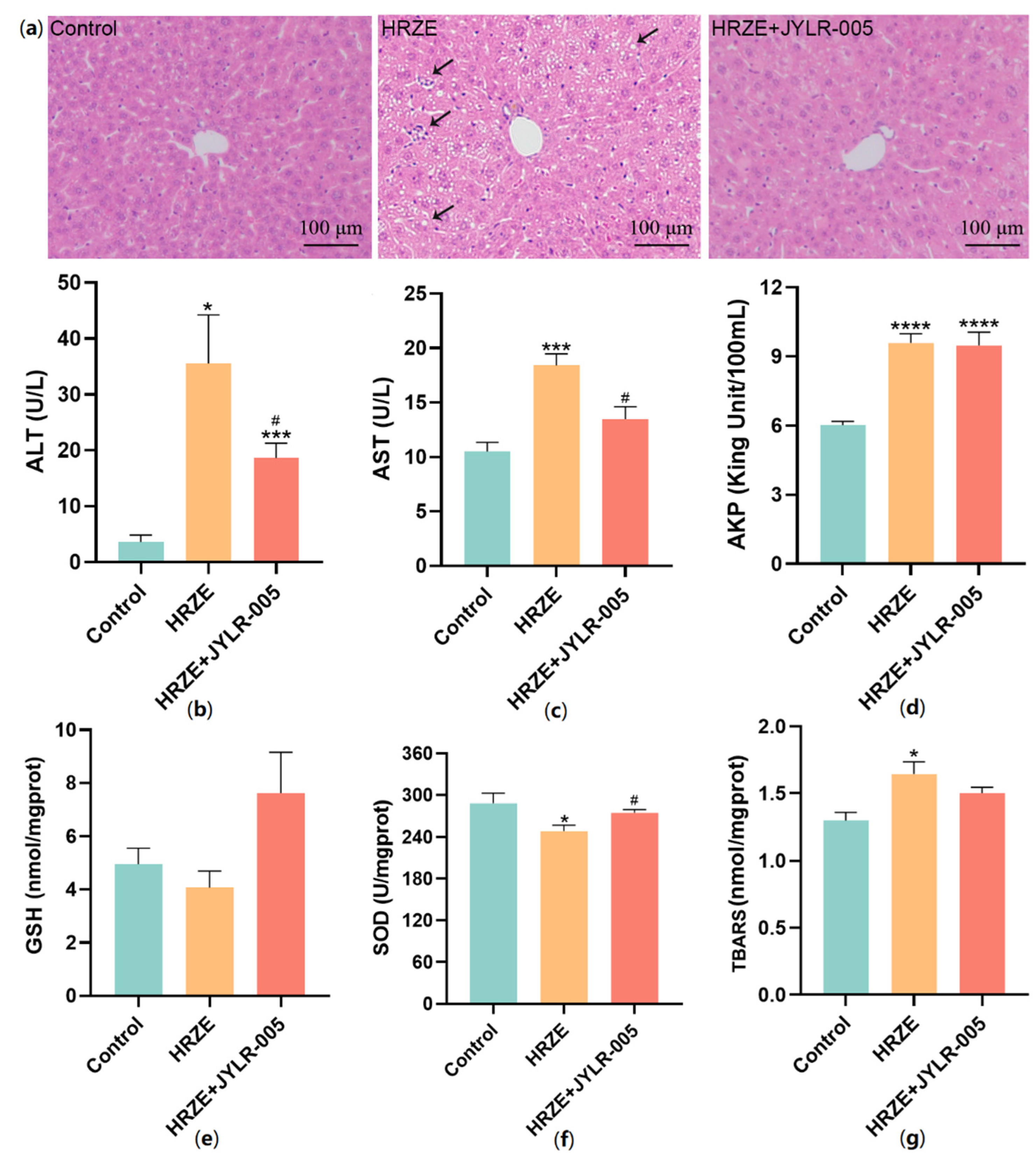
2.5. Supplementation with Lactobacillus Rhamnosus JYLR-005 Alleviates HRZE-Induced Liver Injury
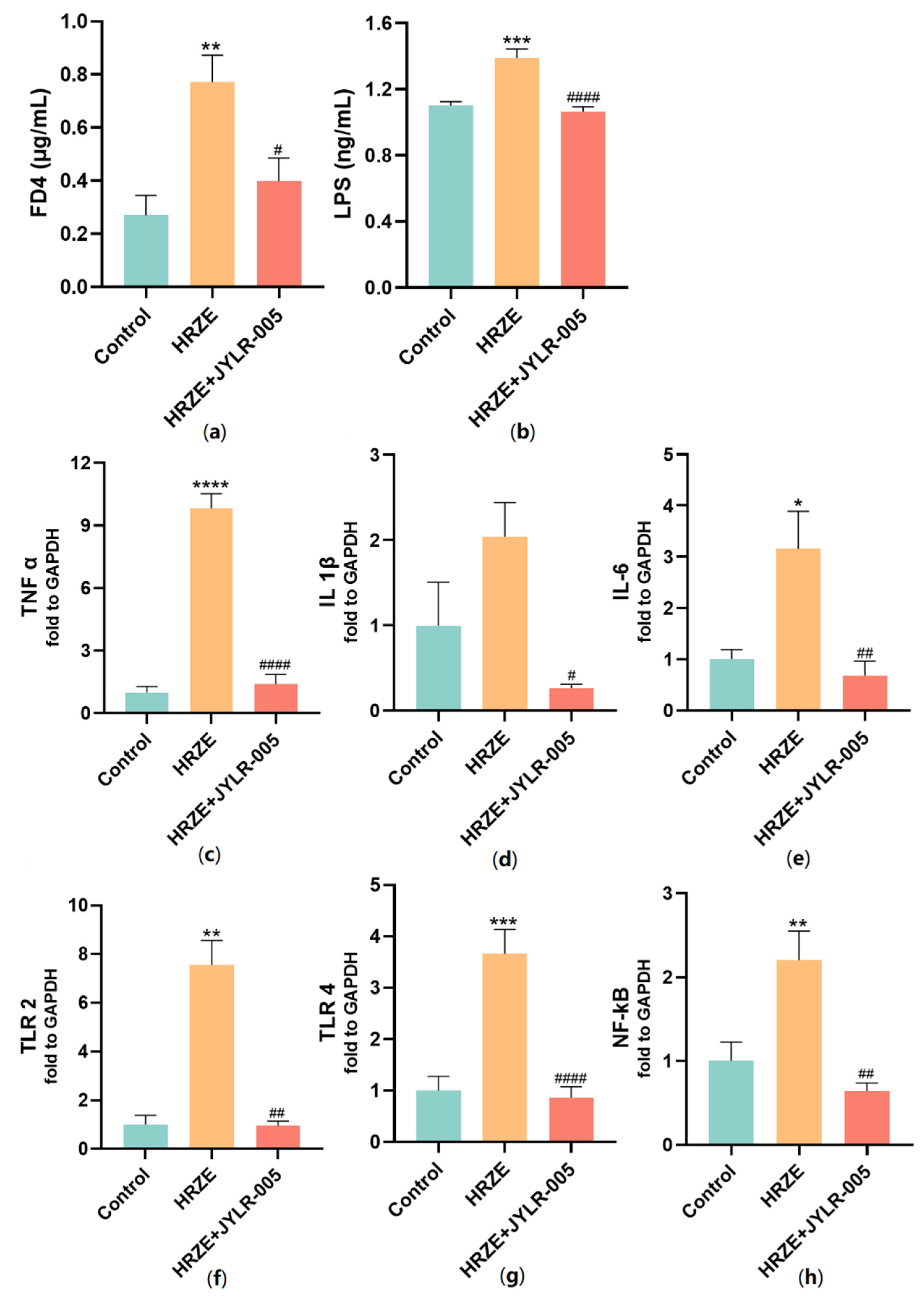
2.6. Supplementation with Lactobacillus Rhamnosus JYLR-005 Decreases HRZE-Induced Intestinal Permeability and Inhibits HRZE-Induced LPS/TLRs/NF-κB Pathway Activation
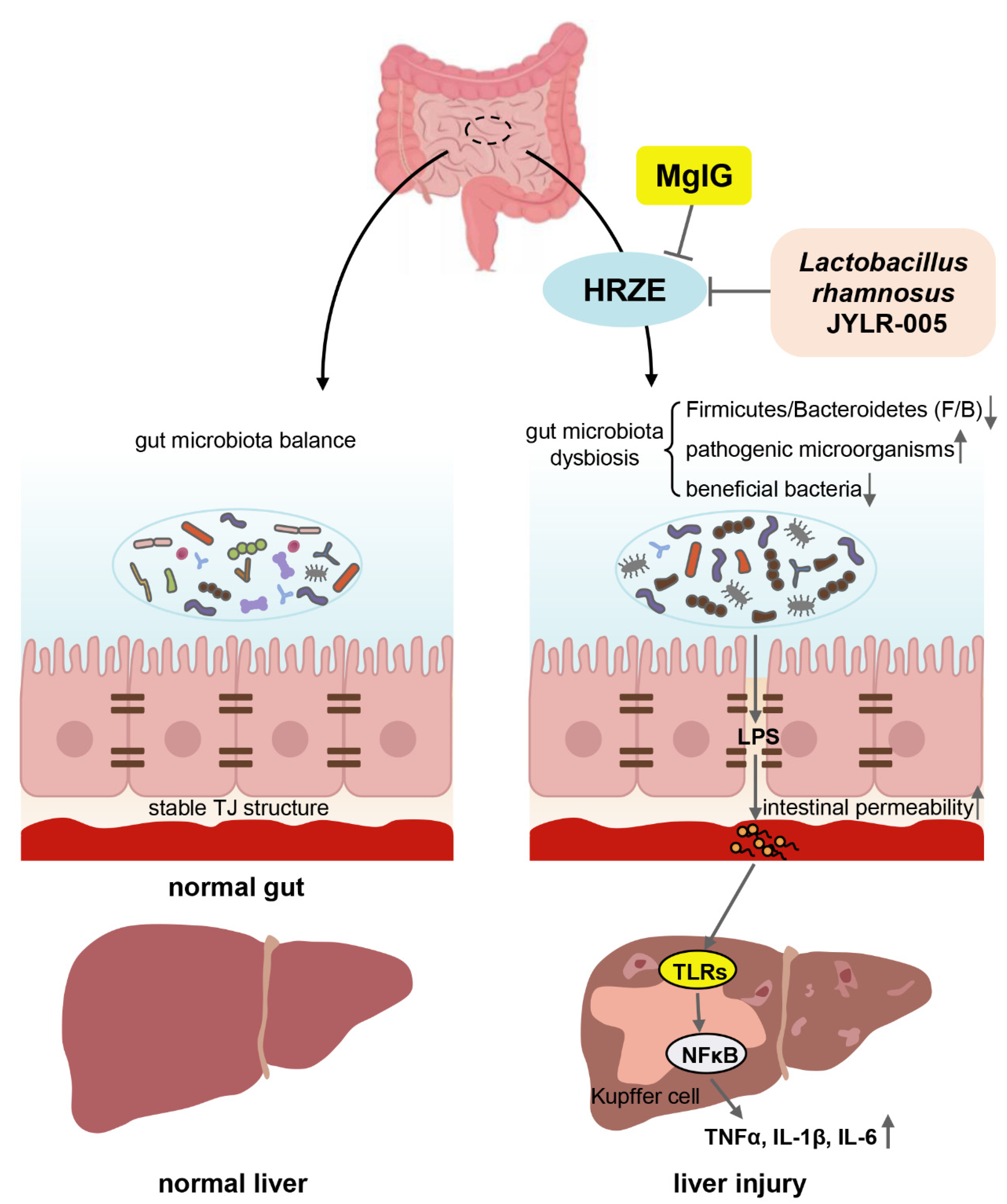
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Animals and Treatments
4.3. Serum ALT, AST, AKP and LPS Assays
4.4. GSH, SOD, and MDA Assays
4.5. Histological Assessment
4.6. Measurement of Intestinal Permeability
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. 16S rDNA Gene Sequencing
4.9. RT-PCR Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2021; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Peloquin, C.A.; Davies, G.R. The Treatment of Tuberculosis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 1455–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, T.; Fan, Y.; Dong, X.L.; Guo, X.; Wong, K.H.; Wong, W.T.; He, D.; Liu, S. An Investigation of the Risk Factors Associated With Anti-Tuberculosis Drug-Induced Liver Injury or Abnormal Liver Functioning in 757 Patients With Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 708522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, E.X.S.; Zheng, Q.; Chan, E.; Lim, S.G. Drug induced liver injury: East versus West—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, R.J.; Chalasani, N.; Bjornsson, E.S.; Suzuki, A.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Watkins, P.B.; Devarbhavi, H.; Merz, M.; Lucena, M.I.; Kaplowitz, N.; et al. Drug-induced liver injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopyk, D.M.; Grakoui, A. Contribution of the Intestinal Microbiome and Gut Barrier to Hepatic Disorders. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschke, R.; Uetrecht, J. Mechanism of idiosyncratic drug induced liver injury (DILI): Unresolved basic issues. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Z.; Ma, Q.; Liu, H.; Nie, C.; Zhang, Z.; An, W.; Li, J. Lycium ruthenicum Anthocyanins Attenuate High-Fat Diet-Induced Colonic Barrier Dysfunction and Inflammation in Mice by Modulating the Gut Microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2000745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Bian, X.; Wu, W.; Lv, L.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Q.; Shi, D.; Fang, D.; et al. Protective effect of Lactobacillus salivarius Li01 on thioacetamide-induced acute liver injury and hyperammonaemia. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 1860–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zuo, S.; Chu, X.; Xu, S.; Ma, D.; Chu, L. Magnesium Isoglycyrrhizinate Alleviates Arsenic Trioxide-Induced Cardiotoxicity: Contribution of Nrf2 and TLR4/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.Y.; Ren, H.; Peng, S.Y.; Xing, K.; Fan, L.; Liu, M.Z.; Luo, Z.Y.; Luo, J.Q. Comparative effectiveness of glycyrrhizic acid preparations aimed at preventing and treating anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury: A network meta-analysis of 97 randomized controlled trials. Phytomedicine 2022, 98, 153942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Shi, H.; Sun, Z.; Wu, J.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, A.; et al. Protective Effects of Magnesium Glycyrrhizinate on Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Intestinal Toxicity May Be by Reducing COX-2. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, X.; Xu, J. Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate attenuates D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharides induced acute liver injury of rat via regulation of the p38-MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2018, 40, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Wu, J.; Geng, S.; Zhong, C. Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate suppresses LPS-induced inflammation and oxidative stress through inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK pathways in RAW264.7 cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Liang, Z.; Deng, F.; Xie, W.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, W.; Geng, S.; et al. Anti-inflammatory Activity of Magnesium Isoglycyrrhizinate Through Inhibition of Phospholipase A2/Arachidonic Acid Pathway. Inflammation 2015, 38, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Qi, D.; Qu, A.; Wang, G. Amelioration of Ethanol-Induced Hepatitis by Magnesium Isoglycyrrhizinate through Inhibition of Neutrophil Cell Infiltration and Oxidative Damage. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 3526903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Xiao, Q.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J. Comparison of the exposure of glycyrrhizin and its metabolites and the pseudoaldosteronism after intravenous administration of alpha- and beta-glycyrrhizin in rat. Drug Res. 2013, 63, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwidu, L.L.; Oboma, Y.I. Telfairia occidentalis (Cucurbitaceae) pulp extract mitigates rifampicin-isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity in an in vivo rat model of oxidative stress. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 17, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, S.; Zeng, T.; Xie, K. Diallyl trisulfide protects the liver against hepatotoxicity induced by isoniazid and rifampin in mice by reducing oxidative stress and activating Kupffer cells. Toxicol. Res. 2016, 5, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messarah, M.; Saoudi, M.; Boumendjel, A.; Kadeche, L.; Boulakoud, M.S.; El Feki, A. Green tea extract alleviates arsenic-induced biochemical toxicity and lipid peroxidation in rats. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2013, 29, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albillos, A.; de Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Cui, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, P. Gut microbiota-an important contributor to liver diseases. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao = J. South. Med. Univ. 2020, 40, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, F.; Sun, M.; Song, Y.; Xu, D.; Mu, G.; Tuo, Y. Lactobacillus plantarum Y44 alleviates oxidative stress by regulating gut microbiota and colonic barrier function in Balb/C mice with subcutaneous d-galactose injection. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Shan, J.; Di, L. Glycyrrhizic acid improving the liver protective effect by restoring the composition of Lactobacillus. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 52, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.J.; Park, H.J.; Cha, M.G.; Park, E.; Won, S.M.; Ganesan, R.; Gupta, H.; Gebru, Y.A.; Sharma, S.P.; Lee, S.B.; et al. The Lactobacillus as a Probiotic: Focusing on Liver Diseases. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.K.; Chen, T.Y.; Chen, Y.P.; Cheng, J. A Kind of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus JYLR-005 and Its Hypoglycemic Products and Application. China Patent CN109055278A, 17 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani, N.; Hara, E. Gut-liver axis-mediated mechanism of liver cancer: A special focus on the role of gut microbiota. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 4433–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Peng, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, T.; Bai, H.; Wu, Q.; Song, J.; Wu, L.; Song, X.; et al. Association of LEPR polymorphisms with predisposition and inflammatory response in anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury: A pilot prospective investigation in Western Chinese Han population. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 75, 103970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.K.; Wei, N. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate alleviates the anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury through JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway: An experimental study. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avlas, O.; Fallach, R.; Shainberg, A.; Porat, E.; Hochhauser, E. Toll-like receptor 4 stimulation initiates an inflammatory response that decreases cardiomyocyte contractility. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1895–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Chen, S.; Guo, S.; Yue, T.; Hou, Q.; Feng, M.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; et al. The administration of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 ameliorates irinotecan-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction and gut microbial dysbiosis in mice. Life Sci. 2019, 231, 116529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulson, J.N.; Pop, M.; Bravo, H.C. Metastats: An improved statistical method for analysis of metagenomic data. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Product Size (bp) | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | Forward: AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | 123 bp | NM_001289726.1 |
| Reverse: TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA | |||
| IL-6 | Forward: TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC | 76 bp | NM_031168.2 |
| Reverse: TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC | |||
| TNF-α | Forward: AGGGTCTGGGCCATAGAACT | 103 bp | NM_013693.3 |
| Reverse: CCACCACGCTCTTCTGTCTAC | |||
| IL-1β | Forward: GAAATGCCACCTTTTGACAGTGATG | 139 bp | NM_008361.4 |
| Reverse: TGTGCTGCTGCGAGATTTG | |||
| NF-κB | Forward: ATGGCAGACGATGATCCCTAC | 111 bp | NM_008689.2 |
| Reverse: TGTTGACAGTGGTATTTCTGGTG | |||
| TLR2 | Forward: CCAAAGAGCTCGTAGCATCC | 125 bp | NM_011905.3 |
| Reverse: AGGGGCTTCACTTCTCTGCT | |||
| TLR4 | Forward: GCCTTTCAGGGAATTAAGCTCC | 114 bp | NM_021297.3 |
| Reverse: GATCAACCGATGGACGTGTAAA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, J.-Y.; Ren, H.; Chen, H.-Q.; Xing, K.; Xiao, C.-L.; Luo, J.-Q. Magnesium Isoglycyrrhizinate Attenuates Anti-Tuberculosis Drug-Induced Liver Injury by Enhancing Intestinal Barrier Function and Inhibiting the LPS/TLRs/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Mice. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091130
Gong J-Y, Ren H, Chen H-Q, Xing K, Xiao C-L, Luo J-Q. Magnesium Isoglycyrrhizinate Attenuates Anti-Tuberculosis Drug-Induced Liver Injury by Enhancing Intestinal Barrier Function and Inhibiting the LPS/TLRs/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Mice. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(9):1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091130
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Jin-Yu, Huan Ren, Hui-Qing Chen, Kai Xing, Chen-Lin Xiao, and Jian-Quan Luo. 2022. "Magnesium Isoglycyrrhizinate Attenuates Anti-Tuberculosis Drug-Induced Liver Injury by Enhancing Intestinal Barrier Function and Inhibiting the LPS/TLRs/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Mice" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 9: 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091130
APA StyleGong, J.-Y., Ren, H., Chen, H.-Q., Xing, K., Xiao, C.-L., & Luo, J.-Q. (2022). Magnesium Isoglycyrrhizinate Attenuates Anti-Tuberculosis Drug-Induced Liver Injury by Enhancing Intestinal Barrier Function and Inhibiting the LPS/TLRs/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Mice. Pharmaceuticals, 15(9), 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091130








