Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of Asperidine B, a Pyrrolidine Derivative from the Soil-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PSU-RSPG178: A Potential Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
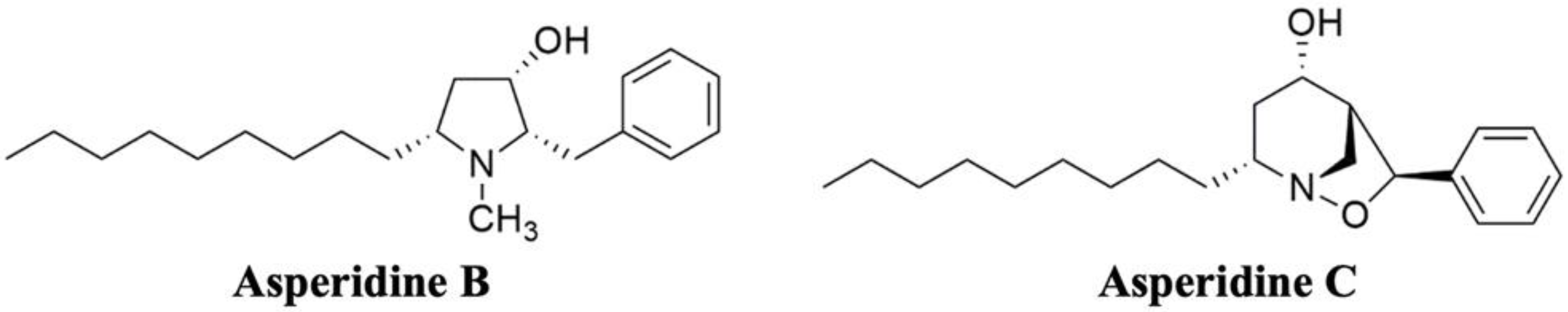
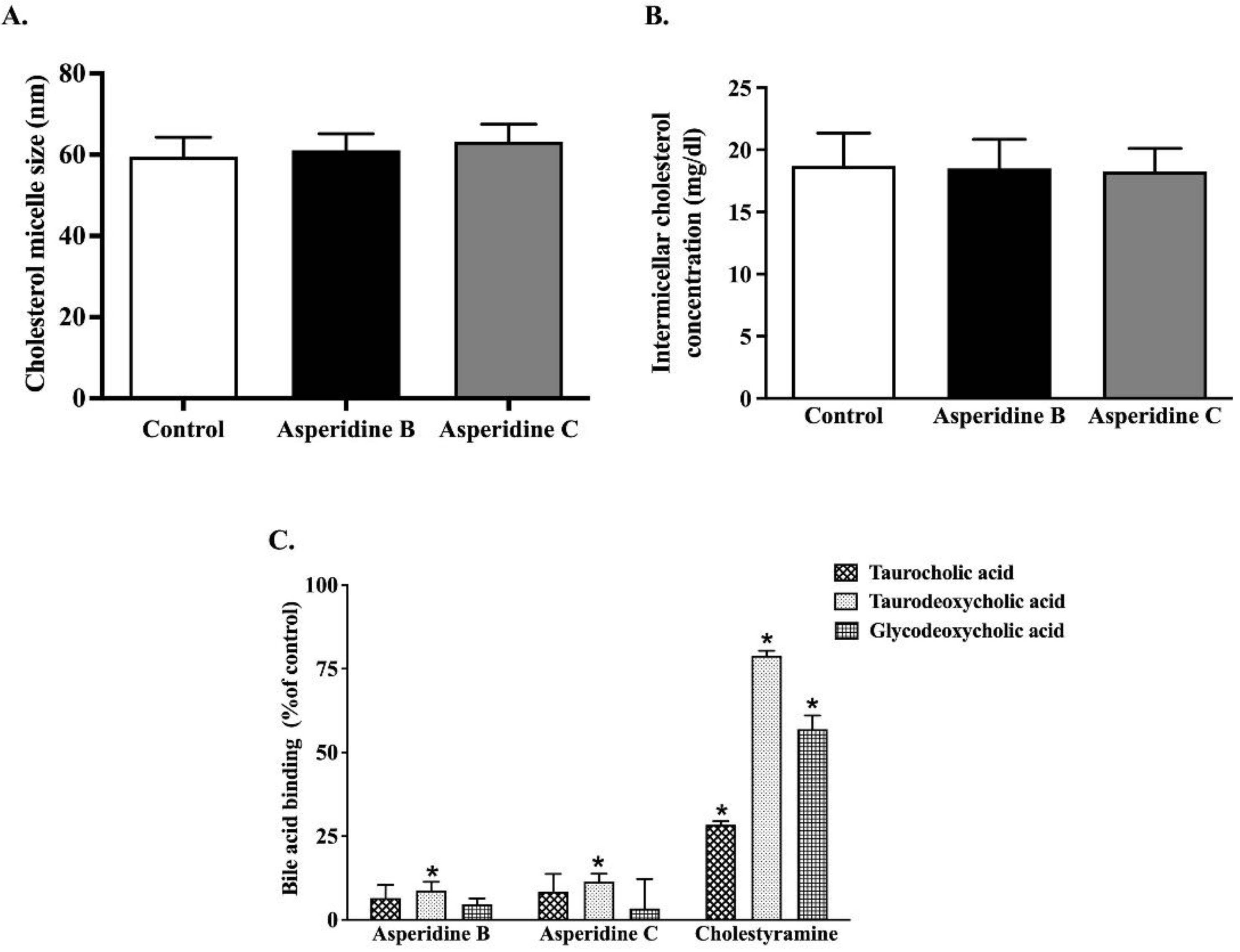
2.1. Asperidines B and C Interfere with the Physicochemical Properties of Cholesterol Micelles by Binding with Secondary Bile Acid
2.2. Asperidine B, but Not Asperidine C, Decreases Cholesterol Absorption in Intestinal Caco-2 Cells
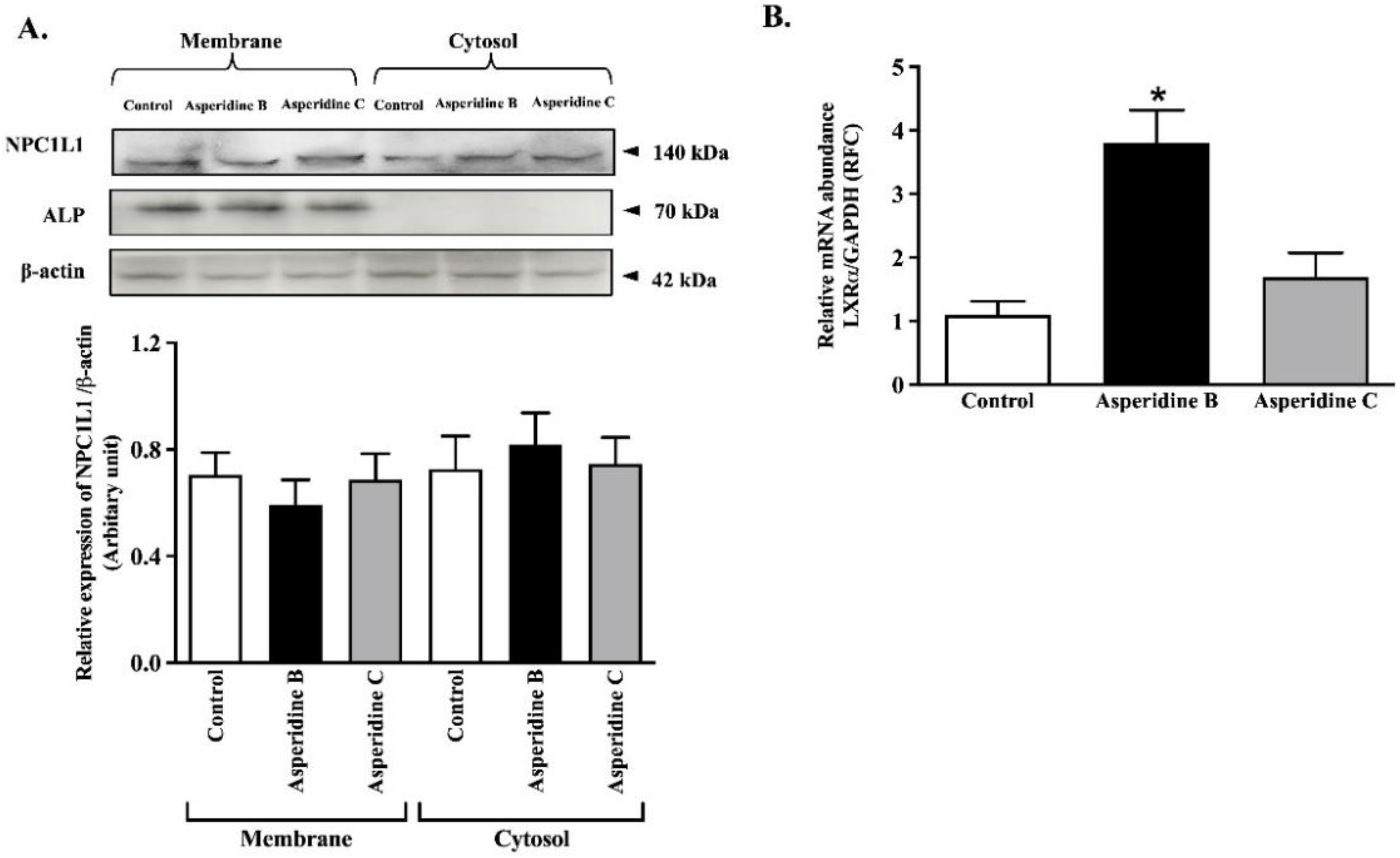
2.3. Asperidine B Up-Regulates LXRα Expression without Alteration of NPC1L1 Membrane Protein Expression in Intestinal Caco-2 Cells
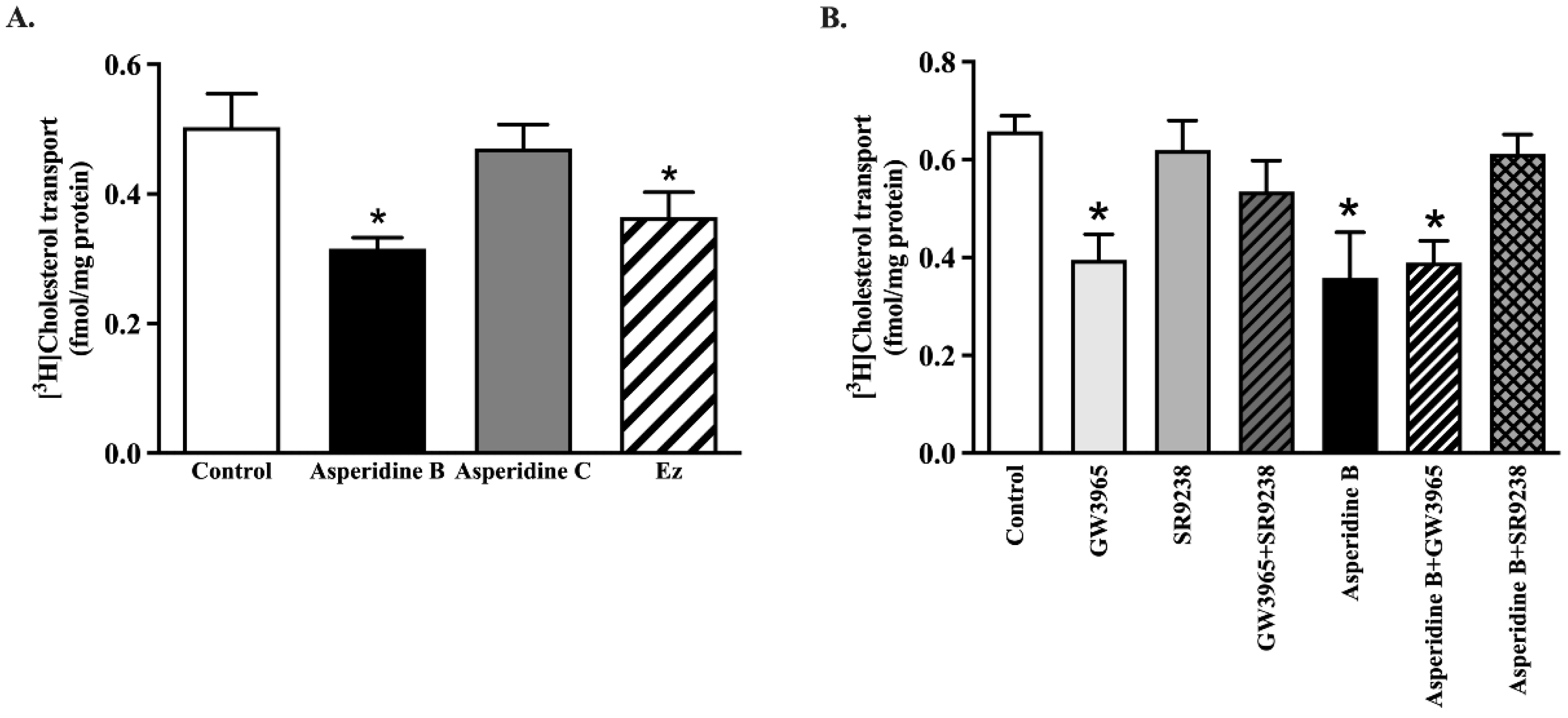
2.4. Asperidine B Strongly Inhibits Cholesterol Transport by Activation of LXRα in Rat Jejunal Loops
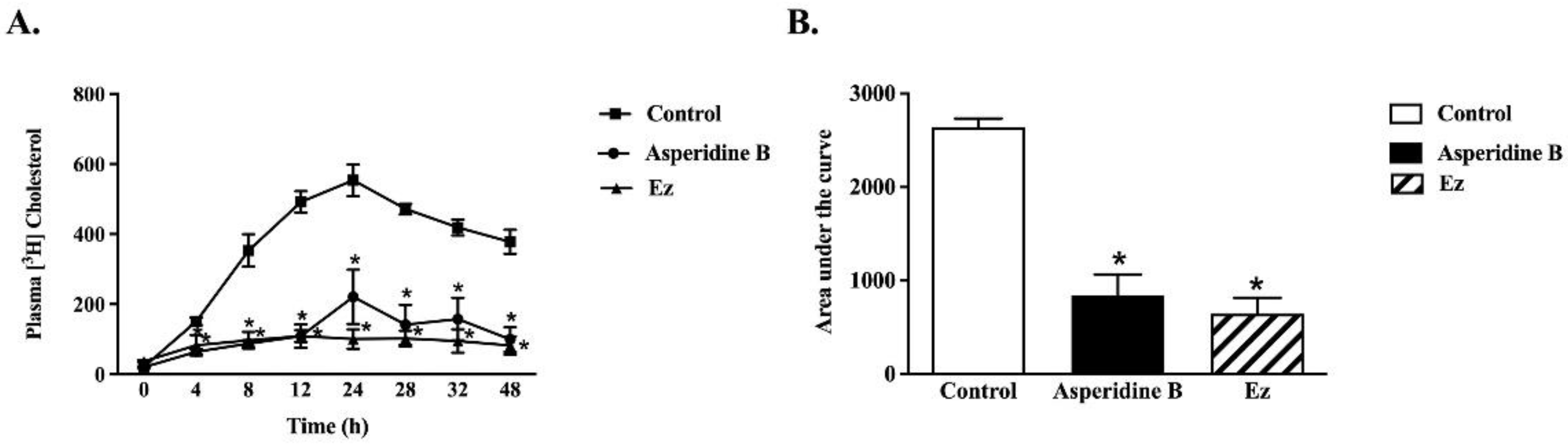
2.5. Asperidine B Acts as a Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitor by Reducing Plasma Cholesterol Levels in Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Determination of Physicochemical Properties of Micellar Complex
4.3. Preparation of Cholesterol Mixed Micelles
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. Cholesterol Transport in Human Intestinal Caco-2 cells
4.6. Determination of Cell Viability
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.8. Subcellular Fractionation and Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Ex vivo and In Vivo Cholesterol Transport Measurements
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barsh, G.S.; Farooqi, I.S.; O’Rahilly, S. Genetics of body-weight regulation. Nature 2000, 404, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchsinger, J.A. A work in progress: The metabolic syndrome. Sci. Aging Knowl. Environ. 2006, 2006, pe19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokdad, A.H.; Ford, E.S.; Bowman, B.A.; Dietz, W.H.; Vinicor, F.; Bales, V.S.; Marks, J.S. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA 2003, 289, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mc Auley, M.T.; Wilkinson, D.J.; Jones, J.J.; Kirkwood, T.B. A whole-body mathematical model of cholesterol metabolism and its age-associated dysregulation. BMC Syst. Biol. 2012, 6, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betters, J.L.; Yu, L. NPC1L1 and cholesterol transport. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 2740–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Bharadwaj, S.; Brown, J.M.; Ma, Y.; Du, W.; Davis, M.A.; Michaely, P.; Liu, P.; Willingham, M.C.; Rudel, L.L. Cholesterol-regulated translocation of NPC1L1 to the cell surface facilitates free cholesterol uptake. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 6616–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.P.; Scott, C.; Oishi, K.; Liapis, A.; Ioannou, Y.A. Inactivation of NPC1L1 causes multiple lipid transport defects and protects against diet-induced hypercholesterolemia. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 12710–12720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, D.E.; Sutherland, B.G.; Edwards, J.Y.; Andrews, J.D.; Barrett, P.H.; Huff, M.W. The molecular mechanisms underlying the reduction of LDL apoB-100 by ezetimibe plus simvastatin. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, C.; Touche, V.; Tailleux, A.; Fruchart, J.C.; Fievet, C.; Clavey, V.; Staels, B.; Lestavel, S. Niemann-Pick C1 like 1 gene expression is down-regulated by LXR activators in the intestine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 340, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.N.; Watt, K.R.; Field, F.J. Regulation of intestinal NPC1L1 expression by dietary fish oil and docosahexaenoic acid. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandor, A.; Ara, R.M.; Tumur, I.; Wilkinson, A.J.; Paisley, S.; Duenas, A.; Durrington, P.N.; Chilcott, J. Ezetimibe monotherapy for cholesterol lowering in 2722 people: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Intern. Med. 2009, 265, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, C.P.; Blazing, M.A.; Giugliano, R.P.; McCagg, A.; White, J.A.; Theroux, P.; Darius, H.; Lewis, B.S.; Ophuis, T.O.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Ezetimibe Added to Statin Therapy after Acute Coronary Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2387–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshir, S.A.; Hussain, N.; Elnor, A.A.; Said, A.S.A. Umbrella Review on Non-Statin Lipid-Lowering Therapy. J. Cardiovasc. Pharm. 2021, 26, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monciardini, P.; Iorio, M.; Maffioli, S.; Sosio, M.; Donadio, S. Discovering new bioactive molecules from microbial sources. Microb. Biotechnol. 2014, 7, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phainuphong, P.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Saithong, S.; Phongpaichit, S.; Bowornwiriyapan, K.; Muanprasat, C.; Srimaroeng, C.; Duangjai, A.; Sakayaroj, J. Lovastatin Analogues from the Soil-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PSU-RSPG178. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewmalee, J.; Ontawong, A.; Duangjai, A.; Tansakul, C.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Muanprasat, C.; Srimaroeng, C. High-Efficacy alpha,beta-Dehydromonacolin S Improves Hepatic Steatosis and Suppresses Gluconeogenesis Pathway in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddell, L.J.N.; Watts, O.F.B.; Saetang, P.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Bates, R.W. Asperidine B: Total synthesis and structure correction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 152078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelshaheed, M.M.; Fawzy, I.M.; El-Subbagh, H.I.; Youssef, K.M. Piperidine nucleus in the field of drug discovery. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 7, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, T.V.; Slater, E.P.; Brummerhop, H.; Bach, T.; Muller, R. Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase activity and induction of apoptosis by preussin in human tumor cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 2794–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagar, H.H. An insight into the possible protective effect of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate against lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress and acute hepatic injury in rats. Saudi Pharm. J. 2009, 17, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.M. Effect of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on hepatic vascular stress gene expression during ischemia and reperfusion. Eur. J. Pharm. 2008, 595, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.-W.; Wang, H.; Yan-Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Ning, H.; Li, X.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Duan, Z.-H.; Zhao, L.; Wei, W.; et al. Differential effects of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on TNF-α-mediated liver injury in two different models of fulminant hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuzzocrea, S.; Rossi, A.; Pisano, B.; Di Paola, R.; Genovese, T.; Patel, N.S.; Cuzzocrea, E.; Ianaro, A.; Sautebin, L.; Fulia, F.; et al. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate attenuates the development of organ failure induced by zymosan in mice. Intensive Care Med. 2003, 29, 2016–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebenezer, P.J.; Mariappan, N.; Elks, C.M.; Haque, M.; Soltani, Z.; Reisin, E.; Francis, J. Effects of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on high-fat diet-induced metabolic and renal alterations in rats. Life Sci. 2009, 85, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Ding, C.Z.; Lai, Z.; Chen, S.S.; Devasthale, P.; Herpin, T.; Morton, G.; Qu, F.; Ryono, D.; Smirk, R.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel pyrrolidine acid analogs as potent dual PPARalpha/gamma agonists. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, D.E. Balancing cholesterol synthesis and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2008, 2, S1–S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruchart, J.-C.; Nierman, M.; Stroes, E.; Kastelein, J.; Duriez, P. New Risk Factors for Atherosclerosis and Patient Risk Assessment. Circulation 2004, 109, III15–III19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, R.H. Hyperlipidemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Prim. Care 2013, 40, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, R.; Cuevas, A.; Cafferata, A. Diagnosis and Management of Statin Intolerance. J. Atheroscler Thromb. 2019, 26, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.; Sheehan, V.; Gurk-Turner, C. Ezetimibe (Zetia): A new type of lipid-lowering agent. Proc. (Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent.) 2003, 16, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.; Kawada-Watanabe, E.; Yamaguchi, J.; Arashi, H.; Otsuki, H.; Matsui, Y.; Sekiguchi, H.; Fujii, S.; Mori, F.; Ogawa, H.; et al. Baseline low-density lipoprotein cholesterol predicts the benefit of adding ezetimibe on statin in statin-naive acute coronary syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliano, R.P.; Cannon, C.P.; Blazing, M.A.; Nicolau, J.C.; Corbalan, R.; Spinar, J.; Park, J.G.; White, J.A.; Bohula, E.A.; Braunwald, E.; et al. Benefit of Adding Ezetimibe to Statin Therapy on Cardiovascular Outcomes and Safety in Patients With Versus Without Diabetes Mellitus: Results From IMPROVE-IT (Improved Reduction of Outcomes: Vytorin Efficacy International Trial). Circulation 2018, 137, 1571–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorucci, S.; Distrutti, E.; Carino, A.; Zampella, A.; Biagioli, M. Bile acids and their receptors in metabolic disorders. Prog. Lipid. Res. 2021, 82, 101094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegård, L.; Andersson, H. Oat bran rapidly increases bile acid excretion and bile acid synthesis: An ileostomy study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ontawong, A.; Duangjai, A.; Muanprasat, C.; Pasachan, T.; Pongchaidecha, A.; Amornlerdpison, D.; Srimaroeng, C. Lipid-lowering effects of Coffea arabica pulp aqueous extract in Caco-2 cells and hypercholesterolemic rats. Phytomedicine 2019, 52, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangjai, A.; Ontawong, A.; Srimaroeng, C. Siamese neem flower extract suppresses cholesterol absorption by interfering NPC1L1 and micellar property in vitro and in intestinal Caco-2 cells. Res Pharm Sci 2019, 14, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, S.I.; Noh, S.K. Green tea as inhibitor of the intestinal absorption of lipids: Potential mechanism for its lipid-lowering effect. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 18, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Feng, D. Lycopene reduces cholesterol absorption through the downregulation of Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 in Caco-2 cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 2225–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.B.; Laffitte, B.A.; Patel, P.H.; Watson, M.A.; Matsukuma, K.E.; Walczak, R.; Collins, J.L.; Osborne, T.F.; Tontonoz, P. Direct and indirect mechanisms for regulation of fatty acid synthase gene expression by liver X receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 11019–11025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, W.; Zeng, J.; Meng, J.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Xing, D. Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 inhibitors for reducing cholesterol absorption. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 230, 114111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, S.; Qosa, H.; Primeaux, B.; Kaddoumi, A. Orlistat limits cholesterol intestinal absorption by Niemann-pick C1-like 1 (NPC1L1) inhibition. Eur. J. Pharm. 2015, 762, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, F.J.; Watt, K.; Mathur, S.N. Ezetimibe interferes with cholesterol trafficking from the plasma membrane to the endoplasmic reticulum in CaCo-2 cells. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Wang, J.; Qi, W.; Miao, H.-H.; Cao, J.; Qu, Y.-X.; Li, B.-L.; Song, B.-L. The Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitor Ezetimibe Acts by Blocking the Sterol-Induced Internalization of NPC1L1. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valasek, M.A.; Clarke, S.L.; Repa, J.J. Fenofibrate reduces intestinal cholesterol absorption via PPARalpha-dependent modulation of NPC1L1 expression in mouse. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 2725–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Veen, J.N.; Kruit, J.K.; Havinga, R.; Baller, J.F.; Chimini, G.; Lestavel, S.; Staels, B.; Groot, P.H.; Groen, A.K.; Kuipers, F. Reduced cholesterol absorption upon PPARdelta activation coincides with decreased intestinal expression of NPC1L1. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ontawong, A.; Duangjai, A.; Sukpondma, Y.; Tadpetch, K.; Muanprasat, C.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Inchai, J.; Vaddhanaphuti, C.S. Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of Asperidine B, a Pyrrolidine Derivative from the Soil-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PSU-RSPG178: A Potential Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitor. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080955
Ontawong A, Duangjai A, Sukpondma Y, Tadpetch K, Muanprasat C, Rukachaisirikul V, Inchai J, Vaddhanaphuti CS. Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of Asperidine B, a Pyrrolidine Derivative from the Soil-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PSU-RSPG178: A Potential Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitor. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(8):955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080955
Chicago/Turabian StyleOntawong, Atcharaporn, Acharaporn Duangjai, Yaowapa Sukpondma, Kwanruthai Tadpetch, Chatchai Muanprasat, Vatcharin Rukachaisirikul, Jakkapong Inchai, and Chutima S. Vaddhanaphuti. 2022. "Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of Asperidine B, a Pyrrolidine Derivative from the Soil-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PSU-RSPG178: A Potential Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitor" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 8: 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080955
APA StyleOntawong, A., Duangjai, A., Sukpondma, Y., Tadpetch, K., Muanprasat, C., Rukachaisirikul, V., Inchai, J., & Vaddhanaphuti, C. S. (2022). Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of Asperidine B, a Pyrrolidine Derivative from the Soil-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PSU-RSPG178: A Potential Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitor. Pharmaceuticals, 15(8), 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080955






