Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist, Montelukast Ameliorates L-NAME-Induced Pre-eclampsia in Rats through Suppressing the IL-6/Jak2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
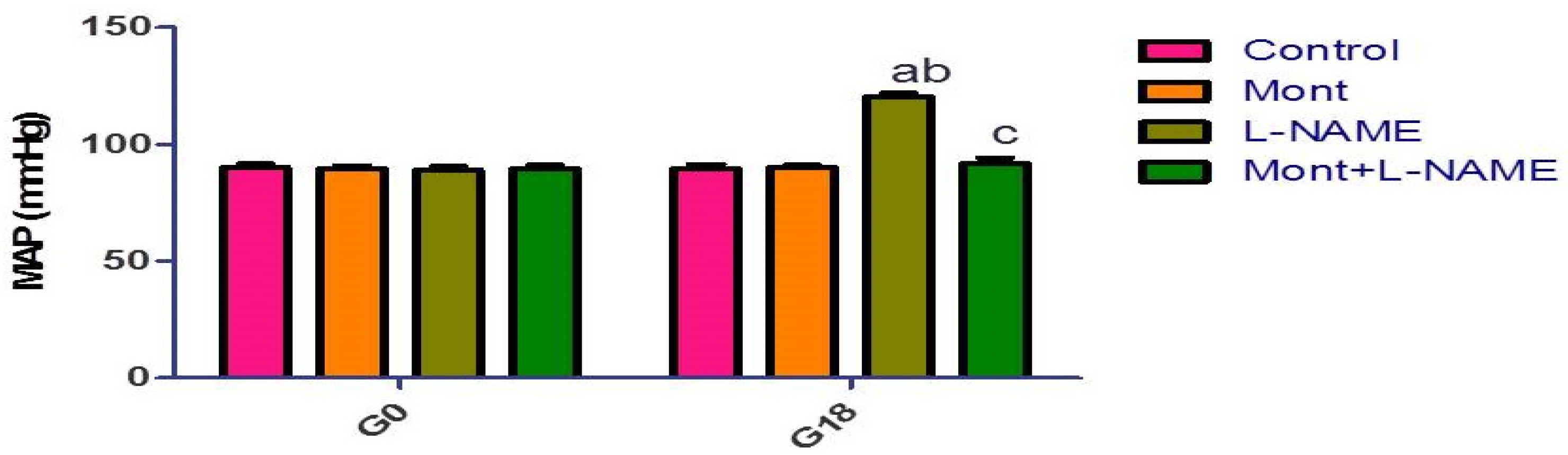
2.1. Effect of Mont on MAP in a Pre-eclampsia Model in Rats
2.2. Effect of Mont on 24 h Urine Protein in a Pre-eclampsia Model in Rats
2.3. Effect of Mont on Placental Parameters in a Pre-eclampsia Model in Rats
2.4. Effect of Mont on Hepatic Parameters in a Pre-eclampsia Model in Rats
2.5. Effect of Mont on Renal Parameters in a Pre-eclampsia Model in Rats
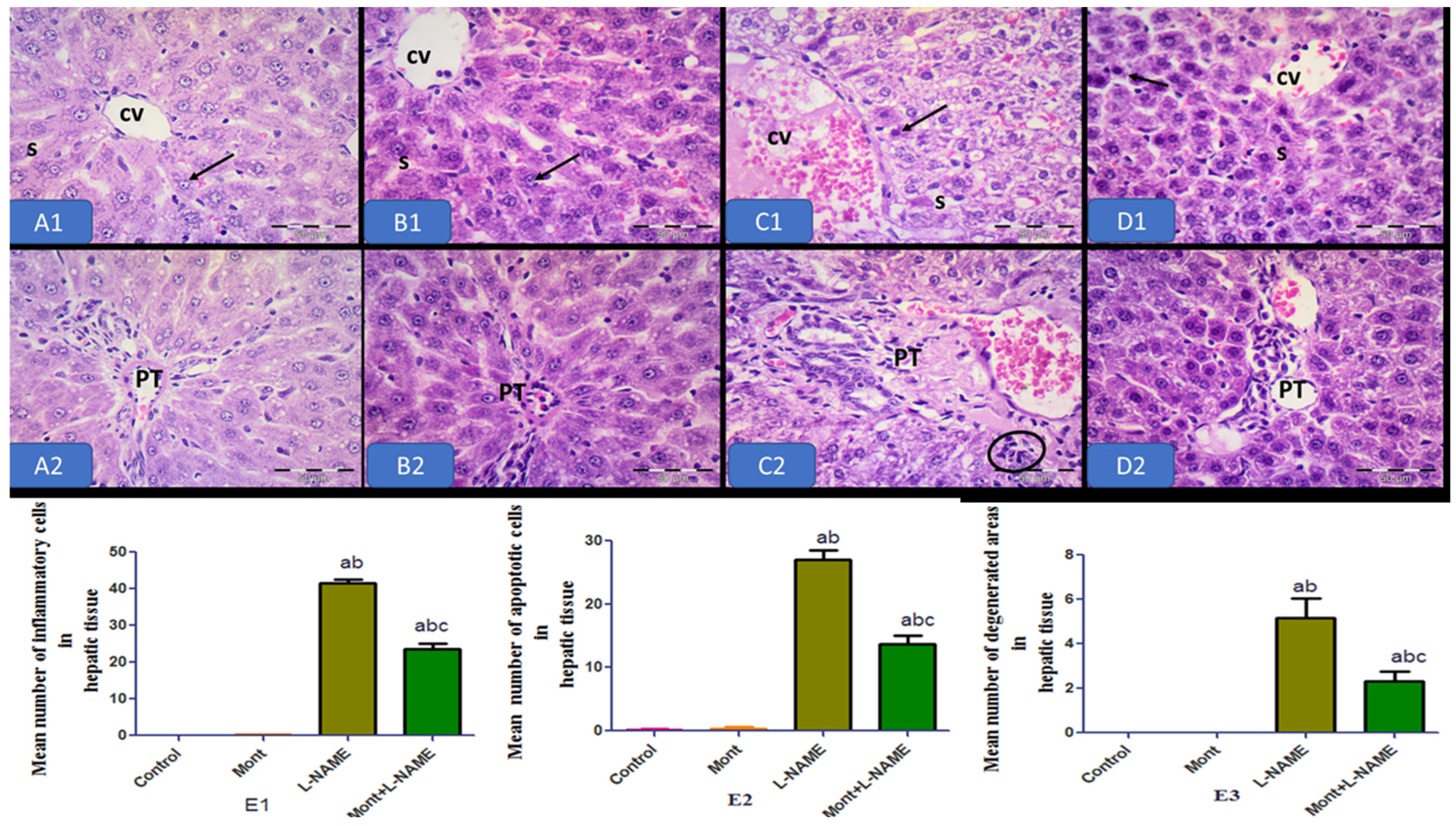
2.6. Histopathological Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics
4.2. Animals and Experimental Design
4.3. Collection of Samples and Measurements
4.3.1. Serum Measurements
4.3.2. Tissue Measurements
4.3.3. Histological Examination
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jena, M.K.; Sharma, N.R.; Petitt, M.; Maulik, D.; Nayak, N.R. Pathogenesis of preeclampsia and therapeutic approaches targeting the placenta. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.K.; Krakowiak, P.; Baker, A.; Hansen, R.L.; Ozonoff, S.; Hertz-Picciotto, I. Preeclampsia, placental insufficiency, and autism spectrum disorder or developmental delay. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipek, A.; Jurewicz, E. Preeclampsia—A disease of pregnant women. Postepy Biochem. 2018, 64, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilekis, J.V.; Reddy, U.M.; Roberts, J.M. Preeclampsia—A pressing problem: An executive summary of a National Institute of Child Health and Human Development workshop. Reprod. Sci. 2007, 14, 508–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, J.G.L.; Sass, N.; Costa, S.H.M. Preeclampsia. Rev. Bras. Ginecol. E Obs. 2017, 39, 496–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fantone, S.; Mazzucchelli, R.; Giannubilo, S.R.; Ciavattini, A.; Marzioni, D.; Tossetta, G. AT-rich interactive domain 1A protein expression in normal and pathological pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 154, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opichka, M.A.; Rappelt, M.W.; Gutterman, D.D.; Grobe, J.L.; McIntosh, J.J. Vascular Dysfunction in Preeclampsia. Cells 2021, 10, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemette, L.; Lacroix, M.; Allard, C.; Patenaude, J.; Battista, M.-C.; Doyon, M.; Moreau, J.; Ménard, J.; Ardilouze, J.-L.; Perron, P.; et al. Preeclampsia is associated with an increased pro-inflammatory profile in newborns. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2015, 112, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwenya, S. Severe preeclampsia and eclampsia: Incidence, complications, and perinatal outcomes at a low-resource setting, Mpilo Central Hospital, Bulawayo, Zimbabwe. Int. J. Women’s Health 2017, 9, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamza, R.Z.; Diab, A.A.A.; Zahra, M.H.; Asalah, A.K.; Attia, M.S.; Moursi, S.M. Ameliorative effect of apelin-13 against renal complications in L-NAME-induced preeclampsia in rats. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmsten, K.; Flores, K.F.; Chambers, C.D.; Weiss, L.A.; Sundaram, R.; Louis, G.M.B. Most frequently reported prescription medications and supplements in couples planning pregnancy: The LIFE study. Reprod. Sci. 2018, 25, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khodir, A.E.; Ghoneim, H.A.; Rahim, M.A.; Suddek, G.M. Montelukast reduces sepsis-induced lung and renal injury in rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 92, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gad, A.M.; El-Raouf, O.M.A.; El-Sayeh, B.M.; Fawzy, H.M.; Abdallah, D.M. Renoprotective effects of montelukast in an experimental model of cisplatin nephrotoxicity in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2017, 31, e21979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Shi, X. Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 (cysLT1R) regulates osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46 (Suppl. 3), S64–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizamani, E.; Ghorbanzadeh, B.; Naserzadeh, R.; Mansouri, M.T. Montelukast, a cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonist, exerts local antinociception in animal model of pain through the L-arginine/nitric oxide/cyclic GMP/KATP channel pathway and PPARγ receptors. Int. J. Neurosci. 2021, 131, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Jin, J.; Shan, X. The effects of estradiol on inflammatory and endothelial dysfunction in rats with preeclampsia. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, D.; Hu, L.; Zheng, X.; Chen, C. Paeoniflorin alleviates NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME)-induced gestational hypertension and upregulates silent information regulator 2 related enzyme 1 (SIRT1) to reduce H2O2-induced endothelial cell damage. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 2248–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Tang, R.; Shi, L.; Zhong, M.; Zhou, Z. Vagus nerve stimulation ameliorates L-NAME-induced preeclampsia-like symptoms in rats through inhibition of the inflammatory response. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2021, 21, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udenze, I.; Amadi, C.; Awolola, N.; Makwe, C.C. The role of cytokines as inflammatory mediators in preeclampsia. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2015, 20, 219. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, W.E.N.; Li, H.; Gong, H.; Zhang, M.; Niu, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cai, W.; Yang, G.; Wei, M.; et al. Evaluation of blood vessel injury, oxidative stress and circulating inflammatory factors in an L-NAME-induced preeclampsia-like rat model. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, J.; Jiang, Z. Melatonin attenuates hypertension and oxidative stress in a rat model of L-NAME-induced gestational hypertension. Vasc. Med. 2020, 25, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, C.O.; Peraçoli, M.T.S.; Weel, I.C.; Bannwart, C.F.; Romão, M.; Nakaira-Takahagi, É.; de Medeiros, L.T.L.; da Silva, M.G.; Peraçoli, J.C. Hepatoprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of silibinin on experimental preeclampsia induced by L-NAME in rats. Life Sci. 2012, 91, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oludare, G.; Jinadu, H.; Aro, O. L-arginine attenuates blood pressure and reverses the suppression of angiogenic risk factors in a rat model of preeclampsia. Pathophysiology 2018, 25, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, E.A.; Thadhani, R.; Benzing, T.; Karumanchi, S.A. Pre-eclampsia: Pathogenesis, novel diagnostics and therapies. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kose, E.; Oguz, F.; Vardi, N.; Sarihan, M.; Beytur, A.; Yucel, A.; Polat, A.; Ekinci, N. Therapeutic and protective effects of montelukast against doxorubicin-induced acute kidney damage in rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2019, 22, 407. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamadin, A.M.; Elberry, A.A.; Elkablawy, M.A.; Gawad, H.S.A.; Al-Abbasi, F.A. Montelukast, a leukotriene receptor antagonist abrogates lipopolysaccharide-induced toxicity and oxidative stress in rat liver. Pathophysiology 2011, 18, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskun, A.K.; Yigiter, M.; Oral, A.; Odabasoglu, F.; Halici, Z.; Mentes, O.; Cadirci, E.; Atalay, F.; Suleyman, H. The effects of Montelukast on antioxidant enzymes and proinflammatory cytokines on the heart, liver, lungs, and kidneys in a rat model of cecal ligation and puncture–induced sepsis. Sci. World J. 2011, 11, 1341–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, C.; Lin, H.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, B. JAK/STAT and PI3K/AKT pathways form a mutual transactivation loop and afford resistance to oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 21, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Zhang, Z.-G.; Tian, X.-Q.; Sun, D.-F.; Liang, Q.-C.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Lu, R.; Chen, Y.-X.; Fang, J.-Y. Inhibition of JAK1, 2/STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and reduces tumor cell invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaśkiewicz, A.; Domoradzki, T.; Pająk, B. Targeting the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway-Can We Compare It to the Two Faces of the God Janus? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.A.; Berardi, E.; Cardillo, V.M.; Acharyya, S.; Aulino, P.; Thomas-Ahner, J.; Wang, J.; Bloomston, M.; Muscarella, P.; Nau, P.; et al. NF-kappaB-mediated Pax7 dysregulation in the muscle microenvironment promotes cancer cachexia. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 4821–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, B.; Jin, H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Ye, J.; Chen, C.; Gao, P.; Zhu, D.; Penninger, J.M.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 attenuates oxidative stress and VSMC proliferation via the JAK2/STAT3/SOCS3 and profilin-1/MAPK signaling pathways. Regul. Pept. 2013, 185, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manea, S.A.; Manea, A.; Heltianu, C. Inhibition of JAK/STAT signaling pathway prevents high-glucose-induced increase in endothelin-1 synthesis in human endothelial cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 340, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Jiang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Sun, L. Role of SOCS3 in the Jak/stat3 pathway in the human placenta: Different mechanisms for preterm and term labor. Acta Obs. Gynecol. Scand. 2015, 94, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeganegi, M.; Leung, C.G.; Martins, A.; Kim, S.O.; Reid, G.; Challis, J.R.G.; Bocking, A.D. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1-induced IL-10 production in human placental trophoblast cells involves activation of JAK/STAT and MAPK pathways. Reprod. Sci. 2010, 17, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, A.M.L.; Pereira, N.R.; da Costa, C.A.; Mann, G.E.; Cordeiro, V.S.C.; De Moura, R.S.; Brunini, T.M.C.; Mendes-Ribeiro, A.C.; Resende, C. L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway and oxidative stress in plasma and platelets of patients with pre-eclampsia. Hypertens. Res. 2013, 36, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.Y.; Fu, D.; Wu, Y.Q.; Gao, Y. Inhibition of the JAK2/STAT3/SOSC1 Signaling Pathway Improves Secretion Function of Vascular Endothelial Cells in a Rat Model of Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.G.; Cavalhieri, L.T.; Ventura, A.C.A.; Aires, F.T.; Garcia, J.M.; Mesquita, M.R.S.; Chaiwangyen, W.; Prieto, S.O.; Sousa, F.L.P.; Sass, N.; et al. PP181. The role of the JAK-STAT pathways and SOCS in preeclampsia. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2012, 2, 338–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, D.; Zhuang, C.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, L. The possible involvement of circRNA DMNT1/p53/JAK/STAT in gestational diabetes mellitus and preeclampsia. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filardi, T.; Varì, R.; Ferretti, E.; Zicari, A.; Morano, S.; Santangelo, C. Curcumin: Could This Compound Be Useful in Pregnancy and Pregnancy-Related Complications? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tossetta, G.; Fantone, S.; Giannubilo, S.R.; Marzioni, D. The Multifaced Actions of Curcumin in Pregnancy Outcome. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafez, S.M.N.A.; Elbassuoni, E.; Abdelzaher, W.Y.; Welson, N.N.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Alzahrani, K.J.; Abdelbaky, F.A.F. Efficacy of vitamin E in protection against methotrexate induced placental injury in albino rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 139, 111637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelzaher, W.Y.; Bahaa, H.A.; Toni, N.D.; Sanad, A.S. Mechanisms underlying the protective effect of montelukast in prevention of endometrial hyperplasia in female rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 62, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buege, J.A.; Steven, D. Microsomal lipid peroxidation methods. Methods Enzymol. 1978, 52, 302–310. [Google Scholar]
- Sastry, K.; Moudgal, R.; Mohan, J.; Tyagi, J.; Rao, G.S. Spectrophotometric determination of serum nitrite and nitrate by copper–cadmium alloy. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 306, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Groups | PGF (pg/mg Tissue) | Placental MDA (nmol/g Tissue) | Placental NOx (nmol/g Tissue) | Placental IL-6 (pg/g Tissue) | Placental TNF-α (pg/g Tissue) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.96 ± 0.12 | 29.7 ± 2.72 | 159.6 ± 7.01 | 42.8 ± 2.47 | 22 ± 1.15 |
| Mont | 1.88 ± 0.09 | 30.18 ± 2.92 | 148.7 ± 6.69 | 44.8 ± 1.89 | 23.8 ± 1.11 |
| L-NAME | 0.70 ± 0.04 ab | 84.2 ± 3.39 ab | 256 ± 3.69 ab | 78.3 ± 2.41 ab | 69.8 ± 3.29 ab |
| Mont + L-NAME | 1.81 ± 0.07 c | 37.7 ± 2.57 c | 138.4 ± 3.75 c | 48.8 ± 2.59 c | 28.9 ± 1.46 c |
| Groups | Serum AST (U/L) | Serum ALT (U/L) | Hepatic MDA (nmol/g Tissue) | Hepatic NOx (nmol/g Tissue) | Hepatic IL-6 (pg/g Tissue) | Hepatic TNF-α (pg/g Tissue) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 34.2 ± 1.58 | 25.9 ± 1.25 | 54.6 ± 3.21 | 65.4 ± 3.57 | 55.9 ± 2.17 | 73.9 ± 2.66 |
| Mont | 36.6 ± 2.27 | 26.4 ± 0.75 | 55.7 ± 2.91 | 68.8 ± 2.97 | 54.5 ± 2.26 | 77.5 ± 3.22 |
| L-NAME | 82.9 ± 3.73 ab | 79.0 ± 2.78 ab | 95.7 ± 2.66 ab | 132 ± 3.06 ab | 101 ± 2.47 ab | 170 ± 0 4.97 ab |
| Mont + L-NAME | 39.4 ± 1.30 c | 30.2 ± 1.85 c | 57.3 ± 2.40 c | 71.2 ± 3.16 c | 57.8 ± 2.54 c | 81 ± 4.13 c |
| Groups | Urea (mg/dL) | Serum Creatinine (mg/dL) | Renal MDA (nmol/gm Tissue) | Renal NOx (nmol/gm Tissue) | Renal IL-6 (pg/g Tissue) | Renal TNF-α (pg/g Tissue) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 40.6 ±1.13 | 0.96 ± 0.05 | 75.8 ± 3.15 | 50.6 ± 2.88 | 42.3 ± 2.03 | 39 ± 2.44 |
| Mont | 42.8 ± 1.52 | 0.99 ± 0.06 | 78.6 ± 3.72 | 50.1 ± 3.57 | 43.8 ± 2.86 | 41.8 ± 2.18 |
| L-NAME | 80.5 ± 2.77 ab | 3.39 ± 0.21 ab | 160 ± 2.85 ab | 96.8 ± 3.92 ab | 72.9 ± 2.74 ab | 97.3 ± 3.69 ab |
| Mont + L-NAME | 43.3 ±1.39 c | 1.03 ±0.08 c | 84 ± 2.86 c | 56.5 ± 2.27 c | 47.7 ± 1.96 c | 48.1 ± 2.23 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelzaher, W.Y.; Mostafa-Hedeab, G.; Bahaa, H.A.; Mahran, A.; Atef Fawzy, M.; Abdel Hafez, S.M.N.; Welson, N.N.; Rofaeil, R.R. Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist, Montelukast Ameliorates L-NAME-Induced Pre-eclampsia in Rats through Suppressing the IL-6/Jak2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080914
Abdelzaher WY, Mostafa-Hedeab G, Bahaa HA, Mahran A, Atef Fawzy M, Abdel Hafez SMN, Welson NN, Rofaeil RR. Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist, Montelukast Ameliorates L-NAME-Induced Pre-eclampsia in Rats through Suppressing the IL-6/Jak2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(8):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080914
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelzaher, Walaa Yehia, Gomaa Mostafa-Hedeab, Haitham Ahmed Bahaa, Ahmad Mahran, Michael Atef Fawzy, Sara Mohamed Naguib Abdel Hafez, Nermeen N. Welson, and Remon Roshdy Rofaeil. 2022. "Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist, Montelukast Ameliorates L-NAME-Induced Pre-eclampsia in Rats through Suppressing the IL-6/Jak2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 8: 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080914
APA StyleAbdelzaher, W. Y., Mostafa-Hedeab, G., Bahaa, H. A., Mahran, A., Atef Fawzy, M., Abdel Hafez, S. M. N., Welson, N. N., & Rofaeil, R. R. (2022). Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist, Montelukast Ameliorates L-NAME-Induced Pre-eclampsia in Rats through Suppressing the IL-6/Jak2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals, 15(8), 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080914






