Characterization of the Mucosally-Adherent Duodenal Microbiome in Children with and without Crohn’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Participants and Samples
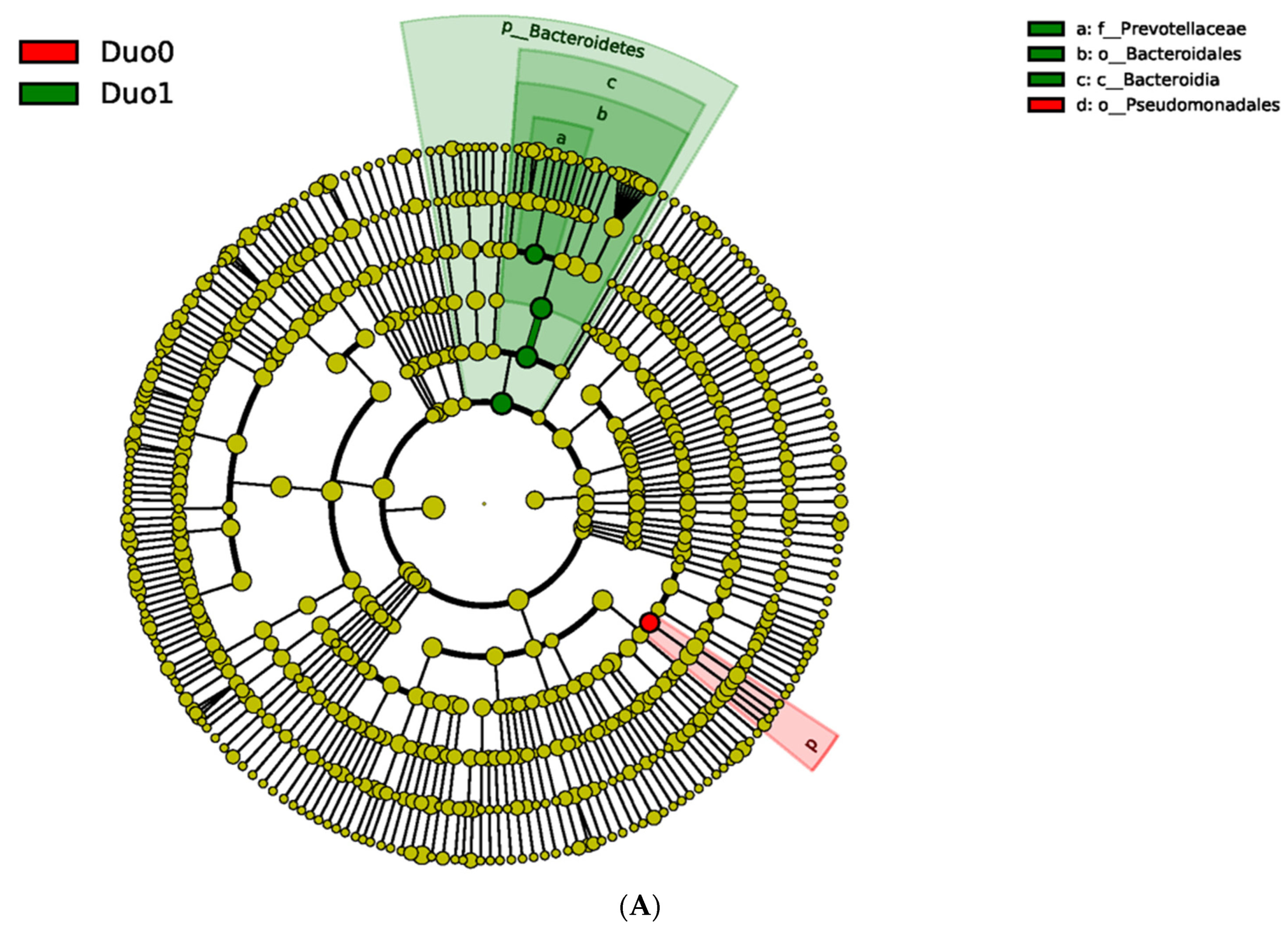
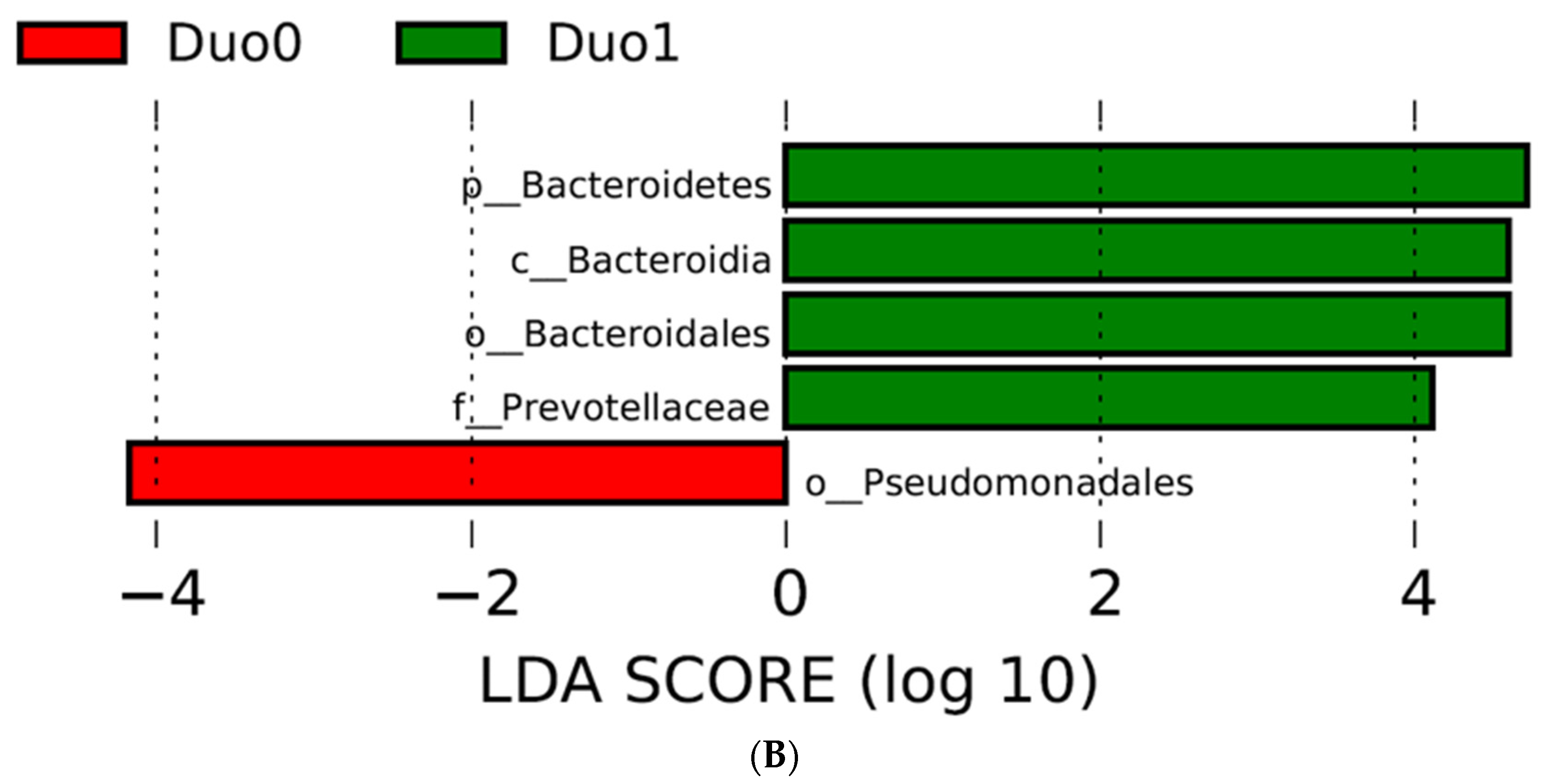
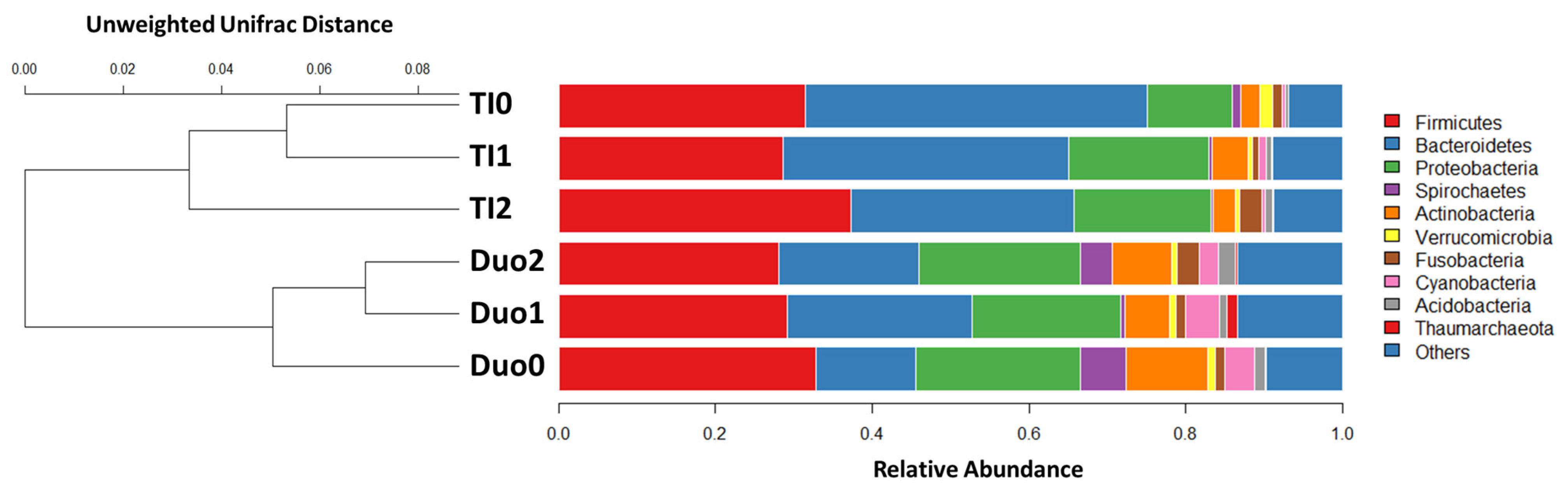
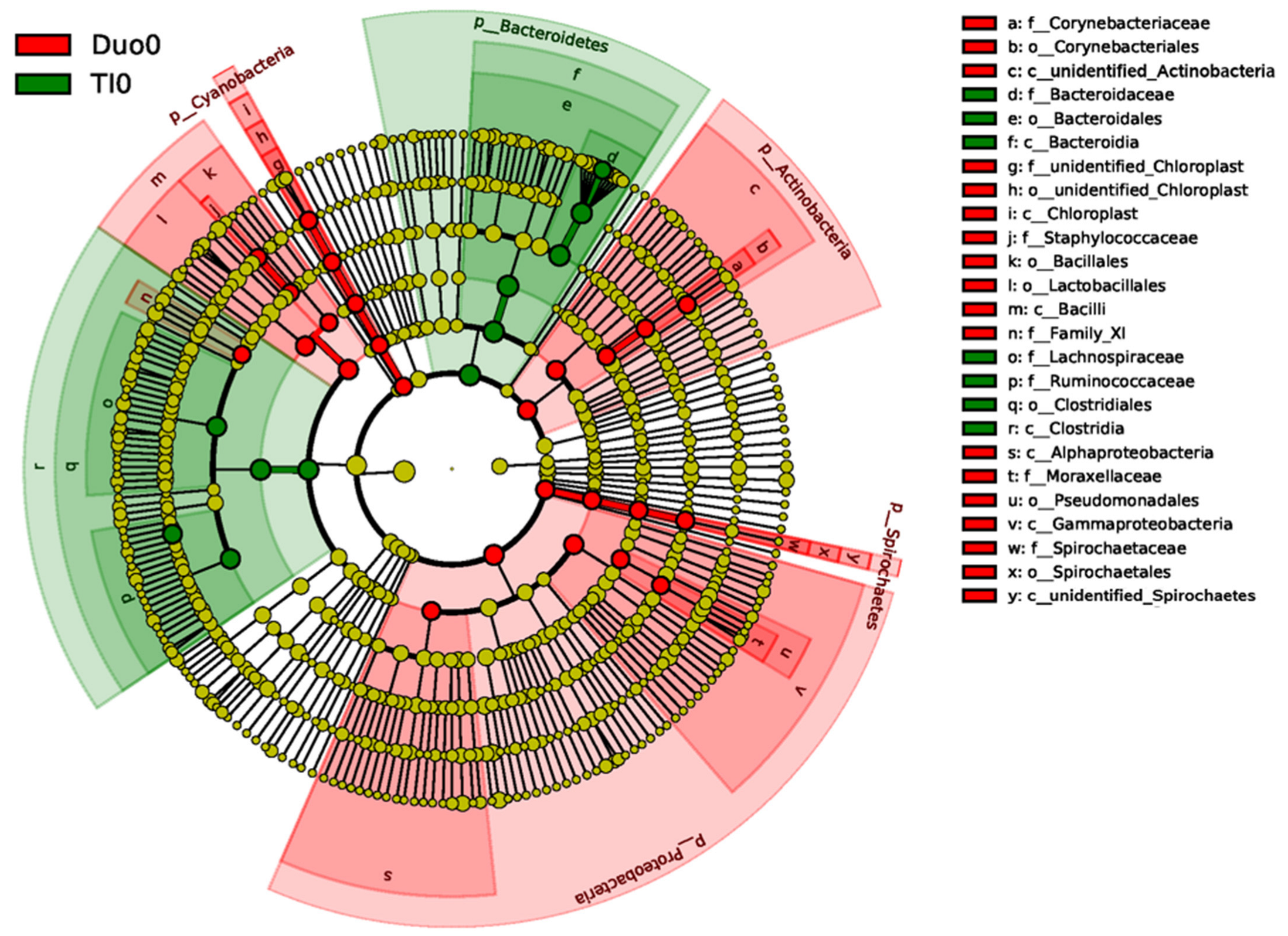
2.2. Characterization of the Duodenal Microbiome
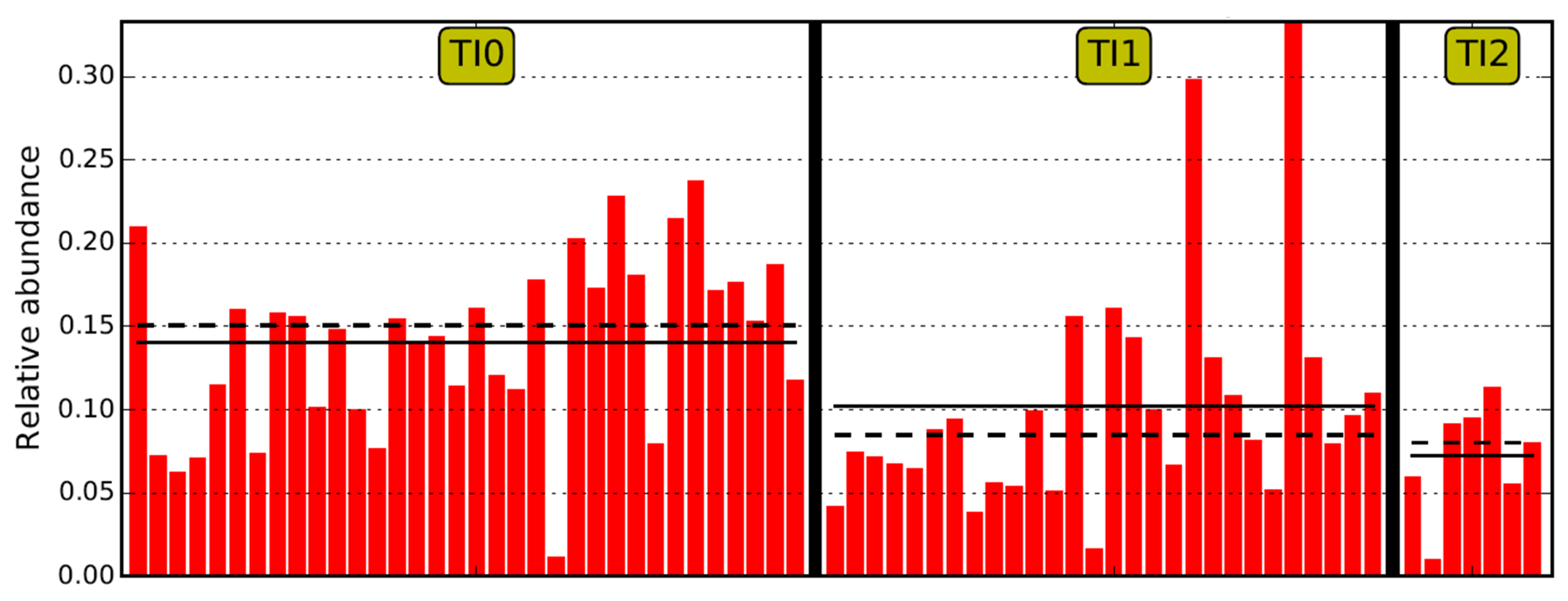
2.3. Characterization of the TI Microbiome
2.4. Comparison of Duodenal and TI Microbiomes
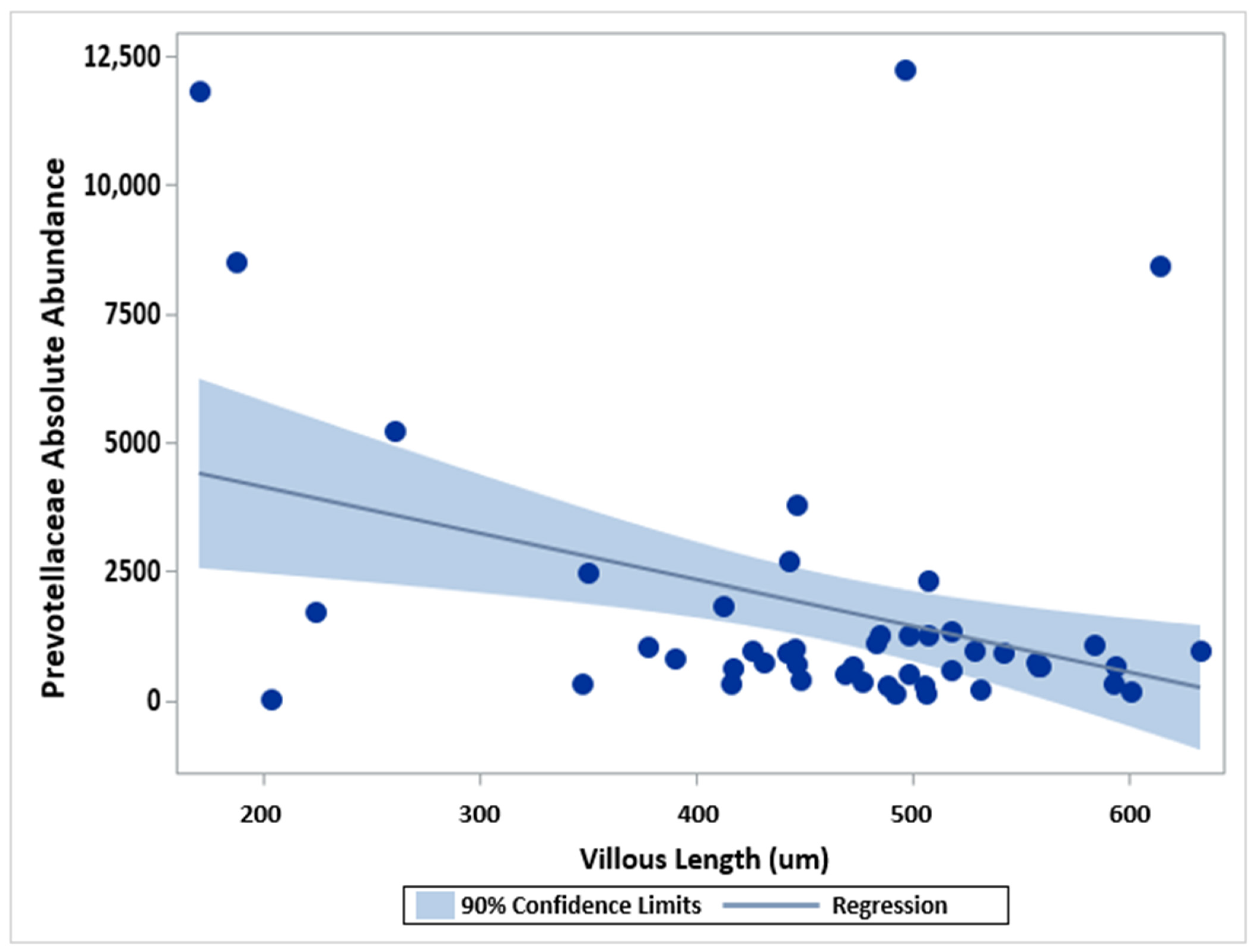
2.5. Microbial Abundance, Age, Sex, and Villous Length
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants
4.2. Sample Collection
4.3. DNA/RNA Extraction and Microbial Sequencing
4.4. Villous Length Measurement
4.5. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torres, J.; Mehandru, S.; Colombel, J.F.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Crohn’s disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungaro, R.; Mehandru, S.; Allen, P.B.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Colombel, J.F. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1756–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocchi, C. Inflammatory bowel disease: Etiology and pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 1998, 115, 182–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, Y.; Sartor, R.B. Manipulating resident microbiota to enhance regulatory immune function to treat inflammatory bowel diseases. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaufin, T.; Tobin, N.H.; Aldrovandi, G.M. The importance of the microbiome in pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2018, 30, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouhy, F.; Watkins, C.; Hill, C.J.; O’Shea, C.-A.; Nagle, B.; Dempsey, E.M.; O’Toole, P.W.; Ross, R.; Ryan, C.A.; Stanton, C. Perinatal factors affect the gut microbiota up to four years after birth. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vuik, F.; Dicksved, J.; Lam, S.Y.; Fuhler, G.M.; Van Der Laan, L.; Van De Winkel, A.; Konstantinov, S.R.; Spaander, M.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Engstrand, L.; et al. Composition of the mucosa-associated microbiota along the entire gastrointestinal tract of human individuals. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2019, 7, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaz, L.; Hernandez-Oquet, R.E.; Deshpande, A.R.; Moshiree, B. Upper Gastrointestinal Involvement in Crohn Disease: Histopathologic and Endoscopic Findings. S. Med. J. 2015, 108, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, T.Z.; ten Kate, F.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Benninga, M.A.; Kindermann, A. Additional value of upper GI tract endoscopy in the diagnostic assessment of childhood IBD. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 54, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, J.M.; Sinha, B.; Ramani, P.; Saleh, A.R.; Murphy, M.S. Upper gastrointestinal mucosal disease in pediatric Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis: A blinded, controlled study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2001, 32, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaerts, C.; Roy, C.C.; Vaillancourt, M.; Weber, A.M.; Morin, C.L.; Seidman, E. High incidence of upper gastrointestinal tract involvement in children with Crohn disease. Pediatrics 1989, 83, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. Primer V5: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2001; Print. [Google Scholar]
- Culliford, A.; Markowitz, D.; Rotterdam, H.; Green, P.H. Scalloping of duodenal mucosa in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2004, 10, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyhlidal, C.A.; Chapron, B.D.; Ahmed, A.; Singh, V.; Casini, R.; Shakhnovich, V. Effect of Crohn’s Disease on Villous Length and CYP3A4 Expression in the Pediatric Small Intestine. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2021, 14, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Kalliomäki, M.; Heilig, H.G.; Palva, A.; Lähteenoja, H.; de Vos, W.M.; Salojärvi, J.; Satokari, R. Duodenal microbiota composition and mucosal homeostasis in pediatric celiac disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manoogian, J.; Butcher, J.; Li, J.; Mack, D.R.; Stintzi, A. A233 CHARACTERIZATION OF THE DUODENAL MICROBIOME IN PEDIATRIC CELIAC AND INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE PATIENTS. J. Can. Assoc. Gastroenterol. 2022, 5 (Suppl 1), 124–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöberg, F.; Barkman, C.; Nookaew, I.; Östman, S.; Adlerberth, I.; Saalman, R.; Wold, A.E. Low-complexity microbiota in the duodenum of children with newly diagnosed ulcerative colitis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pittayanon, R.; Lau, J.T.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Tse, F.; Yuan, Y.; Surette, M.; Moayyedi, P. Differences in Gut Microbiota in Patients With vs Without Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 930–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haberman, Y.; Tickle, T.L.; Dexheimer, P.J.; Kim, M.-O.; Tang, D.; Karns, R.; Baldassano, R.N.; Noe, J.D.; Rosh, J.; Markowitz, J.; et al. Pediatric Crohn disease patients exhibit specific ileal transcriptome and microbiome signature. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3617–3633, Erratum in J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assa, A.; Elkadri, A.; Muise, A.M.; Stintzi, A.; Butcher, J.; Li, J.; Sherman, P.M.; Mack, D. Mucosa-Associated Ileal Microbiota in New-Onset Pediatric Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2016, 22, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albenberg, L.G.; Wu, G.D. Diet and the intestinal microbiome: Associations, functions, and implications for health and disease. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weersma, R.K.; Zhernakova, A.; Fu, J. Interaction between drugs and the gut microbiome. Gut 2020, 69, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Duodenal Study Group | p Value (Duo0, 1, 2) | p Value (Duo0, 1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control [Duo0 (N = 27)] | Active CD [Duo1 (N = 8)] | Inactive CD [Duo2 (N = 13)] | |||
| Sex | 0.207 | 1.000 | |||
| Female | 12 (44.4%) | 3 (37.5%) | 2 (15.4%) | ||
| Male | 15 (55.6%) | 5 (62.5%) | 11 (84.6%) | ||
| Age (years) (mean (SD)) | 13.39 (3.69) | 13.70 (2.73) | 13.52 (2.36) | 0.960 | 0.984 |
| Age (years) (median (IQR)) | 14.25 (11.75, 16.17) | 13.92 (12.29, 15.88) | 13.58 (12.92, 15.58) | 0.960 | 0.984 |
| Villous length (μm) (median (IQR)) | 498 µm (443.00, 557.00) | 242 µm (195.00, 435.50) | 485 µm (448.00, 518.00) | 0.003 | 0.003 |
| Concomitant medications | 9 (33.3%) | 6 (75%) | 10 (76.9%) | 0.013 | 0.051 |
| Acid suppression | 5 (18.5%) | 2 (25.0%) | 1 (7.7%) | 0.577 | 0.648 |
| 5-ASA | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (7.7%) | 0.437 | N/A |
| Antibiotics | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (12.5%) | 2 (15.4%) | 0.077 | 0.229 |
| Probiotics | 1 (3.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (23.1%) | 0.078 | 1.000 |
| Study Group | Duo0 N = 27 | Duo1 N = 8 | Duo2 N = 13 | TI0 N = 33 | TI1 N = 29 | TI2 N = 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duo0 | 1 | −0.003 (0.49) | −0.038 (0.735) | 0.558 (0.001) | 0.301 (0.001) | 0.123 (0.102) |
| Duo1 | - | 1 | −0.099 (0.948) | 0.695 (0.001) | 0.321 (0.007) | 0.070 (0.189) |
| Duo2 | - | - | 1 | 0.668 (0.001) | 0.318 (0.001) | 0.028 (0.352) |
| TI0 | - | - | - | 1 | 0.068 (0.017) | 0.31 (0.033) |
| TI1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 0.047 (0.342) |
| TI2 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| No Medication | Medication | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | OTU | N | Absolute Abundance Mean (std. dev) | N | Absolute Abundance Mean (std. dev) | |
| Duo0 | Prevotellaceae | 18 | 1469.00 (1942.94) | 9 | 768.00 (791.71) | 0.3116 |
| Bacteroidales | 8934.28 (9890.48) | 13,089.78 (20794.81) | 0.4836 | |||
| Bacteroidia | 8938.56 (9891.18) | 13,095.89 (20802.23) | 0.4836 | |||
| Pseudomonadales | 5330.78 (6685.56) | 2682.33 (2566.65) | 0.2660 | |||
| Duo1 | Prevotellaceae | 2 | 2628.00 (3669.88) | 6 | 4097.17 (4838.70) | 0.7130 |
| Bacteroidales | 5987.50 (8122.54) | 21,602.67 (17,613.49) | 0.2883 | |||
| Bacteroidia | 5987.50 (8122.54) | 21,609.00 (17,613.25) | 0.2883 | |||
| Pseudomonadales | 451.00 (545.89) | 872.00 (1145.87) | 0.6466 | |||
| Duo2 | Prevotellaceae | 3 | 833.33 (474.88) | 10 | 2062.20 (3620.96) | 0.5808 |
| Bacteroidales | 15,216.67 (13,674.53) | 13,459.40 (15,400.62) | 0.8629 | |||
| Bacteroidia | 15,226.00 (13,689.13) | 13,473.20 (15,395.57) | 0.8629 | |||
| Pseudoonadales | 426.00 (157.43) | 2974.20 (4620.23) | 0.3743 | |||
| Variables | TI Study Group | p Value (TI0, 1, 2) | p Value (TI0, 1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control [TI0 (N = 33)] | Active CD [TI1 (N = 29)] | Inactive CD [TI2 (N = 6)] | |||
| Sex | 0.496 | 0.245 | |||
| Female | 15 (45.5%) | 9 (31.0%) | 2 (33.3%) | ||
| Male | 18 (54.5%) | 20 (69.0%) | 4 (66.7%) | ||
| Age (years) (mean (SD)) | 13.70 (3.51) | 13.00 (2.55) | 11.25 (6.17) | 0.238 | 0.163 |
| Age (years) (median (IQR)) | 14.25 (11.92, 16.25) | 13.00 (11.58, 15.09) | 11.74 (8.25, 15.17) | 0.238 | 0.163 |
| Villous length (um) (median) Missing | 502.00 (458.00, 552.50) 5 | 241 (97.50, 367.50) 1 | 468.00 (444.00, 490.00) 1 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Concomitant Medications | 14 (42.4%) | 20 (69.0%) | 5 (83.3%) | 0.044 | 0.036 |
| Acid Suppression | 7 (21.2%) | 4 (13.8%) | 3 (50.0%) | 0.113 | 0.445 |
| 5-ASA | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (10.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.204 | 0.097 |
| Budesonide | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (3.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.515 | 0.468 |
| Antibiotics | 0 (0.0%) 33 (100.0%) | 3 (10.3%) 26 (89.7%) | 1 (16.7%) 5 (83.3%) | 0.063 | 0.097 |
| Probiotics | 1 (3.0%) | 3 (10.3%) | 1 (16.7%) | 0.199 | 0.332 |
| Pearson Correlation Coefficients, N = 48 p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Villous length | Prevotellaceae | Bacteroidales | Bacteroidia | Pseudomonadales | |
| Villous Length | 1.00000 | −0.35 (0.0147) | −0.11 (0.4669) | −0.11 (0.4671) | 0.05 (0.7324) |
| Prevotellaceae | 1.00000 | 0.51 (0.0002) | 0.51 (0.0002) | −0.12 (0.4578) | |
| Bacteroidales | 1.00000 | 1.00 (<0.0001) | −0.24 (0.0947) | ||
| Bacteroidia | 1.00000 | −0.24 (0.0947) | |||
| Pseudomonadales | 1.00000 | ||||
| Pearson Correlation Coefficients p-Value Number of Observations | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Villous length | Prevotellaceae | Bacteroidales | Bacteroidia | Pseudomonadales | |
| Villous Length | 1.00000 61 | 0.21871 (0.0904) 61 | 0.10402 (0.4250) 61 | 0.10398 (0.4252) 61 | −0.11788 (0.3656) 61 |
| Prevotellaceae | 0.21871 (0.0904) 61 | 1.00000 68 | 0.23623 (0.0524) 68 | 0.23622 (0.0525) 68 | 0.06367 (0.6060) 68 |
| Bacteroidales | 0.10402 (0.4250) 61 | 0.23623 (0.0524) 68 | 1.00000 68 | 1.00000 (<0.0001) 68 | −0.33609 (0.0051) 68 |
| Bacteroidia | 0.10398 (0.4252) 61 | 0.23622 (0.0525) 68 | 1.00000 (<0.0001) 68 | 1.00000 68 | −0.33608 (0.0051) 68 |
| Pseudomonadales | −0.11788 (0.3656) 61 | 0.06367 (0.6060) 68 | −0.33609 (0.0051) 68 | −0.33608 (0.0051) 68 | 1.00000 68 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schmidt, K.; Noel-MacDonnell, J.; Vyhlidal, C.; Heruth, D.P.; Singh, V.; Ahmed, A.A.; Hudson, T.; Williams, V.; Shakhnovich, V. Characterization of the Mucosally-Adherent Duodenal Microbiome in Children with and without Crohn’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070850
Schmidt K, Noel-MacDonnell J, Vyhlidal C, Heruth DP, Singh V, Ahmed AA, Hudson T, Williams V, Shakhnovich V. Characterization of the Mucosally-Adherent Duodenal Microbiome in Children with and without Crohn’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(7):850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070850
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchmidt, Kenneth, Janelle Noel-MacDonnell, Carrie Vyhlidal, Daniel P. Heruth, Vivekanand Singh, Atif A. Ahmed, Taina Hudson, Veronica Williams, and Valentina Shakhnovich. 2022. "Characterization of the Mucosally-Adherent Duodenal Microbiome in Children with and without Crohn’s Disease" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 7: 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070850
APA StyleSchmidt, K., Noel-MacDonnell, J., Vyhlidal, C., Heruth, D. P., Singh, V., Ahmed, A. A., Hudson, T., Williams, V., & Shakhnovich, V. (2022). Characterization of the Mucosally-Adherent Duodenal Microbiome in Children with and without Crohn’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals, 15(7), 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070850







