TRPM3-Induced Gene Transcription Is under Epigenetic Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
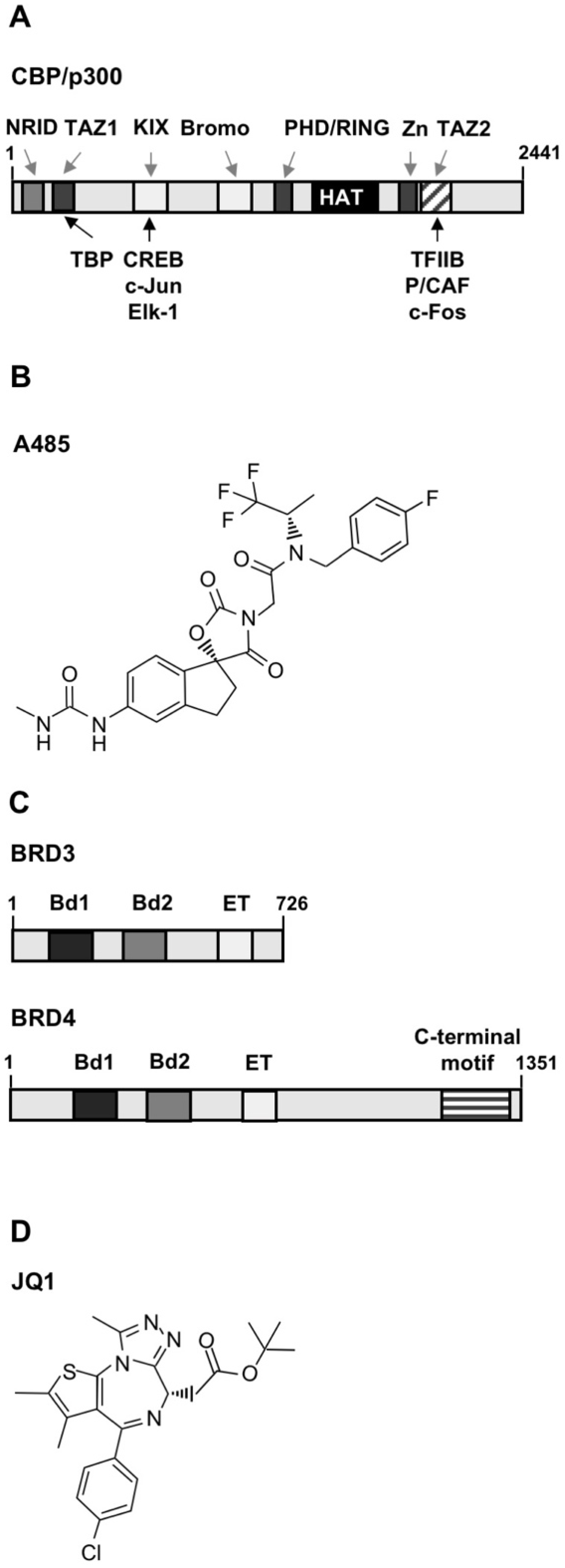
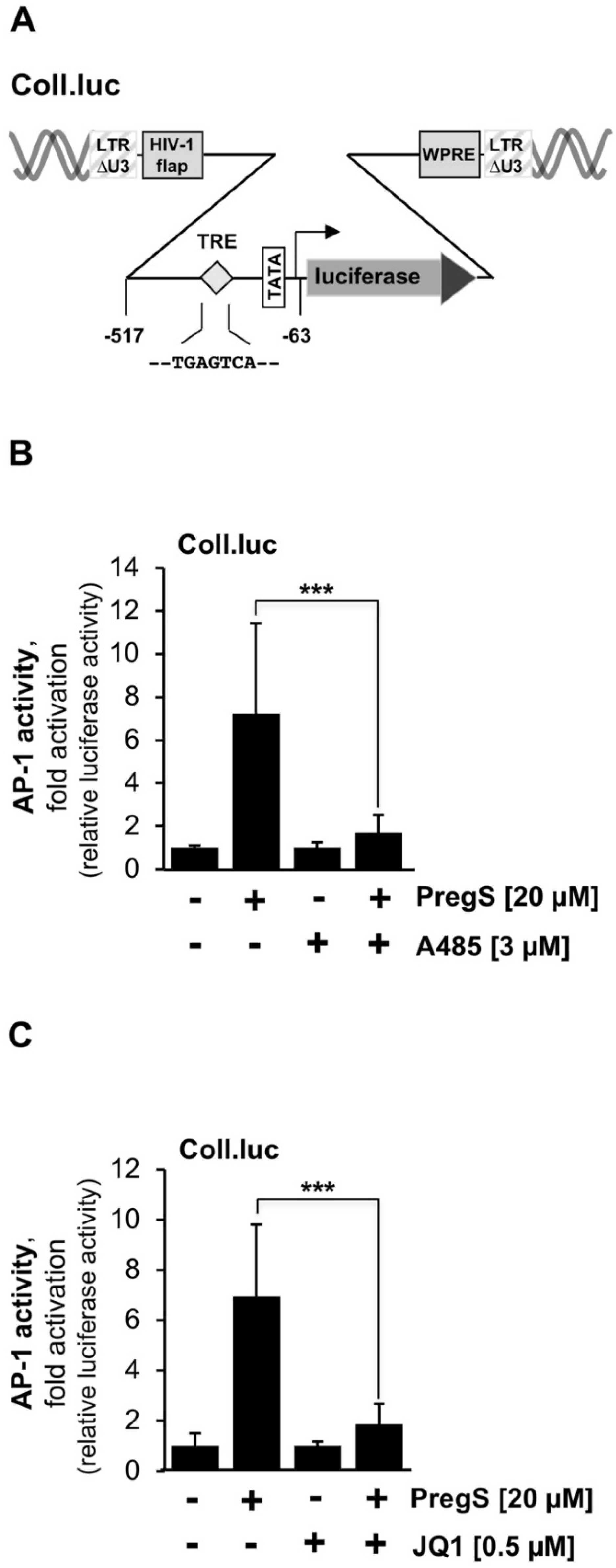
2.1. CBP/p300 and Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal (BET) Inhibitors Attenuate TRPM3-Induced Activation of AP-1
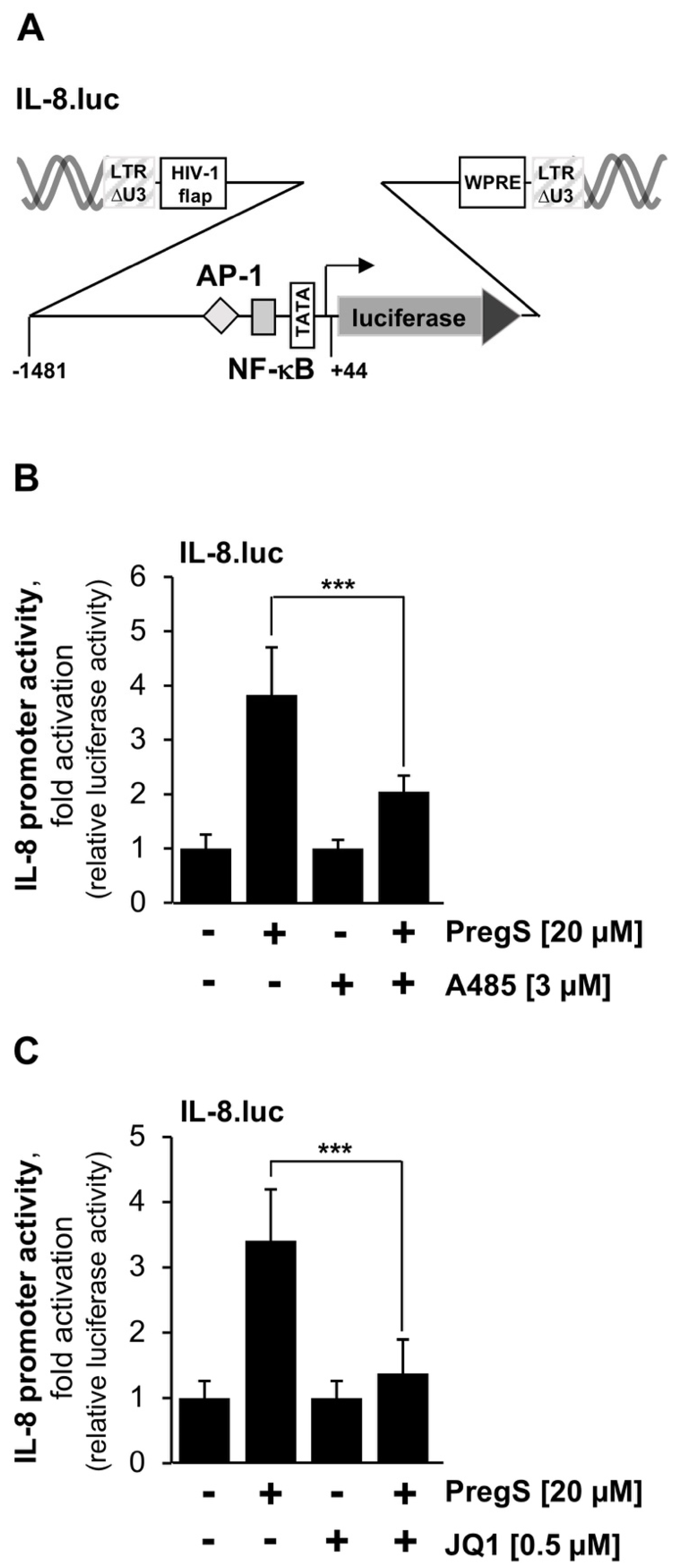
2.2. Inhibitors of CBP/p300 and BET Proteins Reduce the TRPM3-Mediated Stimulation of the Interleukin-8 (IL-8) Promoter
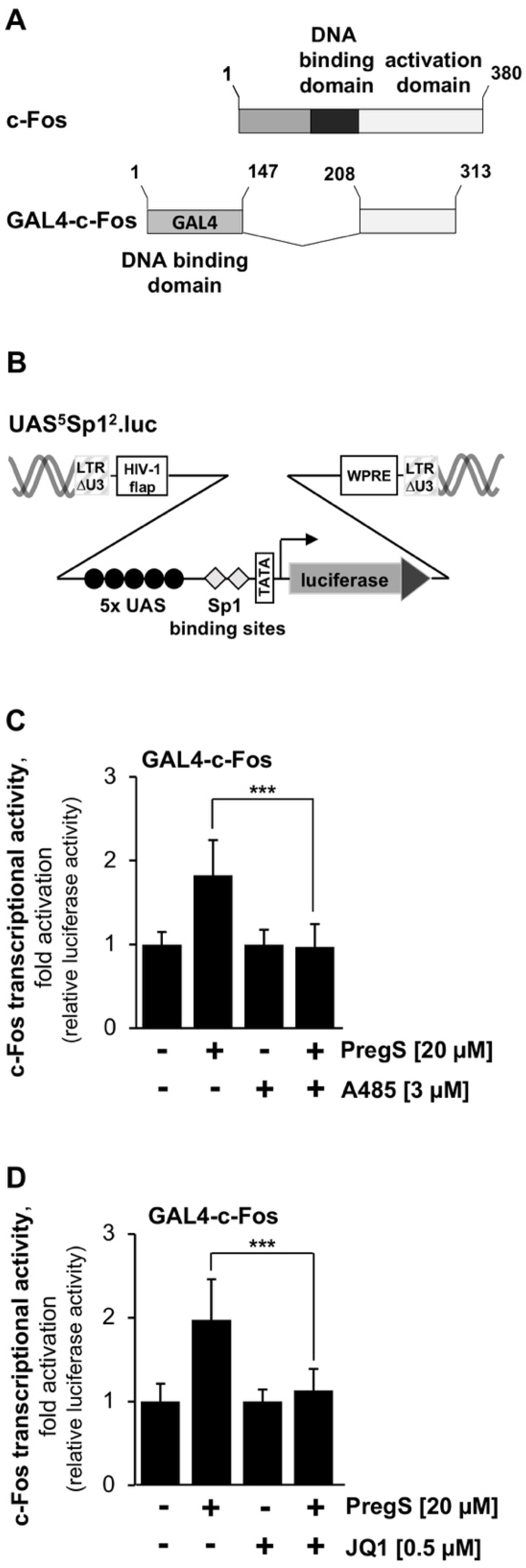
2.3. The Transcriptional Activation Potential of the Transcription Factor c-Fos Was Reduced by CBP/p300 and BET Protein Inhibitors in Stimulated T-REx-TRPM3 Cells
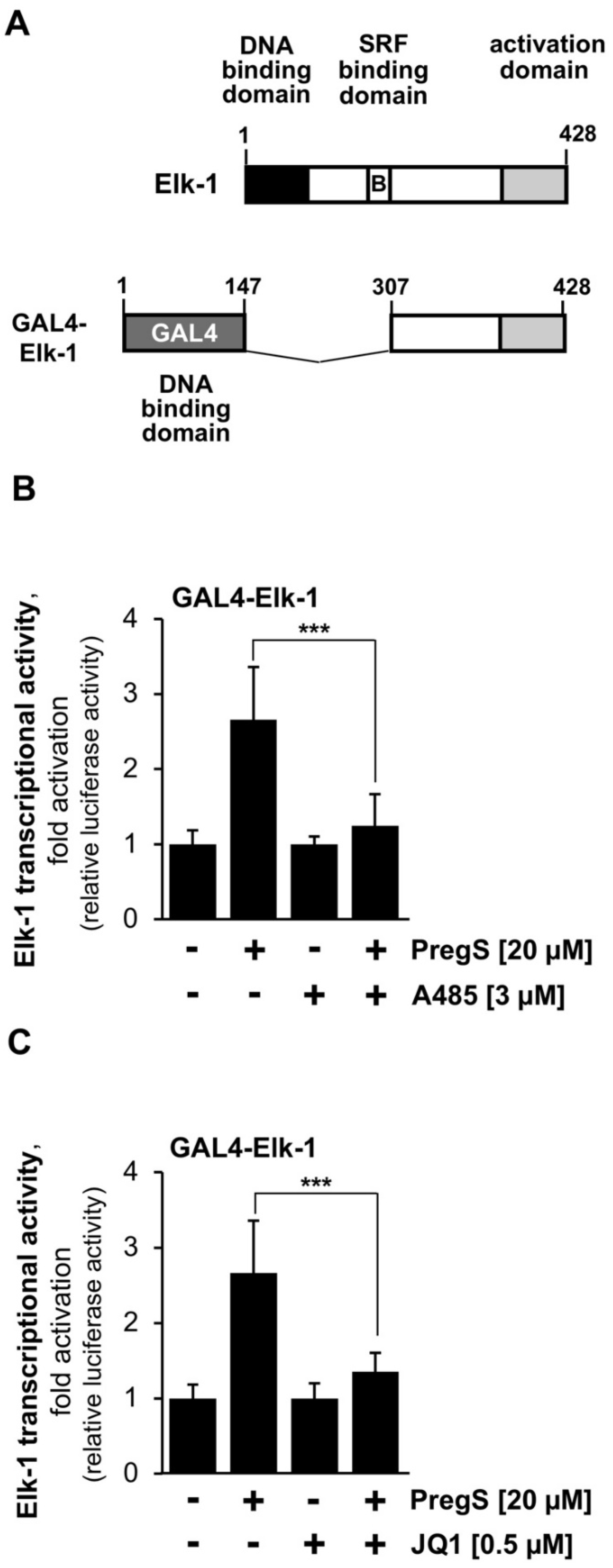
2.4. The Transcriptional Activation Potential of the Ternary Complex Factor Elk-1 Is Reduced in the Presence of Either CBP/p300 or BET Protein Inhibitors in Stimulated T-REx-TRPM3 Cells
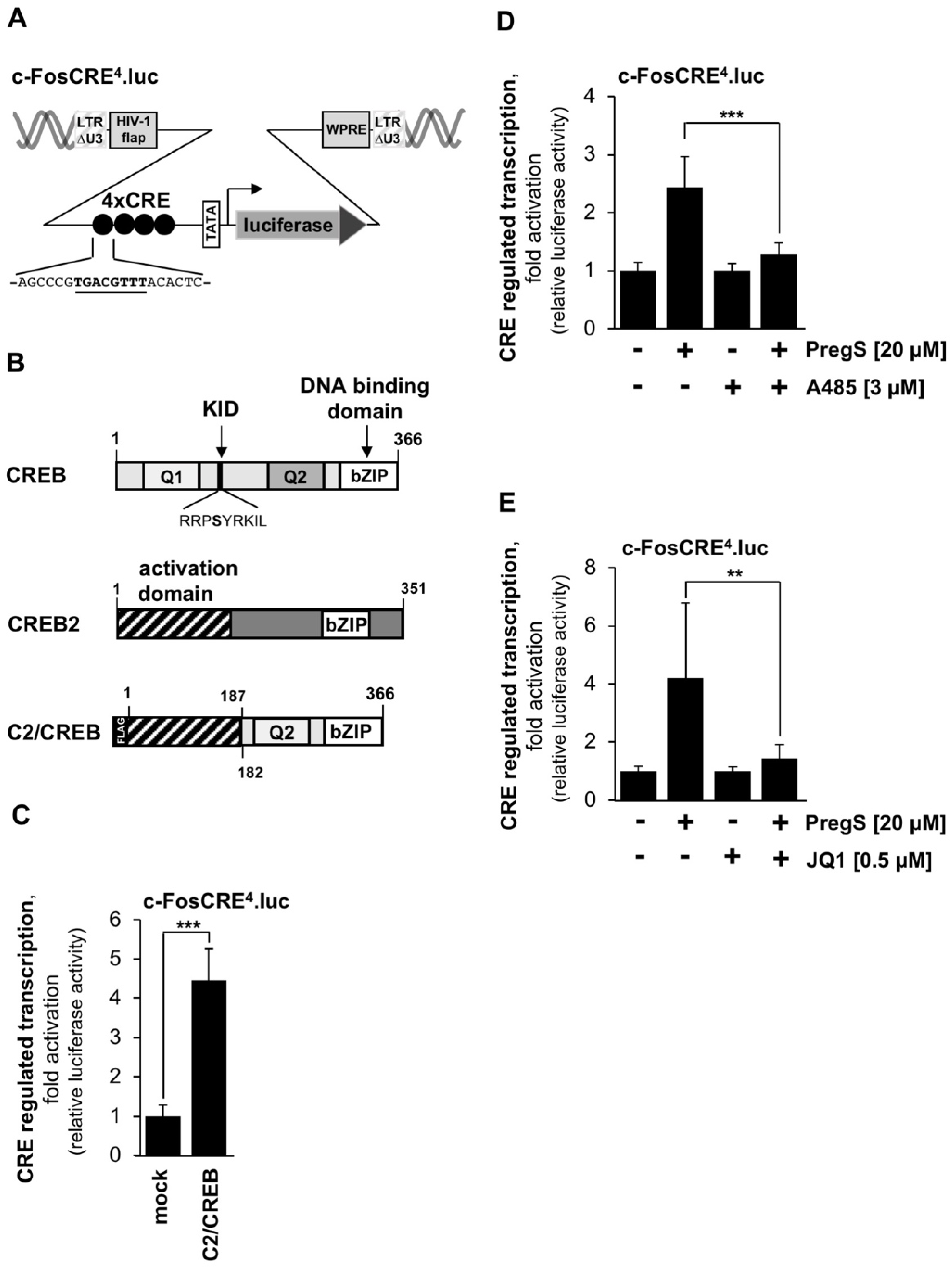
2.5. Measurement of cAMP Response Element-Mediated-Mediated Transcription Using a CRE-Containing Reporter Gene and a CREB Mutant
2.6. CBP/p300 and BET Proteins Control the Activation of CREB-Regulated Gene Transcription in Stimulated T-REx-TRPM3 Cells
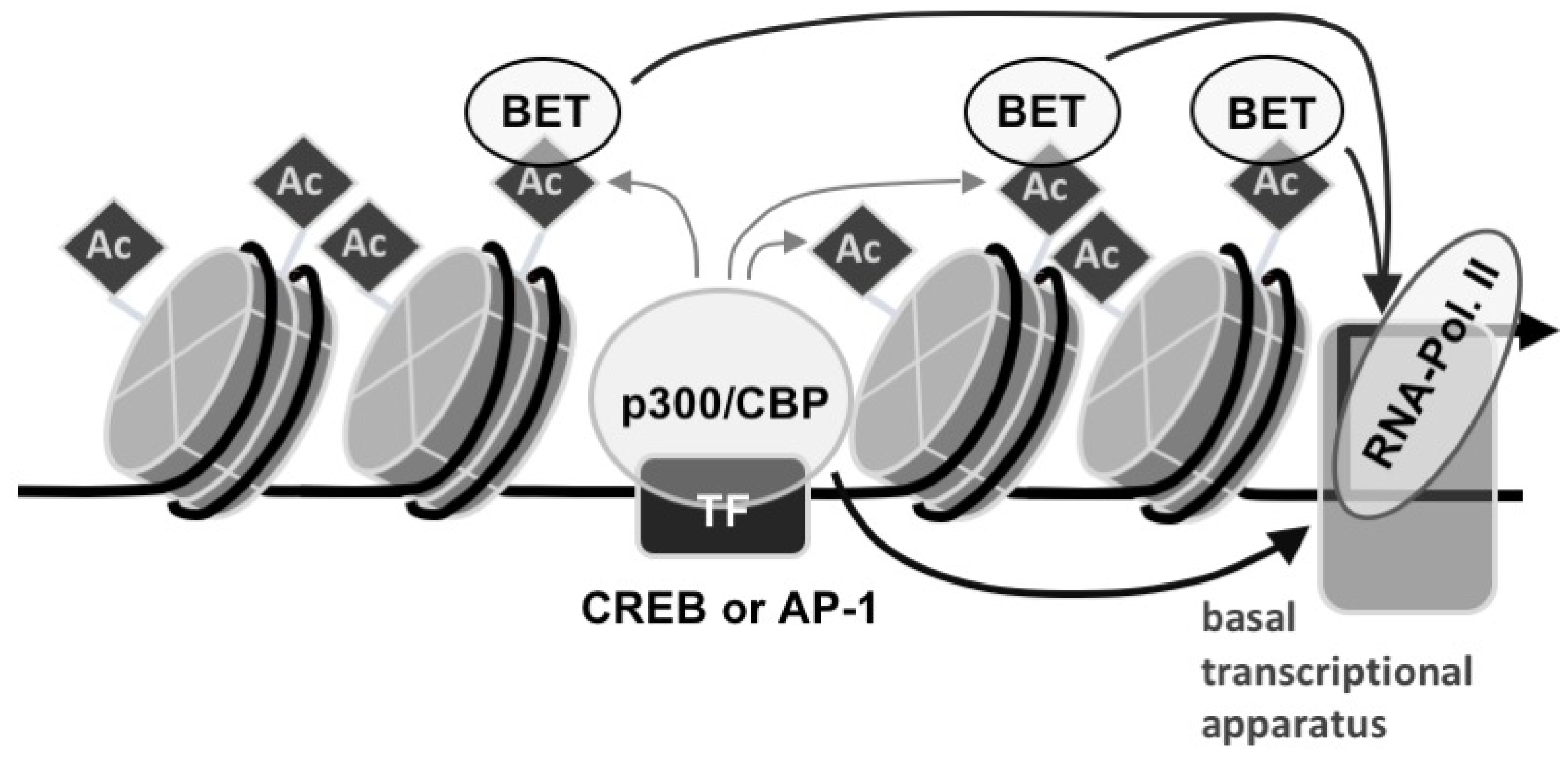
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
4.2. Lentiviral Gene Transfer
4.3. Reporter Assays
4.4. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wagner, T.F.J.; Loch, S.; Lambert, S.; Straub, I.; Mannebach, S.; Mathar, I.; Düfer, M.; Lis, A.; Flockerzi, V.; Philipp, S.E.; et al. Transient receptor potential M3 channels are ionotropic steroid receptors in pancreatic beta cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesch, A.; Rubil, S.; Thiel, G. Activation and inhibition of transient receptor potential TRPM3-induced gene transcription. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 2645–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, G.; Rubil, S.; Lesch, A.; Guethlein, L.A.; Rössler, O.G. Transient receptor potential TRPM3 channels: Pharmacology, signaling, and biological functions. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 124, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vriens, J.; Owsianik, G.; Hofmann, T.; Philipp, S.E.; Stab, J.; Chen, X.; Benoit, M.; Xue, F.; Janssens, A.; Kerselaers, S.; et al. TRPM3 is a nociceptor channel involved in the detection of noxious heat. Neuron 2011, 70, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandewauw, I.; De Clercq, K.; Mulier, M.; Held, K.; Pinto, S.; Van Ranst, N.; Segal, A.; Voet, T.; Vennekens, R.; Zimmermann, K.; et al. A TRP channel trio mediates acute noxious heat sensing. Nature 2018, 555, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesch, A.; Hui, X.; Lipp, P.; Thiel, G. Transient receptor potential melastatin-3 (TRPM3)-induced activation of AP-1 requires Ca2+ ions and the transcription factors c-Jun, ATF2, and ternary complex factor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 87, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubil, S.; Lesch, A.; Mukaida, N.; Thiel, G. Stimulation of transient receptor potential M3 (TRPM3) channels increases interleukin-8 gene promoter activity involving AP-1 and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase. Cytokine 2018, 103, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struhl, K. Histone acetylation and transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvedunova, M.; Akhtar, A. Modulation of cellular processes by histone and non-histone protein acetylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, S.; Zorro Shahidian, L.; Schneider, R. Histone acetylation and chromatin dynamics: Concepts, challenges, and links to metabolism. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e52774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippakopoulos, P.; Knapp, S. Targeting bromodomains: Epigenetic readers of lysine acetylation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokani, S.; Kumar Bhatt, L. Bromodomains: A novel target for the anticancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 911, 174523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, N.; Goodman, R.H. CREB-binding protein and p300 in transcriptional regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 13505–13508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Marshall, C.B.; Ikura, M. Transcriptional/epigenetic regulator CBP/p300 in tumorigenesis: Structural and functional versatility in target recognition. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 3989–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dancy, B.M.; Cole, P.A. Protein lysine acetylation by p300/CBP. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2419–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, G.; Backes, T.M.; Guethlein, L.A.; Rössler, O.G. Chromatin-embedded reporter genes: Quantification of stimulus-induced gene transcription. Gene 2021, 787, 145645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, Y.; Agarwal, A.K.; Naylor, J.; Seymour, V.A.L.; Jiang, S.; Muraki, K.; Fishwick, C.W.; Beech, D.J. Cis-isomerism and other chemical requirements of steroid agonists and partial agonists acting at TRPM3 channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippakopoulos, P.; Qi, J.; Picaud, S.; Shen, Y.; Smith, W.B.; Fedorov, O.; Morse, E.M.; Keates, T.; Hickman, T.T.; Felletar, I.; et al. Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature 2010, 468, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.P.; Lundblad, J.R.; Chrivia, J.C.; Richards, J.P.; Bächinger, H.P.; Brennan, R.G.; Roberts, S.G.; Green, M.R.; Goodman, R.H. Nuclear protein CBP is a coactivator for the transcription factor CREB. Nature 1994, 370, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundblad, J.R.; Kwok, R.P.S.; Laurance, M.E.; Harter, M.L.; Goodman, R.H. Adenoviral E1A-associated protein p300 as a functional homologue of the transcriptional co-activator CBP. Nature 1995, 374, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogryzko, V.V.; Schiltz, R.L.; Russanova, V.; Howard, B.H.; Nakatani, Y. The transcriptional coactivators p300 and CBP are histone acetyltransferases. Cell 1996, 87, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Balbas, M.A.; Bannister, A.J.; Martin, K.; Haus-Seuffert, P.; Meisterernst, M.; Kouzarides, T. The acetyltransferase activity of CBP stimulates transcription. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 2886–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, T.; Ito, S.; Higashijima, Y.; Chu, W.K.; Neumann, K.; Walter, J.; Satpathy, S.; Liebner, T.; Hamilton, W.B.; Maskey, E.; et al. Enhancers are activated by p300/CBP activity-dependent PIC assembly, RNAPII recruitment, and pause release. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 2166–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlin, J.L.; Nelson, K.M.; Strasser, J.M.; Barsyte-Lovejoy, D.; Szewczyk, M.M.; Organ, S.; Cuellar, M.; Singh, G.; Shrimp, J.H.; Nguyen, N.; et al. Assay interference and off-target liabilities of reported histone acetyltransferase inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinert, B.T.; Narita, T.; Satpathy, S.; Srinivasan, B.; Hansen, B.K.; Schölz, C.; Hamilton, W.B.; Zucconi, B.E.; Wang, W.W.; Liu, W.R.; et al. Time-resolved analysis reveals rapid dynamics and broad scope of the CBP/p300 acetylome. Cell 2018, 174, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasko, L.M.; Jakob, C.G.; Edalji, R.P.; Qiu, W.; Montgomery, D.; Digiammario, E.L.; Hansen, T.M.; Risi, R.M.; Frey, R.; Manaves, V.; et al. Discovery of a selective catalytic p300/CBP inhibitor that targets lineage-specific tumours. Nature 2017, 550, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zegar, T.; Lucas, A.; Morrison-Smith, C.; Knox, T.; French, C.A.; Knapp, S.; Müller, S.; Siveke, J.T. Therapeutic targeting of p300/CBP HAT domain for the treatment of NUT midline carcinoma. Oncogene 2020, 39, 4770–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Bosch, T.; Boichenko, A.; Leus, N.G.J.; Ourailidou, M.E.; Wapenaar, H.; Rotili, D.; Mai, A.; Imhof, A.; Bischoff, R.; Haisma, H.J.; et al. The histone acetyltransferase p300 inhibitor C646 reduces pro-inflammatory gene expression and inhibits histone deacetylases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 102, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.-J.; Yang, S.-H.; Maeda, Y.; Sladek, F.M.; Sharrocks, A.D.; Martins-Green, M. MAP kinase phosphorylation-dependent activation of Elk-1 leads to activation of the co-activator p300. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picaud, S.; Leonards, K.; Lambert, J.-P.; Dovey, O.; Wells, C.; Fedorov, O.; Monteiro, O.; Fujisawa, T.; Wang, C.-Y.; Lingard, H.; et al. Promiscuous targeting of bromodomains by bromosporine identifies BET proteins as master regulator of primary transcription response in leukemia. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucconi, B.E.; Makofske, J.L.; Meyers, D.J.; Hwang, Y.; Wu, M.; Kuroda, M.I.; Cole, P.A. Combination targeting of the bromodomain and acetyltransferase active site of p300/CBP. Biochemistry 2019, 58, 2133–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picaud, S.; Fedorov, O.; Thanasopoulou, A.; Leonards, K.; Jones, K.; Meier, J.; Olzscha, H.; Monteiro, O.; Martin, S.; Philpott, M.; et al. Generation of a selective small inhibitor of the CBP/p300 bromodomain for leukemia therapy. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 5106–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, T.-M.; Kluge, M.; Krebs, S.; Shah, N.; Blum, H.; Friedel, C.C.; Eick, D. Transcriptome analysis of dominant-negative Brd4 mutants identifies Brd4-specific target genes of small molecule inhibitor JQ1. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkina, A.C.; Nikolajczyk, B.S.; Denis, G.V. BET protein function is required for inflammation: Brd2 genetic disruption and BET inhibitor JQ1 impair mouse macrophage inflammatory responses. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3670–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Gong, W. JQ1: A novel potential therapeutic target. Pharmazie 2018, 73, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mumby, S.; Gambaryan, N.; Meng, C.; Perros, F.; Humbert, M.; Wort, S.J.; Adcock, I.M. Bromodomain and extra-terminal domain protein mimic JQ1 decreases inflammation in human vascular endothelial cells: Implications for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respirology 2017, 22, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impey, S.; Fong, A.L.; Wang, Y.; Cardinaux, J.-R.; Fass, D.M.; Obrietan, K.; Wayman, G.A.; Storm, D.R.; Soderling, T.R.; Goodman, R.H. Phosphorylation of CBP mediates transcriptional activation by neural activity and CaM kinase IV. Neuron 2002, 34, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.-C.; Chrivia, J.; Ghosh, A. Regulation of CBP-mediated transcription by neuronal calcium signaling. Neuron 1999, 22, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tang, Y.-A.; Xiao, Q.; Lee, W.C.; Cheng, B.; Niu, Z.; Oguz, G.; Feng, M.; Lee, P.L.; Li, B.; et al. Stromal induction of BRD4 phosphorylation results in chromatin remodeling and BET inhibitor resistance in colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, J.; Milligan, C.J.; Zeng, F.; Jones, C.; Beech, D.J. Production of a specific extracellular inhibitor of TRPM3 channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 155, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, G.; Rössler, O.G. Immediate-early transcriptional response to angiotensin II in human adrenocortical cells. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 4211–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Thiel, G.; Rössler, O.G. Resveratrol stimulates cyclic AMP response element-mediated gene transcription. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thiel, G.; Rössler, O.G. TRPM3-Induced Gene Transcription Is under Epigenetic Control. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070846
Thiel G, Rössler OG. TRPM3-Induced Gene Transcription Is under Epigenetic Control. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(7):846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070846
Chicago/Turabian StyleThiel, Gerald, and Oliver G. Rössler. 2022. "TRPM3-Induced Gene Transcription Is under Epigenetic Control" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 7: 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070846
APA StyleThiel, G., & Rössler, O. G. (2022). TRPM3-Induced Gene Transcription Is under Epigenetic Control. Pharmaceuticals, 15(7), 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070846





