A Comprehensive Review of the Cardiovascular Protective Properties of Silibinin/Silymarin: A New Kid on the Block
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Search Strategy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Description, Physicochemical and Biopharmaceutic Properties of Silibinin, Silymarin’s Main Constituent
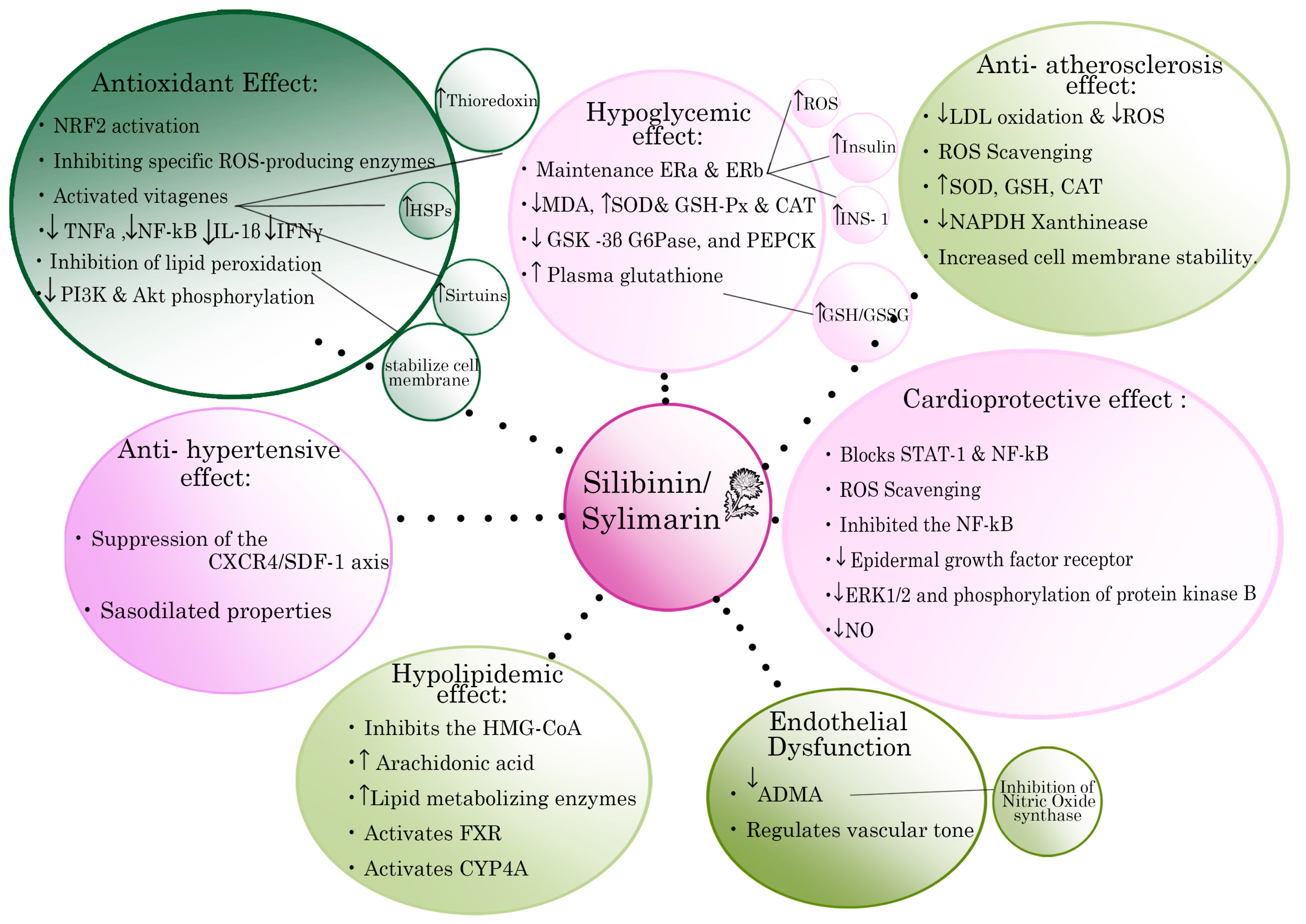
3.2. Antioxidant Actions of Silibinin/Silymarin
3.3. Silibinin/Silymarin in Atherosclerosis and Ischemia
3.4. Silibinin/Silymarin and Metabolic Syndrome (MS)
3.5. Silibinin/Silymarin and Diabetes Mellitus
3.6. Silibinin/Silymarin and Hyperlipidemia
3.7. Silibinin/Silymarin and Hypertension
3.8. Silibinin/Silymarin and Cardiomyopathies
3.9. Silibinin/Silymarin and Cardiovascular Prevention Based on Clinical Studies
| Reference | Total Studies & Cohorts–Dose Range | Study Objectives | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voroneanu, et al., 2016 [55] | 5 RCTs, 270 pts, T2DM Silymarin extract Daily dose 200 and 600 mg | Metabolic parameters, CKD progression, cardiovascular mortality and morbidity | ↓ glycemic indices ↔ lipid profile, indefinite effect on CKD, ↔ cardiovascular mortality, ↓ risk for nonfatal MI (only in intensive treatment) |
| Hadi, et al., 2018 [89] | 7 RCTs, 370 pts, T2DM Silymarin extract Daily dose 200, 420 and 600 mg | Metabolic parameters | ↓ FBG, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ fasting Insulin, ↓ LDL-C, ↑ HDL-C, ↔ TChol, ↔ TG, ↓ MDA |
| Mohammadi, et al., 2018 [90] | 10 RCTs, 620 pts, dyslipidemia Silymarin extract Daily dose range 280 to 2100 mg | Metabolic parameters | ↓ LDL-C, ↓ TG, ↓ TChol, ↑ HDL-C |
| Xiao, et al., 2020 [91] | 15 RCTs & 1 prospective study, 1358 pts, T2DM and/or dyslipidemia Silymarin extract Daily dose range 105 to 1000 mg | Metabolic parameters | ↓ FBG, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ HOMA-IR, ↔ FBI, ↓ LDL-C, ↓ TG, ↓ TChol, ↑ HDL-C, ↓ CRP, ↔ MDA, ↔ ALT, ↔ AST, ↔ CPK, ↔ creatinine, ↔ Phosphokinase |
| Reference | Cohorts | Study Design | Outcomes-Variables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ebrahimpour Koujan, et al., 2015 [92] | 40 pts, T2DM | RCT; Intervention group (20 pts): 140 mg Silymarin orally, 3 times/day, for 45 d Control group (20 pts): placebo | ↑ SOD, ↑ GPX, ↑ TAC, ↓ hs-CRP, ↓ MDA |
| Ebrahimpour-Koujan, et al., 2018 [93] | 40 pts, T2DM, dyslipidemia | RCT; Intervention group (20 pts): 140 mg Silymarin orally, 3 times/day, for 45 d Control group (20 pts): placebo | ↓ FBS, ↓ insulin, ↓ HOMA-IR, ↑ QUICKI, ↓ TG, ↓ TChol, ↑ HDL-C, ↓ LDL-C |
| Hussain SA, et al., 2007 [94] | 51 pts, T2DM | RCT; Group A (18 pts): 200 mg/day Silymarin orally + 10 mg/day oral glibenclamide for 120 d Group B (20 pts): placebo + 10 mg/d oral glibenclamide, for 120 d Group C (control) (21 pts): 10 mg/d glibenclamide | ↓ FBG, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ insulin, ↓ LDL-C, ↓ TG, ↓ TChol, ↓ SGOT, ↓ SGPT, ↓ weight, ↓ SBP ↓ DBP |
| Khalili, et al., 2017 [95] | 60 pts, T2DM | RCT; Intervention group (30 pts): 200 mg Silymarin orally, 3 times/day, for 90 d Control group (30 pts): placebo | ↓ FBG, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ TG, ↓ TChol, ↔ LDL-C, ↔ HDL-C, ↔ SBP, ↔ DBP, ↔ AST, ↔ ALT, ↔ ALP, ↔ BUN, ↔ Creatinine |
| Huseini HF, et al., 2006 [96] | 51 pts, T2DM | RCT; Intervention group (25 pts): 200 mg silymarin orally 3 times/day, for 120 d Control group (26 pts): placebo | ↓ FBG, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ BMI |
| Velussi M., et al., 1997 [97] | 60 pts, insulin-treated DM, liver cirrhosis | Randomized, open, controlled study; Intervention group (30 pts): standard therapy + 200 mg Silymarin orally, 3 times/day, for 360 d Control group (30 pts): standard therapy | ↓ FBG, ↓ glucosuria, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ insulin, ↓ MDA, ↓ C-peptide, ↔ γGT, ↔ ALP ↔ creatinine, ↔ bilirubin, ↔ microalbuminuria, ↓ AST, ↓ ALT, ↓ TChol, ↑ HDL-C, ↑ TG |
| Federico A, et al., 2019 [99] | 90 pts with NAFLD and 60 healthy participants | Prospective study; Intervention group (NAFLD, 60 pts): 1 capsule 2 times/day, for 180 d [capsules: silybin-phospholipid complex (303 mg) of, vitamin D (10 mg), vitamin E (15 mg)]. Control group (NAFLD, 30 pts): no drug Healthy group (60 pts): no drug | ↔ BMI, ↔ weight, ↓ ALT, ↓ γGT, ↔AST, ↓ insulin, ↓ HOMA-IR, ↑ vitamin D, ↓ degree of steatosis ↔ FBG, ↔ TG, ↔ TChol, ↔ LDL-C, ↔ Ferritin |
| Cerletti C, et al., 2020 [100] | RCT, 126 pts, NAFLD | RCT; Intervention group (62 pts): 2 capsules, once a day, for 90 d [capsules: mixture of active ingredients, 70% DHA (250 mg), phosphatidylcholine (150 mg), silymarin (75 mg), choline bitartrate (35 mg), curcumin (35 mg) and D-α-tocopherol (10 mg)] Control group (64 pts): placebo | ↓ AST, ↑ HDL, ↑ LDL, ↑ TChol, ↑ FBG, ↔ weight, ↔ BMI, ↔ waist circumference |
| Sciacqua A, et al., 2019 [102] | 50 pts, Hypertension | Pilot, single arm, interventional, longitudinal study. Dose: 3 g Silibinin, twice a day (Silibinin conjugated to vit E and phosphatidylcholine–oral solution) | ↓ TChol, ↓ TG, ↑ HDL-C, ↓insulin, ↓ FBG, ↓ HOMA-IR, ↑IGF-1, ↑ eGFR, ↓ CRP, ↓ UA, ↓liver enzymes, ↓ SBP, ↓ Pulmonary pressure |
| Alkuraishy, et al., 2012 [103] | 20 pts, Dyslipidemia | RCT; Intervention group (10 pts): 600 mg silymarin orally, once/day, for 14 d Control group (10 pts): placebo | ↓ TChol, ↓ TG, ↑ HDL-C, ↓ LDL-C, ↓ VLDL |
| Altaei T, et al., 2012 [104] | 102, CABG | Prospective study; Intervention group (50 pts): 140 mg silymarin orally, 3 times/day, 3 d before surgery Control group (52 pts): no drug | ↓ cytokine concentrations (IL-6, IL-1a, TNF-a), ↓ CRP, ↑ GSH, ↑ TEAC, ↓ MDA |
| Roozbeh J, et al., 2011 [105] | 80, ESRD, DM, Hypertension | Prospective study; Group 1 (20 pts): 140 mg silymarin, orally, 3 times/day, for 90 d Group 2 (20 pts): vitamin E 400 IU/day, for 90 dGroup 3 (20 pts): 140 mg silymarin, orally, 3 times/day + vit E 400 IU/day, for 90 d Group 4, control (20 pts): no drug | ↑ GPX, ↓ MDA, ↑ mean hemoglobin (all three treatment groups VS control) |
| Firuzi O, et al., 2016 [106] | 60, ESRD | RCT; Intervention group (28 pts): 140 mg silymarin orally, 4 times/day, for 60 d Control group (22 pts): placebo | ↓ FRAP, ↑ Hemoglobin, ↑ serum albumin, ↔ creatinine, ↔ iPF2a |
| Voroneanu L, et al., 2017 [107] | 102, T2DM, Proteinuria, (ischemic heart disease) | RCT; Intervention group (51 pts): 150 mg silymarin, orally, 3 times/day, for 2 years (720 d) Control group (51 pts): placebo | ↔ mortality ↔ progression of CKD indefinite effect on eGFR and proteinuria |
4. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, L.; Davis, M.; Elgendy, I.; Epps, K.; Lindley, K.J.; Mehta, P.K.; Volgman, A.S. Summary of updated recommendations for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in women: JACC state-of-the-art review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 2602–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadoglou, N.P.; Iliadis, F.; Sailer, N.; Athanasiadou, Z.; Vitta, I.; Kapelouzou, A.; Karayannacos, P.E.; Liapis, C.D.; Alevizos, M.; Angelopoulou, N.; et al. Exercise training ameliorates the effects of rosiglitazone on traditional and novel cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2010, 59, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadoglou, N.P.; Sfyroeras, G.S.; Spathis, A.; Gkekas, C.; Gastounioti, A.; Mantas, G.; Nikita, K.S.; Karakitsos, P.; Liapis, C.D. Galectin-3, Carotid Plaque Vulnerability, and Potential Effects of Statin Therapy. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2015, 49, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumgartner, S.; Bruckert, E.; Gallo, A.; Plat, J. The position of functional foods and supplements with a serum LDL-C lowering effect in the spectrum ranging from universal to care-related CVD risk management. Atherosclerosis 2020, 311, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Christodoulou, E.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Valsami, G. The cardiovascular-protective properties of saffron and its potential pharmaceutical applications: A critical appraisal of the literature. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 6735–6753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatakrishnan, K.; Chiu, H.F.; Wang, C.K. Impact of functional foods and nutraceuticals on high blood pressure with a special focus on meta-analysis: Review from a public health perspective. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 2792–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Risi, R.; Masi, D.; Caputi, A.; Balena, A.; Rossini, G.; Tuccinardi, D.; Mariani, S.; Basciani, S.; Manfrini, S.; et al. Current Evidence to Propose Different Food Supplements for Weight Loss: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post-White, J.; Ladas, E.J. Advances in the use of milk thistle (Silybum marianum). Integr. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaroucha, A.K.; Valsami, G.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Lambropoulou, M.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Christodoulou, E.; Falidas, E.; Betsou, A.; Pitiakoudis, M.; Simopoulos, C.E. Silibinin Effect on Fas/FasL, HMGB1, and CD45 Expressions in a Rat Model Subjected to Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. J. Investig. Surg. 2018, 31, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaroucha, A.; Korovesis, G.N.; Valsami, G.; Lambropoulou, M.; Kollaras, V.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Zerbini, E.; Simopoulos, C. Silibinin-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (SLB-HP-β-CD) complex prevents apoptosis in liver and kidney after hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betsou, A.; Lambropoulou, M.; Georgakopoulou, A.-E.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Konstandi, O.; Anagnostopoulos, K.; Tsalikidis, C.; Simopoulos, C.; Valsami, G.; Tsaroucha, A. The hepatoprotective effect of silibinin after hepatic ischemia/reperfusion in a rat model is confirmed by immunohistochemistry and qRT-PCR. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2021, 73, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakopoulos, G.; Lambropoulou, M.; Valsami, G.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Konstandi, O.; Anagnostopoulos, K.; Tsalikidis, C.; Oikonomou, P.; Simopoulos, C.; Tsaroucha, A. Pro-inflammatory cytokines/chemokines, TNFα, IL-6 and MCP-1, as biomarkers for the nephro- and pneumoprotective effect of silibinin after hepatic ischemia/reperfusion: Confirmation by immunihistochemistry and qRT-PCR. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2022, 130, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, C.W.; Gibbons, N. Silibinin-a promising new treatment for cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CheBI. Available online: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI:9144 (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Silibinin (accessed on 9 October 2021).
- Elwekeel, A.; Elfishway, A.; AbouZid, S. Enhanced accumulation of flavonolignans in Silybum marianum cultured roots by methyl jasmonate. Phytochem. Lett. 2012, 5, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althagafy, H.S.; Meza-Avina, M.E.; Oberlies, N.H.; Croatt, M.P. Mechanistic study of the biomimetic synthesis of flavonolignan diastereoisomers in milk thistle. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 7594–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biedermann, D.; Vavrikova, E.; Cvak, L.; Kren, V. Chemistry of silybin. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 1138–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wenum, E.; Jurczakowski, R.; Litwinienko, G. Media effects on the mechanism of antioxidant action of silybin and 2,3-dehydrosilybin: Role of the enol group. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 9102–9112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.C.; Zhu, J.J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.L.; Huang, C.G. Solubility of silybin in aqueous hydrochloric acid solution. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2007, 254, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellici, T.F.; Ntountaniotis, D.; Leonis, G.; Chatziathanasiadou, M.; Chatzikon-stantinou, A.V.; Becker-Baldus, J.; Glaubitz, C.; Tzakos, A.G.; Viras, K.; Chatzigeorgiou, P.; et al. Investigation of the Interactions of Silibinin with 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin through Biophysical Techniques and Computational Methods. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.X.; Amidon, G.L.; Polli, J.E.; Zhao, H.; Mehta, M.U.; Conner, D.P.; Shah, V.P.; Lesko, L.J.; Chen, M.L.; Lee, V.H.; et al. Biopharmaceutics classification system: The scientific basis for biowaiver extensions. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waiver of In Vivo Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Studies for Immediate-Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms Based on a Biopharmaceutics Classification System Guidance for Industry; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER): Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2017.
- EMA. Guideline on the Investigation of Bioequivalence; (CPMP/EWP/QWP/1401/98 Rev. 1/Corr **); European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann, S.; Almukainzi, M.; Bou-Chacra, N.A.; Amidon, G.L.; Lee, B.-J.; Feng, J.; Kanfer, I.; Zuo, J.Z.; Wei, H.; Bolger, M.B.; et al. Provisional biopharmaceutical classification of some common herbs used in western medicine. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milić, N.; Milosević, N.; Suvajdzić, L.; Zarkov, M.; Abenavoli, L. New therapeutic potentials of milk thistle (Silybum marianum). Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Surai, P.F. Silymarin as a Natural Antioxidant: An Overview of the Current Evidence and Perspectives. Antioxidants 2015, 20, 204–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillessen, A.; Schmidt, H.H. Silymarin as Supportive Treatment in Liver Diseases: A Narrative Review. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 1279–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Federico, A.; Dallio, M. Silymarin/Silybin and Chronic Liver Disease: A Marriage of Many Years. Molecules 2017, 22, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radjabian, T.; Huseini, H.F. Anti-hyperlipidemic and anti-atherosclerotic activities of silymarins from cultivated and wild plants of Silybum marianum L. with different content of flavonolignans. Iran. J. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 9, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, Q. Silibinin augments the effect of clopidogrel on atherosclerosis in diabetic ApoE deficiency mice. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2022, 80, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, R.; Keaney, J.F., Jr. Role of oxidative modifications in atherosclerosis. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1381–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekmohammad, K.; Sewell, R.D.E. Antioxidants and Atherosclerosis: Mechanistic Aspects. Biomolecules 2019, 25, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Y.; Zhao, X. Modulatory effect of silymarin on pulmonary vascular dysfunction through HIF-1α-iNOS following rat lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demirci, B.; Dost, T. Silymarin improves vascular function of aged ovariectomized rats. Phytother. Res. 2013, 8, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volti, G.L.; Salomone, S. Effect of silibinin on endothelial dysfunction and ADMA levels in obese diabetic mice. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2011, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.-K.; Hong, Y.-J. Protective effects of silybin on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury induced by H2O2 in vitro. Vasc. Pharm. 2005, 43, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleb, A.; Ahmad, K.A. Antioxidant effects and mechanism of silymarin in oxidative stress induced cardiovascular diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Lin, H. Protective role of silibinin against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced cardiac dysfunction. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1972–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.R.; Viswanath, R.K. Cardioprotective activity of silymarin in ischemia-reperfusion-induced myocardial infarction in albino rats. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2007, 12, 179. [Google Scholar]
- Tajmohammadi, A.; Razavi, B.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Silybum marianum (milk thistle) and its main constituent, silymarin, as a potential therapeutic plant in metabolic syndrome: A review. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 1933–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, M.; Bennati, E.; Cardillo, E.; Passamonte, M.; Ferlito, L.; Malaguarnera, M. The metabolic syndrome (MS) in the elderly: Considerations on the diagnostic criteria of the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and some proposed modifications. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2009, 48, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C.; et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Poruba, M.; Matušková, Z.; Kazdová, L.; Oliyarnyk, O.; Malínská, H.; di Angelo, I.T.; Večeřa, R. Positive effects of different drug forms of silybin in the treatment of metabolic syndrome. Physiol. Res. 2015, 64, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poruba, M.; Kazdová, L.; Oliyarnyk, O.; Malinská, H.; Matusková, Z.; di Angelo, I.T.; Skop, V.; Vecera, R. Improvement bioavailability of silymarin ameliorates severe dyslipidemia associated with metabolic syndrome. Xenobiotica 2015, 45, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.H.; Alex, R.; Bellner, L.; Raffaele, M.; Licari, M.; Vanella, L.; Stec, D.E.; Abraham, N.G. Milk thistle seed cold press oil attenuates markers of the metabolic syndrome in a mouse model of dietary-induced obesity. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, 13522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouderba, S.; Sanchez-Martin, C.; Villanueva, G.R.; Detaille, D.; Koceïr, E.A. Beneficial effects of silibinin against the progression of metabolic syndrome, increased oxidative stress, and liver steatosis in Psammomys obesus, a relevant animal model of human obesity and diabetes. J. Diabetes 2014, 6, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marková, I.; Malínská, H.; Hüttl, M.; Miklánková, D.; Oliyarnyk, O.; Poruba, M.; Rácová, Z.; Kazdová, L.; Večeřa, R. The combination of atorvastatin with silymarin enhances hypolipidemic, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in a rat model of metabolic syndrome. Physiol. Res. 2021, 17, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazzini, V.; Micheli, L.; Luceri, C.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Cinci, L.; Ghelardini, C.; Bilia, A.R.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Bergonzi, M.C. Nanostructured lipid carriers for oral delivery of silymarin: Improving its absorption and in vivo efficacy in type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome model. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 572, 118838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, P.; Singh, V.; Jain, M.; Rana, M.; Khanna, V.; Barthwal, M.K.; Dikshit, M. Silymarin ameliorates fructose induced insulin resistance syndrome by reducing de novo hepatic lipogenesis in the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 727, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.F.; Zhou, F.; Lv, Y.Z.; Hu, Q.H.; Zhang, D.M.; Kong, L.D. Hypouricemic action of selected flavonoids in mice: Structure-activity relationships. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, M.D.; Siegel, L.B.; Alloway, J.A. Gout and hyperuricemia. Am. Fam. Physician 1999, 59, 925–934. [Google Scholar]
- Corry, D.B.; Tuck, M.L. Uric acid and the vasculature. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2006, 8, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Voroneanu, L.; Nistor, I.; Dumea, R.; Apetrii, M.; Covic, A. Silymarin in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 5147468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, C.; Gao, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, R.; Jia, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, D.; Xu, F. Involvement of Estrogen Receptor-α in the Activation of Nrf2-Antioxidative Signaling Pathways by Silibinin in Pancreatic β-Cells. Biomol. Ther. 2020, 1, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheela, N.; Jose, M.A.; Sathyamurthy, D.; Kumar, B.N. Effect of silymarin on streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced type 2 diabetic nephropathy in rats. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 7, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soto, C.P.; Perez, B.L.; Favari, L.P.; Reyes, J.L. Prevention of alloxan-induced diabetes mellitus in the rat by silymarin. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1998, 119, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuorkey, M.J.; El-Desouki, N.I.; Kamel, R.A. Cytoprotective effect of silymarin against diabetes-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis in diabetic rats. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Yang, J.; Negishi, H.; Sun, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Hayashi, T.; Gao, M.; Ikeda, K.; Ikejima, T. Silibinin decreases hepatic glucose production through the activation of gut-brain-liver axis in diabetic rats. Food Funct. 2018, 19, 4926–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Zhao, P.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, S.; Ma, Y.M.; Tong, Q.; et al. Silymarin Ameliorates Metabolic Dysfunction Associated with Diet-Induced Obesity via Activation of Farnesyl X Receptor. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Xu, F.; Liu, W.; Hayashi, T.; Onodera, S.; Tashiro, S.I.; Ikejima, T. Involvement of estrogen receptors in silibinin protection of pancreatic β-cells from TNFα- or IL-1β-induced cytotoxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.M.O.; Agostini, L.D.C.; Lima, W.G.; Camini, F.C.; Costa, D.C. Silymarin Attenuates Hepatic and Pancreatic Redox Imbalance Independent of Glycemic Regulation in the Alloxan-induced Diabetic Rat Model. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 690–700. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Dai, W.; Ye, S. Silibinin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy via improving diabetic condition in the mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 845, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, C.; Recoba, R.; Barrón, H.; Alvarez, C.; Favari, L. Silymarin increases antioxidant enzymes in alloxan-induced diabetes in rat pancreas. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 136, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, H.; Manouchehri, H.; Changizi, R.; Bootorabi, F.; Khorramizadeh, M.R. Concurrent metformin and silibinin therapy in diabetes: Assessments in zebrafish (Danio rerio) animal model. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2020, 19, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malekinejad, H.; Rezabakhsh, A.; Rahmani, F.; Hobbenaghi, R. Silymarin regulates the cytochrome P450 3A2 and glutathione peroxides in the liver of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, G.; Elinos-Báez, C.M.; Jagan, S.; Augustine, T.A.; Kamaraj, S.; Anandakumar, P.; Devaki, T. Silymarin downregulates COX-2 expression and attenuates hyperlipidemia during NDEA-induced rat hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 313, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobalakrishnan, S.; Asirvatham, S.S.; Janarthanam, V. Effect of Silybin on Lipid Profile in Hypercholesterolaemic Rats. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, FF01–FF05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Chen, S.C.; Zhang, T.H.; Tian, H.C.; Guan, Y.; Su, D.F. Protective effects of silybin and tetrandrine on the outcome of spontaneously hypertensive rats subjected to acute coronary artery occlusion. Int. J. Cardiol. 1993, 41, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Kawaguchi, N.; Yoshihara, K.; Hayama, E.; Furutani, Y.; Kawaguchi, K.; Tanaka, T.; Nakanishi, T. Silibinin efficacy in a rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension using monocrotaline and chronic hypoxia. Respir. Res. 2019, 25, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Kawaguchi, N.; Tsuji, K.; Hayama, E.; Furutani, Y.; Sugiyama, H.; Nakanishi, T. Silibinin Upregulates CXCR4 Expression in Cultured Bone Marrow Cells (BMCs) Especially in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Rat Model. Cells 2020, 21, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, N.; Zhang, T.T.; Nakanishi, T. Involvement of CXCR4 in Normal and Abnormal Development. Cells 2019, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Wu, P.; Huang, F.; Xu, M.; Chen, M.; Huang, K.; Li, G.P.; Xu, M.; Yao, D.; Wang, L. Baicalin attenuates chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension via adenosine A2A receptor-induced SDF-1/CXCR4/PI3K/AKT signaling. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Hales, C.A. Effect of chemokine receptor CXCR4 on hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension and vascular remodeling in rats. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, S.; Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xian, H.; Che, H.; Wang, L. Silymarin ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad signaling. Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anestopoulos, I.; Kavo, A.; Tentes, I.; Kortsaris, A.; Panayiotidis, M.; Lazou, A.; Pappa, A. Silibinin protects H9c2 cardiac cells from oxidative stress and inhibits phenylephrine-induced hypertrophy: Potential mechanisms. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kubalak, S.W.; Minamisawa, S.; Price, R.L.; Becker, K.D.; Hickey, R.; Ross, J.; Chien, K.R. Selective Requirement of Myosin Light Chain 2v in Embryonic Heart Function. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Song, T.; Jia, Y.; Qi, L.; Ren, L.; Chen, S. Proteomics study on the effect of silybin on cardiomyopathy in obese mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzarotto, F.; Tayal, U.; Buchan, R.J.; Midwinter, W.; Wilk, A.; Whiffin, N.; Govind, R.; Mazaika, E.; de Marvao, A.; Dawes, T.J.; et al. Reevaluating the Genetic Contribution of Monogenic Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2020, 141, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ingles, J.; Goldstein, J.; Thaxton, C.; Caleshu, C.; Corty, E.W.; Crowley, S.B.; Dougherty, K.; Harrison, S.M.; McGlaughon, J.; Milko, L.V.; et al. Evaluating the Clinical Validity of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Genes. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2019, 12, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raschi, E.; Vasina, V.; Ursino, M.G.; Boriani, G.; Martoni, A.; De Ponti, F. Anticancer drugs and cardiotoxicity: Insights and perspectives in the era of targeted therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 125, 196–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psotová, J.; Chlopčíková, Š.; Grambal, F.; Šimánek, V.; Ulrichova, J. Influence of silymarin and its flavonolignans on doxorubicin-iron induced lipid peroxidation in rat heart microsomes and mitochondria in comparison with quercetin. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlopcikova, S.; Psotová, P.; Miketová, P.; Simánek, V. Chemoprotective Effect of plant phenolics against anthracycline-induced toxicity on rat cardiomyocytes. Phytother. Res. 2004, 18, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rašković, A.; Stilinovic, N.; Kolarović, J.; Vasović, V.; Vukmirović, S.; Mikov, M. The protective effects of silymarin against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and hepatotoxicity in rats. Molecules 2011, 16, 8601–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razavi, B.M.; Karimi, G. Protective effect of silymarin against chemical-induced cardiotoxicity. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2016, 19, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Awady, E.S.E.; Moustafa, Y.M. Cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity: Mechanisms and cardioprotective strategies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 650, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shitany, N.A.; El-Haggar, S. Silymarin prevents adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2422–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi, A.; Pourmasoumi, M.; Mohammadi, H.; Symonds, M.; Miraghajani, M. The effects of silymarin supplementation on metabolic status and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2018, 41, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, H.; Hadi, A.; Arab, A.; Moradi, S.; Rouhani, M.H. Effects of silymarin supplementation on blood lipids: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Gao, F.; Zhou, S.; Wang, L. The therapeutic effects of silymarin for patients with glucose/lipid metabolic dysfunction: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 2, e22249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimpour-Koujan, S.; Gargari, B.P.; Mobasseri, M.; Valizadeh, H.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M. Effects of Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn. (silymarin) extract supplementation on antioxidant status and hs-CRP in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytomedicine 2015, 15, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimpour-Koujan, S.; Gargari, B.P.; Mobasseri, M.; Valizadeh, H.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M. Lower glycemic indices and lipid profile among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients who received novel dose of Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn. (silymarin) extract supplement: A Triple-blinded randomized controlled clinical trial. Phytomedicine 2018, 15, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.A. Silymarin as an adjunct to glibenclamide therapy improves long-term and postprandial glycemic control and body mass index in type 2 diabetes. J. Med. Food 2007, 10, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, N.; Fereydoonzadeh, R.; Mohtashami, R.; Mehrzadi, S.; Heydari, M.; Huseini, H.F. Silymarin, Olibanum, and Nettle, A Mixed Herbal Formulation in the Treatment of Type II Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Clinical Trial. J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 22, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseini, H.F.; Larijani, B.; Heshmat, R.; Fakhrzadeh, H.; Radjabipour, B.; Toliat, T.; Raza, M. The efficacy of Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn. (silymarin) in the treatment of type II diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Phytother. Res. 2006, 20, 1036–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velussi, M.; Cernigoi, A.M.; De Monte, A.; Dapas, F.; Caffau, C.; Zilli, M. Long-term (12 months) treatment with an anti-oxidant drug (silymarin) is effective on hyperinsulinemia, exogenous insulin need and malondialdehyde levels in cirrhotic diabetic patients. J. Hepatol. 1997, 26, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saller, R.; Meier, R.; Brignoli, R. The use of silymarin in the treatment of liver diseases. Drugs 2001, 61, 2035–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federico, A.; Dallio, M.; Masarone, M.; Gravina, A.G.; Di Sarno, R.; Tuccillo, C.; Cossiga, V.; Lama, S.; Stiuso, P.; Morisco, F.; et al. Evaluation of the Effect Derived from Silybin with Vitamin D and Vitamin E Administration on Clinical, Metabolic, Endothelial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress Parameters, and Serological Worsening Markers in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 15, 8742075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerletti, C.; Colucci, M.; Storto, M.; Semeraro, F.; Ammollo, C.T.; Incampo, F.; Costanzo, S.; De Bartolomeo, G.; Portincasa, P.; Barone, M.; et al. Randomised trial of chronic supplementation with a nutraceutical mixture in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 123, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lirussi, F.; Beccarello, A.; Zanette, G.; De Monte, A.; Donadon, V.; Velussi, M.; Crepaldi, G. Silybin-beta-cyclodextrin in the treatment of patients with diabetes mellitus and alcoholic liver disease. Efficacy study of a new preparation of an anti-oxidant agent. Diabetes Nutr. Metab. 2002, 15, 222–231. [Google Scholar]
- Sciacqua, A.; Perticone, M.; Tripepi, G.; Addesi, D.; Cassano, V.; Maio, R.; Sesti, G.; Perticone, F. Metabolic and vascular effects of silybin in hypertensive patients with high 1-h post-load plasma glucose. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2019, 14, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkuraishy, H.M.; Alwindy, S. Beneficial Effects of Silymarin on Lipid Profile in Hyperlipidemic Patients: Placebo Controlled Clinical Trail. WebmedCentral Pharmacol. 2012, 3, WMC002966. [Google Scholar]
- Altaei, T. Protective effect of silymarin during coronary artery bypass grafting surgery. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2012, 17, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Roozbeh, J.; Shahriyari, B.; Akmali, M.; Vessal, G.; Pakfetrat, M.; Jalali, G.A.R.; Afshariani, R.; Hasheminasab, M.; Ghahramani, N. Comparative effects of silymarin and vitamin E supplementation on oxidative stress markers, and hemoglobin levels among patients on hemodialysis. Ren. Fail. 2011, 33, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firuzi, O.; Khajehrezaei, S.; Ezzatzadegan, S.; Nejati, M.; Jahanshahi, K.A.; Roozbeh, J. Effects of silymarin on biochemical and oxidative stress markers in end-stage renal disease patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis. Hemodial. Int. 2016, 20, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voroneanu, L.; Siriopol, D.; Dumea, R.; Badarau, S.; Kanbay, M.; Afsar, B.; Gavrilovici, C.; Covic, A. Addition of silymarin to renin-angiotensin system blockers in normotensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and proteinuria: A prospective randomized trial. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2017, 49, 2195–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallahzadeh, M.K.; Dormanesh, B.; Sagheb, M.M.; Roozbeh, J.; Vessal, G.; Pakfetrat, M.; Daneshbod, Y.; Kamali-Sarvestani, E.; Lankarani, K.B. Effect of addition of silymarin to renin-angiotensin system inhibitors on proteinuria in type 2 diabetic patients with overt nephropathy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 60, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asgharpour, M.; Alirezaei, A. Herbal antioxidants in dialysis patients: A review of potential mechanisms and medical implications. Ren. Fail. 2021, 43, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyhenmeyer, R.; Mascher, H.; Birkmayer, J. Study on dose-linearity of the pharmacokinetics of silibinin diastereomers using a new stereospecific assay. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol. 1992, 30, 134–138. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.; Dumas, T.E.; Schrieber, S.J.; Hawke, R.L.; Fried, M.W.; Smith, P.C. Pharmacokinetics and Metabolic Profile of Free, Conjugated, and Total Silymarin Flavonolignans in Human Plasma after Oral Administration of Milk Thistle Extract. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2008, 36, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sornsuvit, C.; Hongwiset, D.; Yotsawimonwat, S.; Toonkum, M.; Thongsawat, S.; Taesotikul, W. The Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics of Silymarin SMEDDS Formulation Study in Healthy Thai Volunteers. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 1507834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Panayiotou, C.; Vardas, M.; Balaskas, N.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.G.; Tsaroucha, A.K.; Valsami, G. A Comprehensive Review of the Cardiovascular Protective Properties of Silibinin/Silymarin: A New Kid on the Block. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050538
Kadoglou NPE, Panayiotou C, Vardas M, Balaskas N, Kostomitsopoulos NG, Tsaroucha AK, Valsami G. A Comprehensive Review of the Cardiovascular Protective Properties of Silibinin/Silymarin: A New Kid on the Block. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(5):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050538
Chicago/Turabian StyleKadoglou, Nikolaos P. E., Chrystalla Panayiotou, Michail Vardas, Nikolaos Balaskas, Nikolaos G. Kostomitsopoulos, Alexandra K. Tsaroucha, and Georgia Valsami. 2022. "A Comprehensive Review of the Cardiovascular Protective Properties of Silibinin/Silymarin: A New Kid on the Block" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 5: 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050538
APA StyleKadoglou, N. P. E., Panayiotou, C., Vardas, M., Balaskas, N., Kostomitsopoulos, N. G., Tsaroucha, A. K., & Valsami, G. (2022). A Comprehensive Review of the Cardiovascular Protective Properties of Silibinin/Silymarin: A New Kid on the Block. Pharmaceuticals, 15(5), 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050538








