Encapsulation of Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Functional Hybrid Liposomes: Promising Tool for the Reduction of Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
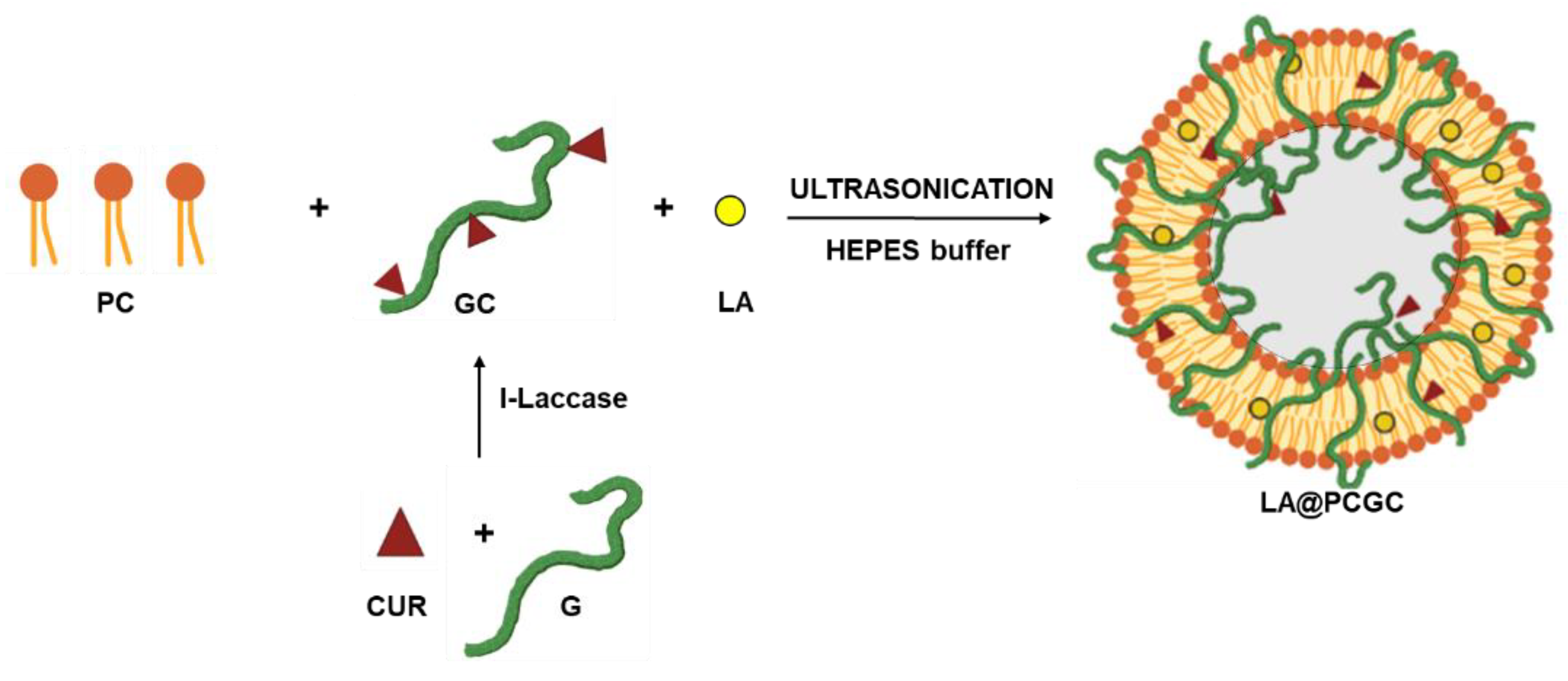
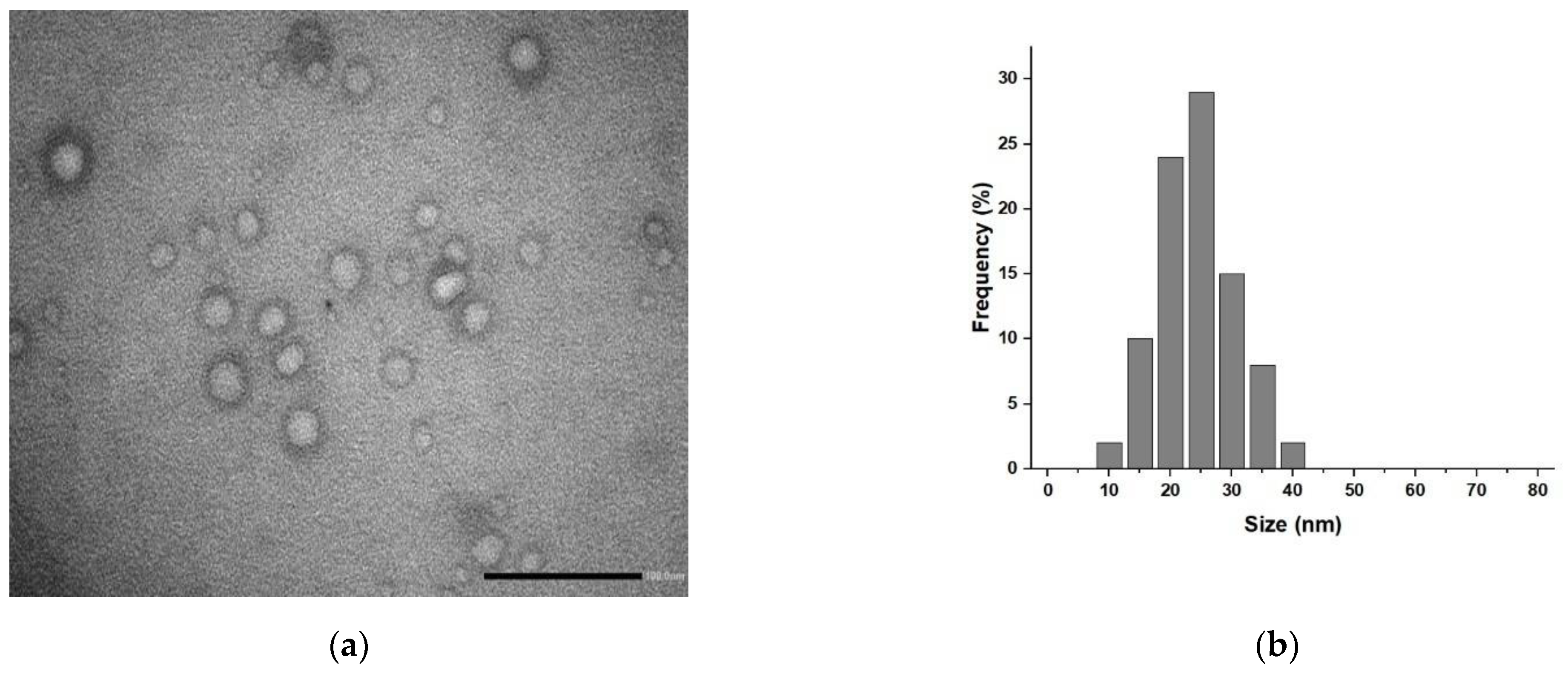
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Hybrid Liposomes
2.2. Biological Characterization
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Hybrid Liposomes Preparation and Characterization
3.2. Release Experiments
3.3. Cell Culture
3.4. Viability Experiments
3.5. Confocal Microscopy Analysis
3.6. Hydrogel Formulation
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheth, S.; Mukherjea, D.; Rybak, L.P.; Ramkumar, V. Mechanisms of Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity and Otoprotection. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, L.P.; Mukherjea, D.; Jajoo, S.; Ramkumar, V. Cisplatin Ototoxicity and Protection: Clinical and Experimental Studies. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2009, 219, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, B.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, M.A.; Ryu, N.; Jung, D.J.; Kim, U.K.; Baek, J.I.; Lee, K.Y. Evaluating protective and therapeutic effects of alpha-lipoic acid on cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasawa, T.; Steyger, P.S. An integrated view of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 237, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellinger, J.; Holzinger, D.; Pollard, R. Mental health of deaf people. Lancet 2012, 379, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lippard, S.J. Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, A.-M.; Büsselberg, D. Cisplatin as an Anti-Tumor Drug: Cellular Mechanisms of Activity, Drug Resistance and Induced Side Effects. Cancers 2011, 3, 1351–1371. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.G.; Chen, Y.Y.; Dubrulle, J.; Stossi, F.; Putluri, V.; Sreekumar, A.; Putluri, N.; Baluya, D.; Lai, S.Y.; Sandulache, V.C. Cisplatin generates oxidative stress which is accompanied by rapid shifts in central carbon metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, C.; Zhu, W.; Li, X.; Chen, T.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, T.-C.; Ma, W. Chemotherapeutic drugs induce oxidative stress associated with DNA repair and metabolism modulation. Life Sci. 2022, 289, 120242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.H.; Gu, J.Y.; Chen, Y.M.; Kang, W.; Wang, X.L.; Wu, H. Current Strategies to Combat Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortot, B.; Mongiat, M.; Valencic, E.; Dal Monego, S.; Licastro, D.; Crosera, M.; Adami, G.; Rampazzo, E.; Ricci, G.; Romano, F.; et al. Nanotechnology-Based Cisplatin Intracellular Delivery to Enhance Chemo-Sensitivity of Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 4793–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.M.; Zhu, W.Y.; Huang, X.S.; Yu, Y.J.; Xiao, H.H.; Jin, L.J.; Pu, J.Y.J.; Xie, X.; She, J.C.; Lui, V.W.Y.; et al. Microneedles loaded with anti-PD-1-cisplatin nanoparticles for synergistic cancer immuno-chemotherapy. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 18885–18898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Paciello, F.; Mezzogori, D.; Rolesi, R.; Eramo, S.L.M.; Paludetti, G.; Troiani, D. Molecular targets for anticancer redox chemotherapy and cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: The role of curcumin on pSTAT3 and Nrf-2 signalling. Brit. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, E.R.; Youn, C.K.; Jun, Y.; Cho, S.I. The protective role of ferulic acid against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhi. 2019, 120, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Choi, Y.; Kim, M.H.; Kang, I.C.; Lee, J.H.; Park, C.; Park, R.; Kim, H.M. Rosmarinic Acid, Active Component of Dansam-Eum Attenuates Ototoxicity of Cochlear Hair Cells through Blockage of Caspase-1 Activity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, L.P.; Whitworth, C.A.; Mukherjea, D.; Rarakumar, V. Mechanisms of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity and prevention. Hear. Res. 2007, 226, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Wang, X.R.; Jin, H.; Mi, Y.J.; Liu, L.F.; Dong, M.Y.; Chen, Y.B.; Zou, Z.Z. Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: Updates on molecular mechanisms and otoprotective strategies. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 163, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, R.; Momtazi, A.A.; Monemi, A.; Sahebkar, A. Curcumin: A potentially powerful tool to reverse cisplatin-induced toxicity. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 117, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goraca, A.; Huk-Kolega, H.; Piechota, A.; Kleniewska, P.; Ciejka, E.; Skibska, B. Lipoic acid-biological activity and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Rep. 2011, 63, 849–858. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Cho, H.J.; Sagong, B.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.T.; So, H.S.; Lee, I.K.; Kim, U.K.; Lee, K.Y.; Choo, Y.S. Alpha-lipoic acid protects against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity via the regulation of MAPKs and proinflammatory cytokines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 449, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, D.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.; Chang, J.; Jung, H.H.; Im, G.J. Comparison of the effects of lipoic acid and glutathione against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in auditory cells. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhi. 2016, 91, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, L.; Ghibu, S.; Richard, C.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Direct and indirect antioxidant properties of alpha-lipoic acid and therapeutic potential. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochette, L.; Ghibu, S.; Muresan, A.; Vergely, C. Alpha-lipoic acid: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential in diabetes. Can. J. Physiol. Pharm. 2015, 93, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molz, P.; Schroder, N. Potential Therapeutic Effects of Lipoic Acid on Memory Deficits Related to Aging and Neurodegeneration. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Beshbishy, H.A.; Bahashwan, S.A.; Aly, H.A.A.; Fakher, H.A. Abrogation of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice by alpha lipoic acid through ameliorating oxidative stress and enhancing gene expression of antioxidant enzymes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 668, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Jung, S.Y.; Yang, K.J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, D.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, D.K. alpha-Lipoic acid prevents against cisplatin cytotoxicity via activation of the NRF2/HO-1 antioxidant pathway. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, L.P.; Husain, K.; Whitworth, C.; Somani, S.M. Dose dependent protection by lipoic acid against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in rats: Antioxidant defense system. Toxicol. Sci. 1999, 47, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shchelkogonov, V.A.; Alyaseva, S.O.; Lotosh, N.Y.; Baranova, O.A.; Chekanov, A.V.; Solov’eva, E.Y.; Kamyshinskii, R.A.; Vasilov, R.G.; Shastina, N.S.; Korepanova, E.A.; et al. Lipoic acid nanoforms based on phosphatidylcholine: Production and characteristics. Eur. Biophys. J. Biophy. 2020, 49, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadinoto, K.; Sundaresan, A.; Cheow, W.S. Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a new generation therapeutic delivery platform: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabizon, A.; Amitay, Y.; Tzemach, D.; Gorin, J.; Shmeeda, H.; Zalipsky, S. Therapeutic efficacy of a lipid-based prodrug of mitomycin C in pegylated liposomes: Studies with human gastro-entero-pancreatic ectopic tumor models. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Waters, A.K.; Kalyan, P.; Achrol, A.S.; Kesari, S.; Yenugonda, V.M. Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a next-generation drug delivery platform: State of the art, emerging technologies, and perspectives. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1937–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, F.; Gigli, G.; Leporatti, S. Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles in cancer therapy: Current overview and future directions. Nano Express 2021, 2, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborova, O.V.; Filippov, S.K.; Chytil, P.; Kovacik, L.; Ulbrich, K.; Yaroslavov, A.A.; Etrych, T. A Novel Approach to Increase the Stability of Liposomal Containers via In Prep Coating by Poly[N-(2-Hydroxypropyl)Methacrylamide] with Covalently Attached Cholesterol Groups. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2018, 219, 1700508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borandeh, S.; van Bochove, B.; Teotia, A.; Seppala, J. Polymeric drug delivery systems by additive manufacturing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 173, 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macha, I.J.; Ben-Nissan, B.; Vilchevskaya, E.N.; Morozova, A.S.; Abali, B.E.; Muller, W.H.; Rickert, W. Drug Delivery From Polymer-Based Nanopharmaceuticals-An Experimental Study Complemented by Simulations of Selected Diffusion Processes. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraveas, C.; Bayer, I.S.; Bartzanas, T. Recent Advances in Antioxidant Polymers: From Sustainable and Natural Monomers to Synthesis and Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, S.K.; Domnina, N.; Vol’eva, V. Future and the past of polymeric antioxidants. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 2655–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinec, G.; Thein, P.; Park, C.; Kalinec, F. HEI-OC1 cells as a model for investigating drug cytotoxicity. Hear. Res. 2016, 335, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaudoin, C.; Carré, F.; Gehrke, M.; Sogaldi, A.; Steinmetz, V.; Hue, N.; Cailleau, C.; Tourrel, G.; Nguyen, Y.; Ferrary, E.; et al. Transtympanic injection of a liposomal gel loaded with N-acetyl-L-cysteine: A relevant strategy to prevent damage induced by cochlear implantation in guinea pigs? Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 604, 120757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, M.J.D.; Navarro, A.S. Liposomes Prepared in Absence of Organic Solvents: Sonication Versus Lipid Film Hydration Method. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2015, 11, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Luca, M.; Curcio, M.; Valli, E.; Cirillo, G.; Voli, F.; Butini, M.E.; Farfalla, A.; Pantuso, E.; Leggio, A.; Nicoletta, F.P.; et al. Combining antioxidant hydrogels with self-assembled microparticles for multifunctional wound dressings. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 4361–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittorio, O.; Cojoc, M.; Curcio, M.; Spizzirri, U.G.; Hampel, S.; Nicoletta, F.P.; Iemma, F.; Dubrovska, A.; Kavallaris, M.; Cirillo, G. Polyphenol Conjugates by Immobilized Laccase: The Green Synthesis of Dextran-Catechin. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2016, 217, 1488–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.; Matama, T.; Kim, S.; Padrao, J.; Prasetyo, E.N.; Kudanga, T.; Nyanhongo, G.S.; Guebitz, G.M.; Casal, M.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Antimicrobial and antioxidant linen via laccase-assisted grafting. React. Funct. Polym. 2011, 71, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittorio, O.; Le Grand, M.; Makharza, S.A.; Curcio, M.; Tucci, P.; Iemma, F.; Nicoletta, F.P.; Hampel, S.; Cirillo, G. Doxorubicin synergism and resistance reversal in human neuroblastoma BE(2)C cell lines: An in vitro study with dextran-catechin nanohybrids. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 122, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakuba, N.; Tabata, Y.; Hato, N.; Fujiwara, T.; Gyo, K. Gelatin Hydrogel With Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor for Tympanic Membrane Regeneration. Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 35, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piu, F.; Bishop, K.M. Local Drug Delivery for the Treatment of Neurotology Disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Tyagi, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Recent Developments in Delivery, Bioavailability, Absorption and Metabolism of Curcumin: The Golden Pigment from Golden Spice. Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 46, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Yadav, A.; Hideg, K.; Kuppusamy, P.; Teknos, T.N.; Kumar, P. A Novel Curcumin Analog (H-4073) Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of Cisplatin Treatment in Head and Neck Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.H.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, G.Q.; Wei, Y.; Xu, Y.S.; Tao, L. Curcumin-polymer conjugates with dynamic boronic acid ester linkages for selective killing of cancer cells. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Sreenivasan, K. Conjugation of curcumin onto alginate enhances aqueous solubility and stability of curcumin. Carbohyd. Polym. 2014, 99, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Kim, B.K.; Nam, Y.; Sohn, U.D.; Park, E.S.; Hong, S.A.; Lee, J.H.; Chung, Y.H.; Jeong, J.H. Protective role of phosphatidylcholine against cisplatin-induced renal toxicity and oxidative stress in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Shen, H.; Tian, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, A.L.; Ji, L.J.; Niu, Z.W.; Wu, D.C.; Qiu, D. Bioactive Nanoparticle-Gelatin Composite Scaffold with Mechanical Performance Comparable to Cancellous Bones. Acs. Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 13061–13068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.V.; Guilherme, M.R.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Mathematical model for the prediction of the overall profile of in vitro solute release from polymer networks. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 310, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Kechai, N.; Geiger, S.; Fallacara, A.; Infante, I.C.; Nicolas, V.; Ferrary, E.; Huang, N.; Bochot, A.; Agnely, F. Mixtures of hyaluronic acid and liposomes for drug delivery: Phase behavior, microstructure and mobility of liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 523, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Shen, R.Z.; Komasa, S.; Xue, Y.X.; Jin, B.Y.; Hou, Y.P.; Okazaki, J.; Gao, J. Drug-Loadable Calcium Alginate Hydrogel System for Use in Oral Bone Tissue Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kechai, N.; Agnely, F.; Mamelle, E.; Nguyen, Y.; Ferrary, E.; Bochot, A. Recent advances in local drug delivery to the inner ear. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 494, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencher, S.W. A constrained regularization method for inverting data represented by linear algebraic or integral equations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1982, 27, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinec, G.M.; Park, C.; Thein, P.; Kalinec, F. Working with Auditory HEI-OC1 Cells. Jove-J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 115, e54425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Sun, L.L.; Webster, T.J. Selective inhibition of MG-63 osteosarcoma cell proliferation induced by curcumin-loaded self-assembled arginine-rich-RGD nanospheres. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3351–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustapha, A.; Peretout, P.A.; Rainey, N.E.; Sureau, F.; Geze, M.; Petit, J.M.; Dewailly, E.; Slomianny, C.; Petit, P.X. Curcumin induces crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis mediated by calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomal destabilization and mitochondrial events. Cell Death Discov. 2015, 1, 15017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Mathematical Model | Parameter | LA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GC | PCGC | ||
| Equation (1) | R2 | 0.9571 | 0.9521 |
| Fmax | 0.92 | 0.16 | |
| α | 10.88 | 0.19 | |
| kR (10−2) | 7.97 | 6.26 | |
| Equation (2) | R2 | 0.5625 | 0.4198 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Curcio, M.; Cirillo, G.; Amato, R.; Guidotti, L.; Amantea, D.; De Luca, M.; Nicoletta, F.P.; Iemma, F.; Garcia-Gil, M. Encapsulation of Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Functional Hybrid Liposomes: Promising Tool for the Reduction of Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15040394
Curcio M, Cirillo G, Amato R, Guidotti L, Amantea D, De Luca M, Nicoletta FP, Iemma F, Garcia-Gil M. Encapsulation of Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Functional Hybrid Liposomes: Promising Tool for the Reduction of Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(4):394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15040394
Chicago/Turabian StyleCurcio, Manuela, Giuseppe Cirillo, Rosario Amato, Lorenzo Guidotti, Diana Amantea, Michele De Luca, Fiore Pasquale Nicoletta, Francesca Iemma, and Mercedes Garcia-Gil. 2022. "Encapsulation of Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Functional Hybrid Liposomes: Promising Tool for the Reduction of Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 4: 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15040394
APA StyleCurcio, M., Cirillo, G., Amato, R., Guidotti, L., Amantea, D., De Luca, M., Nicoletta, F. P., Iemma, F., & Garcia-Gil, M. (2022). Encapsulation of Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Functional Hybrid Liposomes: Promising Tool for the Reduction of Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity. Pharmaceuticals, 15(4), 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15040394









