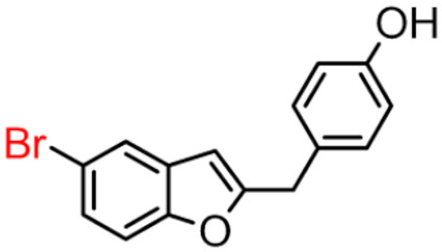
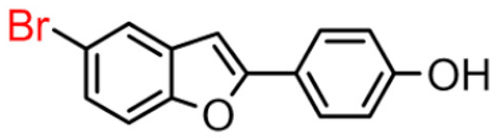
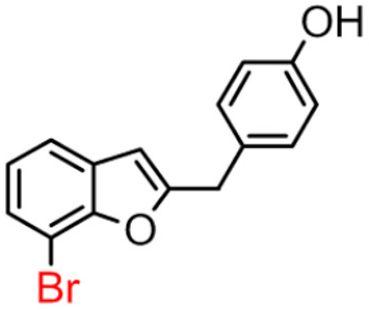
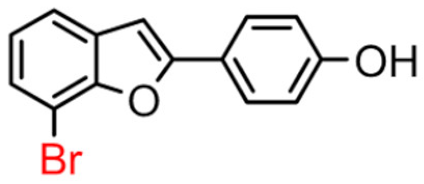
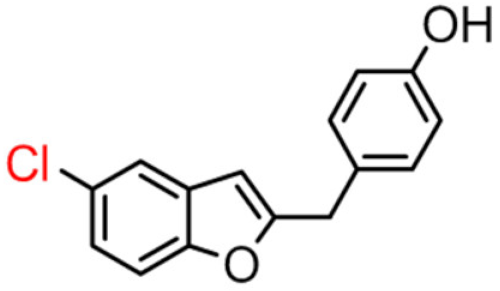
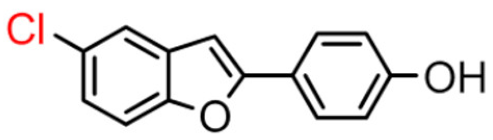
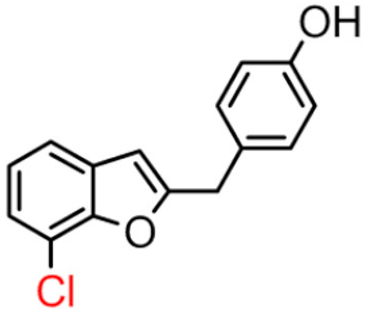
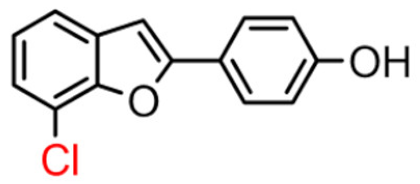
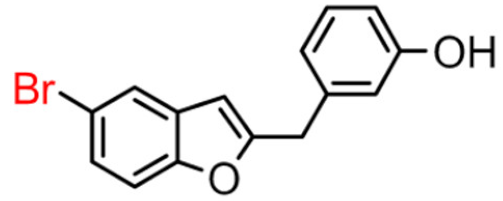
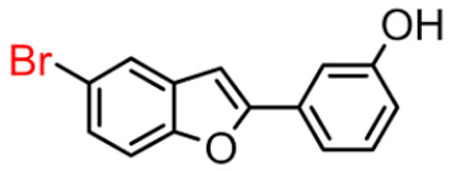
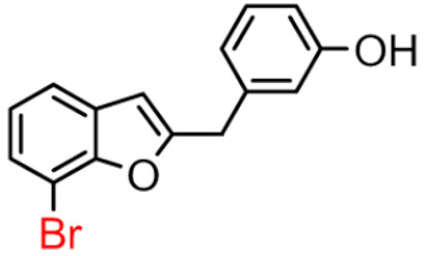
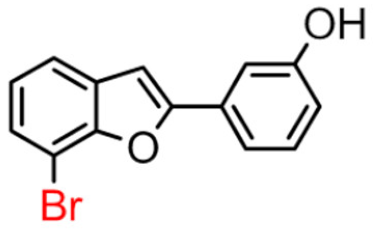
Abstract
In the present work, we use a merger of computational and biochemical techniques as a rational guideline for structural modification of benzofuran derivatives to find pertinent structural features for the butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory activity and selectivity. Previously, we revealed a series of 2-phenylbenzofuran compounds that displayed a selective inhibitory activity for BChE. Here, in an effort to discover novel selective BChE inhibitors with favorable physicochemical and pharmacokinetic profiles, 2-benzylbenzofurans were designed, synthesized, and evaluated as BChE inhibitors. The 2-phenylbenzofuran scaffold structure is modified by introducing one methylene spacer between the benzofuran core and the 2-phenyl ring with a hydroxyl substituent in the para or meta position. Either position 5 or 7 of the benzofuran scaffold was substituted with a bromine or chlorine atom. Further assessment of the selected list of compounds indicated that the substituent’s nature and position determined their activity and selectivity. 5-bromo-2-(4-hydroxybenzyl)benzofuran 9B proved to be the most potent butyrylcholinesterase inhibitor (IC50 = 2.93 µM) of the studied series. Computational studies were carried out to correlate the theoretical and experimental binding affinity of the compounds to the BChE protein.
1. Introduction
The design of enzyme inhibitors has been a topic of accelerated research, especially concerning the discovery of lead compounds as new therapeutic agents owing to the weak pharmacokinetic properties of several bioactive molecules.
Molecular docking is a popular tool in computer-aided drug discovery for rapid screening and predicting the binding characteristics of small molecules to a target protein using its available three-dimensional structure. The action as inhibitors of several molecules is related to their target enzyme interaction. The rational drug design strategy is supported by a detailed understanding of interactions between small molecules and proteins [1,2].
New molecules are conceived either based on similarities with known reference structures or their complementarity with the 3D structure of known active sites.
The beginning for the rational design of inhibitors of enzymes is existing drugs and known pharmacophores. In this regard, benzofuran scaffolds have drawn considerable attention over the last few years due to their deep biological properties, as well as their widespread occurrence in nature.
Many works have delineated that 2-arylbenzofuran compounds have tenacious biological activities—such as antibacterial [3], anti-oxidative [4], anti-tumour [5], anti-viral, and anti-inflammatory properties [6]. The numerous biological latent features in the benzofuran scaffold justify the wide attraction in accepting benzofuran as building blocks of pharmacological medicine. Many of the clinically approved drugs are synthetic or naturally occurring substituted benzofuran derivatives, some of which have other heterocyclic fractions in structure [7].
In our recent studies, we reported that 2-phenylbenzofuran derivatives display promising enzymatic inhibition properties against BChE [8,9,10] and monoamine oxidase (MAO) [11,12,13] enzymes. BChE plays a key role in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), a neurodegenerative disorder. Among many factors that are involved in AD pathogenesis, the primary ones comprise alterations of the cholinergic system; hyperproduction and aggregation of amyloid beta neurotoxic peptide (Aβ); and oxidative stress and aggregation of the Aβ peptide [14,15]. The AChE and BChE inhibition have been documented as a target for the effective management of AD by an increase in the availability of acetylcholine in the brain regions and a decrease in the Aβ deposition [16]. In recent years, there has been ongoing research into the synthesis of more potent and highly effective cholinesterase inhibitors [17].
Our data showed that 2-phenylbenzofuran derivatives with a hydroxyl group at the meta position in the phenyl ring and substitution with bromine and chlorine at position 7 in the benzofuran ring resulted in a high inhibition value. Notably, molecular docking revealed that these compounds interact with two major substrate-binding sites of BChE. The benzofuran moiety interacted with peripheral anionic site (PAS) residues and the 2-phenyl ring moiety with catalytic anionic site (CAS) residues [10].
Recently, the authors reported a new series of 2-benzylbenzofuran isolated from natural sources that showed inhibitory activity for acetylcholinesterase [18]. Hence, we decided to introduce one methylene spacer between the benzofuran core and the 2-phenyl ring with the aim of improving the flexibility of compounds and positively influencing their inhibitory activity against the BChE enzyme.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2-Phenylbenzofurans 1–8(A) and 2-benzylbenzofurans 1–8(B) derivatives were produced efficiently by applying an intramolecular Wittig reaction (Scheme 1).
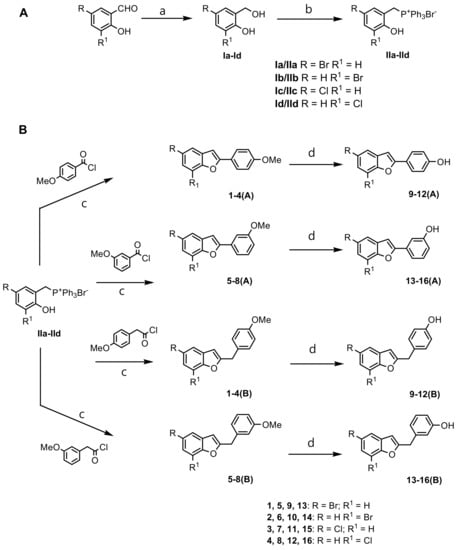
Scheme 1.
Synthesis via Wittig reaction of 2-phenylbenzofuran derivatives 1–16(A) and 2-benzylbenzofuran derivatives 1–16(B). Reagents and conditions: (A) (a) NaBH4, EtOH, 0 °C to rt, 2 h; (b) PPh3 HBr, CH3CN, 82 °C, 2 h; (B) (c) toluene, Et3N, 110 °C, 2 h; (d) HI/AcOH/Ac2O, 0 °C to reflux, 4 h.
Ortho-hydroxybenzyl alcohols Ia–Id [19] were taken as the starting material. The first step involved the formation of Wittig reagents 2-hydroxybenzyltriphosphonium salts IIa–IId from Ia–Id.
The benzofuran ring formation was reached by a reaction between phosphonium salts IIa–IId and convenient acyl chlorides [8,9,10].
Hydrolysis of the methoxy group of compounds 1–8(A) and 1–8(B) was done by treatment with hydrogen iodide in acetic acid/acetic anhydride to provide, in almost quantitative yields, the corresponding hydroxy derivatives 9–16(A) and 9–16(B) [20]. The benzofuran structures were approved by spectroscopic techniques such as 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and elemental analysis (Supporting Information—1. Chemistry).
2.2. Biological Activity
The IC50 values of benzofuran derivatives for BChE inhibition are illustrated in Table 1. The effect of the benzofuran derivatives was evaluated on the commercial enzyme from an animal source due to its low cost and remarkable similarity with the human enzyme.

Table 1.
Inhibitory effect (IC50) of compounds 9–16(A) and 9–16(B) on BChE activity. The data shown are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
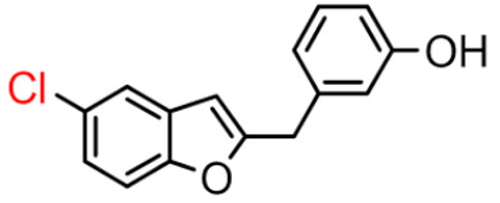
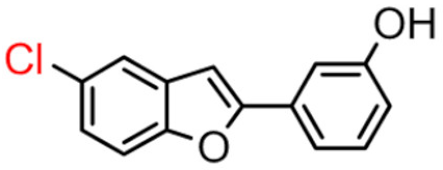
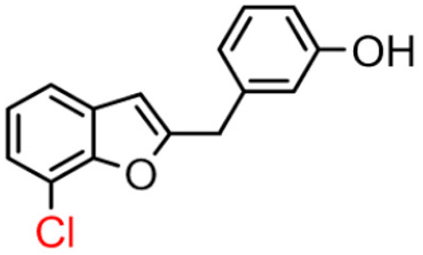
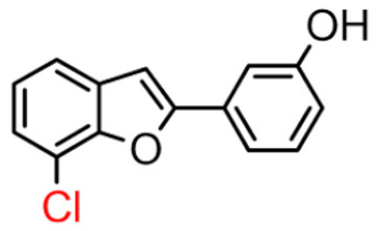
Among derivatives of para-hydroxy substituted 9–12(B), the most active compound is 5-bromo-2-(4-hydroxybenzyl) benzofuran (9B) with an IC50 value of 2.93 µM and with an inhibitory activity 10 times higher than galantamine (IC50 = 28.06 µM), the reference inhibitor. Benzylbenzofuran isomer 10B, with the bromine atom in position 7 in the benzofuran ring, is less active than the previous one, but it has similar inhibitory activity to galantamine. Compounds 11B and 12B, with the chlorine atom in positions 5 and 7 respectively, are the least active of this series. In the series of 2-benzylbenzofurans meta-hydroxy substituted 13–16(B) the most active compound is 5-chloro-2-(3-hydroxybenzyl)benzofuran (15B, IC50 = 27.84 µM).
In Table 1, these data are compared with IC50 values of the synthesized 2-phenylbenzofurans 9–16(A) [8,10]. Overall, the 2-benzylbenzofuran derivatives substituted in para-position 9–11(B) showed better inhibitory activity against BChE than 2-phenylbenzofurans 9–11(A). Only compound 12B displayed a lower inhibitory activity than compound 12A. All 2-benzylbenzofuran derivatives substituted in meta-position 13–16(B) show lower inhibitory activity than 2-phenylbenzofurans 13–16(A).
5-bromo-2-(4-hydroxybenzyl)benzofuran (9B) exhibited about 4-fold higher inhibitory activity than 7-bromo-2-(3-hydroxyphenyl)benzofuran (14A), which showed the greatest enzyme inhibitory activity among the 2-phenylbenzofuran derivatives.
Compound 9B has a statistically different IC50 value from the other compounds, making it the most active of the whole series. For the active compound (9B), the presence of the methylene spacer between the benzofuran core and the 2-phenyl ring was revealed to be fundamental for inhibitory activity. This modification probably allows the molecule to adapt better in the enzymatic pocket and form a more significant interaction with the protein.
This hypothesis could be confirmed by comparing IC50 value of the 2-benzylbenzofuran 9B (compound with the highest activity) and the 2-phenylbenzofuran 9A (with no activity), which differ only in the methylene spacer.
2.3. Molecular and Physicochemical Properties of Compounds
Molecular docking is a proven computational method to identify the most probable orientation between a small molecule (compound) and a protein, human hBChE. In this study, we aimed to enhance the flexibility of compounds to improve inhibitory activity against the BChE enzyme.
Specifically, compounds 9A and 10A—which showed negligible inhibitory activity—were modified respectively to compounds 9B and 10B. Experimental results suggested an improvement in enzyme inhibition for compounds 9B and 10B. Therefore, molecular docking was performed for compounds (9A, 9B, 10A, and 10B) to understand better the outcome of adding a methylene spacer on the compound’s activity against hBChE protein. Docking results (Table 2) suggested superior docking energy values for the compounds with a methylene spacer, and among them, compound 9B displayed the best docking energy value against the target protein hBChE.

Table 2.
Molecular docking energies scores and IC50 values of compounds (9A, 9B, 10A, and 10B) against hBChE. (Docking energies values for all compounds are reported in Supporting Information—2. Molecular modelling studies Table S1).
The docking results of the investigated compound are in good agreement with the experimental IC50 values. In Figure 1, we show the interaction picture for the investigated protein–ligand complexes.
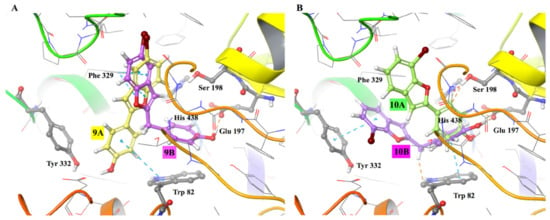
Figure 1.
Protein-ligand interaction picture. (A) The binding site of compounds 9A and 9B; and in (B) for compounds 10A and 10B. The key interacting residues are shown in ball-and-stick representation.
We note an adequate overlap of the benzofuran moiety of compounds 9A and 9B (Figure 1A) and pi–pi interactions with Phe 329. The presence of methylene spacer in compound 9B alters the orientation of the 2-phenyl group compared to compound 9A, such that it can readily nestle inside the catalytic subsite and non-covalently interact with residues Glu 197, Ser 198, and His 438 (Figure 1A). Thus, we can deduce that introducing a methylene spacer provides an impressive inhibition activity of compound 9B against hBChE by facilitating interactions with CAS residues, which is crucial for hBChE inhibition. Differently, we note a nearly exact placement of the 2-phenyl ring of compounds 10A and 10B inside the catalytic subsite, and in this case, the added feature induces a marginally better binding energy value (Table 2). This marginal improvement can be attributed to pi–pi stacking interactions of compound 10B with residues Trp 82 and Tyr 332 (Figure 1B). Our reported trend of docking energy values between the two compounds (10A, 10B) is consistent with a moderate improvement in experimental IC50 values (Table 2). The derivatives’ physicochemical properties, illustrated in Table 3, are a good indicator of their capacity to cross through cellular membranes and predictors of their absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) parameters.

Table 3.
Molecular properties of 9A/10A and 9B/10B were calculated using the Swiss ADME software [21].
Compounds with the same halogen substitution of benzofuran moiety (but different in their position) and a hydroxyl group in the para position of the phenyl ring displayed the same physicochemical properties. All the molecules have two rotatable bonds, thus showing similar flexibility.
Theoretically, all the 2-benzylbenzofuran derivatives have acceptable physicochemical properties to display good bioavailability, and none of them violate the Lipinski rule. The studied compounds exhibit appreciable penetration capability across the biological membranes, and no pan-assay interference structures (PAINS) were detected, according to the obtained results (Table 3).
Therefore, based on desirable physicochemical and structural features shown, the investigated compounds exhibit drug-likeness properties.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
Under an atmosphere of nitrogen with magnetic stirring, reactions were performed in oven-dried glassware. The reagents and starting materials were purchased from retail suppliers (Merck/Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany) and were used without further purification. Melting points (mp) are uncorrected and determined with a Reichert Kofler thermopan or in capillary tubes in a Büchi 510 apparatus.
1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra were recorded with a Varian INOVA 500 spectrometer and a Varian INOVA 600 spectrometer, using CDCl3 as solvent. Chemical shifts (δ) are expressed in parts per million (ppm) using TMS as an internal standard. Coupling constants J are expressed in hertz (Hz). Spin multiplicities are given as s (singlet), d (doublet), dd (doublet of doublets), and m (multiplet). Elemental analyses were performed by using a Perkin Elmer 240B microanalyzer and are within 0.4% of calculated values in all cases. The analytical results indicate 98% purity for all compounds. Flash chromatography (FC) was performed on silica gel (Merck 60, 230–400 mesh); analytical thin-layer chromatography (TLC) was performed on pre-coated silica gel plates (Merck 60 F254), visualized by exposure to UV light. Organic solutions were dried over anhydrous sodium sulphate (Na2SO4). After reaction or extraction, the solvent’s concentration and evaporation were carried out on a rotary evaporator (Büchi Rotavapor, Cornaredo Italia) operating under reduced pressure.
3.2. Determination of Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibition
The cholinesterase inhibition activity was executed using Ellman’s method [22], as previously described with slight modifications [10].
S-Butyrylthiocholine iodide (BTCI) and 5,5′-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic) acid (DTNB) (Merck/Sigma-Aldrich) were used for the determination of the BChE activity. Butyrylcholinesterase (EC 3.1.1.8, BChE) was from equine serum (eqBChE) (Sigma-Aldrich). We used 96-well plates for analysis, to each well we added 70 μL phosphate-buffered (0.1 M, pH 8.0), 4 μL different concentration of the tested compounds or dimethyl sulfoxide (for control experiment), 6 μL enzyme (final concentration 0.15 U/mL in buffer), and 100 μL DTNB (1.5 mM final). The solution was preincubated for 5 min at 37 °C, then 20 μL BTCI 1.5 mM solution as the substrate was added to the reaction mixture. The absorbance change was measured at 405 nm, with a microplate reader FLUOstar OPTIMA (BMG Labtech, Offenburg, Germany). Galantamine was used as a standard inhibitor. Each experiment was done in triplicate. IC50 values were calculated as the concentration of compound with 50% inhibitory activity and were obtained from activity (slope) versus compound concentration plots.
The statistical significance of differences was evaluated using one-way analysis of variation (one-way ANOVA), and Tukey’s multiple comparisons. Results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD), and statistically significant differences were evaluated with p < 0.001 as a minimal significance level.
3.3. Molecular Modelling Studies
The three-dimensional (3D) protein structure of human BChE was downloaded from the protein data bank (PDB id: 4TPK). The chemical structure of the ligands was drawn and converted into 3D coordinates using online openbabel software (http://www.cheminfo.org/Chemistry/Cheminformatics/FormatConverter/index.html, accessed on 22 February 2022). Geometric optimization of the ligand structure was done using density functional theory formulation of quantum mechanics [23], and it was subsequently converted into mol2 format for the docking experiment. Chain A from of the crystal structure (PDB id: 4TPK) for protein and mol2 format for the ligand were submitted for docking using the SwissDock web server [24]. The docking program is based on EADock dihedral space sampling (DSS) engine [25], which uses a multiobjective scoring function based on CHARMM22 force field and an implicit treatment of the solvent by using a fast analytical continuum solvation model. The docking procedure considers the entire protein surface, and 5000 ligand-binding modes are generated, which were then classified and ranked into different clusters using a scoring function. The predictions file provides the user information on cluster Rank, full fitness, and estimated binding free energy ΔG (kcal/mol) values.
To validate our docking method, we performed a study using a co-crystal ligand (N-{[(3R)-1-(2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-2-yl)piperidin-3-yl]methyl}-N-(2-methoxyethyl)naphthalene-2-carboxamide) and the docked structures of the same ligand obtained from Swissdock webserver. The co-crystal structure of the ligand was used as a reference (crystal), and the best docked structure of the same ligand (model) from Swissdock protocol was compared (Supporting Information—2. Molecular modelling studies Figure S1).
The presence of pan-assay interference structures (PAINS) and the conformity to Lipinski’s rule was investigated by employing the free web tool Swiss ADME (http://www.swissadme.ch/, accessed on 22 February 2022) [21].
4. Conclusions
Our research endeavors have focused on developing novel 2-phenylbenzofuran derivatives with improved inhibitory activity against the BChE enzyme, a viable target in AD. In the hope of favorably improving the inhibitory action of our previously synthesized derivatives, we introduced a methylene spacer between the benzofuran and the 2-phenyl ring moieties. The present study shows that introducing a methylene spacer in compound 9A (that showed no BChE inhibition) drastically enhanced the compound’s (9B) action against the enzyme. Therefore, the additive structural feature alters the flexibility of the molecule such that it readily nestles and interacts with catalytic triad residues, which is pivotal for enzyme inhibition. Altogether, our results highlighted the importance of late-stage functionalization as a desirable approach to accelerate the drug discovery process against AD.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ph15030304/s1, General Experimental Procedure for the Synthesis; 1H NMR, 13C NMR spectra; Figure S1: Superimposition of the reference complex (PDB code: 4TPK) and the best docked ligand pose obtained from Swissdock webserver; Table S1: Effect of spacer on the docking and IC50 values of compounds.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.L.D., A.F., B.E. and A.K.; Methodology, G.L.D., F.P., B.E. and A.K.; Software, B.E. and A.K.; Formal analysis, F.P. and C.G.; Investigation, G.L.D., B.E. and A.K.; Resources, G.L.D. and A.F.; Writing—original draft, G.L.D. and B.E.; Writing—review and editing, A.F., F.P., C.G., M.J.M. and A.K.; Visualization, G.L.D., A.F. and B.E.; Supervision, B.E. and A.K.; Funding, A.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the University of Cagliari.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
G. L. Delogu is grateful to Afra Farci for her support during the synthesis of the compounds.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kitchen, D.B.; Decornez, H.; Furr, J.R.; Bajorath, J. Docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: Methods and applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, M.; Zou, X. Docking-based inverse virtual screening: Methods, applications, and challenges. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukai, T.; Oku, Y.; Hano, Y.; Terada, S. Antimicrobial activities of hydrophobic 2-arylbenzofurans and an isoflavone against vancomycin-resistant enterococci and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.J.; Ryu, S.N.; Kang, S.S. A new 2-arylbenzofuran with antioxidant activity from the black colored rice (Oryza sativa L.) bran. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 1365–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khodarahmi, G.A.; Asadi, P.; Hassanzadeh, F.; Khodarahmi, E. Benzofuran as a promising scaffold for the synthesis of antimicrobial and antibreast cancer agents: A review. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2015, 20, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Gao, B.; Huang, W.; Yongmin, L.; Guosheng, H.; Yongxiang, M. Simple, Convenient, and Efficient Synthesis of 2-Aryl-substituted Benzo[b.furans. Synth. Commun. 2009, 39, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.H.; Hu, Y.H.; Yang, J.; Liu, T.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.J. Natural source, bioactivity and synthesis of benzofuran derivatives. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 27510–27540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delogu, G.L.; Matos, M.J.; Fanti, M.; Era, B.; Medda, R.; Pieroni, E.; Fais, A.; Kumar, A.; Pintus, F. 2-Phenylbenzofuran derivatives as butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors: Synthesis, biological activity and molecular modeling. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2308–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Pintus, F.; Di Petrillo, A.; Medda, R.; Caria, P.; Matos, M.J.; Viña, D.; Pieroni, E.; Delogu, F.; Era, B.; et al. Novel 2-pheynlbenzofuran derivatives as selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fais, A.; Kumar, A.; Medda, R.; Pintus, F.; Delogu, F.; Matos, M.J.; Era, B.; Delogu, G.L. Synthesis, molecular docking and cholinesterase inhibitory activity of hydroxylated 2-phenylbenzofuran derivatives. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 84, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delogu, G.L.; Pintus, F.; Mayán, L.; Matos, M.J.; Vilar, S.; Munín, J.; Fontenla, J.A.; Hripcsak, G.; Borges, F.; Viña, D. MAO inhibitory activity of bromo-2-phenylbenzofurans: Synthesis, in vitro study, and docking calculations. MedChemComm 2017, 8, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferino, G.; Cadoni, E.; Matos, M.J.; Quezada, E.; Uriarte, E.; Santana, L.; Vilar, S.; Tatonetti, N.P.; Yáñez, M.; Viña, D.; et al. MAO Inhibitory Activity of 2-Arylbenzofurans versus 3-Arylcoumarins: Synthesis, in vitro Study, and Docking Calculations. ChemMedChem 2013, 8, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delogu, G.L.; Kumar, A.; Gatto, G.; Bustelo, F.; Saavedra, L.M.; Rodríguez-Franco, M.I.; Laguna, R.; Viña, D. Synthesis and in vitro study of nitro- and methoxy-2-phenylbenzofurans as human monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 107, 104616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanabria-Castro, A.; Alvarado-Echeverría, I.; Monge-Bonilla, C. Molecular pathogenesis of alzheimer’s disease: An update. Ann. Neurosci. 2017, 24, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, C.E.; Mostile, G.; Vasta, R.; Rapisarda, V.; Signorelli, S.S.; Ferrante, M.; Zappia, M.; Nicoletti, A. Metals and neurodegenerative diseases. A systematic review. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Singh, B. A review on cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 375–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larik, F.A.; Shah, M.S.; Saeed, A.; Shah, H.S.; Channar, P.A.; Bolte, M.; Iqbal, J. New cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease: Structure activity relationship, kinetics and molecular docking studies of 1–butanoyl–3–arylthiourea derivatives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Ma, Q.; Zhong, G. Anti-Ache Benzylbenzofuran Derivatives from Silene conoidea. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2019, 55, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assoah, B.; Vale, J.R.; Kalenius, E.; Veiros, L.F.; Candeias, N.R. Lewis Base Catalyzed Intramolecular Reduction of Salicylaldehydes by Pinacol-Derived Chlorohydrosilane. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 2018, 2910–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada, E.; Delogu, G.; Picciau, C.; Santana, L.; Podda, G.; Borges, F.; García-Morales, V.; Viña, D.; Orallo, F. Synthesis and vasorelaxant and platelet antiaggregatory activities of a new series of 6-Halo-3-phenylcoumarins. Molecules 2010, 15, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Baccoli, R.; Fais, A.; Cincotti, A.; Pilia, L.; Gatto, G. Substitution effects on the optoelectronic properties of coumarin derivatives. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grosdidier, A.; Zoete, V.; Michielin, O. SwissDock, a protein-small molecule docking web service based on EADock DSS. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanommeslaeghe, A.D.M.J.K.; Hatcher, E.; Acharya, C.; Kundu, S.; Zhong, S.; Shim, J.; Darian, E.; Guvench, O.; Lopes, P.; Vorobyov, I. CHARMM General Force Field: A Force Field for Drug-Like Molecules Compatible with the CHARMM All-Atom Additive Biological Force Fields. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 31, 671–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).