Abstract
Furin cleavage of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein results in a polybasic terminal sequence termed the C-end rule (CendR), which is responsible for the binding to neuropilin 1 (NRP1), enhancing viral infectivity and entry into the cell. Here we report the identification of 20 small-molecule inhibitors that emerged from a virtual screening of nearly 950,000 drug-like compounds that bind with high probability to the CendR-binding pocket of NRP1. In a spike NRP1 binding assay, two of these compounds displayed a stronger inhibition of spike protein binding to NRP1 than the known NRP1 antagonist EG00229, for which the inhibition of the CendR peptide binding to NRP1 was also experimentally confirmed. These compounds present a good starting point for the design of small-molecule antagonists against the SARS-CoV-2 viral entry.
1. Introduction
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the causative agent of the coronavirus-induced disease 2019 (COVID-19) [1], which has spread worldwide. The pandemic resulted in a tremendous pressure on hospital care and caused the deaths of more than four million people [2]. While SARS-CoV-2 symptoms range from mild to severe, and in some cases fatal respiratory manifestations, its involvement in extrapulmonary indications has also been widely observed. Since it affects haematological, cardiovascular, renal, gastrointestinal, and hepatobiliary, endocrinological, neurological, ophthalmological, and dermatological systems [3], it is considered a multisystem disease for which successful treatments are necessary in the early stages of the infection in order to prevent more extensive health damage [4].
SARS-CoV-2 primarily utilises angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2) to mediate cell uptake [5], but alternative entry points have been identified, such as neuropilin-1 (NRP1) [6,7]. NRP1 was found to significantly enhance the infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 by increasing viral entry into host cells rather than strengthening viral binding [6]. Neuropilins (NRPs) represent a class of transmembrane glycoprotein receptors involved in various biological processes, including neuronal development and axon guidance, angiogenesis, vascular permeability, and immune functions [8,9]. They lack direct signalling capabilities and, therefore, act as co-receptors that bind a signalling molecule in addition to the primary receptor, thereby affecting ligand-receptor activity. NRP1 is implicated in several conditions of SARS-CoV-2 infection. The most pronounced is its association with the neurological manifestations of SARS-CoV-2, where it was discovered that NRP1 is elevated in the olfactory epithelial cells of infected humans, enhancing the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the central nervous system [10]. The overexpression of NRP1 in olfactory cells also makes it a strong candidate for the mechanism of anosmia, which is very common in COVID-19 patients [11,12]. Moreover, it has also been suggested that NRP1 may be associated with additional neurological disorders such as headache, dizziness, hallucinations, or motor coordination disorders [10,13]. Furthermore, patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 are at a higher risk of increased blood clotting [14] and since NRP1 modulates blood clotting, it may also play a role in the pathology of blood clotting in COVID-19 patients [12]. Furthermore, NRP1 is involved in immune function, thus its role in the exaggerated immune response in severe COVID-19 cases has also been proposed [10,12]. The involvement of NRP1 in all listed functions makes it an ideal factor for the multisystemic effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection and, more importantly, a good target for attenuating viral infectivity and for preventing the associated disorders.
There exist two very similar isoforms, NRP1 and NRP2, which share 44% amino acid sequence identity and exhibit a similar structural domain organisation consisting of N-terminal extracellular domains, a single transmembrane domain, and a small intracellular C-terminal domain [15]. The individual extracellular regions are responsible for the binding of various endogenous ligands and trigger specific intercellular effects. The two CUB domains (a1/a2) bind semaphorins responsible for the functioning of the neural system, while the two factor V/VIII homology domains (b1/b2) bind vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family ligands (mainly VEGF-A) involved in blood vessel development. The smallest MAM domain (c) mediates NRP multimerization [15,16]. A similar structural composition of NRP1 and NRP2 allows them to be involved in analogous biological processes yet to differ enough to provide selectivity for endogenous ligands [17]. Although NRP2 is an equally important target, only the involvement of NRP1 in COVID-19 disease has been studied and characterised in detail [10].
SARS-CoV-2 entry into human cells is mediated by SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoproteins. The cleavage of the spike protein by host proteases is required for the binding to the host cell surface and cell entry. Accordingly, the spike is cleaved by the furin protease at the S1/S2 junction into the S1 subunit, which is responsible for the binding to host cell receptors, and the S2 subunit, which is responsible for fusion of the viral and cellular membranes [5,18]. After cleavage, the [R/K]XX[R/K] sequence called C-end rule (CendR) becomes exposed on the S1 subunit [18], which represents the key element for spike binding to NRP1. CendR is a common C-terminal sequence that allows the binding to the b1 domain of NRP1 in its highly conserved arginine binding pocket [19]. Endogenous VEGF family ligands use this CendR motif to activate signalling pathways [19], while viruses such as Epstein—Barr virus (EBV) [20] and human T-lymphotropic virus-1 (HTLV-1) [21] use CendR to promote host cell infection. Analogously, SARS-CoV-2 binds to the NRP1 b1 domain with its RRAR CendR motif to facilitate viral entry into the cell [6]. The suitability of the binding pocket to accommodate different ligands with the CendR terminals is evident from the comparison of the crystal complexes of VEGF-A164-NRP1 and SARS-CoV-2-NRP1 (Figure 1A), which show remarkable similarities in the binding mode of their CendR sequences. Amino acid residues Tyr297, Trp301, Thr316, Asp320, Ser346, Thr349, and Tyr353 were identified as critical for the SARS-CoV-2 binding and are virtually identical to the key interactions of VEGF-A164 with NRP1 [17]. The guanidine group of SARS-CoV-2 forms a salt bridge with Asp320, while its free carboxyl group interacts with Ser346, Thr349 and Tyr353 via hydrogen bonds. Tyr297 and Tyr353 are also interacting with the arginine side chains of CendR (Figure 1B) [6]. The binding of SARS-CoV-2 to NRP1 not only prevents the binding of VEGF-A, but also its signalling and function. Consequently, disruption of the VEGF-A/NRP1 complex by the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein was found to impair pain signalling and reduce neuropathic pain, which may contribute to the asymptomatic COVID-19 infections and further spread of the virus [22]. The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 was associated with several amino-acid substitutions that affected its viral properties. However, the spike mutations do not appear to affect the binding of the CendR motif, as a high degree of conservation was observed for the Arg682 and Arg683 CendR residues, whereas the Ala684Val mutation appears to be consistently present. Since Ala684 does not form key interactions, its mutation appears to be without a significant effect [23]. Moreover, no spontaneous mutations were found for the CendR terminal Arg685 [24,25], which contributes most to the spike binding with the b1 domain of NRP1. Therefore, compounds that bind to the same amino-acid residues as CendR are likely to retain a high inhibition potential, even in the case of different variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. No information on the spontaneous mutations of the amino-acid residues in the CendR binding pocket of NRP1 could also be found.
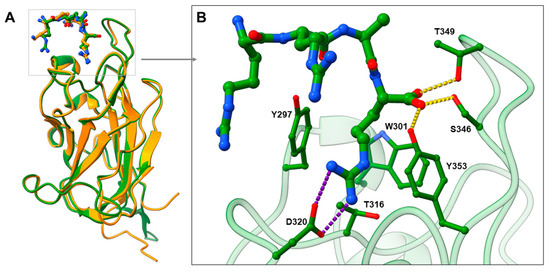
Figure 1.
(A) Comparison of the binding modes of VEGF-A164 (in orange stick representation) and SARS-CoV-2 (in green stick representation) CendR motifs by superimposing VEGF-A-NRP1 (PDB ID: 4DEQ; [17] NRP1 in orange cartoon representation) and SARS-CoV-2-NRP1 (PDB ID: 7JJC; [6] NRP1 in green cartoon representation) complexes. (B) Zoomed view representing SARS-CoV-2 CendR binding mode into the b1 domain of NRP1, highlighting interactions with the key amino-acid residues (in green stick representation). Hydrogen bonding and salt bridge interactions are depicted as yellow and violet dashes, respectively.
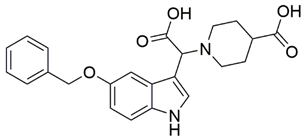
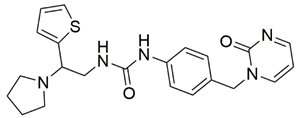
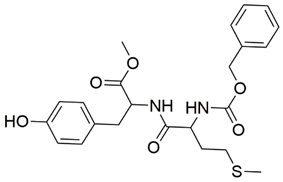
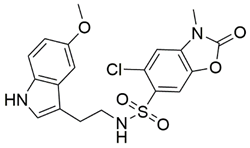
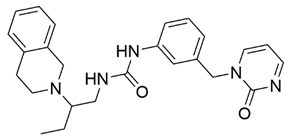
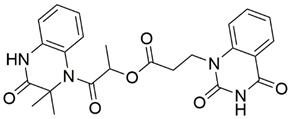
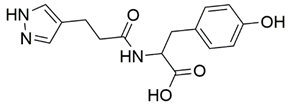
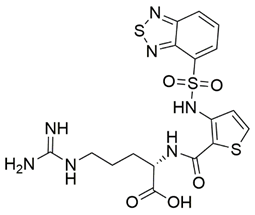
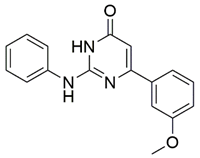
Disrupting the key protein-protein interactions between NRP1 and VEGF-A at the b1 CendR binding site has long been the focus of drug discovery efforts, particularly for cancer therapy. As a result, several peptide [26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34], peptidomimetic [35,36,37,38], and small-molecule NRP1 antagonists (Figure 2A) have been developed that successfully interfere with the VEGF-A binding and prevent its further signaling as reported by Borriello et al. and Starzec et al. [39,40,41,42,43,44,45]. In peptide and peptidomimetic antagonists, the C-terminal arginine residue was generally retained to maintain interactions with the key amino acid Asp320 residue, whereas in small-molecule antagonists, this residue was replaced by a series of moieties. Interestingly, although the interaction with Asp320 was considered crucial for the binding, some studies suggested that a good affinity can also be achieved with antagonists lacking this interaction [40,42], expanding the possibilities for future structural modifications of small-molecule NRP1 antagonists. However, this interaction has still been recognised as critical for the SARS-CoV-2 binding [46], thus targeting it aims at successfully disrupting the SARS-CoV-2 NRP1 binding and is considered an attractive therapeutic approach to prevent viral entry. The well-known peptidomimetic NRP1 antagonist EG00229 (Figure 2A), which binds to the CendR-binding pocket and prevents the VEGF-A binding, was also evaluated for blocking the spike CendR binding in two different assays. In a binding assessment experiment, EG00229 inhibited the direct binding of the S1 CendR peptide to NRP1. Moreover, EG00229 decreased the SARS-CoV-2 infectivity in cells [6]. In the second experiment, EG00229 was tested in a spike-dependent assay for its ability to inhibit vesicular stomatitis virus using the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein for entry and fusion, but unfortunately it was found inactive. Nonetheless, two alternative compounds (Figure 2B) from this study displayed greater than 50% inhibition of spike-mediated viral entry into cells, representing the first step in the effort to develop small-molecule NRP1 antagonists for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection [45].
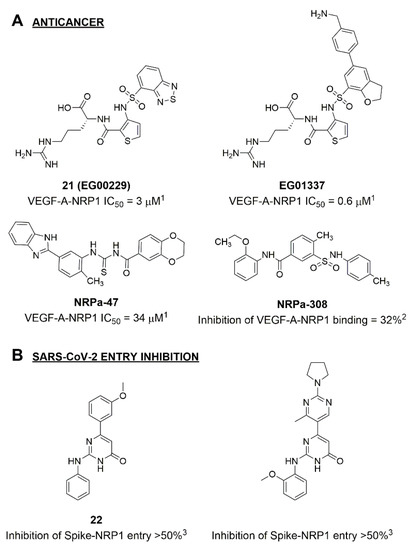
Figure 2.
(A) Some of the best characterized antagonists of the VEGF-A binding to the NRP1 b1 domain. (B) Small-molecules identified as potential antagonists of the spike induced SARS-CoV-2 entry. 1 Cell-free bt-VEGF-A165 binding assay, measuring inhibition of VEGF binding to the b1 domain on NRP1 [35,38,39]. 2 Cell-free bt-VEGF-A165 binding assay measuring inhibition of VEGF binding to the b1 domain on NRP1 at a compound concentration of 10 μM [41]. 3 Vero-E6-TMPRSS2 cell-based assay measuring inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein dependent entry using GFP-expressing vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) recombinant protein, encoding the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein [45].
With the aim of identifying non-peptide hit compounds capable of preventing spike CendR binding to the b1 domain of NRP1, we performed an extensive virtual screening campaign using molecular docking and a large library of small-molecules with drug-like properties. The compounds with the top scoring binding modes in the CendR binding pocket of NRP1 were further biologically evaluated for the spike binding blockade. We successfully identified two novel compounds with high inhibitory activity that exhibit a great potential for further developments of small-molecule antagonists of SARS-CoV-2 Sprot-NRP1 binding.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Molecular Docking and Selection of Top Compounds
With the intention of identifying compounds that prevent the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein from binding to NRP1, a subset of the available compounds from the ZINC15 [47] library was prepared and screened against the CendR binding site on the NRP1 b1 domain. Library preparation (Figure 3) was performed in order to filter out structural faults, eliminate known and predicted aggregators, allow elements: H, C, N, O, F, S, Cl, Br, I, P, filter for pains (pan-assay interference compounds) [48,49] and REOS (rapid elimination of swill) structures to eliminate reactive and labile functional groups as well as to apply Lipinski [50] and Veber [51] medicinal chemistry filters. Therefore, KNIME software with RDKit software nodes was used to compare all structures in the library to the selection of SMARTS-formatted flags and to remove hits from the database [52].
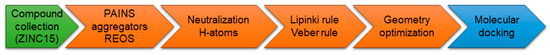
Figure 3.
Library preparation for molecular docking calculations on the b1 domain of NRP1. The final library contained 956,355 molecules.
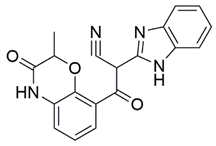
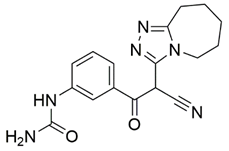
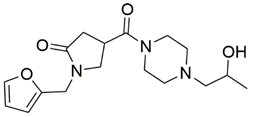
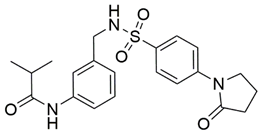
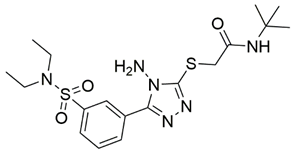
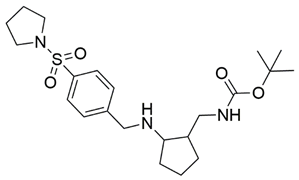
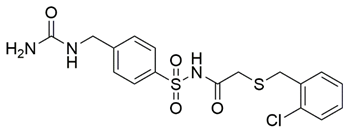
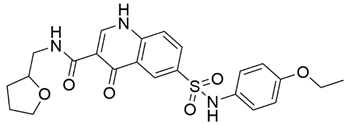
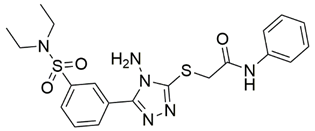
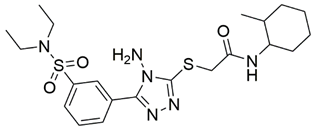
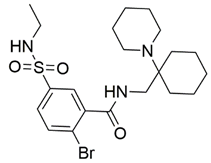
Two screenings were performed, the first with lower search efficiency to estimate the binding of the compounds and to select the compounds with the best predicted binding poses as well as the second screening with a higher search efficiency. We employed the GOLD implementation of ChemPLP empirical scoring function in order to achieve the best HTVS results [53]. Finally, the 20 highest scoring compounds predicted to have hydrogen bonding interactions with Asp320, Ser346, Thr349 and Tyr353 were selected for the subsequent biological evaluation (Table 1). Chemical descriptor analyses of the docking-hits also confirmed the suitable calibration of input libraries as hit compounds covered the complete and similar chemical space.

Table 1.
Inhibition of the spike S1 binding to NRP1 by the compounds selected using molecular docking calculations.
2.2. In Vitro Evaluation of the Spike Binding Inhibition to NRP1
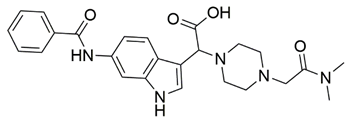
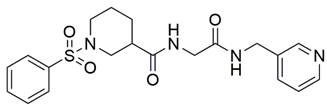
The ability of the compounds to inhibit the binding of the spike S1 protein to the b1 domain of NRP1 was evaluated by an in vitro spike-NRP1 binding assay, in which the potential antagonist competes with the spike S1 protein for the binding to NRP1. The results presented in Table 1 show that all docked compounds were able to inhibit the binding of the spike S1 to a certain extent, but only compounds 16 and 17 were able to prevent more than 60% of the binding. To evaluate the results, the inhibitory activities of the tested compounds were compared with the inhibitory activity of EG00229 (21) [35] and compound 22 [45], which had previously shown inhibition of spike-mediated cell entry, and which were used as controls in our assay. Compound 21 displayed 50.57 ± 2.26% inhibition of spike S1 binding to NRP1, while 22 was less active with 28.71 ± 0.80 inhibition. According to our results, the compounds 16 and 17 act as stronger antagonists of spike binding than compound 21, suggesting that they represent a good starting point for further development of small-molecule SARS-CoV-2 antagonists.
2.3. Prediction of Compounds’ 16 and 17 Binding to NRP1
In the spike protein NRP1 binding assay, compounds 16 and 17 were identified as the most active, so we examined their predicted binding modes in more detail. As indicated with the crucial criteria for selecting the top 20 compounds, both 16 and 17 predictably form interactions with key amino acids Asp320, Ser346, Thr349, and Tyr353. The predicted binding pose of compound 16 is shown in Figure 4A, where the sulfonyl group forms hydrogen bonds with Ser346, Thr349 and Tyr353, while the amino group on the cyclohexane ring forms a salt bridge interaction with Asp320. The single aromatic ring is involved in π-π stacking with Tyr297 and Trp301. The predicted binding mode of compound 17 in Figure 4B shows that the carbonyl group of the ester forms hydrogen bonds with the key amino acids Ser346, Thr349 and Tyr353. Moreover, the free amino group of the dihydroquinoxalinone moiety is involved in hydrogen bonding with Asp320. The same moiety also participates in π-π stacking with Trp301 and Tyr353. Furthermore, the compound is bound to Ser298 and Trp301 via two different carbonyl groups of the dihydroquinoxalinedione moiety. Comparing the predicted binding modes of compounds 16 and 17 with the binding pose of compound 21 (Figure 4C, PDB ID: 3i97) [35], the binding mode of 17 is consistent with the conformation of compound 21. While the functional groups of 17 and 21 extend towards the upper polar region of the receptor formed by amino-acid residues Ser298 and Asn300, thus enhancing the binding, compound 16 extends towards, but does not interact with, the lower open region of the binding pocket surrounded by amino-acid residues Gly318 and Glu319 (Figure 4D). Therefore, targeting these residues could further stabilize the binding of the ligand in the lower part of the binding pocket. Moreover, compound 16 has the potential to introduce functional groups that occupy the upper part of the binding pocket. The importance of amino acid residues in the upper (Ser298 and Asn300) and lower (Gly318 and Glu319) parts of the binding pocket has been previously considered as a possibility for the design of compounds that could fully occupy the binding pocket and thus enhance the binding, potentially leading to stronger antagonistic effects [45].
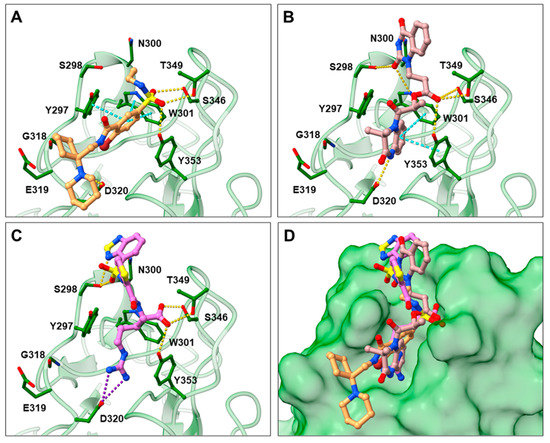
Figure 4.
Predicted binding poses of compounds 16 (A) and 17 (B) as well as the binding mode of compound 21 ((C); PDB ID 3i97) [35] within the SARS-CoV-2 CendR binding pocket on the b1 NRP1 domain (PDB ID: 6FMC) [38]. NRP1 is depicted in green cartoon representation, while ligands and key amino acids are in stick representation. Hydrogen, salt bridge and π-π stacking interactions are depicted as yellow, violet, and cyan dashes, respectively. Overlay of the predicted binding modes of compounds 16 and 17 with the binding pose of compound 21 (D).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Molecular Docking Calculations
A subset of “now” available compounds was downloaded from the ZINC15 database [47]. The library was prepared for screening using an in-house derived KNIME [54] protocol (Figure 3) removing PAINS [48,49], known aggregators [55] and REOS structures to eliminate reactive functional groups as well as providing neutralization, drug-like properties, adding hydrogens and optimizing geometry with RDKit software nods, which yielded ∼950K compounds.
The structure of the NRP1 b1 domain with the highest available resolution of 0.90 Å (PDB ID: 6FMC) [38] was selected for subsequent docking calculations. Prior to molecular docking studies, the protein was prepared using the Prepare Protein Wizard in the Maestro 12.6 program (Release 2020–4, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, USA). The high throughput virtual screening of the library was performed using the GOLD (Version 2020.2.0, CCDC, Cambridge, UK) docking suite within the CendR binding pocket of the NRP1 b1 domain [56]. The experimental coordinates of the co-crystallized ligand (EG01377) were used to define the binding site (cavity radius of 17 Å). The molecular docking protocol was validated by triple docking of the co-crystallized ligand (EG01377) to reproduce its spatial conformation and orientation (Supplementary Materials: Figure S1). The root-mean-square deviation (RMSD ≤ 2.0 Å) between each calculated docking pose and the co-crystallized ligand conformation served as the crucial criterion for the quality of all structure-based settings [57]. Furthermore, we calculated the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve to validate the performance of classifier docking method. We selected a set of known NRP1 inhibitors from the ChEMBL database (CHEMBL5174) with experimental values consisting of compounds with reported IC50 (28 compounds) as well as of compounds with reported Kd employing the cutoff of 5 µM (27 compounds), following this we concatenated and prepared the ligands with Schrödinger SMD suite. We then created a testing database by the addition of the negative control compounds that were calculated decoys based on employed actives using DUD-E: A Database of Useful (Docking) Decoys [58]. Upon using 3% and 10% of actives in the test database, we obtained a ROC AUC of 0.76 and 0.74, respectively, indicating that the docking protocol can indeed identify active compounds and produce enriched libraries. Identical settings and technical parameters of the GOLD genetic algorithm (automatic) were used for all calculations (Supplementary Materials: GOLD configuration file). Hydrogen bonding constraints were set for residues Asp320, Ser346, Thr349, and Tyr353 to favour the formation of specific hydrogen bonds. The calculated docking poses were evaluated according to two criteria. First, for each docking pose, the distance between the H-bond donor/acceptor atoms of the ligand and the H-bond donor/acceptor atoms of the key amino acids (Asp320, Ser346, Thr349, and Tyr353) were measured. Here, the binding poses with a distance from each key donor or acceptor atom greater than 2.5 Å were filtered out by an internally developed application. Among the binding poses meeting these hydrogen-bonding criteria, poses with a ChemPLP greater than 65 were considered acceptable. Compounds belonging to these poses (∼700 compounds) were subsequently subjected to more accurate docking calculations using analogous settings with 200% search efficiency. Finally, the predicted binding poses were ranked based on the ChemPLP scoring (Supplementary Materials: Table S1), and the highly ranked poses were also visually scored using the Maestro 12.6 program (Release 2020–4, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, USA). Among the 20 compounds predicted to have hydrogen bonding interactions with Asp320, Ser346, Thr349, and Tyr353, all 20 were selected for biological evaluation.
3.2. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Binding to NRP1
The selected compounds were obtained from MolPort Inc. (Riga, Latvia; Supplementary Materials: Table S1). The COVID-19 Spike-NRP1 Binding Assay Kit was purchased from RayBiotech Life, Inc. (Peachtree Corners, GA, USA) to measure the binding affinity of spike S1 to NRP1 in the presence of a potential antagonist. The assay was performed on 96-well plates coated with recombinant NRP1 according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Potential antagonists in DMSO (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and the recombinant spike S1 protein were diluted with assay diluent and 100 μL were added to the wells. Since compound 21 was in the form of a trifluoroacetic acid salt, we converted it to the neutral form by adding one molar equivalent of triethylamine (Merck, Kenilworth, NJ, USA) to the solution of the compound, spike, and assay buffer. The plate was incubated at room temperature for 2.5 h using gentle shaking. Unbound S1 was then removed with a wash solution, and 100 μL of a mouse anti-S1 IgG detection antibody were added and incubated at room temperature for 1 h using gentle shaking to establish binding to the S1-NRP1 complex. After washing, 100 μL of an HRP-conjugated secondary anti-mouse IgG were added to the wells and incubated for 1 h with gentle shaking. Finally, after washing, 100 μL of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) substrate were added to the wells and incubated for an additional 30 min using gentle shaking. In this step, the horseradish peroxidase (HRP) reacted with the TMB solution to produce a blue colour proportional to the amount of S1 bound. The HRP-TMB reaction was quenched by the addition of 50 μL of the stop solution, resulting in a colour change from blue to yellow. The intensity of the yellow colour was then measured at 450 nm. The positive control (spike S1), vehicle control (DMSO), triethylamine control, and potential antagonist samples were all run in triplicate. The percentage of binding inhibition of spike S1 was determined using the following equation: BI = [1 − (potential antagonist sample − vehicle control)/positive control] × 100. The screening was performed at a potential antagonist concentration of 100 μM. The VEGF-A antagonist EG00229 (21) [35] and compound 22 [45], which possesses the ability to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 mediated entry, were used as controls at the identical concentration of 100 μM.
4. Conclusions
In the present work, we identified novel small-molecule inhibitors of spike S1 protein binding to NRP1 that could weaken SARS-CoV-2 infectivity. Compounds 16 and 17 displayed more than 60% inhibition and were more active than the EG00229 control (compound 21), a known antagonist that prevents VEGF-A binding to NRP1 and has also been shown to block spike protein binding to NRP1. These results represent starting hit compounds suitable for additional in vitro and cell-based biological evaluations, with the ultimate goal of discovering and optimizing small-molecule inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 spike-NRP1 binding with in vivo activity. As the COVID-19 pandemic seems to be far from over, novel medicinal chemistry approaches and the design of new drugs or biochemical probes are urgently needed.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ph15020165/s1, Figure S1: Molecular docking validation, GOLD configurational file, Table S1: ZINC15 names and MolPort IDs of selected compounds.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K., U.B. and M.J.; experimental, A.K.; analysis, A.K. and M.J.; resources, U.B.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K.; writing—review and editing, M.J. and U.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Slovenian research agency (ARRS) programme and project grants P2-0046 and J1-2471 as well as by the Slovenian Ministry of Education, Science and Sports program grant OP20.04342.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the support of NVIDIA Corporation with the donation of GPU hardware that was used in this research. We also thank Schrödinger LLC and OpenEye software for their support in our research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19---5-october-2021 (accessed on 6 October 2021).
- Gupta, A.; Madhavan, M.V.; Sehgal, K.; Nair, N.; Mahajan, S.; Sehrawat, T.S.; Bikdeli, B.; Ahluwalia, N.; Ausiello, J.C.; Wan, E.Y.; et al. Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Leon, S.; Wegman-Ostrosky, T.; Perelman, C.; Sepulveda, R.; Rebolledo, P.A.; Cuapio, A.; Villapol, S. More than 50 Long-term effects of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, J.L.; Simonetti, B.; Klein, K.; Chen, K.-E.; Kavanagh Williamson, M.; Antón-Plágaro, C.; Shoemark, D.K.; Simón-Gracia, L.; Bauer, M.; Holland, R.; et al. Neuropilin-1 is a host factor for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Science 2020, 370, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantuti-Castelvetri, L.; Ojha, R.; Pedro, L.D.; Djannatian, M.; Franz, J.; Kuivanen, S.; van der Meer, F.; Kallio, K.; Kaya, T.; Anastasina, M.; et al. Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity. Science 2020, 370, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellet-Many, C.; Frankel, P.; Jia, H.; Zachary, I. Neuropilins: Structure, function and role in disease. Biochem. J. 2008, 411, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, S.; Bag, A.K.; Singh, R.K.; Talmadge, J.E.; Batra, S.K.; Datta, K. Multifaceted role of neuropilins in the immune system: Potential targets for immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gudowska-Sawczuk, M.; Mroczko, B. The Role of Neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, F.; Karimi, E.; Firouzifar, M.; Khamushian, P.; Ansari, R.; Mohammadi Ardehali, M. Anosmia as a prominent symptom of COVID-19 infection. Rhinology 2020, 58, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayi, B.S.; Leibowitz, J.A.; Woods, A.T.; Ammon, K.A.; Liu, A.E.; Raja, A. The role of Neuropilin-1 in COVID-19. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlit, P.; Bösel, J.; Gahn, G.; Isenmann, S.; Meuth, S.G.; Nolte, C.H.; Pawlitzki, M.; Rosenow, F.; Schoser, B.; Thomalla, G.; et al. Neurological manifestations of COVID-19—Guideline of the German society of neurology. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machhi, J.; Herskovitz, J.; Senan, A.M.; Dutta, D.; Nath, B.; Oleynikov, M.D.; Blomberg, W.R.; Meigs, D.D.; Hasan, M.; Patel, M.; et al. The natural history, pathobiology, and clinical manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infections. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 359–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, B.; Xu, Y. Targeting VEGF–neuropilin interactions: A promising antitumor strategy. Drug Discov. 2019, 24, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niland, S.; Eble, J.A. Neuropilin: Handyman and power broker in the tumor microenvironment. In Tumor Microenvironment. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1st ed.; Birbrair, A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1223, pp. 31–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.W.; Xu, P.; Li, X.; Vander Kooi, C.W. Structural basis for selective vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) binding to neuropilin-1. JBC 2012, 287, 11082–11089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osman, E.E.A.; Rehemtulla, A.; Neamati, N. Why all the fury over furin? J. Med. Chem. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teesalu, T.; Sugahara, K.N.; Kotamraju, V.R.; Ruoslahti, E. C-end rule peptides mediate neuropilin-1-dependent cell, vascular, and tissue penetration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16157–16162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.P.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Feng, G.K.; Du, Y.; Xiong, D.; Zhong, Q.; Liu, W.-L.; et al. Neuropilin 1 is an entry factor that promotes EBV infection of nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, S.; Bouttier, M.; Vassy, R.; Seigneuret, M.; Petrow-Sadowski, C.; Janvier, S.; Heveker, N.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Perret, G.; Jones, K.S.; et al. HTLV-1 uses HSPG and neuropilin-1 for entry by molecular mimicry of VEGF165. Blood 2009, 113, 5176–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moutal, A.; Martin, L.F.; Boinon, L.; Gomez, K.; Ran, D.; Zhou, Y.; Stratton, H.J.; Cai, S.; Luo, S.; Gonzalez, K.B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein co-opts VEGF-A/Neuropilin-1 receptor signaling to induce analgesia. Pain 2021, 162, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showers, W.M.; Leach, S.M.; Kechris, K.; Strong, M. Longitudinal analysis of SARS-CoV-2 spike and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase protein sequences reveals the emergence and geographic distribution of diverse mutations. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022, 97, 105153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, A.; Basiouni, S.; Parvin, R.; Hafez, H.M.; Shehata, A.A. Evolutionary insights into the furin cleavage sites of SARS-CoV-2 variants from humans and animals. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 2541–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; Dong, Q. Natural polymorphisms are present in the furin cleavage site of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Bagherzadeh, A.; Hartzoulakis, B.; Jarvis, A.; Löhr, M.; Shaikh, S.; Aqil, R.; Cheng, L.; Tickner, M.; Esposito, D.; et al. Characterization of a bicyclic peptide neuropilin-1 (NP-1) antagonist (EG3287) reveals importance of vascular endothelial growth factor exon 8 for NP-1 binding and role of NP-1 in KDR signaling. JBC 2006, 281, 13493–13502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, H.; Aqil, R.; Cheng, L.; Chapman, C.; Shaikh, S.; Jarvis, A.; Chan, A.W.E.; Hartzoulakis, B.; Evans, I.M.; Frolov, A.; et al. N-terminal modification of VEGF-A C terminus-derived peptides delineates structural features involved in neuropilin-1 binding and functional activity. ChemBioChem 2014, 15, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starzec, A.; Vassy, R.; Martin, A.; Lecouvey, M.; Di Benedetto, M.; Crépin, M.; Perret, G.Y. Antiangiogenic and antitumor activities of peptide inhibiting the vascular endothelial growth factor binding to neuropilin-1. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 2370–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tymecka, D.; Puszko, A.K.; Lipiński, P.F.; Fedorczyk, B.; Wilenska, B.; Sura, K.; Perret, G.; Misicka, A. Branched pentapeptides as potent inhibitors of the vascular endothelial growth factor 165 binding to Neuropilin-1: Design, synthesis and biological activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, K.; Puszko, A.K.; Lipiński, P.F.; Laskowska, A.K.; Wileńska, B.; Witkowska, E.; Misicka, A. Design, synthesis and in vitro biological evaluation of a small cyclic peptide as inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor binding to neuropilin-1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2843–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, K.; Puszko, A.K.; Lipiński, P.F.; Laskowska, A.K.; Wileńska, B.; Witkowska, E.; Perret, G.Y.; Misicka, A. Structure-activity relationship study of a small cyclic peptide Hc [Lys-Pro-Glu]-Arg-OH: A potent inhibitor of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor interaction with Neuropilin-1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymecka, D.; Lipiński, P.F.; Fedorczyk, B.; Puszko, A.K.; Wileńska, B.; Perret, G.Y.; Misicka, A. Structure-activity relationship study of tetrapeptide inhibitors of the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A binding to Neuropilin-1. Peptides 2017, 94, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorczyk, B.; Lipiński, P.F.; Tymecka, D.; Puszko, A.K.; Wilenska, B.; Perret, G.Y.; Misicka, A. Conformational latitude–activity relationship of KPPR tetrapeptide analogues toward their ability to inhibit binding of vascular endothelial growth factor 165 to neuropilin-1. J. Pept. Sci. 2017, 23, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Z.; Yu, F.; Han, S.; Yang, S.; Wu, L.; Li, P.; Jiao, S. New peptide MY1340 revert the inhibition effect of VEGF on dendritic cells differentiation and maturation via blocking VEGF-NRP-1 axis and inhibit tumor growth in vivo. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 60, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, A.; Allerston, C.K.; Jia, H.; Herzog, B.; Garza-Garcia, A.; Winfield, N.; Ellard, K.; Aqil, R.; Lynch, R.; Chapman, C.; et al. Small molecule inhibitors of the neuropilin-1 vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2215–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoa, A.; Pellegrini-Moïse, N.; Bechet, D.; Barberi-Heyob, M.; Chapleur, Y. Sugar-based peptidomimetics as potential inhibitors of the vascular endothelium growth factor binding to neuropilin-1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 3285–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, M.; Chateau, A.; Jelsch, C.; Didierjean, C.; Manival, X.; Charron, C.; Bernardi, M.; Murielc, B.-H.; Yvesa, C.; Cédricc, B.; et al. Carbohydrate-based peptidomimetics targeting neuropilin-1: Synthesis, molecular docking study and in vitro biological activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 5315–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.; Mota, F.; Steadman, D.; Soudy, C.; Miyauchi, J.T.; Crosby, S.; Jarvis, A.; Reisinger, T.; Winfield, N.; Evans, G.; et al. Small molecule neuropilin-1 antagonists combine antiangiogenic and antitumor activity with immune modulation through reduction of transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) production in regulatory T-cells. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 4135–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borriello, L.; Montès, M.; Lepelletier, Y.; Leforban, B.; Liu, W.Q.; Demange, L.; Delhomme, B.; Pavoni, S.; Jarray, R.; Boucher, J.L.; et al. Structure-based discovery of a small non-peptidic Neuropilins antagonist exerting in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity on breast cancer model. Cancer Lett. 2014, 349, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starzec, A.; Miteva, M.A.; Ladam, P.; Villoutreix, B.O.; Perret, G.Y. Discovery of novel inhibitors of vascular endothelial growth factor-A–Neuropilin-1 interaction by structure-based virtual screening. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 4042–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Q.; Lepelletier, Y.; Montès, M.; Borriello, L.; Jarray, R.; Grépin, R.; Leforban, B.; Loukaci, A.; Benhida, R.; Hermine, O.; et al. NRPa-308, a new neuropilin-1 antagonist, exerts in vitro anti-angiogenic and anti-proliferative effects and in vivo anti-cancer effects in a mouse xenograft model. Cancer Lett. 2018, 414, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Q.; Megale, V.; Borriello, L.; Leforban, B.; Montès, M.; Goldwaser, E.; Gresh, N.; Piquemal, J.-P.; Hadj-Slimane, R.; Hermine, O.; et al. Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of non-peptidic antagonists of neuropilin-1 receptor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 4254–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachet, E.; Dumond, A.; Liu, W.Q.; Fabre, M.; Selkti, M.; Raynaud, F.; Hermine, O.; Benhida, R.; Belmont, P.; Garbay, C.; et al. Synthesis, 3D-structure and stability analyses of NRPa-308, a new promising anti-cancer agent. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 126710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, K.; Li, Y.; Bai, Y.; Jiang, T.; Sun, H.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, Y. Discovery of novel nonpeptide small-molecule NRP1 antagonists: Virtual screening, molecular simulation and structural modification. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Miller, S.; Patek, M.; Moutal, A.; Duran, P.; Cabel, C.R.; Thorne, C.A.; Campos, S.K.; Khanna, R. Novel compounds targeting neuropilin receptor 1 with potential to interfere with SARS-CoV-2 virus entry. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaewkla, M.; Charoenwongpaiboon, T.; Mahalapbutr, P. Molecular basis of the new COVID-19 target neuropilin-1 in complex with SARS-CoV-2 S1 C-end rule peptide and small-molecule antagonists. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 335, 116537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZINC. Available online: https://zinc15.docking.org/ (accessed on 6 October 2021).
- Shoichet, B.K. Interpreting steep dose-response curves in early inhibitor discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 7274–7277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baell, J.B.; Holloway, G.A. New substructure filters for removal of pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2719–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kopple, K.D. Molecular properties that influence the oral bioavailability of drug candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saubern, S.; Guha, R.; Baell, J.B. KNIME workflow to assess PAINS filters in SMARTS format. Comparison of RDKit and Indigo cheminformatics libraries. Mol. Inform. 2011, 30, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, R. Comparative assessment of scoring functions on an updated benchmark: 2. Evaluation methods and general results. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 1717–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthold, M.R.; Cebron, N.; Dill, F.; Gabriel, T.R.; Kötter, T.; Meinl, T.; Ohl, P.; Thiel, K.; Wiswedel, B. KNIME-the Konstanz information miner: Version 2.0 and beyond. SIGKDD Explor. 2009, 11, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irwin, J.J.; Duan, D.; Torosyan, H.; Doak, A.K.; Ziebart, K.T.; Sterling, T.; Tumanian, G.; Shoichet, B.K. An aggregation advisor for ligand discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7076–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, G.; Willett, P.; Glen, R.C.; Leach, A.R.; Taylo, R. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 267, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verdonk, M.L.; Cole, J.C.; Hartshorn, M.J.; Murray, C.W.; Taylor, R.D. Improved protein-ligand docking using GOLD. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinf. 2003, 52, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysinger, M.M.; Carchia, M.; Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. Directory of useful decoys, enhanced (DUD-E): Better ligands and decoys for better benchmarking. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 6582–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).