Beyond Lipid-Lowering: Effects of Statins on Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases and Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
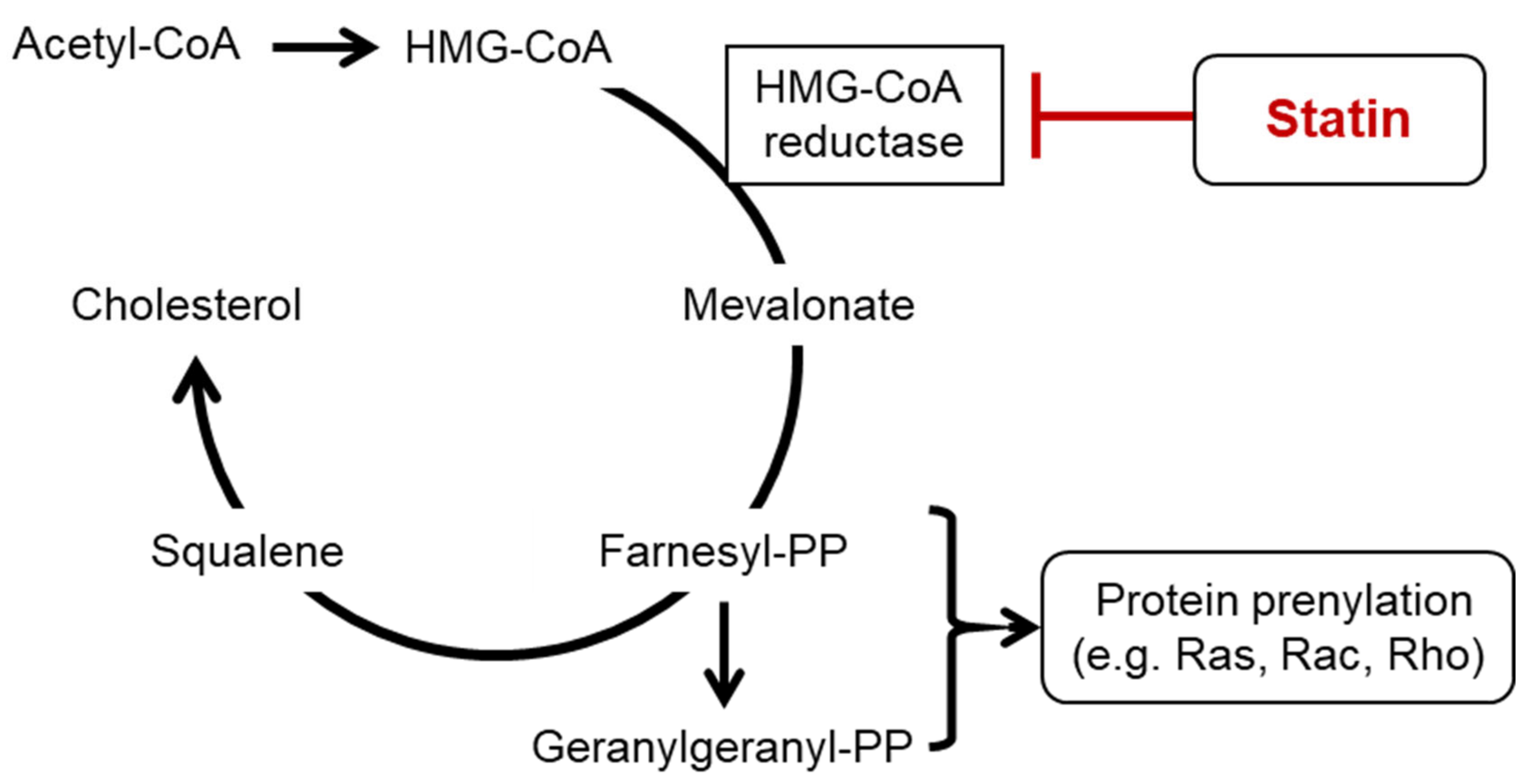
2. Pharmacological Action of Statins
3. Statins and Cardiovascular Diseases
4. Statins and Cerebrovascular Diseases
4.1. Cerebral Infarction
4.2. Intracerebral Hemorrhage
4.3. Cerebral Aneurysm and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
5. Statins and Cancer
5.1. Effective Molecular Markers
5.2. Clinical Studies
5.3. Clinical Studies
5.3.1. Breast Cancer: One of the Promising Scenarios
5.3.2. Leukemia
5.3.3. Multiple Myeloma
5.3.4. Esophageal Cancer
5.3.5. Gastric Cancer
5.3.6. Colorectal Cancer
5.3.7. Hepatocellular Carcinoma
5.3.8. Pancreatic Cancer
5.3.9. Lung Cancer
5.3.10. Renal Cell Carcinoma
5.3.11. Bladder Cancer
5.3.12. Prostate Cancer
5.3.13. Malignant Melanoma
5.4. Limitations
5.4.1. Drawbacks of Epidemiological Studies
5.4.2. Off-Label Use
5.4.3. Natural History: Is Hypocholesterolemia or Hypercholesterolemia Harmful to Malignancies?
5.4.4. Do Statins and Lipid-Lowering Drugs Have Carcinogenicity?
5.4.5. Do Statins and/or Lipid-Lowering Drugs Improve the True Endpoint, All-Cause Mortality?
5.5. Perspective
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schachter, M. Chemical, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of statins: An update. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 19, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Barzi, F.; Jamrozik, K.; TLam, H.; Ueshima, H.; Whitlock, G.; Woodward, M. Asia Pacific cohort studies. Serum triglycerides as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases in the Asia-Pacific region. Circulation 2004, 110, 2678–2686. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarwar, N.; Danesh, J.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Sigurdsson, G.; Wareham, N.; Bingham, S.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Khaw, K.T.; Gudnason, V. Triglycerides and the risk of coronary heart disease: 10,158 incident cases among 262,525 participants in 29 Western prospective studies. Circulation 2007, 115, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iso, H.; Naito, Y.; Sato, S.; Kitamura, A.; Okamura, T.; Sankai, T.; Shimamoto, T.; Iida, M.; Komachi, Y. Serum triglycerides and risk of coronary heart disease among Japanese men and women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 153, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagasawa, S.Y.; Okamura, T.; Iso, H.; Tamakoshi, A.; Yamada, M.; Watanabe, M.; Murakami, Y.; Miura, K.; Ueshima, H. Evidence for cardiovascular prevention from observational cohorts in Japan research. Relation between serum total cholesterol level and cardiovascular disease stratified by sex and age group: A pooled analysis of 65,594 individuals from 10 cohort studies in Japan. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2012, 1, e001974. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Assmann, G.; Schulte, H.; von Eckardstein, A.; Huang, Y. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol as a predictor of coronary heart disease risk. The PROCAM. experience and pathophysiological implications for reverse cholesterol transport. Atherosclerosis 1996, 124, S11–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, A.; Iso, H.; Naito, Y.; Iida, M.; Konishi, M.; Folsom, A.R.; Sato, S.; Kiyama, M.; Nakamura, M.; Sankai, T.; et al. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and premature coronary heart disease in urban Japanese men. Circulation 1994, 89, 2533–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamura, T.; Kokubo, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Higashiyama, A.; Miyamoto, Y.; Yoshimasa, Y.; Okayama, A. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and the incidence of cardiovascular disease in an urban Japanese cohort study: The Suita study. Atherosclerosis 2009, 203, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Amiri, S.; Pecic, S.; Machaj, F.; Rosik, J.; Los, M.J.; Alizadeh, J.; Mahdian, R.; Rosa, S.C.d.; Schaafsma, D.; et al. Pleiotropic effects of statins: A focus on cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, O.; Schlezinger, S.; Rosenblat, M.; Keidar, S.; Aviram, M. Reduced susceptibility of low density lipoprotein (LDL) to lipid peroxidation after fluvastatin therapy is associated with the hypocholesterolemic effect of the drug and its binding to the LDL. Atherosclerosis 1997, 128, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agewall, S.; Hernberg, A. Atorvastatin normalizes endothelial function in healthy smokers. Clin. Sci. 2006, 111, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verma, S.; Rao, V.; Weisel, R.D.; Li, S.H.; Fedak, P.W.; Miriuka, S.; Li, R.K. Novel cardioprotective effects of pravastatin in human ventricular cardiomyocytes subjected to hypoxia and reoxygenation: Beneficial effects of statins independent of endothelial cells. J. Surg. Res. 2004, 119, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorabi, A.M.; Kiaie, N.; Bianconi, V.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Al-Rasadi, K.; Johnston, T.P.; Pirro, M.; Sahebkar, A. Antiviral effects of statins. Prog. Lipid Res. 2020, 79, 101054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorabi, A.M.; Kiaie, N.; Bianconi, V.; Pirro, M.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. Statins attenuate fibrotic manifestations of cardiac tissue damage. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 782–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorabi, A.M.; Kiaie, N.; Pirro, M.; Bianconi, V.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. Effects of statins on the biological featuRes. of mesenchymal stem cells and therapeutic implications. Heart Fail. Rev. 2021, 26, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassano, A.; Platanias, L.C. Statins in tumor suppression. Cancer Lett. 2008, 260, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayengbam, S.S.; Singh, A.; Pillai, A.D.; Bhat, M.K. Influence of cholesterol on cancer progression and therapy. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, A.; Kuroda, M.; Tanzawa, K. Competitive inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase by ML-236A and ML-236B fungal metabolites, having hypocholesterolemic activity. FEBS Lett. 1976, 72, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maeda, K.; Sugiyama, Y. Impact of genetic polymorphisms of transporters on the pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and toxicological properties of anionic drugs. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2008, 23, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitara, Y.; Sugiyama, Y. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic alterations of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors: Drug-drug interactions and interindividual differences in transporter and metabolic enzyme functions. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 112, 71–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirtori, C.R. The pharmacology of statins. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 88, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, J.D.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. SREBPs: Activators of the complete progrAm. of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, C.; Wang, X.; Briggs, M.R.; Admon, A.; Wu, J.; Hua, X.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. SREBP-1, a basic-helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper protein that controls transcription of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene. Cell 1993, 75, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimano, H.; Sato, R. SREBP-regulated lipid metabolism: Convergent physiology—Divergent pathophysiology. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 710–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, E.J.; Rachlis, B.; Wu, P.; Devereaux, P.J.; Arora, P.; Perri, D. Primary prevention of cardiovascular mortality and events with statin treatments: A network meta-analysis involving more than 65,000 patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1769–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oesterle, A.; Laufs, U.; Liao, J.K. Pleiotropic effects of statins on the cardiovascular system. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kavalipati, N.; Shah, J.; Ramakrishan, A.; Vasnawala, H. Pleiotropic effects of statins. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 19, 554–562. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Liao, J.K. Pleiotropic effects of statins. Basic research and clinical perspectives. Circ. J. 2010, 74, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, J.M.; Raut, N.G.R.; Seifert, J.L.; Hynds, D.L. Regulation of small GTPase prenylation in the nervous system. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 2220–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mraiche, F.; Cena, J.; Das, D.; Vollrath, B. Effects of statins on vascular function of endothelin-1. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 144, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ichiki, T.; Takeda, K.; Tokunou, T.; Iino, N.; Egashira, K.; Shimokawa, H.; Hirano, K.; Kanaide, H.; Takeshita, A. Downregulation of angiotensin II type 1 receptor by hydrophobic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors in vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 1896–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Yamanouchi, D.; Komori, K. Therapeutic approach against intimal hyperplasia of vein grafts through endothelial nitric oxide synthase/nitric oxide (eNOS/NO) and the Rho/Rho-kinase pathway. Surg. Today 2009, 39, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M.K.; Ridker, P.M. Anti-inflammatory effects of statins: Clinical evidence and basic mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, G.; Duez, H.; Blanquart, C.; Berezowski, V.; Poulain, P.; Fruchart, J.C.; Najib-Fruchart, J.; Glineur, C.; Staels, B. Statin-induced inhibition of the Rho-signaling pathway activates PPARalpha and induces HDL apoA-I. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yano, M.; Matsumura, T.; Senokuchi, T.; Ishii, N.; Murata, Y.; Taketa, K.; Motoshima, H.; Taguchi, T.; Sonoda, K.; Kukidome, D.; et al. Statins activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma through extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder-Nascimento, T.; Callera, G.E.; Montezano, A.C.; de Chantemele, E.J.B.; Tostes, R.C.; Touyz, R.M. Atorvastatin inhibits pro-inflammatory actions of aldosterone in vascular smooth muscle cells by reducing oxidative stress. Life Sci. 2019, 221, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder-Nascimento, T.; Callera, G.E.; Montezano, A.C.; He, Y.; Antunes, T.T.; Cat, A.N.D.; Tostes, R.C.; Touyz, R.M. Vascular injury in diabetic db/db mice is ameliorated by atorvastatin: Role of Rac1/2-sensitive Nox-dependent pathways. Clin. Sci. 2015, 128, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyi, M.; Buday, L.; Hegedus, B. K-Ras prenylation as a potential anticancer target. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, G.H.; Kwon, M.; Jung, H.; Ko, E.; Kim, S.A.; Choi, Y.; Song, S.J.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, G.B.; et al. Statin-mediated inhibition of RAS prenylation activates ER stress to enhance the immunogenicity of KRAS mutant cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri-Sacca, M.; Barba, M.; Pizzuti, L.; Vici, P.; di Lauro, L.; Dattilo, R.; Vitale, I.; Bartucci, M.; Mottolese, M.; de Maria, R. The Hippo transducers TAZ and YAP in breast cancer: Oncogenic activities and clinical implications. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2015, 17, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Osada, H.; Murakami-Tonami, Y.; Horio, Y.; Hida, T.; Sekido, Y. Statin suppresses Hippo pathway-inactivated malignant mesothelioma cells and blocks the YAP/CD44 growth stimulatory axis. Cancer Lett. 2017, 385, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Mei, L.; Fang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Interplay of mevalonate and Hippo pathways regulates RHAMM transcription via YAP to modulate breast cancer cell motility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E89–E98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dichtl, W.; Dulak, J.; Frick, M.; Alber, H.F.; Schwarzacher, S.P.; Ares, M.P.; Nilsson, J.; Pachinger, O.; Weidinger, F. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors regulate inflammatory transcription factors in human endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ridker, P.M.; Danielson, E.; Fonseca, F.A.; Genest, J.; Gotto, A.M., Jr.; Kastelein, J.J.; Koenig, W.; Libby, P.; Lorenzatti, A.J.; Macfadyen, J.G.; et al. Reduction in C-reactive protein and LDL cholesterol and cardiovascular event rates after initiation of rosuvastatin: A prospective study of the JUPITER trial. Lancet 2009, 373, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousoulis, D.; Psarros, C.; Demosthenous, M.; Patel, R.; Antoniades, C.; Stefanadis, C. Innate and adaptive inflammation as a therapeutic target in vascular disease: The emerging role of statins. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2491–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, X.; Xie, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Liao, X.; Shen, J.; Shi, M.; Li, W.; Zheng, H.; Jiang, B. Statin use and risk of pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control 2012, 23, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Z.; Chase, A.J.; Newby, A.C. Statins inhibit secretion of metalloproteinases-1, -2, -3, and -9 from vascular smooth muscle cells and macrophages. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eto, M.; Kozai, T.; Cosentino, F.; Joch, H.; Luscher, T.F. Statin prevents tissue factor expression in human endothelial cells: Role of Rho/Rho-kinase and Akt pathways. Circulation 2002, 105, 1756–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourcier, T.; Libby, P. HMG CoA reductase inhibitors reduce plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression by human vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, F.Y.; Armstrong, P.C.; Dhanji, A.R.; Tucker, A.T.; Paul-Clark, M.J.; Mitchell, J.A.; Warner, T.D. Antiplatelet actions of statins and fibrates are mediated by PPARs. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llevadot, J.; Murasawa, S.; Kureishi, Y.; Uchida, S.; Masuda, H.; Kawamoto, A.; Walsh, K.; Isner, J.M.; Asahara, T. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor mobilizes bone marrow--derived endothelial progenitor cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimmeler, S.; Aicher, A.; Vasa, M.; Mildner-Rihm, C.; Adler, K.; Tiemann, M.; Rutten, H.; Fichtlscherer, S.; Martin, H.; Zeiher, A.M. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) increase endothelial progenitor cells via the PI 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, M.; Heeschen, C.; Glassford, A.J.; Cooke, J.P. Statins have biphasic effects on angiogenesis. Circulation 2002, 105, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Fahmy, U.A.; Ahmed, O.A.A.; Asfour, H.Z.; Althagafi, A.A.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Rizg, W.Y.; Mahdi, W.A.; Alghaith, A.F.; et al. Cytotoxic and pro-apoptotic effects of a sub-toxic concentration of fluvastatin on OVCAR3 ovarian cancer cells after its optimized formulation to melittin nano-conjugates. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 642171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawber, T.R.; Moore, F.E.; Mann, G.V. Coronary heart disease in the Framingham study. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1957, 47, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baigent, C.; Keech, A.; Kearney, P.M.; Blackwell, L.; Buck, G.; Pollicino, C.; Kirby, A.; Sourjina, T.; Peto, R.; Collins, R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of cholesterol-lowering treatment: Prospective meta-analysis of data from 90,056 participants in 14 randomised trials of statins. Lancet 2005, 366, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trialists, C.C.T.; Baigent, C.; Blackwell, L.; Emberson, J.; Holland, L.E.; Reith, C.; Bhala, N.; Peto, R.; Barnes, E.H.; Keech, A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of more intensive lowering of LDL cholesterol: A meta-analysis of data from 170,000 participants in 26 randomised trials. Lancet 2010, 376, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskinas, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; de Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019, ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boekholdt, S.M.; Hovingh, G.K.; Mora, S.; Arsenault, B.J.; Amarenco, P.; Pedersen, T.R.; LaRosa, J.C.; Waters, D.D.; DeMicco, D.A.; Simes, R.J.; et al. Very low levels of atherogenic lipoproteins and the risk for cardiovascular events: A meta-analysis of statin trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reiner, Z. Managing the residual cardiovascular disease risk associated with HDL-cholesterol and triglycerides in statin-treated patients: A clinical update. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Joshi, P.H.; Rinehart, S.; Thakker, K.M.; Lele, A.; Voros, S. Baseline very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol is associated with the magnitude of triglyceride lowering on statins, fenofibric acid, or their combination in patients with mixed dyslipidemia. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2014, 7, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barter, P.J.; Brandrup-Wognsen, G.; Palmer, M.K.; Nicholls, S.J. Effect of statins on HDL-C: A complex process unrelated to changes in LDL-C: Analysis of the VOYAGER Database. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ford, I.; Murray, H.; McCowan, C.; Packard, C.J. Long-term safety and efficacy of lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol with statin therapy: 20-year follow-up of west of scotland coronary prevention study. Circulation 2016, 133, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, C.B.; Preiss, D.; Tobert, J.A.; Jacobson, T.A.; Page, R.L., 2nd; Goldstein, L.B.; Chin, C.; Tannock, L.R.; Miller, M.; Raghuveer, G.; et al. Statin safety and associated adverse events: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, e38–e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfeffer, M.A.; Sacks, F.M.; Moye, L.A.; Brown, L.; Rouleau, J.L.; Hartley, L.H.; Rouleau, J.; Grimm, R.; Sestier, F.; Wickemeyer, W.; et al. Cholesterol and recurrent events: A secondary prevention trial for normolipidemic patients, CARE Investigators. Am. J. Cardiol. 1995, 76, 98C–106C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simes, R.J.; Marschner, I.C.; Hunt, D.; Colquhoun, D.; Sullivan, D.; Stewart, R.A.; Hague, W.; Keech, A.; Thompson, P.; White, H.; et al. Relationship between lipid levels and clinical outcomes in the Long-term Intervention with Pravastatin in Ischemic Disease (LIPID) Trial: To what extent is the reduction in coronary events with pravastatin explained by on-study lipid levels? Circulation 2002, 105, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, R.; Armitage, J.; Parish, S.; Sleight, P.; Peto, R.; Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group. Effects of cholesterol-lowering with simvastatin on stroke and oTher. major vascular events in 20536 people with cerebrovascular disease or oTher. high-risk conditions. Lancet 2004, 363, 757–767. [Google Scholar]
- Amarenco, P.; Bogousslavsky, J.; Callahan, A., 3rd; Goldstein, L.B.; Hennerici, M.; Rudolph, A.E.; Sillesen, H.; Simunovic, L.; Szarek, M.; Welch, K.M.; et al. Stroke prevention by aggressive reduction in cholesterol levels. High-dose atorvastatin after stroke or transient ischemic attack. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 549–559. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S. Role of blood lipid levels and lipid-lowering therapy in stroke patients with different levels of cerebral artery diseases: Reconsidering recent stroke guidelines. J. Stroke 2021, 23, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevas, K.I.; Tzovaras, A.A.; Briana, D.D.; Mikhailidis, D.P. Emerging indications for statins: A pluripotent family of agents with several potential applications. Curr. Pharm Des. 2007, 13, 3622–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevas, K.I.; Veith, F.J.; Eckstein, H.H.; Ricco, J.B.; Mikhailidis, D.P. Cholesterol, carotid artery disease and stroke: What the vascular specialist needs to know. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasińska, M.; Owczarek, J.; Orszulak-Michalak, D. Statins: A new insight into their mechanisms of action and consequent pleiotropic effects. Pharmacol. Rep. 2007, 59, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bedi, O.; Dhawan, V.; Sharma, P.L.; Kumar, P. Pleiotropic effects of statins: New therapeutic targets in drug design. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2016, 389, 695–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosomi, N.; Nagai, Y.; Kohriyama, T.; Ohtsuki, T.; Aoki, S.; Nezu, T.; Maruyama, H.; Sunami, N.; Yokota, C.; Kitagawa, K.; et al. The Japan statin treatment against recurrent stroke (J-STARS): A multicenter, randomized, open-label, parallel-group study. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flint, A.C.; Kamel, H.; Navi, B.B.; Rao, V.A.; Faigeles, B.S.; Conell, C.; Klingman, J.G.; Sidney, S.; Hills, N.K.; Sorel, M.; et al. Statin use during ischemic stroke hospitalization is strongly associated with improved poststroke survival. Stroke 2012, 43, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshimura, S.; Uchida, K.; Daimon, T.; Takashima, R.; Kimura, K.; Morimoto, T.; Investigator, A.T. Randomized controlled trial of early versus delayed statin therapy in patients with acute ischemic stroke: ASSORT trial (Administration of Statin on Acute Ischemic Stroke Patient). Stroke 2017, 48, 3057–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhao, K.; Bao, Q.; Yang, J.; Yang, M. Statin use and outcomes of patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with intravenous thrombolysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 734927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gu, F.; Ding, J.; Bian, J.; Wang, N.; Shu, R.; Li, Q.; Xu, X. The predictors and prognosis for unexpected reocclusion after mechanical thrombectomy: A meta-analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marto, J.P.; Strambo, D.; Hajdu, S.D.; Eskandari, A.; Nannoni, S.; Sirimarco, G.; Bartolini, B.; Puccinelli, F.; Maeder, P.; Saliou, G.; et al. Twenty-four-hour reocclusion after successful mechanical thrombectomy: Associated factors and long-term prognosis. Stroke 2019, 50, 2960–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Shin, H.S.; Oh, I. The protective effects of statins towards vessel wall injury caused by a stent retrieving mechanical thrombectomy device: A histological analysis of the rabbit carotid artery model. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2021, 64, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanos, A.H.; Lioutas, V.A.; Charidimou, A.; Catanese, L.; Ng, K.K.H.; Perera, K.; de Boasquevisque, D.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Smith, E.E.; Sharma, M.; et al. Statin treatment and accrual of covert cerebral ischaemia on neuroimaging: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Shen, L.; Mai, H.; Zang, J.; Liu, Y.; Tsang, C.K.; Li, K.; Xu, A. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors attenuate neuronal damage by suppressing oxygen glucose deprivation-induced activated microglial cells. Neural Plast. 2019, 2019, 7675496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Lu, D.; Yang, W.; Shi, C.; Zang, J.; Shen, L.; Mai, H.; Xu, A. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors relieve endoplasmic reticulum stress by autophagy inhibition in rats with permanent brain ischemia. Front. NeuroSci. 2018, 12, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.J.; Dai, T.M.; Shen, Y.Y.; He, J.L.; Li, J.; Tu, J.L. Atorvastatin pretreatment attenuates ischemic brain edema by suppressing aquaporin 4. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 3247–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, S.; Tanaka, T.; Tomari, S.; Fukuma, K.; Ishiyama, H.; Abe, S.; Arimizu, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ogata, S.; Nishimura, K.; et al. Statin treatment can reduce incidence of early seizure in acute ischemic stroke: A propensity score analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Ding, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhou, C.; Lin, W. Effects of atorvastatin and aspirin on post-stroke epilepsy and usage of levetiracetam. Medicine 2020, 99, e23577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Xie, D.; Li, Y. Efficacy of Statin therapy in post-stroke seizure prophylaxis: Clues from an observational study of routine secondary prevention treatment. Seizure 2019, 71, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackam, D.G.; Woodward, M.; Newby, L.K.; Bhatt, D.L.; Shao, M.; Smith, E.E.; Donner, A.; Mamdani, M.; Douketis, J.D.; Arima, H.; et al. Statins and intracerebral hemorrhage: Collaborative systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation 2011, 124, 2233–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J. Is the Benefit of antithrombotics and statins worth the risk of intracerebral hemorrhage? It depends. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e020460. [Google Scholar]
- Katsanos, A.H.; Lioutas, V.A.; Charidimou, A.; Catanese, L.; Ng, K.K.H.; Perera, K.; de Boasquevisque, D.; Falcone, G.J.; Sheth, K.N.; Romero, J.R.; et al. Statin treatment and cerebral microbleeds: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 420, 117224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, W.; Rennert, H.S.; Barnett-Griness, O.; Gronich, N.; Molad, J.; Rennert, G.; Auriel, E. Association of statin use with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: A cohort study. Neurology 2018, 91, e400–e409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Knight, R.A.; Han, Y.; Karki, K.; Zhang, J.; Chopp, M.; Seyfried, D.M. Statins protect the blood brain barrier acutely after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Behav. Brain Sci. 2013, 3, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.J.; Wang, D.; Gao, F.; Li, Y.R. Effects of atorvastatin on pathological changes in brain tissue and plasma MMP-9 in rats with intracerebral hemorrhage. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 62, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewen, T.; Qiuting, L.; Chaogang, T.; Tao, T.; Jun, W.; Liming, T.; Guanghong, X. Neuroprotective effect of atorvastatin involves suppression of TNF-α and upregulation of IL-10 in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 66, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Ding, D.; Ironside, N.; Buell, T.J.; Elder, L.J.; Warren, A.; Adams, A.P.; Ratcliffe, S.J.; James, R.F.; Naval, N.S.; et al. Statins for neuroprotection in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2019, 93, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, L.; Zhou, W.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Li, N.; Xu, J.; You, C.; Wang, C.; Tian, M. Rosuvastatin nanomicelles target neuroinflammation and improve neurological deficit in a mouse model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 2933–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Cao, D.; Li, Y.; Peng, A.; Wang, Y.; Gao, K.; Tao, C.; Wu, Y. Atorvastatin ameliorates early brain injury through inhibition of apoptosis and ER stress in a rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. BioSci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20171035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.H.; Wu, T.; Yang, L.K.; Chen, L.; Zhu, J.; Li, P.P.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.H. Protective effects of atorvastatin on cerebral vessel autoregulation in an experimental rabbit model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Yang, L.K.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.H.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, B.J.; Zhu, J.; Li, P.P. Atorvastatin ameliorates early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage via inhibition of AQP4 expression in rabbits. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Li, M.; Zhu, X.; Chen, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, C.; Wu, T.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q. Atorvastatin reduces cerebral vasospasm and infarction after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in elderly Chinese adults. Aging 2020, 12, 2939–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.J.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, J. The impact of statin therapy after surgical or endovascular treatment of cerebral aneurysms. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 133, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Naraoka, M.; Matsuda, N.; Shimamura, N.; Asano, K.; Akasaka, K.; Takemura, A.; Hasegawa, S.; Ohkuma, H. Long-acting statin for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, J.R.; Wang, H.; McGirt, M.J.; Floyd, J.; Friedman, A.H.; Coon, A.L.; Blessing, R.; Alexander, M.J.; Graffagnino, C.; Warner, D.S.; et al. Simvastatin reduces vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: Results of a pilot randomized clinical trial. Stroke 2005, 36, 2024–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.H.; Xu, W.; Hai, J.; Wu, Y.F.; Yu, F. Effects of statins-use for patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, J.; Shen, J.; Zhu, K.; Zhou, H.; Tian, H.; Yu, G. Efficacy of statins in cerebral vasospasm. mortality, and delayed cerebral ischemia in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. World Neurosurg. 2019, 131, e65–e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohara, S.; Gaonkar, V.B.; Garg, K.; Rajpal, P.M.S.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, M.; Suri, A.; Chandra, P.S.; Kale, S.S. Effect of statins on functional outcome and mortality following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage—Results of a meta-analysis, metaregression and trial sequential analysis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 207, 106787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergouwen, M.D.; Meijers, J.C.; Geskus, R.B.; Coert, B.A.; Horn, J.; Stroes, E.S.; van der Poll, T.; Vermeulen, M.; Roos, Y.B. Biologic effects of simvastatin in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2009, 29, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Liu, H.; Jiang, J.; Jia, C.; Zhang, B.; Gao, X. Clinical evidence of efficacy of simvastatin for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Int. Med. Res. 2017, 45, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Can, A.; Castro, V.M.; Dligach, D.; Finan, S.; Yu, S.; Gainer, V.; Shadick, N.A.; Savova, G.; Murphy, S.; Cai, T.; et al. Lipid-Lowering agents and high HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) are inversely associated with intracranial aneurysm rupture. Stroke 2018, 49, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terceno, M.; Remollo, S.; Silva, Y.; Bashir, S.; Werner, M.; Vera-Monge, V.A.; Serena, J.; Castano, C. Effect of combined acetylsalicylic acid and statins treatment on intracranial aneurysm rupture. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Uwano, I.; Sasaki, M.; Takahashi, O.; Sakai, N.; Tsuruta, W.; Nakase, H.; Ogasawara, K.; Osato, T.; Takahashi, J.C.; et al. Small unruptured aneurysm verification-prevention effect against growth of cerebral aneurysm study using statin. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2021, 61, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, J.; van Leeuwen, J.E.; Elbaz, M.; Branchard, E.; Penn, L.Z. Statins as anticancer agents in the era of precision medicine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 5791–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgquist, S.; Bjarnadottir, O.; Kimbung, S.; Ahern, T.P. Statins: A role in breast cancer therapy? J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guerra, B.; Recio, C.; Aranda-Tavio, H.; Guerra-Rodriguez, M.; Garcia-Castellano, J.M.; Fernandez-Perez, L. The mevalonate pathway, a metabolic target in cancer therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 626971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, N.; Dhayer, M.; Boileau, M.; Fovez, Q.; Kluza, J.; Marchetti, P. Lipid metabolism and resistance to anticancer treatment. Biology 2020, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Hu, J.W.; He, X.R.; Jin, W.L.; He, X.Y. Statins: A repurposed drug to fight cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garwood, E.R.; Kumar, A.S.; Baehner, F.L.; Moore, D.H.; Au, A.; Hylton, N.; Flowers, C.I.; Garber, J.; Lesnikoski, B.A.; Hwang, E.S.; et al. Fluvastatin reduces proliferation and increases apoptosis in women with high grade breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 119, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feldt, M.; Bjarnadottir, O.; Kimbung, S.; Jirstrom, K.; Bendahl, P.O.; Veerla, S.; Grabau, D.; Hedenfalk, I.; Borgquist, S. Statin-induced anti-proliferative effects via cyClin. D1 and p27 in a window-of-opportunity breast cancer trial. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 133. [Google Scholar]
- Alarfi, H.; Youssef, L.A.; Salamoon, M. A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled study of a combination of simvastatin and chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 4174395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulian, E.D.; Bajuadji, N.C.S. Combination of simvastatin and FAC improves response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in advanced local breast cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 53, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornblau, S.M.; Banker, D.E.; Stirewalt, D.; Shen, D.; Lemker, E.; Verstovsek, S.; Estrov, Z.; Faderl, S.; Cortes, J.; Beran, M.; et al. Blockade of adaptive defensive changes in cholesterol uptake and synthesis in AML by the addition of pravastatin to idarubicin + high-dose Ara-C: A phase 1 study. Blood 2007, 109, 2999–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Advani, A.S.; McDonough, S.; Copelan, E.; Willman, C.; Mulford, D.A.; List, A.F.; Sekeres, M.A.; Othus, M.; Appelbaum, F.R. SWOG0919: A Phase 2 study of idarubicin and cytarabine in combination with pravastatin for relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol 2014, 167, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Advani, A.S.; Li, H.; Michaelis, L.C.; Medeiros, B.C.; Liedtke, M.; List, A.F.; O’Dwyer, K.; Othus, M.; Erba, H.P.; Appelbaum, F.R. Report of the relapsed/refractory cohort of SWOG S0919: A phase 2 study of idarubicin and cytarabine in combination with pravastatin for acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). Leuk. Res. 2018, 67, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidmaier, R.; Baumann, P.; Bumeder, I.; Meinhardt, G.; Straka, C.; Emmerich, B. First clinical experience with simvastatin to overcome drug resistance in refractory multiple myeloma. Eur. J. Haematol 2007, 79, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hus, M.; Grzasko, N.; Szostek, M.; Pluta, A.; Helbig, G.; Woszczyk, D.; Adamczyk-Cioch, M.; Jawniak, D.; Legiec, W.; Morawska, M.; et al. Thalidomide, dexamethasone and lovastatin with autologous stem cell transplantation as a salvage immunomodulatory therapy in patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. Ann. Hematol. 2011, 90, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexandre, L.; Clark, A.B.; Walton, S.; Lewis, M.P.; Kumar, B.; Cheong, E.C.; Warren, H.; Kadirkamanathan, S.S.; Parsons, S.L.; Dresner, S.M.; et al. Adjuvant statin therapy for oesophageal adenocarcinoma: The STAT-ROC feasibility study. BJS Open 2020, 4, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.S.; Kim, M.M.; Choi, H.J.; Yoon, S.S.; Lee, M.H.; Park, K.; Park, C.H.; Kang, W.K. Phase II study of high-dose lovastatin in patients with advanced gastric adenocarcinoma. Investig. New Drugs 2001, 19, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konings, I.R.; van der Gaast, A.; van der Wijk, L.J.; de Jongh, F.E.; Eskens, F.A.; Sleijfer, S. The addition of pravastatin to chemotherapy in advanced gastric carcinoma: A randomised phase II trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 3200–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, J.; Park, S.H.; Park, J.O.; Park, Y.S.; Lim, H.Y.; Hwang, I.G.; Lee, S.C.; Park, K.W.; et al. Simvastatin plus capecitabine-cisplatin versus placebo plus capecitabine-cisplatin in patients with previously untreated advanced gastric cancer: A double-blind randomised phase 3 study. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2822–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Kim, T.W.; Hong, Y.S.; Han, S.W.; Lee, K.H.; Kang, H.J.; Hwang, I.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.T.; et al. A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled multi-centre phase III trial of XELIRI/FOLFIRI plus simvastatin for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jouve, J.L.; Lecomte, T.; Bouche, O.; Barbier, E.; Akouz, F.K.; Riachi, G.; Khac, E.N.; Ollivier-Hourmand, I.; Debette-Gratien, M.; Faroux, R.; et al. Pravastatin combination with sorafenib does not improve survival in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanc, J.F.; Khemissa, F.; Bronowicki, J.P.; Monterymard, C.; Perarnau, J.M.; Bourgeois, V.; Obled, S.; Abdelghani, M.B.; Mabile-Archambeaud, I.; Faroux, R.; et al. Phase 2 trial comparing sorafenib, pravastatin, their combination or supportive care in HCC with Child-Pugh B cirrhosis. Hepatol. Int. 2021, 15, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riano, I.; Martin, L.; Varela, M.; Serrano, T.; Nunez, O.; Minguez, B.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Perugorria, M.J.; Banales, J.M.; Arenas, J.I. Efficacy and safety of the combination of pravastatin and sorafenib for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (ESTAHEP clinical trial). Cancers 2020, 12, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawata, S.; Yamasaki, E.; Nagase, T.; Inui, Y.; Ito, N.; Matsuda, Y.; Inada, M.; Tamura, S.; Noda, S.; Imai, Y.; et al. Effect of pravastatin on survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. A randomized controlled trial. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 84, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, J.Y.; Nam, E.M.; Lee, J.; Park, J.O.; Lee, S.C.; Song, S.Y.; Choi, S.H.; Heo, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Lim, H.Y.; et al. Randomized double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase II trial of simvastatin and gemcitabine in advanced pancreatic cancer patients. Cancer ChemoTher. Pharmacol. 2014, 73, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seckl, M.J.; Ottensmeier, C.H.; Cullen, M.; Schmid, P.; Ngai, Y.; Muthukumar, D.; Thompson, J.; Harden, S.; Middleton, G.; Fife, K.M.; et al. Multicenter, phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of pravastatin added to first-line standard chemotherapy in small-cell lung cancer (LUNGSTAR). J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, G.K.; Lee, S.H.; Lim, K.Y.; Joo, J.; Go, Y.J.; Lee, J.S.; Han, J.Y. Randomized phase II study of afatinib plus simvastatin versus afatinib alone in previously treated patients with advanced nonadenocarcinomatous non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 49, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Yoo, N.J.; Hyung, L.S.; Moon, Y.J.; Yun, T.; Kim, H.T.; Lee, J.S. A randomized phase II study of gefitinib plus simvastatin versus gefitinib alone in previously treated patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, L.J.; Melnichouk, O.; Huszti, E.; Connelly, P.W.; Greenberg, C.V.; Minkin, S.; Boyd, N.F. Serum lipids, lipoproteins, and risk of breast cancer: A nested case-control study using multiple time points. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Undela, K.; Srikanth, V.; Bansal, D. Statin use and risk of breast cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 135, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menamin, U.C.M.; Murray, L.J.; Hughes, C.M.; Cardwell, C.R. Statin use and breast cancer survival: A nationwide cohort study in Scotland. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borgquist, S.; Broberg, P.; Tojjar, J.; Olsson, H. Statin use and breast cancer survival—A Swedish nationwide study. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nowakowska, M.K.; Lei, X.; Thompson, M.T.; Shaitelman, S.F.; Wehner, M.R.; Woodward, W.A.; Giordano, S.H.; Nead, K.T. Association of statin use with clinical outcomes in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer 2021, 127, 4142–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goard, C.A.; Chan-Seng-Yue, M.; Mullen, P.J.; Quiroga, A.D.; Wasylishen, A.R.; Clendening, J.W.; Sendorek, D.H.; Haider, S.; Lehner, R.; Boutros, P.C.; et al. Identifying molecular features that distinguish fluvastatin-sensitive breast tumor cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 143, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warita, K.; Warita, T.; Beckwitt, C.H.; Schurdak, M.E.; Vazquez, A.; Wells, A.; Oltvai, Z.N. Statin-induced mevalonate pathway inhibition attenuates the growth of mesenchymal-like cancer cells that lack functional E-cadherin mediated cell cohesion. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viswanathan, V.S.; Ryan, M.J.; Dhruv, H.D.; Gill, S.; Eichhoff, O.M.; Seashore-Ludlow, B.; Kaffenberger, S.D.; Eaton, J.K.; Shimada, K.; Aguirre, A.J.; et al. Dependency of a therapy-resistant state of cancer cells on a lipid peroxidase pathway. Nature 2017, 547, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Longo, J.; van Leeuwen, J.E.; Mullen, P.J.; Ba-Alawi, W.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Penn, L.Z. Statin-induced cancer cell death can be mechanistically uncoupled from prenylation of RAS family proteins. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghasemi, A.; Ghashghai, Z.; Akbari, J.; Yazdani-Charati, J.; Salehifar, E.; Hosseinimehr, S.J. Topical atorvastatin 1% for prevention of skin toxicity in patients receiving radiation therapy for breast cancer: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 75, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabati, M.; Janbabai, G.; Esmailian, J.; Yazdani, J. Effect of rosuvastatin in preventing chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity in women with breast cancer: A randomized. single-blind. placebo-controlled trial. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 24, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvillo-Arguelles, O.; Abdel-Qadir, H.; Michalowska, M.; Billia, F.; Suntheralingam, S.; Amir, E.; Thavendiranathan, P. Cardioprotective effect of statins in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer receiving trastuzumab therapy. Can. J. Cardiol. 2019, 35, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradelli, D.; Soranna, D.; Zambon, A.; Catapano, A.; Mancia, G.; la Vecchia, C.; Corrao, G. Statins use and the risk of all and subtype hematological malignancies: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponvilawan, B.; Charoenngam, N.; Rittiphairoj, T.; Ungprasert, P. Receipt of statins is associated with lower risk of multiple myeloma: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020, 20, e399–e413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, B. Statin use and the risk of multiple myeloma: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, A.G.; Singh, P.P.; Murad, M.H.; Iyer, P.G. Statins are associated with reduced risk of esophageal cancer, particularly in patients with Barrett’s esophagus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassanabad, A.F.; Wong, J.V.S. Statins as potential therapeutics for esophageal cancer. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2021, 52, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyamsundar, M.; McAuley, D.F.; Shields, M.O.; MacSweeney, R.; Duffy, M.J.; Johnston, J.R.; McGuigan, J.; Backman, J.T.; Calfee, C.S.; Matthay, M.M.; et al. Effect of simvastatin on physiological and biological outcomes in patients undergoing esophagectomy: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Surg. 2014, 259, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.F.; Ho, S.C.; Chang, C.C.; Wu, T.N.; Yang, C.Y. Statins are associated with a reduced risk of gastric cancer: A population-based case-control study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 2098–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.P.; Singh, S. Statins are associated with reduced risk of gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.D.; Zeng, K.; Xue, F.Q.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, Y.Q. Statins are associated with reduced risk of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 69, 1855–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.S.; Chan, E.W.; Wong, A.Y.S.; Chen, L.; Seto, W.K.; Wong, I.C.K.; Leung, W.K. Statins were associated with a reduced gastric cancer risk in patients with eradicated helicobacter pylori infection: A territory-wide propensity score matched study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nseir, W.; Diab, H.; Mahamid, M.; Abu-Elheja, O.; Samara, M.; Abid, A.; Mograbi, J. Randomised clinical trial: Simvastatin as adjuvant therapy improves significantly the Helicobacter pylori eradication rate--a placebo-controlled study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 36, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkeshikian, S.S.; Ghadir, M.R.; Alemi, F.; Jalali, S.M.; Hormati, A.; Mohammadbeigi, A. Atorvastatin in combination with conventional antimicrobial treatment of Helicobacter pylori eradication: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poynter, J.N.; Gruber, S.B.; Higgins, P.D.; Almog, R.; Bonner, J.D.; Rennert, H.S.; Low, M.; Greenson, J.K.; Rennert, G. Statins and the risk of colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2184–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, W.; Wang, J.; Xie, L.; Li, T.; He, Y.; Deng, Y.; Peng, Q.; Li, S.; Qin, X. Association between statin use and colorectal cancer risk: A meta-analysis of 42 studies. Cancer Causes Control 2014, 25, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourlotfi, A.; Ahl, R.; Sjolin, G.; Forssten, M.P.; Bass, G.A.; Cao, Y.; Matthiessen, P.; Mohseni, S. Statin therapy and postoperative short-term mortality after rectal cancer surgery. Colorectal Dis. 2021, 23, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krens, L.L.; Simkens, L.H.; Baas, J.M.; Koomen, E.R.; Gelderblom, H.; Punt, C.J.; Guchelaar, H.J. Statin use is not associated with improved progression free survival in cetuximab treated KRAS mutant metastatic colorectal cancer patients: Results from the CAIRO2 study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112201. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, K.; Ogino, S.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Chan, J.A.; Chan, A.T.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Hollis, D.; Saltz, L.B.; Mayer, R.J.; Benson, A.B., 3rd; et al. Relationship between statin use and colon cancer recurrence and survival: Results from CALGB 89803. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 1540–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, M.B.; Gormly, K.; Espinoza, D.; Hague, W.; Asghari, G.; Jeffery, G.M.; Price, T.J.; Karapetis, C.S.; Arendse, M.; Armstrong, J.; et al. SPAR—A randomised, placebo-controlled phase II trial of simvastatin in addition to standard chemotherapy and radiation in preoperative treatment for rectal cancer: An AGITG clinical trial. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, B.W.; Weiss, J.M. Chemoprevention of colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 368–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradelli, D.; Soranna, D.; Scotti, L.; Zambon, A.; Catapano, A.; Mancia, G.; la Vecchia, C.; Corrao, G. Statins and primary liver cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 22, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.C.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Y.Y.; Hao, F.B.; Wang, K.; Gong, J.P. Meta-analysis of studies using statins as a reducer for primary liver cancer risk. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, M.; Zheng, H.; Nie, B.; Gong, W.; Cui, X. Statin use and risk of liver cancer: An update meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e005399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, V.; Sheth, A.; Caldito, G.; Barkin, J.S. Statins reduce the risk of pancreatic cancer in humans: A case-control study of half a million veterans. Pancreas 2007, 34, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Song, X.; Zhang, G.; Peng, A.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C. Statins and the risk of lung cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L.; Qin, X. Lipid-lowering medication use and cancer-specific survival among endometrial or lung cancer patients: An Australian nationwide cohort study. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 77, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Thuren, T.; Everett, B.M.; Libby, P.; Glynn, R.J.; Group, C.T. Effect of interleukin-1beta inhibition with canakinumab on incident lung cancer in patients with atherosclerosis: Exploratory results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, M.S.; Chen, I.C.; Lee, C.P.; Huang, R.J.; Chen, P.C.; Tsai, Y.H.; Yang, Y.H. Statin improves survival in patients with EGFR-TKI lung cancer: A nationwide population-based study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, P.A.; Chang, C.C.; Galvin, C.J.; Wang, Y.C.; An, S.Y.; Huang, C.W.; Wang, Y.H.; Hsu, M.H.; Li, Y.J.; Yang, H.C. Statins use and its impact in EGFR-TKIs resistance to prolong the survival of lung cancer patients: A Cancer registry cohort study in Taiwan. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 2965–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantini, L.; Pecci, F.; Hurkmans, D.P.; Belderbos, R.A.; Lanese, A.; Copparoni, C.; Aerts, S.; Cornelissen, R.; Dumoulin, D.W.; Fiordoliva, I.; et al. High-intensity statins are associated with improved clinical activity of PD-1 inhibitors in malignant pleural mesothelioma and advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 144, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Liu, M.; Qian, J.; Zheng, J.H.; Zhang, X.P.; Guo, C.C.; Geng, J.; Peng, B.; Che, J.P.; Wu, Y. Statin use and risk of kidney cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies and randomized trials. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 77, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Choueiri, T.K.; Cho, E. Statin use and the risk of renal cell carcinoma in 2 prospective US cohorts. Cancer 2012, 118, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chou, Y.C.; Lin, C.H.; Wong, C.S.; Chou, W.Y.; Chang, J.Y.; Sun, C.A. Statin use and the risk of renal cell carcinoma: National cohort study. J. Investig. Med. 2020, 68, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boegemann, M.; Schlack, K.; Rink, M.; Bernhardt, S.; Moran, M.; Hubbe, M.; Bergmann, L.; Schmid, M.; Strauss, A. Effect of comorbidities/comedications on sunitinib outcomes for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: The STAR-TOR registry. Future Oncol. 2020, 16, 2939–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortellini, A.; Tucci, M.; Adamo, V.; Stucci, L.S.; Russo, A.; Tanda, E.T.; Spagnolo, F.; Rastelli, F.; Bisonni, R.; Santini, D.; et al. Integrated analysis of concomitant medications and oncological outcomes from PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoInt. inhibitors in clinical practice. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001361. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.K.; Min, G.E.; Jeon, S.H.; Lee, H.L.; Chang, S.G.; Yoo, K.H. Effects of statins on the prognosis of local and locally advanced renal cell carcinoma following nephrectomy. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 1, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamilton, R.J.; Morilla, D.; Cabrera, F.; Leapman, M.; Chen, L.Y.; Bernstein, M.; Hakimi, A.A.; Reuter, V.E.; Russo, P. The association between statin medication and progression after surgery for localized renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2014, 191, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zang, T. Association between statin usage and prostate cancer prevention: A refined meta-analysis based on literature from the years 2005–2010. Urol. Int. 2013, 90, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, E.; Hagberg, O.; Jahnson, S.; Ljungberg, B. Association between occurrence of urinary bladder cancer and treatment with statin medication. Turk. J. Urol. 2019, 45, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, P.O.; Ahmad, A.E.; Bashir, S.; Hamilton, R.J.; Nam, R.K.; Leao, R.; Jeldres, C.; Kulkarni, G.S. Effect of statins as a secondary chemopreventive agent among individuals with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A population-based analysis. Urol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guercio, V.; Turati, F.; Bosetti, C.; Polesel, J.; Serraino, D.; Montella, M.; Libra, M.; Galfano, A.; la Vecchia, C.; Tavani, A. Bladder cancer risk in users of selected drugs for cardiovascular disease prevention. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 28, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourbeer, K.N.; Howard, L.E.; Andriole, G.L.; Moreira, D.M.; Castro-Santamaria, R.; Freedland, S.J.; Vidal, A.C. Metabolic syndrome-like components and prostate cancer risk: Results from the reduction by dutasteride of prostate cancer events (REDUCE) study. BJU Int. 2015, 115, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.; Howard, L.E.; Vidal, A.C.; Moreira, D.M.; Castro-Santamaria, R.; Andriole, G.L.; Freedland, S.J. Serum cholesterol and risk of lower urinary tract symptoms progression: Results from the reduction by dutasteride of prostate cancer events study. Int. J. Urol. 2017, 24, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pernar, C.H.; Ebot, E.M.; Wilson, K.M.; Mucci, L.A. The epidemiology of prostate cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a030361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, D.; Undela, K.; D’Cruz, S.; Schifano, F. Statin use and risk of prostate cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46691. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhu, N.; Kapur, N.; Catalona, W.; Leikin, R.; Helenowski, I.; Jovanovich, B.; Gurley, M.; Okwuosa, T.M.; Kuzel, T.M. Statin use and risk of prostate cancer biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 130.e9–130.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyad, M.A.; Merrick, G.S.; Butler, W.M.; Wallner, K.E.; Galbreath, R.W.; Kurko, B.; Adamovich, E. Statins, especially atorvastatin, may favorably influence clinical presentation and biochemical progression-free survival after brachytherapy for clinically localized prostate cancer. Urology 2005, 66, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.K.; Han, B.K.; Jeong, S.J.; Byun, S.S.; Lee, S.E. Effect of statin therapy on early return of potency after nerve sparing radical retropubic prostatectomy. J. Urol. 2007, 178, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allott, E.H.; Howard, L.E.; Vidal, A.C.; Moreira, D.M.; Castro-Santamaria, R.; Andriole, G.L.; Freedland, S.J. Statin use, serum lipids, and prostate inflammation in men with a negative prostate biopsy: Results from the REDUCE trial. Cancer Prev. Res. 2017, 10, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allott, E.H.; Csizmadi, I.; Howard, L.E.; Muller, R.L.; Moreira, D.M.; Andriole, G.L.; Roehrborn, C.G.; Freedland, S.J. Statin use and longitudinal changes in prostate volume; results from the reduction by DUtasteride of prostate cancer events (REDUCE) trial. BJU Int. 2020, 125, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.J.; Yaxley, J.W.; Coughlin, G.D.; Gianduzzo, T.R.; Esler, R.C.; Dunglison, N.T.; Chambers, S.K.; Medcraft, R.J.; Chow, C.W.; Schirra, H.J.; et al. Can atorvastatin with metformin change the natural history of prostate cancer as characterized by molecular, metabolomic, imaging and pathological variables? A randomized controlled trial protocol. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2016, 50, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Downs, J.R.; Clearfield, M.; Weis, S.; Whitney, E.; Shapiro, D.R.; Beere, P.A.; Langendorfer, A.; Stein, E.A.; Kruyer, W.; Gotto, A.M., Jr. Primary prevention of acute coronary events with lovastatin in men and women with average cholesterol levels: Results of AFCAPS/TexCAPS. Air force/texas coronary atherosclerosis prevention study. JAMA 1998, 279, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.L.; Qin, X. Does adherence to lipid-lowering medications improve cancer survival? A nationwide study of breast and colorectal cancer, and melanoma. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 1847–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannesdottir, S.A.; Chang, E.T.; Mehnert, F.; Schmidt, M.; Olesen, A.B.; Sorensen, H.T. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the risk of skin cancer: A population-based case-control study. Cancer 2012, 118, 4768–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, S.R.; Drake, A.L.; Heilig, L.F.; Graber, M.; McNealy, K.; Schilling, L.M.; Dellavalle, R.P. Statins, fibrates, and melanoma risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linden, K.G.; Leachman, S.A.; Zager, J.S.; Jakowatz, J.G.; Viner, J.L.; McLaren, C.E.; Barr, R.J.; Carpenter, P.M.; Chen, W.P.; Elmets, C.A.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II clinical trial of lovastatin for various endpoints of melanoma pathobiology. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emilsson, L.; Garcia-Albeniz, X.; Logan, R.W.; Caniglia, E.C.; Kalager, M.; Hernan, M.A. Examining bias in studies of statin treatment and survival in patients with cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.; Lewis, R.J. Immortal time bias in observational studies. JAMA 2021, 325, 686–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.M.; Castelli, W.P.; Levy, D. Cholesterol and mortality. 30 years of follow-up from the FraminghAm. study. JAMA 1987, 257, 2176–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iso, H.; Naito, Y.; Kitamura, A.; Sato, S.; Kiyama, M.; Takayama, Y.; Iida, M.; Shimamoto, T.; Sankai, T.; Komachi, Y. Serum total cholesterol and mortality in a Japanese population. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1994, 47, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannamethee, G.; Shaper, A.G.; Whincup, P.H.; Walker, M. Low serum total cholesterol concentrations and mortality in middle aged British men. BMJ 1995, 311, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.M.; Sung, J.; Kim, J.S. Which cholesterol level is related to the lowest mortality in a population with low mean cholesterol level: A 6.4-year follow-up study of 482,472 Korean men. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 151, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuzaki, M.; Kita, T.; Mabuchi, H.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Nakaya, N.; Oikawa, S.; Saito, Y.; Sasaki, J.; Shimamoto, K.; Itakura, H.; et al. Large scale cohort study of the relationship between serum cholesterol concentration and coronary events with low-dose simvastatin therapy in Japanese patients with hypercholesterolemia. Circ. J. 2002, 66, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malmborg, M.; Christiansen, C.B.; Schmiegelow, M.D.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Gislason, G.; Schou, M. Incidence of new onset cancer in patients with a myocardial infarction—A nationwide cohort study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2018, 18, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pursnani, A.; Massaro, J.M.; D’Agostino, R.B., Sr.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Hoffmann, U. Guideline-based statin eligibility. Cancer events, and noncardiovascular mortality in the Framingham. Heart Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2927–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Ji, S.; Mei, Z.; Li, T. Association of metabolic syndrome and its components with risk of stroke recurrence and mortality: A meta-analysis. Neurology 2021, 97, e695–e705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sijbrands, E.J.; Westendorp, R.G.; Defesche, J.C.; de Meier, P.H.; Smelt, A.H.; Kastelein, J.J. Mortality over two centuries in large pedigree with familial hypercholesterolaemia: Family tree mortality study. BMJ 2001, 322, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spiegel, R.J.; Schaefer, E.J.; Magrath, I.T.; Edwards, B.K. Plasma lipid alterations in leukemia and lymphoma. Am. J. Med. 1982, 72, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, C.G.; Blatsios, B.; Avgerinos, A. Serum lipids and lipoprotein disorders in cancer patients. Cancer 1987, 60, 3065–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.J.; Sacks, F.M.; Mitchell, J.S.; East, C.; Glasser, S.; Kell, S.; Letterer, R.; Limacher, M.; Moye, L.A.; Rouleau, J.L.; et al. Effect of pravastatin on cardiovascular events in women after myocardial infarction: The cholesterol and recurrent events (CARE) trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1998, 32, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwata, H.; Matsuo, K.; Hara, S.; Takeuchi, K.; Aoyama, T.; Murashige, N.; Kanda, Y.; Mori, S.; Suzuki, R.; Tachibana, S.; et al. Use of hydroxy-methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors is associated with risk of lymphoid malignancies. Cancer Sci. 2006, 97, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agalliu, I.; Salinas, C.A.; Hansten, P.D.; Ostrander, E.A.; Stanford, J.L. Statin use and risk of prostate cancer: Results from a population-based epidemiologic study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 168, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, P.; Roumeguere, T.; Schulman, C.; van Velthoven, R. Use of statins and outcome of BCG treatment for bladder cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2705–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsheikh-Ali, A.A.; Trikalinos, T.A.; Kent, D.M.; Karas, R.H. Statins, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and risk of cancer. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ford, I.; Blauw, G.J.; Murphy, M.B.; Shepherd, J.; Cobbe, S.M.; Bollen, E.L.; Buckley, B.M.; Jukema, J.W.; Hyland, M.; Gaw, A.; et al. A prospective study of pravastatin in the elderly at risk (PROSPER): Screening experience and baseline characteristics. Curr. Control Trials Cardiovasc. Med. 2002, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hunt, D.; Young, P.; Simes, J.; Hague, W.; Mann, S.; Owensby, D.; Lane, G.; Tonkin, A. Benefits of pravastatin on cardiovascular events and mortality in older patients with coronary heart disease are equal to or exceed those seen in younger patients: Results from the LIPID trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 134, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, M.R.; Mascitelli, L.; Pezzetta, F. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with statins: Cautionary notes. QJM 2009, 102, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliver, M.F. Cholesterol-lowering and cancer in the prevention of cardiovascular disease. QJM 2010, 103, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, H.; Arakawa, K.; Itakura, H.; Kitabatake, A.; Goto, Y.; Toyota, T.; Nakaya, N.; Nishimoto, S.; Muranaka, M.; Yamamoto, A.; et al. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with pravastatin in Japan (MEGA Study): A prospective randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2006, 368, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, S.; Bosch, J.; Dagenais, G.; Zhu, J.; Xavier, D.; Liu, L.; Pais, P.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Leiter, L.A.; Dans, A.; et al. Cholesterol lowering in intermediate-risk persons without cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2021–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yusuf, S.; Joseph, P.; Dans, A.; Gao, P.; Teo, K.; Xavier, D.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Yusoff, K.; Santoso, A.; Gamra, H.; et al. Polypill with or without aspirin in persons without cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, T.B.; Hulley, S.B. Carcinogenicity of lipid-lowering drugs. JAMA 1996, 275, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, C.P.; Blazing, M.A.; Giugliano, R.P.; McCagg, A.; White, J.A.; Theroux, P.; Darius, H.; Lewis, B.S.; Ophuis, T.O.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Ezetimibe added to statin therapy after acute coronary syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2387–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossebo, A.B.; Pedersen, T.R.; Boman, K.; Brudi, P.; Chambers, J.B.; Egstrup, K.; Gerdts, E.; Gohlke-Barwolf, C.; Holme, I.; Kesaniemi, Y.A.; et al. Intensive lipid lowering with simvastatin and ezetimibe in aortic stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1343–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giugliano, R.P.; Gencer, B.; Wiviott, S.D.; Park, J.G.; Fuchs, C.S.; Goessling, W.; Musliner, T.A.; Tershakovec, A.M.; Blazing, M.A.; Califf, R.; et al. Prospective evaluation of malignancy in 17,708 patients randomized to ezetimibe versus placebo: Analysis from IMPROVE-IT. JACC Cardiooncol. 2020, 2, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.; Ramey, D.R.; Emneus, M.; Iachina, M.; Stavem, K.; Bolin, K.; McNally, R.; Busch-Sorensen, M.; Willenheimer, R.; Egstrup, K.; et al. Incidence of cancer and mortality in patients from the simvastatin and ezetimibe in aortic stenosis (SEAS) trial. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 114, 1518–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Keech, A.C.; Honarpour, N.; Wiviott, S.D.; Murphy, S.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Wasserman, S.M.; et al. Evolocumab and clinical outcomes in patients with cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A co-operative trial in the primary prevention of ischaemic heart disease using clofibrate. Report from the Committee of Principal Investigators. Br. Heart J. 1978, 40, 1069–1118. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokomichi, H.; Nagai, A.; Hirata, M.; Tamakoshi, A.; Kiyohara, Y.; Kamatani, Y.; Muto, K.; Ninomiya, T.; Matsuda, K.; Kubo, M.; et al. Statin use and all-cause and cancer mortality: BioBank Japan cohort. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, S84–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morofuji, Y.; Nakagawa, S. Drug development for central nervous system diseases using in vitro blood-brain barrier models and drug repositioning. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 1466–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
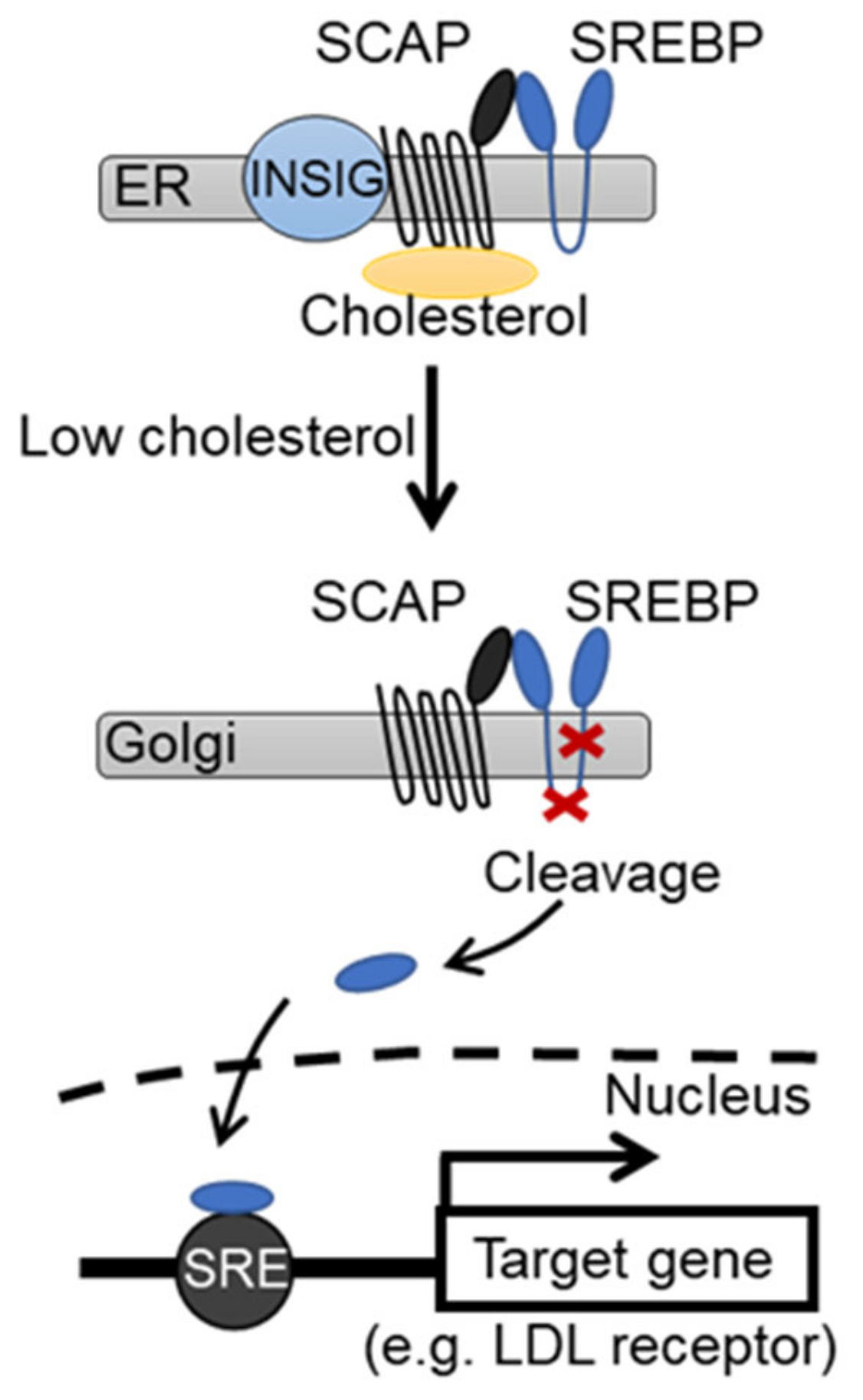
| Lipid-lowering activities | |
| Cholesterol biosynthesis ↓ | [1] |
| LDL-receptors ↑ | [22,23] |
| Endothelial function | |
| Expression and activity of Nitric oxide ↑ | [32] |
| Endothelin-1 ↓ | [30] |
| Angiotensin II receptor ↓ | [31] |
| NF-κB activation ↓ | [43] |
| Anti-inflammatory effects | |
| Pro-inflammatory cytokines ↓ | [33,34,35] |
| C-reactive protein ↓ | [44] |
| Adhesion molecules ↓ | [45] |
| Matrix Metalloprotease ↓ | [46,47] |
| NF-κB activation ↓ | [43] |
| Antioxidant activity | |
| NADPH oxidase activity ↓ | [37] |
| Reactive oxygen species production ↓ | [36] |
| Antithrombotic activities | |
| Tissue factor expression ↓ | [48] |
| Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression ↓ | [49] |
| Platelet activation ↓ | [50] |
| Tissue-type plasminogen activator expression ↑ | [49] |
| Angiogenesis | |
| Endothelial progenitor cells ↑ | [51,52] |
| PI3 kinase activity ↑ | [52] |
| Angiogenesis ↑ | [53] |
| (Statins have biphasic effects on angiogenesis; high-dose statins inhibit angiogenesis) | |
| Antitumor activity | |
| Pro-apoptotic protein ↑ | [54] |
| Cell proliferation ↓ | [38,39] |
| Angiogenesis (High dose) ↓ | [53] |
| Hippo-Yap/TAZ pathway ↓ | [40,41,42] |
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Economically reasonable and well-tolerated | Off-label use |
| Except for hypocholesterolemia | Hypercholesterolemia |
| Favorable for malignancies? | Carcinogenic? |
| Many observational studies | Biases |
| Statins improve cardiovascular outcomes | Lipid-lowering drugs may not necessarily improve all causes of death |
| Authors, Year | Study Type | Patients | Evaluation | Comparison | Outcome | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Garwood, 2010 [117] | II | High grade ER- negative breast cancer | High dose fluvastatin | Low dose fluvastatin | Ki-67 index, caspase 3 cleavage | Fluvastatin increases apoptosis and decreases proliferation of cancer cells. |
| Feldt, 2015 [118] | II | Invasive breast cancer | Atorvastatin | None | p27, cyclin D1 | Atorvastatin induces anti-proliferative effects through up-regulation of tumor suppressor p27 and down-regulation of cyclin D1. |
| Alarfi, 2020 [119] | II RCT | Metastatic breast cancer | Simvastatin, carboplatin, vinorelbine | Carboplatin, vinorelbine | ORR, OS | The chemo-sensitizing effect was investigated, but simvastatin did not improve ORR, and OS. |
| Yulian, 2021 [120] | II RCT | Advanced breast cancer | Simvastatin, FU, ADM, CPA | FU, ADM, CPA | ORR, OS | Simvastatin increased pathlogical ORR but did not improve OS. |
| Kornblau, 2007 [121] | I | New AML and recurrent AML | Pravastatin, idarubicin, cytarabine | Historical control | ORR | Pravastatin idarubicin, and high-dose cytarabine induce CR in 11 new patients and 9 salvage patients. |
| Advani, 2014 [122] | II | Relapsed AML | Pravastatin, idarubicin, cytarabine | Historical control | ORR | Idarubicin, cytarabine, and pravastatin improve the ORR. |
| Advani, 2018 [123] | II RCT | New AML | Pravastatin, idarubicin, cytarabine | Idarubicin, cytarabine | ORR | Pravastatin did not meet the prespecified efficacy criteria in newly diagnosed 24 AML patients. |
| Schmidmaier, 2007 [124] | II | Multiple myeloma, treated with two cycles of bortezomib or bendamustine | Simvastatin plus additional 2 cycles of bortezomib or bendamustine | Additional 2 cycles of bortezomib or bendamustine | Chemotherapy resistance | Simvastatin reduces chemotherapy resistance in 6 patients with refractory MM compared to 10 patients treated with chemotherapy alone. |
| Hus, 2011 [125] | II RCT | Relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma | Lovastatin, thalidomide, dexamethasone | Thalidomide, dexamethasone | OS, PFS | Lovastatin prolongs OS and PFS. |
| Alexandre, 2020 [126] | II RCT | Esophageal cancer | Esophagectomy with simvastatin | Esophagectomy without simvastatin | OS, PFS | The one-year simvastatin administration for patients with esophageal cancer who had undergone esophagectomy did not conclude the survival outcomes. |
| Kim, 2001 [127] | II | Advanced gastric cancer | Lovastatin, ubiquinone | None | ORR, toxicity | Lovastatin with ubiquinone was ineffective. NO ORR improvement was observed. |
| Konings, 2010 [128] | II RCT | Advanced gastric carcinoma | Pravastatin, epirubicin, cisplatin, capecitabine | Epirubicin, cisplatin, capecitabine | OS, PFS | Pravastatin did not improve OS and PFS. |
| Kim, 2014 [129] | III RCT | Metastatic gastric or EC junction adenocarcinoma | Simvastatin, capecitabine, cisplatin | Capecitabine, cisplatin | PFS | Simvastatin did not increase PFS compared with chemotherapy alone. |
| Lim, 2015 [130] | III RCT | Metastatic colorectal cancer | Simvastatin, FOLFIRI or XELIRI | FOLFIRI or XELIRI | OS, PFS | Simvastatin plus chemotherapy did not increase OS and PFS compared with chemotherapy alone. |
| Jouve, 2019 [131] | RCT | Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma | Pravastatin, sorafenib | Sorafenib | OS, PFS, TTP | Sorafenib plus pravastatin did not improve TTP, PFS, and OS compared with sorafenib alone. |
| Blanc, 2021 [132] | II RCT | Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma | Pravastatin, sorafenib | Sorafenib alone or pravastatin alone. | OS PFS | Sorafenib or pravastatin did not improve outcomes. Sorafenib is potentially effective. |
| Riano, 2020 [133] | II RCT | Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma | Pravastatin, sorafenib | Sorafenib | OS, TTP | Sorafenib plus pravastatin did not improve TTP compared with sorafenib alone. |
| Kawata, 2001 [134] | RCT | Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma | Pravastatin, embolization, FU | Embolization, FU | OS | Transcatheter arterial embolization followed by fluorouracil and pravastatin prolongs OS compared with the standard therapy alone. |
| Hong, 2014 [135] | II RCT | Advanced pancreatic cancer | Simvastatin, gemcitabine | Gemcitabine | TTP | Gemcitabine plus simvastatin did not decrease TTP compared with gemcitabine alone. |
| Seckl, 2017 [136] | III RCT | Small cell lung cancer | Pravastatin, etoposide plus cisplatin or carboplatin | Etoposide plus cisplatin or carboplatin | OS, PFS | Pravastatin did not offer additional benefits. |
| Lee, 2017 [137] | II RCT | Lung cancer (NSCLC, non- adenocarcinomas) | Simvastatin, afatinib | Afatinib | ORR | Simvastatin did not improve response rates. compared with afatinib alone in patients with non-adenocarcinomas |
| Han, 2011 [138] | II RCT | Lung cancer (NSCLC) | Simvastatin, gefitinib | Gefitinib | PFS, ORR | No outcome improvement was observed. Simvastatin increases response rates and PFS only in patients with EGFR wild type non-adenocarcinoma. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morofuji, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; Ujifuku, K.; Fujimoto, T.; Otsuka, K.; Niwa, M.; Tsutsumi, K. Beyond Lipid-Lowering: Effects of Statins on Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases and Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020151
Morofuji Y, Nakagawa S, Ujifuku K, Fujimoto T, Otsuka K, Niwa M, Tsutsumi K. Beyond Lipid-Lowering: Effects of Statins on Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases and Cancer. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(2):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020151
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorofuji, Yoichi, Shinsuke Nakagawa, Kenta Ujifuku, Takashi Fujimoto, Kaishi Otsuka, Masami Niwa, and Keisuke Tsutsumi. 2022. "Beyond Lipid-Lowering: Effects of Statins on Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases and Cancer" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 2: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020151
APA StyleMorofuji, Y., Nakagawa, S., Ujifuku, K., Fujimoto, T., Otsuka, K., Niwa, M., & Tsutsumi, K. (2022). Beyond Lipid-Lowering: Effects of Statins on Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases and Cancer. Pharmaceuticals, 15(2), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020151







