Photolytic Controlled Release Formulation of Methotrexate Loaded in Chitosan/TiO2 Nanoparticles for Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
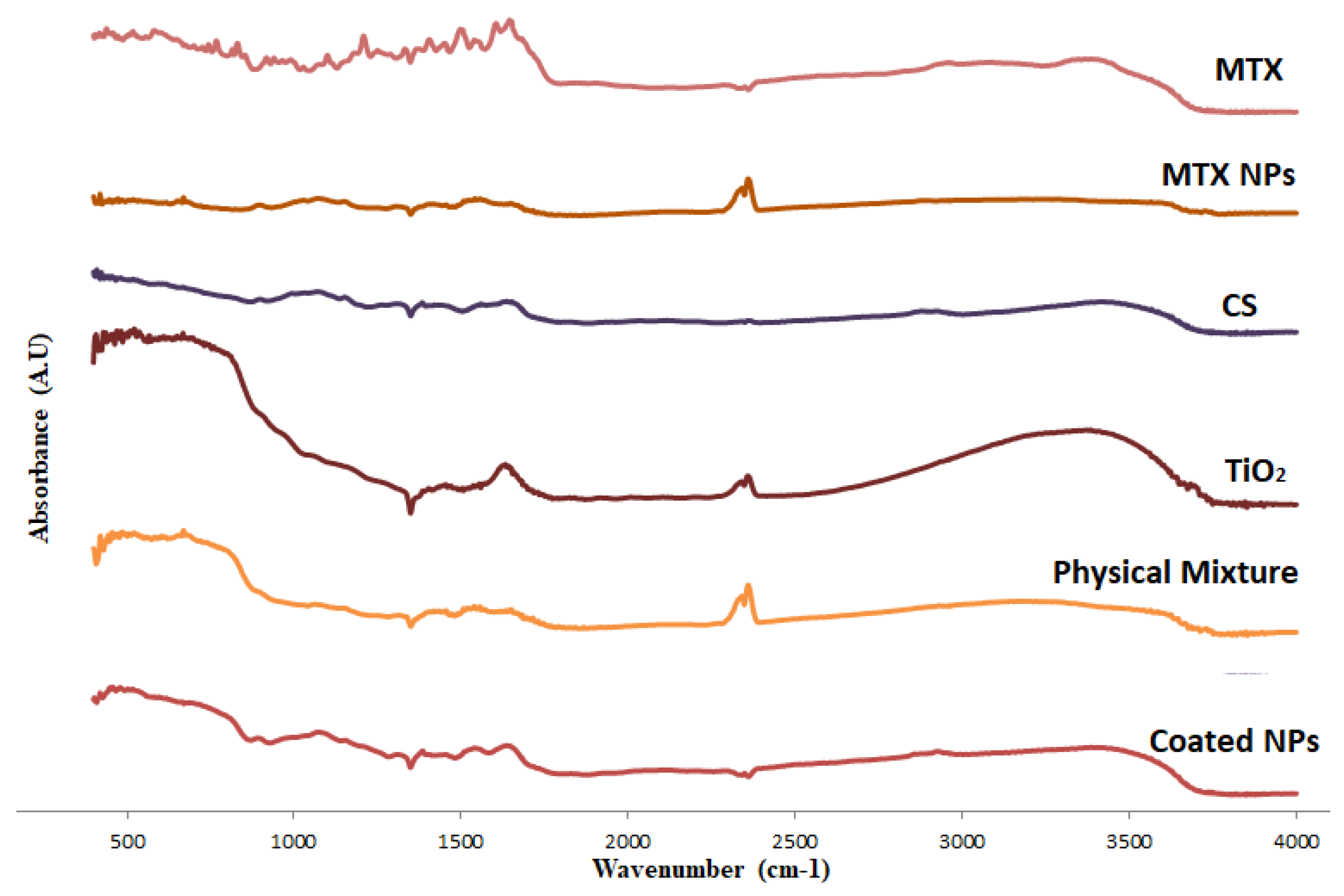
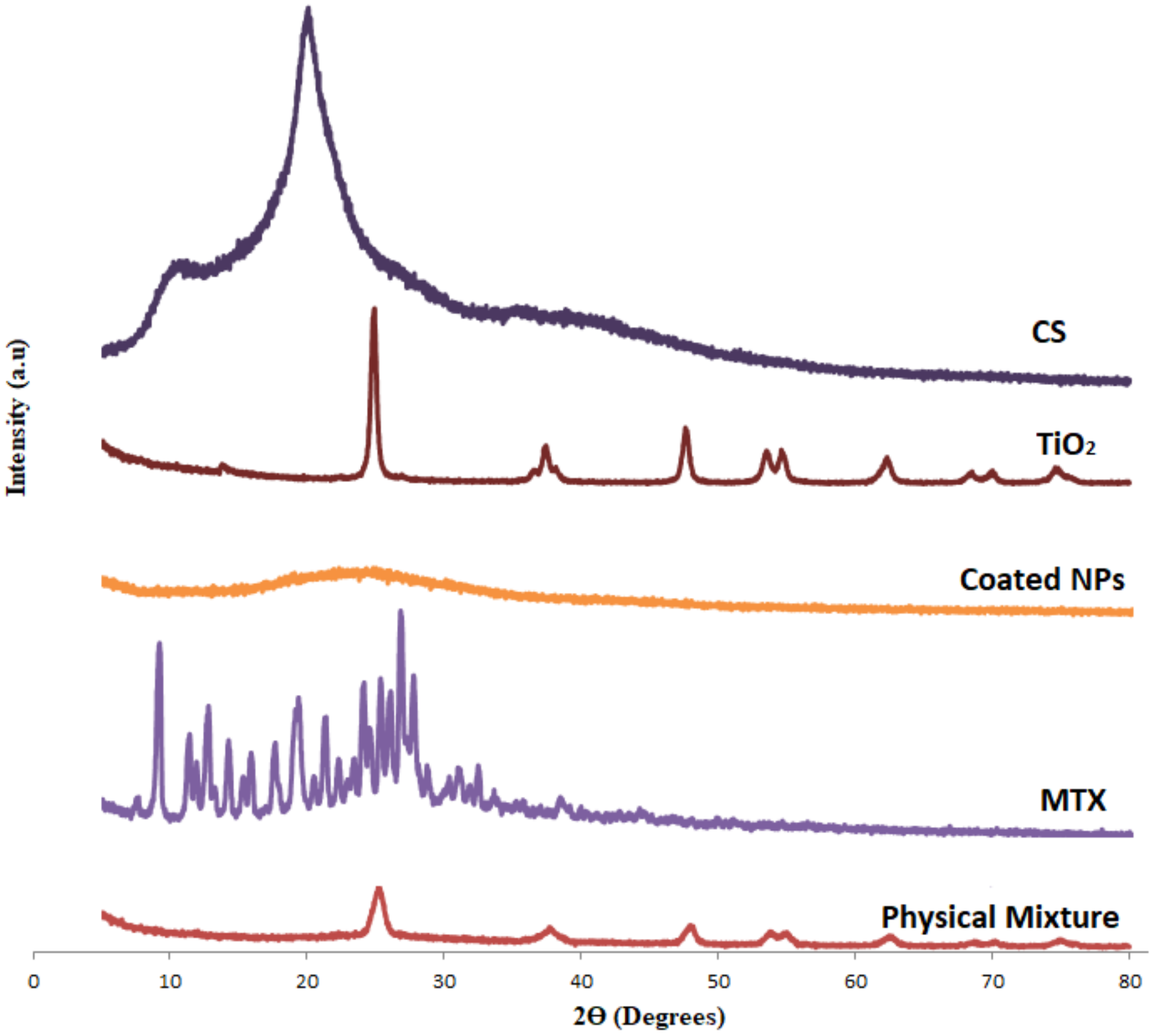
2.1. Characterization of MTX-CS-NPs Coated with TiO2-NPs
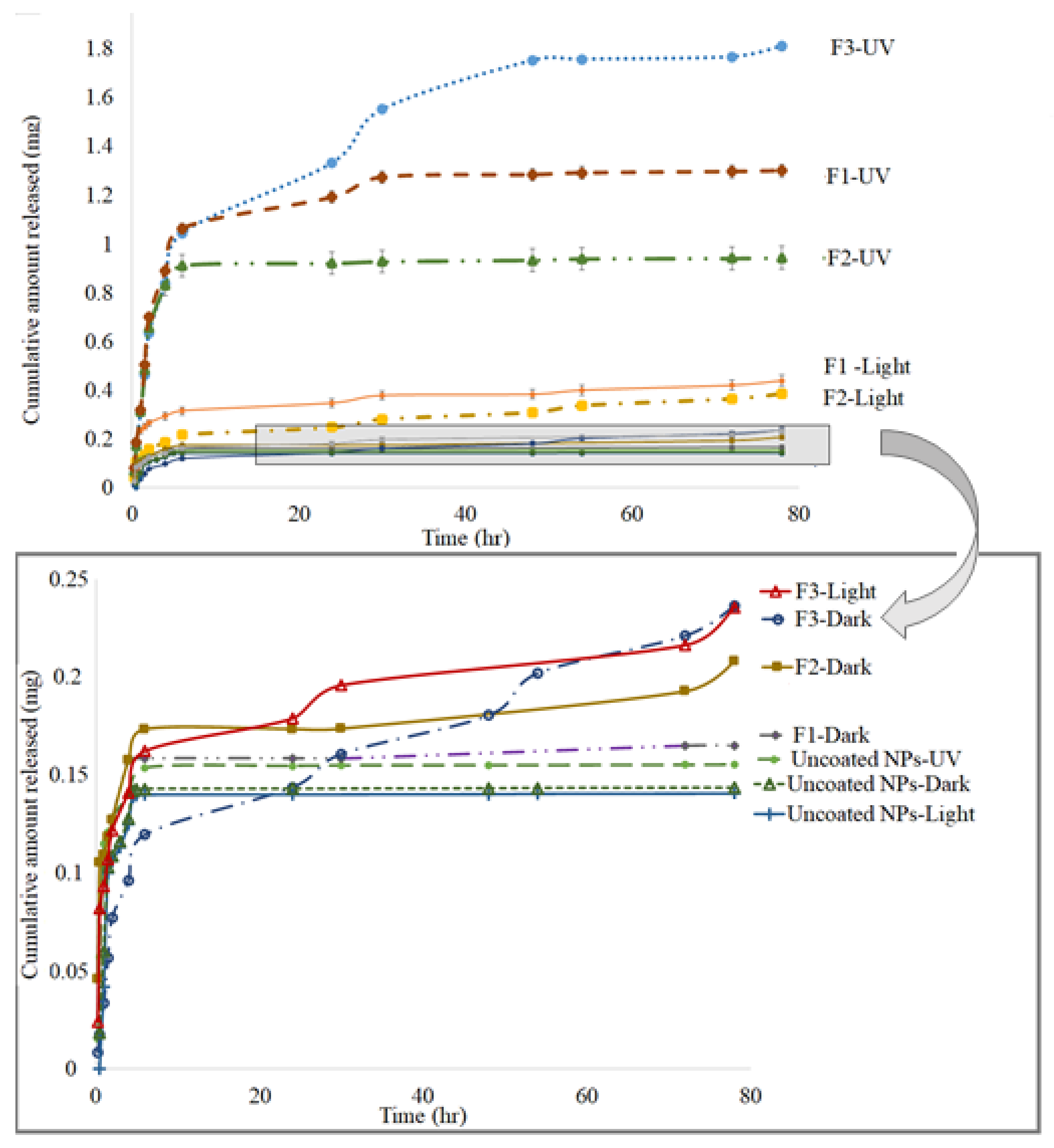
2.2. In Vitro Drug Release from MTX-CS-NPs Coated with TiO2-NPs
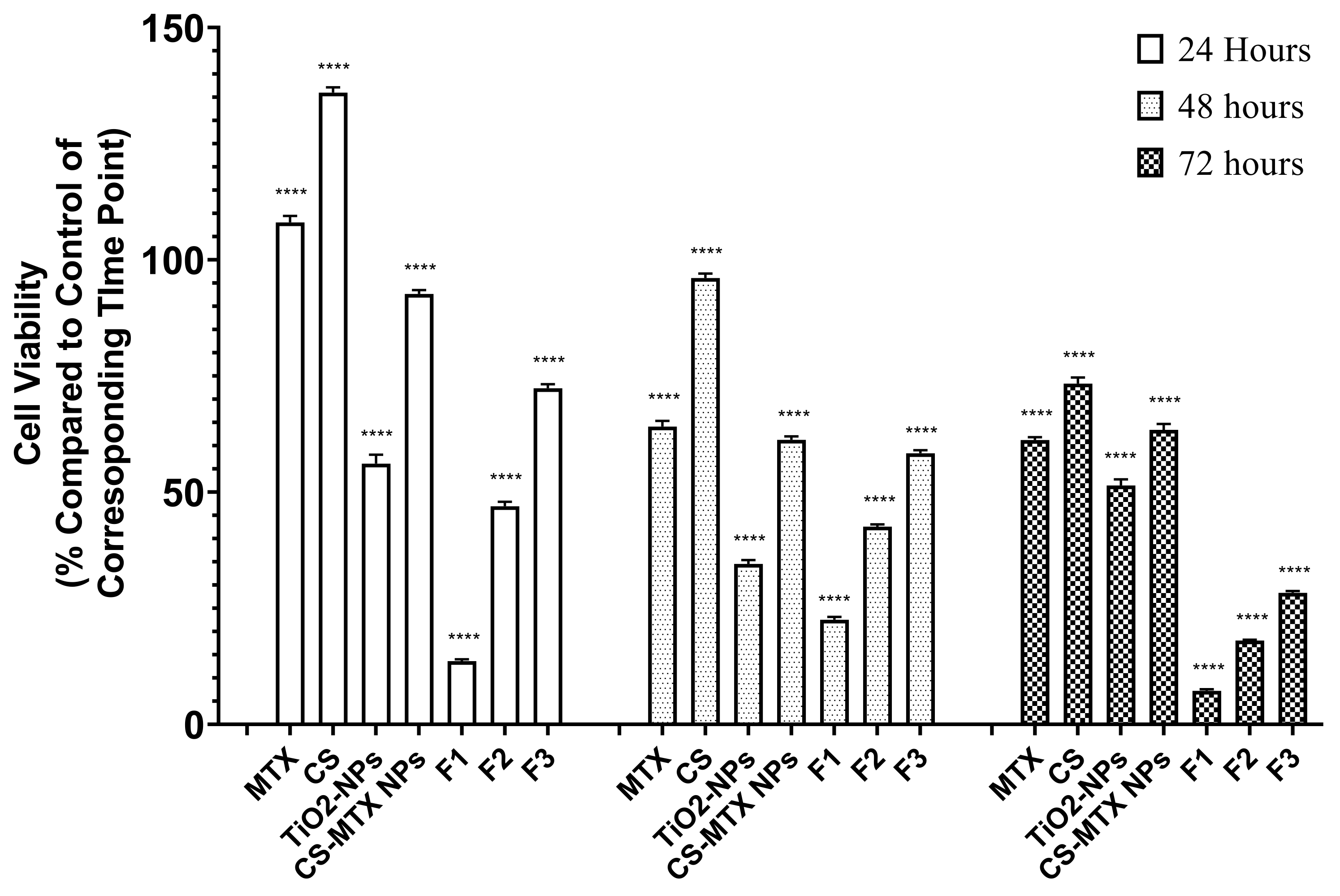
2.3. Cell Culture
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials Used
3.2. Preparation of Chitosan Methotrexate Nanoparticles
3.3. Coating Chitosan Methotrexate Nanoparticles with Titanium Dioxide
3.4. Characterization of MTX-CS-NPs before and after Coating with TiO2-NPs
3.5. In Vitro Drug Release from MTX-CS-NPs Coated with TiO2-NPs
3.6. Cell Culture
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jolivet, J.; Cowan, K.H.; Curt, G.A.; Clendeninn, N.J.; Chabner, B.A. The Pharmacology and Clinical Use of Methotrexate. Available online: https://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJM198311033091805 (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Bischoff, K.B.; Dedrick, R.L.; Zaharko, D.S.; Longstreth, J.A. Methotrexate Pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Sci. 1971, 60, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, R.W.; Hill, J.M.; Steinherz, P.G.; Meyers, P.A.; Finlay, J.L. Neuropsychologic effects of cranial irradiation, intrathecal methotrexate, and systemic methotrexate in childhood cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1994, 12, 2621–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.A.; Tripathi, R.; Mishra, B. Methotrexate: A detailed review on drug delivery and clinical aspects. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, D.R.; Tavano, L.; Mitjans, M.; Pérez, L.; Infante, M.R.; Vinardell, M.P. In vitro antitumor activity of methotrexate via pH-sensitive chitosan nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2758–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Nemrawi, N.K.; Alshraiedeh, N.H.; Zayed, A.L.; Altaani, B.M. Low Molecular Weight Chitosan-Coated PLGA Nanoparticles for Pulmonary Delivery of Tobramycin for Cystic Fibrosis. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Nemrawi, N.K.; Alsharif, S.S.M.; Alzoubi, K.H.; Alkhatib, R.Q. Preparation and characterization of insulin chitosan-nanoparticles loaded in buccal films. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 24, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgadir, M.A.; Uddin, M.S.; Ferdosh, S.; Adam, A.; Chowdhury, A.J.K.; Sarker, M.Z.I. Impact of chitosan composites and chitosan nanoparticle composites on various drug delivery systems: A review. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Nemrawi, N.K.; Alsharif, S.S.M.; Dave, R.H. Preparation of chitosan-TPP nanoparticles: The influence of chitosan polymeric properties and formulation variables. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2018, 10, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Huang, L.; Lai, H.; Lu, C.; Fang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, X. Methotrexate-Loaded PEGylated Chitosan Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and in Vitro and in Vivo Antitumoral Activity. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 2213–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, M.A.; Brem, H.; Langer, R. Advancing the field of drug delivery: Taking aim at cancer. Cancer Cell 2003, 4, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Nemrawi, N.K.; Marques, J.; Tavares, C.J.; Oweis, R.J.; Al-Fandi, M.G. Synthesis and characterization of photocatalytic polyurethane and poly(methyl methacrylate) microcapsules for the controlled release of methotrexate. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 2083–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, K.; Imai, Y.; Koumoto, K.; Kaiden, T.; Kono, K.; Aoshima, S. Magnetoresponsive On-Demand Release of Hybrid Liposomes Formed from Fe3O4 Nanoparticles and Thermosensitive Block Copolymers. Small 2011, 7, 1683–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Yoshida, K.; Takahashi, S.; Anzai, J. pH- and sugar-sensitive layer-by-layer films and microcapsules for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppolu, B.; Bhavsar, Z.; Wadajkar, A.S.; Nattama, S.; Rahimi, M.; Nwariaku, F.; Nguyen, K.T. Temperature-Sensitive Polymer-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Potential Drug Delivery System for Targeted Therapy of Thyroid Cancer. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2012, 8, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Li, Q.; Al-Rehili, S.; Omar, H.; Almalik, A.; Alshamsan, A.; Zhang, J.; Khashab, N.M. Hybrid Iron Oxide–Graphene Oxide–Polysaccharides Microcapsule: A Micro-Matryoshka for On-Demand Drug Release and Antitumor Therapy In Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6859–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Bromberg, L.; Concheiro, A. Light-sensitive Intelligent Drug Delivery Systems. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, A.; Goldberg, M.S.; Kastrup, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Joseph, B.J.; Levins, C.G.; Kannan, S.T.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D.G. Remotely Activated Protein-Producing Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2685–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabral, H.; Nakanishi, M.; Kumagai, M.; Jang, W.-D.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K. A Photo-Activated Targeting Chemotherapy Using Glutathione Sensitive Camptothecin-Loaded Polymeric Micelles. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaza, A.; Mahmoud, G.A.; Hegazy, E.A.; Amin, M.; Shoukry, E.; Elsheikh, B. Cytotoxic Effect of Chitosan Based Nanocomposite Synthesized by Radiation: In Vitro Liver and Breast Cancer Cell Line; Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Le Cunff, J.; Tomašić, V.; Wittine, O. Photocatalytic degradation of the herbicide terbuthylazine: Preparation, characterization and photoactivity of the immobilized thin layer of TiO2/chitosan. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Chem. 2015, 309, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, W.M.M.; Rastogi, T.; Kümmerer, K. Application of titanium dioxide nanoparticles as a photocatalyst for the removal of micropollutants such as pharmaceuticals from water. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2017, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziental, D.; Czarczynska-Goslinska, B.; Mlynarczyk, D.T.; Glowacka-Sobotta, A.; Stanisz, B.; Goslinski, T.; Sobotta, L. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Prospects and Applications in Medicine. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Çeşmeli, S.; Avci, C.B. Application of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles in cancer therapies. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nemrawi, N.; Nimrawi, S. A novel formulation of chitosan nanoparticles functionalized with titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2021, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Zhang, Q.; Dai, Z. Near-infrared light-activatable polymeric nanoformulations for combined therapy and imaging of cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 115, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, A.; Cimas, F.J.; Bravo, I.; Pandiella, A.; Ocaña, A.; Alonso-Moreno, C. An Overview of Antibody Conjugated Polymeric Nanoparticles for Breast Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabanel, J.-M.; Adibnia, V.; Tehrani, S.F.; Sanche, S.; Hildgen, P.; Banquy, X.; Ramassamy, C. Nanoparticle heterogeneity: An emerging structural parameter influencing particle fate in biological media? Nanoscale 2019, 11, 383–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index on the Clinical Applications of Lipidic Nanocarrier Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demeler, B.; Nguyen, T.-L.; Gorbet, G.E.; Schirf, V.; Brookes, E.H.; Mulvaney, P.; El-Ballouli, A.O.; Pan, J.; Bakr, O.M.; Demeler, A.K.; et al. Characterization of Size, Anisotropy, and Density Heterogeneity of Nanoparticles by Sedimentation Velocity. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7688–7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chorny, M.; Fishbein, I.; Danenberg, H.D.; Golomb, G. Lipophilic drug loaded nanospheres prepared by nanoprecipitation: Effect of formulation variables on size, drug recovery and release kinetics. J. Control. Release 2002, 83, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nemrawi, N.K.; Altawabeyeh, R.M.; Darweesh, R.S. Preparation and Characterization of Docetaxel-PLGA Nanoparticles Coated with Folic Acid-chitosan Conjugate for Cancer Treatment. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 111, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nemrawi, N.K.; Dave, R.H. Formulation and characterization of acetaminophen nanoparticles in orally disintegrating films. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrie, G.; Keen, I.; Drew, B.; Chandler-Temple, A.; Rintoul, L.; Fredericks, P.; Grøndahl, L. Interactions between Alginate and Chitosan Biopolymers Characterized Using FTIR and XPS. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2533–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsalani, N.; Nezhad-Mokhtari, P.; Jabbari, E. Microwave-assisted and one-step synthesis of PEG passivated fluorescent carbon dots from gelatin as an efficient nanocarrier for methotrexate delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sibeko, B.; Choonara, Y.E.; du Toit, L.C.; Modi, G.; Naidoo, D.; Khan, R.A.; Kumar, P.; Ndesendo, V.M.K.; Iyuke, S.E.; Pillay, V. Composite Polylactic-Methacrylic Acid Copolymer Nanoparticles for the Delivery of Methotrexate. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jdd/2012/579629/ (accessed on 6 October 2020).
- Luo, F.; Li, Y.; Jia, M.; Cui, F.; Wu, H.; Yu, F.; Lin, J.; Yang, X.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, Q. Validation of a Janus role of methotrexate-based PEGylated chitosan nanoparticles in vitro. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Praveen, P.; Viruthagiri, G.; Mugundan, S.; Shanmugam, N. Structural, optical and morphological analyses of pristine titanium di-oxide nanoparticles–Synthesized via sol–gel route. Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 117, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Oktiani, R.; Ragadhita, R. How to Read and Interpret FTIR Spectroscope of Organic Material. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.-G.; Xu, B.; Huang, F.; Wu, J.-J.; Chen, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles of anticancer drugs against MCF-7 cell line and a murine breast cancer model. Pharm.-Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 67, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benga, G.; Holmes, R.P. Interactions between components in biological membranes and their implications for membrane function. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1984, 43, 195–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.K.; Kumar, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Singh, S.S.; Dhawan, A. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Induce Oxidative Stress-Mediated Apoptosis in Human Keratinocyte Cells. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 100–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, R.; Arami, M.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Bahrami, H.; Khorramfar, S. Novel biocompatible composite (Chitosan–zinc oxide nanoparticle): Preparation, characterization and dye adsorption properties. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 80, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.; Assays, C.; Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar]

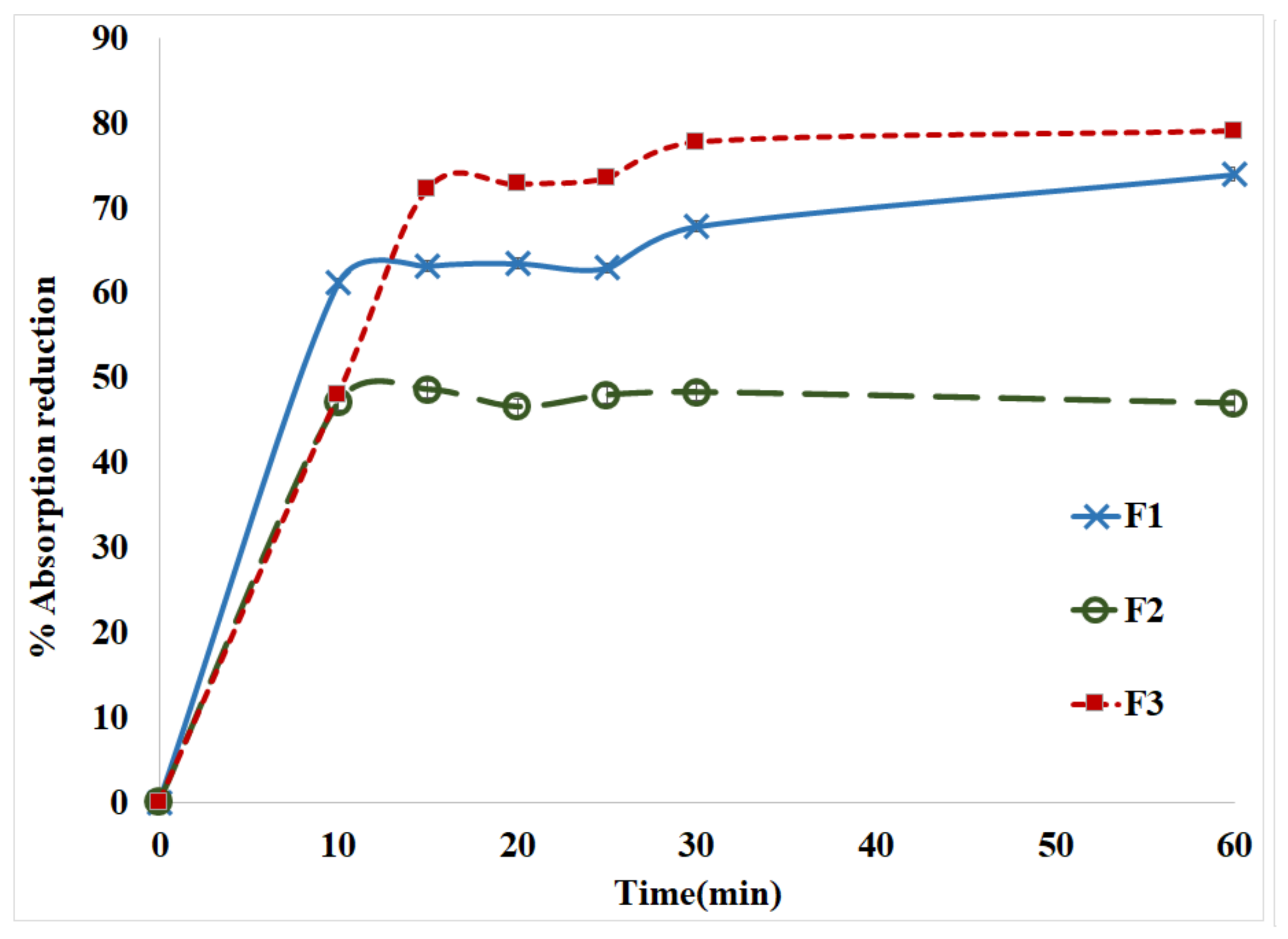
| Formula | Ratio of MTX-CS-NPs to TiO2 | Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta (mV) | % EE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS-MTX NPs | Without TiO2 NPs | 169.00 ± 3.15 | 0.27 ± 0.04 | +9.37 ± 0.35 | 68.31 ± 0.98 |
| F1 | 1:1 | 411.93 ± 17.04 | 0.49 ± 0.01 | +24.20 ± 1.41 | 60.23 ± 1.23 |
| F2 | 1:2 | 241.13 ± 3.64 | 0.25 ± 0.04 | +26.10 ± 0.70 | 78.96 ± 1.40 |
| F3 | 2:1 | 262.27 ± 2.81 | 0.54 ± 0.07 | +25.77 ± 0.76 | 63.90 ± 2.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Nemrawi, N.; Hameedat, F.; Al-Husein, B.; Nimrawi, S. Photolytic Controlled Release Formulation of Methotrexate Loaded in Chitosan/TiO2 Nanoparticles for Breast Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020149
Al-Nemrawi N, Hameedat F, Al-Husein B, Nimrawi S. Photolytic Controlled Release Formulation of Methotrexate Loaded in Chitosan/TiO2 Nanoparticles for Breast Cancer. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(2):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020149
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Nemrawi, Nusaiba, Fatima Hameedat, Belal Al-Husein, and Sukaina Nimrawi. 2022. "Photolytic Controlled Release Formulation of Methotrexate Loaded in Chitosan/TiO2 Nanoparticles for Breast Cancer" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 2: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020149
APA StyleAl-Nemrawi, N., Hameedat, F., Al-Husein, B., & Nimrawi, S. (2022). Photolytic Controlled Release Formulation of Methotrexate Loaded in Chitosan/TiO2 Nanoparticles for Breast Cancer. Pharmaceuticals, 15(2), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020149






