Real-World Comparative Evaluation of Add-On Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist in Type 2 Diabetes Treated with or without Insulin
Abstract
1. Introduction
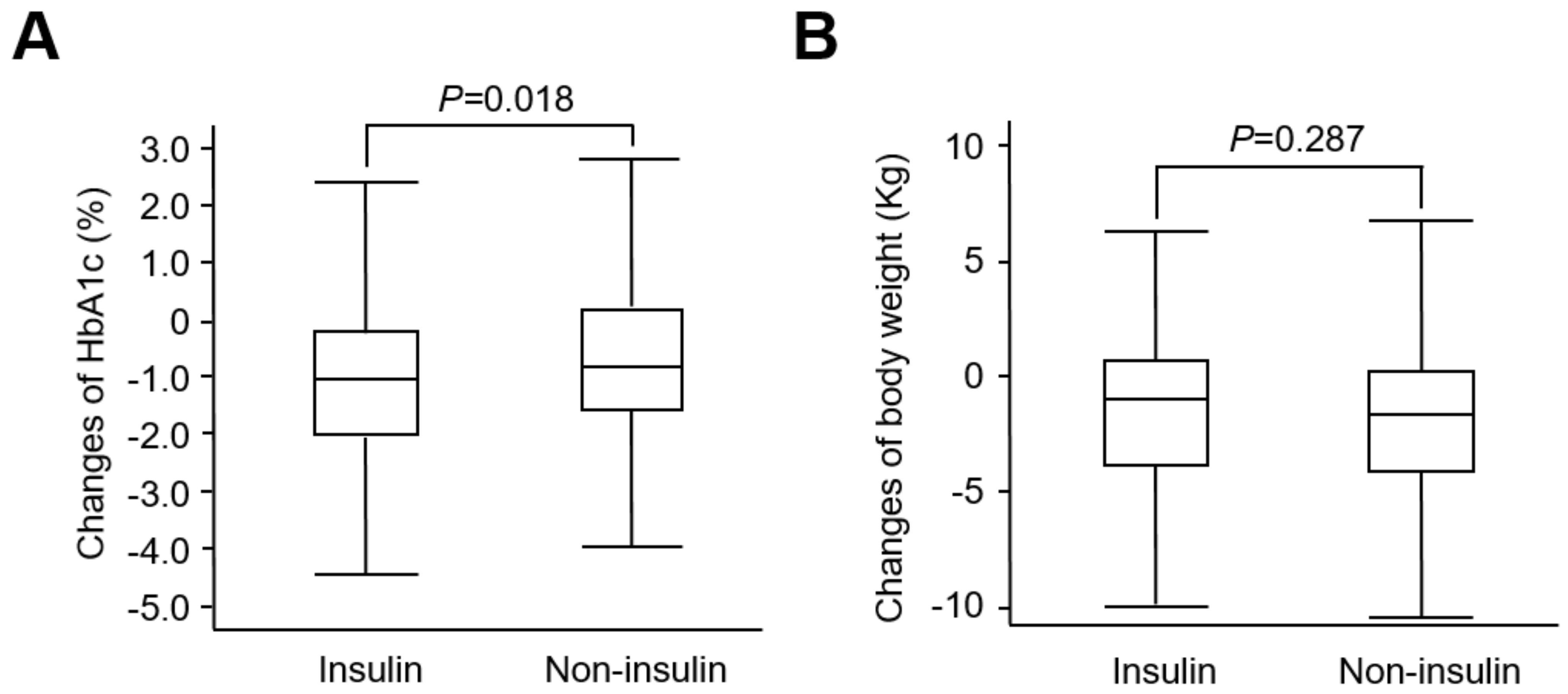
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes—Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Abdalla, M.A.; Deshmukh, H.; Sathyapalan, T. Therapeutics for type-2 diabetes mellitus: A glance at the recent inclusions and novel agents under development for use in clinical practice. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 12, 20420188211042145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, M.S.; Manzano, A.; Olivar, L.C.; Nava, M.; Salazar, J.; D’Marco, L.; Ortiz, R.; Chacín, M.; Guerrero-Wyss, M.; de Bravo, M.C.; et al. The Role of the α Cell in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes: A World beyond the Mirror. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.M. The Role of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes in Asia. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Rørth, R.; Jhund, P.S.; Docherty, K.F.; Sattar, N.; Preiss, D.; Køber, L.; Petrie, M.C.; McMurray, J.J.V. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Daniels, G.H.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Kristensen, P.; Mann, J.F.E.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Ravn, L.S.; et al. LEADER Steering Committee; LEADER Trial Investigators. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. SUSTAIN-6 Investigators. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Riddle, M.C.; Rydén, L.; et al. REWIND Investigators. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; Draznin, B.; Aroda, V.R.; Bakris, G.; Benson, G.; Brown, F.M.; Freeman, R.; Green, J.; Huang, E.; Isaacs, D.; et al. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S125–S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippatos, T.D.; Panagiotopoulou, T.V.; Elisaf, M.S. Adverse Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2014, 11, 202–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, J.; Ping, F.; Yang, N.; Huang, J.; Li, Y. Association of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Use With Risk of Gallbladder and Biliary Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. JAMA Intern. Med. 2022, 182, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipowsky, C.; Sze, L.; Krull, I.; Brändle, M. Liraglutide as add-on therapy to insulin in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A retrospective, observational study from a daily clinical practice setting in Switzerland. Diabetes Ther. 2015, 6, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blonde, L.; Russell-Jones, D. The safety and efficacy of liraglutide with or without oral antidiabetic drug therapy in type 2 diabetes: An overview of the LEAD 1–5 studies. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2009, 11, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cho, Y.K.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, C.H.; Park, J.-Y.; Lee, W.J. Dulaglutide as an Add-on to Insulin in Type 2 Diabetes; Clinical Efficacy and Parameters Affecting the Response in Real-World Practice. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 2745–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhinehart, A.S. Adding GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Therapy to Basal Insulin for Postprandial Glucose Control. Clin. Diabetes 2015, 33, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyorffy, J.B.; Keithler, A.N.; Wardian, J.L.; Zarzabal, L.A.; Rittel, A.; True, M.W. The Impact of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists on Patients with Diabetes on Insulin Therapy. Endocr. Pract. 2019, 25, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, J.B.; Wexler, D.J.; Tsapas, A.; Rossing, P.; Mingrone, G.; Mathieu, C.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Davies, M.J. 2019 update to: Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2020, 63, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroda, V.R.; González-Galvez, G.; Grøn, R.; Halladin, N.; Haluzík, M.; Jermendy, G.; Kok, A.; Őrsy, P.; Sabbah, M.; Sesti, G.; et al. Durability of insulin degludec plus liraglutide versus insulin glargine U100 as initial injectable therapy in type 2 diabetes (DUAL VIII): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3b, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study Group. U.K. prospective diabetes study 16. Overview of 6 years’ therapy of type II diabetes: A progressive disease. Diabetes 1995, 44, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitout, V.; Robertson, R.P. Minireview: Secondary beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes--a convergence of glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanefeld, M. Use of insulin in type 2 diabetes: What we learned from recent clinical trials on the benefits of early insulin initiation. Diabetes Metab. 2014, 40, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysham, C.; Shubrook, J. Beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes: Mechanisms, markers, and clinical implications. Postgrad. Med. 2020, 132, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, D.R.; Cull, C.A.; Stratton, I.M.; Holman, R.R.; Turner, R.C. UKPDS 26: Sulphonylurea failure in non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients over six years. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Diabet. Med. 1998, 15, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneto, H.; Kimura, T.; Shimoda, M.; Obata, A.; Sanada, J.; Fushimi, Y.; Nakanishi, S.; Mune, T.; Kaku, K. Favorable Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist against Pancreatic β-Cell Glucose Toxicity and the Development of Arteriosclerosis: “The Earlier, the Better” in Therapy with Incretin-Based Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.G.; McDonald, T.J.; Shields, B.M.; Hill, A.V.; Hyde, C.J.; Knight, B.A.; Hattersley, A.T. PRIBA Study Group. Markers of β-Cell Failure Predict Poor Glycemic Response to GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2016, 39, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Mosca, C.; Brancario, C.; Chiodini, P.; Ceriello, A.; Giugliano, D. GLP-1 receptor agonists and HBA1c target of <7% in type 2 diabetes: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2011, 27, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Babenko, A.Y.; Savitskaya, D.A.; Kononova, Y.A.; Trofimova, A.Y.; Simanenkova, A.V.; Vasilyeva, E.Y.; Shlyakhto, E.V. Predictors of Effectiveness of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 1365162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Tsujimoto, T.; Goto, A.; Goto, M.; Kishimoto, M.; Yamamoto-Honda, R.; Noto, H.; Kajio, H.; Noda, M. Prediction of response to GLP-1 receptor agonist therapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozawa, J.; Inoue, K.; Iwamoto, R.; Kurashiki, Y.; Okauchi, Y.; Kashine, S.; Kitamura, T.; Maeda, N.; Okita, K.; Iwahashi, H.; et al. Liraglutide is effective in type 2 diabetic patients with sustained endogenous insulin-secreting capacity. J. Diabetes Investig. 2012, 3, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttall, F.Q. Body Mass Index: Obesity, BMI, and Health: A Critical Review. Nutr. Today 2015, 50, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; Draznin, B.; Aroda, V.R.; Bakris, G.; Benson, G.; Brown, F.M.; Freeman, R.; Green, J.; Huang, E.; Isaacs, D.; et al. Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S83–S96. [Google Scholar]

| Insulin User | Non-Insulin User | p-Value (Insulin User vs. Non-Insulin User) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 147 | 211 | |
| Age (years) | 56.7 ± 13.1 | 50.6 ± 12.9 | <0.001 |
| Male (%) | 51 | 51 | NS |
| DM duration (years) | 12.1 ± 7.1 | 8.7 ± 6.5 | <0.001 |
| BW (kg) | 77.2± 16.0 | 83.7 ± 16.1 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.4 ± 5.2 | 31.3± 5.3 | 0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 136 ± 18 | 135 ± 16 | NS |
| DBP (mmHg) | 81 ± 10 | 82 ± 10 | NS |
| Enrollment into “Diabetes Shared Care Program” (%) | 86 | 91 | NS |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Cerebrovascular disease (%) | 19 | 17 | NS |
| Coronary artery disease (%) | 19 | 17 | NS |
| Stroke (%) | 11 | 9 | NS |
| Peripheral artery disease (%) | 0 | 1 | NS |
| Congestive heart failure (%) | 3 | 7 | NS |
| Biochemical data | |||
| Fasting plasma glucose (mg/dL) | 186.01 ± 72.88 | 174.98 ± 55.87 | 0.12 |
| A1C (%) | 9.50 ± 1.70 | 8.84 ± 1.60 | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.15 ± 1.60 | 0.83 ± 0.43 | 0.007 |
| Estimated GFR (ml/min/1.73 m2) < 45 (%) | 16 | 6 | 0.002 |
| ALT (U/L) | 36 ± 28 | 43 ± 26 | 0.017 |
| Urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (mg/g) | 604 ± 1136 | 274 ± 747 | 0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 158.8 ± 38.2 | 167.0 ± 42.8 | NS |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 191.8 ± 207.8 | 203.2 ± 164.1 | NS |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 44.6 ± 13.6 | 44.0 ± 11.6 | NS |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 95.6 ± 32.34 | 98.3 ± 32.4 | NS |
| Other anti-diabetes medications | |||
| Metformin (%) | 72 | 91 | <0.001 |
| Insulin secretagogues (%) | 42 | 72 | <0.001 |
| Pioglitazone (%) | 14 | 12 | NS |
| Acarbose (%) | 10 | 8 | NS |
| DPP-4 inhibitor (%) | 1 | 3 | NS |
| SGLT-2 inhibitor (%) | 5 | 8 | NS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chou, H.-W.; Cheng, K.-P.; Lin, A.-C.; Hung, H.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; Wu, H.-T.; Ou, H.-Y. Real-World Comparative Evaluation of Add-On Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist in Type 2 Diabetes Treated with or without Insulin. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121569
Chou H-W, Cheng K-P, Lin A-C, Hung H-C, Lin C-H, Wang C-C, Wu H-T, Ou H-Y. Real-World Comparative Evaluation of Add-On Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist in Type 2 Diabetes Treated with or without Insulin. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(12):1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121569
Chicago/Turabian StyleChou, Hsuan-Wen, Kai-Pi Cheng, An-Chi Lin, Hao-Chang Hung, Ching-Han Lin, Chih-Chen Wang, Hung-Tsung Wu, and Horng-Yih Ou. 2022. "Real-World Comparative Evaluation of Add-On Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist in Type 2 Diabetes Treated with or without Insulin" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 12: 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121569
APA StyleChou, H.-W., Cheng, K.-P., Lin, A.-C., Hung, H.-C., Lin, C.-H., Wang, C.-C., Wu, H.-T., & Ou, H.-Y. (2022). Real-World Comparative Evaluation of Add-On Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist in Type 2 Diabetes Treated with or without Insulin. Pharmaceuticals, 15(12), 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121569






