Aspirin Inhibits Fibronectin Expression and Reverses Fibronectin-Mediated Cell Invasiveness by Activating Akt Signaling in Preeclampsia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
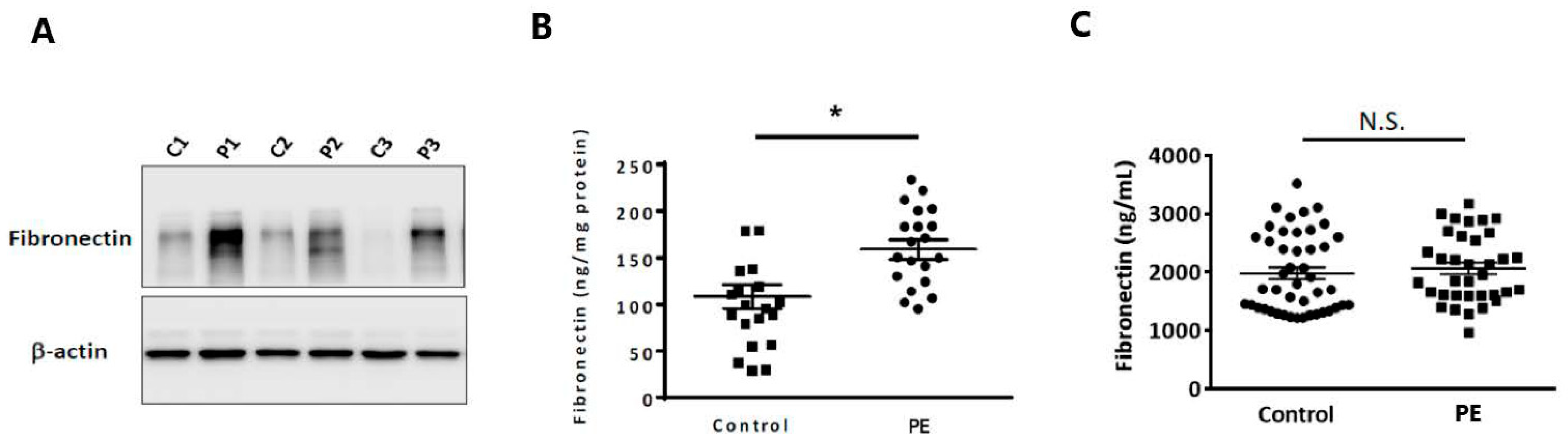
2.1. Fibronectin Protein Expression Was Elevated in the Placentas of Preeclamptic Patients
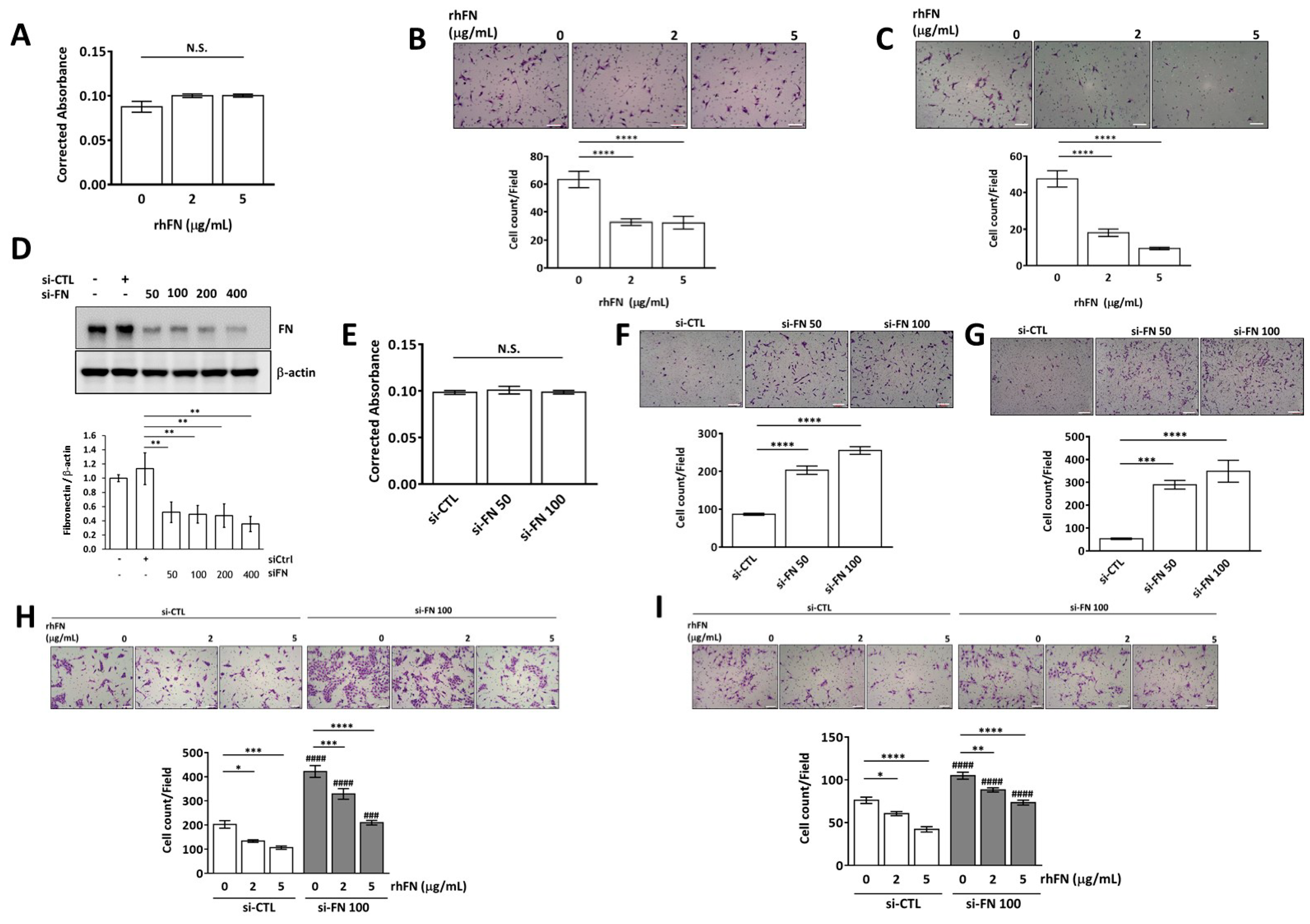
2.2. Fibronectin Inhibits Trophoblast Invasion and Migration without Affecting Cell Viability
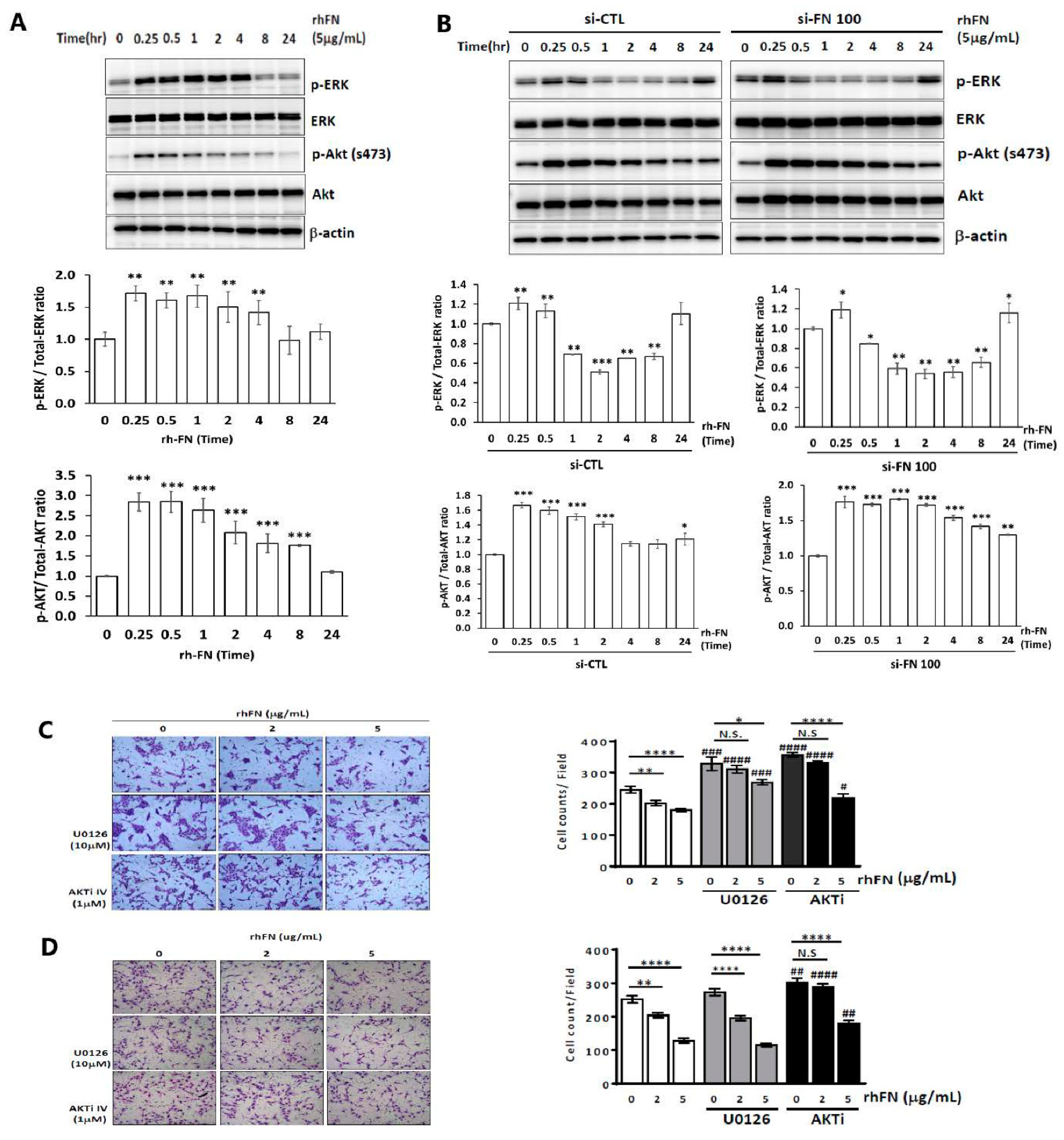
2.3. Fibronectin Regulates Trophoblast Invasiveness and Migration by Activating the ERK and Akt Signaling Pathways
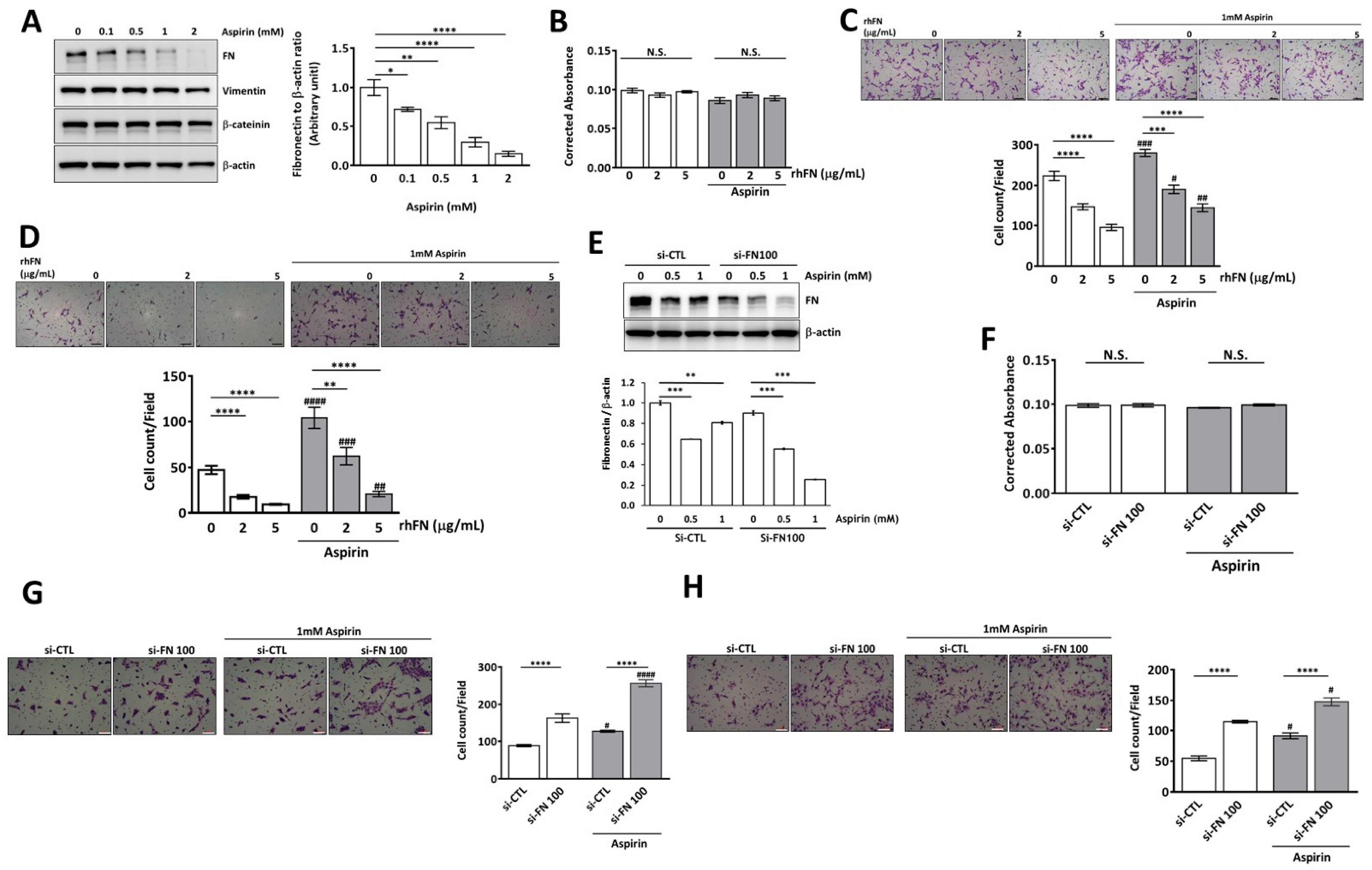
2.4. Aspirin Inhibits Cellular Fibronectin Expression and Reverses Fibronectin-Mediated Cell Motility in Trophoblasts through the ERK and Akt Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Specimens
4.2. Cell Cultures and Treatments
4.3. Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) Transfection Experiments
4.4. Cell Viability Assays
4.5. Transwell Invasion and Migration Assays
4.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duley, L. The global impact of pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. Semin. Perinatol. 2009, 33, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Díaz, S.; Toh, S.; Cnattingius, S. Risk of pre-eclampsia in first and subsequent pregnancies: Prospective cohort study. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2009, 338, b2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.J.; Redman, C.W.; Roberts, J.M.; Moffett, A. Pre-eclampsia: Pathophysiology and clinical implications. BMJ 2019, 366, l2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, C.J.; Lemmon, C.A. Fibronectin: Molecular structure, fibrillar structure and mechanochemical signaling. Cells 2021, 10, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankov, R.; Yamada, K.M. Fibronectin at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 3861–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, W.S.; Midwood, K.S. Plasma and cellular fibronectin: Distinct and independent functions during tissue repair. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2011, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, U.; Estlin, C.; Bulmer, J.N. Fibronectin and laminin in the early human placenta. Placenta 1990, 11, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasanen, J.; Quinn, M.J.; Laurie, A.; Bean, E.; Roberts, C.T., Jr.; Nagalla, S.R.; Gravett, M.G. Maternal serum glycosylated fibronectin as a point-of-care biomarker for assessment of preeclampsia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 212, e81–e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhn, E.A.; Hoffmann, I.; Martinez De Tejada, B.; Lange, S.; Sage, K.M.; Roberts, C.T.; Gravett, M.G.; Nagalla, S.R.; Lapaire, O. Maternal serum glycosylated fibronectin as a short-term predictor of preeclampsia: A prospective cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2020, 20, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostlund, E.; Hansson, L.O.; Bremme, K. Fibronectin is a marker for organ involvement and may reflect the severity of preeclampsia. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2001, 20, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagalla, S.R.; Janaki, V.; Vijayalakshmi, A.R.; Chayadevi, K.; Pratibha, D.; Rao, P.V.; Sage, K.M.; Nair-Schaef, D.; Bean, E.; Roberts, C.T., Jr.; et al. Glycosylated fibronectin point-of-care test for diagnosis of pre-eclampsia in a low-resource setting: A prospective southeast asian population study. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2020, 127, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolnik, D.L.; Wright, D.; Poon, L.C.; O’Gorman, N.; Syngelaki, A.; de Paco Matallana, C.; Akolekar, R.; Cicero, S.; Janga, D.; Singh, M.; et al. Aspirin versus placebo in pregnancies at high risk for preterm preeclampsia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberge, S.; Bujold, E.; Nicolaides, K.H. Aspirin for the prevention of preterm and term preeclampsia: Systematic review and metaanalysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 218, 287–293.e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ittaman, S.V.; VanWormer, J.J.; Rezkalla, S.H. The role of aspirin in the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Clin. Med. Res. 2014, 12, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soodi, D.; VanWormer, J.J.; Rezkalla, S.H. Aspirin in primary prevention of cardiovascular events. Clin. Med. Res. 2020, 18, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.Z.; Jin, W.L. The updated landscape of tumor microenvironment and drug repurposing. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.K.; Nasti, T.H.; Buchwald, Z.S.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Kron, S.J. Repurposing drugs for cancer radiotherapy: Early successes and emerging opportunities. Cancer J. 2019, 25, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Li, G.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.L.; Yang, H. Low-dose aspirin reduces hypoxia-induced sflt1 release via the jnk/ap-1 pathway in human trophoblast and endothelial cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 18928–18941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanabdali, R.; Shakouri-Motlagh, A.; Wilkinson, S.; Murthi, P.; Georgiou, H.M.; Brennecke, S.P.; Kalionis, B. Low-dose aspirin treatment enhances the adhesion of preeclamptic decidual mesenchymal stem/stromal cells and reduces their production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 96, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, K.Y.; Nishiyama, T. Developmental changes in extracellular matrix messenger rnas in the mouse placenta during the second half of pregnancy: Possible factors involved in the regulation of placental extracellular matrix expression. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 77, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplin, J.D.; Haigh, T.; Jones, C.J.; Church, H.J.; Vićovac, L. Development of cytotrophoblast columns from explanted first-trimester human placental villi: Role of fibronectin and integrin alpha5beta1. Biol. Reprod. 1999, 60, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Armant, D.R. Integrin-mediated adhesion and signaling during blastocyst implantation. Cells Tissues Organs 2002, 172, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiworapongsa, T.; Chaemsaithong, P.; Yeo, L.; Romero, R. Pre-eclampsia part 1: Current understanding of its pathophysiology. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutifaris, C.; Omigbodun, A.; Coukos, G. The fibronectin receptor alpha5 integrin subunit is upregulated by cell-cell adhesion via a cyclic amp-dependent mechanism: Implications for human trophoblast migration. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 192, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danen, E.H.; Sonneveld, P.; Brakebusch, C.; Fassler, R.; Sonnenberg, A. The fibronectin-binding integrins alpha5beta1 and alphavbeta3 differentially modulate rhoa-gtp loading, organization of cell matrix adhesions, and fibronectin fibrillogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 159, 1071–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Mejia, I.C.; De Toledo, M.; Della Seta, F.; Fafet, P.; Rebouissou, C.; Deleuze, V.; Blanchard, J.M.; Jorgensen, C.; Tazi, J.; Vignais, M.L. Tissue-specific and srsf1-dependent splicing of fibronectin, a matrix protein that controls host cell invasion. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 3164–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massimiani, M.; Vecchione, L.; Piccirilli, D.; Spitalieri, P.; Amati, F.; Salvi, S.; Ferrazzani, S.; Stuhlmann, H.; Campagnolo, L. Epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 promotes migration and invasion of human trophoblast cells through activation of MAPK, PI3K and NOTCH signaling pathways. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 21, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gao, F.; Zhou, C.; Qiu, W.; Wu, H.; Li, J.; Peng, J.; Qiu, M.; Liang, C.; Gao, J.; Luo, S. Total flavonoids from Semen Cuscutae target MMP9 and promote invasion of EVT cells via Notch/AKT/MAPK signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, L.; Brown, A.G.; Parry, S.; Elovitz, M.A. Lipopolysaccharide induces cytokine production and decreases extravillous trophoblast invasion through a mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated pathway: Possible mechanisms of first trimester placental dysfunction. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Nie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J. NOD1 and NOD2 control the invasiveness of trophoblast cells via the MAPK/p38 signaling pathway in human first-trimester pregnancy. Placenta 2015, 36, 652660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.T.; Wang, C.Y.; Tsai, P.Y.; Chen, T.Y.; Tsai, H.L.; Kuo, P.L. Aspirin enhances trophoblast invasion and represses soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 production: A putative mechanism for preventing preeclampsia. J. Hypertens. 2019, 37, 2461–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodova, K.B.; Biringer, K.; Dokus, K.; Ivankova, J.; Stasko, J.; Danko, J. Fibronectin, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (pai-1) and uterine artery doppler velocimetry as markers of preeclampsia. Dis. Mrk. 2011, 30, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, H.; Konukoglu, D.; Albayrak, M.; Benian, A.; Madazli, R.; Aydin, S.; Gelisgen, R.; Uludag, S. Increased maternal serum and cord blood fibronectin concentrations in preeclampsia are associated with higher placental hyaluronic acid and hydroxyproline content. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2010, 29, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasaki, I.; Chobanian, A.V.; Mamuya, W.S.; Brecher, P. Hypertension induces alternatively spliced forms of fibronectin in rat aorta. Hypertension 1992, 20, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, A.; Lecarpentier, E.; Goffinet, F.; Doret-Dion, M.; Gaucherand, P.; Tsatsaris, V. Aspirin for prevention of preeclampsia. Drugs 2017, 77, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Zou, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, T.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, M.; Ge, Z.; Jiang, Z. Aspirin reduces sflt-1-mediated apoptosis of trophoblast cells in preeclampsia. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2021, 27, gaaa089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.T.; Tsai, P.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Tsai, H.L.; Kuo, P.L. Aspirin facilitates trophoblast invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating the mir-200-zeb1 axis in preeclampsia. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 139, 111591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Han, Y.; Liang, C.; Xie, Q.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, Z. Aspirin modulates stox1 expression and reverses stox1-induced insufficient proliferation and migration of trophoblast cells. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2020, 19, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ma, L.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y.L.; Yang, H. The intervention effect of aspirin on a lipopolysaccharide-induced preeclampsia-like mouse model by inhibiting the nuclear factor-κb pathway. Biol. Reprod. 2018, 99, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, F.P., Jr.; Slivova, V.; Valachovicova, T.; Sliva, D. Aspirin inhibits highly invasive prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2003, 23, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, G.; Tang, H.; Shi, Y.; Kang, X.; Lyu, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, M.; Yang, M.; Mu, M.; et al. Aspirin inhibits inflammation and scar formation in the injury tendon healing through regulating jnk/stat-3 signalling pathway. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Duxbury, M.; Benoit, E.; Farivar, R.S.; Gardner-Thorpe, J.; Zinner, M.J.; Ashley, S.W.; Whang, E.E. Fibronectin-induced cox-2 mediates mmp-2 expression and invasiveness of rhabdomyosarcoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 318, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, M.-T.; Tsai, C.-W.; Tsai, P.-Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Tsai, H.-L. Aspirin Inhibits Fibronectin Expression and Reverses Fibronectin-Mediated Cell Invasiveness by Activating Akt Signaling in Preeclampsia. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121523
Su M-T, Tsai C-W, Tsai P-Y, Wang C-Y, Tsai H-L. Aspirin Inhibits Fibronectin Expression and Reverses Fibronectin-Mediated Cell Invasiveness by Activating Akt Signaling in Preeclampsia. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(12):1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121523
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Mei-Tsz, Ching-Wei Tsai, Pei-Yin Tsai, Chia-Yih Wang, and Hui-Ling Tsai. 2022. "Aspirin Inhibits Fibronectin Expression and Reverses Fibronectin-Mediated Cell Invasiveness by Activating Akt Signaling in Preeclampsia" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 12: 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121523
APA StyleSu, M.-T., Tsai, C.-W., Tsai, P.-Y., Wang, C.-Y., & Tsai, H.-L. (2022). Aspirin Inhibits Fibronectin Expression and Reverses Fibronectin-Mediated Cell Invasiveness by Activating Akt Signaling in Preeclampsia. Pharmaceuticals, 15(12), 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121523





