Adverse Events Associated with Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir: A Pharmacovigilance Analysis Based on FAERS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of Adverse Event Reports
2.2. Adverse Drug Events
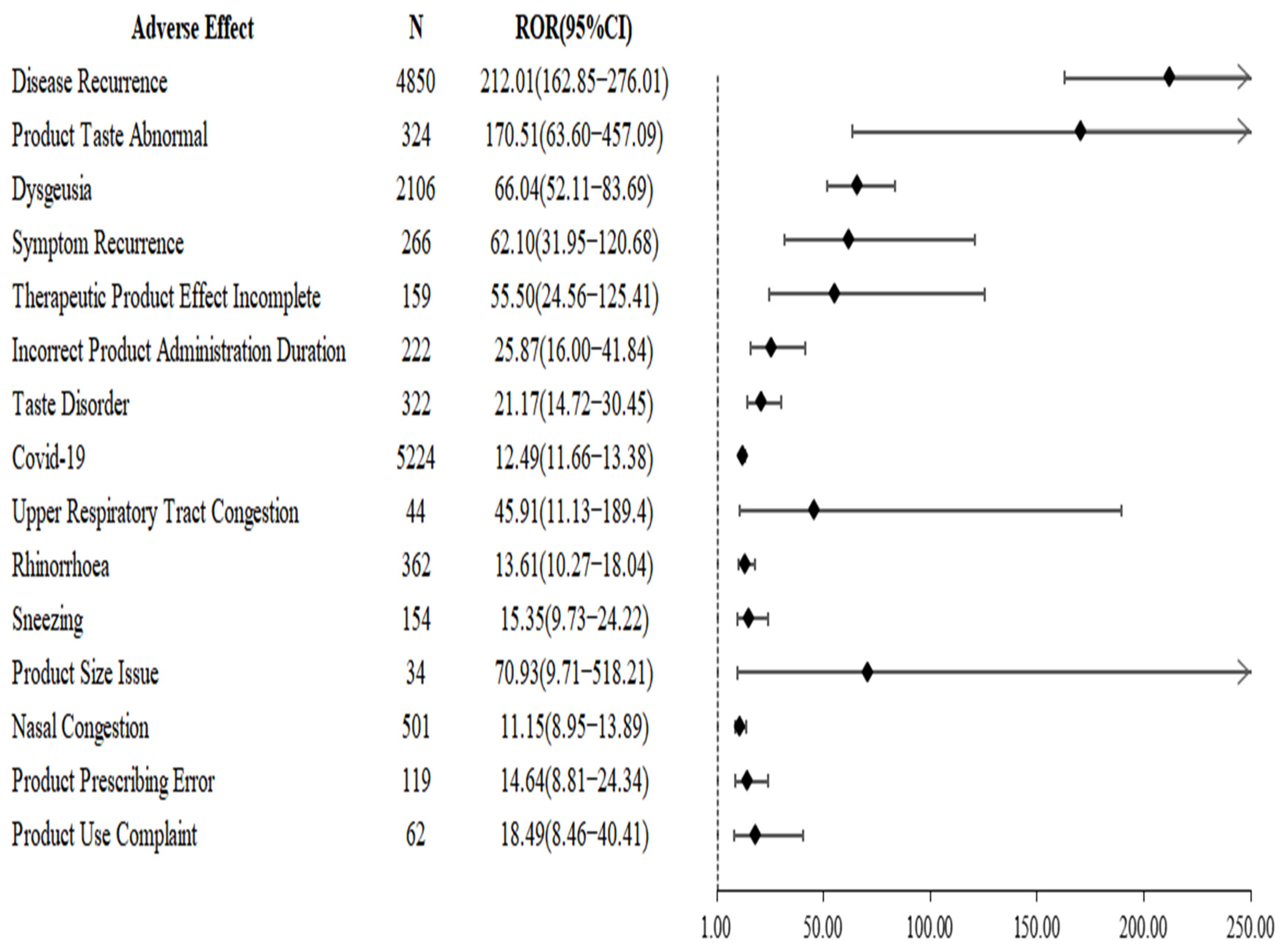
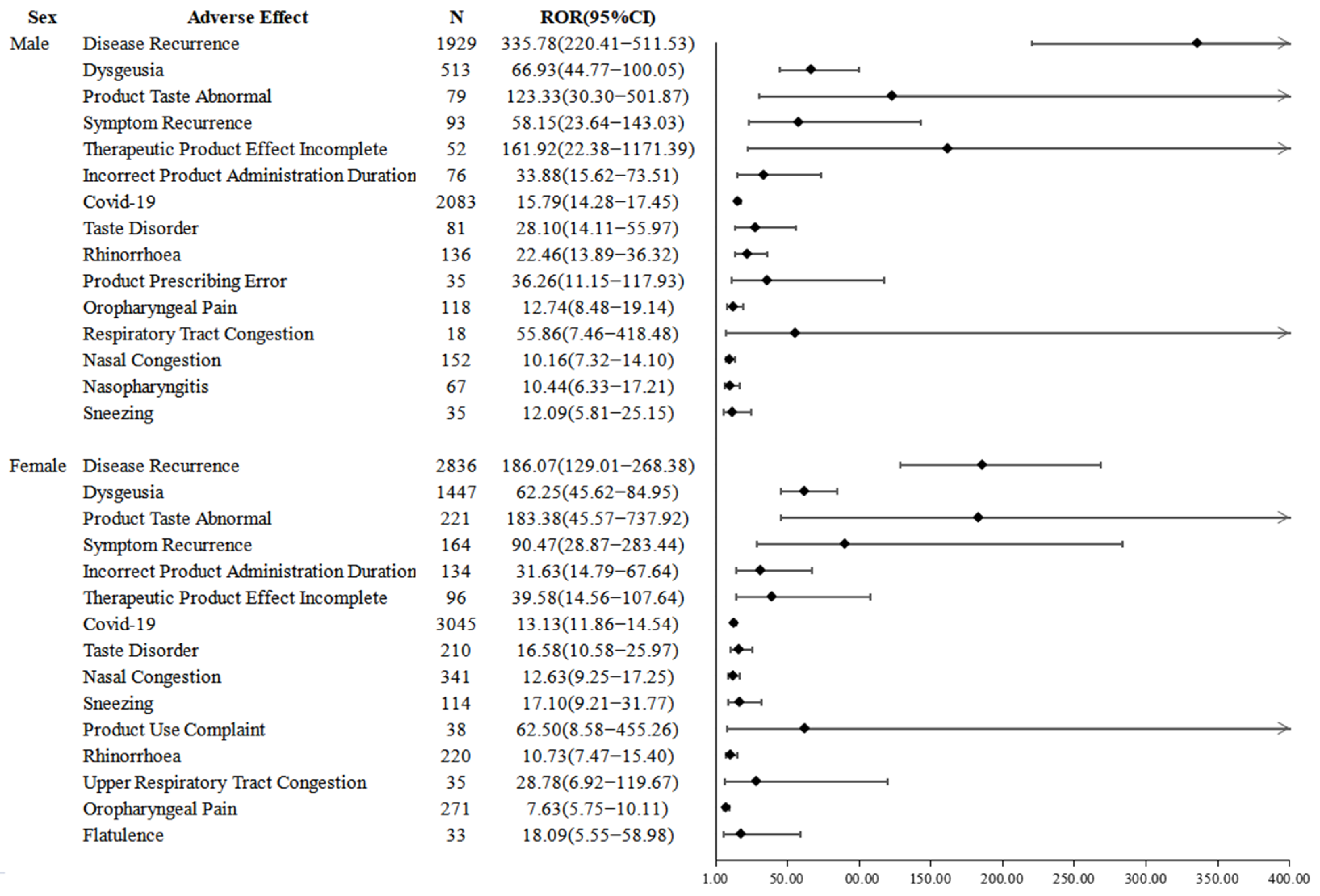
2.3. Disproportionality Analysis
3. Discussion
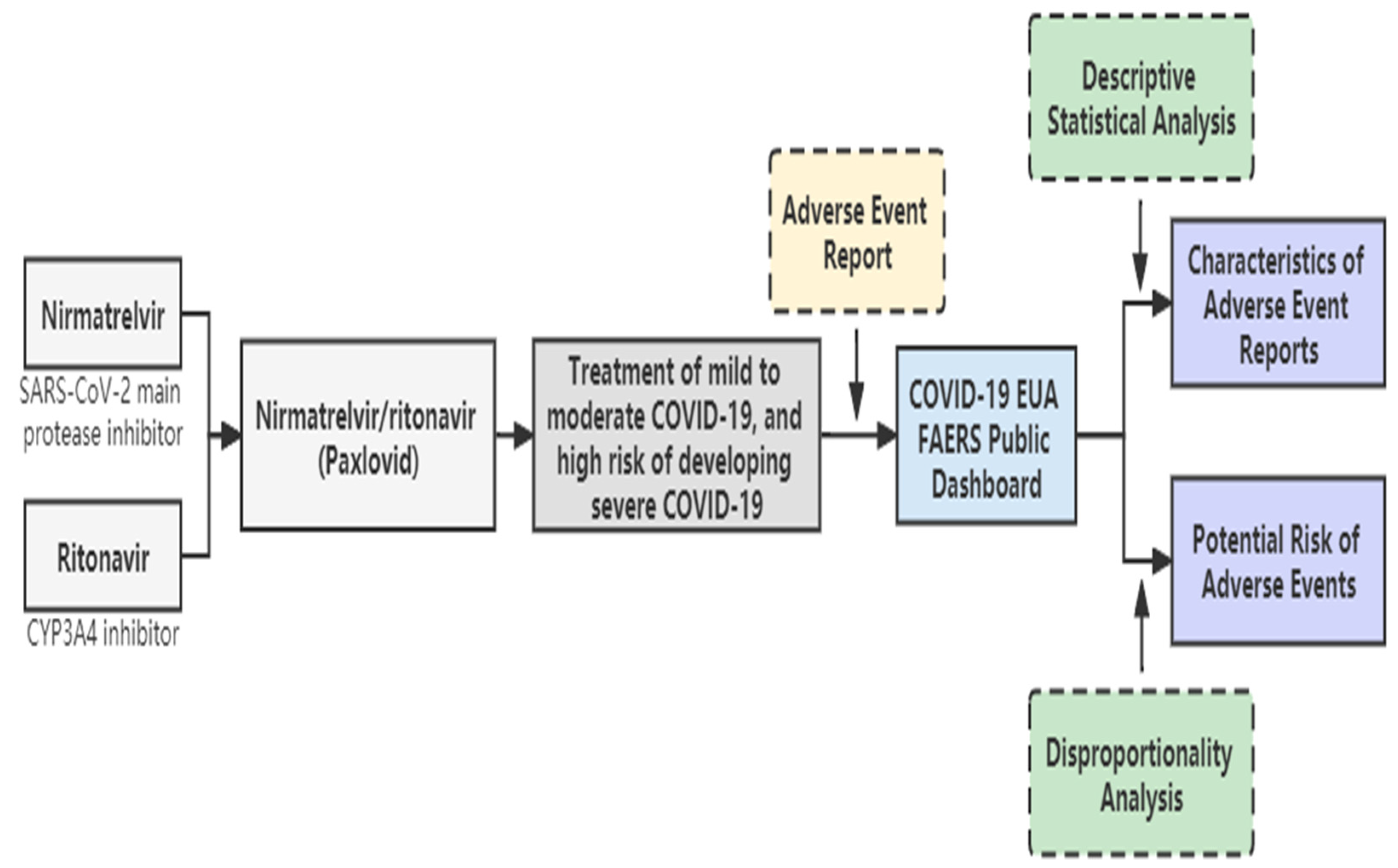
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Collection and Processing
4.2. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wiersinga, W.J.; Rhodes, A.; Cheng, A.C.; Peacock, S.J.; Prescott, H.C. Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) A Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanh Le, T.; Andreadakis, Z.; Kumar, A.; Gómez Román, R.; Tollefsen, S.; Saville, M.; Mayhew, S. The COVID-19 vaccine development landscape. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, J.; Leister-Tebbe, H.; Gardner, A.; Abreu, P.; Bao, W.; Wisemandle, W.; Baniecki, M.; Hendrick, V.M.; Damle, B.; Simón-Campos, A.; et al. Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.R.; Allerton, C.M.N.; Anderson, A.S.; Aschenbrenner, L.; Avery, M.; Berritt, S.; Boras, B.; Cardin, R.D.; Carlo, A.; Coffman, K.J.; et al. An oral SARS-CoV-2 M-pro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19. Science 2021, 374, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, Y.N. Nirmatrelvir Plus Ritonavir: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxtall, J.D.; Perry, C.M. Lopinavir/Ritonavir A Review of its Use in the Management of HIV-1 Infection. Drugs 2010, 70, 1885–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polus, A.; Bociaga-Jasik, M.; Czech, U.; Goralska, J.; Cialowicz, U.; Chojnacka, M.; Polus, M.; Jurowski, K.; Dembinska-Kiec, A. The Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV 1) Protease Inhibitor Sanquinavir Activates Autophagy and REMOVES LIPIDS deposited in Lipid Droplets. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 68, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- FDA. Emergency Use Authorization. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/mcm-legal-regulatory-and-policy-framework/emergency-use-authorization#coviddrugs (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency. Summary of Product Characteristics for Paxlovid. Available online: http://www.gov.uk.zzulib.vpn358.com/government/publications/regulatory-approval-of-paxlovid/summary-of-product-characteristics-for-paxlovid#date-of-first-authorisationrenewal-of-the-authorisation (accessed on 7 September 2022).
- Health Canada. PAXLOVID. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/news/2022/01/health-canada-authorizes-paxlovidtm-for-patients-with-mild-to-moderate-covid-19-at-high-risk-of-developing-serious-disease.html (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Australian Government Therapeutic Goods Administration. Paxlovid. Available online: https://www.tga.gov.au/resources/auspmd/paxlovid (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- European Medicines Agency. Paxlovid. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/paxlovid (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Saravolatz, L.D.; Depcinski, S.; Sharma, M. Molnupiravir and Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir: Oral COVID Antiviral Drugs. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, ciac180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulson, J.; Adams, A.; Gray, L.; Evans, A. COVID-19 "Rebound" associated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir pre-hospital therapy. J. Infect. 2022, 85, 476–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Rebound after Paxlovid Treatment. Available online: http://emergency.cdc.gov.zzulib.vpn358.com/han/2022/han00467.asp (accessed on 7 September 2022).
- Carlin, A.F.; Clark, A.E.; Chaillon, A.; Garretson, A.F.; Bray, W.; Porrachia, M.; Santos, A.T.; Rana, T.M.; Smith, D.M. Virologic and Immunologic Characterization of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Recrudescence after Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Treatment. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, ciac496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucau, J.; Uddin, R.; Marino, C.; Regan, J.; Flynn, J.P.; Choudhary, M.C.; Chen, G.; Stuckwisch, A.M.; Mathews, J.; Liew, M.Y.; et al. Characterization of Virologic Rebound Following Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Treatment for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, ciac512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DAILYMED. PAXLOVID-Nirmatrelvir and Ritonavir Kit. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=7bdddfba-bd31-44cb-ba9e-23a4e17a4691. (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Drugs.com. Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Side Effects. Available online: https://www.drugs.com/sfx/nirmatrelvir-ritonavir-side-effects.html (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- RITONAVIR Tablet. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=a32cb2e3-d4e5-4bbf-9d88-20b2b249e779#LINK_b53c25c0-8d39-4af4-ac5b-2c9d0ac5167e (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Lechien, J.R.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; De Siati, D.R.; Horoi, M.; Le Bon, S.D.; Rodriguez, A.; Dequanter, D.; Blecic, S.; El Afia, F.; Distinguin, L.; et al. Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions as a clinical presentation of mild-to-moderate forms of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A multicenter European study. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2020, 277, 2251–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinato, G.; Fabbris, C.; Polesel, J.; Cazzador, D.; Borsetto, D.; Hopkins, C.; Boscolo-Rizzo, P. Alterations in Smell or Taste in Mildly Symptomatic Outpatients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection. JAMA 2020, 323, 2089–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, P.; Rabold, E.M.; Laws, R.L.; Conners, E.E.; Gharpure, R.; Yin, S.; Buono, S.A.; Dasu, T.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Westergaard, R.P.; et al. Loss of Taste and Smell as Distinguishing Symptoms of Coronavirus Disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechien, J.R.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Place, S.; Van Laethem, Y.; Cabaraux, P.; Mat, Q.; Huet, K. Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of 1420 European patients with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 288, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-U.; Kim, M.-J.; Ra, S.-H.; Lee, J.; Bae, S.; Jung, J.; Kim, S.-H. Clinical characteristics of asymptomatic and symptomatic patients with mild COVID-19. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, e1–e948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malden, D.E.; Hong, V.; Lewin, B.J.; Ackerson, B.K.; Lipsitch, M.; Lewnard, J.A.; Tartof, S.Y. Hospitalization and Emergency Department Encounters for COVID-19 After Paxlovid Treatment-California, December 2021–May 2022. MMWR-Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 830–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryden-Peterson, S.; Kim, A.; Kim, A.Y.; Caniglia, E.C.; Lennes, I.; Patel, R.; Gainer, L.; Dutton, L.; Donahue, E.; Gandhi, R.T.; et al. Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir for early COVID-19 and hospitalization in a large US health system. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar-Debbiny, R.; Gronich, N.; Weber, G.; Khoury, J.; Amar, M.; Stein, N.; Goldstein, L.H.; Saliba, W. Effectiveness of Paxlovid in Reducing Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Mortality in High-Risk Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, ciac443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Puijenbroek, E.P.; Bate, A.; Leufkens, H.G.M.; Lindquist, M.; Orre, R.; Egberts, A.C.G. A comparison of measures of disproportionality for signal detection in spontaneous reporting systems for adverse drug reactions. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2002, 11, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Suspected Drug | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir | 11,997 | 40.14 |
| Casirivimab/Imdevimab | 4478 | 14.98 |
| Remdesivir | 4047 | 13.54 |
| Bamlanivimab | 3889 | 13.01 |
| Bamlanivimab/Etesevimab | 1968 | 6.58 |
| Sotrovimab | 1032 | 3.45 |
| Baricitinib | 652 | 2.18 |
| Bebtelovimab | 621 | 2.08 |
| Cilgavimab/Tixagevimab | 466 | 1.56 |
| Tocilizumab | 253 | 0.85 |
| Characteristics | Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir (N = 11,997) | Other COVID-19 Drugs (N = 17,891) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 7138 | 59.50 | 8430 | 47.12 |
| Male | 4082 | 34.03 | 8590 | 48.01 |
| Not Specified | 777 | 6.48 | 871 | 4.87 |
| Age | ||||
| Median | 60 | 62 | ||
| <18 | 27 | 0.23 | 331 | 1.85 |
| 18–44 | 2357 | 19.65 | 3272 | 18.29 |
| 45–64 | 3887 | 32.40 | 5309 | 29.67 |
| ≥65 | 4132 | 34.44 | 6864 | 38.37 |
| Not Specified | 1594 | 13.29 | 2115 | 11.82 |
| Reporter Type | ||||
| Consumer | 8542 | 71.20 | 2551 | 14.26 |
| Healthcare Professional | 3415 | 28.47 | 14,749 | 82.44 |
| Not Specified | 40 | 0.33 | 591 | 3.30 |
| Country | ||||
| US | 10,553 | 87.96 | 13,245 | 74.03 |
| Other Countries | 818 | 6.82 | 718 | 4.01 |
| Not Specified | 626 | 5.22 | 3928 | 21.96 |
| Outcome | ||||
| Death | 59 | 0.49 | 1831 | 10.23 |
| Life Threatening | 61 | 0.51 | 782 | 4.37 |
| Required Intervention | 29 | 0.24 | 848 | 4.74 |
| Disabled | 48 | 0.40 | 83 | 0.46 |
| Hospitalizations | 339 | 2.83 | 4446 | 24.85 |
| Congenital Anomaly | 0 | 0.00 | 5 | 0.03 |
| Other Outcomes | 944 | 7.87 | 4658 | 26.04 |
| Non-Serious | 10,517 | 87.66 | 5238 | 29.28 |
| Preferred Terms | System Organ Classes | N | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| COVID-19 | Infections and infestations | 5224 | 43.54 |
| Disease Recurrence | General disorders and administration site conditions | 4850 | 40.43 |
| Dysgeusia a | Nervous system disorders | 2106 | 17.55 |
| Diarrhoea | Gastrointestinal disorders | 1056 | 8.80 |
| Nausea | Gastrointestinal disorders | 637 | 5.31 |
| Cough b | Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | 632 | 5.27 |
| Fatigue b | General disorders and administration site conditions | 579 | 4.83 |
| Headache b | Nervous system disorders | 572 | 4.77 |
| Nasal Congestion b | Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | 501 | 4.18 |
| Oropharyngeal Pain b | Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | 409 | 3.41 |
| Rhinorrhoea | Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | 362 | 3.02 |
| Pyrexia | General disorders and administration site conditions | 359 | 2.99 |
| Vomiting c | Gastrointestinal disorders | 346 | 2.88 |
| Incorrect Dose Administered | Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | 345 | 2.88 |
| Malaise b | General disorders and administration site conditions | 331 | 2.76 |
| Outcomes | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Death | 1 | 0.02 |
| Life Threatening | 4 | 0.08 |
| Disabled | 9 | 0.19 |
| Hospitalization | 45 | 0.93 |
| Other Outcomes | 88 | 1.81 |
| Non-Serious | 4703 | 96.97 |
| Target Adverse Event | All other Adverse Event | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target drug | n11 | n12 | n1+ |
| All other drugs | n21 | n22 | n2+ |
| Total | n + 1 | n + 2 | n++ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Zhang, Q.-S.; Liu, X.-L.; Wang, H.-L.; Liu, W. Adverse Events Associated with Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir: A Pharmacovigilance Analysis Based on FAERS. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121455
Li M, Zhang Q-S, Liu X-L, Wang H-L, Liu W. Adverse Events Associated with Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir: A Pharmacovigilance Analysis Based on FAERS. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(12):1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121455
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Meng, Qing-Song Zhang, Xin-Ling Liu, Hui-Ling Wang, and Wei Liu. 2022. "Adverse Events Associated with Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir: A Pharmacovigilance Analysis Based on FAERS" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 12: 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121455
APA StyleLi, M., Zhang, Q.-S., Liu, X.-L., Wang, H.-L., & Liu, W. (2022). Adverse Events Associated with Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir: A Pharmacovigilance Analysis Based on FAERS. Pharmaceuticals, 15(12), 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121455






