Optimization of Formulation Parameters in Preparation of Fructus ligustri lucidi Dropping Pills by Solid Dispersion Using 23 Full Experimental Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
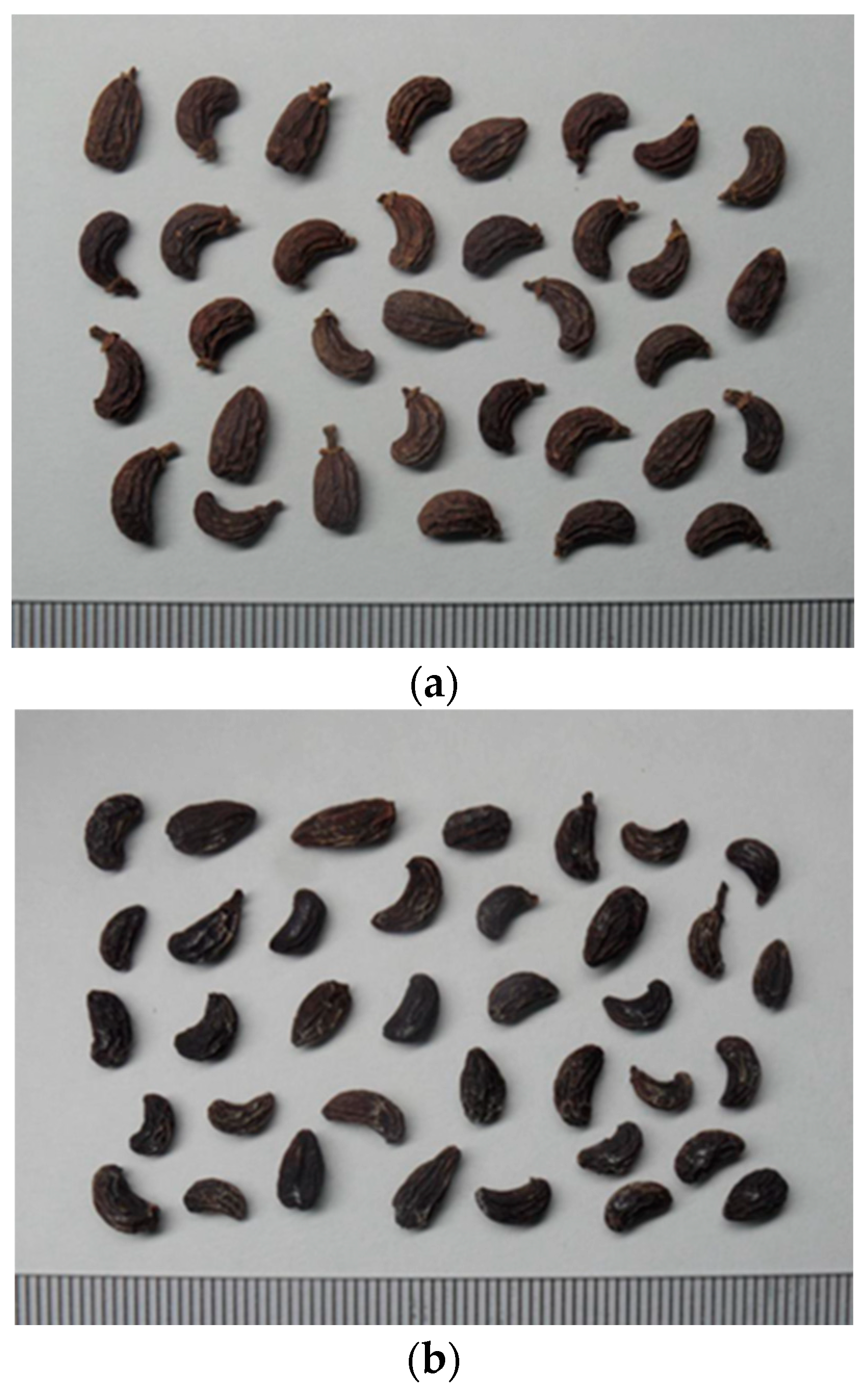
2.1. FLL Concoction
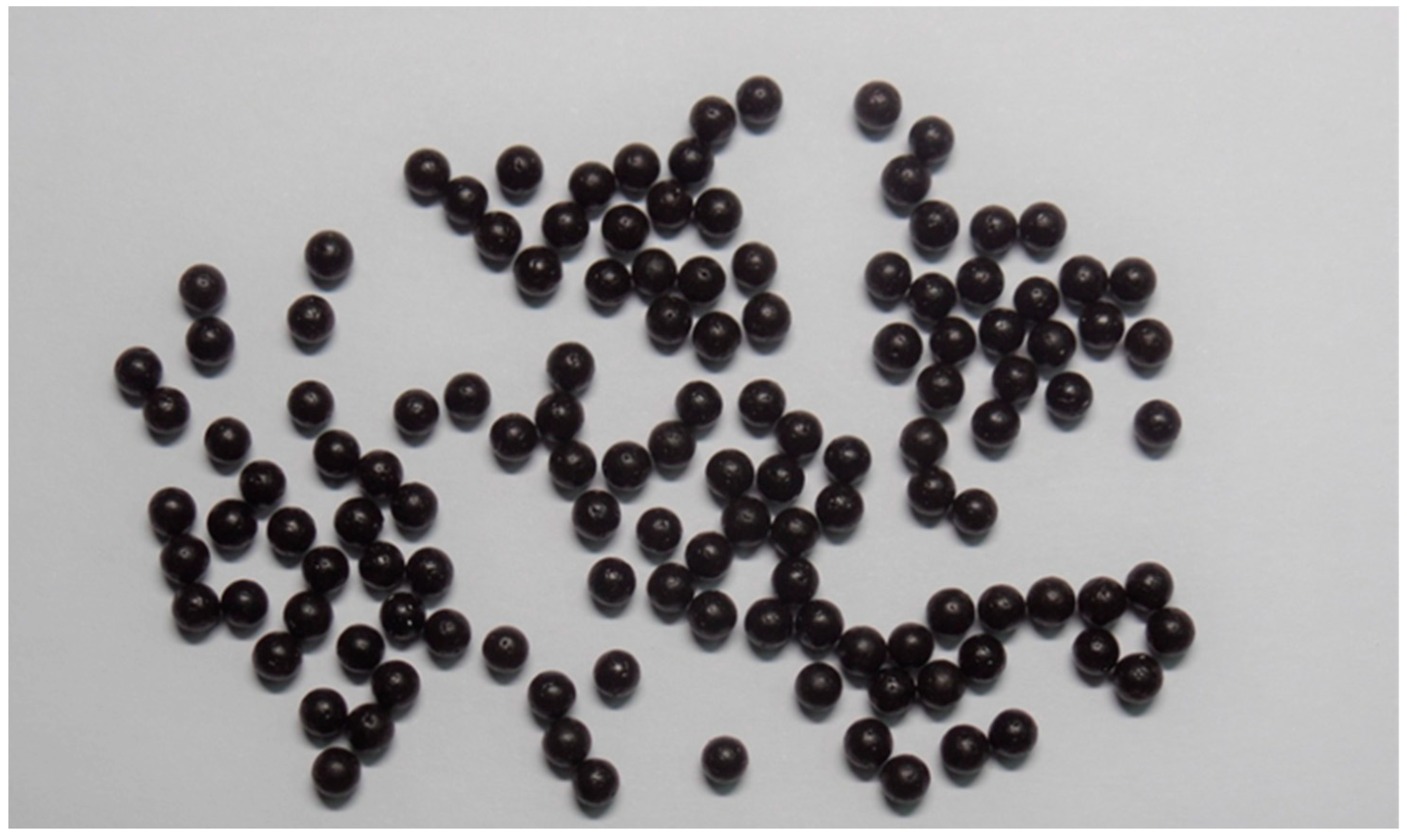
2.2. Preparation of FLL Dropping Pills
2.2.1. Preliminary Test (Variables and Level Range Screening)
Type and Ratio of Substrate
Condensate Selection
FLL Extract Loading
Surfactant Selection
2.3. The 23 Experimental Design
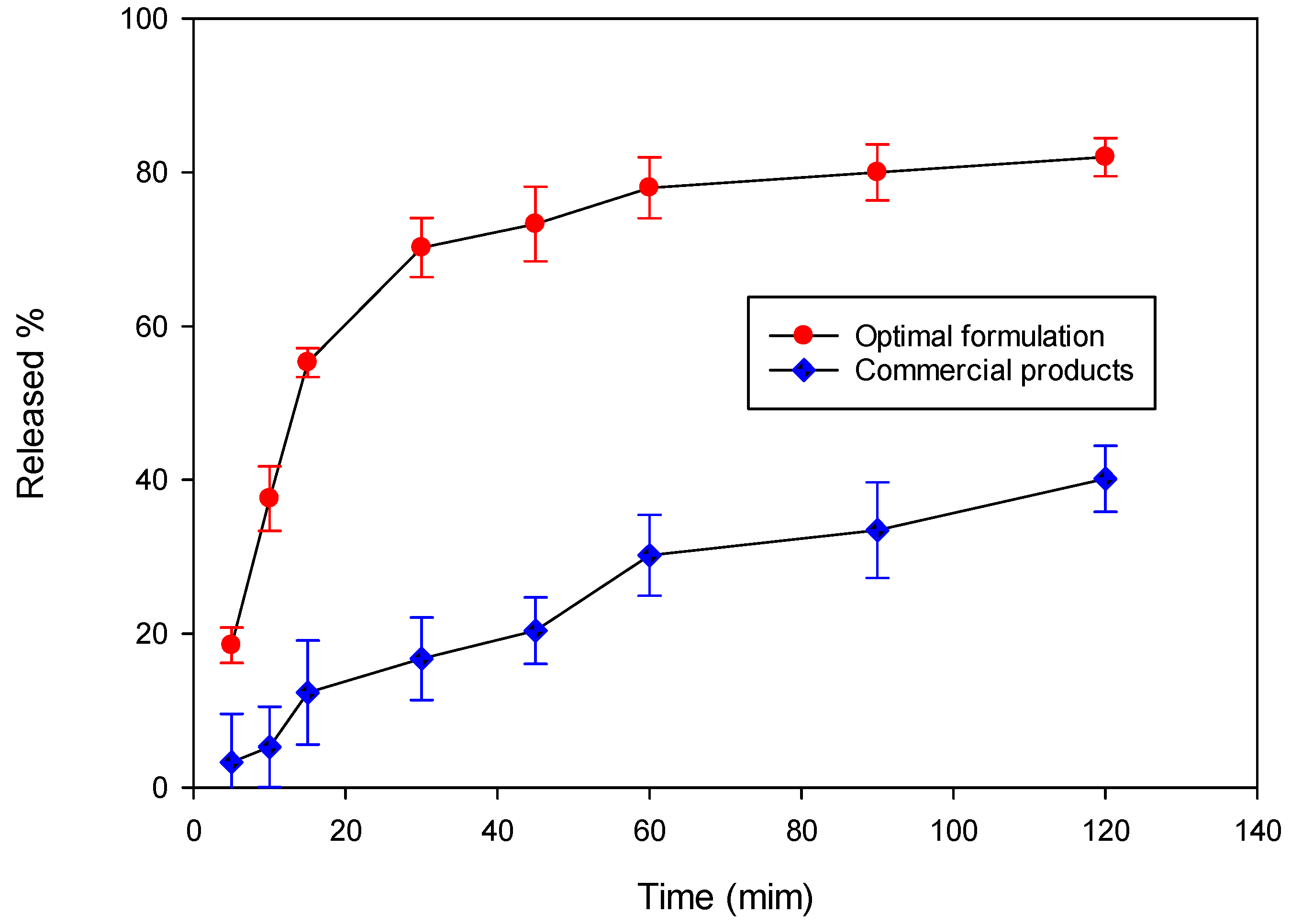
2.4. Evaluation of the Optimal Formulation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Drug and Excipients
3.2. Preparation of FLL Extract
3.2.1. Concoction of FLL Wine Steaming Product
3.2.2. Ultrafine Pulverization of FLL
3.2.3. Extraction and Concentration of FLL Components
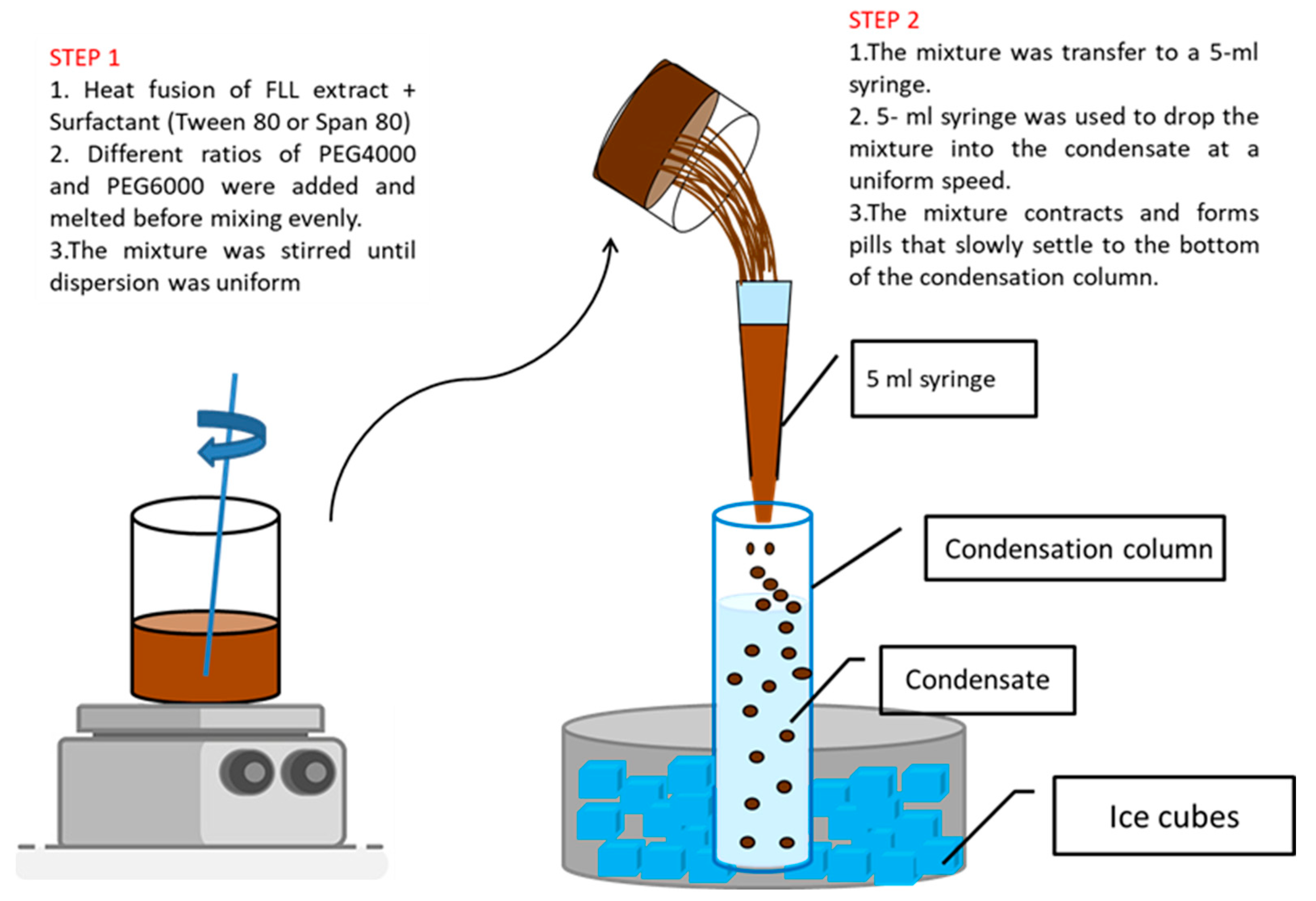
3.3. Preparation of FLL Dropping Pills
3.3.1. Preliminary Test
Type and Ratio of Substrates
Condensate Screening
FLL Extract Loading
Surfactant Screening
3.3.2. Preparation Process of Dropping Pills
3.3.3. The 23 Experimental Design
3.4. Physical Evaluation of FLL Dropping Pills
3.4.1. Roundness
3.4.2. Weight Variation
3.4.3. Disintegration Test
3.5. Evaluation of the Optimal FLL Dropping Pill Formulation
3.5.1. Solubility Study
3.5.2. Content Uniformity
3.5.3. HPLC Analysis Conditions for OA
3.5.4. Dissolution Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pang, Z.T.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Wang, W.; Ma, Y.; Niu, F.J.; Zhang, X.; Han, C.C. The advances in research on the pharmacological effects of Fructus Ligustri Lucidi. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 281873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.B.; Wang, L.L.; Li, L.; Zhu, R.U.; Liu, H.X.; Liu, C.Y.; Ma, R.F.; Jia, Q.Q.; Zhao, D.D.; Niu, J.Z.; et al. Fructus Ligustri Lucidi in Osteoporosis: A Review of its Pharmacology, Phytochemistry, Pharmacokinetics and Safety. Molecules 2017, 22, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.L.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.Q.; You, Y.; Wei, H.; Guo, T. Ligustri lucidi fructus as a traditional Chinese medicine: A review of its phytochemistry and pharmacology. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Cao, L.X.; Zhang, R.; Wei, P.F. Anti-diabetic activity of aqueous extract of Fructus Ligustri Lucidi in a rat model of type 2 diabetes. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 17, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollier, J.; Goossens, A. Oleanolic acid. Phytochem. 2012, 77, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, J.M.; Ramos-Romero, S.; Perona, J.S. Oleanolic acid: Extraction, characterization and biological activity. Nutrients 2022, 14, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.J.; Wang, Y.L.; Han, X.X.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, H.; Chen, J.; Ji, D.; Mao, C.Q.; Lu, T.L. A Modern Technology Applied in Traditional Chinese Medicine: Progress and Future of the Nanotechnology in TCM. Dose-Response 2019, 17, 1559325819872854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, M. The combination of nanotechnology and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) inspires the modernization of TCM: Review on nanotechnology in TCM-based drug delivery systems. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 1306–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, S.P.; Lu, J.R.; Jing, Y.; Li, M.X.; Cao, J.L.; Bian, B.L.; Hu, C.J. Seeing the unseen of Chinese herbal medicine processing (Paozhi): Advances in new perspectives. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Verpoorte, R.; Yen, H.R.; Peng, W.H.; Cheng, Y.C.; Chao, J.; Pao, L.H. Effects of processing adjuvants on traditional Chinese herbs. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, s96–s114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.J.; Sun, L.L.; Mao, B.B.; Zhao, D.S.; Cui, Y.L.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, X.L. Analysis of chemical variations between raw and wine-processed Ligustri Lucidi Fructus by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-Q-Exactive Orbitrap/MS combined with multivariate statistical analysis approach. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2021, 35, e5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.X.; Deng, L.H.; Lee, A.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhong, W.F.; Huang, G.F.; Cheng, X.R. Study on Processing Procedure of Wine-Processed Ligustri Lucidi Fructus Based on UPLC Characteristic Chromatogram and Multicomponent Content Determination. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 38, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali1, H.S.; Suliman, R.S.; Elhaj, B.; Suliman, R. A recent progresses and manufacturing techniques in pharmaceutical powders and granulation. Int. J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2019, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Surender, V.; Aruna, R.; Mahima, K.; Sapna, S. Solid dispersion: A strategy for solubility enhancement. Int. J. Pharm. Technol. 2011, 3, 1062–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Kiran, S.S.; Jagannath, S.; Seema, A.; Asha, K. Solid dispersions: A technology for improving bioavailability. J. Anal. Pharm. Res. 2019, 8, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Mogal, S.A.; Gurjar, P.N.; Yamgar, D.S.; Kamod, A.C. Solid dispersion technique for improving solubility of some poorly soluble drugs. Der. Pharm. Lett. 2012, 4, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Pharmacopoeia Commission of China. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, 11th ed.; China Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume 4, pp. 10–11a, 137b. [Google Scholar]
- Amir, B.S.; Parya, R.N.; Piroska, S.R.; Róbert, R. Preparation of a Solid Dispersion by a Dropping Method to Improve the Rate of Dissolution of Meloxicam. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2008, 34, 781–788. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.L.; Zhu, Q.; Bian, T.Z.; Liu, K.H. Preparation of Vitamin C Dripping Pill and its Quality Evaluation. Adv. Mat. Res. 2012, 602–604, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Cui, B.J.; Guo, S.Y. Study on the Preparation Technology of Fanhuncao Sustained-release Dropping Pills. China Pharm. 2015, 12, 4837–4840. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Qu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, B.; Liud, C.; Gao, W. Shunaoxin dropping pill, a Chinese herb compound preparation, attenuates memory impairment in Dgalactose-induced aging mice. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 10163–10171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hani, U.; Osmani, R.A.M.; Alqahtani, A.; Ghazwani, M.; Rahamathulla, M.; Almordy, S.A.; Alsaleh, H.A. 23 Full Factorial Design for Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Oral In Situ Gelling System of Piroxicam. J. Pharm. Innov. 2021, 16, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya Teja, S.P.; Damodharan, N. 23 Full Factorial Model for Particle Size Optimization of Methotrexate Loaded Chitosan Nanocarriers: A Design of Experiments (DoE) Approach. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 7834159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawaba, H.M.; Samy1, A.M.; Fetouh, M.I.; Abd-Allah, F.I.; Nutan, M.T. Application of 23 full-factorial design for development and optimization of biocompatible, biodegradable solid lipid nanoparticles containing curcumin. Az. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 84–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharmacopoeia Commission of China. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, 11th ed.; China Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, R.C.; Sheskey, P.J.; Quinn, M.E. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, 6th ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2009; pp. 517–522a, 445–447b, 233–234c, 549–553d. [Google Scholar]
- Foo, K.S.; Bavoh, C.B.; Lal, B.; Shari, A.M. Rheology Impact of Various Hydrophilic-Hydrophobic Balance (HLB) Index Non-Ionic Surfactants on Cyclopentane Hydrates. Molecules 2020, 25, 3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuo, W.H.; Lo, Y.K.; Huang, Y.T.; Wu, C.S. Statistical Optimization And Stability Study Of Quercetin-Loaded Microemulsion. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 13, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.W.; Wang, C.Y.; Wu, Y.T.; Hsu, M.C. Enhanced solubility, dissolution, and absorption of lycopene by a solid dispersion technique: The dripping pill delivery system. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuner, C.; Dressman, J. Improving drug solubility for oral delivery using solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.D. Studies on the preparation and dissolution of sodium ferulate dropping pill. J. Pharm. Pract. 2006, 5, 281–283. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.D.; Shi, Y.J.; Li, J.H.; Gao, N.; Ji, J.; Niu, F.; Chen, Q.T.; Yang, X.N.; Wang, S.C. Enhancement of Oral Bioavailability of Curcumin by a Novel Solid Dispersion System. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2015, 16, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.W. The Industrialization and Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine. In The Book of Chinese Medicine: The Timeless Science of Balance and Harmony for Modern Life; Sun, H.H., Meng, J.Y., Yan, K.J., Eds.; Cambridge Scholars Publishing, Lady Stephenson Library: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2021; Volume 2, pp. 327–334. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.T. Optimization of preparation process and dissolution test of tetrandrine dropping pills. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2018, 24, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Christopher Vimalso, D.; Parimalakrishnan, S.; Jeganathan, N.S.; Anbazhagan, S. Techniques to Enhance Solubility of Hydrophobic Drugs: An Overview. Asian J. Pharm. 2016, 10, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Pharmacopoeia Commission of the Ministry of Public Health. Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare. Chinese Pharmacopoeia, 8th ed.; Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare: Taipei, Taiwan, 2016; General Chapter; p. 120.

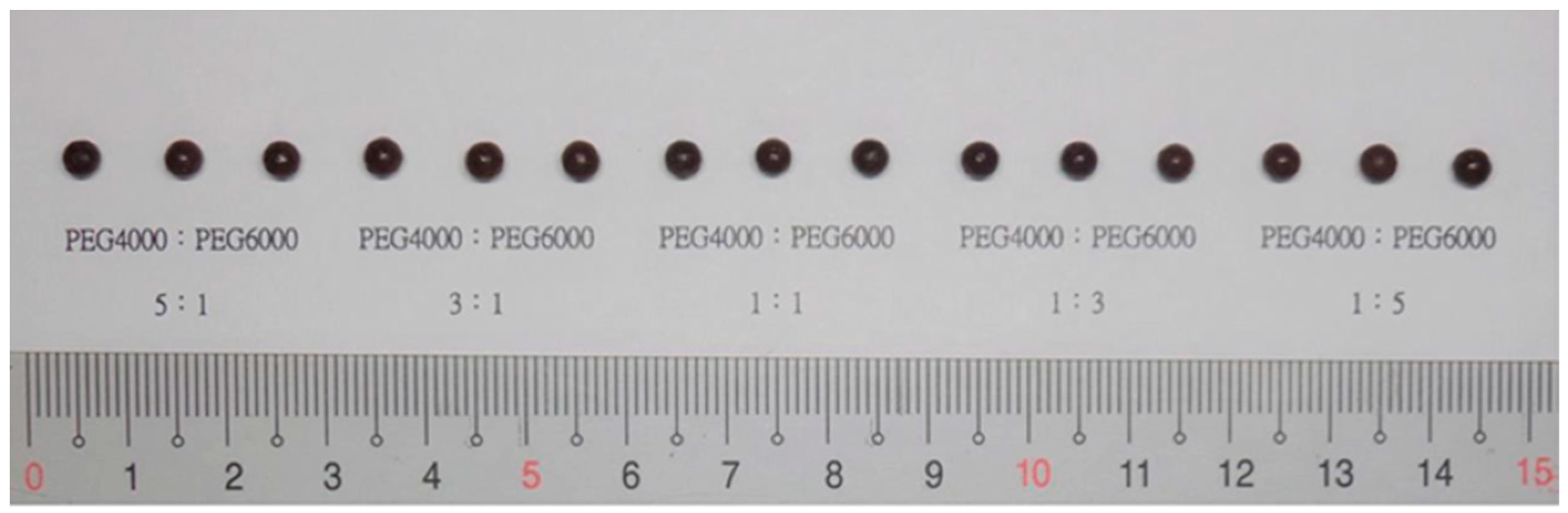

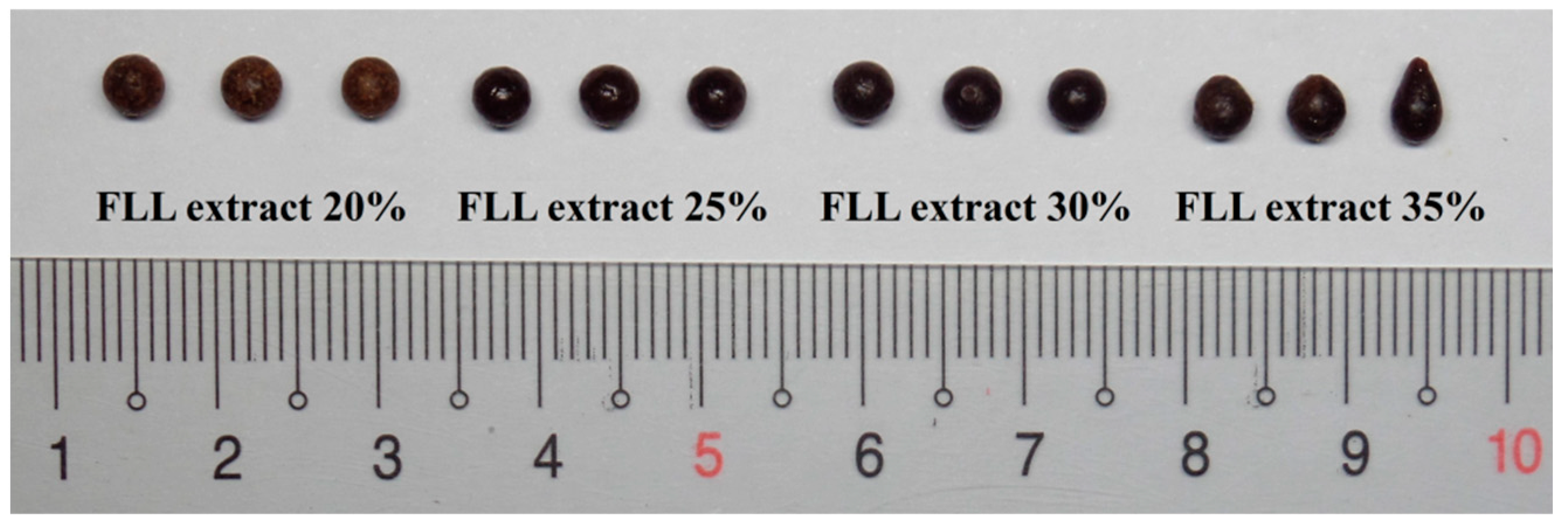

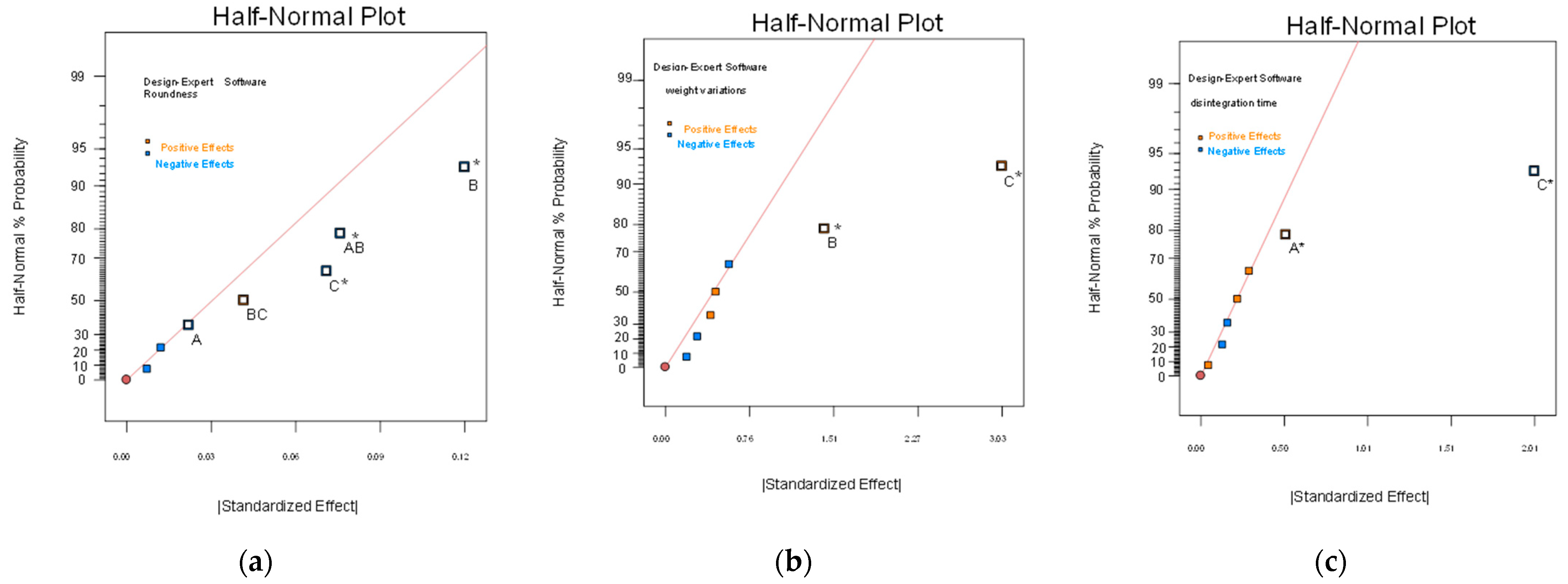
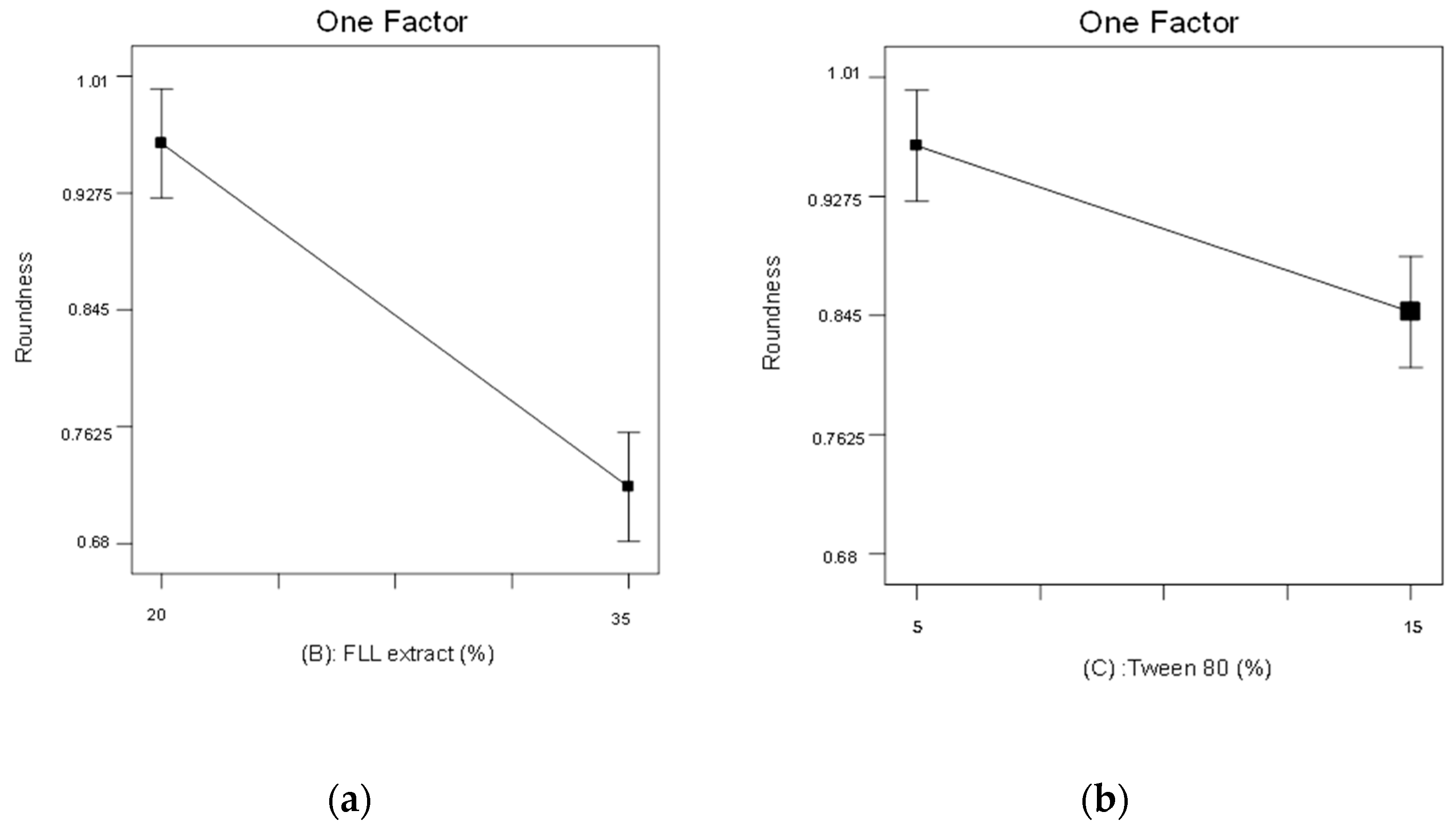
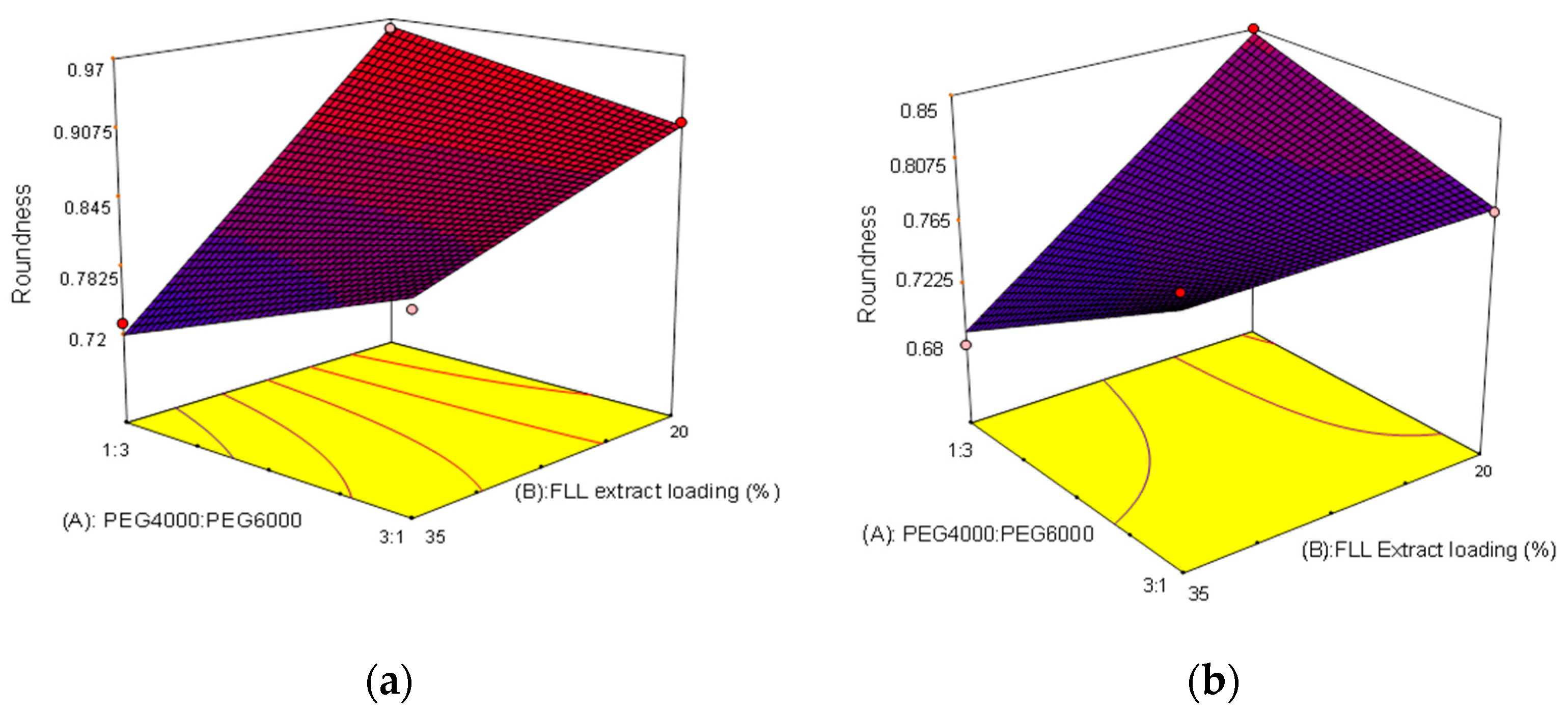
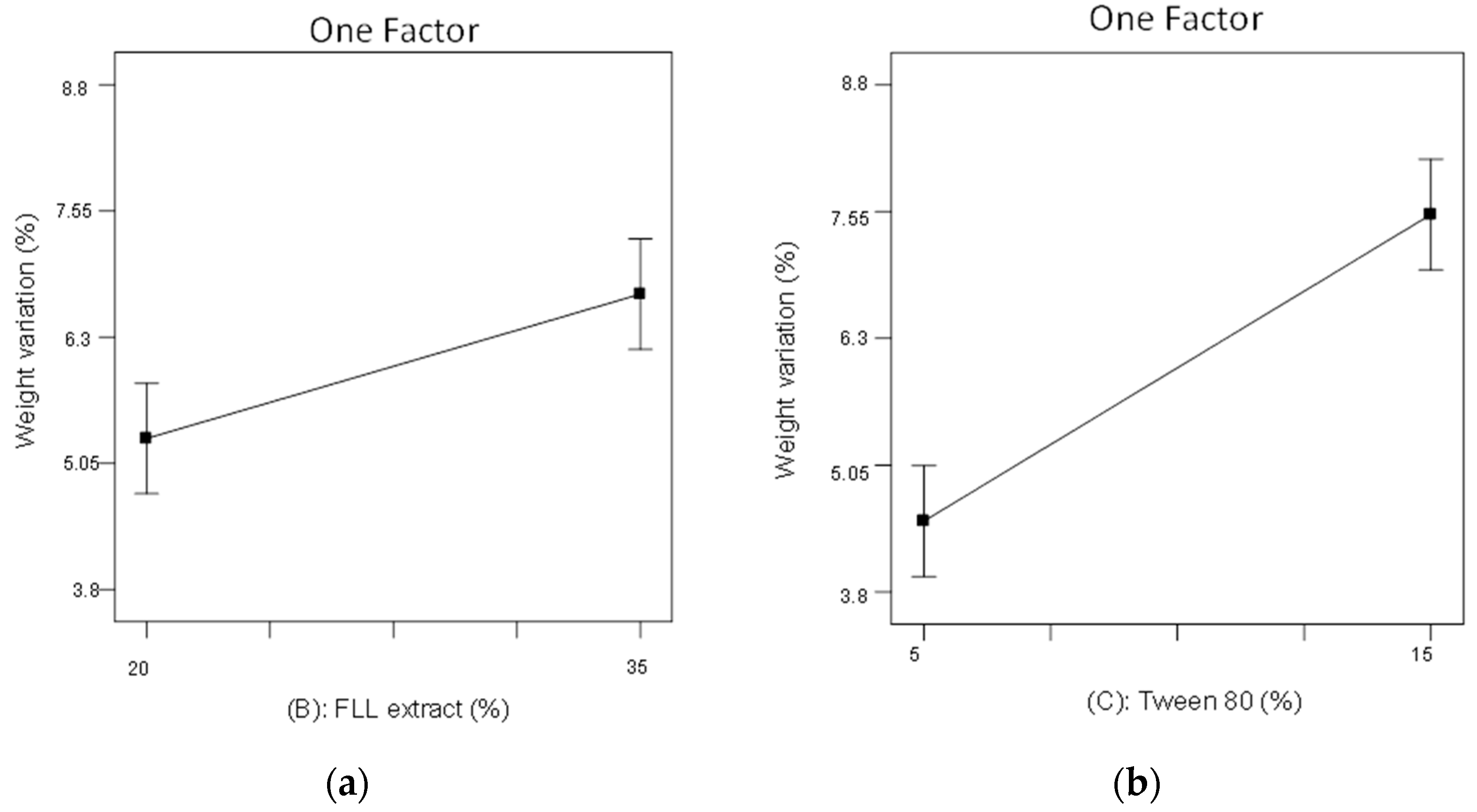


| Independent Variables | Dependent Variable | |||||
| Formulation | A | B | C | Roundness | Weight Variation(%) | Disintegration Time(min) |
| F1 | 1:3 | 35 | 15 | 0.68 ± 0.06 | 8.14 | 4.68 ± 0.20 |
| F2 | 3:1 | 35 | 5 | 0.81 ± 0.04 | 4.54 | 6.09 ± 0.16 |
| F3 | 3:1 | 20 | 5 | 0.91 ± 0.05 | 4.17 | 5.84 ± 0.29 |
| F4 | 1:3 | 35 | 5 | 0.73 ± 0.05 | 5.43 | 6.94 ± 0.23 |
| F5 | 3:1 | 35 | 15 | 0.81 ± 0.04 | 8.79 | 4.06 ± 0.36 |
| F6 | 1:3 | 20 | 5 | 0.96 ± 0.02 | 3.85 | 6.34 ± 0.30 |
| F7 | 3:1 | 20 | 15 | 0.79 ± 0.04 | 7.12 | 4.17 ± 0.12 |
| F8 | 1:3 | 20 | 15 | 0.85 ± 0.03 | 6.04 | 4.25 ± 0.17 |
| Independent variables | Levels | |||||
| Low level | High level | |||||
| Ratio of PEG4000/PEG6000 (A) c | 3:1 | 1:3 | ||||
| FLL extract loading (B) a,b | 20% | 35% | ||||
| Percentage of Tween 80 (C) a,b,c | 5% | 15% | ||||
| No. | Content Uniformity (%) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 92.69 |
| 2 | 88.32 |
| 3 | 94.42 |
| 4 | 93.40 |
| 5 | 92.08 |
| 6 | 89.34 |
| 7 | 96.45 |
| 8 | 93.10 |
| 9 | 89.34 |
| 10 | 86.29 |
| Mean(%) | 91.54 |
| S.D. | 3.11 |
| C.V.% | 3.40 |
| Mean (μg/mL) | S.D. | C.V.% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optimal formulation | 70.60 | 2.40 | 3.40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, K.-R.; Chuo, W.-H.; Huang, Y.-T. Optimization of Formulation Parameters in Preparation of Fructus ligustri lucidi Dropping Pills by Solid Dispersion Using 23 Full Experimental Design. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111433
Wu K-R, Chuo W-H, Huang Y-T. Optimization of Formulation Parameters in Preparation of Fructus ligustri lucidi Dropping Pills by Solid Dispersion Using 23 Full Experimental Design. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(11):1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111433
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Kai-Rong, Wen-Ho Chuo, and Yuh-Tyng Huang. 2022. "Optimization of Formulation Parameters in Preparation of Fructus ligustri lucidi Dropping Pills by Solid Dispersion Using 23 Full Experimental Design" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 11: 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111433
APA StyleWu, K.-R., Chuo, W.-H., & Huang, Y.-T. (2022). Optimization of Formulation Parameters in Preparation of Fructus ligustri lucidi Dropping Pills by Solid Dispersion Using 23 Full Experimental Design. Pharmaceuticals, 15(11), 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111433






