Pembrolizumab and Chemotherapy Combination Prolonged Progression-Free Survival in Patients with NSCLC with High PD-L1 Expression and Low Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
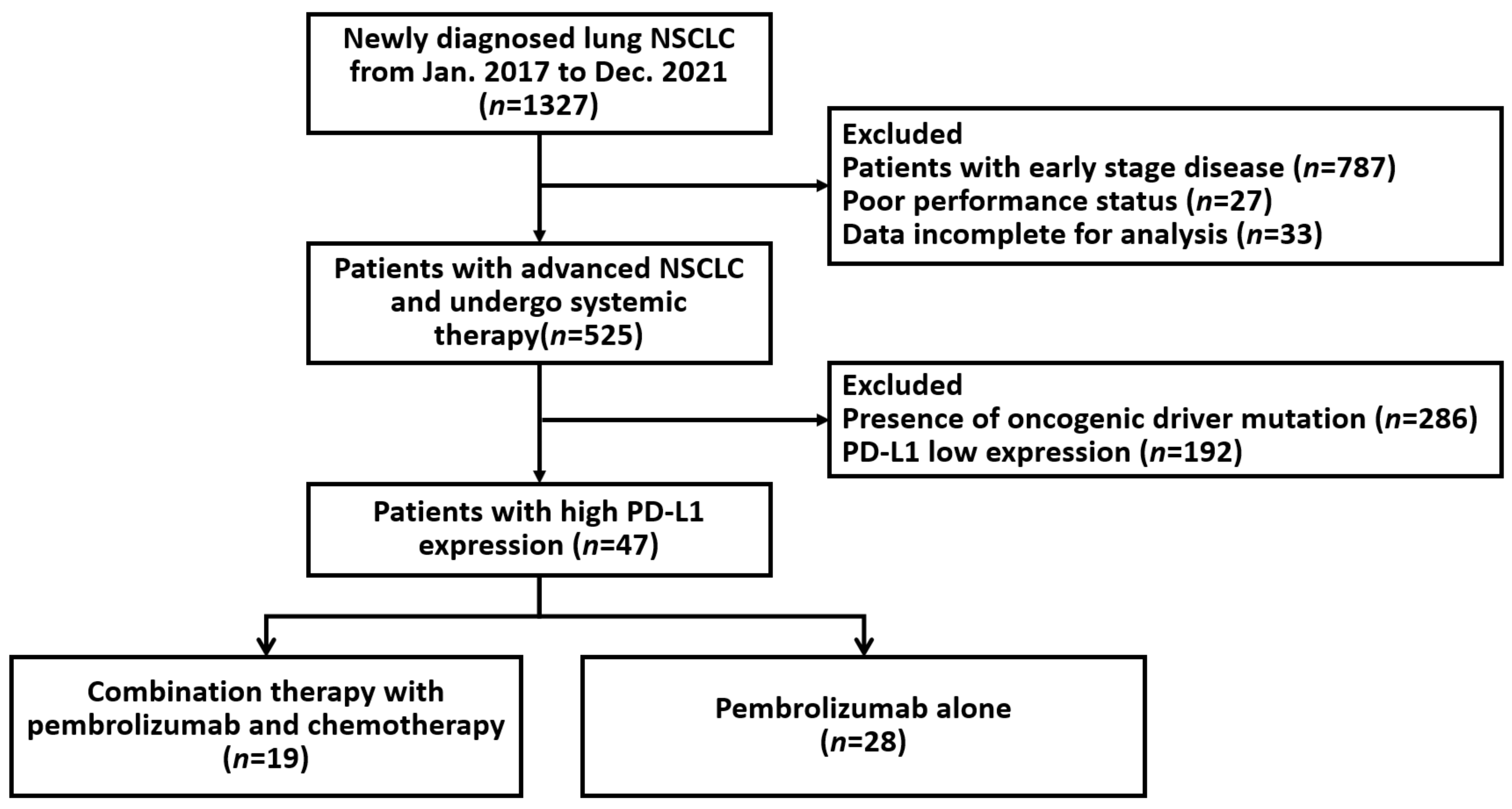
2.1. Patient Characteristics
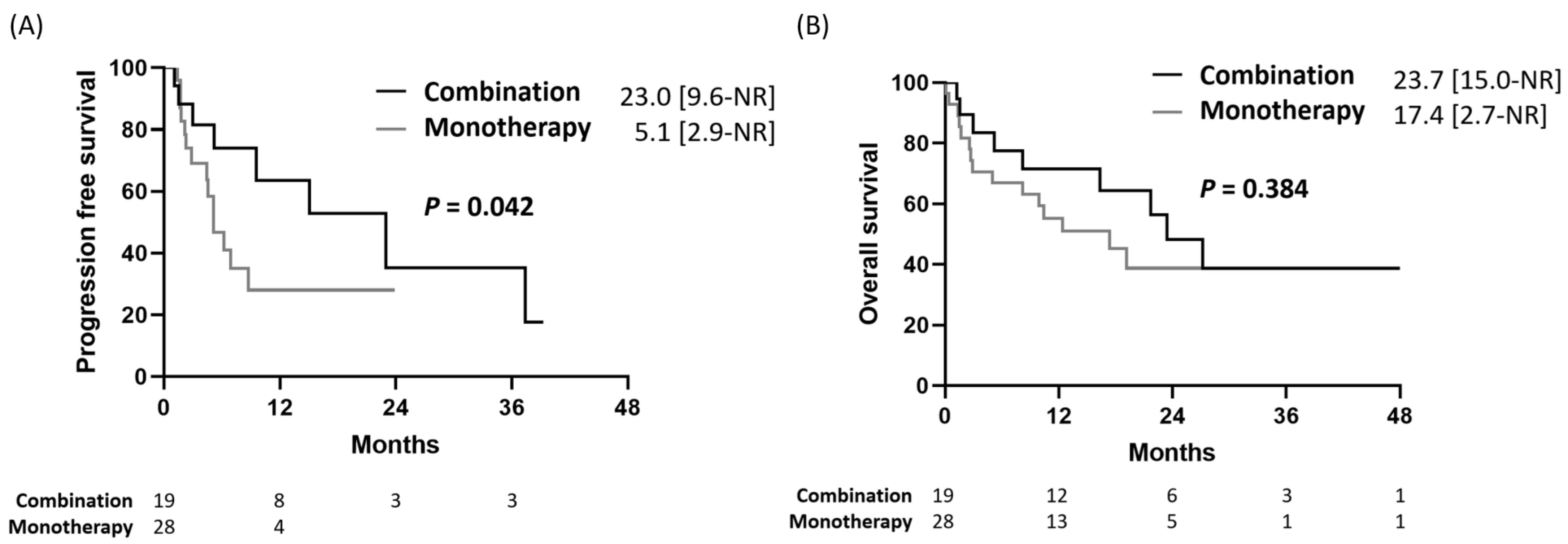
2.2. Progression-Free Survival and Overall Survival
2.3. Subgroup Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. PFS and OS Analysis
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.C.; Tan, D.S.W. Targeted Therapies for Lung Cancer Patients with Oncogenic Driver Molecular Alterations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Remon, J.; Hellmann, M.D. First-Line Immunotherapy for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab vs. Chemotherapy for PD-L1–Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.K.; Wu, Y.-L.; Kudaba, I.; Kowalski, D.M.; Cho, B.C.; Turna, H.Z.; Castro, G., Jr.; Srimuninnimit, V.; Laktionov, K.K.; Bondarenko, I.; et al. Pembrolizumab vs. chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): A randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Giaccone, G.; de Marinis, F.; Reinmuth, N.; Vergnenegre, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Morise, M.; Felip, E.; Andric, Z.; Geater, S.; et al. Atezolizumab for First-Line Treatment of PD-L1–Selected Patients with NSCLC. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meric-Bernstam, F.; Larkin, J.; Tabernero, J.; Bonini, C. Enhancing anti-tumour efficacy with immunotherapy combinations. Lancet 2020, 397, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theelen, W.; Chen, D.; Verma, V.; Hobbs, B.P.; Peulen, H.M.U.; Aerts, J.G.V.; Bahce, I.; Niemeijer, A.L.N.; Chang, J.Y.; Groot, P.M.; et al. Pembrolizumab with or without radiotherapy for metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: A pooled analysis of two randomised trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, L.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Gadgeel, S.; Esteban, E.; Felip, E.; De Angelis, F.; Domine, M.; Clingan, P.; Hochmair, M.J.; Powell, S.F.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Metastatic Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2078–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Luft, A.; Vicente, D.; Tafreshi, A.; Gümüş, M.; Mazières, J.; Hermes, B.; Çay Şenler, F.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy for Squamous Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2040–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudnik, E.; Moskovitz, M.; Rottenberg, Y.; Lobachov, A.; Mandelboim, R.; Shochat, T.; Urban, D.; Wollner, M.; Nechushtan, H.; Rotem, O.; et al. Pembrolizumab as a monotherapy or in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer with PD-L1 tumor proportion score (TPS) ≥50%: Real-world data. OncoImmunology 2021, 10, 1865653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isono, T.; Kagiyama, N.; Shibata, S.; Nakajima, H.; Matsui, Y.; Takano, K.; Nishida, T.; Hosoda, C.; Kawate, E.; Kobayashi, Y.; et al. A retrospective analysis of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy vs. pembrolizumab monotherapy for advanced or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Somekawa, K.; Fukuda, N.; Kaneko, A.; Kamimaki, C.; Kubo, S.; Tanaka, K.; Tagami, Y.; Teranishi, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab monotherapy vs. pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: A multicenter retrospective trial. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takumida, H.; Horinouchi, H.; Masuda, K.; Shinno, Y.; Okuma, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Goto, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Ohe, Y. Comparison of time to failure of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy vs. pembrolizumab monotherapy: A consecutive analysis of patients having NSCLC with high PD-L1 expression. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diem, S.; Schmid, S.; Krapf, M.; Flatz, L.; Born, D.; Jochum, W.; Templeton, A.J.; Früh, M. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte ratio (PLR) as prognostic markers in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with nivolumab. Lung Cancer 2017, 111, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wan, J.; Shi, H. Platelet-to-lymphocyte and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios are associated with the efficacy of immunotherapy in stage III/IV non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 24, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, C.; Lee, M.; Hoen, D.; Weiss, K.; Kelly, D.W.; Adusumilli, P.S.; Paik, P.K.; Plitas, G.; Ladanyi, M.; Postow, M.A.; et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and mutational burden as biomarkers of tumor response to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Gastaldo, A.; Muñoz-Fuentes, M.A.; Molina-Pinelo, S.; Alonso-García, M.; Boyero, L.; Bernabé-Caro, R. Correlation of peripheral blood biomarkers with clinical outcomes in NSCLC patients with high PD-L1 expression treated with pembrolizumab. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 2509–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessi, J.V.; Ricciuti, B.; Alden, S.L.; ABertram, A.; Lin, J.J.; Sakhi, M.; Nishino, M.; Vaz, V.R.; Lindsay, J.; Turner, M.M.; et al. Low peripheral blood derived neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (dNLR) is associated with increased tumor T-cell infiltration and favorable outcomes to first-line pembrolizumab in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e003536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzman, L.; Moskovitz, M.; Urban, D.; Nechushtan, H.; Keren, S.; Reinhorn, D.; Wollner, M.; Daher, S.; Rottenber, Y.; Rovitzky, Y.; et al. dNLR-based score predicting overall survival benefit for the addition of platinum-based chemotherapy to pembrolizumab in advanced NSCLC with PD-L1 tumor proportion score ≥50. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngwa, W.; Irabor, O.C.; Schoenfeld, J.D.; Hesser, J.; Demaria, S.; Formenti, S.C. Using immunotherapy to boost the abscopal effect. Nat. Cancer 2018, 18, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Liang, H.; Burnette, B.; Beckett, M.; Darga, T.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Fu, Y.-X. Irradiation and anti–PD-L1 treatment synergistically promote antitumor immunity in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twyman-Saint Victor, C.; Rech, A.J.; Maity, A.; Rengan, R.; Pauken, K.E.; Stelekati, E.; Benci, J.L.; Xu, B.; Dada, H.; Odorizzi, P.M.; et al. Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer. Nature 2015, 520, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, T.; Xie, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Zhou, C. Combined Radiotherapy and Anti–PD-L1 Antibody Synergistically Enhances Antitumor Effect in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovedi, S.J.; Cheadle, E.J.; Popple, A.L.; Poon, E.; Morrow, M.; Stewart, R.; Yusko, E.C.; Sanders, C.M.; Vignali, M.; Emerson, R.O.; et al. Fractionated Radiation Therapy Stimulates Antitumor Immunity Mediated by Both Resident and Infiltrating Polyclonal T-cell Populations when Combined with PD-1 Blockade. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5514–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theelen, W.; Peulen, H.; Lalezari, F.; van der Noort, V.; de Vries, J.; Averts, J.; Dumoulin, D.W.; Bahce, I.; Miemeijer, A.-L.; de Langen, A.; et al. Effect of pembrolizumab after stereotactic body radiotherapy vs pembrolizumab alone on tumor response in patients with advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results of the PEMBRO-RT phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.; Menon, H.; Chen, D.; Verma, V.; Tang, C.; Altan, M.; Hess, K.; de Groot, P.; Nguyen, Q.-N.; Varghese, R.; et al. Pembrolizumab with or without radiation therapy for metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A randomized phase I/II trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciuti, B.; Arbour, K.C.; Lin, J.J.; Vajdi, A.; Vokes, N.; Hong, L.; Zhang, J.; Tolstorukov, M.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Spurr, L.F.; et al. Diminished Efficacy of Programmed Death-(Ligand)1 Inhibition in STK11- and KEAP1-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma Is Affected by KRAS Mutation Status. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, H.J.; McCleland, M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Reck, M.; Mok, T.S.; Jotte, R.M.; Nishio, M.; Kim, E.; Morris, S.; Zou, W.; et al. Clinical efficacy of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy in KRAS-mutated non-small cell lung cancer with STK11, KEAP1, or TP53 comutations: Subgroup results from the phase III IMpower150 trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papillon-Cavanagh, S.; Doshi, P.; Dobrin, R.; Szustakowski, J.; Walsh, A.M. STK11 and KEAP1 mutations as prognostic biomarkers in an observational real-world lung adenocarcinoma cohort. ESMO Open. 2020, 5, e000706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirkes, T.; Hollar, M.A.; Tann, M.; Kohli, M.D.; Akisik, F.; Sandrasegaran, K. Response Criteria in Oncologic Imaging: Review of Traditional and New Criteria. RadioGraphics 2013, 33, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.-L.; Wu, Y.-L.; Chang, W.-Y.; Ho, C.-L.; Tseng, Y.-L.; Lai, W.-W.; Su, W.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Yang, S.-C. Preventing and treating brain metastases with three first-line EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ther. Adv. Med Oncol. 2018, 10, 1758835918797589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Total Population (%) | Pembrolizumab Monotherapy | Combination Therapy | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 47 | n = 28 | n = 19 | ||
| Age | 71 (63–77) | 73 (66–80) | 69 (62–77) | 0.246 |
| <65 y/o | 13 (27.6%) | 6 | 7 | |
| ≥65 y/o | 34 (72.4%) | 22 | 12 | |
| Gender | 0.919 | |||
| Female | 12 (25.5%) | 7 | 5 | |
| Male | 35 (74.5%) | 21 | 14 | |
| Smoking | 0.188 | |||
| Smoker | 13 (27.6%) | 9 | 4 | |
| Non-smoker | 21 (44.8%) | 14 | 7 | |
| Ex-smoker | 13 (27.6%) | 5 | 8 | |
| ECOG PS | 0.705 | |||
| 0–1 | 41 (87.2%) | 24 | 17 | |
| >2 | 6 (12.8%) | 4 | 2 | |
| Histology | 0.698 | |||
| Non-squamous NSCLC | 36 (76.6%) | 22 | 14 | |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 11 (23.4%) | 6 | 5 | |
| Brain metastasis | 0.143 | |||
| Yes | 12 (25.5%) | 5 | 7 | |
| No | 35 (74.5%) | 23 | 12 | |
| Treatment modality | ||||
| Pembrolizumab | 28 (59.5%) | 28 | 0 | |
| Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy | 11 (23.4%) | 0 | 11 | |
| Pembrolizumab plus radiotherapy | 8 (17.0%) | 0 | 8 |
| Hazard Ratio 95% CI | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| ≥65 vs. <65 y/o | 0.63 (0.20–2.01) | 0.437 |
| Gender | ||
| Male vs. female | 1.78 (0.52–6.14) | 0.36 |
| Smoking | ||
| Smoker vs. non-smoker | 0.07 (0.01–0.48) | 0.007 |
| Ex-smoker vs. non-smoker | 1.38 (0.40–4.73) | 0.608 |
| ECOG PS | ||
| ≤1 vs. >2 | 1.83 (0.44–7.51) | 0.402 |
| Histology | ||
| Non-squamous vs. squamous NSCLC | 0.47 (0.13–1.74) | 0.26 |
| Brain metastasis | ||
| Presence vs. Absence | 0.98 (0.23–3.21) | 0.97 |
| Treatment | ||
| Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy vs. pembrolizumab monotherapy | 0.17 (0.05–0.62) | 0.006 |
| Pembrolizumab plus radiotherapy vs. pembrolizumab monotherapy | 0.26 (0.05–1.30) | 0.101 |
| Hazard Ratio 95% CI | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| ≥65 vs. <65 y/o | 1.79 (0.61–5.26) | 0.293 |
| Gender | ||
| Male vs. female | 1.51 (0.43–5.35) | 0.523 |
| Smoking | ||
| Smoker vs. non-smoker | 0.73 (0.21–2.46) | 0.605 |
| Ex-smoker vs. non-smoker | 1.081 (0.31–3.81) | 0.904 |
| ECOG PS | ||
| ≤1 vs. >2 | 2.02 (0.51–8.07) | 0.318 |
| Histology | ||
| Non-squamous vs. squamous NSCLC | 1.20 (0.45–3.18) | 0.711 |
| Brain metastasis | ||
| Presence vs. absence | 0.93 (0.33–2.60) | 0.892 |
| Treatment | ||
| Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy vs. pembrolizumab monotherapy | 0.66 (0.22–1.97) | 0.457 |
| Pembrolizumab plus radiotherapy vs. pembrolizumab monotherapy | 0.81 (0.24–2.78) | 0.742 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, J.-S.; Wei, S.-H.; Chen, C.-W.; Yang, S.-C.; Tseng, Y.-L.; Su, P.-L.; Lin, C.-C.; Su, W.-C. Pembrolizumab and Chemotherapy Combination Prolonged Progression-Free Survival in Patients with NSCLC with High PD-L1 Expression and Low Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111407
Tsai J-S, Wei S-H, Chen C-W, Yang S-C, Tseng Y-L, Su P-L, Lin C-C, Su W-C. Pembrolizumab and Chemotherapy Combination Prolonged Progression-Free Survival in Patients with NSCLC with High PD-L1 Expression and Low Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(11):1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111407
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Jeng-Shiuan, Sheng-Huan Wei, Chian-Wei Chen, Szu-Chun Yang, Yau-Lin Tseng, Po-Lan Su, Chien-Chung Lin, and Wu-Chou Su. 2022. "Pembrolizumab and Chemotherapy Combination Prolonged Progression-Free Survival in Patients with NSCLC with High PD-L1 Expression and Low Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 11: 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111407
APA StyleTsai, J.-S., Wei, S.-H., Chen, C.-W., Yang, S.-C., Tseng, Y.-L., Su, P.-L., Lin, C.-C., & Su, W.-C. (2022). Pembrolizumab and Chemotherapy Combination Prolonged Progression-Free Survival in Patients with NSCLC with High PD-L1 Expression and Low Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio. Pharmaceuticals, 15(11), 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111407







