Indole-3-Carbinol Stabilizes p53 to Induce miR-34a, Which Targets LDHA to Block Aerobic Glycolysis in Liver Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
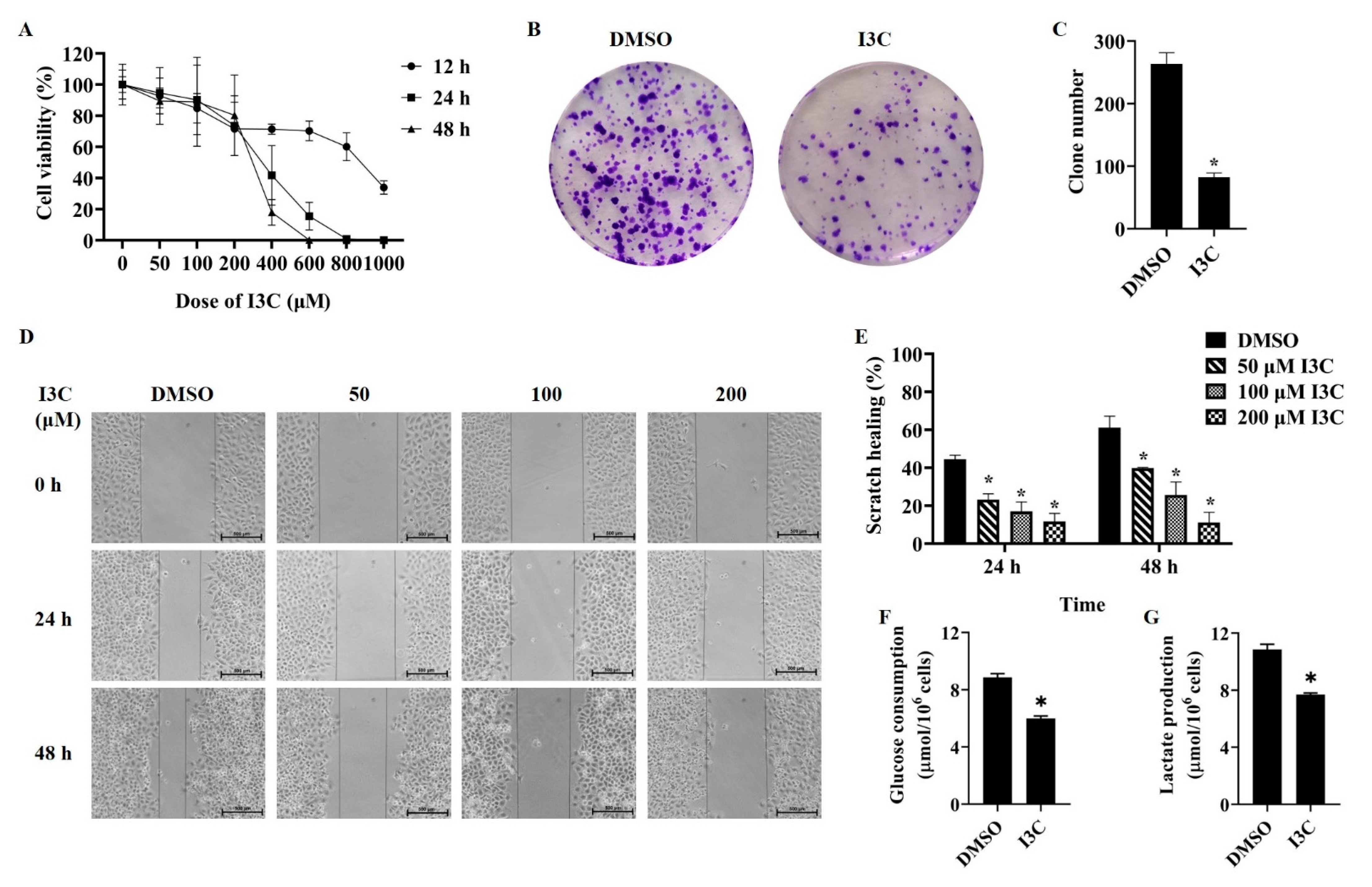
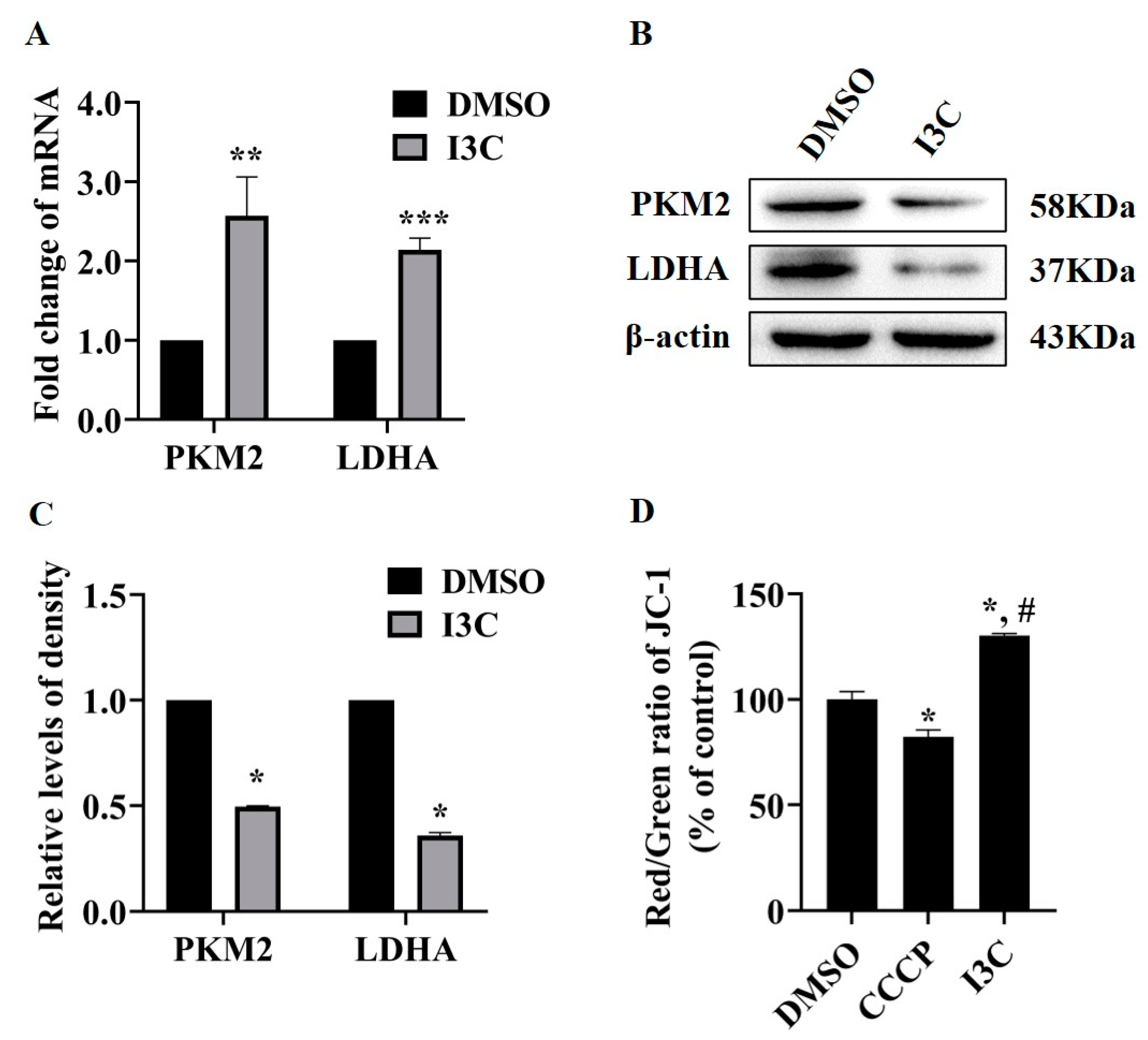
2.1. I3C Suppresses Liver Cancer Cells Proliferation and Migration and Inhibits Aerobic Glycolysis
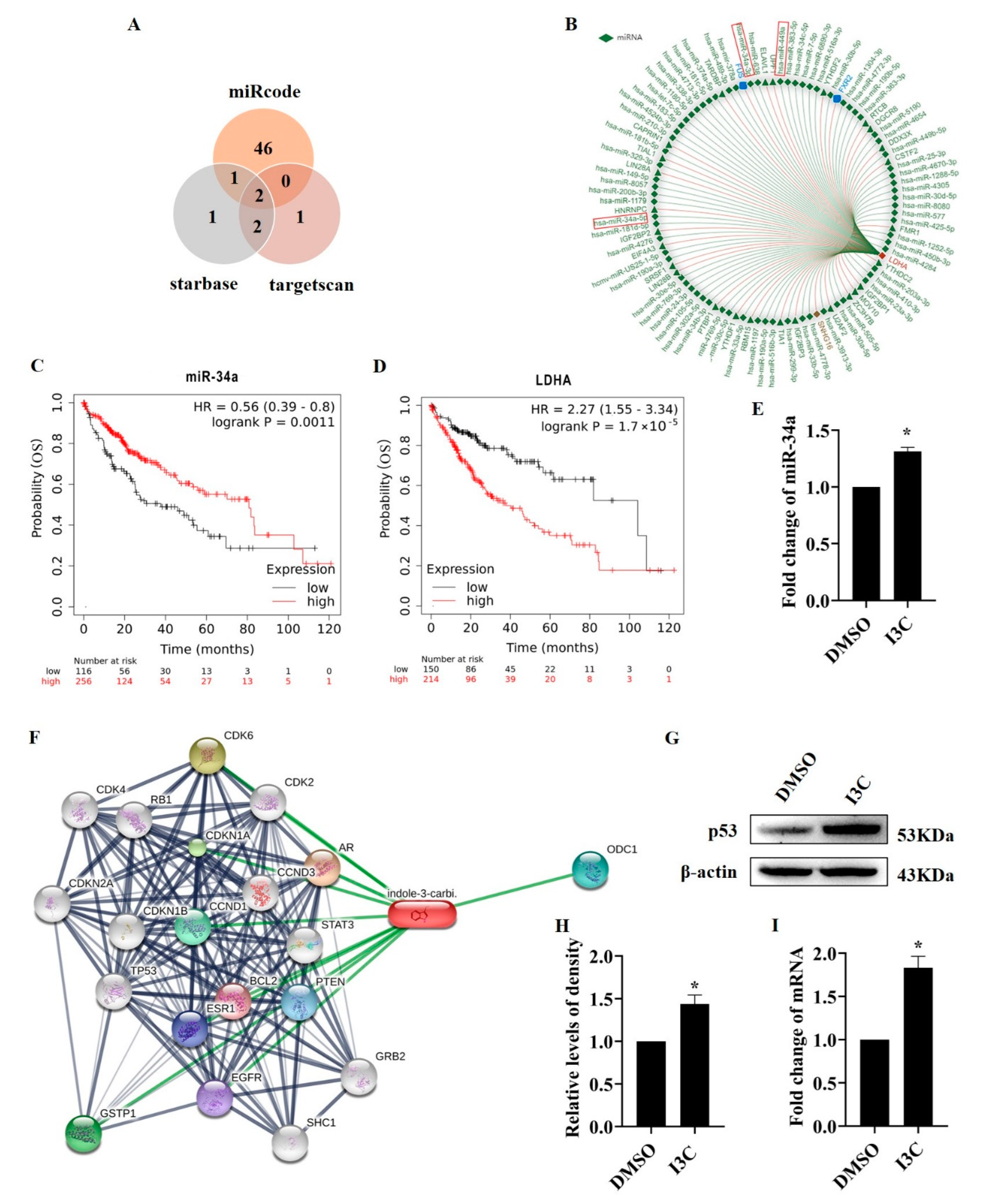
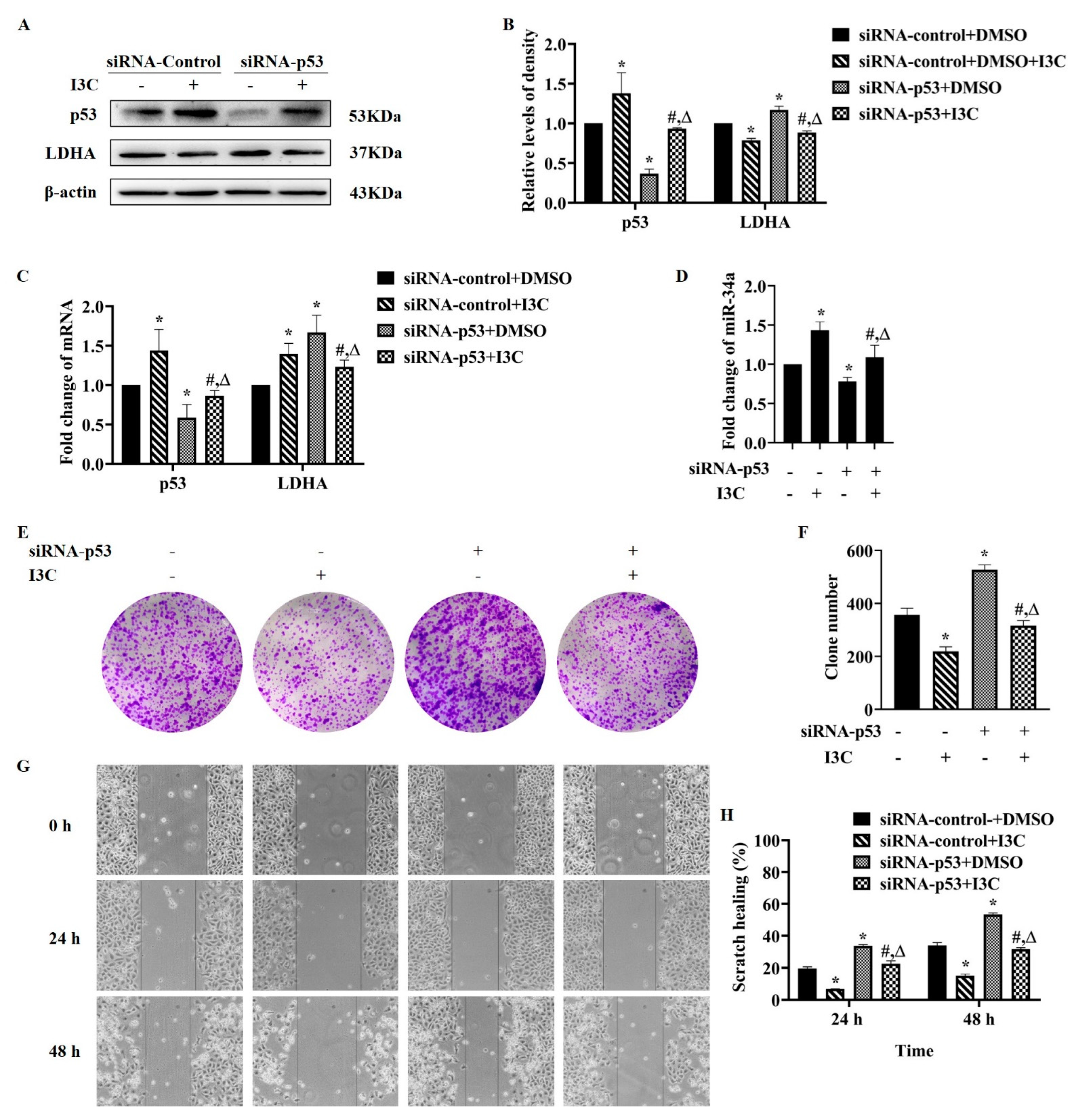
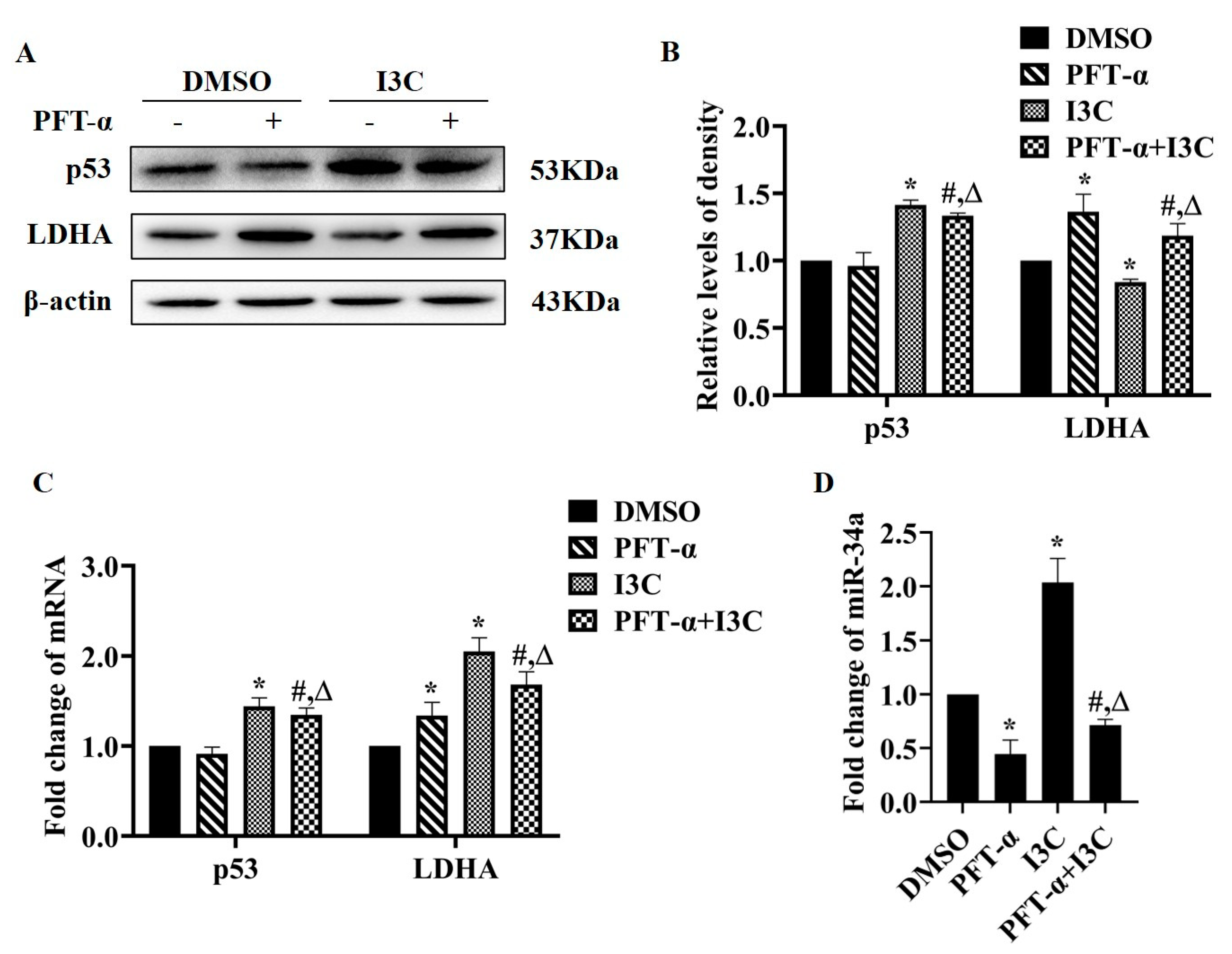
2.2. I3C Regulates LDHA Expression through miR-34a in a p53-Dependent Manner
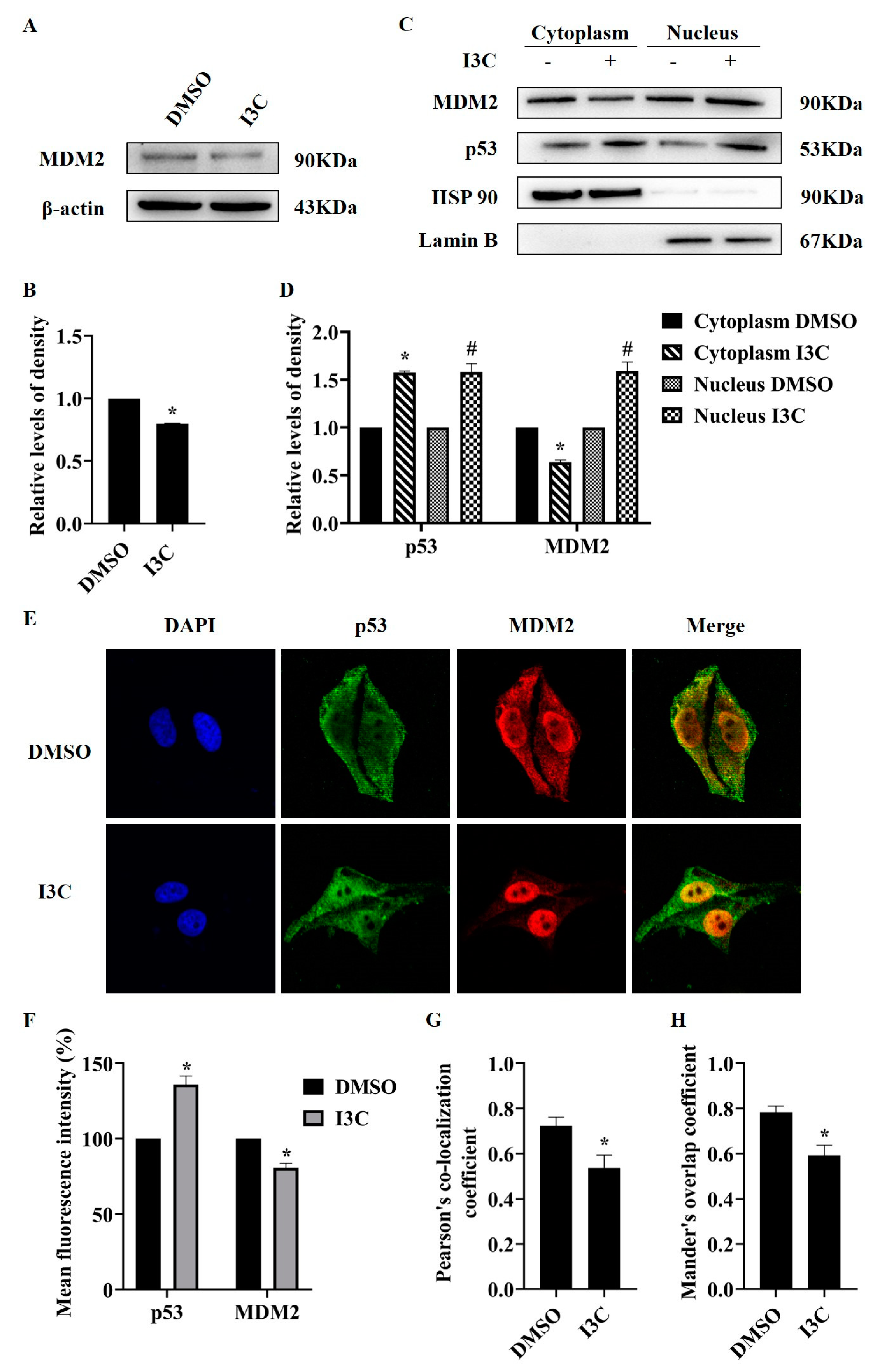
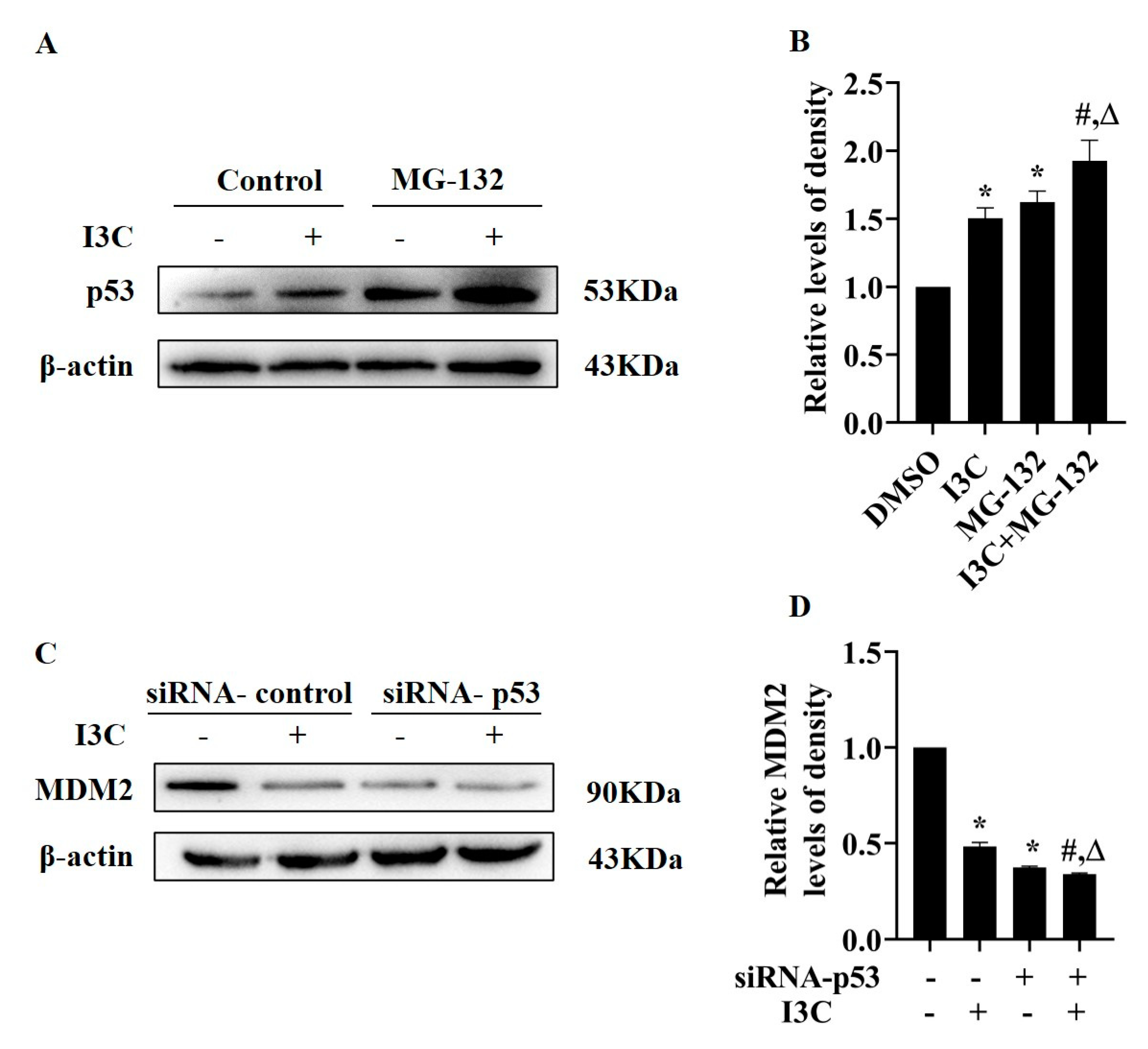
2.3. I3C Treatment Downregulates MDM2 and Stabilizes p53
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Line, Reagents, and Treatment
4.2. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8) Assay
4.3. Colony Formation Assay
4.4. Wound Scratch Assay
4.5. Glucose Consumption and Lactate Release Assay
4.6. Isolation of Total RNA and Real-Time PCR
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Fractionation
4.9. Determination of the Levels of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
4.10. Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) Transfection
4.11. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.12. Identification of Candidate miRNAs
4.13. Survival Analysis
4.14. Construction of Protein–Chemical Interaction Networks by Bioinformatic Analysis
4.15. Statistical Analysis
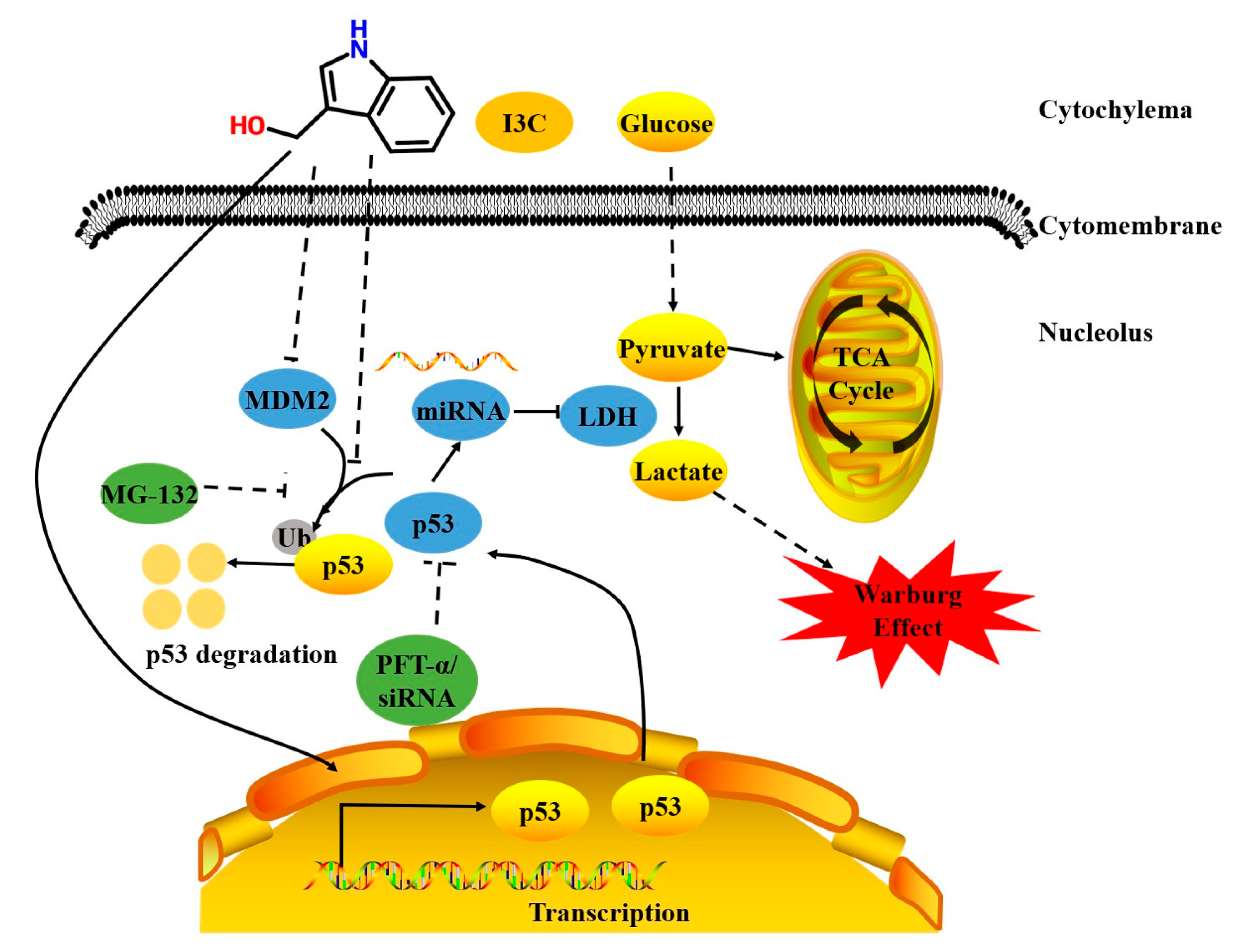
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956, 123, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz-López, K.G.; Castro-Muñoz, L.J.; Reyes-Hernández, D.O.; García-Carrancá, A.; Manzo-Merino, J. Lactate in the Regulation of Tumor Microenvironment and Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, C.; Jansen, G.; Giovannetti, E. Drug resistance in pancreatic cancer: Impact of altered energy metabolism. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 114, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ždralević, M.; Brand, A.; Di Ianni, L.; Dettmer, K.; Reinders, J.; Singer, K.; Peter, K.; Schnell, A.; Bruss, C.; Decking, S.M.; et al. Double genetic disruption of lactate dehydrogenases A and B is required to ablate the "Warburg effect" restricting tumor growth to oxidative metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 15947–15961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodford, M.R.; Chen, V.Z.; Backe, S.J.; Bratslavsky, G.; Mollapour, M. Structural and functional regulation of lactate dehydrogenase-A in cancer. Future Med. Chem. 2020, 12, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yu, X.; Hu, S.; Yu, J. A brief review on the mechanisms of miRNA regulation. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2009, 7, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cai, T.; Zeng, X.; Cai, D.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.; Gan, H.; Zhuo, J.; Zhao, Z.; Pan, H.; et al. Astragaloside IV reverses MNNG-induced precancerous lesions of gastric carcinoma in rats: Regulation on glycolysis through miRNA-34a/LDHA pathway. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Huang, X.; Ye, F.; Chen, B.; Song, C.; Wen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, G.; Tang, H.; Xie, X. The miR-34a-LDHA axis regulates glucose metabolism and tumor growth in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández Borrero, L.J.; El-Deiry, W.S. Tumor suppressor p53: Biology, signaling pathways, and therapeutic targeting. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermeking, H. MicroRNAs in the p53 network: Micromanagement of tumour suppression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K.D.; Galbraith, M.D.; Andrysik, Z.; Espinosa, J.M. Mechanisms of transcriptional regulation by p53. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, U.M.; Petrenko, O. The MDM2-p53 interaction. Mol. Cancer Res. 2003, 1, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzenberg-Bar-Yoseph, F.; Armoni, M.; Karnieli, E. The tumor suppressor p53 down-regulates glucose transporters GLUT1 and GLUT4 gene expression. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2627–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, H.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Guo, X.; Chang, L.J.; Zhang, Y.; You, M.J.; et al. Hexokinase 2-mediated Warburg effect is required for PTEN- and p53-deficiency-driven prostate cancer growth. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1461–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yue, X.; Wu, H.; Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Tomsky, K.; Xie, H.; Khella, C.A.; et al. Parkin targets HIF-1α for ubiquitination and degradation to inhibit breast tumor progression. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E. Indoles Derived From Glucobrassicin: Cancer Chemoprevention by Indole-3-Carbinol and 3,3′-Diindolylmethane. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 734334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Gao, X.; Chen, G.; Sun, J.; Chu, J.; Jing, K.; Li, P.; Zeng, R.; Wei, B. Indole-3-carbinol as inhibitors of glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in osteoblastic cells through blocking ROS-mediated Nrf2 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Park, S.H.; Nam, M.J. Anticarcinogenic effect of indole-3-carbinol (I3C) on human hepatocellular carcinoma SNU449 cells. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusoodhanan, R.; Natarajan, M.; Veeraraghavan, J.; Herman, T.S.; Aravindan, N. NFkappaB activity and transcriptional responses in human breast adenocarcinoma cells after single and fractionated irradiation. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jin, L.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Hong, C.; Jiang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Q.; et al. Epigallocatechin gallate promotes p53 accumulation and activity via the inhibition of MDM2-mediated p53 ubiquitination in human lung cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 1983–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.; Quinn, B.A.; Das, S.K.; Dash, R.; Emdad, L.; Dasgupta, S.; Wang, X.Y.; Dent, P.; Reed, J.C.; Pellecchia, M.; et al. Targeting the Bcl-2 family for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pani, S.; Sahoo, A.; Patra, A.; Debata, P.R. Phytocompounds curcumin, quercetin, indole-3-carbinol, and resveratrol modulate lactate-pyruvate level along with cytotoxic activity in HeLa cervical cancer cells. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2021, 68, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brew, C.T.; Aronchik, I.; Hsu, J.C.; Sheen, J.H.; Dickson, R.B.; Bjeldanes, L.F.; Firestone, G.L. Indole-3-carbinol activates the ATM signaling pathway independent of DNA damage to stabilize p53 and induce G1 arrest of human mammary epithelial cells. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.R.; Chen, M.; Lee, J.D.; Zhang, J.; Lin, S.Y.; Fu, T.M.; Chen, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Chiang, S.Y.; Katon, J.; et al. Reactivation of PTEN tumor suppressor for cancer treatment through inhibition of a MYC-WWP1 inhibitory pathway. Science 2019, 364, eaau0159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Li, H.; Cao, M.; He, S.; Lei, L.; Peng, J.; Chen, W. Cancer burden in China: Trends, risk factors and prevention. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 879–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Zhang, H.L.; Li, D.D.; Yang, K.L.; Tang, J.; Li, X.; Ji, J.; Yu, Y.; Wu, R.Y.; Ravichandran, S.; et al. Regulation of glycolytic metabolism by autophagy in liver cancer involves selective autophagic degradation of HK2 (hexokinase 2). Autophagy 2018, 14, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, D.; Baxter, B.; Campbell, B.C.V.; Carpenter, J.S.; Cognard, C.; Dippel, D.; Eesa, M.; Fischer, U.; Hausegger, K.; Hirsch, J.A.; et al. Multisociety Consensus Quality Improvement Revised Consensus Statement for Endovascular Therapy of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Stroke 2018, 13, 612–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, P.S.; Thompson, C.B. Metabolic reprogramming: A cancer hallmark even warburg did not anticipate. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.; Greinert, T.; Reichard, M.; Held, C.; Harms, H.; Maskow, T. Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Glycolytic Reactions. Part I: Kinetic Modeling Based on Irreversible Thermodynamics and Validation by Calorimetry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valcarcel-Jimenez, L.; Gaude, E.; Torrano, V.; Frezza, C.; Carracedo, A. Mitochondrial Metabolism: Yin and Yang for Tumor Progression. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Stancliffe, E.; Fowle-Grider, R.; Wang, R.; Wang, C.; Schwaiger-Haber, M.; Shriver, L.P.; Patti, G.J. Saturation of the mitochondrial NADH shuttles drives aerobic glycolysis in proliferating cells. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 3270.e9–3283.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Z. MicroRNA Control of p53. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, S.L.; Levine, A.J. The p53 pathway: Positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene 2005, 24, 2899–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Park, S.U. Current results on the biological and pharmacological activities of Indole-3-carbinol. EXCLI J. 2018, 17, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, P.; Sheng, S.; Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Huang, G. Lactate dehydrogenase A in cancer: A promising target for diagnosis and therapy. IUBMB Life 2013, 65, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Karp, J.E.; Emadi, A. Elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) can be a marker of immune suppression in cancer: Interplay between hematologic and solid neoplastic clones and their microenvironments. Cancer Biomark. 2017, 19, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Blattner, C. Regulation of p53 by E3s. Cancers 2021, 13, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tin, A.S.; Park, A.H.; Sundar, S.N.; Firestone, G.L. Essential role of the cancer stem/progenitor cell marker nucleostemin for indole-3-carbinol anti-proliferative responsiveness in human breast cancer cells. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Zhao, M.; Qiu, H.; Shi, D.; Wang, J.; Tian, Y.; Lin, L.; Deng, W. Effusanin E suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell growth by inhibiting NF-κB and COX-2 signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeggari, A.; Marks, D.S.; Larsson, E. miRcode: A map of putative microRNA target sites in the long non-coding transcriptome. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2062–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H.; Yang, J.H. starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, T.; Dou, Y.; Tan, P.; Ni, Z.; Liu, T.; Wang, D.; Huang, Y.; Cai, K.; Zhao, X.; Xu, D.; et al. RNALocate v2.0: An updated resource for RNA subcellular localization with increased coverage and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lánczky, A.; Győrffy, B. Web-Based Survival Analysis Tool Tailored for Medical Research (KMplot): Development and Implementation. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e27633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Santos, A.; von Mering, C.; Jensen, L.J.; Bork, P.; Kuhn, M. STITCH 5: Augmenting protein-chemical interaction networks with tissue and affinity data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene Name | Sequences |
|---|---|
| IDH1 | Forward: 5′-TCAGTGGCGGTTCTGTGGTA-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-CTTGGTGACTTGGTCGTTGGT-3′ | |
| LDHA | Forward: 5′-ATGGCAACTCTAAAGGATCAGC-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-CCAACCCCAACAACTGTAATCT-3′ | |
| PKM2 | Forward: 5′-CTGTGGACTTGCCTGCTGTG-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-TGCCTTGCGGATGAATGACG-3′ | |
| p53 | Forward: 5′- ACAACGTTCTGTCCCCCTTG-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′- TCATCTGGACCTGGGTCTTC -3′ | |
| β-actin | Forward: 5′-CATGTACGTTGCTATCCAGGC-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-CTCCTTAATGTCACGCACGAT-3′ | |
| miR-34a | Forward: 5′-TGGCAGTGTCTTAGCTGGTTGT-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGA GGTATTCGCACTGGATACGAC-3′ | |
| miR-449a | Forward: 5′-TGGCAGTGTATTGTTAGCTGGT-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG TATTCGCACTGG ATACGAC-3′ | |
| U6 | Forward: 5′-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W. Indole-3-Carbinol Stabilizes p53 to Induce miR-34a, Which Targets LDHA to Block Aerobic Glycolysis in Liver Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101257
Qi Y, Zhang C, Wu D, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Li W. Indole-3-Carbinol Stabilizes p53 to Induce miR-34a, Which Targets LDHA to Block Aerobic Glycolysis in Liver Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(10):1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101257
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Yuehua, Chunjing Zhang, Di Wu, Yue Zhang, Yunfeng Zhao, and Wenjuan Li. 2022. "Indole-3-Carbinol Stabilizes p53 to Induce miR-34a, Which Targets LDHA to Block Aerobic Glycolysis in Liver Cancer Cells" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 10: 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101257
APA StyleQi, Y., Zhang, C., Wu, D., Zhang, Y., Zhao, Y., & Li, W. (2022). Indole-3-Carbinol Stabilizes p53 to Induce miR-34a, Which Targets LDHA to Block Aerobic Glycolysis in Liver Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 15(10), 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101257






