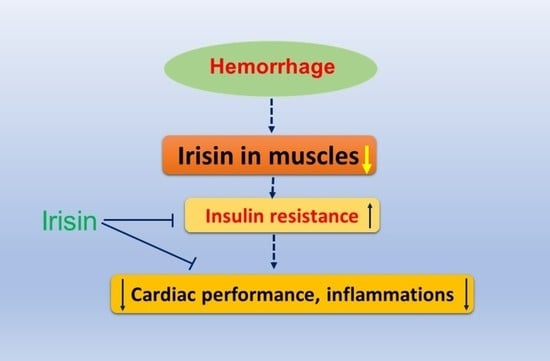
Irisin Preserves Cardiac Performance and Insulin Sensitivity in Response to Hemorrhage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
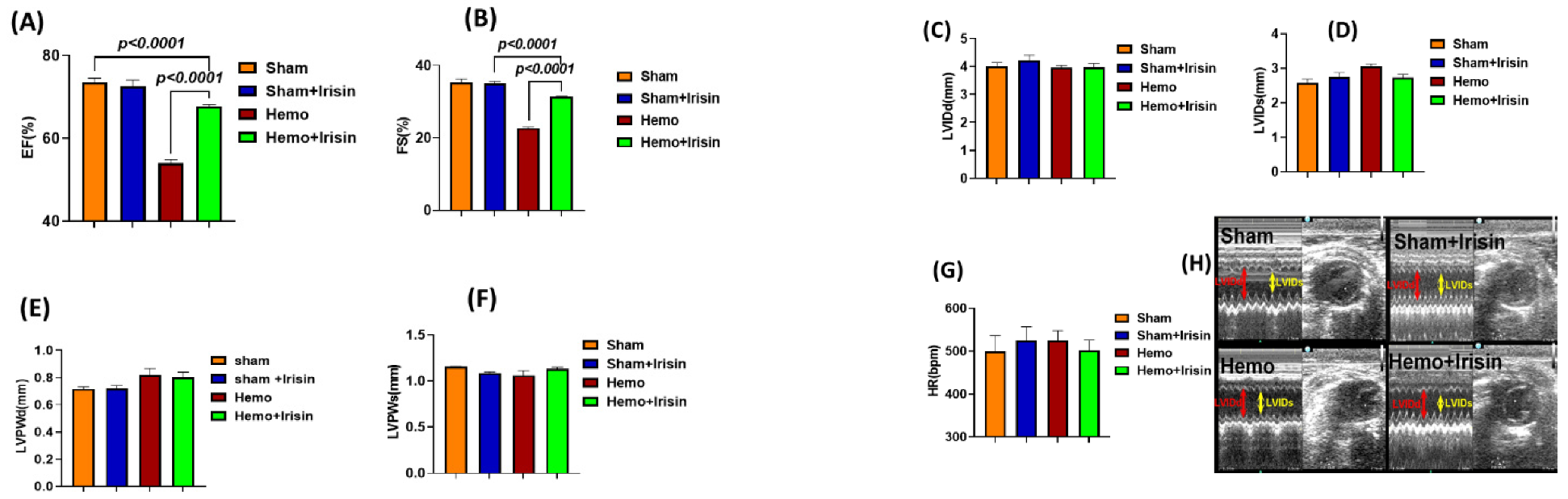
2.1. Effects of Irisin on Hemodynamics and Cardiac Performance in Mice Exposed to Hemorrhage
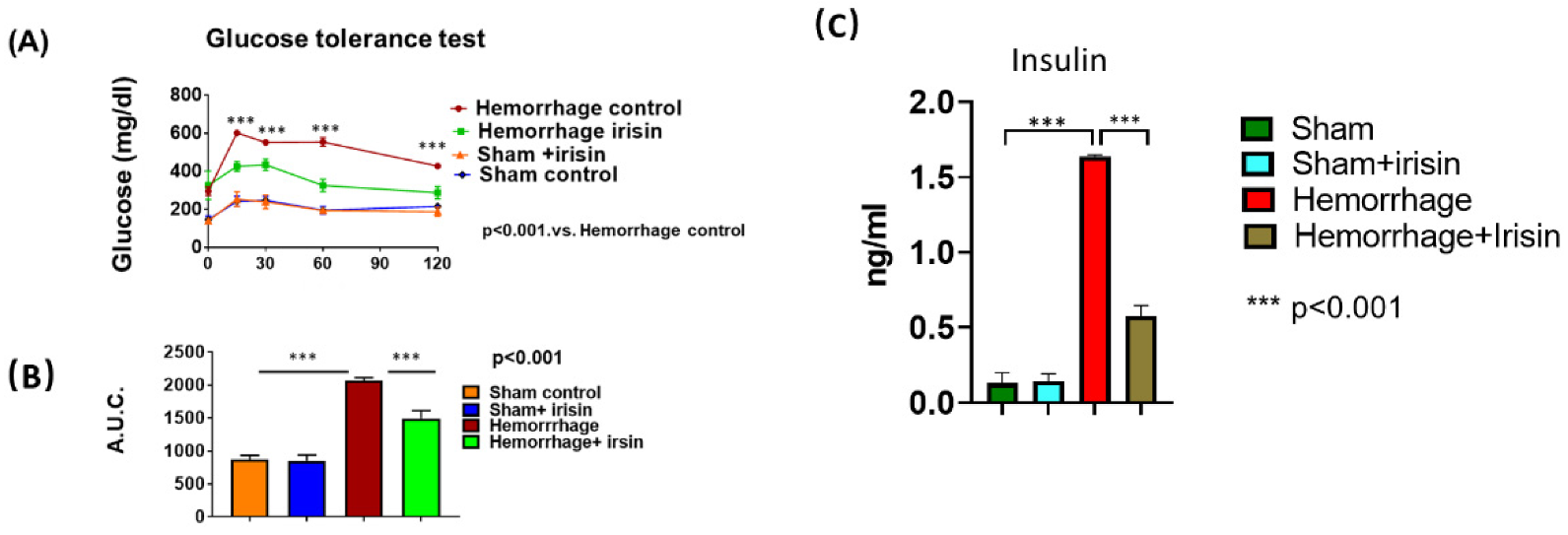
2.2. Irisin Attenuates Insulin Resistance in Hemorrhage
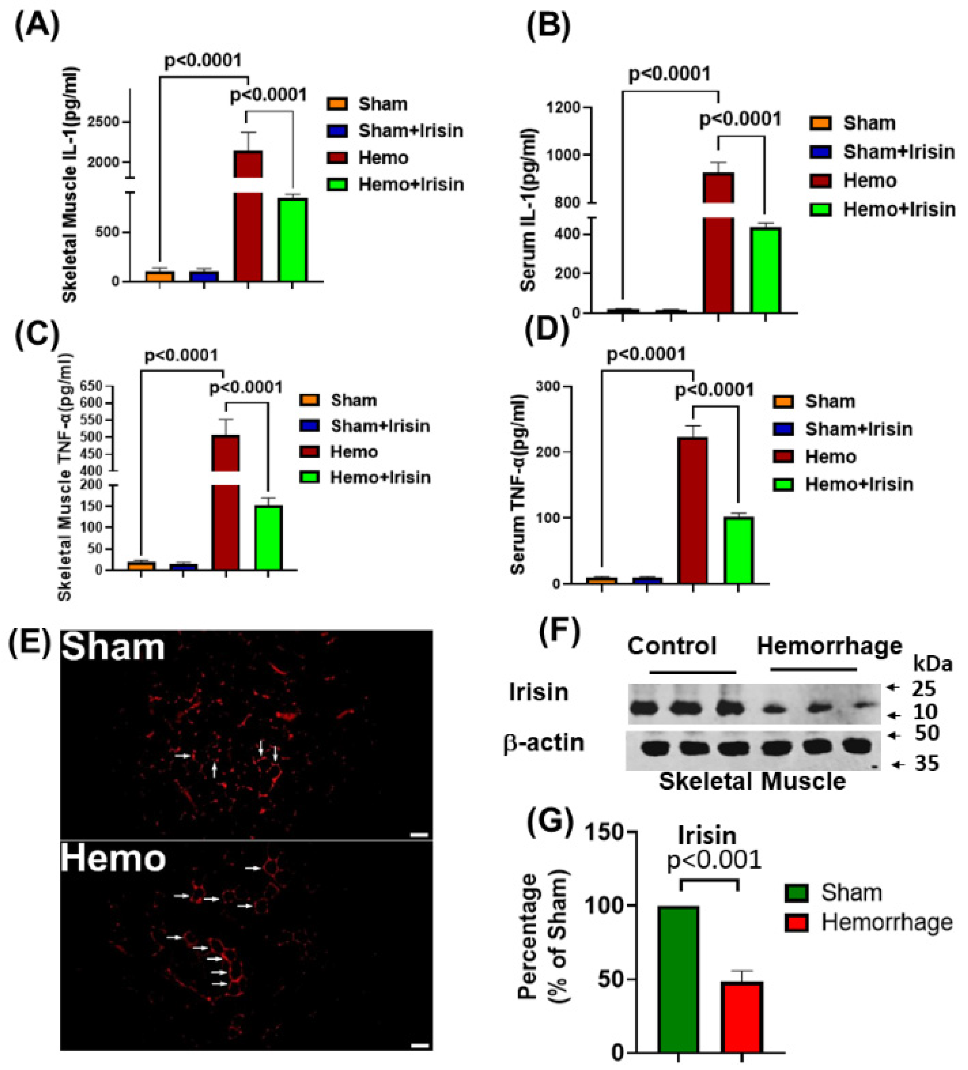
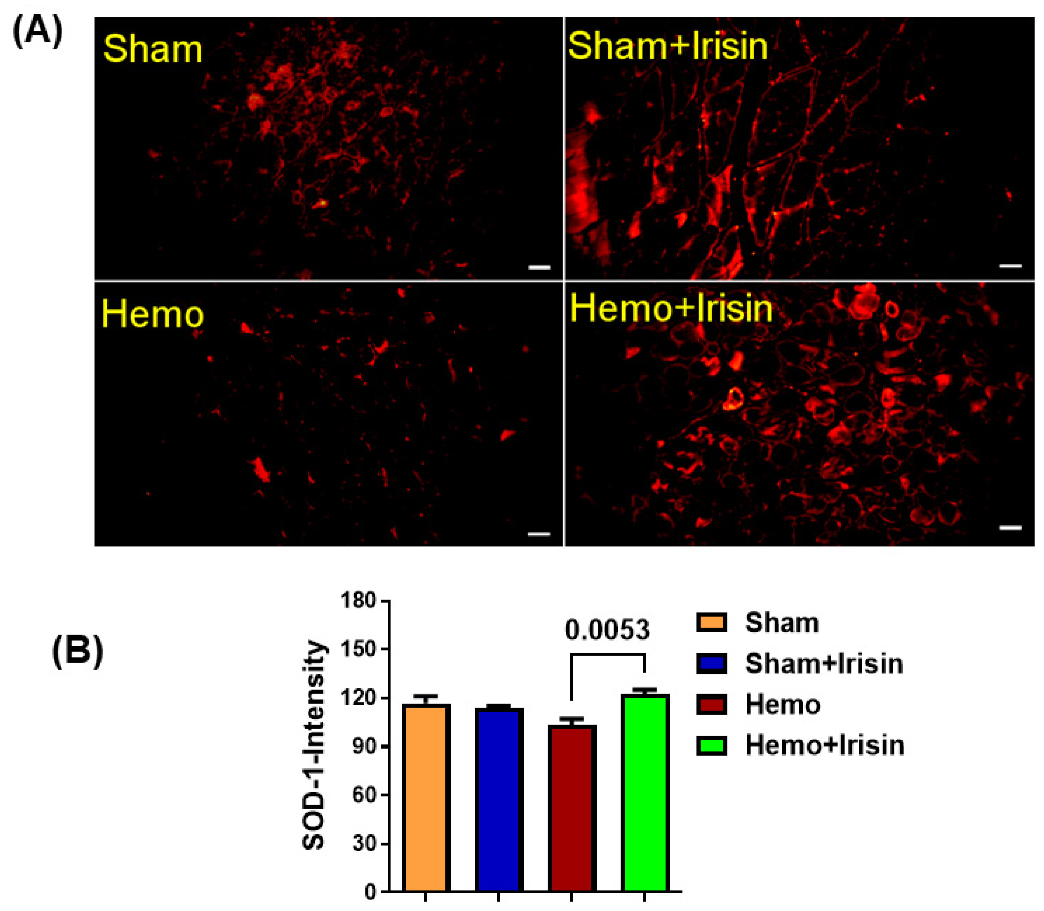
2.3. Irisin Attenuated Levels of Inflammatory Cytokines, IL-1 and TNF-α in Hemorrhage
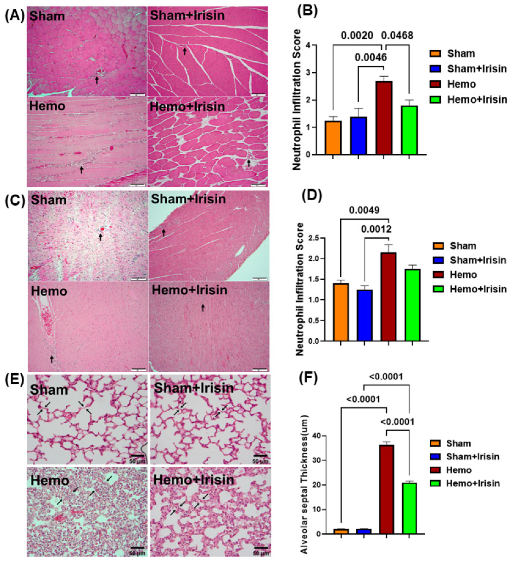
2.4. Irisin Alleviated Histological Damage in Skeletal Muscle, and Cardiac Muscle and Lung in Hemorrhagic Shock
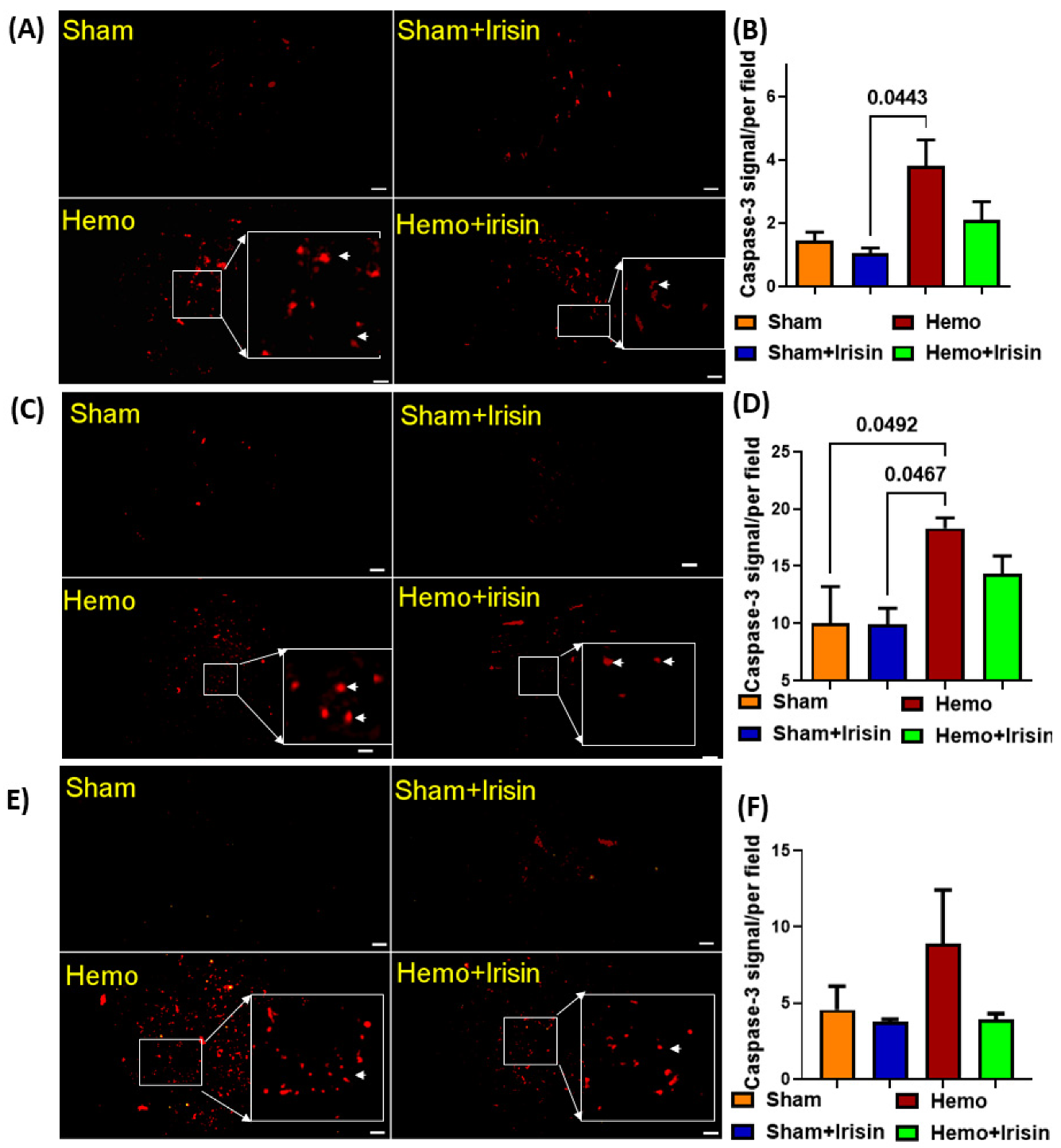
2.5. Irisin Reduced Apoptosis in Hemorrhage
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Experimental Group Design
4.3. Echocardiographic Measurements
4.4. Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT)
4.5. Measurement of Cytokines Using Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay (ELISA)
4.6. Measurement of Blood Insulin Content Using Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay (ELISA)
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Histological and Immunochemical Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cannon, J.W. Hemorrhagic Shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckbert, S.R.; Vedder, N.B.; Hoffman, W.; Winn, R.K.; Hudson, L.D.; Jurkovich, J.L.; Copass, M.K.; Harlan, J.M.; Rice, C.L.; Maier, R.V. Outcome after hemorrhagic shock in trauma patients. J. Trauma 1998, 45, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostrom, P.; Wu, J.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Korde, A.; Ye, L.; Lo, J.C.; Rasbach, K.A.; Boström, E.A.; Choi, J.H.; Long, J.Z.; et al. A PGC1-alpha-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature 2012, 481, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maak, S.; Norheim, F.; Drevon, C.A.; Erickson, H.P. Progress and Challenges in the Biology of FNDC5 and Irisin. Endocr. Rev. 2021, 42, 436–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Shen, Y.; Ni, C.; Ye, J.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ren, Y.Z. Irisin reverses insulin resistance in C2C12 cells via the p38-MAPK-PGC-1α pathway. Peptides 2019, 119, 170120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Chen, N.; Kang, X.; Hu, Y.; Shi, S. Irisin alleviates FFA induced β-cell insulin resistance and inflammatory response through activating PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway. Endocrine 2022, 75, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.J.; Sun, S.J.; Fu, J.T.; Ouyang, S.-X.; Zhao, Q.-J.; Su, L.; Ji, Q.-X.; Sun, D.-Y.; Zhu, J.-H.; Zhang, G.-Y.; et al. NAD(+)-boosting therapy alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via stimulating a novel exerkine Fndc5/irisin. Theranostics 2021, 11, 4381–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Sahar, N.E.; Javaid, H.M.A.; Pak, E.S.; Liang, G.; Wang, Y.; Ha, H.; Huh, J.Y. Exercise-Induced Irisin Decreases Inflammation and Improves NAFLD by Competitive Binding with MD2. Cells 2021, 10, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.T.; Zhang, L.; Dubielecka, P.M.; Zhuang, S.; Qin, G.; Chin, Y.E.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, T.C. Irisin Improves Myocardial Performance and Attenuates Insulin Resistance in Spontaneous Mutation (Lepr (db)) Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Kim, H.T.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhai, L.; Kokorina, N.; Wang, P.; Messina, J.L. Trauma and hemorrhage-induced acute hepatic insulin resistance: Dominant role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 2369–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.T.; Zhang, S.; Dubielecka, P.M.; Du, J.; Yano, N.; Chin, Y.E.; Zhuang, S.; Qin, G.; Zhao, T.C. Irisin plays a pivotal role to protect the heart against ischemia and reperfusion injury. J. Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 3775–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.T.; Wang, J.; Yano, N.; Zhang, L.X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Qin, G.; Dubielecka, P.M.; Zhuang, S.; Liu, P.L.; et al. Irisin promotes cardiac progenitor cell-induced myocardial repair and functional improvement in infarcted heart. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, G.; Reines, H.D.; Wulf-Gutierrez, M.E. Clinical review: Hemorrhagic shock. Crit Care 2004, 8, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raje, V.; Ahern, K.W.; Martinez, B.A.; Howell, N.L.; Oenarto, V.; Granade, M.E.; Kim, J.W.; Tundup, S.; Bottermann, K.; Gödecke, A.; et al. Adipocyte lipolysis drives acute stress-induced insulin resistance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Gavrikova, T.A.; Messina, J.L. Regulation of hepatic insulin receptor activity following injury. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 306, G886–G892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, L. Irisin attenuates oxidized low-density lipoprotein impaired angiogenesis through AKT/mTOR/S6K1/Nrf2 pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 18951–18962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhat, D.; El-Bana, M.A.; El-Daly, S.M.; Ashour, M.N.; Elias, T.R.; Mohamed, R.A.; Yassen, N.N.; Abdel-Monem, M.A.; Hussein, J. Influence of irisin on diet-induced metabolic syndrome in experimental rat model. J. Complement Integr. Med. 2021, 18, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertsmeier, M.; Pratschke, S.; Chaudry, I.; Angele, M.K. Gender-Specific Effects on Immune Response and Cardiac Function after Trauma Hemorrhage and Sepsis. Viszeralmedizin 2014, 30, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Schwartz, R.; Diamond, M.P.; Raju, R.P. A Combination Treatment Strategy for Hemorrhagic Shock in a Rat Model Modulates Autophagy. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, R. Immune and metabolic alterations following trauma and sepsis—An overview. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 2523–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, J.G.; Nemoto, S.; Ishiyama, M.; Yu, B.; Knuefermann, P.; Diwan, A.; Baker, J.S.; Defreitas, G.; Tweardy, D.J.; Mann, D.L. Functional significance of inflammatory mediators in a murine model of resuscitated hemorrhagic shock. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 288, H1272–H1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Boyle, J.J.; Weissberg, P.L.; Bennett, M.R. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha promotes macrophage-induced vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis by direct and autocrine mechanisms. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 1553–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parameswaran, N.; Patial, S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha signaling in macrophages. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2010, 20, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, N.; Kurata, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Morikawa, S.; Masumoto, J. The role of interleukin-1 in general pathology. Inflamm. Regen. 2019, 39, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur-Bialy, A.I. Superiority of the Non-Glycosylated Form Over the Glycosylated Form of Irisin in the Attenuation of Adipocytic Meta-Inflammation: A Potential Factor in the Fight Against Insulin Resistance. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Jamal, M.; Guo, P.; Jin, Z.; Zheng, F.; Song, X.; Zhan, J.; Wu, H. Irisin alleviates pulmonary epithelial barrier dysfunction in sepsis-induced acute lung injury via activation of AMPK/SIRT1 pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, J.; Naganathar, S.; Praditsuktavorn, B.; Bugg, O.F.; McArthur, S.; Thiemermann, C.; Tremoleda, J.L.; Brohi, K. Modeling Cardiac Dysfunction Following Traumatic Hemorrhage Injury: Impact on Myocardial Integrity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De’Ath, H.D.; Rourke, C.; Davenport, R.; Manson, J.; Renfrew, I.; Uppal, R.; Davies, L.C.; Brohi, K. Clinical and biomarker profile of trauma-induced secondary cardiac injury. Br. J. Surg. 2012, 99, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhao, Y.T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.X.; Qin, G.; Zhuang, S.; Kadin, M.; Chin, Y.E.; Liu, P.Y.; Zhao, T.C. The Essential Role of PRAK in Preserving Cardiac Function and Insulin Resistance in High-Fat Diet-Induced Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, E.W.; Tharakan, B.; Hunter, F.A.; Tinsley, J.H.; Cao, X. Apoptotic signaling induces hyperpermeability following hemorrhagic shock. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 292, H3179–H3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Levy, R.M.; Fan, J.J.; Hackam, D.J.; Vodovotz, Y.; Yang, H.; Tracey, K.J.; Billiar, T.R.; Wilson, M.A. Hemorrhagic shock induces NAD(P)H oxidase activation in neutrophils: Role of HMGB1-TLR4 signaling. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 6573–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs, E.W.; Udobi, K.F.; Wood, J.G.; Hunter, F.A.; Smalley, D.M.; Cheung, L.Y. In vivo visualization of reactive oxidants and leukocyte-endothelial adherence following hemorrhagic shock. Shock 2002, 18, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; Zhou, T.; Pannell, B.K.; Ziegler, A.C.; Best, T.M. Biological and physiological role of reactive oxygen species—The good, the bad and the ugly. Acta Physiol. 2015, 214, 329–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogeris, T.; Baines, C.P.; Krenz, M.; Korthuis, R.J. Ischemia/Reperfusion. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 7, 113–170. [Google Scholar]
- Granger, D.N.; Kvietys, P.R. Reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species: The evolution of a concept. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 524–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xiong, X.; Wu, X.; Ye, Y.; Jian, Z.; Zhi, Z.; Gu, L. Targeting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation to Prevent Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur-Bialy, A.I.; Pochec, E. The Time-Course of Antioxidant Irisin Activity: Role of the Nrf2/HO-1/HMGB1 Axis. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zhang, S.; Hou, N.; Wang, D.; Sun, X. Irisin improves endothelial function in obese mice through the AMPK-eNOS pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H1501–H1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlwain, D.R.; Berger, T.; Mak, T.W. Caspase functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2013, 5, a008656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, N.; Zhang, L.; Wei, D.; Dubielecka, P.M.; Wei, L.; Zhuang, S.; Zhu, P.; Qin, G.; Liu, P.Y.; Chin, Y.E.; et al. Irisin counteracts high glucose and fatty acid-induced cytotoxicity by preserving the AMPK-insulin receptor signaling axis in C2C12 myoblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E791–E805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kulthinee, S.; Wang, L.; Yano, N.; Dubielecka, P.M.; Zhang, L.X.; Zhuang, S.; Qin, G.; Zhao, Y.T.; Eugene Chin, Y.; Zhao, T.C. Irisin Preserves Cardiac Performance and Insulin Sensitivity in Response to Hemorrhage. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101193
Kulthinee S, Wang L, Yano N, Dubielecka PM, Zhang LX, Zhuang S, Qin G, Zhao YT, Eugene Chin Y, Zhao TC. Irisin Preserves Cardiac Performance and Insulin Sensitivity in Response to Hemorrhage. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(10):1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101193
Chicago/Turabian StyleKulthinee, Supaporn, Lijiang Wang, Naohiro Yano, Patrycja M. Dubielecka, Ling X. Zhang, Shougang Zhuang, Gangjian Qin, Yu Tina Zhao, Yue Eugene Chin, and Ting C. Zhao. 2022. "Irisin Preserves Cardiac Performance and Insulin Sensitivity in Response to Hemorrhage" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 10: 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101193
APA StyleKulthinee, S., Wang, L., Yano, N., Dubielecka, P. M., Zhang, L. X., Zhuang, S., Qin, G., Zhao, Y. T., Eugene Chin, Y., & Zhao, T. C. (2022). Irisin Preserves Cardiac Performance and Insulin Sensitivity in Response to Hemorrhage. Pharmaceuticals, 15(10), 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101193