Preparation of Solid Dispersions of Simvastatin and Soluplus Using a Single-Step Organic Solvent-Free Supercritical Fluid Process for the Drug Solubility and Dissolution Rate Enhancement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
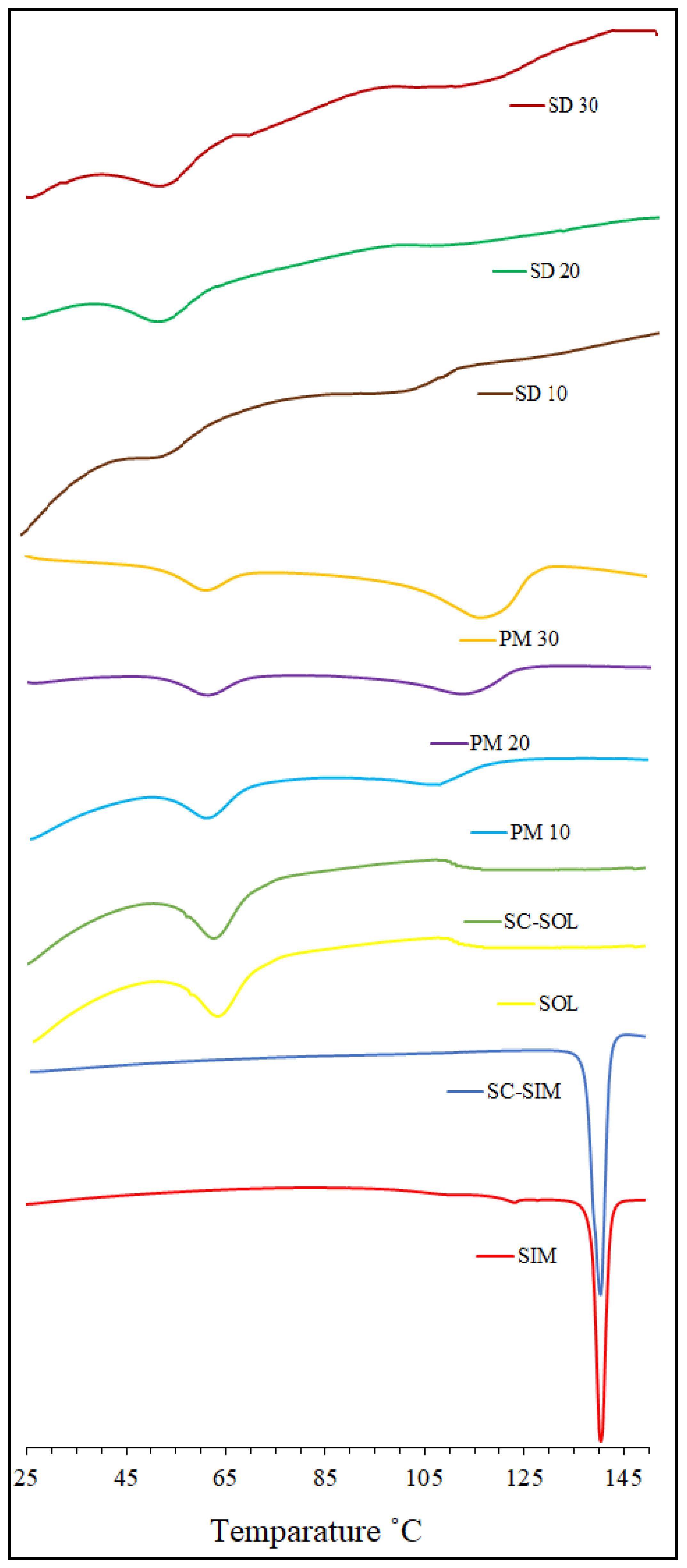
2.1. DSC Analysis
2.2. XRD Analysis
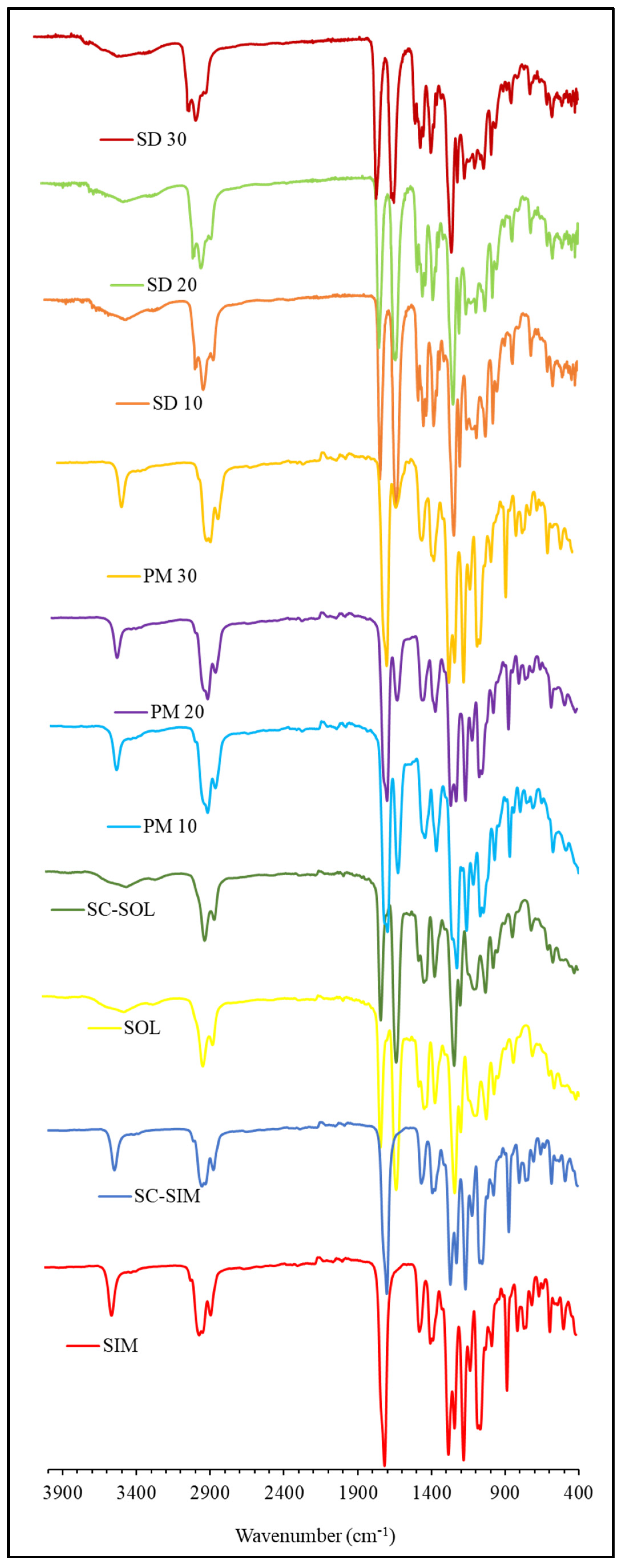
2.3. ATR-FTIR Analysis
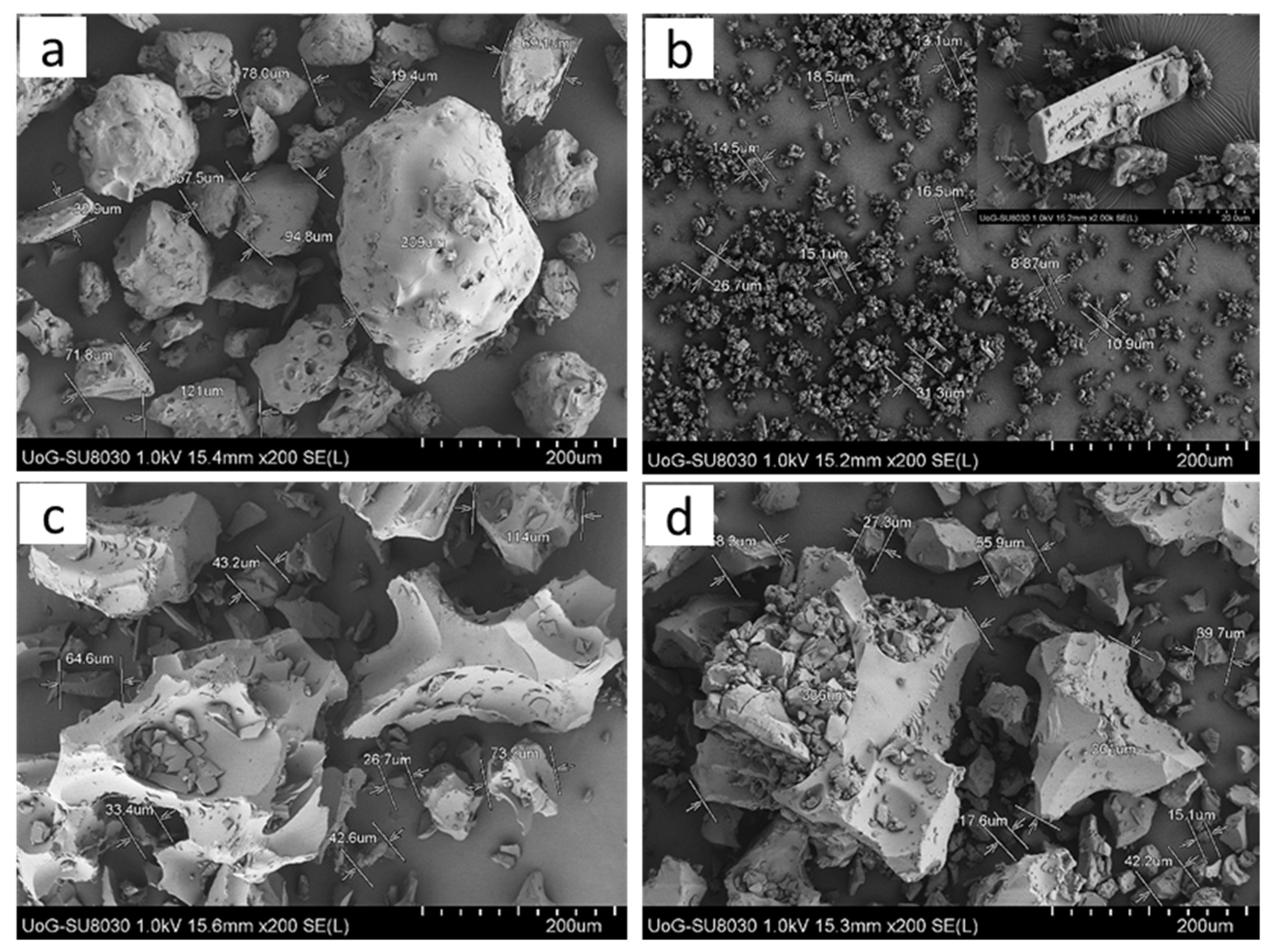
2.4. SEM Analysis
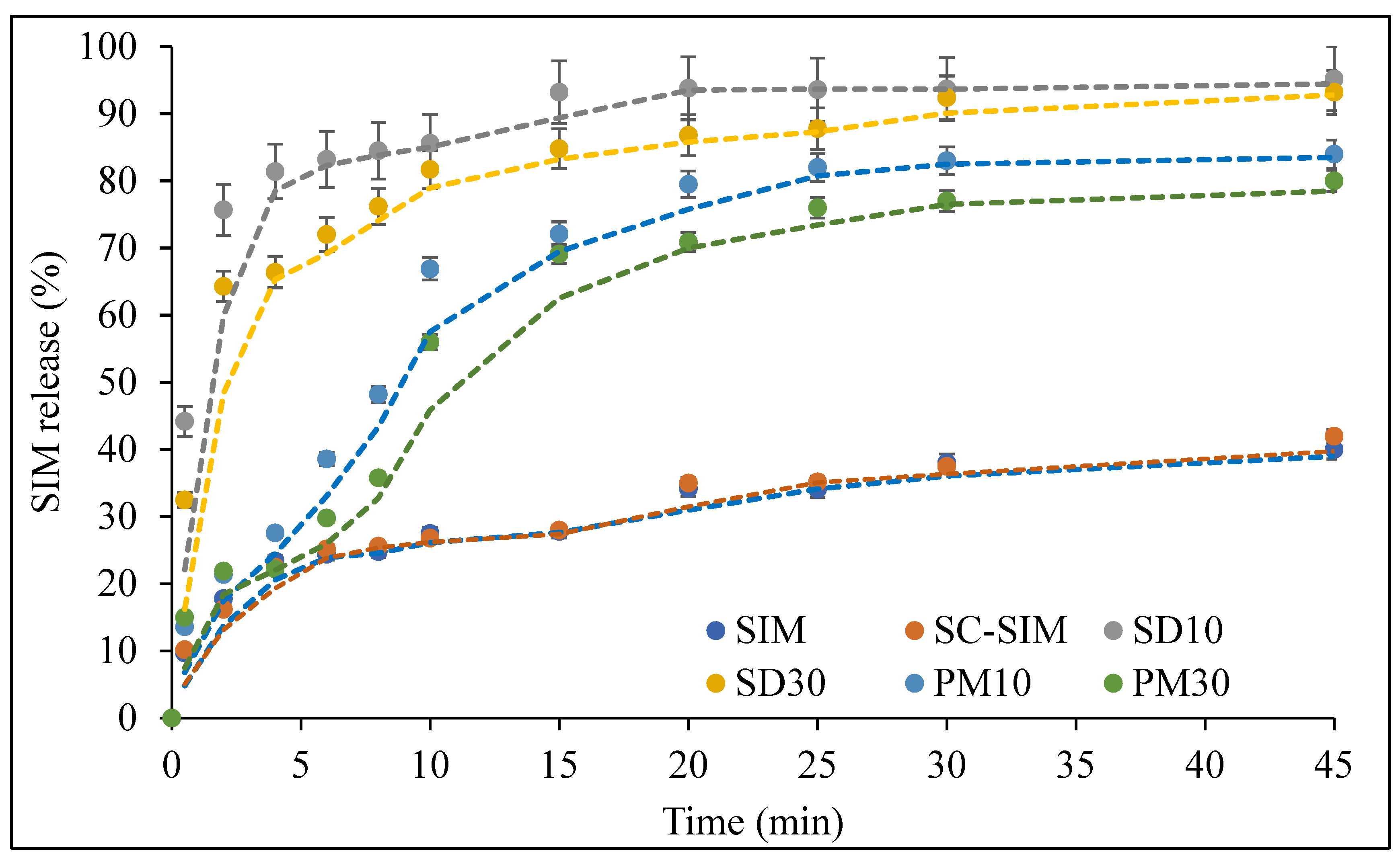
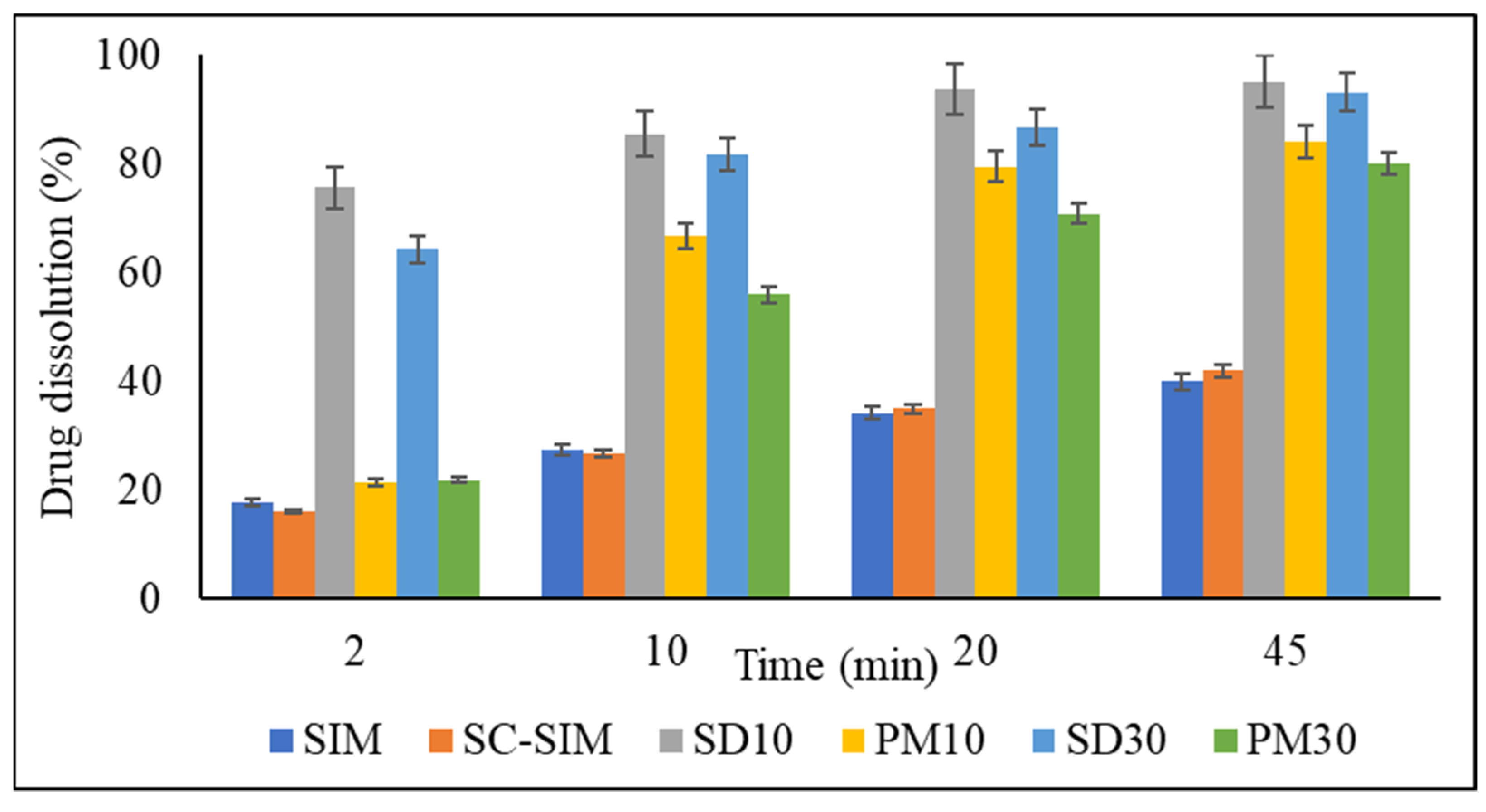
2.5. In Vitro Dissolution Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of SIM–SOL SDs
3.2.1. Physical Mixtures
3.2.2. Solid Dispersion via scCO2 Processing
3.3. Analysis of the Prepared Solid Dispersions
3.3.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
3.3.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
3.3.3. Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) Spectroscopy
3.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.4. In Vitro Dissolution Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Savjani, K.T.; Gajjar, A.K.; Savjani, J.K. Drug Solubility: Importance and Enhancement Techniques. ISRN Pharm. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Bedi, N.; Tiwary, A.K. Enhancing solubility of poorly aqueous soluble drugs: Critical appraisal of techniques. J. Pharm. Investig. 2018, 48, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Ali, R.; Al-Jenoobi, F.I.; Al-Mohizea, A.M. Solid dispersions: A strategy for poorly aqueous soluble drugs and technology updates. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 1419–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serajuddin, A.T.M. Solid dispersion of poorly water-soluble drugs: Early promises, subsequent problems, and recent breakthroughs. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhirendra, K.; Lewis, S.; Udupa, N.; Atin, K. Solid dispersions: A review. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 22, 234–246. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva Júnior, W.F.; De Oliveira Pinheiro, J.G.; Moreira, C.D.; de Souza, F.J.J.; de Lima, Á.A.N. Alternative technologies to improve solubility and stability of poorly water-soluble drugs. In Multifunctional Systems for Combined Delivery, Biosensing and Diagnostics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 281–305. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, D.-J.; Sim, T.; Oh, E. Formulation and optimization of spray-dried amlodipine solid dispersion for enhanced oral absorption. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushida, I.; Gotoda, M. Investigation for the amorphous state of ER-34122, a dual 5-lipoxygenase/cyclooxygenase inhibitor with poor aqueous solubility, in HPMC solid dispersion prepared by the solvent evaporation method. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Pei, L.; Tong, H.H.Y.; Zheng, Y. Comparison of spray freeze drying and the solvent evaporation method for preparing solid dispersions of baicalein with Pluronic F68 to improve dissolution and oral bioavailability. AAPS Pharmscitech. 2011, 12, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maniruzzaman, M.; Rana, M.M.; Boateng, J.S.; Mitchell, J.C.; Douroumis, D. Dissolution enhancement of poorly water-soluble APIs processed by hot-melt extrusion using hydrophilic polymers. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniruzzaman, M.; Morgan, D.J.; Mendham, A.P.; Pang, J.; Snowden, M.J.; Douroumis, D. Drug–polymer intermolecular interactions in hot-melt extruded solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 443, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuris, J.; Milovanovic, S.; Medarevic, D.; Dobricic, V.; Dapčević, A.; Ibric, S. Selection of the suitable polymer for supercritical fluid assisted preparation of carvedilol solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 554, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, S.; Djuris, J.; Dapčević, A.; Medarevic, D.; Ibric, S.; Zizovic, I. Soluplus®, Eudragit®, HPMC-AS foams and solid dispersions for enhancement of Carvedilol dissolution rate prepared by a supercritical CO2 process. Polym. Test. 2019, 76, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Daintree, L.S.; Ding, S.; Ledger, D.M.; Wang, B.; Zhao, W.; Qi, J.; Wu, W. Itraconazole solid dispersion prepared by a supercritical fluid technique: Preparation, in vitro characterization, and bioavailability in beagle dogs. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 2801. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, K.; Viboonkiat, R.; Rehman, I.U.; Buckton, G.; Darr, J.A. Formation and characterization of porous indomethacin-PVP coprecipitates prepared using solvent-free supercritical fluid processing. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 2583–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhomia, R.; Trivedi, V.; Mitchell, J.C.; Coleman, N.J.; Snowden, M.J. Effect of pressure on the melting point of pluronics in pressurized carbon dioxide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 10820–10825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, L.L.; Wei, L.L.; Hong-Guo Nie, S.F.; Yang, X.G.; Tang, R.; Pan, W.S. Preparation of budesonide-poly (ethylene oxide) solid dispersions using supercritical fluid technology. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2007, 33, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudrangi, S.R.S.; Bhomia, R.; Trivedi, V.; Vine, G.J.; Mitchell, J.C.; Alexander, B.D.; Wicks, S.R. Influence of the preparation method on the physicochemical properties of indomethacin and methyl-β-cyclodextrin complexes. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 479, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuji, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Kawashima, Y. Particle design of poorly water-soluble drug substances using supercritical fluid technologies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badens, E.; Majerik, V.; Horváth, G.; Szokonya, L.; Bosc, N.; Teillaud, E.; Charbit, G. Comparison of solid dispersions produced by supercritical antisolvent and spray-freezing technologies. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 377, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moneghini, M.; Kikic, I.; Voinovich, D.; Perissutti, B.; Filipović-Grčić, J. Processing of carbamazepine–PEG 4000 solid dispersions with supercritical carbon dioxide: Preparation, characterisation, and in vitro dissolution. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 222, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazarian, S.G.; Martirosyan, G.G. Spectroscopy of polymer/drug formulations processed with supercritical fluids: In situ ATR–IR and Raman study of impregnation of ibuprofen into PVP. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 232, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Xi, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, S.; Xu, L. Applying supercritical fluid technology to prepare ibuprofen solid dispersions with improved oral bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, N.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dang, B. Improved dissolution and bioavailability of silymarin delivered by a solid dispersion prepared using supercritical fluids. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, D.-H.; Kim, M.-S.; Lee, S.; Park, J.-S.; Hwang, S.-J. Improved physicochemical characteristics of felodipine solid dispersion particles by supercritical anti-solvent precipitation process. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 301, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, H.J.; Cho, W.K.; Cha, K.-H.; Hwang, S.-J. Enhanced bioavailability of sirolimus via preparation of solid dispersion nanoparticles using a supercritical antisolvent process. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2997. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, S.W.; Kim, M.S.; Jo, G.H.; Lee, S.; Woo, J.S.; Park, J.S.; Hwang, S.J. Cefuroxime axetil solid dispersions prepared using solution enhanced dispersion by supercritical fluids. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2005, 57, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, R.T.Y.; Ng, W.K.; Tan, R.B.H. Amorphization of pharmaceutical compound by co-precipitation using supercritical anti-solvent (SAS) process (Part I). J. Supercrit. Fluids 2010, 53, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Cho, W.; Cha, K.-H.; Ahn, J.; Han, K.; Hwang, S.-J. Solubilization of the poorly water soluble drug, telmisartan, using supercritical anti-solvent (SAS) process. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Municio, M.; Montilla, A.; Herrero, M.; Olano, A.; Ibáñez, E. Supercritical CO2 impregnation of lactulose on chitosan: A comparison between scaffolds and microspheres form. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2011, 57, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Gong, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Deng, H.; Deng, S. Development of nimesulide amorphous solid dispersions via supercritical anti-solvent process for dissolution enhancement. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zordi, N.; Moneghini, M.; Kikic, I.; Grassi, M.; Castillo, A.E.D.R.; Solinas, D.; Bolger, M.B. Applications of supercritical fluids to enhance the dissolution behaviors of Furosemide by generation of microparticles and solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabbakhian, M.; Hasanzadeh, F.; Tavakoli, N.; Jamshidian, Z. Dissolution enhancement of glibenclamide by solid dispersion: Solvent evaporation versus a supercritical fluid-based solvent-antisolvent technique. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 337. [Google Scholar]
- Riekes, M.K.; Caon, T.; da Silva, J., Jr.; Sordi, R.; Kuminek, G.; Bernardi, L.S.; Rambo, C.R.; de Campos, C.E.M.; Fernandes, D.; Stulzer, H.K. Enhanced hypotensive effect of nimodipine solid dispersions produced by supercritical CO2 drying. Powder Technol. 2015, 278, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, R.M.; Tashtoush, B.M.; Awad, A.A.; Al Bustami, R.T. Using supercritical fluid technology (SFT) in preparation of tacrolimus solid dispersions. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2017, 18, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, S.S.; Chalasani, N. Lipid-Lowering Agents That Cause Drug-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Clin. Liver Dis. 2007, 11, 597–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaza, G. Solubility enhancement of simvastatin: A review. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2012, 69, 581–590. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yao, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Tian, B.; Tang, X. Extruded Soluplus/SIM as an oral delivery system: Characterization, interactions, in vitro and in vivo evaluations. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1902–1911. [Google Scholar]
- Obaidat, R.; Alnaief, M.; Jaeger, P. Significant solubility of carbon dioxide in Soluplus® facilitates impregnation of ibuprofen using supercritical fluid technology. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamma, R.N.; Basha, M. Soluplus®: A novel polymeric solubilizer for optimization of carvedilol solid dispersions: Formulation design and effect of method of preparation. Powder Technol. 2013, 237, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.K.; Sutariya, V.B. Micronisation of simvastatin by the supercritical antisolvent technique: In vitro–in vivo evaluation. J. Microencapsul. 2015, 32, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Octavia, M.D.; Halim, A.; Zaini, E. Preparation of Simvastatin-β-Cyclodextrin inclusion complexes using co-evaporation technique. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 740–747. [Google Scholar]
- Essa, E.A.; Dwaikat, M. Enhancement of Simvastatin dissolution by surface solid dispersion: Effect of carriers and wetting agents. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, F.; Ning, J.; Fan, H.; Wu, C.; Wang, Y. Preparation and characterization of simvastatin/DMβCD complex and its pharmacokinetics in rats. Acta Pharm. 2018, 68, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, J.N.; Shete, R.T.; Gangurde, A.B.; Moravkar, K.K.; Javeer, S.D.; Jaiswar, D.R.; Amin, P.D. Development of amorphous dispersions of artemether with hydrophilic polymers via spray drying: Physicochemical and in silico studies. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 11, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.B.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.J.; Kang, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.; Khang, G. Dissolution properties of control released solid dispersion of carvedilol with HPMC and Eudragit RS. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 42, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douroumis, D.; Bouropoulos, N.; Fahr, A. Physicochemical characterization of solid dispersions of three antiepileptic drugs prepared by solvent evaporation method. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Chi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Kao, C.; Lin, S. DSC-FTIR Combined Approaches Used to Simultaneously Prepare/Determine the Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Indomethacin/Soluplus in Real-time. EC Pharm. Sci. 2015, 2, 183–193. [Google Scholar]
- Löbmann, K.; Strachan, C.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T.; Korhonen, O.; Laitinen, R. Co-amorphous simvastatin and glipizide combinations show improved physical stability without evidence of intermolecular interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, T.J.; Amin, A.F.; Parikh, J.R.; Parikh, R.H. Process optimization and characterization of poloxamer solid dispersions of a poorly water-soluble drug. Aaps Pharmscitech. 2007, 8, E18–E24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugaonkar, S.; Nunes, A.C.; Needham, T.E. Effect of n-scCO2 on crystalline to amorphous conversion of carbamazepine. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 333, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodier, E.; Lochard, H.; Sauceau, M.; Letourneau, J.-J.; Freiss, B.; Fages, J. A three step supercritical process to improve the dissolution rate of Eflucimibe. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 26, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Craig, D.Q.M. The mechanisms of drug release from solid dispersions in water-soluble polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 231, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndayishimiye, J.; Popat, A.; Kumeria, T.; Blaskovich, M.A.T.; Falconer, J.R. Supercritical carbon dioxide assisted complexation of benznidazole: γ-cyclodextrin for improved dissolution. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 596, 120240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alopaeus, J.F.; Hagesæther, E.; Tho, I. Micellisation mechanism and behaviour of Soluplus®–furosemide micelles: Preformulation studies of an oral nanocarrier-based system. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.C.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Gong, T.; Sun, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z.R. Soluplus micelles for improving the oral bioavailability of scopoletin and their hypouricemic effect in vivo. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela-Garcia, A.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Soluplus micelles for acyclovir ocular delivery: Formulation and cornea and sclera permeability. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 552, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, P.; Maestrelli, F.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Luceri, C.; Cirri, M. Evaluation and comparison of solid lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) and Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) as vectors to develop Hydrochlorothiazide effective and safe pediatric oral liquid formulations. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, C.; Tian, Y.; Walker, G.; McCoy, C.; Hornsby, P.; Donnelly, C.; Jones, D.S.; Andrews, G.P. Novel supercritical carbon dioxide impregnation technique for the production of amorphous solid drug dispersions: A comparison to hot melt extrusion. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1377–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, V.; Bhomia, R.; Mitchell, J.C.; Coleman, N.J.; Douroumis, D.; Snowden, M.J. Study of the Effect of Pressure on Melting Behavior of Saturated Fatty Acids in Liquid or Supercritical Carbon Dioxide. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 2013, 58, 1861–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudrangi, S.R.S.; Trivedi, V.; Mitchell, J.C.; Wicks, S.R.; Alexander, B.D. Preparation of olanzapine and methyl-β-cyclodextrin complexes using a single-step, organic solvent-free supercritical fluid process: An approach to enhance the solubility and dissolution properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 494, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
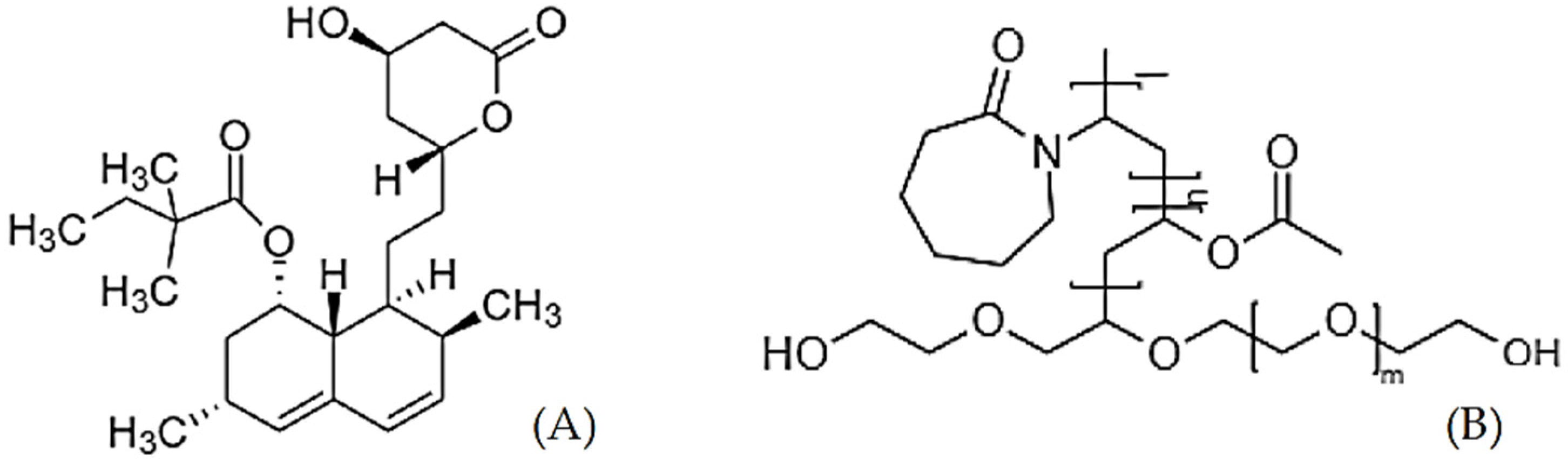

| Drug | Polymer/s | T (°C) | P (bar) | Co-Solvent | Outcome | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxeglitazar | Poloxamer 188 & 407, PEG 8000, PVP K17 | 35 | 80 | DCM, CHCl3, EtOH | Improved dissolution rate. | [20] |
| Carbamazepine | PEG 4000 | 40 | 70 | Acetone | Particle size reduction. | [21] |
| Ibuprofen | PVP | 35–45 | 80–220 | - | Amorphous drug dispersion in polymer matrix. | [22] |
| Ibuprofen | Kollidon CL-SF | 40 | 250 | - | Amorphous drug in SD. Improvement in in vitro and in vivo performance. | [23] |
| Silymarin | PVP- K17 & K30, HPMC- K4M & K15M | 50 | 150 | EtOH & DCM + EtOH | Drug dispersion in amorphous state. Improved drug dissolution and oral absorption. | [24] |
| Felodipine | HPMC, Poloxamer 188 & 407, HCO-60 | 45 | 100 | EtOH & methylene chloride | Drug amorphisation. Improved dissolution (>90% in 2 h). | [25] |
| Sirolimus | PVP-K30, SLS, TPGS, Sucroester 15, Gelucire 50/30, Myrj 52 | 40 | 120 | EtOH or DCM + EtOH | Enhanced drug supersaturation, dissolution, stability, and oral bioavailability. | [26] |
| Cefuroxime axetil | HPMC 2910/PVP-K30 | 45 | 100 | DCM + EtOH | Drug in amorphous form due to intermolecular H-bonds between drug and polymers. | [27] |
| Indomethacin | PVP | 35 | 85 | Acetone + DCM | Drug amorphisation. Impact of polymer content. | [28] |
| Telmisartan | HPMC + PVP | 45 | 120 | EtOH + methylene chloride | Drug in amorphous state but prone to re-crystallization. | [29] |
| Lactulose | Chitosan scaffolds/microspheres | 60, 100 | 100 | EtOH + Water | Drug impregnation of chitosan with mono-or disaccharides. | [30] |
| Nimesulide | HPMC + PVP | 40 | 80 | DCM + MeOH | Complete amorphisation of drug. Increased drug solubility of >5 folds. | [31] |
| Furosemide | Crospovidone | 39.85 | 100, 200 | Acetone | Amorphous SD, with stability >6 months. | [32] |
| Glibenclamide | HPMCE5, PEG6000, Poloxamer 407 | 50 | 103–206 | Acetone, methanol | Drug amorphisation. Improved dissolution. | [33] |
| Nimodipine | PVP K-30 | 40 | 100 | - | Long processing time (3 days). Drug amorphisation and improved dissolution. | [34] |
| Tacrolimus | Soluplus, Chitosan, PVP, HPMC, TPGS | 40 | 100–300 | - | Best SDs with Soluplus with improved drug dissolution. | [35] |
| Drug Content (% w/w) | Temperature (°C) | Pressure (bar) | Duration (min) | Observation (Drug Form) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 40 | 100 | 60 | Crystalline |
| 40 | 100 | 120 | Crystalline | |
| 50 | 100 | 60 | Crystalline | |
| 50 | 100 | 120 | Crystalline | |
| 40 | 150 | 60 | Crystalline | |
| 40 | 150 | 120 | Crystalline | |
| 50 | 150 | 60 | Semi-crystalline | |
| 50 | 150 | 120 | Amorphous | |
| 20 | 40 | 100 | 60 | Crystalline |
| 40 | 100 | 120 | Crystalline | |
| 50 | 100 | 60 | Crystalline | |
| 50 | 100 | 120 | Crystalline | |
| 40 | 150 | 60 | Crystalline | |
| 40 | 150 | 120 | Crystalline | |
| 50 | 150 | 60 | Semi-crystalline | |
| 50 | 150 | 120 | Amorphous | |
| 30 | 40 | 100 | 60 | Crystalline |
| 40 | 100 | 120 | Crystalline | |
| 50 | 100 | 60 | Crystalline | |
| 50 | 100 | 120 | Crystalline | |
| 40 | 150 | 60 | Crystalline | |
| 40 | 150 | 120 | Crystalline | |
| 50 | 150 | 60 | Semi-crystalline | |
| 50 | 150 | 120 | Semi-crystalline * |
| Kinetic Model | SD10 | SD30 |
|---|---|---|
| Zero-order | 0.5844 | 0.6839 |
| First-order | 0.8577 | 0.7796 |
| Higuchi | 0.3322 | 0.3239 |
| Hixson–Crowell | 0.4657 | 0.3612 |
| Korsmeyer–Peppas | 0.9566 | 0.9645 |
| Korsmeyer–Peppas (n) | 0.123 | 0.174 |
| Factor | Name (Unit) | Low | Mid | High |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Drug (%) | 10 | 20 | 30 |
| B | Temperature (°C) | 40 | - | 50 |
| C | Pressure (bar) | 100 | - | 150 |
| D | Time (min) | 60 | - | 120 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nandi, U.; Ajiboye, A.L.; Patel, P.; Douroumis, D.; Trivedi, V. Preparation of Solid Dispersions of Simvastatin and Soluplus Using a Single-Step Organic Solvent-Free Supercritical Fluid Process for the Drug Solubility and Dissolution Rate Enhancement. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090846
Nandi U, Ajiboye AL, Patel P, Douroumis D, Trivedi V. Preparation of Solid Dispersions of Simvastatin and Soluplus Using a Single-Step Organic Solvent-Free Supercritical Fluid Process for the Drug Solubility and Dissolution Rate Enhancement. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(9):846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090846
Chicago/Turabian StyleNandi, Uttom, Adejumoke Lara Ajiboye, Preksha Patel, Dennis Douroumis, and Vivek Trivedi. 2021. "Preparation of Solid Dispersions of Simvastatin and Soluplus Using a Single-Step Organic Solvent-Free Supercritical Fluid Process for the Drug Solubility and Dissolution Rate Enhancement" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 9: 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090846
APA StyleNandi, U., Ajiboye, A. L., Patel, P., Douroumis, D., & Trivedi, V. (2021). Preparation of Solid Dispersions of Simvastatin and Soluplus Using a Single-Step Organic Solvent-Free Supercritical Fluid Process for the Drug Solubility and Dissolution Rate Enhancement. Pharmaceuticals, 14(9), 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090846








