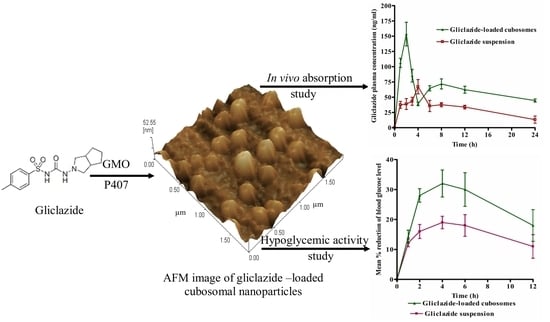
Bioavailability and Antidiabetic Activity of Gliclazide-Loaded Cubosomal Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Particle Size, Polydispersity Index, and Zeta Potential
2.2. Entrapment Efficiency
2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
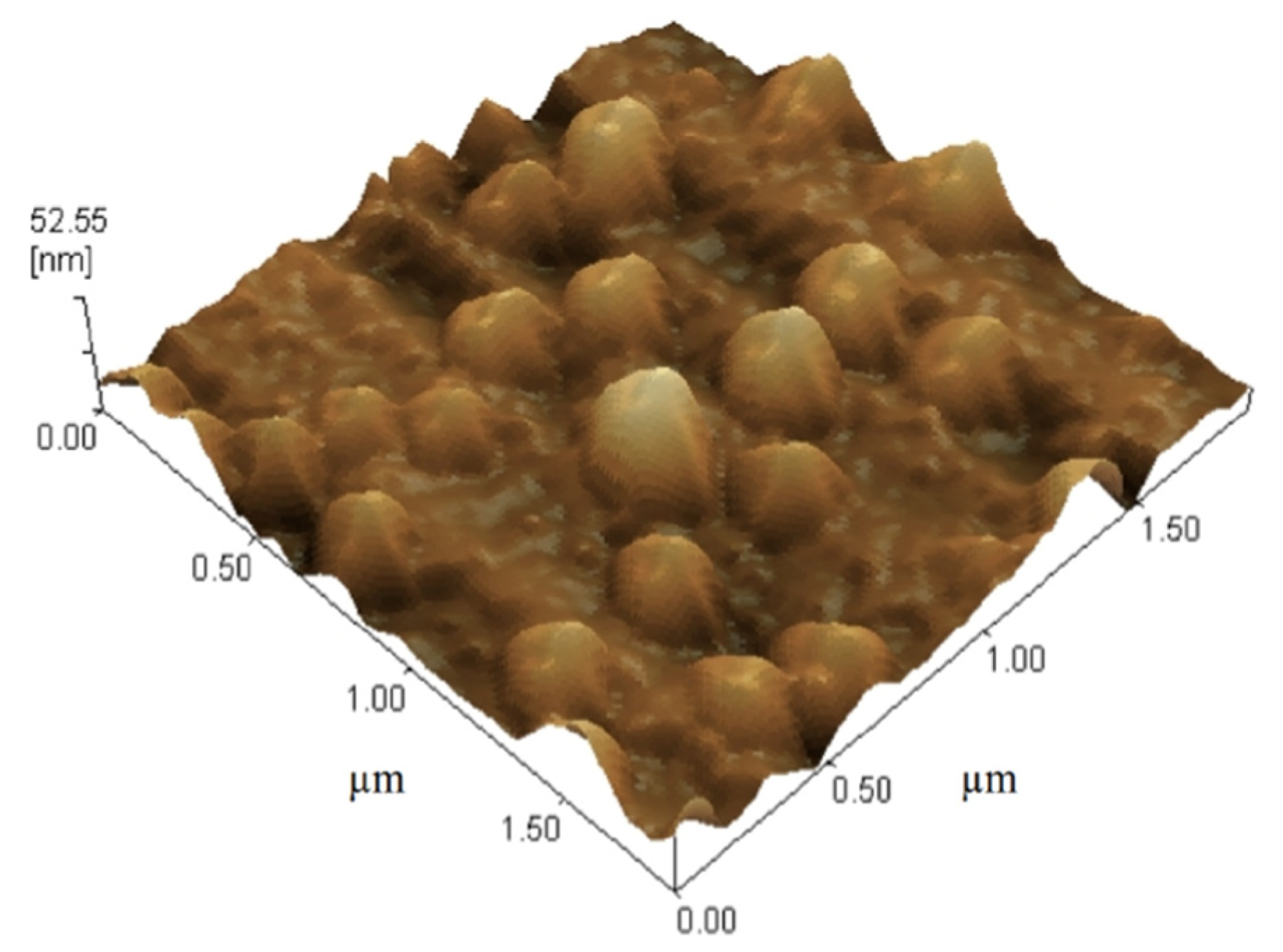
2.4. Morphology of Gliclazide-Loaded Cubosomes
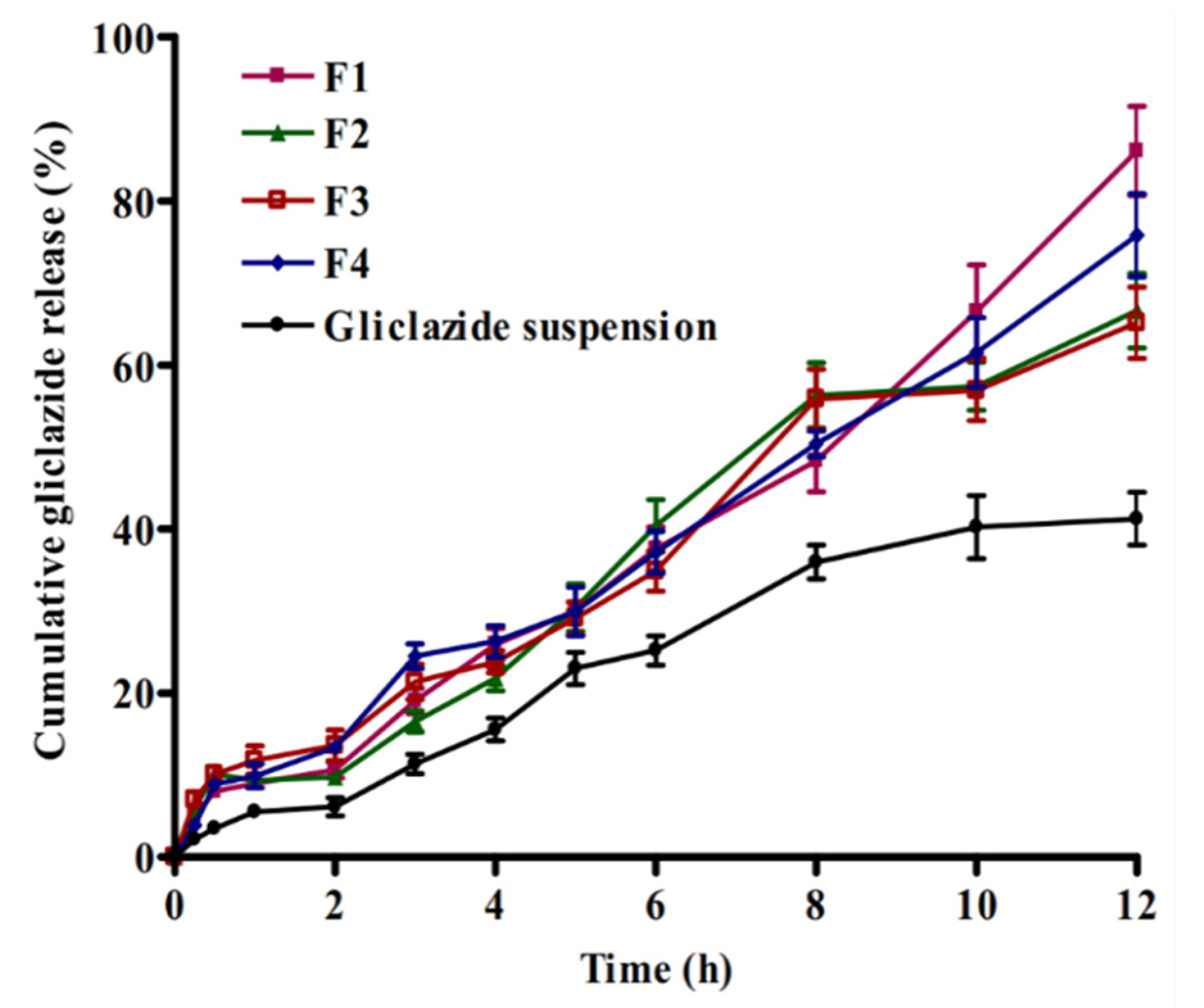
2.5. In Vitro Gliclazide Release
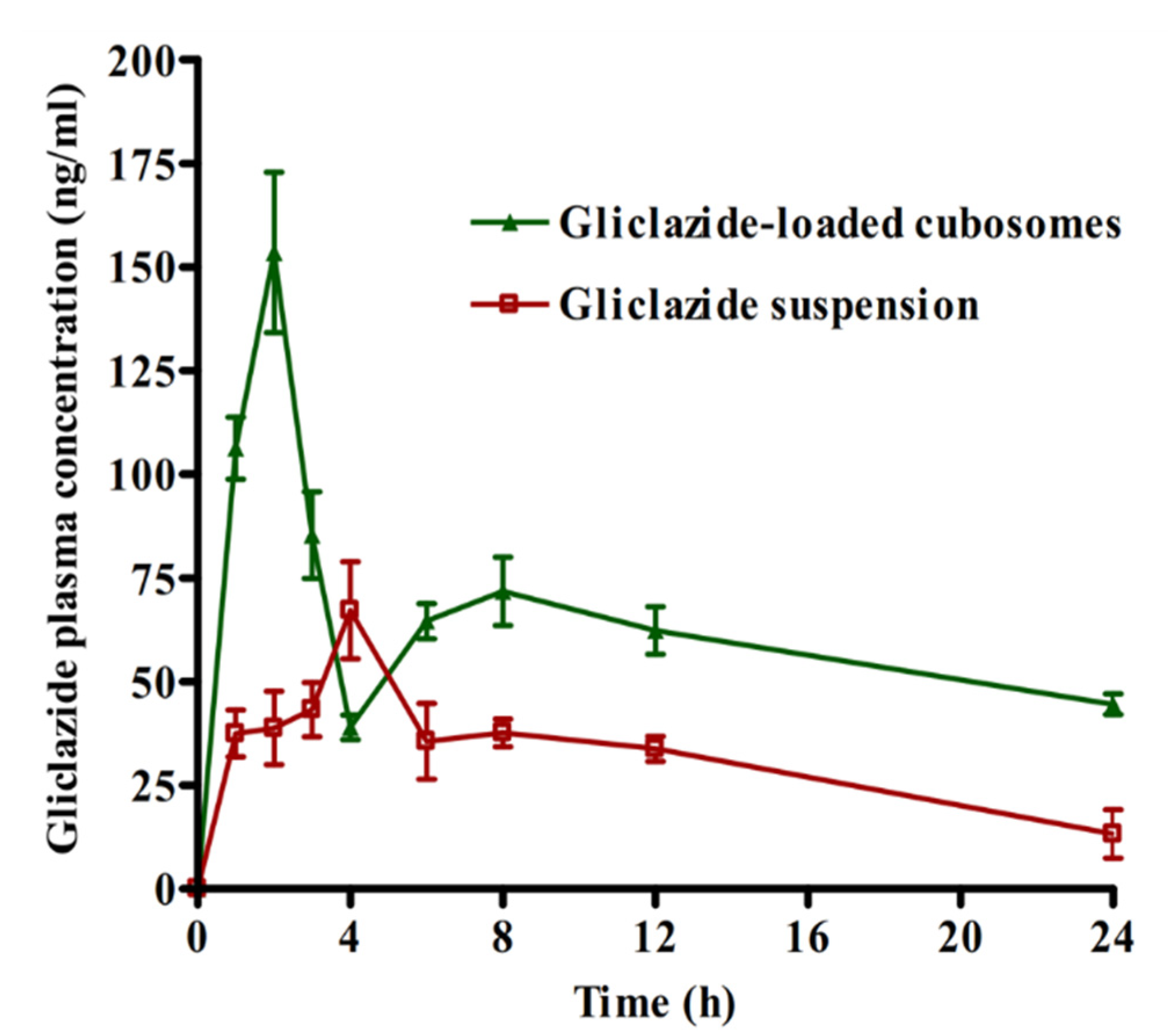
2.6. Bioavailability Study
2.7. Evaluation of the Hypoglycemic Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Gliclazide-Loaded Cubosomes
3.3. Characterization of Gliclazide-Loaded Cubosomes
3.3.1. Particle Size, Polydispersity Index, and Zeta Potential
3.3.2. Entrapment Efficiency Percentage (EE %)
3.3.3. Morphology of Cubosomal Nanoparticles
3.3.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.3.5. In Vitro Drug Release Study
3.3.6. Bioavailability Study
3.3.7. Antidiabetic Activity Study
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campbell, D.B.; Lavielle, R.; Nathan, C. The mode of action and clinical pharmacology of gliclazide: A review. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1991, 14, S21–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nipun, T.S.; Islam, S.M.A. SEDDS of gliclazide: Preparation and characterization by in-vitro, ex-vivo and in-vivo techniques. Saudi Pharm. J. 2014, 22, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amidon, G.L.; Lennernas, H.; Shah, V.P.; Crison, J.R. A Theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: The correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shewale, B.D.; Fursule, R.A.; Sapkal, N.P. Effect of pH and hydroxylpropyl-β-cyclodextrin on solubility and stability of gliclazide. Int. J. Health Res. 2008, 1, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Özkan, Y.; Atay, T.; Dikmen, N.; Işimer, A.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Improvement of water solubility and in vitro dissolution rate of gliclazide by complexation with β-cyclodextrin. Pharm. Acta Helv. 2000, 74, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.M.E.; Daly, F.; Walsh, J.P.; Ilett, K.F.; Beilby, J.P.; Dusci, L.J.; Barrett, P.H. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of gliclazide in Caucasians and Australian Aborigines with type 2 diabetes. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000, 49, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palmer, K.J.; Brogden, R.N. Gliclazide-an update of its pharmaco- logical properties and therapeutic efficcacy in non-insulin-de- pendent diabetes mellitus. Drugs 1993, 46, 92–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, C.G.; Dabhade, P.S.; Jain, N.P.; Aher, B.O. Solubility and dissolution enhancement of gliclazide by solid dispersion technique. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. Anal. 2015, 2, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- El Maghraby, G.M.; Alomrani, A. Effect of binary and ternary solid dispersions on the in vitro dissolution and in- situ rabbit intestinal absorption of gliclazide. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 24, 459–468. [Google Scholar]
- Hiremath, S.N.; Raghavendra, R.K.; Sunil, F.; Danki, L.S. Dissolution enhancement of gliclazide by preparation of inclusion complexes with β-cyclodextrin. Asian J. Pharm. 2008, 2, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravouru, N.; Venna, R.S.A.; Penjuri, S.C.B. Fabrication and characterization of gliclazide nanocrystals. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 8, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, H. Liquisolid compact of gliclazide for enhanced dissolution and oral bioavailability. Indian J. Nov. Drug Deliv. 2013, 6, 314–320. [Google Scholar]
- Nazief, A.M.; Hassaan, P.S.; Khalifa, H.M.; Sokar, M.S.; El-Kamel, A.H. Lipid-Based Gliclazide Nanoparticles for Treatment of Diabetes: Formulation, Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Subacute Toxicity Study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 1129–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, H.; Pandey, N.; Patel, B.; Ranch, K.; Bodiwala, K.; Vyas, B. Enhancement of in vivo hypoglycemic effect of gliclazide by developing self-microemulsifying pellet dosage form Future. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, N.M.; Yalavarthi, P.R.; Vadlamudi, H.C.; Thanniru, J.; Yaga, G.; Haritha, K. Cubosomes as targeted drug delivery systems a biopharmaceutical approach. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2014, 11, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.M.; Aramakim, K. Effect of molecular weight of triglycerides on the formation and rheological behavior of cubic and hexagonal phase-based gel emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 336, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.Y.; Nguyen, T.H.; Hanley, T.; Boyd, B.J. Nanostructure of liquid crystalline matrix determines in vitro sustained release and in vivo oral absorption kinetics for hydrophilic model drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 365, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, K.M.; Douroumis, D.; Bunjes, H. Drug release from differently structured monoolein/poloxamer nanodispersions studied with differential pulse polarography and ultrafiltration at low pressure. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 1564–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Han, K.; Peng, X.; Yang, Z.; Qin, L.; Zhu, C.; Huang, X.; Shi, X.; Dian, L.; Lu, M.; et al. Nanostructed cubosomes as advanced drug delivery system. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 6290–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Sun, J.; Hu, F.; Yin, Z.; Wu, W. Glyceryl Monooleate/Poloxamer 407 Cubic Nanoparticles as Oral Drug Delivery Systems. In Vitro Evaluation and Enhanced Oral Bioavailability of the Poorly Water-Soluble Drug Simvastatin. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, J.; Lu, Y.; Yin, Z.; Hu, F.; Wu, W. Pharmacokinetics and enhanced oral bioavailability in beagle dogs of cyclosporine A encapsulated in glyceryl monooleate/poloxamer 407 cubic nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, M.; Elmowafy, E.; Gad, H.A. Intranasal versus intraperitoneal Myrj 59-stabilized cubosomes: A potential armamentarium of effective anti-diabetic therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 199, 111534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos-Hernandez, J.R.; Muller-Goymann, C.C. Novel nanoparticulate carrier system based on carnauba wax and decyl oleate for the dispersion of inorganic sunscreens in aqueous media. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 60, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswal, S.; Sahoo, J.; Murthy, P.N.; Giradkar, R.P.; Avari, J.G. Enhancement of dissolution rate of gliclazide using solid dispersions with polyethylene glycol 6000. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Badry, M.; Hassan, M.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Elsaghir, H. Performance of poloxamer 407 as hydrophilic carrier on the binary mixtures with nimesulide. Farmacia 2013, 61, 1137–1150. [Google Scholar]
- El-Laithy, H.M.; Badawi, A.; Abdelmalak, N.S.; El-Sayyad, N. Cubosomes as oral drug delivery systems: A promising approach for enhancing the release of clopidogrel bisulphate in the intestine. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 66, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clogston, J.; Caffrey, M. Controlling release from the lipidic cubic phase. Amino acids, peptides, proteins and nucleic acids. J. Control. Release 2005, 107, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsabawi, D.; Hamdan, I. Improvement of dissolution rate of gliclazide through sodium salt formation. Dissolution Technol. 2014, 21, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grbic, S.; Parojcic, J.; Ibric, S.; Djuric, Z. In vitro-in vivo correlation for gliclazide immediate-release tablets based on mechanistic absorption simulation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jagadeesh, H.; Devi, V. Tamoxifen loaded poly (ε-caprolactone) based injectable microspheres for breast cancer. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 2, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, R.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S. Nanostructured lipid matrices for improved microencapsulation of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priano, L.; Esposti, D.; Esposti, R. Solid lipid nanoparticles incorporating melatonin as new model for sustained oral and transdermal delivery systems. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 3596–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boge, L.; Hallstensson, K.; Ringstad, L.; Johansson, J.; Andersson, T.; Davoudi, M.; Larsson, P.T.; Mahlapuu, M.; Håkansson, J.; Andersson, M. Cubosomes for topical delivery of the antimicrobial peptide LL-37. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 134, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, G.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S. Cubosomes: An overview. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pal, D.; Nayak, A.K. Development, optimization, and anti-diabetic activity of gliclazide-loaded alginate–methyl cellulose mucoadhesive microcapsules. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasr, M.; Ghorab, M.K.; Abdelazem, A. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of cubosomes containing 5-fluorouracil for liver targeting. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, S.L.; Sun, E.; Tan, X.B.; Song, J.; Jia, X.B. A nanostructured liquid crystalline formulation of 20 (S)-protopanaxadiol with improved oral absorption. Fitoterapia 2013, 84, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.; Kim, J.; Um, J.Y.; Kwon, I.C.; Jeong, S.Y. Self-assembled “nanocubicle” as a carrier for peroral insulin delivery. Diabetologia 2002, 45, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Resztak, M.; Hermann, T.; Sawicki, W.; Danielak, D.Z. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of gliclazide from immediate and modified release formulation tablets in rats. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.K.; Hung, C.T.; Perrier, D.G. Quantitation of the release of doxorubicin from colloidal dosage forms using dynamic dialysis. J. Pharm. Sci. 1987, 76, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shavi, G.V.; Kumar, A.R.; Usha, Y.N. Enhanced dissolution and bioavailability of gliclazide using solid dispersion techniques. Int. J. Drug Deliv. 2010, 2, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
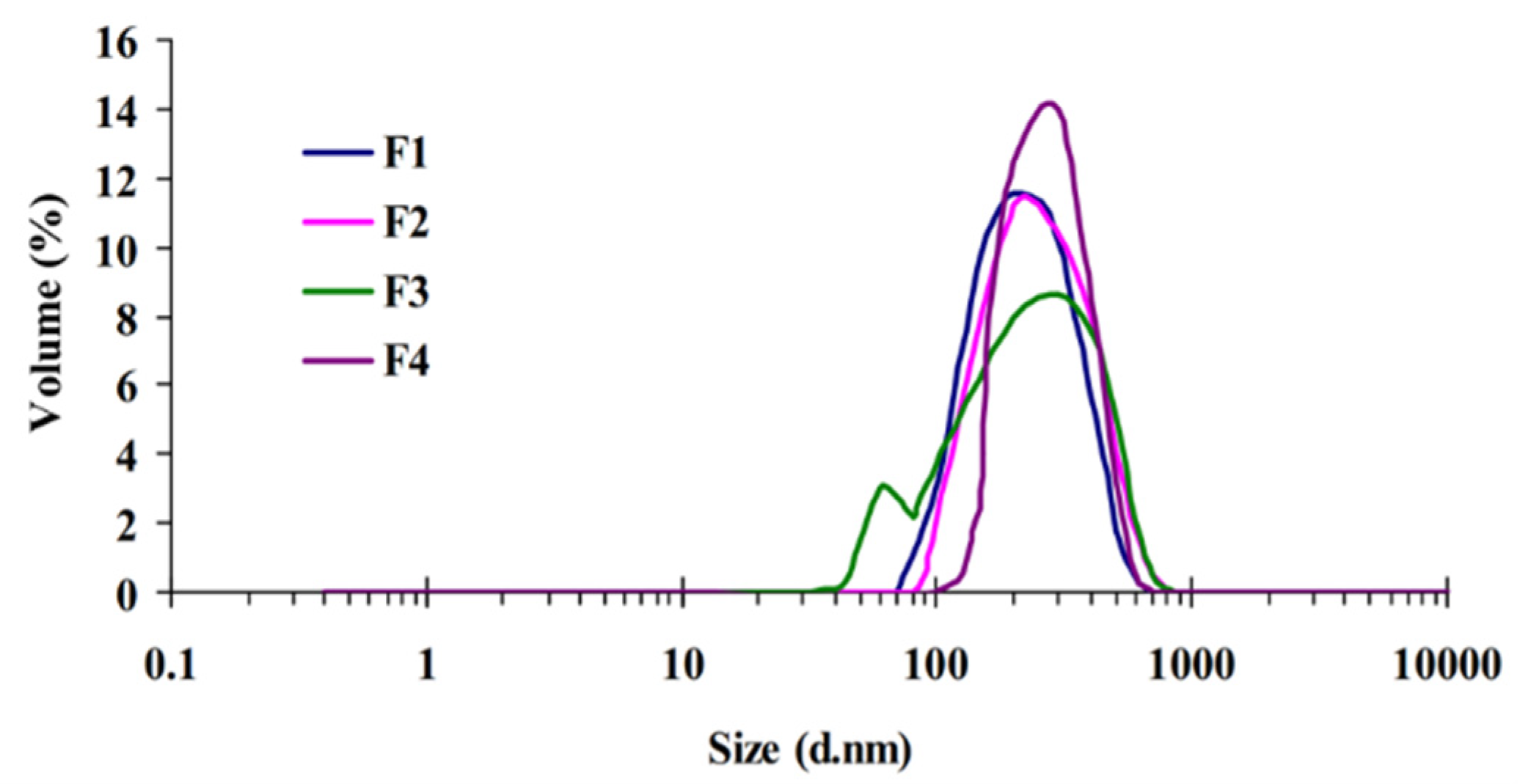


| EE % | Zeta Potential mV | PDI | Particle Size (nm) | GMO % w/w | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 73.84 ± 3.03 | −19.40 ± 0.80 | 0.172 ± 0.002 | 220.60 ± 1.39 | 1.25 | F1 |
| 80.68 ± 1.85 | −21.80 ± 0.50 | 0.142 ± 0.035 | 225.30 ± 2.40 | 2.50 | F2 |
| 88.81 ± 0.94 | −24.20 ± 0.91 | 0.155 ± 0.012 | 226.50 ± 1.50 | 5.00 | F3 |
| 87.42 ± 1.28 | −25.30 ± 0.22 | 0.098 ± 0.017 | 234.00 ± 2.90 | 7.50 | F4 |
| Bioavailability Parameters | Gliclazide Aqueous Suspension | Gliclazide-Loaded Cubosomal Dispersion (F3) |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 67.10 ± 11.73 | 153.50 ± 19.35 * |
| Tmax (h) | 4.00 | 2.00 * |
| AUC0-24 (ng.h/mL) | 754.51 ± 67.83 | 1513.99 ± 196.39 * |
| Relative bioavailability | - | 200.5% ± 10.55 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nasr, M.; Almawash, S.; Al Saqr, A.; Bazeed, A.Y.; Saber, S.; Elagamy, H.I. Bioavailability and Antidiabetic Activity of Gliclazide-Loaded Cubosomal Nanoparticles. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080786
Nasr M, Almawash S, Al Saqr A, Bazeed AY, Saber S, Elagamy HI. Bioavailability and Antidiabetic Activity of Gliclazide-Loaded Cubosomal Nanoparticles. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(8):786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080786
Chicago/Turabian StyleNasr, Mohamed, Saud Almawash, Ahmed Al Saqr, Alaa Y. Bazeed, Sameh Saber, and Heba I. Elagamy. 2021. "Bioavailability and Antidiabetic Activity of Gliclazide-Loaded Cubosomal Nanoparticles" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 8: 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080786
APA StyleNasr, M., Almawash, S., Al Saqr, A., Bazeed, A. Y., Saber, S., & Elagamy, H. I. (2021). Bioavailability and Antidiabetic Activity of Gliclazide-Loaded Cubosomal Nanoparticles. Pharmaceuticals, 14(8), 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080786