Insulin-Mimic Components in Acer truncatum Leaves: Bio-Guided Isolation, Annual Variance Profiling and Regulating Pathway Investigated by Omics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
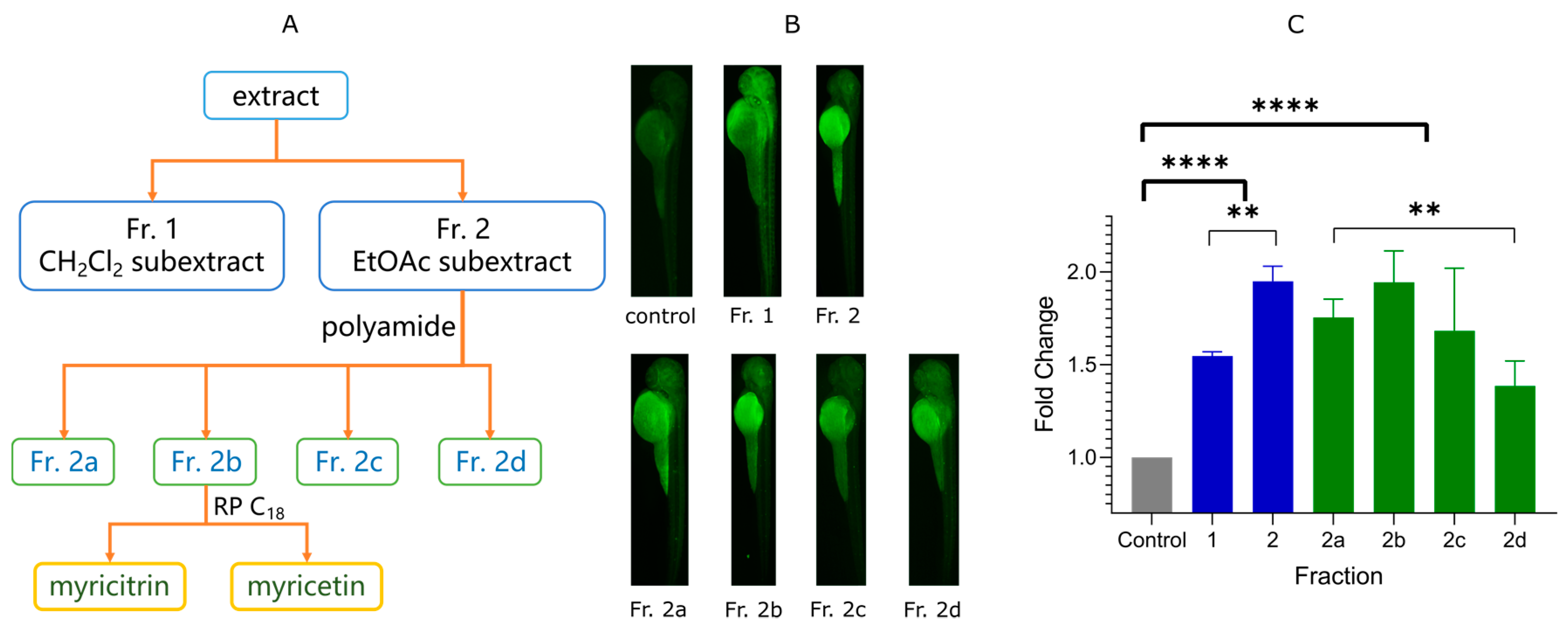
2.1. Bioactivity-Guided Isolation
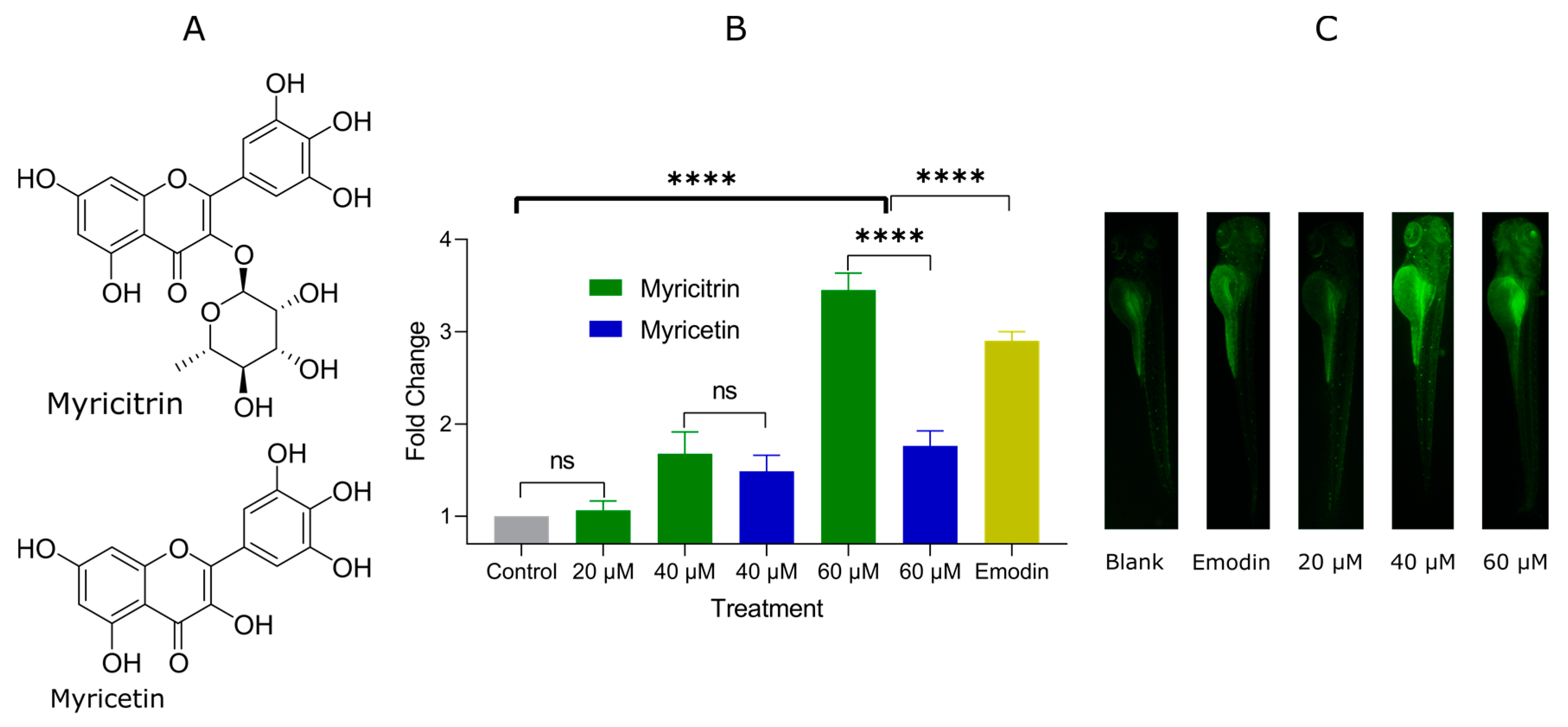
2.2. Glucose Uptake Promotion of Myricitrin and Myricetin
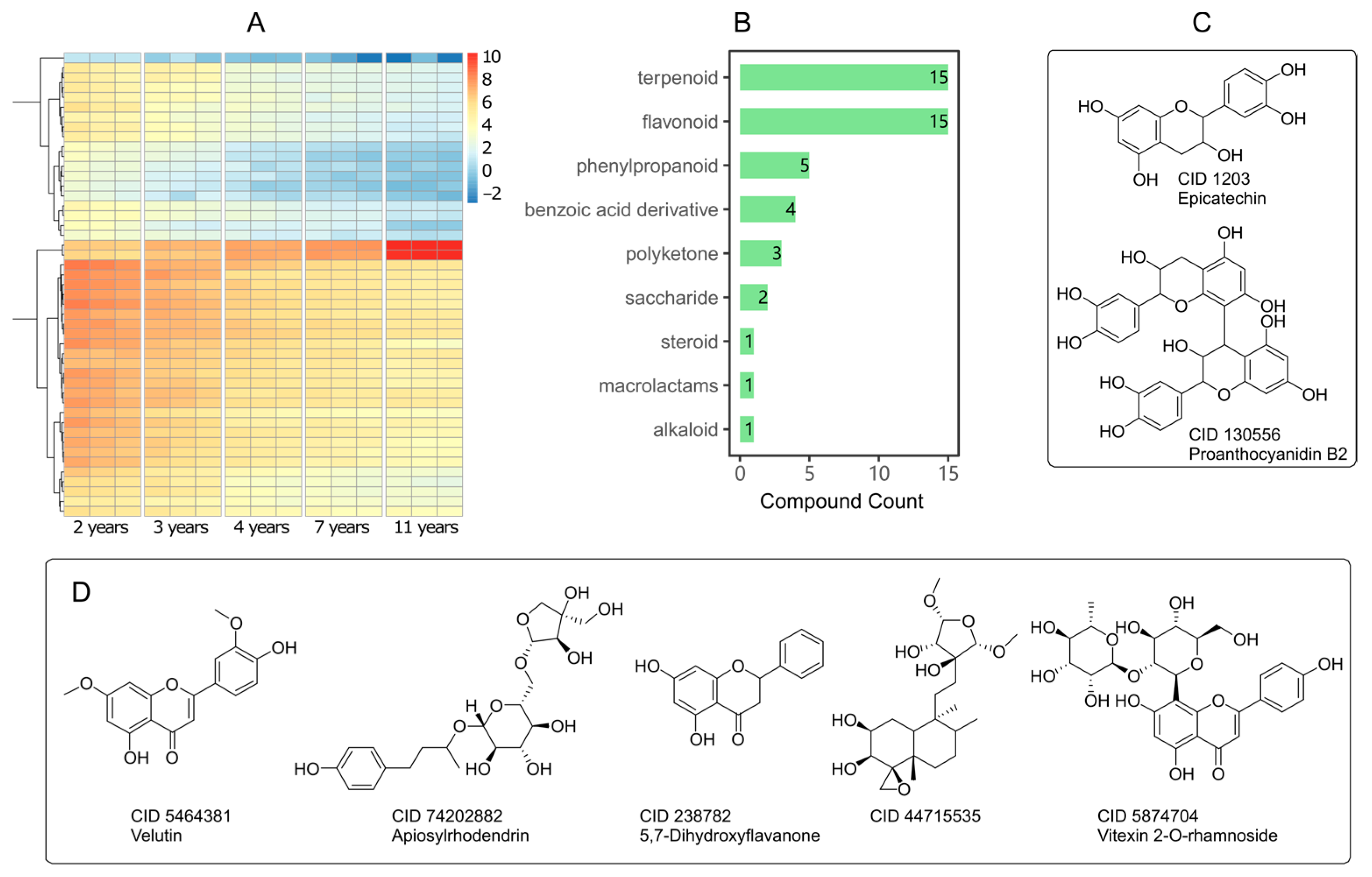
2.3. LC-MS/MS Profiling of Leaves Components form Different Age Trees
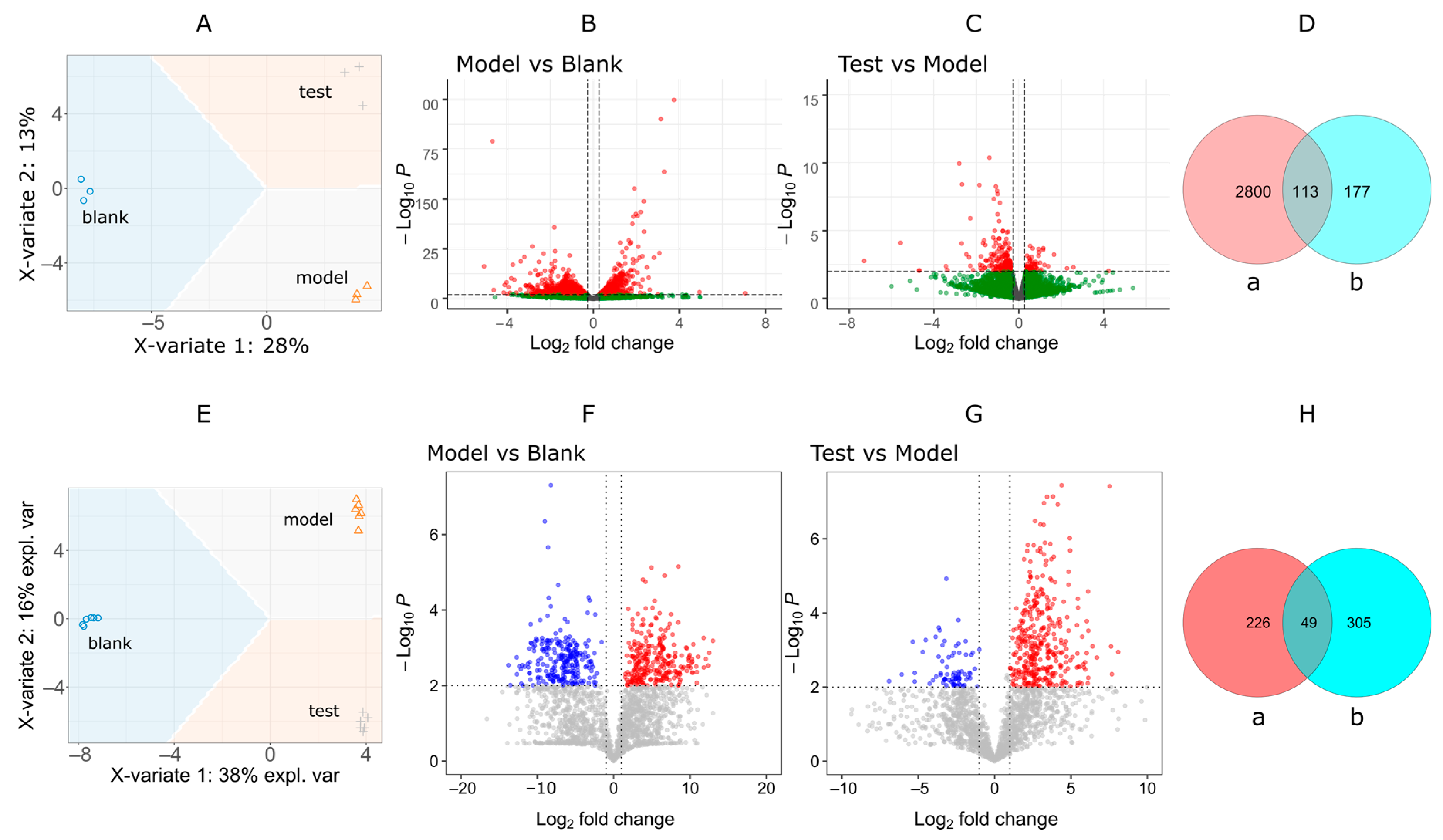
2.4. Pathway of Myricitrn Effects Based on Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Investigation
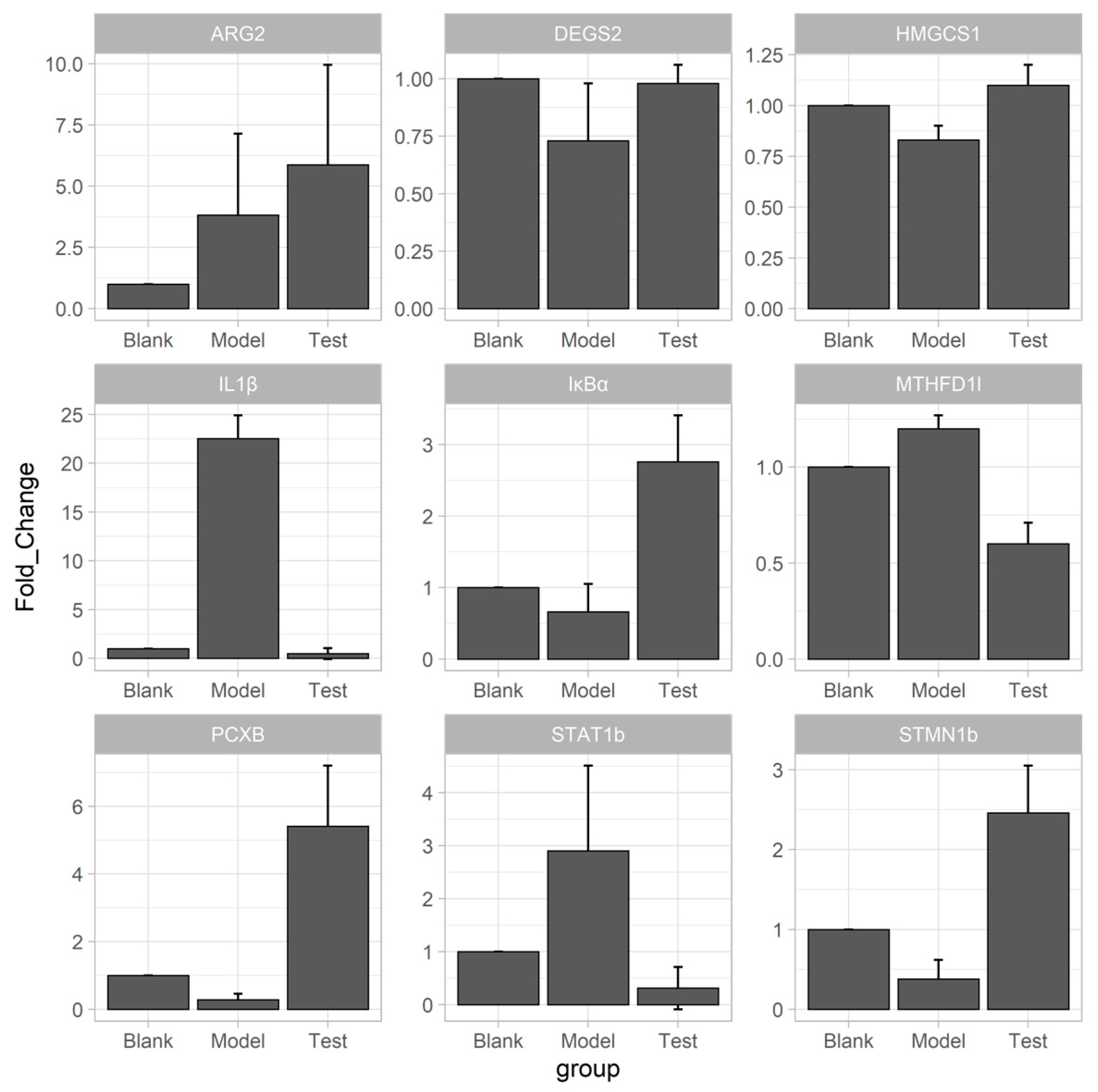
2.5. qRT-PCR Verification
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Bio-Guided Isolation of Myricitrin
3.2.1. Myricitrin
3.2.2. Myricetin
3.3. HPLC-DAD Profiling of A. truncatum Leaves
3.4. Zebrafish Maintenance
3.5. Insulin Mimetic Bioassay on Zebrafish Larvae
3.6. LC-MS/MS Analysis of A. truncatum Leaves
3.7. Zebrafish Larvae RNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
3.8. Zebrafish Larvae Metabonomics Analysis
3.9. qRT-PCR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Diabetes Federation Annual Report 2019. Available online: https://idf.org/our-activities/advocacy-awareness/resources-and-tools/164:idf-annual-report-2019.html (accessed on 7 June 2021).
- Miaffo, D.; Ntchapda, F.; Mahamad, T.A.; Maidadi, B.; Kamanyi, A. Hypoglycemic, Antidyslipidemic and Antioxydant Effects of Vitellaria paradoxa Barks Extract on High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Rats. Metab. Open 2021, 9, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and Regional Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2019 and Projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldenberg, J.Z.; Day, A.; Brinkworth, G.D.; Sato, J.; Yamada, S.; Jönsson, T.; Beardsley, J.; Johnson, J.A.; Thabane, L.; Johnston, B.C. Efficacy and Safety of Low and Very Low Carbohydrate Diets for Type 2 Diabetes Remission: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Published and Unpublished Randomized Trial Data. BMJ 2021, 372, m4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Xuan, L.; Dai, H.; Zhu, W.; Deng, C.; Wang, T.; Li, M.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, Y.; Lu, J.; et al. Fruit Intake, Genetic Risk and Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Gene–Diet Interaction Analysis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, H.M.; Mathew, T.C.; Al-Zaid, N.S. Efficacy of Low-Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Med. Princ. Pract. 2020, 30, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jung, D.-W.; Kim, W.-H.; Um, J.-I.; Yim, S.-H.; Oh, W.K.; Williams, D.R. Development of a Highly Visual, Simple, and Rapid Test for the Discovery of Novel Insulin Mimetics in Living Vertebrates. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Kong, H.; Jin, M.; Li, X.; Stoika, R.; Lin, H.; Liu, K. Synthesis of Disaccharide Modified Berberine Derivatives and Their Anti-Diabetic Investigation in Zebrafish Using a Fluorescence-Based Technology. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 3563–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarque, D.P.; Dusi, R.G.; de Sousa, F.D.M.; Grossi, S.M.; Silvério, M.R.S.; Lopes, N.P.; Espindola, L.S. Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Approach in the Isolation of Bioactive Natural Products. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leão, T.; Wang, M.; Moss, N.; da Silva, R.; Sanders, J.; Nurk, S.; Gurevich, A.; Humphrey, G.; Reher, R.; Zhu, Q.; et al. A Multi-Omics Characterization of the Natural Product Potential of Tropical Filamentous Marine Cyanobacteria. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Xia, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H. Multi-Omics and Temporal Dynamics Profiling Reveal Disruption of Central Metabolism in Helicobacter pylori on Bismuth Treatment. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 7488–7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pulley, J.M.; Rhoads, J.P.; Jerome, R.N.; Challa, A.P.; Erreger, K.B.; Joly, M.M.; Lavieri, R.R.; Perry, K.E.; Zaleski, N.M.; Shirey-Rice, J.K.; et al. Using What We Already Have: Uncovering New Drug Repurposing Strategies in Existing Omics Data. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 60, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Li, A.; Sekiya, M.; Beckmann, N.D.; Quan, X.; Schrode, N.; Fernando, M.B.; Yu, A.; Zhu, L.; Cao, J.; et al. Transformative Network Modeling of Multi-Omics Data Reveals Detailed Circuits, Key Regulators, and Potential Therapeutics for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuron 2021, 109, 257–272.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Gao, X.; Meng, M.; Xue, H.; Qin, X. Multi-Omics Reveals the Mechanisms of Antidepressant-like Effects of the Low Polarity Fraction of Bupleuri Radix. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 256, 112806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Rybalov, L.; Negrin, A.; Morcol, T.; Long, W.; Myers, A.K.; Isaac, G.; Yuk, J.; Kennelly, E.J.; Long, C. Metabolic Profiling of Different Parts of Acer truncatum from the Mongolian Plateau Using UPLC-QTOF-MS with Comparative Bioactivity Assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1585–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yin, P.; Fan, H.; Xue, Q.; Li, K.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y. Response Surface Methodology Optimization of Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of Acer truncatum Leaves for Maximal Phenolic Yield and Antioxidant Activity. Molecules 2017, 22, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Tian, W.; Wu, L.; Cao, X.; Ito, Y. Isolation of Quercetin-3-O-l-Rhamnoside from Acer truncatum Bunge by High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1070, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Morcol, T.; Liu, B.; Shi, M.; Kennelly, E.J.; Long, C. GC–MS, UPLC-QTOF-MS, and Bioactivity Characterization of Acer truncatum Seeds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 138, 111480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.-P.; Ni, W.; Dong, J.-Y.; Li, J.-Z.; Chen, C.-X.; Liu, H.-Y. A New Neolignan Glycoside from the Leaves of Acer truncatum. Molecules 2006, 11, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delvecchio, C.; Tiefenbach, J.; Krause, H.M. The Zebrafish: A Powerful Platform for In Vivo, HTS Drug Discovery. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2011, 9, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jijie, R.; Mihalache, G.; Balmus, I.-M.; Strungaru, S.-A.; Baltag, E.S.; Ciobica, A.; Nicoara, M.; Faggio, C. Zebrafish as a Screening Model to Study the Single and Joint Effects of Antibiotics. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, K.E.; Bouwer, M.F.; Louters, L.L.; Looyenga, B.D. Cellular Binding and Uptake of Fluorescent Glucose Analogs 2-NBDG and 6-NBDG Occurs Independent of Membrane Glucose Transporters. Biochimie 2021, 190, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.W.; Park, E.J.; Cho, H.M.; An, J.-P.; Chin, Y.W.; Kim, J.; Sung, S.H.; Oh, W.K. Glucose Uptake-Stimulating Galloyl Ester Triterpenoids from Castanopsis sieboldii. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 3093–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.H.; Lee, J.; Jung, D.-W.; Williams, D.R. Visualizing Sweetness: Increasingly Diverse Applications for Fluorescent-Tagged Glucose Bioprobes and Their Recent Structural Modifications. Sensors 2012, 12, 5005–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, S.-K.; Kim, Y.-C.; Takaya, Y.; Terashima, K.; Niwa, M. Novel Flavonol Glycoside, 7-O-Methyl Mearnsitrin, from Sageretia theezans and Its Antioxidant Effect. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 4664–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, C.; Ahn, E.-K.; Kang, J.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Oh, J.S.; Hong, S.S. Excavasides A and B, Two New Flavonoid Glycosides from Clausena excavata Burm. f. (Rutaceae). Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 20, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Kim, S.R.; Jung, U.J. Myricitrin Ameliorates Hyperglycemia, Glucose Intolerance, Hepatic Steatosis, and Inflammation in High-Fat Diet/Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tripathi, A.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Gauglitz, J.M.; Wang, M.; Dührkop, K.; Nothias-Esposito, M.; Acharya, D.D.; Ernst, M.; van der Hooft, J.J.J.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Chemically Informed Analyses of Metabolomics Mass Spectrometry Data with Qemistree. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reher, R.; Kim, H.W.; Zhang, C.; Mao, H.H.; Wang, M.; Nothias, L.-F.; Caraballo-Rodriguez, A.M.; Glukhov, E.; Teke, B.; Leao, T.; et al. A Convolutional Neural Network-Based Approach for the Rapid Annotation of Molecularly Diverse Natural Products. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4114–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.C.; Ibáñez, R.; Nothias, L.-F.; Caraballo-Rodríguez, A.M.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Gutiérrez, M. Metabolites from Microbes Isolated from the Skin of the Panamanian Rocket Frog Colostethus Panamansis (Anura: Dendrobatidae). Metabolites 2020, 10, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannochio-Russo, H.; Bueno, P.C.P.; Bauermeister, A.; de Almeida, R.F.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Cavalheiro, A.J.; Bolzani, V.S. Can Statistical Evaluation Tools for Chromatographic Method Development Assist in the Natural Products Workflow? A Case Study on Selected Species of the Plant Family Malpighiaceae. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 3239–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Li, K.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, L.; Liu, L.; Li, M.; Ren, H.; Liu, X.; Fang, C.; et al. Cross-Species Comparison of Metabolomics to Decipher the Metabolic Diversity in Ten Fruits. Metabolites 2021, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal Component Analysis: A Review and Recent Developments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lê Cao, K.-A.; Boitard, S.; Besse, P. Sparse PLS Discriminant Analysis: Biologically Relevant Feature Selection and Graphical Displays for Multiclass Problems. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.S.; Han, M.S.; Chung, K.W.; Kim, S.; Kim, E.; Kim, M.J.; Jang, E.; Lee, H.A.; Youn, J.; Akira, S.; et al. Toll-like Receptor 2 Senses β-Cell Death and Contributes to the Initiation of Autoimmune Diabetes. Immunity 2007, 27, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aldridge, S. Toll-like Receptor Blocker Slows Beta Cell Death in Type 1 Diabetes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, S.; Ma, Y.; Bai, X.-Y.; Chen, X. Role of Toll-like Receptors in Diabetic Renal Lesions in a Miniature Pig Model. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1400183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, F.; Pham, M.; Luttrell, I.; Bannerman, D.D.; Tupper, J.; Thaler, J.; Hawn, T.R.; Raines, E.W.; Schwartz, M.W. Toll-Like Receptor-4 Mediates Vascular Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Diet-Induced Obesity. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroeder, A.B.; Dobson, E.T.A.; Rueden, C.T.; Tomancak, P.; Jug, F.; Eliceiri, K.W. The ImageJ Ecosystem: Open-Source Software for Image Visualization, Processing, and Analysis. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-Independent MS/MS Deconvolution for Comprehensive Metabolome Analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, Y.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. SOAP: Short Oligonucleotide Alignment Program. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 713–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A Fast Spliced Aligner with Low Memory Requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate Transcript Quantification from RNA-Seq Data with or without a Reference Genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Yuan, Y. Lignin Involvement in Programmed Changes in Peach-Fruit Texture Indicated by Metabolite and Transcriptome Analyses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12627–12640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

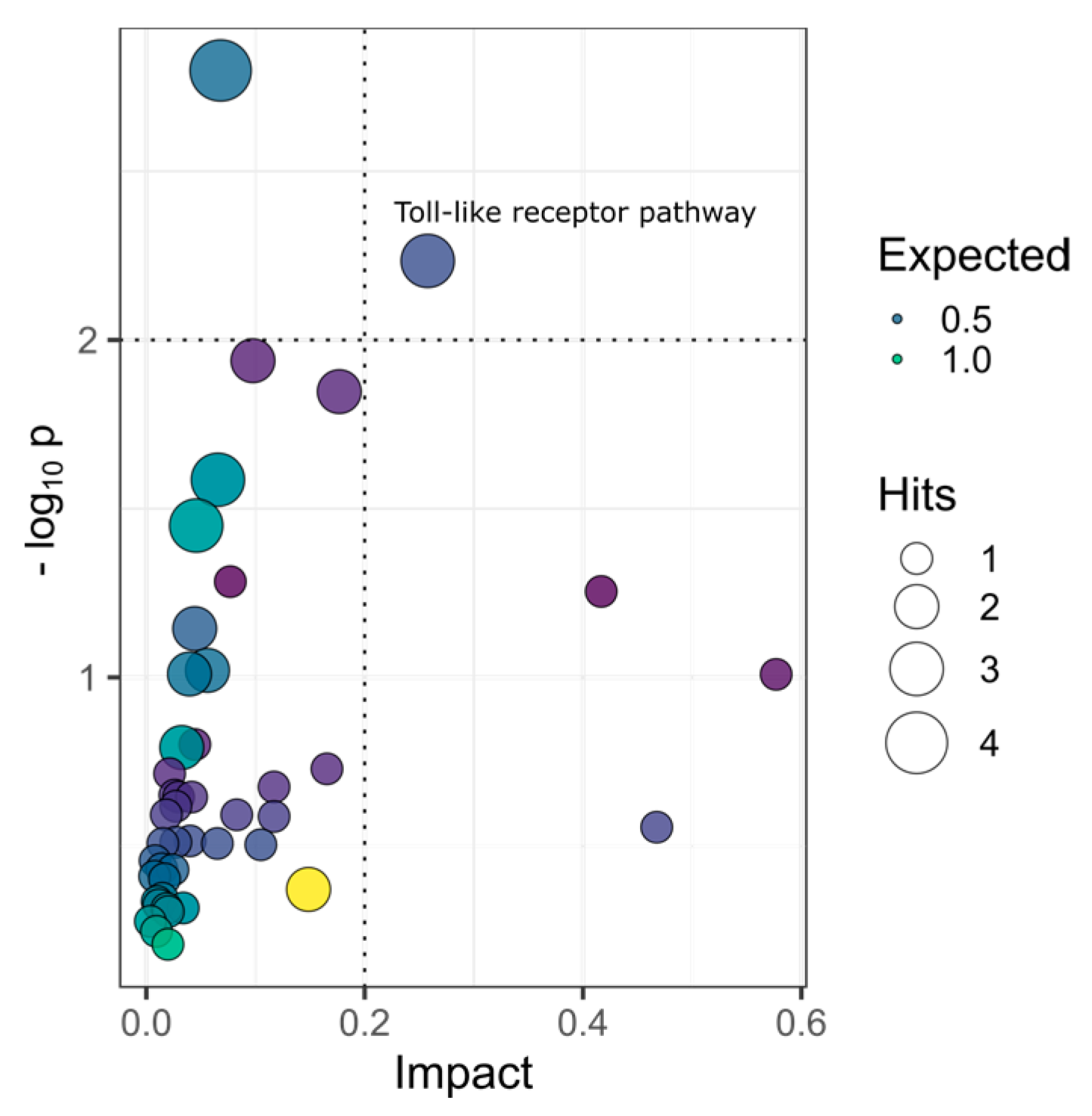
| Pathway | −logP | Impact | Matched Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| One carbon pool by folate | 1.01 | 0.58 | MTHFD1l |
| Sphingolipid metabolism | 0.57 | 0.47 | DEGS2 |
| Synthesis and degradation of ketone bodies | 1.25 | 0.42 | HMGCS1 |
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 2.23 | 0.26 | IL1β; STAT1b; IκBα |
| Arginine biosynthesis | 1.85 | 0.18 | ARG2, L-Ornithine |
| Citrate cycle (TCA cycle) | 0.73 | 0.16 | PCXB |
| MAPK signaling pathway | 0.37 | 0.15 | STMN1b; IL1β |
| PPAR signaling pathway | 0.59 | 0.12 | HMGCS1 |
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.68 | 0.12 | IκBα |
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | 0.50 | 0.10 | IκBα |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.-Y.; Liu, Y.-H.; Liu, D.-Z.; Xu, J.-Y.; Zhang, Q. Insulin-Mimic Components in Acer truncatum Leaves: Bio-Guided Isolation, Annual Variance Profiling and Regulating Pathway Investigated by Omics. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070662
Zhang X-Y, Liu Y-H, Liu D-Z, Xu J-Y, Zhang Q. Insulin-Mimic Components in Acer truncatum Leaves: Bio-Guided Isolation, Annual Variance Profiling and Regulating Pathway Investigated by Omics. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(7):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070662
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiao-Yue, Yi-Han Liu, Da-Zhi Liu, Jia-Yang Xu, and Qiang Zhang. 2021. "Insulin-Mimic Components in Acer truncatum Leaves: Bio-Guided Isolation, Annual Variance Profiling and Regulating Pathway Investigated by Omics" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 7: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070662
APA StyleZhang, X.-Y., Liu, Y.-H., Liu, D.-Z., Xu, J.-Y., & Zhang, Q. (2021). Insulin-Mimic Components in Acer truncatum Leaves: Bio-Guided Isolation, Annual Variance Profiling and Regulating Pathway Investigated by Omics. Pharmaceuticals, 14(7), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070662







