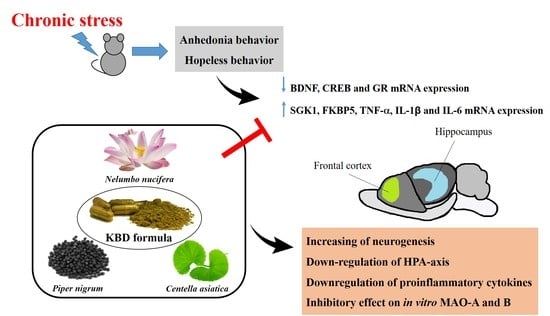
Merging the Multi-Target Effects of Kleeb Bua Daeng, a Thai Traditional Herbal Formula in Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Depression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
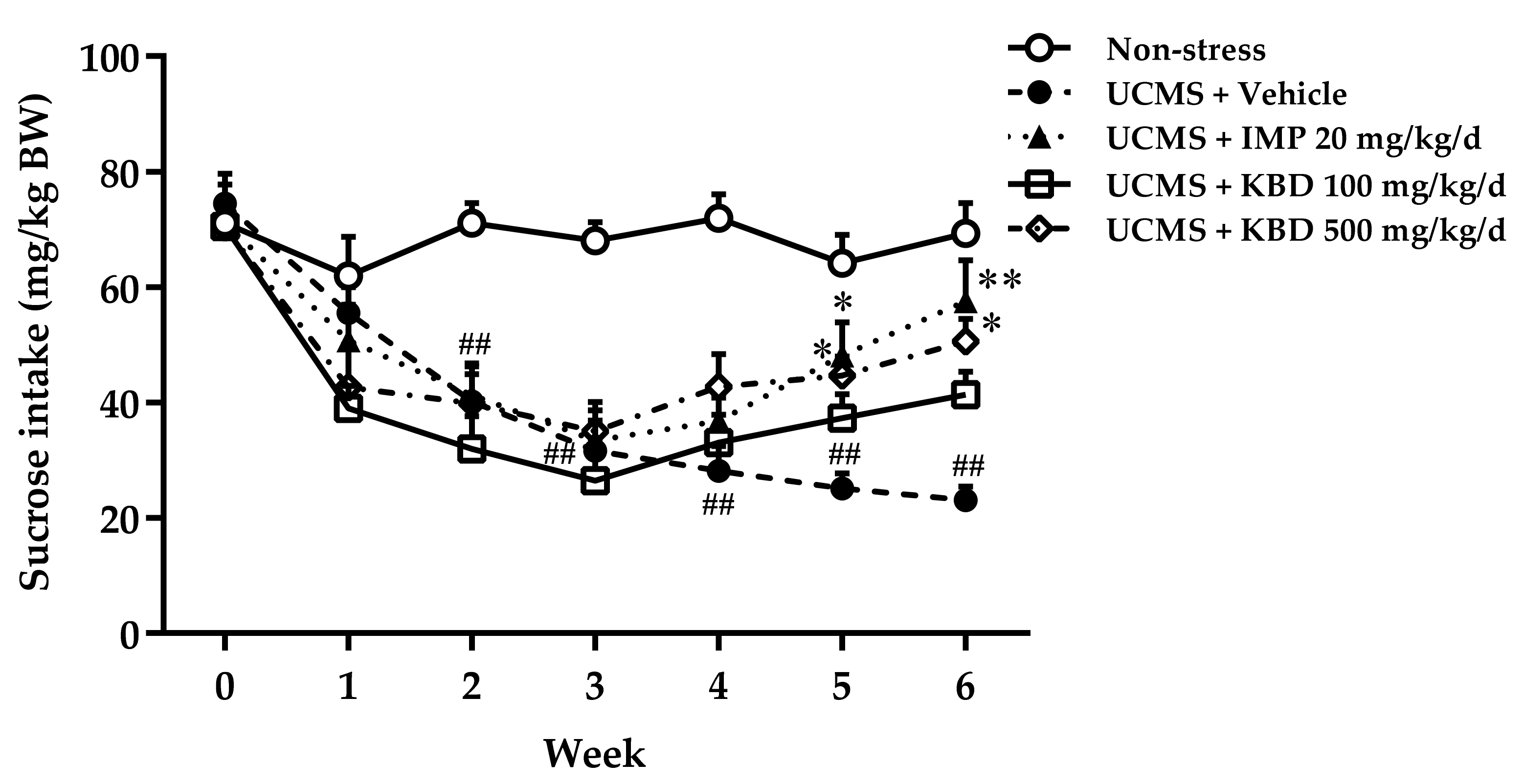
2.1. Effects of Kleeb Bua Daeng Formula on UCMS-Induced Anhedonia in Mice Using the Sucrose Preference Test
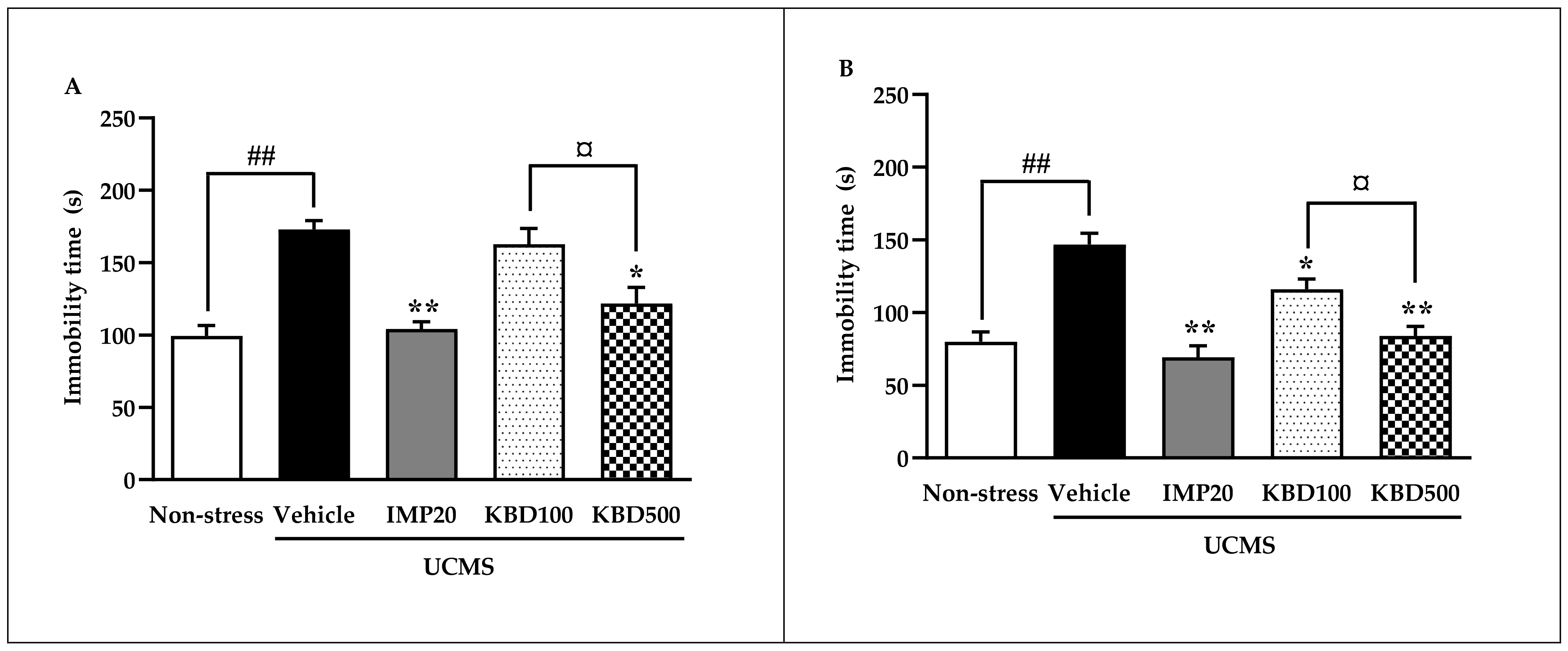
2.2. Effects of Kleeb Bua Daeng Formula on UCMS-Induced Hopeless Behavior in Mice Using the Forced Swimming and Tail Suspension Tests
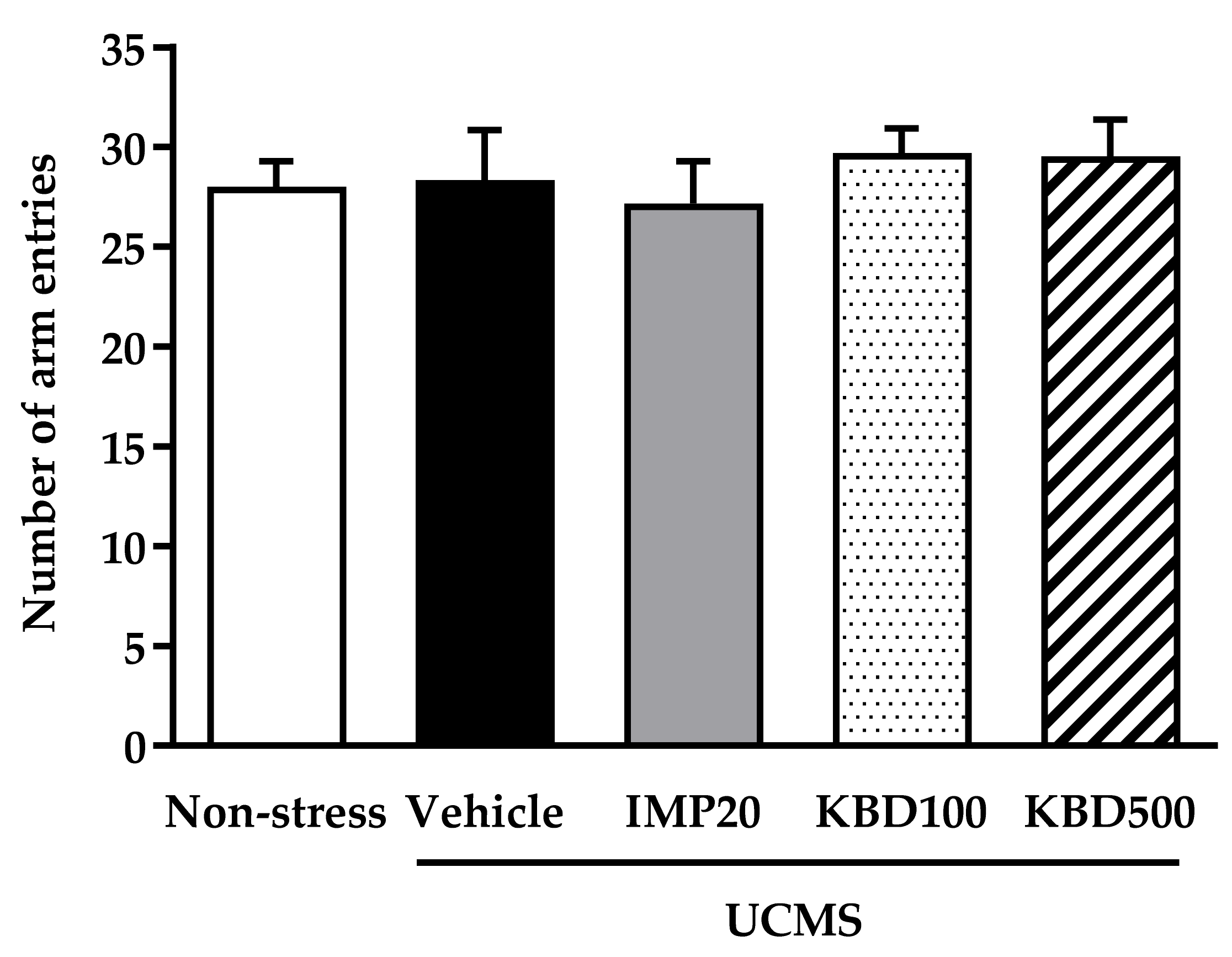
2.3. Effects of UCMS and Kleeb Bua Daeng Formula on the Locomotor Activity of Mice Using the Y-Maze Test
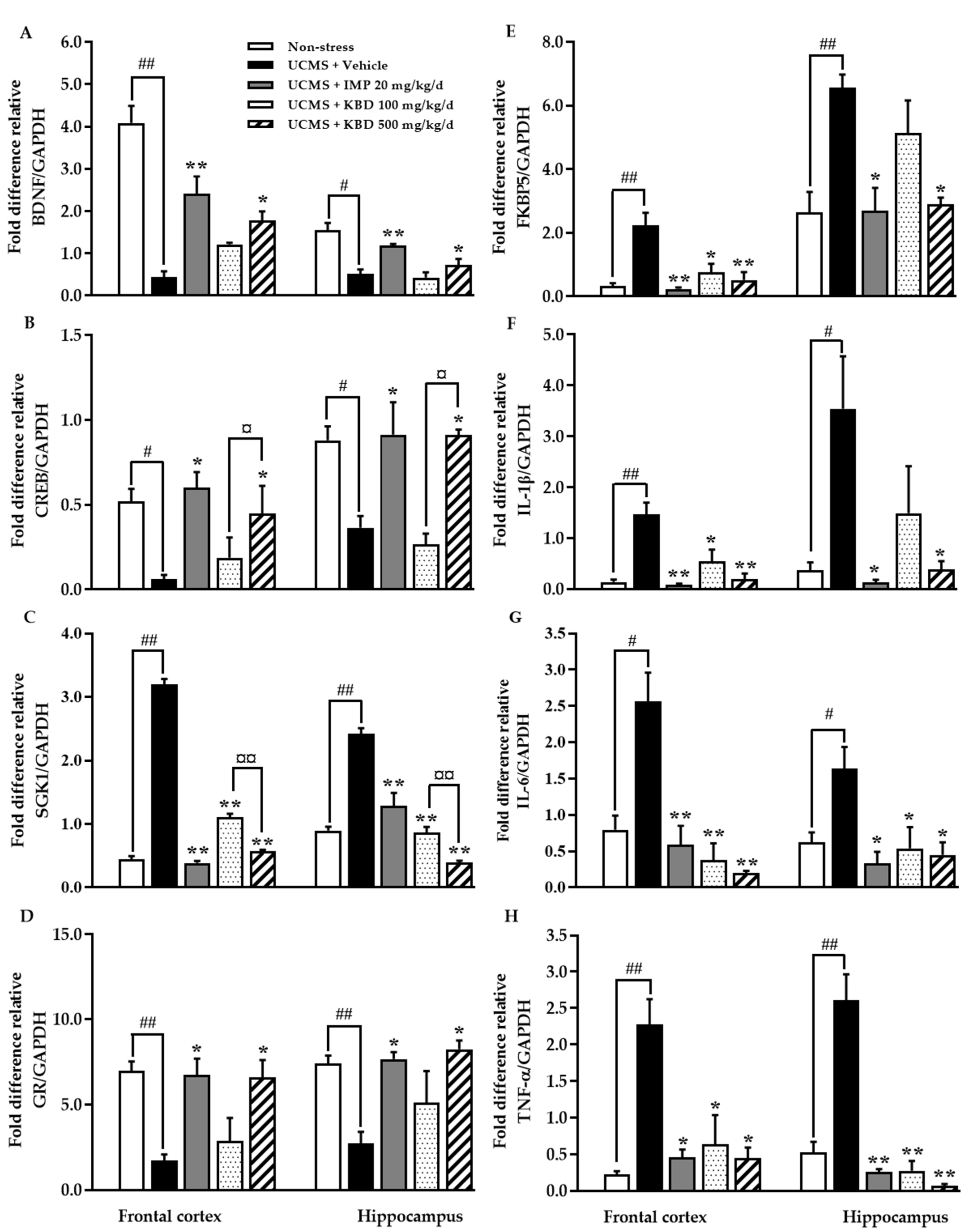
2.4. Effect of Kleeb Bua Daeng Formula on UCMS-Induced Changes to the Frontal Cortex and Hippocampus Brain Regions of Mice
2.5. Effect of Kleeb Bua Daeng and Its Component Extracts on Monoamine Oxidase (MAO)-A and MAO-B Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Kleeb Bua Daeng Extract
4.2. Animals and Ethics
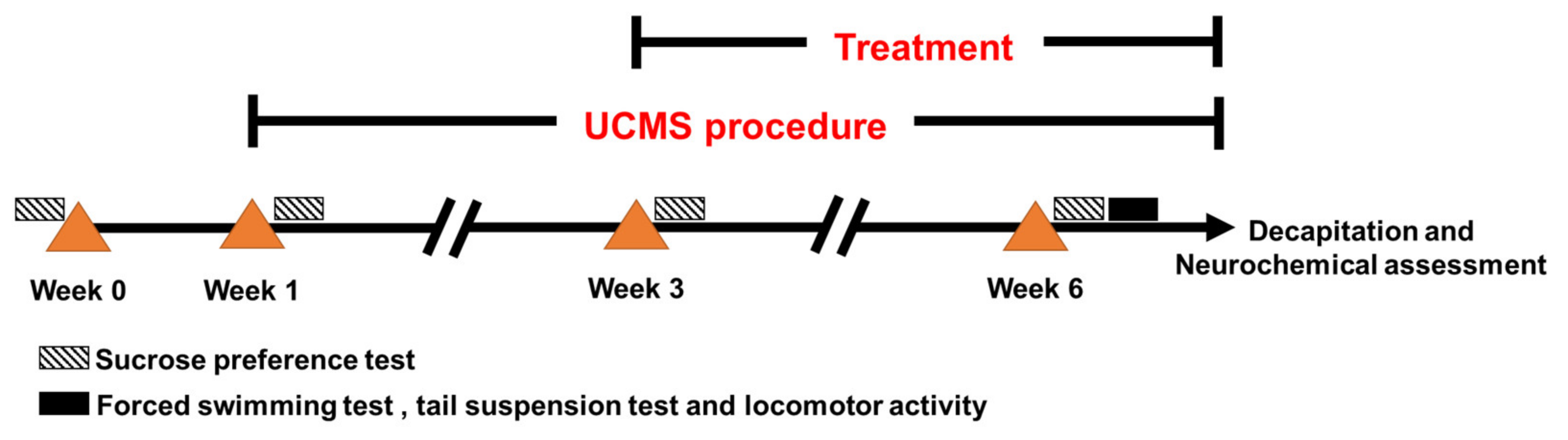
4.3. Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress
4.4. Drug Administration
4.5. Sucrose Preference Test
4.6. Forced Swimming Test
4.7. Tail Suspension Test
4.8. Locomotor Activity
4.9. Quantitative Real Time PCR
4.10. Human Monoamine Oxidase A and B Inhibitory Activity Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarris, J.; Panossian, A.; Schweitzer, I.; Stough, C.; Scholey, A. Herbal medicine for depression, anxiety and insomnia: A review of psychopharmacology and clinical evidence. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 21, 841–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Bae, H. Therapeutic effects of phytochemicals and medicinal herbs on depression. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, J.; Keshavan, M. The neurobiology of depression: An integrated view. Asian J. Psychiatry 2017, 27, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Cui, R. The effects of psychological stress on depression. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuki, D.; Matsumoto, K.; Tanaka, K.; Le, X.T.; Fujiwara, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Higuchi, Y. Antidepressant-like effect of Butea superba in mice exposed to chronic mild stress and its possible mechanism of action. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 156, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daodee, S.; Monthakantirat, O.; Ruengwinitwong, K.; Gatenakorn, K.; Maneenet, J.; Khamphukdee, C.; Sekeroglu, N.; Chulikhit, Y.; Kijjoa, A. Effects of the ethanol extract of Dipterocarpus alatus leaf on the unpredictable chronic mild stress-induced depression in ICR mice and its possible mechanism of action. Molecules 2019, 24, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, F.P.; Brown, E.S. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in major depressive disorder. Prim. Care Companion J. Clin. Psychiatry 2001, 3, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, J.P.; McKlveen, J.M.; Ghosal, S.; Kopp, B.; Wulsin, A.; Makinson, R.; Scheimann, J.; Myers, B. Regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical stress response. In Comprehensive Physiology; Terjung, R., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 603–621. ISBN 9780470650714. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, M.A.C.; Wand, G. Stress and the HPA axis. Alcohol Res. Curr. Rev. 2012, 34, 468–483. [Google Scholar]
- Gjerstad, J.K.; Lightman, S.; Spiga, F. Role of glucocorticoid negative feedback in the regulation of HPA axis pulsatility. Stress 2018, 21, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bodegom, M.; Homberg, J.R.; Henckens, M.J.A.G. Modulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis by early life stress exposure. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, G.R.; Gassen, N.C.; Rein, T. The FKBP51 glucocorticoid receptor co-chaperone: Regulation, function, and implications in health and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, J.C.; Zhang, B.; Koren, J.; Blair, L.; Dickey, C.A. The role of FKBP5 in mood disorders: Action of FKBP5 on steroid hormone receptors leads to questions about its evolutionary importance. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 12, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Numakawa, T.; Odaka, H.; Adachi, N. Impact of glucocorticoid on neurogenesis. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anacker, C.; Cattaneo, A.; Musaelyan, K.; Zunszain, P.; Horowitz, M.; Molteni, R.; Luoni, A.; Calabrese, F.; Tansey, K.; Gennarelli, M.; et al. Role for the kinase SGK1 in stress, depression, and glucocorticoid effects on hippocampal neurogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8708–8713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maydych, V. The interplay between stress, inflammation, and emotional attention: Relevance for depression. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-S.; Kim, W.-Y.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-B.; Lee, D.-S.; Son, C.-G. Antidepressant-like activity of Myelophil via attenuation of microglial-mediated neuroinflammation in mice undergoing unpredictable chronic mild stress. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.H.; Raison, C.L. The role of inflammation in depression: From evolutionary imperative to modern treatment target. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hritcu, L.; Noumedem, J.A.; Cioanca, O.; Hancianu, M.; Kuete, V.; Mihasan, M. Methanolic Extract of Piper nigrum fruits improves memory impairment by decreasing brain oxidative stress in amyloid beta(1–42) rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 34, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochmah, M.A.; Harini, I.M.; Septyaningtrias, D.E.; Sari, D.C.R.; Susilowati, R. Centella asiatica prevents increase of hippocampal tumor necrosis factor-α independently of its effect on brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rat model of chronic stress. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneenet, J.; Daodee, S.; Monthakantirat, O.; Boonyarat, C.; Khamphukdee, C.; Kwankhao, P.; Pitiporn, S.; Awale, S.; Chulikhit, Y.; Kijjoa, A. Kleeb Bua Daeng, a Thai traditional herbal formula, ameliorated unpredictable chronic mild stress-induced cognitive impairment in ICR mice. Molecules 2019, 24, 4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chheng, C.; Waiwut, P.; Plekratoke, K.; Chulikhit, Y.; Daodee, S.; Monthakantirat, O.; Pitiporn, S.; Musigavong, N.; Kwankhao, P.; Boonyarat, C. Multitarget activities of Kleeb Bua Daeng, a Thai traditional herbal formula, against Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Harbi, K.S. Treatment-resistant depression: Therapeutic trends, challenges, and future directions. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2012, 6, 369–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penn, E.; Tracy, D.K. The drugs don’t work? Antidepressants and the current and future pharmacological management of depression. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 2, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Tao, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, W.; Huang, F.; Wu, X. Long-term stability and characteristics of behavioral, biochemical, and molecular markers of three different rodent models for depression. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, P. The chronic mild stress (CMS) model of depression: History, evaluation and usage. Neurobiol. Stress 2017, 6, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Wang, J.-Y.; Luo, F. Depression shows divergent effects on evoked and spontaneous pain behaviors in rats. J. Pain 2010, 11, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzagalli, D.A. Depression, stress, and anhedonia: Toward a synthesis and integrated model. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2014, 10, 393–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grippo, A.J.; Beltz, T.G.; Weiss, R.M.; Johnson, A.K. The effects of chronic fluoxetine treatment on chronic mild stress-induced cardiovascular changes and anhedonia. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T.; Bisgaard, C.; Wiborg, O. Biomarkers of anhedonic-like behavior, antidepressant drug refraction, and stress resilience in a rat model of depression. Neuroscience 2011, 196, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, depression, and physical activity: Making the neuroplastic connection. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapolsky, R.M. Depression, antidepressants, and the shrinking hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12320–12322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowiański, P.; Lietzau, G.; Czuba, E.; Waśkow, M.; Steliga, A.; Moryś, J. BDNF: A key factor with multipotent impact on brain signaling and synaptic plasticity. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Wang, W.; Gong, T.; Zhang, H.; Tao, W.; Xue, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, G. PKA-CREB-BDNF signaling regulated long lasting antidepressant activities of Yueju but not ketamine. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Sun, L.H.; Yang, W.; Cui, R.J.; Xu, S.B. The role of BDNF in the neuroimmune axis regulation of mood disorders. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colucci-D’Amato, L.; Speranza, L.; Volpicelli, F. Neurotrophic factor BDNF, physiological functions and therapeutic potential in depression, neurodegeneration and brain cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.; Vaidya, V.A. Cyclic AMP response element binding protein and brain-derived neurotrophic factor: Molecules that modulate our mood? J. Biosci. 2006, 31, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numakawa, T.; Odaka, H.; Adachi, N. Actions of brain-derived neurotrophin factor in the neurogenesis and neuronal function, and its involvement in the pathophysiology of brain diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Ku, B.; Tie, L.; Yao, H.; Jiang, W.; Ma, X.; Li, X. Curcumin reverses the effects of chronic stress on behavior, the HPA axis, BDNF expression and phosphorylation of CREB. Brain Res. 2006, 1122, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: A key molecule for memory in the healthy and the pathological brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anacker, C.; Zunszain, P.; de Carvalho, L.A.; Pariante, C.M. The glucocorticoid receptor: Pivot of depression and of antidepressant treatment? Psychoneuroendocrinology 2011, 36, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dattilo, V.; Amato, R.; Perrotti, N.; Gennarelli, M. The emerging role of SGK1 (Serum- and Glucocorticoid-Regulated Kinase 1) in major depressive disorder: Hypothesis and mechanisms. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, E.B. The role of FKBP5, a co-chaperone of the glucocorticoid receptor in the pathogenesis and therapy of affective and anxiety disorders. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, S186–S195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skupio, U.; Tertil, M.; Sikora, M.; Golda, S.; Wawrzczak-Bargiela, A.; Przewlocki, R. Behavioral and molecular alterations in mice resulting from chronic treatment with dexamethasone: Relevance to depression. Neuroscience 2015, 286, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, K.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, X.; Du, Y.; Sun, J.; Yi, T.; Dong, J.; Liu, B. Icariin alters the expression of glucocorticoid receptor, FKBP5 and SGK1 in rat brains following exposure to chronic mild stress. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, G.; Calabrese, F.; Anacker, C.; Racagni, G.; Pariante, C.M.; Riva, M.A. Glucocorticoid receptor and FKBP5 expression is altered following exposure to chronic stress: Modulation by antidepressant treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Yang, P.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Fang, Z.; Wu, C.; Huang, Q.-J. Changes in proinflammatory cytokines and white matter in chronically stressed rats. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Golovatscka, V.; Ennes, H.; Mayer, E.A.; Bradesi, S. Chronic stress-induced changes in pro-inflammatory cytokines and spinal glia markers in the rat: A time course study. Neuroimmunomodulation 2012, 19, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ho, R.C.-M.; Mak, A. Interleukin (IL)-6, tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and soluble interleukin-2 receptors (sIL-2R) are elevated in patients with major depressive disorder: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 139, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-N.; Peng, Y.-L.; -Liu, L.; Wu, T.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lian, Y.-J.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Kelley, K.W.; Jiang, C.-L.; Wang, Y.-X. TNFα mediates stress-induced depression by upregulating indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in a mouse model of unpredictable chronic mild stress. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2015, 26, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Feng, R.; Yang, Y. Changes in the serum levels of inflammatory cytokines in antidepressant drug-naïve patients with major depression. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.H.; Maletic, V.; Raison, C.L. Inflammation and its discontents: The role of cytokines in the pathophysiology of major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, R.K.; Asghar, K.; Kanwal, S.; Zulqernain, A. Role of inflammatory cytokines in depression: Focus on interleukin-1β. Biomed. Rep. 2017, 6, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laban, T.S.; Saadabadi, A. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI); StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Barchas, J.D.; Altemus, M. Monoamine hypotheses of mood disorders. In Basic Neurochemistry: Molecular, Cellular and Medical Aspects, 6th ed.; Siegel, G.J., Agranoff, B.W., Albers, R.W., Fisher, S.K., Uhler, M.D., Eds.; Lippincott-Raven: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Cheng, C.; Xin, C.; Wang, Z. The antidepressant-like effect of flavonoids from Trigonella foenum-graecum seeds in chronic restraint stress mice via modulation of monoamine regulatory pathways. Molecules 2019, 24, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, T.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Y. Asiaticoside produces an antidepressant-like effect in a chronic unpredictable mild stress model of depression in mice, involving reversion of inflammation and the PKA/pCREB/BDNF signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 2364–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-R. Effect of madecassoside on depression behavior of mice and activities of MAO in different brain regions of rats. J. Chin. Integr. Med. 2004, 2, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mao, Q.-Q.; Huang, Z.; Zhong, X.-M.; Xian, Y.-F.; Ip, S.-P. Piperine reverses chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced behavioral and biochemical alterations in rats. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 34, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Lei, S.; Zhou, S.; Jin, L.; Zeng, S.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, H. Luteolin shows antidepressant-like effect by inhibiting and downregulating plasma membrane monoamine transporter (PMAT, Slc29a4). J. Funct. Foods 2019, 54, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Sim, Y.-B.; Han, P.-L.; Lee, J.-K.; Suh, H.-W. Antidepressant-like effect of kaempferol and quercitirin, isolated from Opuntia ficus-indica var. Saboten. Exp. Neurobiol. 2010, 19, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parashar, A.; Mehta, V.; Udayabanu, M. Rutin alleviates chronic unpredictable stress-induced behavioral alterations and hippocampal damage in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 656, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lin, D.; Zhang, C.; Li, G.; Zhang, N.; Ruan, L.; Yan, Q.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Xie, X.; et al. Antidepressant-like effects of ferulic acid: Involvement of serotonergic and norepinergic systems. Metab. Brain Dis. 2014, 30, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeni, A.L.B.; Zomkowski, A.D.E.; Maraschin, M.; Rodrigues, A.L.; Tasca, C.I. Ferulic acid exerts antidepressant-like effect in the tail suspension test in mice: Evidence for the involvement of the serotonergic system. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 679, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Bertin, A.; Jalfre, M. Behavioral despair in mice: A primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1977, 229, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, M.; Jaiswal, M.; Palit, G. Comparative evaluation of forced swim test and tail suspension test as models of negative symptom of schizophrenia in rodents. ISRN Psychiatry 2012, 2012, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steru, L.; Chermat, R.; Thierry, B.; Simon, P. The tail suspension test: A new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology 1985, 85, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantipongpiradet, A.; Monthakantirat, O.; Vipatpakpaiboon, O.; Khampukdee, C.; Umehara, K.; Noguchi, H.; Fujiwara, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Sekeroglu, N.; Kijjoa, A.; et al. Effects of puerarin on the ovariectomy-induced depressive-like behavior in ICR mice and its possible mechanism of action. Molecules 2019, 24, 4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamphukdee, C.; Chulikhit, Y.; Daodee, S.; Monthakantirat, O. Potential of Alternanthera philoxeroides on improvement of anxiety-like behavior induced by ovariectomized mice model. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2017, 51, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
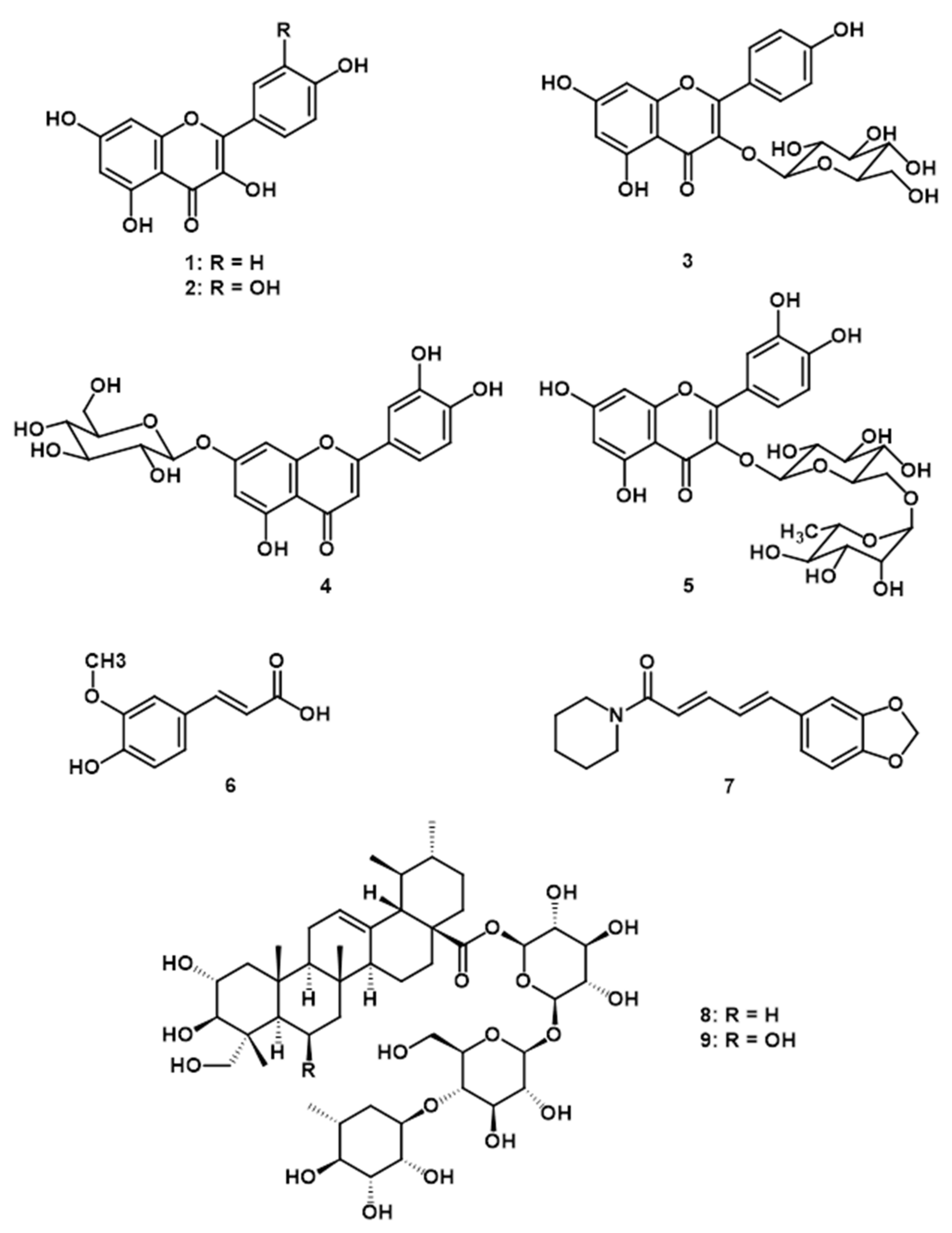
| Extract | IC50 (µg/mL) | Ki (µg/mL) 3 | Si 4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAO-A | MAO-B | MAO-A | MAO-B | MAO-A | MAO-B | |
| KBD | 342.4 ± 0.849 | 110.2 ± 0.546 | 90.223 | 47.425 | 1.903 | 0.526 |
| P. nigrum | 396.7 ± 0.058 | 211.9 ± 0.055 | 104.531 | 97.274 | 1.145 | 0.873 |
| C. asiatica | 127.0 ± 0.065 | 141.3 ± 0.106 | 33.465 | 60.864 | 0.550 | 1.819 |
| N. nucifera | 141.9 ± 0.065 | 412.3 ± 0.220 | 37.391 | 177.594 | 0.211 | 4.750 |
| Clorgyline 1 | 0.0015 ± 0.00001 µM | 2.99 ± 0.162 µM | 0.0004 | 1.288 | 0.00031 | 3213.46 |
| Deprenyl 2 | 687.6 ± 4.879 µM | 0.291 ± 0.044 µM | 181.200 | 0.125 | 1445.58 | 0.0007 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maneenet, J.; Monthakantirat, O.; Daodee, S.; Boonyarat, C.; Chotritthirong, Y.; Kwankhao, P.; Pitiporn, S.; Awale, S.; Chulikhit, Y. Merging the Multi-Target Effects of Kleeb Bua Daeng, a Thai Traditional Herbal Formula in Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Depression. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070659
Maneenet J, Monthakantirat O, Daodee S, Boonyarat C, Chotritthirong Y, Kwankhao P, Pitiporn S, Awale S, Chulikhit Y. Merging the Multi-Target Effects of Kleeb Bua Daeng, a Thai Traditional Herbal Formula in Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Depression. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(7):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070659
Chicago/Turabian StyleManeenet, Juthamart, Orawan Monthakantirat, Supawadee Daodee, Chantana Boonyarat, Yutthana Chotritthirong, Pakakrong Kwankhao, Supaporn Pitiporn, Suresh Awale, and Yaowared Chulikhit. 2021. "Merging the Multi-Target Effects of Kleeb Bua Daeng, a Thai Traditional Herbal Formula in Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Depression" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 7: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070659
APA StyleManeenet, J., Monthakantirat, O., Daodee, S., Boonyarat, C., Chotritthirong, Y., Kwankhao, P., Pitiporn, S., Awale, S., & Chulikhit, Y. (2021). Merging the Multi-Target Effects of Kleeb Bua Daeng, a Thai Traditional Herbal Formula in Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Depression. Pharmaceuticals, 14(7), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070659