Potential Antimetastatic Effect of Timosaponin AIII against Human Osteosarcoma Cells through Regulating the Integrin/FAK/Cofilin Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
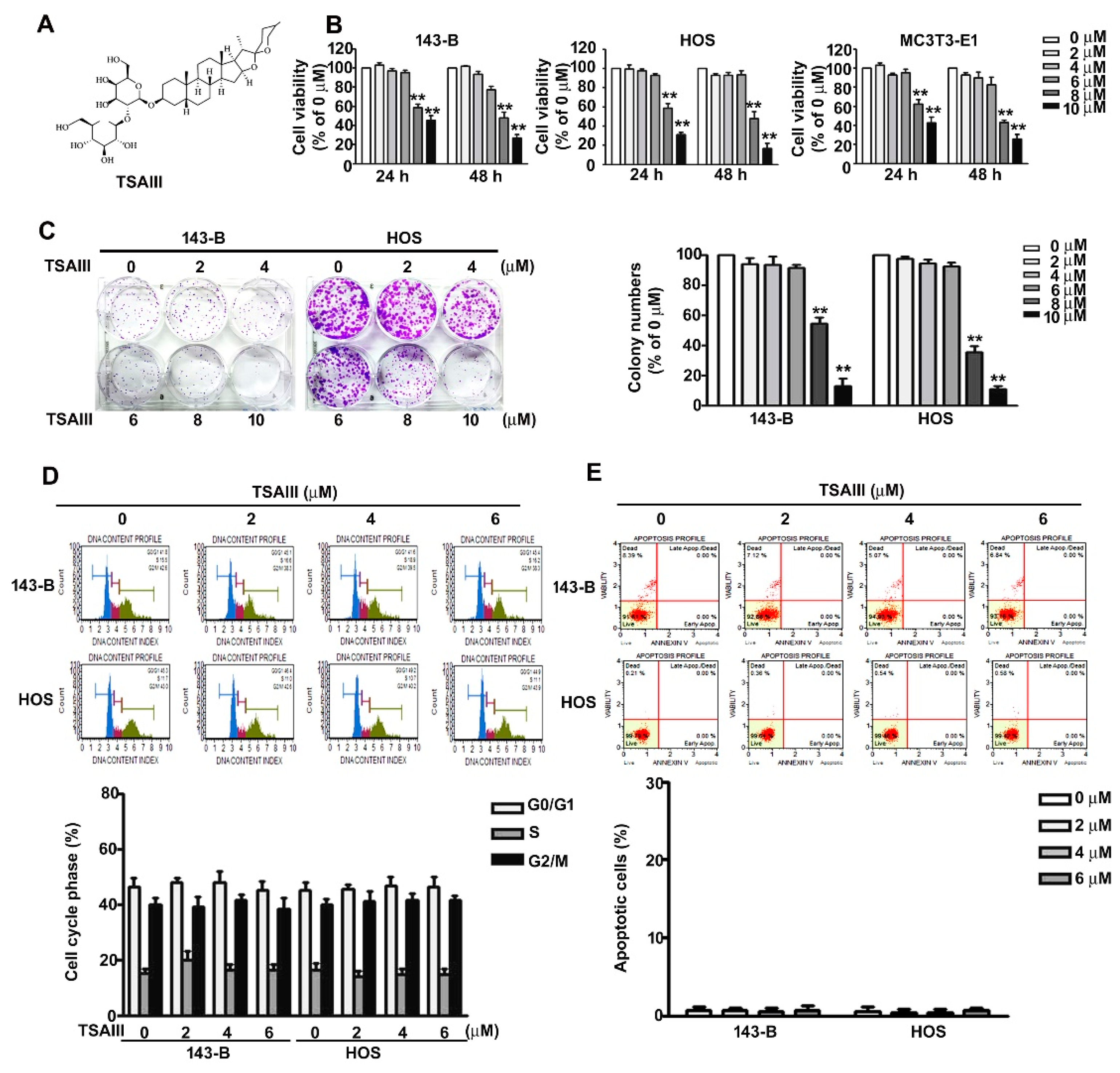
2.1. Effect of TSAIII on Cell Viability in Human Osteosarcoma Cells
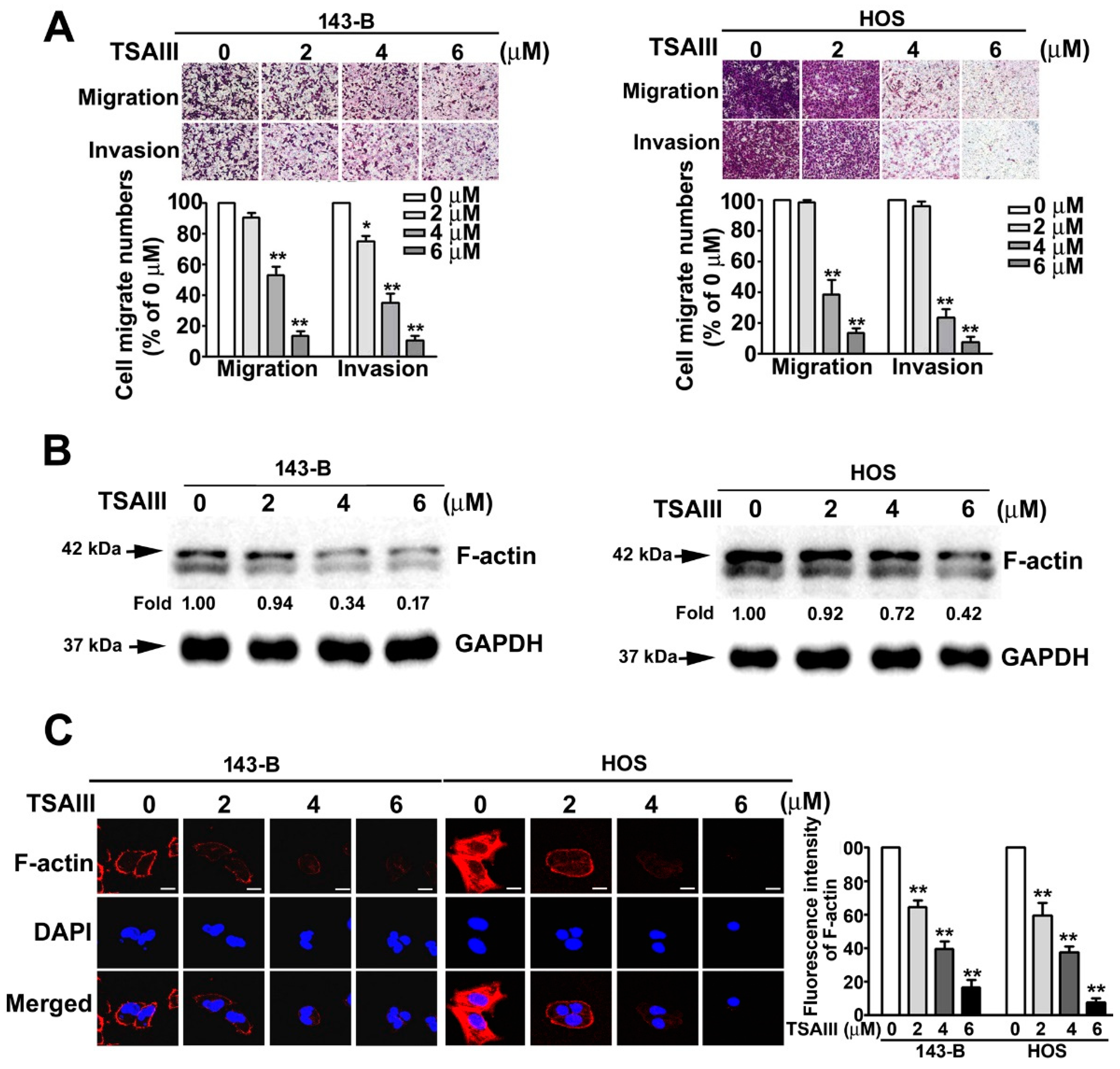
2.2. TSAIII Inhibits Cell Migration, Invasion, and F-Actin Expression in Human Osteosarcoma Cells
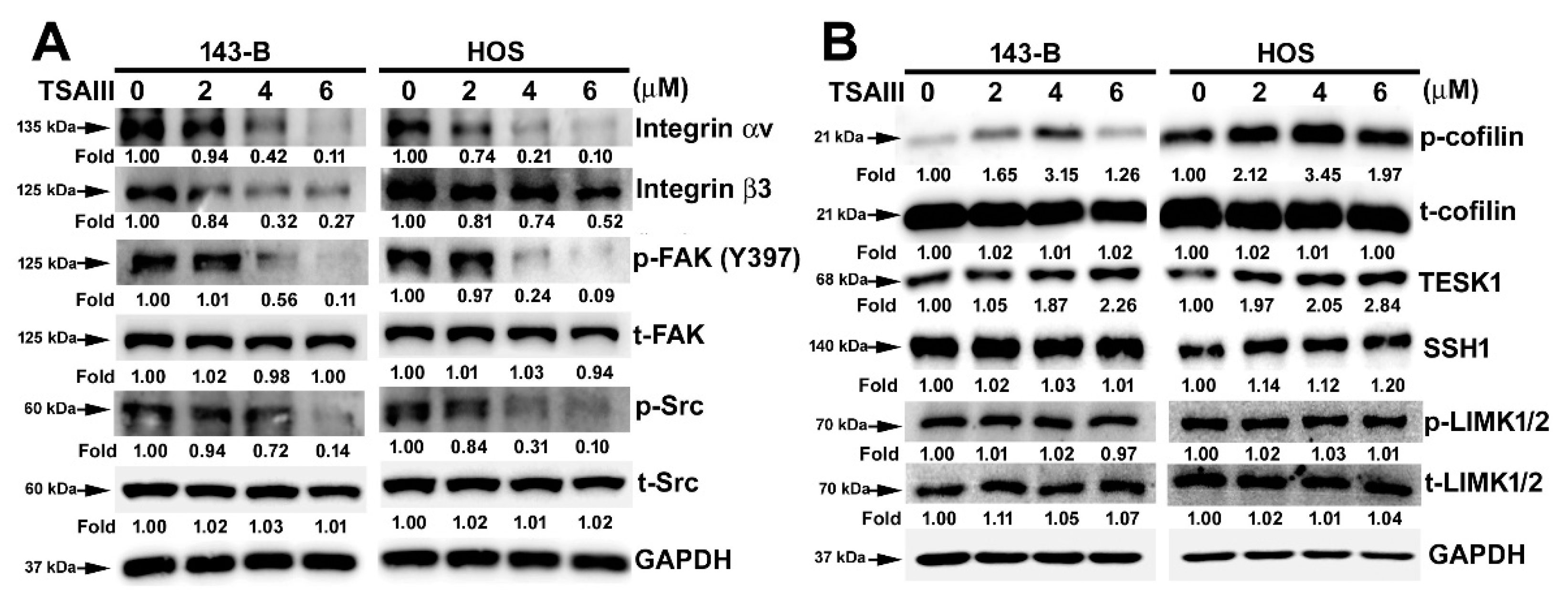
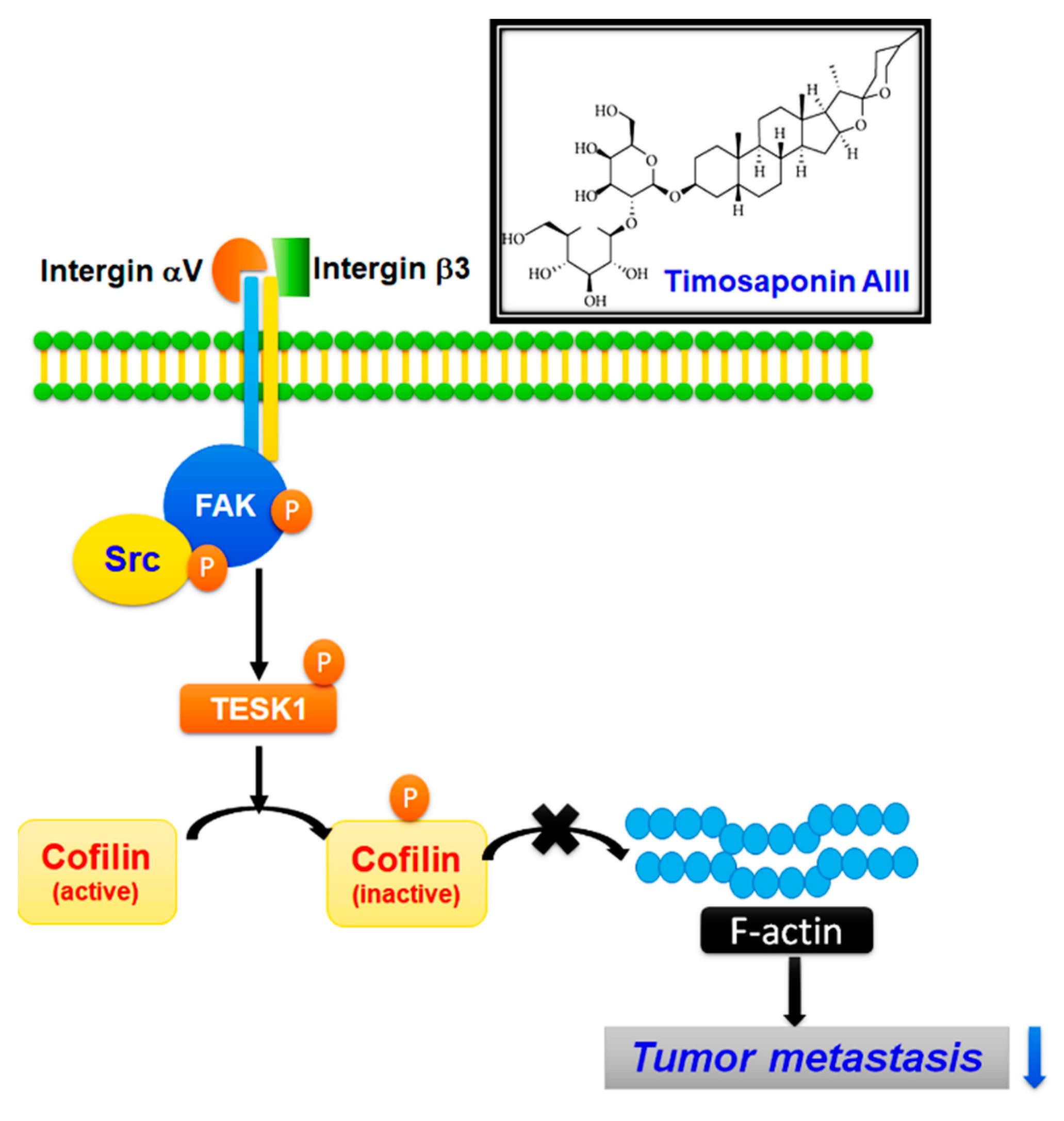
2.3. TSAIII Suppresses the Expression and Activation of Integrin-Mediated Cytoskeletal-Related Proteins in Human Osteosarcoma Cells
2.4. TSAIII and Cyclo Synergistically Suppress Cell Migration, Invasion, and F-Actin Expression in Human Osteosarcoma Cells
2.5. TSAIII and PF Synergistically Suppress Cell Migration, Invasion, and F-actin Expression in Human Osteosarcoma Cells
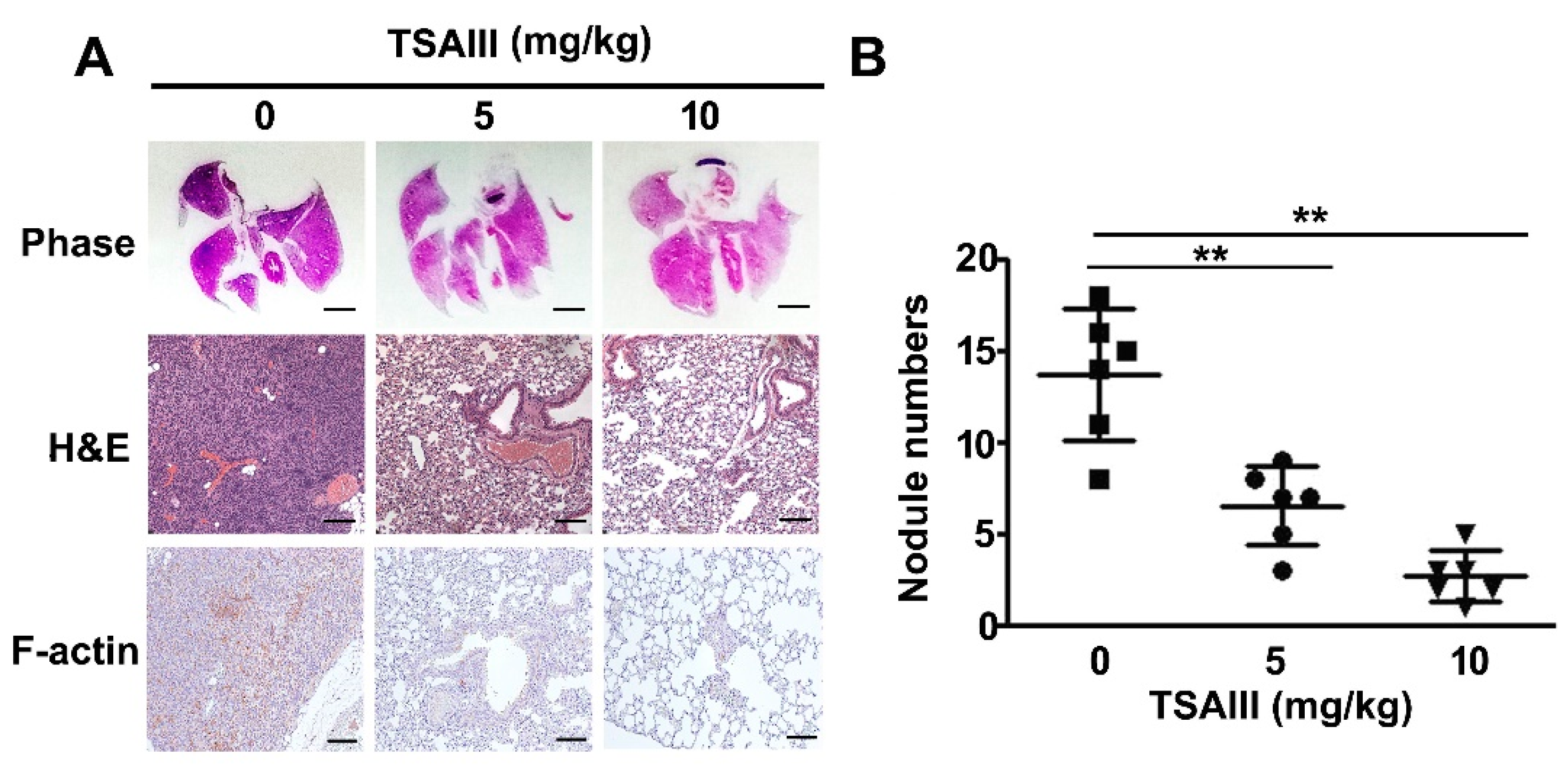
2.6. TSAII Inhibits Lung Metastasis of Human Osteosarcoma Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Colony Formation Assay
4.5. Annexin V/PI Staining by Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.6. Immunoblotting Analysis
4.7. Migration and Invasion Assay
4.8. In Vivo Metastasis Animal Experiments and Immunohistochemistry
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hameed, M.; Mandelker, D. Tumor Syndromes Predisposing to Osteosarcoma. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2018, 25, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampo, M.; Koivikko, M.; Taskinen, M.; Kallio, P.; Kivioja, A.; Tarkkanen, M.; Bohling, T. Incidence, epidemiology and treatment results of osteosarcoma in Finland—A nationwide population-based study. Acta Oncol. 2011, 50, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Dean, D.; Hornicek, F.J.; Chen, Z.; Duan, Z. The role of extracelluar matrix in osteosarcoma progression and metastasis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valastyan, S.; Weinberg, R.A. Tumor metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell 2011, 147, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakebusch, C.; Fassler, R. The integrin-actin connection, an eternal love affair. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2324–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carragher, N.O.; Westhoff, M.A.; Fincham, V.J.; Schaller, M.D.; Frame, M.C. A novel role for FAK as a protease-targeting adaptor protein: Regulation by p42 ERK and Src. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, R.L.; Reddig, P.; Alahari, S.; Edin, M.; Howe, A.; Aplin, A. Integrin regulation of cell signalling and motility. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2004, 32, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, R.O. A reevaluation of integrins as regulators of angiogenesis. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilcrease, M.Z. Integrin signaling in epithelial cells. Cancer Lett. 2007, 247, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juliano, R.L. Signal transduction by cell adhesion receptors and the cytoskeleton: Functions of integrins, cadherins, selectins, and immunoglobulin-superfamily members. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2002, 42, 283–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, A.A.; Govek, E.E.; Bottner, B.; Van Aelst, L. Rho GTPases: Signaling, migration, and invasion. Exp. Cell Res. 2000, 261, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Kim, J.; Hong, H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.K.; Jung, E.; Kim, J. Actin remodeling confers BRAF inhibitor resistance to melanoma cells through YAP/TAZ activation. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 462–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Eddy, R.; Condeelis, J. The cofilin pathway in breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohla, A.; Birkenfeld, J.; Bokoch, G.M. Chronophin, a novel HAD-type serine protein phosphatase, regulates cofilin-dependent actin dynamics. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggelou, H.; Chadla, P.; Nikou, S.; Karteri, S.; Maroulis, I.; Kalofonos, H.P.; Papadaki, H.; Bravou, V. LIMK/cofilin pathway and Slingshot are implicated in human colorectal cancer progression and chemoresistance. Virchows Arch. 2018, 472, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, M.; Hutterer, M.; Sabo, A.; Hoja, S.; Lorenz, J.; Rothhammer-Hampl, T.; Herold-Mende, C.; Flossbach, L.; Monoranu, C.; Riemenschneider, M.J. Chronophin regulates active vitamin B6 levels and transcriptomic features of glioblastoma cell lines cultured under non-adherent, serum-free conditions. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Xu, L.; Yin, L.; Han, X.; Qi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Song, S.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, J. Dioscin induces prostate cancer cell apoptosis through activation of estrogen receptor-beta. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.H.; Li, T.; Fong, C.M.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.J.; Wang, Y.T.; Huang, M.Q.; Lu, J.J. Saponins from Chinese Medicines as Anticancer Agents. Molecules 2016, 21, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Qi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, L.; Han, X.; Tao, X.; Song, S.; Peng, J. Dioscin Inhibits HSC-T6 Cell Migration via Adjusting SDC-4 Expression: Insights from iTRAQ-Based Quantitative Proteomics. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, O.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Yun, J.M.; Son, Y.J.; Cho, J.Y.; Ryou, C.; Lee, S.Y. Timosaponin AIII inhibits migration and invasion of A549 human non-small-cell lung cancer cells via attenuations of MMP-2 and MMP-9 by inhibitions of ERK1/2, Src/FAK and beta-catenin signaling pathways. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3963–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Chung, H.J.; Nam, J.W.; Park, H.J.; Seo, E.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.K. Cytotoxic and antineoplastic activity of timosaponin A-III for human colon cancer cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.M.; Im, A.R.; Kim, S.H.; Hyun, J.W.; Chae, S. Timosaponin AIII inhibits melanoma cell migration by suppressing COX-2 and in vivo tumor metastasis. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.H.; Yang, C.W.; Wang, J.Y.; Tsai, Y.F.; Tseng, L.M.; King, K.L.; Chen, W.S.; Chiu, J.H.; Shyr, Y.M. Timosaponin AIII Suppresses Hepatocyte Growth Factor-Induced Invasive Activity through Sustained ERK Activation in Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 421051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Kuo, S.J.; Liu, S.C.; Wang, S.W.; Tsai, C.H.; Fong, Y.C.; Tang, C.H. Apelin Affects the Progression of Osteoarthritis by Regulating VEGF-Dependent Angiogenesis and miR-150-5p Expression in Human Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells 2020, 9, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Guan, J.L. Signal transduction by focal adhesion kinase in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009, 28, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izdebska, M.; Zielinska, W.; Halas-Wisniewska, M.; Grzanka, A. Involvement of Actin and Actin-Binding Proteins in Carcinogenesis. Cells 2020, 9, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, M.S.; Deng, S.; Halim, C.E.; Cai, W.; Tan, T.Z.; Huang, R.Y.; Sethi, G.; Hooi, S.C.; Kumar, A.P.; Yap, C.T. Cytoskeletal Proteins in Cancer and Intracellular Stress: A Therapeutic Perspective. Cancers 2020, 12, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, B.W.; Bamburg, J.R. ADF/cofilin: A functional node in cell biology. Trends Cell Biol. 2010, 20, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, K. Roles of cofilin in development and its mechanisms of regulation. Dev. Growth Differ. 2015, 57, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshima, J.; Toshima, J.Y.; Amano, T.; Yang, N.; Narumiya, S.; Mizuno, K. Cofilin phosphorylation by protein kinase testicular protein kinase 1 and its role in integrin-mediated actin reorganization and focal adhesion formation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 1131–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maschietto, M.; Trape, A.P.; Piccoli, F.S.; Ricca, T.I.; Dias, A.A.; Coudry, R.A.; Galante, P.A.; Torres, C.; Fahhan, L.; Lourenco, S.; et al. Temporal blastemal cell gene expression analysis in the kidney reveals new Wnt and related signaling pathway genes to be essential for Wilms’ tumor onset. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgot, I.; Primac, I.; Louis, T.; Noel, A.; Maquoi, E. Reciprocal Interplay Between Fibrillar Collagens and Collagen-Binding Integrins: Implications in Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamarajan, P.; Ateia, I.; Shin, J.M.; Fenno, J.C.; Le, C.; Zhan, L.; Chang, A.; Darveau, R.; Kapila, Y.L. Periodontal pathogens promote cancer aggressivity via TLR/MyD88 triggered activation of Integrin/FAK signaling that is therapeutically reversible by a probiotic bacteriocin. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.N.; Nam, J.O.; Kim, S.; Kim, I.S. Multiple FAS1 domains and the RGD motif of TGFBI act cooperatively to bind alphavbeta3 integrin, leading to anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor effects. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 2378–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.B.; Choi, S.; Choi, M.C.; Oh, M.A.; Lee, S.A.; Cho, M.; Mizuno, K.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.W. Cell adhesion-dependent cofilin serine 3 phosphorylation by the integrin-linked kinase.c-Src complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 10089–10096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Deng, X.; Sun, X.; Dong, J.; Huang, J. Inhibition of autophagy enhances timosaponin AIII-induced lung cancer cell apoptosis and anti-tumor effect in vitro and in vivo. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.Y.; Han, F.Y.; Chen, J.J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, G.D.; Song, S.J. Timosaponin AIII, a steroidal saponin, exhibits anti-tumor effect on taxol-resistant cells in vitro and in vivo. Steroids 2019, 146, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dong, R.; Fan, W.W.; Zheng, X.C.; Li, A.M.; Wang, W.D. Timosaponin AIII induces autophagy of Tcell acute lymphoblastic leukemia Jurkat cells via inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 2937–2944. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, I.S.; Park, J.Y.; Na, Y.C.; Chung, W.S.; Jang, H.J. Apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest induced by a timosaponin A3 from Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bunge on AsPC-1 pancreatic cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 56, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, K.C.; Lai, C.Y.; Chiou, H.L.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, Y.S.; Kao, S.H.; Hsieh, Y.H. Timosaponin AIII inhibits metastasis of renal carcinoma cells through suppressing cathepsin C expression by AKT/miR-129-5p axis. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 13332–13341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.C.; Yang, S.F.; Chiou, H.L.; Hsieh, S.C.; Wen, S.H.; Lu, K.H.; Hsieh, Y.H. Licochalcone A-Induced Apoptosis Through the Activation of p38MAPK Pathway Mediated Mitochondrial Pathways of Apoptosis in Human Osteosarcoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Cells 2019, 8, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.H.; Wu, P.R.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Lin, C.L.; Liu, C.J.; Ying, T.H. Silencing PROK2 Inhibits Invasion of Human Cervical Cancer Cells by Targeting MMP15 Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.H.; Chiu, Y.F.; Wu, W.J.; Wu, P.L.; Lin, C.Y.; Lin, C.L.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Liu, C.J. Synergistic antimetastatic effect of cotreatment with licochalcone A and sorafenib on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the inactivation of MKK4/JNK and uPA expression. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsieh, Y.-H.; Hsu, W.-H.; Yang, S.-F.; Liu, C.-J.; Lu, K.-H.; Wang, P.-H.; Lin, R.-C. Potential Antimetastatic Effect of Timosaponin AIII against Human Osteosarcoma Cells through Regulating the Integrin/FAK/Cofilin Axis. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030260
Hsieh Y-H, Hsu W-H, Yang S-F, Liu C-J, Lu K-H, Wang P-H, Lin R-C. Potential Antimetastatic Effect of Timosaponin AIII against Human Osteosarcoma Cells through Regulating the Integrin/FAK/Cofilin Axis. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(3):260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030260
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsieh, Yi-Hsien, Wen-Hung Hsu, Shun-Fa Yang, Chung-Jung Liu, Ko-Hsiu Lu, Pei-Han Wang, and Renn-Chia Lin. 2021. "Potential Antimetastatic Effect of Timosaponin AIII against Human Osteosarcoma Cells through Regulating the Integrin/FAK/Cofilin Axis" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 3: 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030260
APA StyleHsieh, Y.-H., Hsu, W.-H., Yang, S.-F., Liu, C.-J., Lu, K.-H., Wang, P.-H., & Lin, R.-C. (2021). Potential Antimetastatic Effect of Timosaponin AIII against Human Osteosarcoma Cells through Regulating the Integrin/FAK/Cofilin Axis. Pharmaceuticals, 14(3), 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030260








