Abstract
Since the first characterization of the 5-hydroxytryptamine 2B receptor (5-HT2BR) in 1992, significant progress has been made in 5-HT2BR research. Herein, we summarize the biological function, structure, and small-molecule pharmaceutical ligands of the 5-HT2BR. Emerging evidence has suggested that the 5-HT2BR is implicated in the regulation of the cardiovascular system, fibrosis disorders, cancer, the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and the nervous system. Eight crystal complex structures of the 5-HT2BR bound with different ligands provided great insights into ligand recognition, activation mechanism, and biased signaling. Numerous 5-HT2BR antagonists have been discovered and developed, and several of them have advanced to clinical trials. It is expected that the novel 5-HT2BR antagonists with high potency and selectivity will lead to the development of first-in-class drugs in various therapeutic areas.
1. Introduction
5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), or serotonin, was first isolated from beef serum and characterized in the late 1940s [1]. Biochemically, 5-HT is derived from the amino acid tryptophan, undergoing hydroxylation and decarboxylation processes that are catalyzed by tryptophan hydroxylase and aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, respectively [2]. As a biogenic amine, 5-HT plays important roles in cardiovascular function, bowel motility, platelet aggregation, hormone release, and psychiatric disorders [2]. 5-HT achieves its physiological functions by targeting various 5-HT receptors (5-HTRs), which are composed of six classes of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) (5-HT1, 5-HT2, 5-HT4, 5-HT5, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7 receptors, a total of 13 subtypes) and a class of cation-selective ligand-gated ion channels, the 5-HT3 receptor [3].
The 5-HT2 receptor (5-HT2R) subfamily is subdivided into 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors. The 5-HT2BR was the last identified 5-HT2R family member and was first cloned in rat stomach fundus in 1992 [4], before the cloning of human 5-HT2BR in several tissues two years later [5,6]. In humans, the 5-HT2BR shares nearly 50% homology with the 5-HT2AR and 5-HT2CR, with about 70% homology in the transmembrane region [5]. Expressions of human 5-HT2BR mRNA have been detected in many different tissues, including the liver, kidney, intestine, pancreas, stomach, heart, lung, brain, uterus, trachea, testis, prostate, and placenta [5,6]. The 5-HT2BR is a Gq/11 protein-coupled receptor. The activation of Gq/11 results in several parallel signaling pathways. One branch of the canonical Gq/11 signal transduction pathway is involved in the hydrolysis of guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP) and is mediated by the Gq/11 protein. The GTP-bound Gq/11 stimulates the effector protein phospholipase Cβ (PLCβ) and leads to the generation of diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol triphosphate (IP3), further increasing intracellular calcium ions and activating the protein kinase C (PKC) [7,8].
Significant progress has been made in the field of 5-HT2BR research in the past decade. Here, we review the recent updates of the biological functions, experimentally determined structures and pharmaceutical ligands of the 5-HT2BR, with a particular focus on clinical applications of 5-HT2BR antagonists. First, we elaborate on the important role that the 5-HT2BR plays in regulating the cardiovascular system, fibrosis disorders, cancer, the GI tract, and the nervous system. Second, we analyze the insights of the activation mechanism and biased signaling provided by the crystal structures. Finally, we summarize 5-HT2BR ligands that are clinically relevant or which have recently reported experimental verification data.
2. Function
2.1. Cardiovascular System
The 5-HT2BR is expressed in cardiovascular tissues, including myocardial, endothelial, and vascular smooth muscle cells [9]. Increasing evidence has revealed that the 5-HT2BR is involved in multiple cardiovascular diseases, including cardiomyopathy, valvular heart disease (VHD) and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) [2,10].
2.1.1. Cardiomyopathy
Since 2000, Nebigil et al. have suggested that the 5-HT2BR is implicated in regulating cardiac structure and function during embryogenesis and adulthood [9]. The ablation of the 5-HT2BR in mice led to embryonic and neonatal death. Surviving 5-HT2BR knockout mice exhibited cardiomyopathy with decreased cardiomyocyte number and size. On the contrary, specifically overexpressing the 5-HT2BR in the heart led to compensated hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, characterized by ventricular wall thickening [11].
Numerous animal model studies further confirmed the role played by the 5-HT2BR in cardiomyopathy. The 5-HT2BR has been found to be associated with isoproterenol- and noradrenaline-induced cardiac hypertrophy [12,13,14]. Chronic isoproterenol perfusion in mice imitating sympathetic stimulation induced cardiac hypertrophy, which could be prevented by treatment with 5-HT2BR antagonists, through regulating the hypertrophic cytokines produced by cardiac fibroblasts [12] and the production of superoxide anion [13]. In rats, a 5-HT2BR antagonist attenuated cardiac hypertrophy and myocardial apoptosis induced by chronic noradrenaline treatment [14]. In dogs with dilated cardiomyopathy, the 5-HT2BR was overexpressed in cardiomyocytes [15].
2.1.2. VHD
The normal mammalian heart has four valves to ensure unidirectional blood flow during the cardiac cycle: the mitral valve (from the left atrium to the left ventricle), the tricuspid valve (from the right atrium to the right ventricle), the aortic valve (from the left ventricle to the aorta), and the pulmonary valve (from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery). Any damaged or diseased heart valve can result in VHD. Abnormal valves cannot be fully open (stenosis) or fully close (regurgitation) so that the blood cannot be effectively pumped throughout the body, resulting in heart failure, sudden cardiac arrest and even death in more severe cases. Fully formed heart valves consist of valvular endothelial cells and valvular interstitial cells (VICs). The two types of cells regulate the generation of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and thus play critical roles in valve function [2]. Excessive ECM alters valve structure and leads to VHD.
Several drugs are known to associate with VHD side effects, including therapeutic agents for the treatment of obesity (fenfluramine and its stereoisomer dexfenfluramine, and benfluorex), Parkinson’s disease (pergolide and cabergoline), and migraine (methysergide and ergotamine), as well as the recreational drug 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, commonly known as ecstasy) [16,17]. Drug-induced VHD has led to the withdrawal of fenfluramine and dexfenfluramine from the U.S. market in 1997, followed by the withdrawal of pergolide in 2007. Either these drugs or their metabolites have been demonstrated to be partial or full 5-HT2BR agonists with high affinity, and the pathogenesis of drug-induced VHD was correlated to the “off-target” activation of the 5-HT2BR [2,18]. Consequently, drug candidates with possible 5-HT2BR agonism effects are now required to be evaluated before approval [19]. Additionally, the signaling mechanism of drug-induced VHD has been studied [2,20]. Apart from the canonical Gq/11 signal transduction pathway involved in the activation of PLCβ and PKC, the activation of the 5-HT2BR may also activate mitogenic pathways through the phosphorylation of the Src kinase and extracellular regulated kinases (ERK) and further enhance the activity of the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β). All pathways lead to VIC proliferation and ECM accumulation, and subsequently to the occurrence of VHD.
The 5-HT2BR was shown to be involved in vascular heart diseases, including mitral valve prolapse (MVP) [21] and calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD) [22,23]. Overexpression of the 5-HT2BR in the mitral valve leaflets was found in humans with MVP. Blockade of the 5-HT2BR mitigated mitral valve thickening and the activation of mitral valve interstitial cells, which are involved in the pathophysiology of MVP [21]. A study in isolated aortic valve interstitial cells (AVICs) in vitro showed that 5-HT2BR antagonism could prevent AVIC activation, a process associated with CAVD [22]. Recently, the same research group reported that in a high cholesterol diet mouse model, aortic valve hemodynamic development of CAVD could be attenuated by the ablation of the 5-HT2B gene, but not 5-HT2BR antagonism [23].
2.1.3. PAH
PAH is a progressive disorder characterized by abnormally high blood pressure in pulmonary arterial and pulmonary vasculature remodeling. The involvement of the 5-HT2BR in PAH has long been suggested. A significantly increased expression of the 5-HT2BR in pulmonary arteries was found in pulmonary hypertension (PH) patients and mice [24]. Moreover, the upregulation of the 5-HT2BR has been found in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells derived from PAH patients [25]. In vivo studies on animal models suggested that chronic hypoxia or chemicals, such as deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA) salt and monocrotaline (MCT), could induce PH, which can be prevented or alleviated through blocking the 5-HT2BR or by genetic ablation [24,25,26,27]. In a BMPR2 mutant imitating heritable PAH mouse model, 5-HT2BR antagonism prevents PAH through reducing Src phosphorylation and downstream activity [28].
Emerging evidence has shown that bone marrow (BM)-derived cells contribute to 5-HT2BR-mediated PAH. Launay et al. found that lung cells overexpressing 5-HT2BRs for vascular remodeling during PAH originate from BM precursors in mice [29]. They found that the specific expression of 5-HT2BR in the BM is necessary and sufficient for PAH development, whereas the ablation of 5-HT2BR on BM cells leads to resistance to PH. More recently, Bloodworth et al. demonstrated that BM-derived proangiogenic cells play a role in PH by mediating pulmonary arteriole stiffening and remodeling via the 5-HT2BR [30]. Both the ablation of BM-derived proangiogenic cells and 5-HT2BR antagonism prevented PH in mice with reductions in the number and stiffness of muscularized pulmonary arterioles.
2.2. Fibrosis Disorders
The 5-HT2BR has been implicated in fibrotic disorders such as liver fibrosis [31,32,33], pulmonary fibrosis [34,35,36,37,38], systemic sclerosis (SSc) [39,40,41,42,43], and pancreatic fibrosis [44].
2.2.1. Liver Fibrosis
Liver fibrosis is generally believed to be caused by the excessive production of ECM, which is promoted by activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) transdifferentiating into myofibroblasts [45,46]. Ebrahimkhani et al. found that the 5-HT2BR was highly expressed in the diseased liver by activated HSCs and that 5-HT2BR antagonism exerted an antifibrogenic effect and improved liver function in a mouse model of progressive liver disease with fibrogenesis [31]. In a carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver fibrosis mouse model, Li et al. found that chronic restraint stress alleviated liver fibrosis by inhibiting the activation of HSCs via the 5-HT2BR [32]. More recently, Xiang et al. revealed that two microRNAs (miR-221 and miR-222) were regulated by 5-HT during HSC activation and that the 5-HT2BR was essential for this regulation, as demonstrated by the discovery that 5-HT did not increase the expression of miR-221/miR-222 in 5-HT2B knockdown HSCs [33].
2.2.2. Pulmonary Fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis is one of the most studied 5-HT associated fibrosis. Fibroblasts (effector cells) differentiate into myofibroblasts and subsequently synthesize ECM, which are considered key events in pulmonary fibrogenesis. Fabre et al. found that the 5-HT2BR was highly expressed by fibroblasts in the fibroblastic foci in human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) samples [34]. In the lungs of IPF patients, Königshoff et al. found that the 5-HT2BR mainly localized to the epithelium and showed a significant increase in expression compared to transplant donors [35].
In vivo studies in the bleomycin (BLM)-induced pulmonary fibrosis mouse model suggested the involvement of 5-HT2AR and 5-HT2BR in pulmonary fibrosis. The expression of 5-HT2AR and 5-HT2BR were increased in the lung after the intratracheal treatment with BLM [34,35]. Blockade of the 5-HT2AR and 5-HT2BR could ameliorate BLM-induced lung fibrosis and improve lung function by reducing lung collagen content [34,35]. In vitro studies in human lung, fibroblasts showed that the antifibrotic effect of 5-HT2AR and 5-HT2BR antagonism was mediated by the TGF-β1 and WNT3α signaling pathways [35]. Moreover, Löfdahl et al. utilized two 5-HT2BR antagonists EXT5 and EXT9 (also with low to moderate affinity to the 5-HT2A/5-HT2C receptors), to investigate the role of the 5-HT2BR in pulmonary fibrosis, suggesting their potential to prevent myofibroblast differentiation and subsequent fibrotic responses in a BLM-treated mouse model and human lung fibroblasts (see Section 4.2.1 for more details) [36]. Further studies suggested that the antiproliferative effects of EXT5 and EXT9 were related to the pAkt/p21 signaling pathway [38]. It is worth mentioning that in vivo studies in the BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis rat model showed that 5-HT2CR and 5-HT7R were also implicated in pulmonary fibrosis [37,47,48].
2.2.3. Systemic Sclerosis (SSc)
SSc is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by progressive vascular disease and fibrosis of the skin and internal organs. Emerging evidence has suggested that 5-HT2BR plays an important role in SSc. In 2011, Dees et al. found that the expression of the 5-HT2BR was significantly increased in the skin of SSc patients compared with the normal skin of healthy individuals [39]. In vitro studies on SSc dermal fibroblasts suggested that the profibrotic effects of 5-HT are mediated by the 5-HT2BR, excluding the 5-HT1BR and 5-HT2AR, which are also expressed in dermal fibroblasts [39]. In vivo studies on BLM-induced dermal fibrosis and tight-skin-1 (tsk-1) mouse models showed that 5-HT2BR antagonists ameliorated fibrosis. In addition, mice lacking the 5-HT2B gene could be protected from BLM-induced fibrosis [39]. In 2018, Chaturvedi et al. studied human adult dermal fibroblasts (HADF) isolated from SSc patients and showed that stimulation of 5-HT/TGF-β1 in HADF significantly increased the expression of profibrotic genes. Profibrotic genes were downregulated by the 5-HT2BR antagonist SB-204741, whose antifibrotic effect might be involved in the suppression of TGF-β1-mediated non-canonical (non-Smad dependent) signaling pathways [40]. Moreover, Wenglén et al. discovered selective antagonists of the 5-HT2BR (AM1125 and AM1476) and suggested their antifibrotic effects for the potential treatment of SSc (see Section 4.2.1 for details) [42,43].
2.3. Cancer
5-HT is involved in human cancer progression [49], and strong evidence has suggested that the 5-HT2BR plays a role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), neuroendocrine tumor (NET) and pancreatic tumor.
2.3.1. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
Through the analysis of liver tissues from patients with HCC, Sarrouilhe et al. found that the 5-HT1BR and the 5-HT2BR were overexpressed in tumor tissues and that their antagonists inhibited proliferation of HCC cell lines, such as Huh7 and HepG2 [50]. Liang et al. suggested that 5-HT promoted the proliferation of serum-deprived Huh7 cells by upregulating the transcription factor FOXO3a, although this pro-proliferative effect was not observed in serum-deprived HepG2 or Hep3B cells [51]. They further found that the pro-proliferative effect of 5-HT could be blocked by the 5-HT2BR antagonist SB-204741 in Huh7 cells and that 5-HT2BR mRNA was significantly higher expressed in Huh7 cells compared to HepG2 and Hep3B cells, which may contribute to the distinct 5-HT effects in different serum-deprived HCC cells [51]. Using zebrafish HCC models, Yang et al. suggested that the 5-HT2BR was involved in HCC carcinogenesis [52,53]. In zebrafish, the expression of the 5-HT2BR was found to be high in HSCs, much lower in hepatocytes, and practically absent in neutrophils and macrophages [53]. The activation of the 5-HT2BR could increase both the proliferation and the activation of HSCs, as well as the expression of TGF-β1, resulting in liver enlargement and accelerating HCC carcinogenesis. In contrast, blocking the 5-HT2BR led to opposite effects [52,53].
2.3.2. Neuroendocrine Tumor (NET)
NET is a rare type of tumor that most commonly arises in the GI tract and can lead to carcinoid syndrome [54,55]. Svejda et al. studied KRJ-I cells, a small intestinal-NET (SI-NET) cell line, and found that treatment with 5-HT2BR antagonist PRX-08066 inhibited the 5-HT secretion and KRJ-I cell proliferation, simultaneously decreasing the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and the transcript levels and secretion of profibrotic growth factors, including TGF-β1, connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and fibroblast growth factor (FGF2). The antiproliferative and antifibrotic effects of the 5-HT2BR suggested that this is a promising target for intervening SI-NETs [56].
2.3.3. Pancreatic Tumor
In 2017, Jiang et al. reported that the 5-HT2BR could be used as a potential therapeutic target for intervening pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDACs) [57]. 5-HT was found to be increased in human PDAC tissues. Moreover, the incubation of 5-HT with PDAC cell lines resulted in an increase in PDAC cell proliferation and a decrease of PDAC cell apoptosis. Both in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that the pro-survival effect of 5-HT is mediated by the 5-HT2BR, but not other 5-HTRs. The 5-HT2BR agonist α-Me-HTP promoted the survival of PDAC cells, whereas the 5-HT2BR antagonist SB-204741 or genetic silencing of the 5-HT2BR blocked the pro-survival effect of 5-HT in PDAC cells and significantly reduced the tumor burden of PDAC in mice [57]. Moreover, the tumor-suppressive effects of 5-HT2BR antagonism were further confirmed in transgenic mice with pancreatic tumors. Notably, the mechanism behind 5-HT mediated PDAC cell survival involved the activation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling and the enhancement of aerobic glycolysis (Warburg effect) [57].
2.4. Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract
Previous studies have suggested a role for the 5-HT2BR in the GI system. 5-HT2BR mRNA was widely expressed throughout the human GI tract [58]. The high expression of 5-HT2BR was detected in colonic smooth muscle, and the excitatory effects of 5-HT in the human colon were demonstrated to be mediated by the 5-HT2BR [58]. The 5-HT2BR was also found in the interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC), the “pacemaker cells” of the GI tract, which are expressed throughout the entire GI tract and required for normal GI motility. The activation of the 5-HT2BR in mouse models increased the proliferation of ICC in vitro and in vivo [59,60]. The 5-HT2BR triggered ICC proliferation was found to be mediated by PLC, intracellular calcium release and PKCγ [61].
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common functional GI disorder that is characterized by abdominal discomfort and abnormal defecation. Visceral hypersensitivity is considered a hallmark characteristic of IBS. Many animal studies have demonstrated that the 5-HT2BR antagonism could help to modulate visceral hypersensitivity, colonic motility, and defecation [62,63,64,65], which indicates that the 5-HT2BR is a potential therapeutic target for GI disorders, especially for IBS. Notably, a study in conscious dogs showed that 5-HT2BR antagonism had no contractile effect on normal colonic motor activity and suggested that 5-HT2BR antagonists may be utilized for the treatment of diarrhea-predominant IBS without resulting in a constipation side effect [66].
2.5. Nervous System
As a neurotransmitter, 5-HT plays an essential role in the nervous system [67,68]. The 5-HT2BR has been suggested to mediate 5-HT functions in cognitive processes such as learning and memory [69,70,71], motor activities like breathing [72,73,74], as well as pain disorders, neuroglia function, and the dopaminergic pathway.
2.5.1. Regulation of Pain Disorders
The 5-HT2BR has been implicated in migraine and neuropathic pain, which are two common forms of pain disorders in humans [75,76,77]. Migraine is a common primary headache disorder characterized by moderate to severe recurrent headaches. In 1989, Fozard et al. proposed that the initiation of migraine is caused by the activation of the 5-HT2CR [78]. However, this hypothesis was challenged after the cloning of rat 5-HT2BR in 1992 [4]. Subsequent studies demonstrated that the 5-HT2BR activation stimulated nitric oxide (NO) synthesis, which may be involved in migraine pathogenesis [75]. In guinea pigs, selective 5-HT2BR antagonists have been found to inhibit the 5-HT2BR/5-HT2CR agonist meta-chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) or the 5-HT2BR agonist BW723C686-induced dural plasma protein extravasation (PPE), an indicator for migraine attacks in animal models [79]. In addition, 5-HT2BR antagonism also prevented mCPP-induced dural PPE under hypoxia in mice [80].
Increasing evidence has revealed that the 5-HT2BR also plays a role in neuropathic pain [77]. In mouse dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons, the mechanical hyperalgesia induced by 5-HT or the 5-HT2R agonist α-m5-HT was inhibited by the 5-HT2BR/5-HT2CR antagonist SB-206553 [81]. Given that the 5-HT2BR was mainly expressed in DRGs, whereas the 5-HT2CR was detected only in trace amounts, 5-HT-induced mechanical hyperalgesia is most likely mediated by the 5-HT2BR [81]. Another signal transduction study suggested that the 5-HT2BR mediates the 5-HT-induced mechanical hyperalgesia through the PLCβ-PKCε pathway to regulate the function of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 [82]. Cervantes-Durán et al. assessed the role played by peripheral and spinal 5-HT2Rs in formalin-induced secondary allodynia and hyperalgesia in rats. Local peripheral ipsilateral or intrathecal injection of selective 5-HT2BR antagonist significantly prevented formalin-induced nociceptive behavior monitored by flinching frequency [83]. Ipsilateral treatment with subtype-selective antagonists of 5-HT2AR, 5-HT2BR or 5-HT2CR, prevented formalin-induced long-term secondary mechanical allodynia and hyperalgesia [84]. Additionally, intrathecal treatment with the same antagonists inhibited formalin-induced long-term secondary mechanical allodynia and hyperalgesia in both ipsilateral and contralateral hind paws [85]. In the spinal nerve ligation-induced neuropathic pain rat model, intrathecal injection of 5-HT2BR antagonists not only impaired spinal nerve ligation-induced allodynia but also inhibited the spinal nerve injury-induced increased expression of the 5-HT2BR in both DRGs and spinal cord [86]. More recently, studies in female rats revealed that blocking the spinal 5-HT2BR diminished preoperative anxiety-induced postoperative hyperalgesia [87]. However, opposite findings were reported in other pain models. For example, in a rat model of neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury (CCI) of the sciatic nerve, Urtikova et al. found that intrathecal injection of the 5-HT2BR agonist BW723C86 evidently relieved CCI-induced allodynia [88]. Clearly, further mechanistic studies are needed to explain the opposite experimental observations.
2.5.2. Regulation of Neuroglia Function
The 5-HT2BR is also expressed in neuroglia, including microglia and astroglia, playing a role in regulating neuroglia function. Microglia, as the resident macrophages in the brain and the spinal cord, are responsible for the immune defense of the central nervous system (CNS) [89]. It was reported that the 5-HT2BR was expressed on postnatal microglia and participated in postnatal brain maturation [90]. More recently, the same group showed that the ablation of the 5-HT2BR gene in neonatal microglia was sufficient to cause enhanced weight loss and prolonged neuroinflammation in mice caused by exposure to lipopolysaccharides in adulthood. This suggested that the 5-HT2BR is required in neonatal microglia to prevent sickness behavior in adulthood [91].
Astrocytes are primary homeostatic cells of the CNS and account for about one-quarter of brain cortical volume. The expression of 5-HTRs, including the 5-HT2BR, has been found in both cultured and freshly isolated astrocytes [92]. Studies have suggested that conventional serotonin-specific reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) such as fluoxetine act as agonists of astroglial 5-HT2BR [92]. The 5-HT2BR agonist BW723C86 could mimic the behavioral and neurogenic SSRI effects, which could be eliminated by the genetic or pharmacological inactivation of the 5-HT2BR [93]. In cultured mouse astrocytes, fluoxetine was found to induce EGFR transactivation and ERK1/2 phosphorylation, mediated by the stimulation of the 5-HT2BR [94], which is consistent with the observation that the drug-induced VHD involves the activation of the 5-HT2BR and consequent ERK phosphorylation [2,20]. Similarly, 5-HT was also found to cause ERK1/2 phosphorylation, which is mediated by the stimulation of the 5-HT2BR with high affinity and the 5-HT2CR with low-affinity [95]. Increasing evidence has suggested that astroglial 5-HT2BR is involved in depression [96]. In both 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced and 6-hydroxydopamine-induced Parkinson’s disease mouse models [97,98], the decrease of astroglial 5-HT2BR expression paralleled the development of depressive behavior. Treatment with fluoxetine corrected both the decrease of astroglial 5-HT2BR expression and depressive behavior. All of these indicate that the downregulation of the astroglial 5-HT2BR may promote the development of depressive behavior in Parkinson’s disease. In addition, astroglial 5-HT2BR was also found to play a role in depressive behavior associated with sleep deprivation [99,100]. Specifically, the expression of the 5-HT2BR in a sleep deprivation mouse model was downregulated selectively in astrocytes, which was controlled by the activation of the P2X7 receptor [99]. Interestingly, leptin was found to increase the expression of astrocytic 5-HT2BRs and thus enhance the action of fluoxetine on depressive-like behaviors induced by sleep deprivation [100].
2.5.3. Regulation of the Dopaminergic Pathway
The 5-HT2BR has been implicated in the modulation of central dopamine (DA) activity, with potential applications in DA-dependent neuropsychiatric disorders, especially in schizophrenia and drug addiction [7,101].
Schizophrenia is a serious long-term mental disorder with multimodal symptomatology, characterized by positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms [102]. There is a classical hypothesis about schizophrenia proposed that positive symptoms are the result of a specific DA hyperfunction in the nucleus accumbens (NAc), whereas negative and cognitive symptoms are associated with a DA hypofunction in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) [102]. Several microdialysis studies in rats suggested that the 5-HT2BR blockade exerts a differential control of DA ascending pathways, with increased, decreased and unaltered effects on DA outflow in the mPFC, the NAc, and the striatum, respectively. This is in accordance with the role played by DA neurotransmission in schizophrenia symptomatology [7,103,104,105]. An additional study indicated that the distinct effects caused by 5-HT2BR antagonists on mPFC and NAc DA outflow resulted from a functional interplay with mPFC 5-HT1AR [102]. Moreover, behavioral experiments in rats revealed that 5-HT2BR antagonists reduce phencyclidine-induced hyperlocomotion and reverse the phencyclidine-induced deficit in the novel object recognition test. These observations suggested that 5-HT2BR antagonists have the potential to alleviate the positive and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia [105]. However, it was also reported that the ablation of the 5-HT2BR induces schizophrenic-like phenotypes, and contradictory results were observed in the DA outflow and behavior compared with 5-HT2BR antagonism in rats [106]. Hence, additional research studies are needed in order to explain the observed discrepancies and to confirm the role of the 5-HT2BR in the treatment of schizophrenia.
Several studies suggested that the 5-HT2BR may represent a potential pharmaceutical target for the treatment of drug addiction. From a behavioral point of view, blocking the 5-HT2BR may help to prevent MDMA-, amphetamine-, and cocaine-induced hyperlocomotion [103,104,107]. However, neurochemical responses vary according to different drugs. For example, 5-HT2BR antagonists inhibit MDMA- and amphetamine-induced DA outflow in the NAc [103,107], but no effects were observed on cocaine-induced DA outflow in the NAc [104]. Recent findings showed that the dorsal raphe nucleus 5-HT2BR blockade suppresses cocaine-induced hyperlocomotion resulting from the facilitation of mPFC DA outflow, which would subsequently inhibit accumbal DA neurotransmission [108].
3. Structure
3.1. Crystal Structures
The 5-HT2BR belongs to the class A GPCRs, the largest subfamily of GPCRs, and shares a conserved architecture: seven transmembrane helices (I-VII) followed by an 8th helix (VIII), three extracellular loops (ECL1–ECL3), three intracellular loops (ICL1–ICL3), an extracellular N-terminus and an intracellular C-terminus [109]. The 5-HT2BR contains 481 amino acids with a molecular mass of about 54.3 kDa.
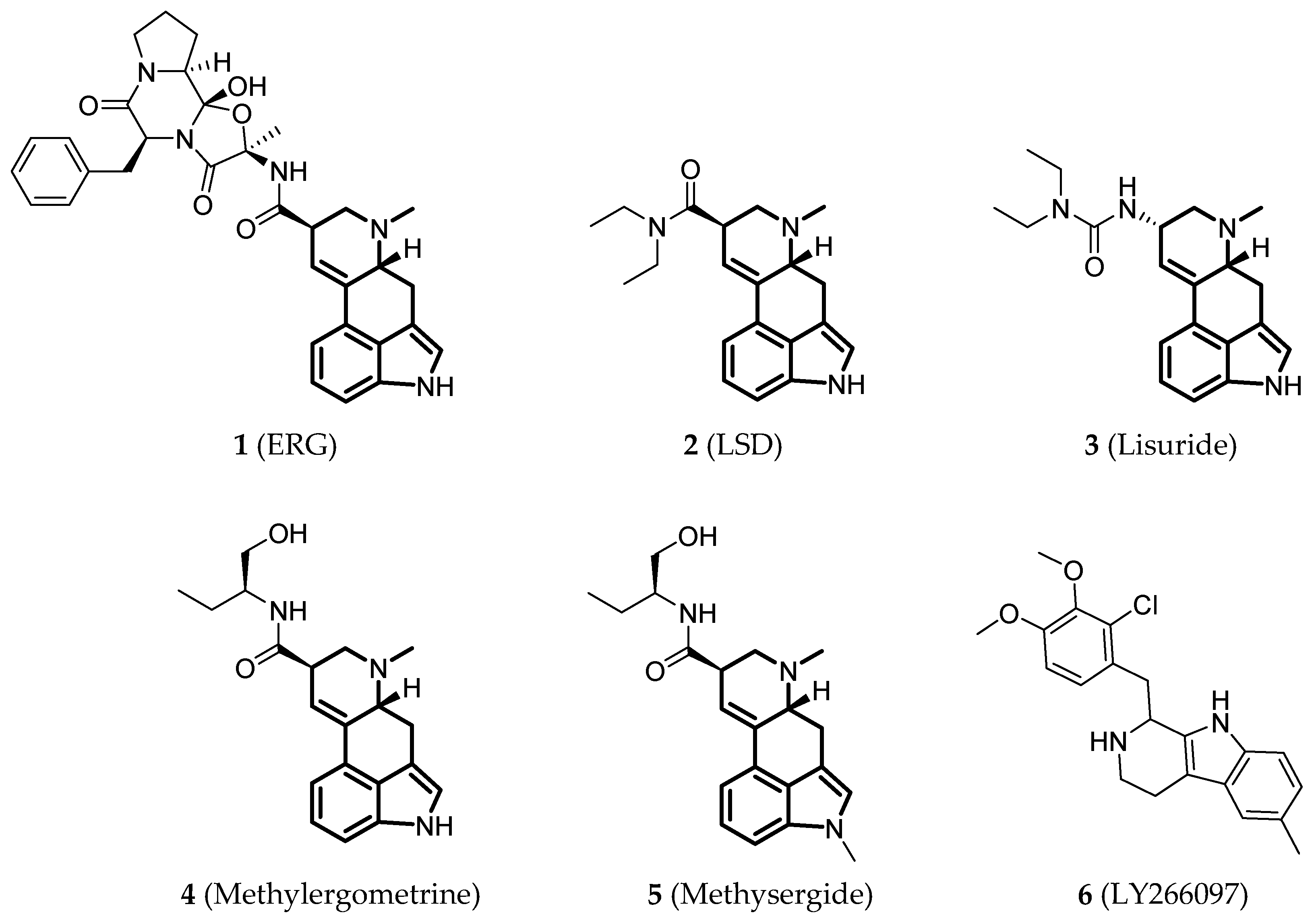
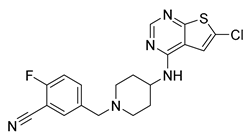
Since the 5-HT2BR crystal structure was first determined in 2013 [110], a total of eight crystal complex structures of the 5-HT2BR bound with small-molecule ligands were published to date (Table 1). These include five representative ergolines (ergotamine (ERG, 1), lysergic acid diethylamine (LSD, 2), lisuride (3), methylergometrine (4, also called methylergonovine), methysergide (5)), and one selective antagonist of the 5-HT2BR (LY266097 (6)) (Figure 1) [110,111,112,113,114]. These ergolines are promiscuous ligands for many types of aminergic GPCRs and possess distinct functions. For example, despite ERG and LSD are both β-arrestin-biased agonists of the 5-HT2BR, ERG has antimigraine effects whereas LSD is hallucinogenic; lisuride is structurally similar to LSD, but it shows antagonistic effects towards the 5-HT2BR; methysergide is an antagonist of the 5-HT2BR with an antimigraine effect that in vivo it rapidly undergoes N-demethylation and transforms into methylergometrine, a potent agonist of the 5-HT2BR. In one crystal structure (PDB ID: 5TUD), the 5-HT2BR binds with ERG and an antibody Fab fragment on its extracellular side in an active-like conformation [113]. Taken together, the structural information provides an unprecedented opportunity to understand the ligand recognition, activation mechanism and biased signaling.

Table 1.
Published 5-hydroxytryptamine 2B receptor (5-HT2BR) crystal structures.
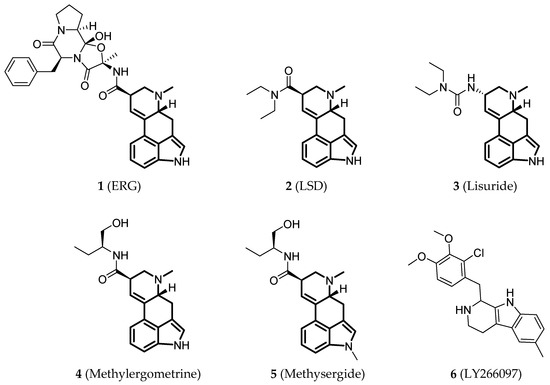
Figure 1.
Small-molecule ligands in co-crystal structures of 5-HT2BR-ligand complexes.
3.2. Conformational States
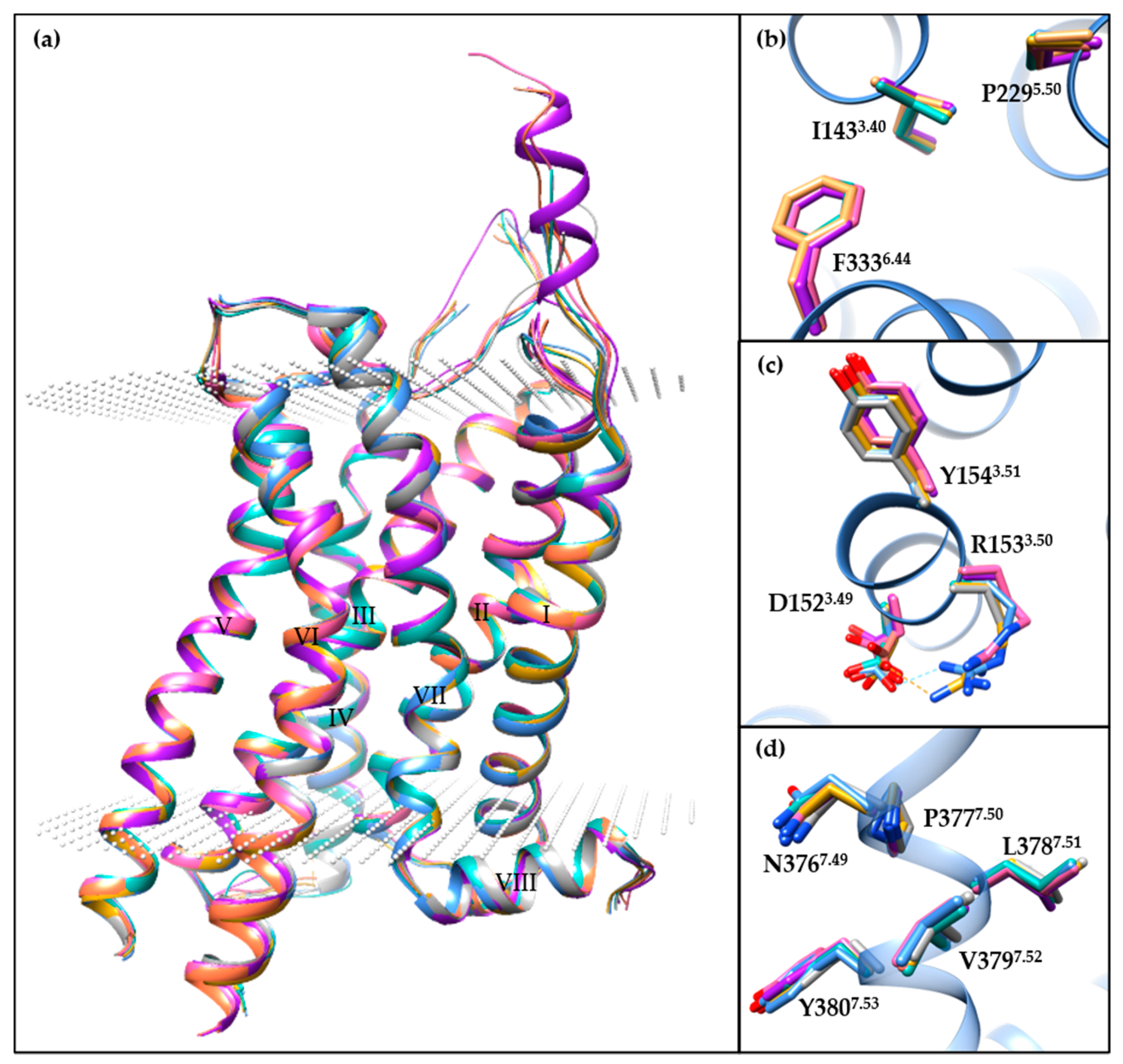
Apart from the 5-HT2BR/ERG-Fab structure (PDB ID: 5TUD), the other seven small-molecule-bound crystal structures show similar conformations (Figure 2a), especially in the helical region. Specifically, the Cα root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) values range from 0.34 to 0.60 Å using the 5-HT2BR/ERG structure as the reference (PDB ID: 4IB4). For the most classical microswitches in class A GPCRs, the seven structures show extremely similar conformations in PIF (Figure 2b) and NPxxY (Figure 2d) motifs and a slightly different conformation in the D(E)RY motif (Figure 2c). The salt bridge in the D(E)RY motif between D1523.49 and R1533.50 can only be observed in two of the structures (PDB IDs: 4IB4 and 6DS0). The electron densities for R1533.50 side chains in four other structures are not well-defined (PDB IDs: 4NC3, 6DRX, 6DRY, and 6DRZ), and the D1523.49 side chains are in different orientations. An analysis of the B-factor distributions suggests that the conformations of D1523.49 and R1533.50 side chains are unstable with relatively large B-factor values.
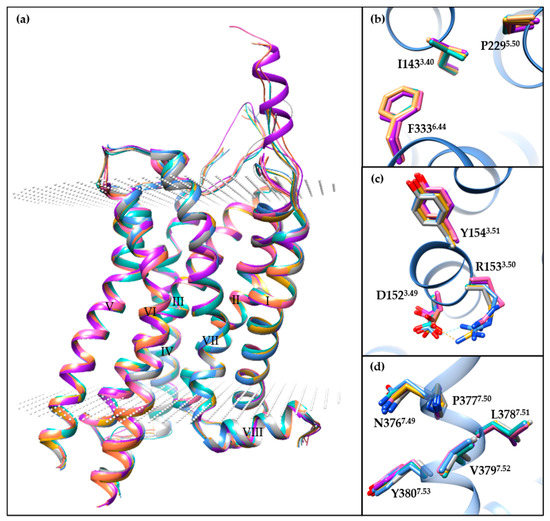
Figure 2.
A comparison of the different small-molecule-bound 5-HT2BR crystal structures. (a) The overall architecture of 5-HT2BR/ERG (cornflower blue, PDB ID: 4IB4), 5-HT2BR/ERG (dark gray, PDB ID: 4NC3), 5-HT2BR/LSD (hot pink, PDB ID: 5TVN), 5-HT2BR/lisuride (light sea green, PDB ID: 6DRX), 5-HT2BR/methylergometrine (salmon, PDB ID: 6DRY), 5-HT2BR/methysergide (purple, PDB ID: 6DRZ), 5-HT2BR/LY266097 (goldenrod, PDB ID: 6DS0) structures aligned through the Cα atoms of residues in helices I to VIII. The 5-HT2BRs are displayed as ribbon cartoons, and the membrane boundaries are displayed as white dots, according to the Orientations of Proteins in Membranes database. (b–d) Specific comparison of residues in (b) PIF, (c) D(E)RY and (d) NPxxY motifs. For clear visualization, residues apart from the motif are hidden, with the exception of the 5-HT2BR/ERG structure (PDB ID: 4IB4). Molecular images were generated using the UCSF Chimera software [115].
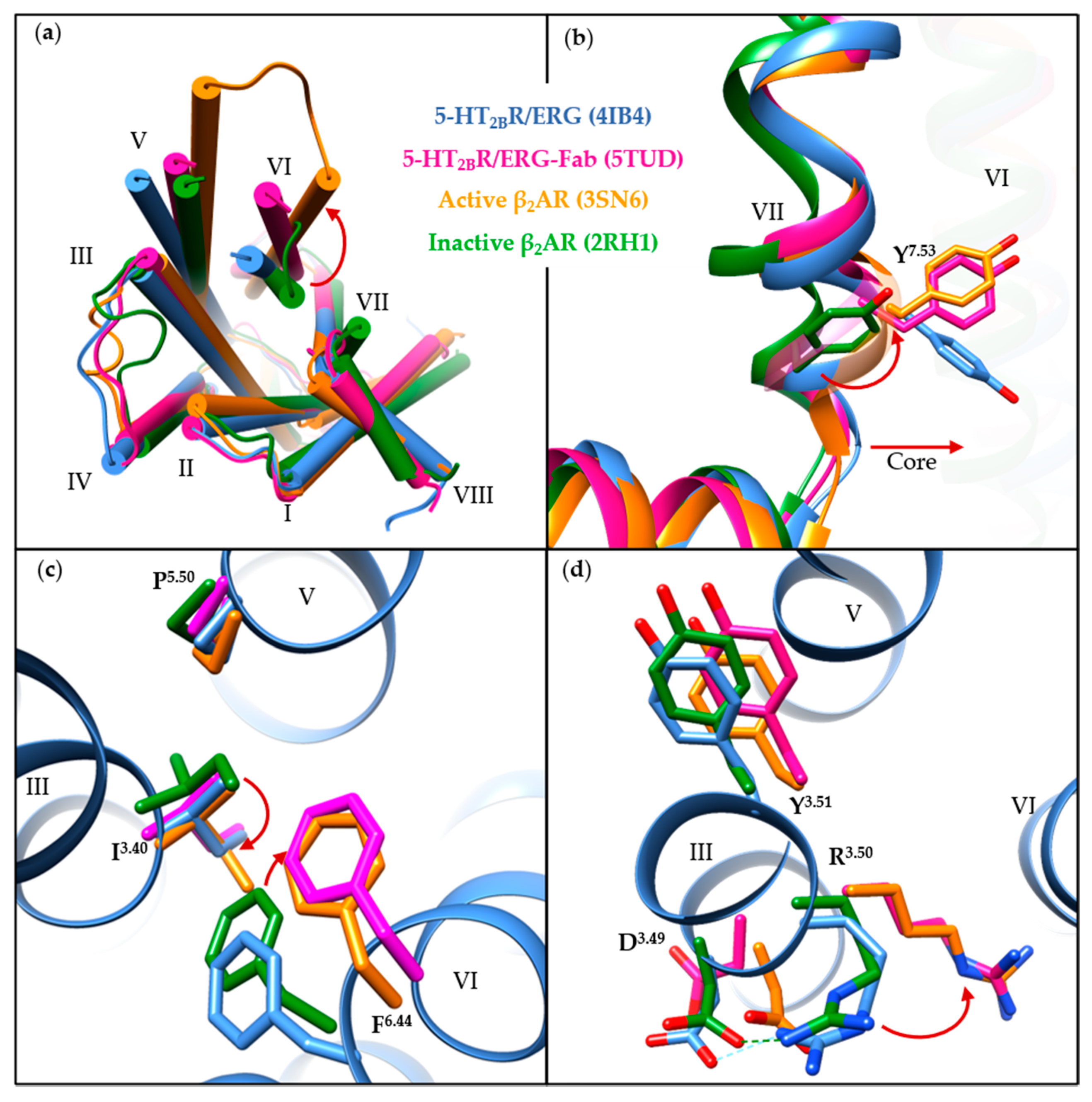
5-HT2BR/ERG-Fab (PDB ID: 5TUD) structure shows distinct features compared with the other seven structures. Since the determined small-molecule-bound structures share common structural features in the transmembrane regions and the key motifs, we compared the 5-HT2BR/ERG structure (PDB ID: 4IB4) with the 5-HT2BR/ERG-Fab structure in order to illustrate the conformational changes of the 5-HT2BR, using the well-known active-state (PDB ID: 3SN6) [116] and inactive-state (PDB ID: 2RH1) [117] β2-adrenergic receptor (β2AR) structures as references (Figure 3a). Upon activation, an outward movement of the intracellular helix VI (Figure 3a), and an inward shift of helix VII along with a side-chain rotation of Y7.53 (Figure 3b), are believed to represent common features in class A GPCRs [118,119]. When compared to the 5-HT2BR/ERG structure, the 5-HT2BR/ERG-Fab structure shows a more evident outward movement of the intracellular helix VI (Figure 3a). The backbone atoms of helix VII in both the 5-HT2BR/ERG and the 5-HT2BR/ERG-Fab structures overlapped well with the active-state β2AR structure, whereas the orientation of the Y7.53 side chain in 5-HT2BR/ERG is slightly different (Figure 3b). In the PIF motif, the three residues in the 5-HT2BR/ERG-Fab structure show active-like conformations. Although the P2295.50 and the I1433.40 residues show active-like conformations in the 5-HT2BR/ERG structure, the F3336.44 residue shows an inactive-like conformation (Figure 3c). In the D(E)RY motif, the R1533.50 in the 5-HT2BR/ERG-Fab structure displays an extended conformation towards helix VI, similar to the active-state β2AR structure. Hence, the salt bridge between D1523.49 and R1533.50 is fully broken (Figure 3d). In summary, considering the helical movement and microswitches, the 5-HT2BR/ERG-Fab structure shows an active-like state, whereas the 5-HT2BR/ERG and other small-molecule bound 5-HT2BR structures are in intermediate states.
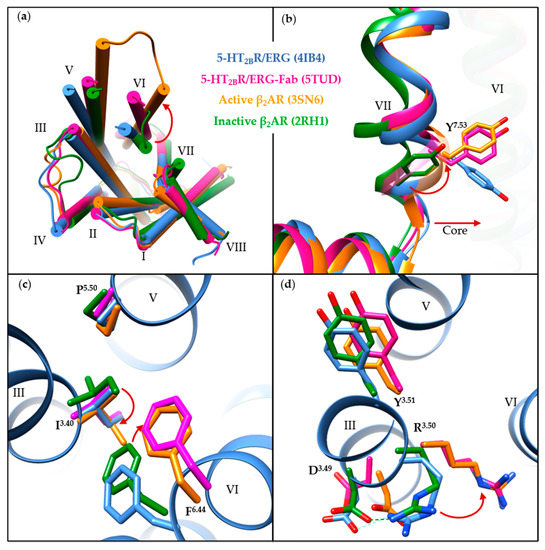
Figure 3.
A comparison of the 5-HT2BR/ERG (cornflower blue, PDB ID: 4IB4), the 5-HT2BR/ERG-Fab (magenta, PDB ID: 5TUD), the active-state β2AR (orange, PDB ID: 3SN6) and the inactive-state β2AR (forest green, PDB ID: 2RH1) crystal structures. (a) Intracellular view of the overall architecture. The outward movement of helix VI upon activation is indicated by a red arrow. (b) A comparison of structural features in helix VII. The slight inward movement of helix VII and rotation of Y7.53 in the NPxxY motif towards helix VI are highlighted by red arrows. (c,d) A comparison of the residues in (c) PIF and (d) D(E)RY motifs. For clear visualization, residues apart from the motif are hidden, with the exception of the 5-HT2BR/ERG structure (PDB ID: 4IB4). The obvious conformational changes of specific residues upon activation are shown as red arrows. Molecular images were generated using the UCSF Chimera software [115].
3.3. Orthosteric Binding Pocket (OBP)
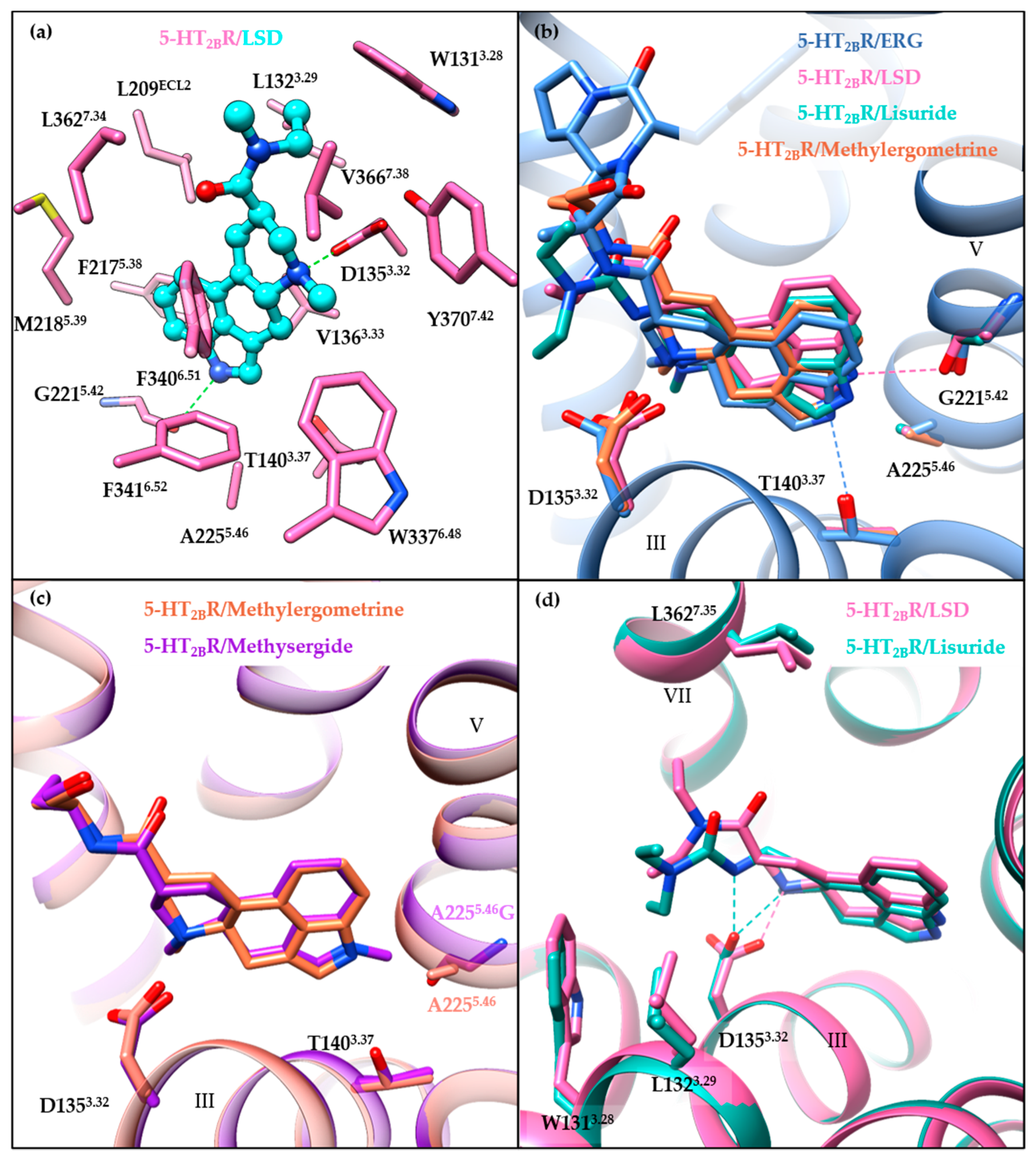
All of the small-molecule ligands in the published 5-HT2BR co-crystal structures occupy the OBP that is presumed as the 5-HT’s binding pocket, as well as regions outside the OBP and close to the extracellular loops, termed as the extended binding pocket (EBP) [120]. Taking LSD’s binding mode as an example, the ergoline ring system occupies the OBP by interacting residues in helices III, V, VI, and VII (Figure 4a). These interactions are commonly observed in aminergic GPCRs structures, including a conserved salt bridge between the positively charged nitrogen of the ligand and the carboxylic acid of D3.32, and π-π stacking interactions formed by the aromatic system of the ligand with residues F6.51 and F6.52 in helix VI. In the EBP, the diethylamide moiety of LSD interacts with residues in the extracellular side of helices III and VII as well as ECL2.
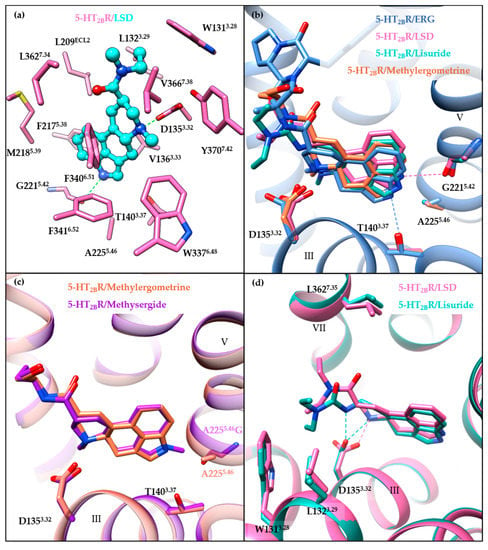
Figure 4.
Overview of receptor–ligand interactions in the binding pocket. (a) Receptor–ligand interactions in the binding pocket of the 5-HT2BR/LSD structure (PDB ID: 5TVN). Residues of the 5-HT2BR are colored in hot pink, and LSD is colored in cyan. (b) A comparison of the specific interactions in the OBP of ergoline ligand-bound structures: 5-HT2BR/ERG (cornflower blue, PDB ID: 4IB4), 5-HT2BR/LSD (hot pink, PDB ID: 5TVN), 5-HT2BR/lisuride (light sea green, PDB ID: 6DRX), and 5-HT2BR/methylergometrine (salmon, PDB ID: 6DRY). For clear visualization, only the backbone of 5-HT2BR/ERG is shown as a ribbon cartoon. The hydrogen bond interactions are displayed as dashed lines. (c) Comparison of the binding mode of the 5-HT2BR/methylergometrine (salmon, PDB ID: 6DRY) and the A2255.46G mutant 5-HT2BR/methysergide (purple, PDB ID: 6DRZ) structures. (d) Comparison of the specific interactions in the EBP of the 5-HT2BR/LSD (hot pink, PDB ID: 5TVN) and the 5-HT2BR/lisuride structures (light sea green, PDB ID: 6DRX). Hydrogen bond interactions are shown as dashed lines. Molecular images were generated using the UCSF Chimera software [115].
A comparison of the binding modes of ergoline ligands (ERG, LSD, lisuride, and methylergometrine) shows subtle differences (Figure 4b). Different orientations of the ergoline scaffolds seem to be caused by the different ergoline substituents, along with the rotation of D1353.32 side chains and the different orientations of the indole nitrogens towards helix V residues. The indole nitrogen atom of LSD points towards the backbone carbonyl oxygen of G2215.42, whereas the indole nitrogen atoms of ERG, lisuride, and methysergide point towards the A2255.46 residue and form hydrogen bonds (for ERG) or electrostatic interactions (for lisuride and methysergide) with the hydroxyl oxygen of L362. In fact, both T1403.37 and A2255.46 have been suggested to play significant roles in the activation mechanism [114]. On one hand, the T140A3.37 mutant substantially disrupted methylergometrine’s Gq agonism and β-arrestin2 recruitment. On the other hand, the A225G5.46 mutant restored both methysergide’s Gq agonism and β-arrestin2 recruitment. Moreover, the crystal structure of methysergide-bound 5-HT2BR with A225G5.46 mutation further explained the methysergide antagonism. Methysergide adopts a similar binding mode with methylergometrine in the 5-HT2BR/methylergometrine structure (Figure 4c), and its N-methyl group (which is the only difference between the two ligands) is oriented towards the mutated G2255.46 residue, suggesting that the A225G5.46 mutant results in larger space accommodate the ligands. Thus, pushing outward on helix V may be responsible for methysergide’s antagonism. Hence, both A2255.46 and T1403.37 are key residues in the OBP for the 5-HT2BR activation with equal contributions for Gq and β-arrestin2 activation mechanisms.
3.4. Extended Binding Pocket (EBP)
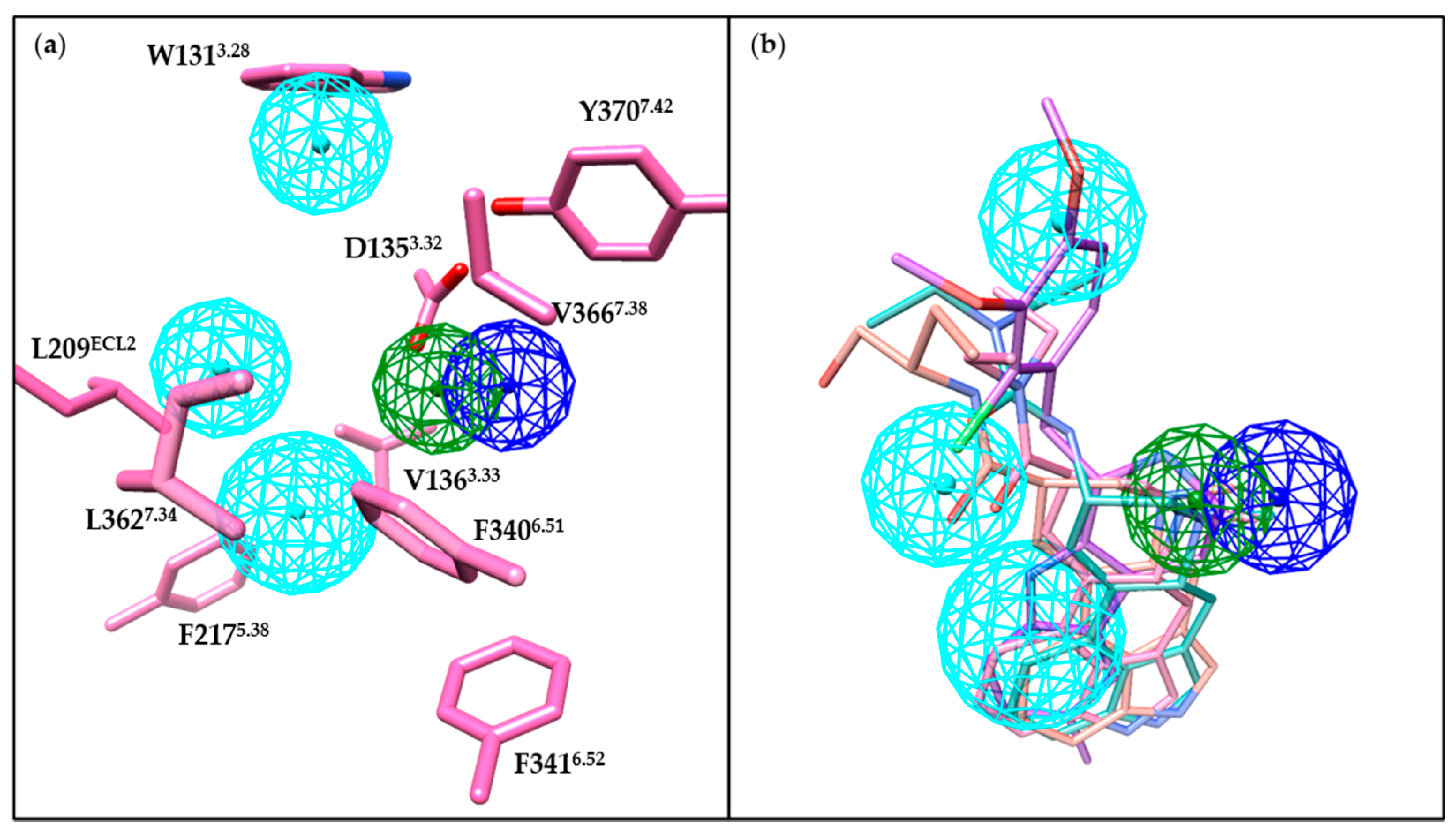
The role played by the EBP in receptor activation has been illustrated by comparing chemically similar but functionally distinct compounds such as LSD (5-HT2BR agonist) and lisuride (5-HT2BR antagonist). LSD and lisuride bear different substitutions on the ergoline scaffold, containing an (R)-diethylamide and an (S)-diethylurea substitution, respectively (Figure 1). Therefore, the main differences between their binding modes arise from the EBP. Lisuride’s (S)-diethylurea points towards helix III, forming hydrophobic interactions with W1313.28 and L1323.29, and an additional hydrogen bond with D1353.32 (Figure 4d). While LSD’s (R)-diethylamide interacts with helices III and VII, and forms additional interactions with L3627.35 in helix VII. Consequently, contact with helix VII appears to be essential for 5-HT2BR activation. A mutagenesis experiment of the L3627.35 residue in the 5-HT2BR has highlighted its crucial role in receptor activation, as mutants facilitating the contact with helix VII (L362N7.35, L362F7.35, L362Y7.35) restored lisuride’s Gq agonism. On the contrary, L362A7.35 mutant impaired LSD’s Gq agonism [114].
Moreover, the ligand recognition at helix VII in the EBP was also suggested to play an essential role in biased signaling. The L362F7.35 mutant restored lisuride’s Gq agonism, but not β-arrestin2 recruitment agonism [114]. For LSD, the L362F7.35 mutant abolished LSD’s β-arrestin2 recruitment without affecting its Gq agonism [114]. LY266097, a selective 5-HT2BR antagonist with modest Gq partial agonism and potent β-arrestin2 antagonism, interacts with residues in helix VII, including L3627.35. LY266097’s agonist potency was abolished in the L362F7.35 mutant [114]. Moreover, structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies showed that an analog of LY266097 lacking substituents on the benzyl moiety was able to fully abolish its Gq agonism [114].
Notably, residues in ECL2 have also been indicated to play a role in LSD’s long residence time and biased signaling [112]. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation results suggested that the fluctuation of the “lid” in ECL2 (residues 207–214) may influence LSD’s dissociation and that the L209ECL2A mutant may act by increasing the flexibility of the lid [112]. Further experimental verification found that the L209ECL2A mutant decreased LSD’s residence time and significantly reduced the β-arrestin2 recruitment potency and efficacy without affecting Gq agonism [112]. In addition, LSD’s β-arrestin2 recruitment was found to be time-dependent for both the 5-HT2AR and the 5-HT2BR. The L229ECL2A and L209ECL2A mutants could selectively abolish the 5-HT2AR’s, and the 5-HT2BR’s time-dependent β-arrestin2 recruitment, respectively [112].
In summary, key residues have been suggested to play important roles in receptor activation and biased signaling. Ligand recognition at helices III (T1403.37) and V (G2215.42, A2255.46) in the OBP appear to contribute equivalently to Gq and β-arrestin2 potency, whereas ligand recognition at helix VII (L3627.35) and ECL2 (L209ECL2) contributes to either Gq or β-arrestin2 activity. All of these would guide the discovery of novel 5-HT2BR ligands, especially for biased ligands. It is expected that biased ligands may provide more possibilities for enhancing therapeutic efficiencies and reducing adverse effects [121]. For example, a β-arrestin biased antagonist of dopamine D2 receptor (BRD5814) was shown to have considerable antipsychotic efficacy and reduced motoric side effects in a mouse model [122].
4. Pharmaceutical Ligands
As 5-HT2BR agonism has been considered as a side effect related to VHD, pharmaceutical ligand discovery has focused on the potential application of 5-HT2BR antagonism. Considering that many 5-HT2BR ligands early identified have been previously summarized [123,124], we mainly focus on reviewing the clinical-related pharmaceutical ligands and promising antagonists of the 5-HT2BR that were reported since 2010. Note that the Ki values mentioned below were determined by radiobinding assays.
4.1. Clinical-Related Pharmaceutical Ligands of the 5-HT2BR
4.1.1. MT-500
MT-500 (7, RS-127445, Table 2) is a 5-HT2BR antagonist with high affinity (Ki = 0.3 nM) and high selectivity over many other 5-HT receptor subtypes (especially about 1000-fold selectivity over the closely related human 5-HT2AR and 5-HT2CR) [125]. In vitro functional assays demonstrated that MT-500 could inhibit the 5-HT-induced increases of inositol phosphates and intracellular calcium concentration (IC50 = 0.1 nM) and block the 5-HT-induced contraction of the rat stomach fundus [125]. In addition, in vivo pharmacokinetic studies in rats showed that MT-500 was readily absorbed by oral or intraperitoneal routes [125]. Several studies used MT-500 as a tool compound to investigate the functions of the 5-HT2BR [62,63,83,85,108]. In 1999, POZEN acquired MT-500 from Roche and took full charge of its development for migraine prophylaxis. The phase 1 clinical trial of MT-500 was completed and showed an encouraging safety profile. However, the development of MT-500 was discontinued in 2002 for unknown reasons.

Table 2.
5-HT2BR antagonists once came into clinical trials or are in clinical trials.
4.1.2. PRX-08066
PRX-08066 (8, Table 2) is a potent (Ki ~ 3.4 nM) and selective antagonist of the 5-HT2BR discovered by Porvasnik et al. [126]. In the study using the MCT-induced PAH rat model, PRX-08066 eased the severity of PAH by significantly reducing the elevation in PA pressure and right ventricle hypertrophy [126].
In May 2005, PRX-08066 entered a phase 1 clinical trial. The results of a dose-escalation study in healthy volunteers indicated that PRX-08066 was well-tolerated over a dose ranged from 25 mg to 800 mg, and no serious adverse events were observed. Later, PRX-08066 phase 1b safety and pharmacodynamic studies in healthy athletes started in November 2005. When volunteers took 200 mg of PRX-08066 orally, the increase in pulmonary artery blood pressure was significantly reduced (by 40%) during hypoxic exercise and did not influence systemic blood pressure. PRX-08066 thus advanced into phase 2 clinical trials in June 2006 (NCT00345774). The short-term safety and efficacy of PRX-08066 were evaluated in patients with PH associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The results were positive and indicated that PRX-08066 could significantly lower systolic pulmonary arterial pressure and was well-tolerated without any obvious effect on systemic blood pressure. In August 2008, PRX-08066 open-label phase 2 clinical trials commenced in order to assess its safety and efficacy in PH and COPD patients (NCT00677872). However, the trial was also later terminated, with no results reported.
4.1.3. BF-1
BF-1 (9, Table 2) is a selective and high-affinity antagonist of the 5-HT2BR (Ki = 2.7 nM) [79]. Tested in a guinea pig model for dural neurogenic PPE induced by mCPP or BW723C86, BF-1 exhibited significant reductions of dural PPE, indicating its potential as a migraine drug [79]. In December 2012, BF-1 commenced phase 1 clinical trials prophylactic for the treatment of migraine. However, no progress has since been reported, and the clinical trial was postulated to be discontinued.
4.1.4. AMAP102
AMAP102 (10, Table 2) is an orally available antagonist of the 5-HT2BR (structure and binding affinity are undisclosed) [127]. In vitro studies showed that AMAP102 decreased the release of proinflammatory cytokine TNF-α in human macrophages and IL-6 in rat synovial fibroblasts [127]. In vivo studies on several animal models, including collagen and glucose-6-phosphate isomerase-induced arthritis induced arthritis in mice and antigen-induced arthritis in rats, showed that AMAP102 exhibited anti-arthritic effects and reduced inflammatory pain responses [127].
In April 2009, AMAP102 entered a phase 1 clinical trial (NCT00995605) to evaluate its safety and tolerability in healthy subjects. The trial was successfully completed in August 2009, and the results showed that AMAP102 was safe and well-tolerated without any serious adverse events. In October 2014, AnaMar AB company reported the phase 2a results of AMAP102 for the treatment of inflammatory pain in osteoarthritis patients. However, compared with placebo, AMAP102 did not show a statistically significant reduction in pain over a 28-day period, and the AMAP102 clinical trial was thus discontinued.
4.1.5. AM1030
AM1030 (11, Table 2) [128], an aminoguanidine derivative (structure is not disclosed), is a 5-HT2BR antagonist (Ki = 330 nM). In vivo and in vitro studies on various human and rodent models suggested that AM1030 has therapeutic potential in various inflammatory diseases and is able to significantly reduce both T cell-dependent and T cell-independent inflammatory responses. Moreover, a first-in-man study in atopic dermatitis (AD) patients showed that topical administration of AM1030 was suitable for treatment. AM1030 phase 1/2 clinical trials studied in AD patients were completed in June 2015 (NCT02379910), but the results were not reported. Considering no development has since been disclosed, the development of AM1030 is assumed to be discontinued.
4.1.6. RQ-00310941
RQ-00310941 (12, Table 2) is an antagonist of the 5-HT2BR with high affinity (Ki = 2.0 nM) and good selectivity (>2000-fold selectivity against more than 60 GPCRs, ion channels, and enzymes) [64]. In vivo studies in the trinitrobenzene sulfonate-induced visceral hypersensitivity rat model indicated that RQ-00310941 has the therapeutic potential for diarrhea-predominant IBS [64]. Specifically, RQ-00310941 could attenuate the distal colon sensitivity (61% inhibition at 1 mg/kg, per os (p.o.)) and suppress the restraint stress-induced defecation (95% inhibition at 10 mg/kg, p.o.) without affecting normal defecation at high dose (30 mg/kg, p.o.) [64].
In July 2015, RQ-00310941 entered phase 1 clinical trials. Specifically, the safety/tolerability and pharmacokinetics in healthy subjects and the preliminary efficacy in mild to moderate ulcerative colitis (UC) patients with IBS-like symptoms were investigated [129]. The released results showed that RQ-00310941 was safe and well-tolerated without any serious adverse events in both healthy subjects and UC patients. Although there was no statistically significant difference observed between RQ-00310941 and placebo with respect to primary and secondary efficacy evaluations, most efficacy measures suggested slightly favorable outcomes compared to placebo, indicating a therapeutic potential for RQ-00310941 in the treatment of IBS-like symptoms in UC patients.
4.2. Representative Pharmaceutical Ligands of the 5-HT2BR
4.2.1. EXT5, EXT9, AM1125, and AM1476
AnaMar AB company is focused on the discovery and development of 5-HT2BR antagonists to prevent pathological inflammatory and fibrotic processes. Apart from AMAP102 (10) (Section 4.1.4) and AM1030 (11) (Section 4.1.5), which were mentioned above, they have also developed EXT5 (13), EXT9 (14), AM1125 (15), and AM1476 (16). The exact structures of these compounds are undisclosed. EXT5 and EXT9 are both benzylidene aminoguanidine derivatives [36], while AM1125 and AM1476 have general formula containing a 1-amidino-3-aryl-2-pyrazoline scaffold [130].
EXT5 (13) and EXT9 (14) are both mainly antagonizing the 5-HT2BR (EXT5: Ki = 45 nM, IC50 = 82 nM in IP1 accumulation assay; EXT9: Ki = 26 nM, IC50 = 29 nM in IP1 accumulation assay), and also exhibit low to moderate binding affinities to the 5-HT2AR and the 5-HT2CR. As mentioned above (Section 2.2.2), EXT5 and EXT9 were utilized for investigating the role played by the 5-HT2BR in fibrosis [36]. In vitro, the co-cultivation of TGF-β1 and 5-HT resulted in an increased α-SMA and proteoglycan production, which could be significantly decreased after the treatment with either EXT5 or EXT9. Additionally, in vivo studies on BLM-treated mice showed that both EXT5 and EXT9 could attenuate the fibrotic tissue remodeling, demonstrated by a decrease in tissue density, collagen-producing cells, myofibroblasts, and decorin expression [36]. Further gene expression studies suggested that the antiproliferative effects of EXT5 and EXT9 may be associated with the pAkt/p21 signaling pathway, a cell-cycle regulation pathway [38]. More recently, EXT5 and EXT9 were also used for investigating the role played by the 5-HT2BR on airway function and remodeling [131]. Studies showed that EXT5 and EXT9 inhibited 5-HT-induced bronchoconstriction, TGF-β1 release and the proliferation of smooth muscle cells [131]. Notably, the 5-HT-induced bronchoconstriction could also be suppressed by the 5-HT2AR/5-HT2CR antagonist ketanserin, but not by the 5-HT2BR selective antagonists RS-127445 or PRX-08066 [131]. The inhibitory effects of bronchoconstriction may involve a combination of 5-HT2 receptors and deserves further research efforts in the future.
AM1125 (15) is a highly selective 5-HT2BR antagonist (Ki = 0.9 nM). In November 2016, preclinical data of AM1125 was presented at the ACR annual meeting [132]. Treatment with AM1125 at 50 mg/kg reduced fibrosis parameters (hypodermal thickness, myofibroblast counts, and hydroxyproline content) in the tsk-1 model of SSc, which indicated a potential treatment opportunity for SSc. In May 2017, preclinical data on the antifibrotic effects of AM1125 was reported at the ATS International Conference [42]. In in vitro studies on human lung, fibroblasts showed that treatment with AM1125 significantly reduced TGF-β mRNA, plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 mRNA, and phosphorylated Smad 2/3. Further in vivo studies on BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis mice showed that the oral administration of AM1125 ameliorated pulmonary fibrosis with a reduction of the fibrotic area, myofibroblast counts and the amount of collagen protein. These results reflected the potential of AM1125 for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis.
AM1476 (16), an orally available 5-HT2BR antagonist with high selectivity (activity data are undisclosed), is currently in the late preclinical phase and under development for SSc [43]. Orally administration of AM1476 in the murine sclerodermatous chronic graft-versus-host disease model showed that it could significantly reduce all measured dermal and pulmonary fibrosis readouts [43]. Dermal fibrosis studied in the tsk-1 model of SSc showed reduced hypodermal thickening and the number of myofibroblast and hydroxyproline content. In addition, the number of pSmad3 positive cells was significantly reduced in skin samples suggested the inhibitory effect on the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway [43].
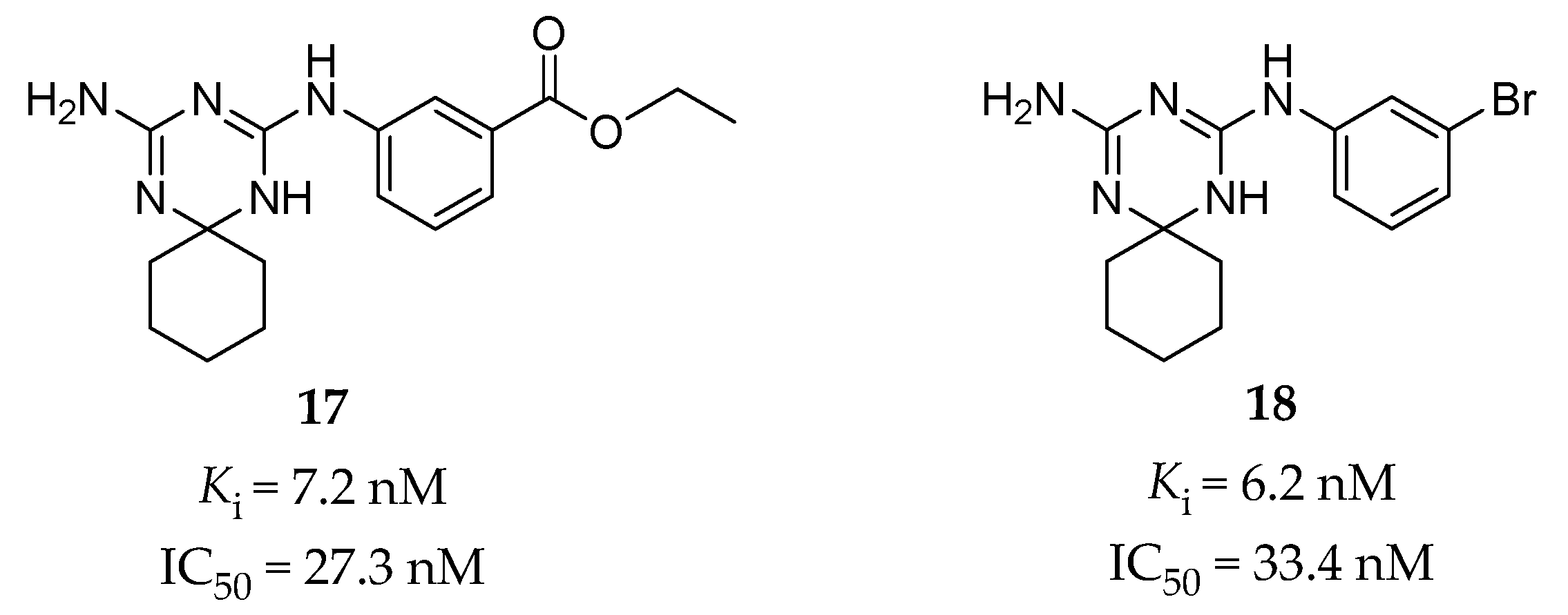
4.2.2. Bis-Amino-Triazine Derivatives
Using the structure-based hierarchical virtual screening approach [133], Huang et al. have identified a series of bis-amino-triazine derivatives as potent 5-HT2BR antagonists [65]. Two compounds (compound 17 and 18, Figure 5) were highlighted with comparable potency in the binding and functional assays in vitro (17: Ki = 7.2 nM, IC50 = 27.3 nM in calcium flux assay; 18: Ki = 6.2 nM, IC50 = 33.4 nM in calcium flux assay). Without the classical tertiary amine group, these compounds performed good binding selectivity for the 5-HT2BR over ten other tested 5-HT receptors [65]. In vivo studies further indicated that compound 18 could significantly attenuate visceral hypersensitivity in an IBS rat model [65].
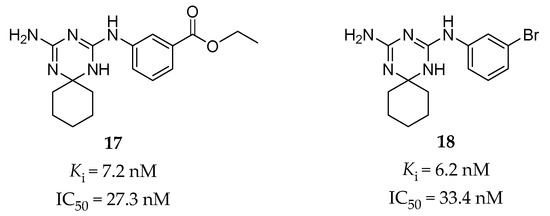
Figure 5.
Representative triazine derivatives as selective 5-HT2BR antagonists [65].
The predicted binding mode for compound 17 was verified by SAR analysis of a series of structural analogs [65]. The key interactions contain a typical salt bridge interaction between the protonated triazine ring and the carboxyl group of the conserved D1353.32 residue, hydrogen bonds between one amino (NH) group on the triazine ring and the D1353.32 residue, between the other amino (NH2) group and the N3446.55 residue, and between the ethyl benzoate moiety and the T1403.37 residue [65]. Notably, further assessment of the binding model for compound 18 showed that its potent binding affinity might be due to a halogen bonding interaction between the bromine atom and the carbonyl oxygen atom of the F2175.38 residue, which was supported by the subsequent SAR study and MD simulation [134].
4.2.3. Guanidine Derivatives
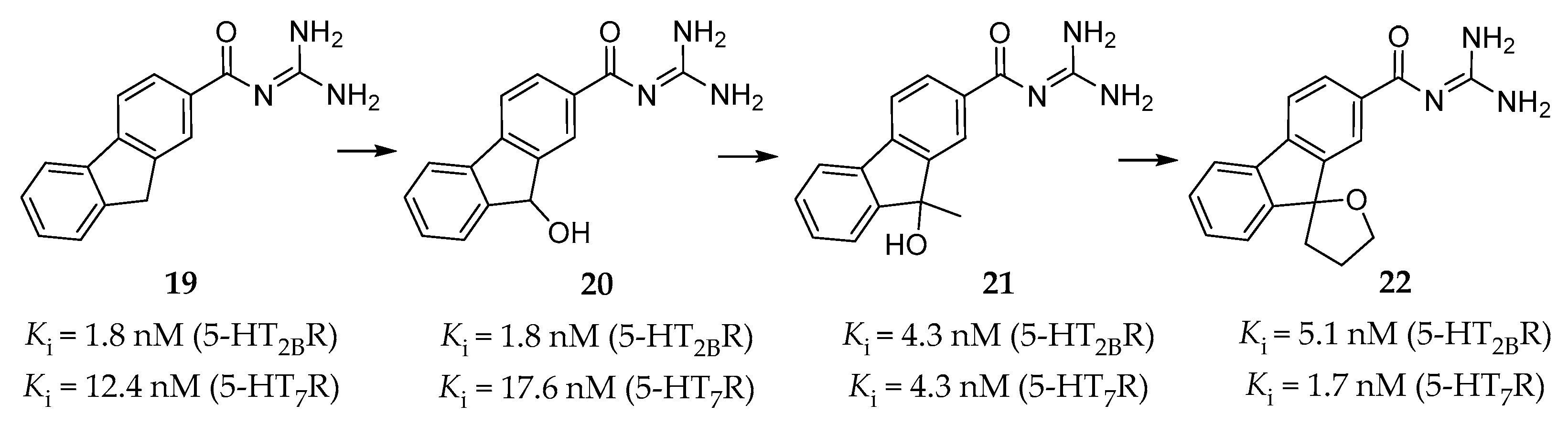
Inspired by the synergistic effect of the 5-HT2BR selective antagonist RS-127445 and the 5-HT7R selective antagonist SB-269970 found in the guinea pig model evaluating the antimigraine effect, Moritomo et al. discovered a series of carbonyl guanidine derivatives as dual 5-HT2BR and 5-HT7R antagonists for the treatment of migraines.
Originally, high throughput screening (HTS) led to the discovery of compound 19 (Figure 6) [135], which showed a high affinity for the 5-HT2BR (Ki = 1.8 nM) and the 5-HT7R (Ki = 12.4 nM), but poor aqueous solubility. Further SAR studies on a series of guanidine derivatives led to the identification of compound 20 (Figure 6), with a similar binding affinity (Ki = 1.8 nM for the 5-HT2BR, Ki = 17.6 nM for the 5-HT7R) and better aqueous solubility when compared to compound 19. The off-target assessment showed that compound 20 was selective for the 5-HT2BR and the 5-HT7R over several other monoaminergic GPCRs, and further functional assay determined its antagonistic activity towards the 5-HT2BR and the 5-HT7R [135]. Furthermore, in vivo studies showed that compound 20 had an inhibitory effect on 5-HT-induced dural PPE in guinea pigs at 3 mg/kg intraperitoneal administration. However, it was not able to reduce the amount of leaked protein from the dural blood vessel to the reference value at 30 mg/kg oral administration [135], which indicates a deficient oral bioavailability.
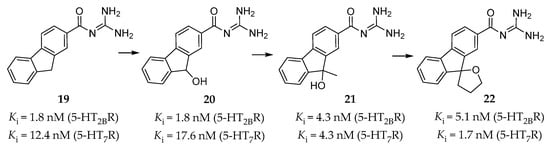
Figure 6.
Carbonyl guanidine derivatives as dual 5-HT2BR and 5-HT7R antagonists [135,136,137].
In order to improve oral potency and keep high affinity, the researchers further optimized guanidine 20 by taking the balance between lipophilicity and polar surface area into consideration [136]. SAR studies based on molecular modeling results led to the identification of compound 21, which showed both high affinity (Ki = 4.3 nM for the 5-HT2BR, Ki = 4.3 nM for the 5-HT7R, Figure 6) and selectivity [136]. When orally administered at 30 mg/kg in in vivo studies, compound 21 reversed the hypothermic effect of 5-carboxamidotryptamine in mice and showed a suppressing effect to normal levels on 5-HT-induced dural PPE in guinea pigs [136].
Considering about oxidation or conjugate metabolism of 9-OH in the fluorene ring of compound 21, a spiro cycloalkane ring was thus introduced to eliminate the concern about drug metabolism. This design led to a guanidine derivative 22 (Figure 6), which was found to be a high-affinity and selective antagonist of the 5-HT2BR and the 5-HT7R (Ki = 5.1 nM for the 5-HT2BR, Ki = 1.7 nM for the 5-HT7R) [137]. In vitro studies showed that both its optically pure isomers, (R)-22 and (S)-22, exhibited similar binding affinities and antagonistic activities against the 5-HT2BR and the 5-HT7R. Moreover, they both suppressed 5-HT-induced dural PPE and the amount of leaked protein to near normal levels at 10 mg/kg, p.o. in guinea pigs [137].
4.2.4. Chromone Derivatives
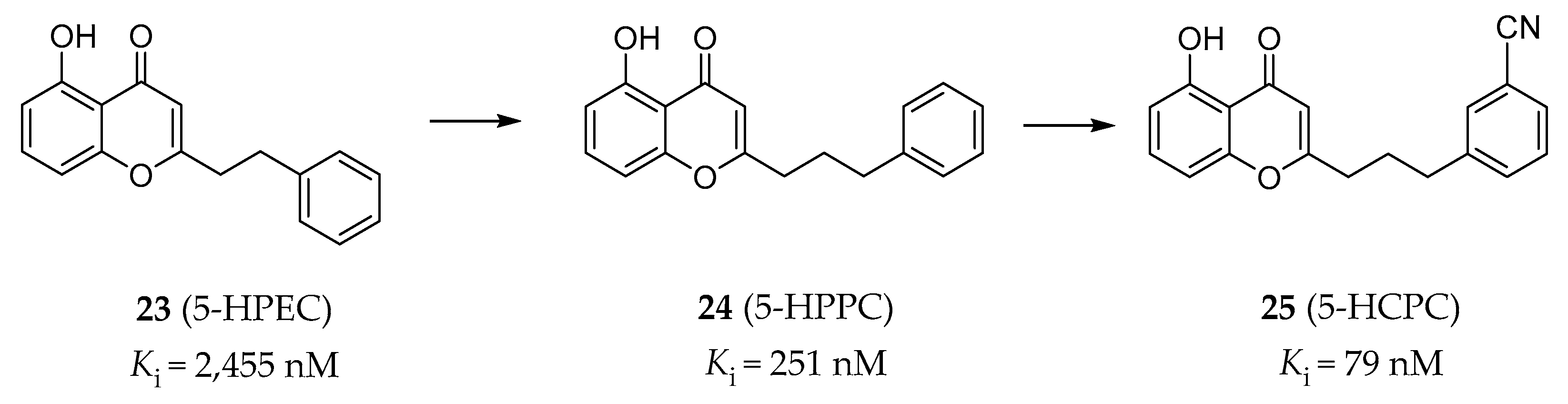
In order to study the molecular mechanism of the neuroprotective activity of 5-hydroxy-2-(2-phenylethyl)chromone (5-HPEC) (23, Figure 7) [138], a natural product isolated from Imperata cylindrical, Williams and colleagues performed a screening campaign against the CNS receptors, transporters and ion channels. The results showed that 5-HPEC is a 5-HT2BR antagonist, as was verified in radiobinding assays (Ki = 2455 nM) and calcium flux functional assays (IC50 = 8913 nM). 5-HPEC showed selectivity for the 5-HT2BR over other 5-HT2Rs. A subsequent SAR study on a series of synthesized and 5-HPEC’s natural analogs was performed and showed that the most potent analog, 5-hydroxy-2-(2-phenylpropyl)chromone (5-HPPC) (24, Figure 7), exhibited a 10-fold improvement in the 5-HT2BR affinity (Ki = 251 nM) and was able to maintain the 5-HT2BR antagonism [139]. Recently, further optimization of 5-HPPC guided by molecular modeling approaches helped to identify 5-hydroxy-2-(3-(3-cyanophenyl)propyl)chromone (5-HCPC) (25, Figure 7), which exhibited an improved binding affinity (Ki = 79 nM) compared with 5-HPPC and maintained inhibitory activity (IC50 = 6310 nM in calcium flux assay) at the 5-HT2BR, as well as selectivity over the 5-HT2AR and the 5-HT2CR [140]. It is worth mentioning that these chromone derivatives are non-nitrogenous, which are different from the typical nitrogen-containing ligands of the 5-HT2BR. Although the binding modes of this type of ligands were predicted by molecular docking, the evidence was insufficient to effectively demonstrate that these non-nitrogenous ligands bind to the orthosteric site of the 5-HT2BR. Considering the relatively weak cellular activity of 5-HCPC with much stronger binding affinity, it is not possible to exclude the possibility that they represent allosteric-site binders.
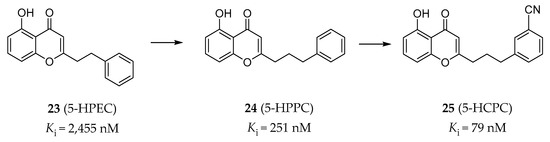
Figure 7.
Representative chromone derivatives as non-nitrogenous 5-HT2BR antagonists [138,139,140].
4.2.5. C4 Phenyl Aporphines and Tris-(phenylalkyl)amines
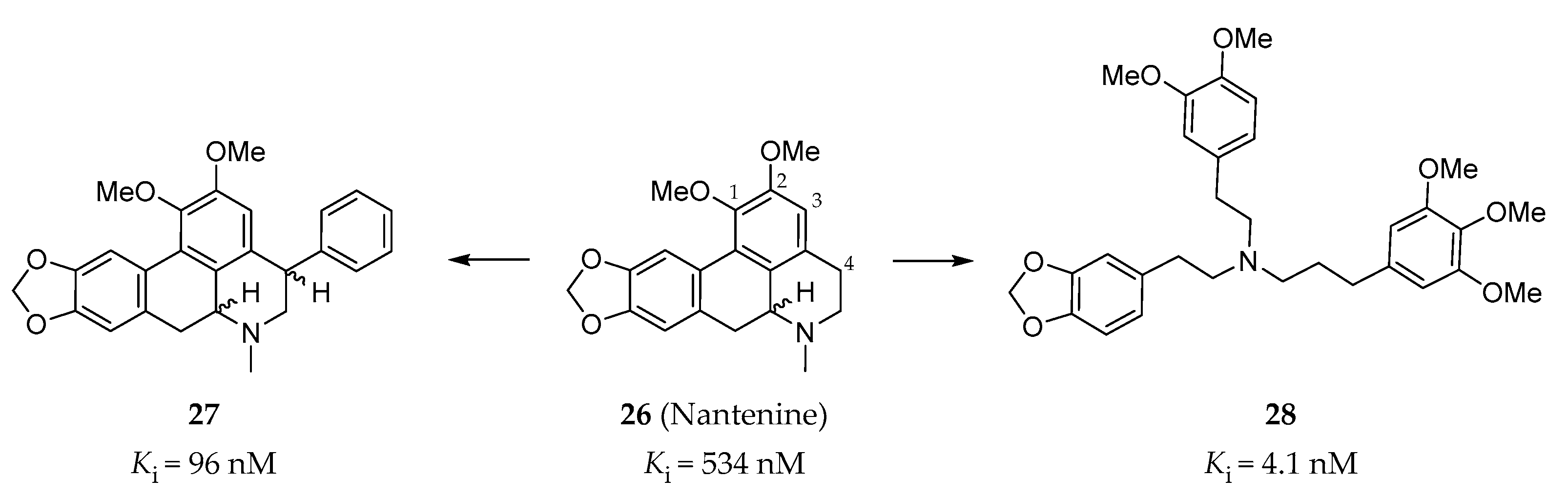
The Harding group at Hunter college focused on the synthesis and evaluation of nantenine analogs as 5-HT2AR antagonists. Nantenine (26, Figure 8) is a natural product with binding affinities to a number of CNS receptors (α1AR: Ki = 2 nM; 5-HT2AR: Ki = 850 nM, 5-HT2BR: Ki = 534 nM) [141]. In order to increase the 5-HT2AR affinity of nantenine, a series of nantenine analogs were designed. Surprisingly, nantenine analogs bearing a phenyl ring substituent at the C4 position displayed selective affinities to the 5-HT2BR [142]. Compound 27 (Figure 8) exhibited the best binding affinity (Ki = 96 nM) and was found to be a 5-HT2BR antagonist (IC50 = 1000 nM in calcium flux assay) with good selectivity over other tested CNS receptors [142]. In addition, in order to investigate whether the molecular rigidity of the aporphine template of nantenine affects the 5-HT2AR antagonism, a series of tris-(phenylalkyl)amines with increased flexibility compared with nantenine were synthesized. Similarly, these tris-(phenylalkyl)amines were found to have a high affinity and selectivity, as well as antagonist activity to the 5-HT2BR [143]. Among them, compound 28 (Figure 8) showed the best binding affinity to the 5-HT2BR (Ki = 4.1 nM, IC50 = 1259 nM in calcium flux assay), with a > 30-fold selectivity over the 5-HT2AR and the 5-HT2CR [143].
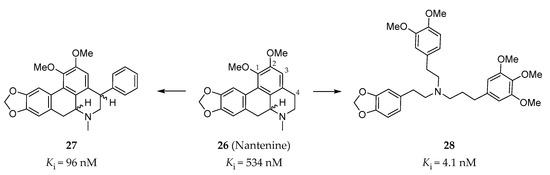
Figure 8.
Representative C4 phenyl aporphines (27) and tris-(phenylalkyl)amines (28) as 5-HT2BR antagonists [142,143].
4.2.6. Biphenyl Amide Derivatives
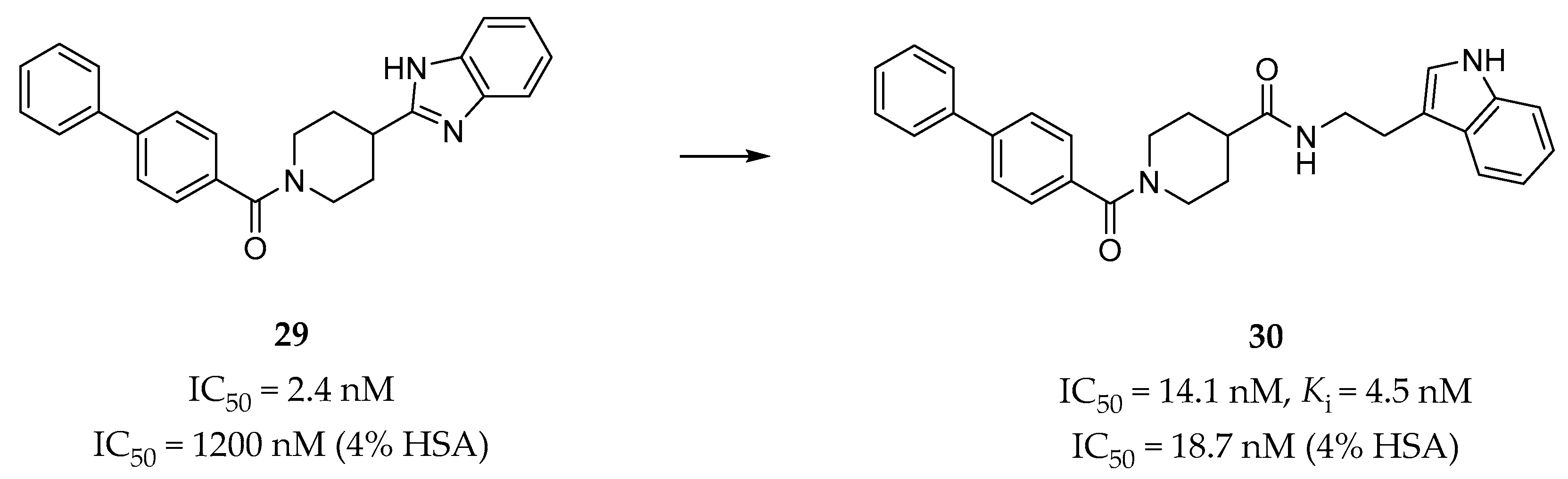
Gabr et al. identified a series of biphenyl amide derivatives as 5-HT2BR antagonists by rational drug design utilizing a pharmacophore-based approach [144]. The pharmacophore map was based on a previously published doxepin induced-fit model of the 5-HT2BR [65]. The pharmacophore of the lead compound 29 (Figure 9) [145], a potent 5-HT2BR antagonist (IC50 = 2.4 nM in calcium flux assay) with poor potency in the presence of human serum albumin (HSA) (IC50 = 1200 nM in 4% HSA), was initially overlaid with the receptor-based pharmacophore in order to provide directions for optimization. Finally, compound 30 (Ki = 4.5 nM, IC50 = 14.1 nM in calcium flux assay, Figure 9) was identified with high potency and selectivity for the 5-HT2BR over six other 5-HT receptors. In vitro, pharmacokinetic profile evaluation showed that compound 30 was able to almost completely maintain its antagonistic potency in the presence of 4% HSA (IC50 = 18.7 nM). In terms of the predicted binding mode, compound 30 could form an additional hydrogen bond with residue N3446.55, and hydrophobic interactions with several residues in the ECL2 of the receptor compared with compound 29 [145]. These additional interactions were regarded as contributing to both the potency and the selectivity of compound 30.
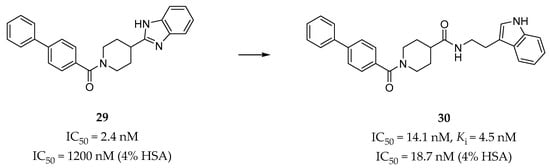
Figure 9.
Representative biphenyl amide derivative (30) as 5-HT2BR antagonists [144].
4.2.7. Chromane Derivatives
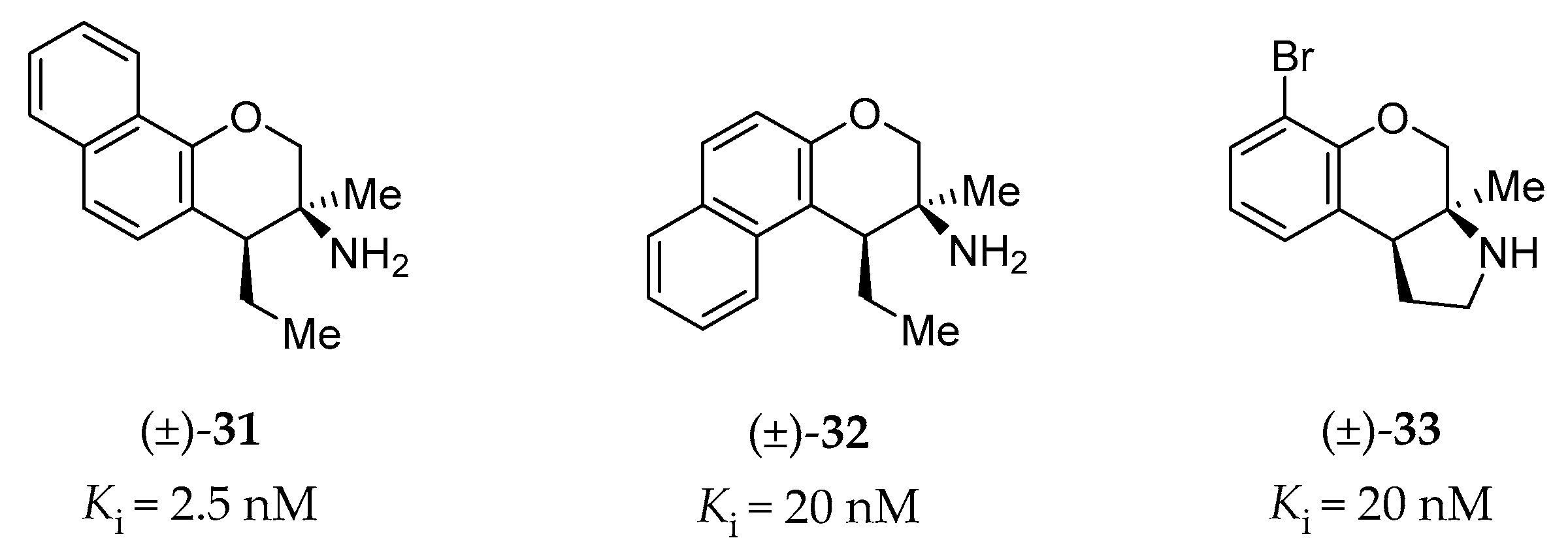
Porter et al. have investigated the GPCR affinity for a variety of heterocyclic phenethylamine derivatives, which helped them to identify several subtype-selective ligands, including 5-HT2BR ligands [146]. High-affinity (<100 nM) and high selectivity (>10-fold affinity over other tested GPCRs: 5-HT1AR, 5-HT7R, σ1, and σ2 receptors) 5-HT2BR ligands are shown in Figure 10 (racemic compound 31, 32 and 33), all of which are chromane derivatives.
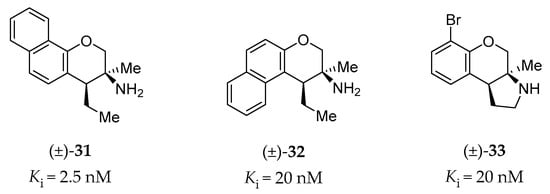
Figure 10.
Representative chromane derivatives as 5-HT2BR high-affinity ligands [146].
4.2.8. Other Pharmaceutical Ligands of the 5-HT2BR
In 2010, a urea type of ligand 34 (Ki = 42 nM, Table 3) was coincidentally discovered as a 5-HT2BR antagonist by Kwon et al. [147]. Notably, this compound showed strong selectivity for the 5-HT2BR over other serotonin receptors, as well as dopamine, histamine, muscarinic and opiate receptors. In 2011, C-122 (35, Table 3) was reported by Zopf et al. as a 5-HT2BR antagonist (Ki = 5.2 nM) [148]. It is worth mentioning that C-122 is not selective for the 5-HT2BR and also exhibit binding affinities against serotonin receptors such as the 5-HT7R (Ki = 4.4 nM), the 5-HT2AR (Ki = 61 nM), and several other monoaminergic GPCRs. In vivo studies on the MCT-induced PAH rat model showed that C-122 prevented MCT-induced elevations in the pulmonary arterial circuit pressure, right ventricular hypertrophy and pulmonary arteriole muscularization when orally administered at 10 mg/kg daily for 3 weeks [148]. In 2015, Rodrigues et al. carried out a proof-of-concept study of a large-scale multidimensional de novo design approach, combining computational molecular design and quantitative activity prediction with microfluidics synthesis, and discovered new chemical entities for the 5-HT2BR [149]. Several computationally designed compounds with a good predicted affinity and selectivity were subjected to experimental validation. As a result, piperazine 36 (Table 3) was identified as a 5-HT2BR antagonist (Ki = 251 nM), with high binding and functional selectivity [149]. In 2016, considering that adenosine derivatives were reported with micromolar activity at the 5-HT2BR and the 5-HT2CR, Tosh et al. applied a structure-based drug design approach to further improve the 5-HT2R affinity and simultaneously reduce the affinity to adenosine receptors (ARs) [150]. A SAR study on a series of adenosine derivatives assisted them in identifying several antagonists of the 5-HT2B/5-HT2C receptors with selectivity over ARs. Among them, compound 37 (Table 3) showed high binding affinity (Ki = 23 nM) and antagonist activity for the 5-HT2BR, with 12-fold binding selectivity and 170-fold functional selectivity for the 5-HT2BR over the 5-HT2CR [150]. In 2018, Rataj et al. combined a fingerprint-based machine learning approach and molecular docking that led to the identification of compound 38 (Table 3) [151]. Notably, compound 38 showed potent binding affinity (Ki = 0.3 nM) and >10,000-fold selectivity over other five tested 5-HTRs [151]. In addition, in 2018, as a proof-of-concept of halogen bonding in designing 5-HT2BR ligands, a series of halogen-substituted analogs of doxepin (Ki = 25.3 nM for the 5-HT2BR) were synthesized. As expected, the bromine-substituted compound 39 (Table 3) showed a 10-fold increased binding affinity towards the 5-HT2BR (Ki = 2.5 nM), a 10-fold improvement when compared to doxepin, and exhibited superior potency in a mouse model of diarrhea [134].

Table 3.
Other representative pharmaceutical ligands of the 5-HT2BR.
4.3. Summary of Binding Features of 5-HT2BR Ligands
The crystal structures of the 5-HT2BR facilitate our detailed understanding of receptor-ligand binding interactions. Therefore, we generated a receptor-based pharmacophore model (Figure 11a) to reconcile the critical binding interactions of the pharmaceutical ligands mentioned above. Notably, co-crystal ligands fit well in this pharmacophore model (Figure 11b). Most of the 5-HT2BR ligands bear positively charged nitrogens or polar NH groups to form favorable salt bridge or hydrogen bond interaction with the carboxylic side chain of residue D1353.32 (Figure 11a). Moreover, aromatic rings or hydrophobic fragments of 5-HT2BR ligands shall form π-π stacking or hydrophobic interactions with residues in the OBP in helices III, V, VI and VII; and residues in the EBP in helices III and VII, as well as in the ECL2 (Figure 11a). Such a pharmacophore model can be expected to guide the discovery and development of new 5-HT2BR ligands.
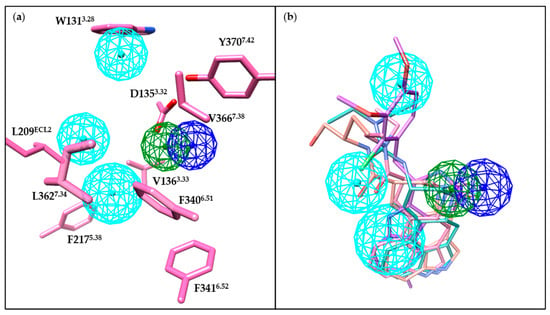
Figure 11.
Key pharmacophore features of the 5-HT2BR. Positive electrostatic, hydrogen bond donor and hydrophobic pharmacophore features are colored in blue, green, and cyan, respectively. Pharmacophore features were generated based on the 5-HT2BR crystal structure (PDB ID: 5TVN) using the CavityPlus web server [152]. (a) Association of 5-HT2BR residues and pharmacophore features. Residues close the pharmacophore and contributing to the protein–ligand interactions are shown in hot pink sticks. (b) Association of co-crystal ligands and pharmacophore features. LSD (PDB ID: 5TVN), lisuride (PDB ID: 6DRX), methylergometrine (PDB ID: 6DRY), and LY266097 (PDB ID: 6DS0) are shown as hot pink, light sea green, salmon, and purple stick, respectively. These ligands are aligned based on residues in the binding pocket. Molecular images were generated using the UCSF Chimera software [115].
5. Conclusions
The 5-HT2BR has been implicated in multiple diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, fibrosis disorders, cancer, IBS, migraine and neuropsychiatric disorders. The increasing number of crystal complex structures of the 5-HT2BR has provided great insights into ligand recognition, activation mechanism, and biased signaling. Nonetheless, inactive-state 5-HT2BR structural information and G protein and β-arrestin bound 5-HT2BR structures are still desirable to be obtained to further promote the development of novel 5-HT2BR ligands. Although many 5-HT2BR antagonists have been identified, with several candidates having advanced into clinical trials, no approved drug currently exists for the 5-HT2BR. Based on the recently solved crystal structures of GPCRs, particularly the closest homologs 5-HT2AR and 5-HT2CR [153,154,155], more research efforts should be employed to develop subtype-selective 5-HT2BR antagonists. Moreover, most existing 5-HT2BR ligands were discovered without the consideration of biased signaling, while it is desirable to study the biased signaling of the identified 5-HT2BR ligands, which may not only facilitate to understand the therapeutic effect-related signaling but also develop therapeutic drugs to avoid side effects.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.W. and N.H.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.W. and Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.H. and N.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21807007) to Y.Z., and the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Project (Z161100000116024) to N.H.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
5-HT2BR, 5-hydroxytryptamine 2B receptor; 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine; GPCRs, G protein-coupled receptors; 5-HTRs, 5-HT receptors; 5-HT2R, 5-HT2 receptor; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; GDP, guanosine diphosphate; PLCβ, phospholipase Cβ; DAG, diacylglycerol; IP3, inositol triphosphate; VHD, valvular heart disease; PAH, pulmonary arterial hypertension; VICs, valvular interstitial cells; ECM, extracellular matrix; MDMA, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine; BM, bone marrow; MVP, mitral valve prolapse; CAVD, calcific aortic valve disease; DOCA, deoxycorticosterone acetate; MCT, monocrotaline; PH, pulmonary hypertension; IPF, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; BLM, bleomycin; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor β1; SSc, systemic sclerosis; tsk-1, tight-skin-1; HADF, human adult dermal fibroblasts; ICC, interstitial cells of Cajal; PLC, phospholipase C; PKCγ, protein kinase Cγ; IBS, irritable bowel syndrome; NO, nitric oxide; mCPP, meta-chlorophenylpiperazine; PPE, plasma protein extravasation; CNS, central nervous system; SSRIs, serotonin-specific reuptake inhibitors; DA, dopamine; NAc, nucleus accumbens; mPFC, medial prefrontal cortex; GI, gastrointestinal; ERG, ergotamine; LSD, lysergic acid diethylamine; RMSD, root-mean-square deviation; OBP, orthosteric binding pocket; EBP, extended binding pocket; SAR, structure–activity relationship; MD, molecular dynamics; UC, ulcerative colitis; AD, atopic dermatitis; HTS, high throughput screening; p.o., per os; 5-HPEC, 5-hydroxy-2-(2-phenylethyl)chromone; 5-HPPC, 5-hydroxy-2-(2-phenylpropyl)chromone; 5-HCPC, 5-hydroxy-2-(3-(3-cyanophenyl)propyl)chromone; ARs, adenosine receptors.
References
- Rapport, M.M.; Green, A.A.; Page, I.H. Crystalline Serotonin. Science 1948, 108, 329–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhariya, K.; Bhandare, R.; Canney, D.; Velingkar, V. Cardiovascular Concern of 5-HT2B Receptor and Recent Vistas in the Development of Its Antagonists. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. Drug Targets. 2017, 17, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göthert, M.; Bönisch, H.; Malinowska, B.; Schlicker, E. Serotonin Discovery and Stepwise Disclosure of 5-HT Receptor Complexity over Four Decades. Part II. Some Contributions of Manfred Göthert. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020, 72, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foguet, M.; Nguyen, H.; Le, H.; Lübbert, H. Structure of the Mouse 5-HT1C, 5-HT2 and Stomach Fundus Serotonin Receptor Genes. Neuroreport 1992, 3, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmuck, K.; Ullmer, C.; Engels, P.; Lübbert, H. Cloning and Functional Characterization of the Human 5-HT2B Serotonin Receptor. FEBS Lett. 1994, 342, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursar, J.D.; Nelson, D.L.; Wainscott, D.B.; Baez, M. Molecular Cloning, Functional Expression, and MRNA Tissue Distribution of the Human 5-Hydroxytryptamine2B Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 1994, 46, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Devroye, C.; Cathala, A.; Piazza, P.V.; Spampinato, U. The Central Serotonin2B Receptor as a New Pharmacological Target for the Treatment of Dopamine-Related Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Rationale and Current Status of Research. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 181, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, A.; Holst, K.; Ponimaskin, E. How Serotonin Receptors Regulate Morphogenic Signalling in Neurons. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 151, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebigil, C.G.; Choi, D.-S.; Dierich, A.; Hickel, P.; Meur, M.L.; Messaddeq, N.; Launay, J.-M.; Maroteaux, L. Serotonin 2B Receptor Is Required for Heart Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9508–9513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroteaux, L.; Ayme-Dietrich, E.; Aubertin-Kirch, G.; Banas, S.; Quentin, E.; Lawson, R.; Monassier, L. New Therapeutic Opportunities for 5-HT2 Receptor Ligands. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 170, 14–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebigil, C.; Jaffré, F.; Messaddeq, N.; Hickel, P.; Monassier, L.; Launay, J.-M.; Maroteaux, L. Overexpression of the Serotonin 5-HT 2B Receptor in Heart Leads to Abnormal Mitochondrial Function and Cardiac Hypertrophy. Circulation 2003, 107, 3223–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffré, F.; Callebert, J.; Sarre, A.; Etienne, N.; Nebigil, C.G.; Launay, J.-M.; Maroteaux, L.; Monassier, L. Involvement of the Serotonin 5-HT2B Receptor in Cardiac Hypertrophy Linked to Sympathetic Stimulation: Control of Interleukin-6, Interleukin-1beta, and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Cytokine Production by Ventricular Fibroblasts. Circulation 2004, 110, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Monassier, L.; Laplante, M.-A.; Jaffré, F.; Bousquet, P.; Maroteaux, L.; de Champlain, J. Serotonin 5-HT(2B) Receptor Blockade Prevents Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy in Mice. Hypertension 2008, 52, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, C.-F.; Liu, J.-C.; Zhao, R.; Cao, W.; Liu, S.-B.; Zhang, X.-N.; Guo, H.-J.; Yang, Q.; Yi, D.-H.; Zhao, M.-G. Role of 5-HT2B Receptors in Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis in Noradrenaline-Induced Cardiomyopathy in Rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 37, e145–e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonfara, S.; Hetzel, U.; Oyama, M.A.; Kipar, A. The Potential Role of Myocardial Serotonin Receptor 2B Expression in Canine Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Vet. J. 2014, 199, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceron, C.; Goyal, A.; Makaryus, A.N. Drug Induced Valvular Heart Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fortier, J.H.; Pizzarotti, B.; Shaw, R.E.; Levy, R.J.; Ferrari, G.; Grau, J. Drug-Associated Valvular Heart Diseases and Serotonin-Related Pathways: A Meta-Analysis. Heart 2019, 105, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayme-Dietrich, E.; Lawson, R.; Côté, F.; de Tapia, C.; Silva, S.D.; Ebel, C.; Hechler, B.; Gachet, C.; Guyonnet, J.; Rouillard, H.; et al. The Role of 5-HT2B Receptors in Mitral Valvulopathy: Bone Marrow Mobilization of Endothelial Progenitors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 4123–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoian, T.; Jagadeesh, G.; Saulnier, M.; Simpson, N.; Ravindran, A.; Yang, B.; Laniyonu, A.A.; Khan, I.; Szarfman, A. Regulatory Forum Review*: Utility of in Vitro Secondary Pharmacology Data to Assess Risk of Drug-Induced Valvular Heart Disease in Humans: Regulatory Considerations. Toxicol. Pathol. 2017, 45, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, B.L. Drugs and Valvular Heart Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driesbaugh, K.H.; Branchetti, E.; Grau, J.B.; Keeney, S.J.; Glass, K.; Oyama, M.A.; Rioux, N.; Ayoub, S.; Sacks, M.S.; Quackenbush, J.; et al. Serotonin Receptor 2B Signaling with Interstitial Cell Activation and Leaflet Remodeling in Degenerative Mitral Regurgitation. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2018, 115, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutcheson, J.D.; Ryzhova, L.M.; Setola, V.; Merryman, W.D. 5-HT2B Antagonism Arrests Non-Canonical TGF-Β1-Induced Valvular Myofibroblast Differentiation. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 53, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joll, J.E.; Clark, C.R.; Peters, C.S.; Raddatz, M.A.; Bersi, M.R.; Merryman, W.D. Genetic Ablation of Serotonin Receptor 2B Improves Aortic Valve Hemodynamics of Notch1 Heterozygous Mice in a High-Cholesterol Diet Model. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Launay, J.-M.; Hervé, P.; Peoc’h, K.; Tournois, C.; Callebert, J.; Nebigil, C.G.; Etienne, N.; Drouet, L.; Humbert, M.; Simonneau, G.; et al. Function of the Serotonin 5-Hydroxytryptamine 2B Receptor in Pulmonary Hypertension. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitrascu, R.; Kulcke, C.; Konigshoff, M.; Kouri, F.; Yang, X.; Morrell, N.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Weissmann, N.; Reiter, R.; Seeger, W.; et al. Terguride Ameliorates Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 1104–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, S.W.; Fink, G.D. 5-HT2B-Receptor Antagonist LY-272015 Is Antihypertensive in DOCA-Salt-Hypertensive Rats. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 1999, 276, H944–H952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, L.; Hawkinson, J.; Cantillon, M.; Reddy, D.G.; Bhat, S.R.; Laurent, C.E.; Bouchard, A.; Biernat, M.; Salvail, D. RP5063, a Novel, Multimodal, Serotonin Receptor Modulator, Prevents Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 810, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.D.; Carrier, E.J.; Bloodworth, N.C.; Schroer, A.K.; Chen, P.; Ryzhova, L.M.; Gladson, S.; Shay, S.; Hutcheson, J.D.; Merryman, W.D. Serotonin 2B Receptor Antagonism Prevents Heritable Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launay, J.-M.; Hervé, P.; Callebert, J.; Mallat, Z.; Collet, C.; Doly, S.; Belmer, A.; Diaz, S.L.; Hatia, S.; Côté, F.; et al. Serotonin 5-HT2B Receptors Are Required for Bone-Marrow Contribution to Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Blood 2012, 119, 1772–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloodworth, N.C.; Clark, C.R.; West, J.D.; Snider, J.C.; Gaskill, C.; Shay, S.; Scott, C.; Bastarache, J.; Gladson, S.; Moore, C.; et al. Bone Marrow-Derived Proangiogenic Cells Mediate Pulmonary Arteriole Stiffening via Serotonin 2B Receptor Dependent Mechanism. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, e51–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimkhani, M.R.; Oakley, F.; Murphy, L.B.; Mann, J.; Moles, A.; Perugorria, M.J.; Ellis, E.; Lakey, A.F.; Burt, A.D.; Douglass, A.; et al. Stimulating Healthy Tissue Regeneration by Targeting the 5-HT2B Receptor in Chronic Liver Disease. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1668–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, Q.; Li, S.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, B.; Lu, J. Chronic Restraint Stress Reduces Carbon Tetrachloride-induced Liver Fibrosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Ma, Y.-S.; Liu, J.-B.; Wu, Z.-J.; Wang, X.-P.; Liu, L.-P.; Wang, G.-R.; Fu, D.; Shi, W. Serotonin-Induced MiR-221/222 Contribute to the Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells. Biologia (Bratisl.) 2020, 75, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, A.; Marchal-Sommé, J.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Quesnel, C.; Borie, R.; Dehoux, M.; Ruffié, C.; Callebert, J.; Launay, J.-M.; Hénin, D.; et al. Modulation of Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis by Serotonin Receptor Antagonists in Mice. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 32, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Königshoff, M.; Dumitrascu, R.; Udalov, S.; Amarie, O.V.; Reiter, R.; Grimminger, F.; Seeger, W.; Schermuly, R.T.; Eickelberg, O. Increased Expression of 5-Hydroxytryptamine2A/B Receptors in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Rationale for Therapeutic Intervention. Thorax 2010, 65, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löfdahl, A.; Rydell-Törmänen, K.; Müller, C.; Holst, C.M.; Thiman, L.; Ekström, G.; Wenglén, C.; Larsson-Callerfelt, A.-K.; Westergren-Thorsson, G. 5-HT2B Receptor Antagonists Attenuate Myofibroblast Differentiation and Subsequent Fibrotic Responses in Vitro and in Vivo. Physiol. Rep. 2016, 4, e12873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Alla, S.; Elaidy, S.; Essawy, S. Evaluation of the Antifibrotic Effect of Serotonin Receptor Antagonists on Bleomycin Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats. Egypt. J. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 7, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfdahl, A.; Rydell-Törmänen, K.; Larsson-Callerfelt, A.-K.; Wenglén, C.; Westergren-Thorsson, G. Pulmonary Fibrosis in vivo Displays Increased P21 Expression Reduced by 5-HT 2B Receptor Antagonists in Vitro—A Potential Pathway Affecting Proliferation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dees, C.; Akhmetshina, A.; Zerr, P.; Reich, N.; Palumbo, K.; Horn, A.; Jüngel, A.; Beyer, C.; Krönke, G.; Zwerina, J.; et al. Platelet-Derived Serotonin Links Vascular Disease and Tissue Fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Misra, D.P.; Prasad, N.; Rastogi, K.; Singh, H.; Rai, M.K.; Agarwal, V. 5-HT2 and 5-HT2B Antagonists Attenuate pro-Fibrotic Phenotype in Human Adult Dermal Fibroblasts by Blocking TGF-Β1 Induced Non-Canonical Signaling Pathways Including STAT3: Implications for Fibrotic Diseases like Scleroderma. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Rai, M.; Singh, H.; Misra, D.; Prasad, N.; Agrawal, V.; Agarwal, V. Dual Inhibition by Phosphodiesterase 5 and 5-HT 2B Inhibitor Leads to near Complete Amelioration of Fibrotic Potential of Human Adult Dermal Fibroblasts Isolated from a Scleroderma Patient. Indian J. Rheumatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenglén, C.; Pettersson, L.; Arozenius, H.; Ekström, G. SAT0314 A Novel Highly Selective 5-Hydroxytryptamine 2B (5-HT2B) Receptor Antagonist Ameliorating Fibrosis in Preclinical Models of Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenglén, C.; Arozenius, H.; Pettersson, L.; Ekstrom, G. THU0353 AN ORALLY AVAILABLE HIGHLY SELECTIVE 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE 2B (5-HT2B) RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST AMELIORATING PULMONARY AND DERMAL FIBROSIS IN PRECLINICAL MODELS OF SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 457–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Pande, G.; Rai, M.; Misra, D.; Gupta, L.; Agarwal, V. The Convergence of Fibrosis and Immune Pathways: 5-HT2 and 5-HT2B Antagonists Attenuate Profibrotic Phenotype in Human Pancreatic Stellate Cells by Modulating Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Phosphorylation. Indian J. Rheumatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, T.; Friedman, S.L.; Hoshida, Y. Hepatic Stellate Cells as Key Target in Liver Fibrosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 121, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khomich, O.; Ivanov, A.V.; Bartosch, B. Metabolic Hallmarks of Hepatic Stellate Cells in Liver Fibrosis. Cells 2020, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elaidy, S.M.; Essawy, S.S. The Antifibrotic Effects of Alveolar Macrophages 5-HT2C Receptors Blockade on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats. Pharmacol. Rep. PR 2016, 68, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, M.K.; Makary, S. 5-HT7 Receptor Antagonism (SB-269970) Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats via Downregulating Oxidative Burden and Inflammatory Cascades and Ameliorating Collagen Deposition: Comparison to Terguride. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 814, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrouilhe, D.; Mesnil, M. Serotonin and Human Cancer: A Critical View. Biochimie 2019, 161, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soll, C.; Riener, M.-O.; Oberkofler, C.E.; Hellerbrand, C.; Wild, P.J.; DeOliveira, M.L.; Clavien, P.-A. Expression of Serotonin Receptors in Human Hepatocellular Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5902–5910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Chen, W.; Zhi, X.; Ma, T.; Xia, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, X.; et al. Serotonin Promotes the Proliferation of Serum-Deprived Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via Upregulation of FOXO3a. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yan, C.; Yin, C.; Gong, Z. Serotonin Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells Contribute to Sex Disparity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 3, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Yan, C.; Gong, Z. Interaction of Hepatic Stellate Cells with Neutrophils and Macrophages in the Liver Following Oncogenic Kras Activation in Transgenic Zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.A.; Banchs, J.; Iliescu, C.; Dasari, A.; Lopez-Mattei, J.; Yusuf, S.W. Carcinoid Heart Disease. Heart 2017, 103, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, A.R.; Davar, J.; Caplin, M.E. Carcinoid Heart Disease: A Review. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. 2018, 47, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svejda, B.; Kidd, M.; Giovinazzo, F.; Eltawil, K.; Gustafsson, B.I.; Pfragner, R.; Modlin, I.M. The 5-HT2B Receptor Plays a Key Regulatory Role in Both Neuroendocrine Tumor Cell Proliferation and the Modulation of the Fibroblast Component of the Neoplastic Microenvironment. Cancer 2010, 116, 2902–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.-H.; Li, J.; Dong, F.-Y.; Yang, J.-Y.; Liu, D.-J.; Yang, X.-M.; Wang, Y.-H.; Yang, M.-W.; Fu, X.-L.; Zhang, X.-X.; et al. Increased Serotonin Signaling Contributes to the Warburg Effect in Pancreatic Tumor Cells Under Metabolic Stress and Promotes Growth of Pancreatic Tumors in Mice. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 277–291.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borman, R.A.; Tilford, N.S.; Harmer, D.W.; Day, N.; Ellis, E.S.; Sheldrick, R.L.G.; Carey, J.; Coleman, R.A.; Baxter, G.S. 5-HT 2B Receptors Play a Key Role in Mediating the Excitatory Effects of 5-HT in Human Colon in Vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, M.M.; Gibbons, S.J.; Roeder, J.L.; Distad, M.; Ou, Y.; Strege, P.R.; Szurszewski, J.H.; Farrugia, G. Exogenous Serotonin Regulates Proliferation of Interstitial Cells of Cajal in Mouse Jejunum Through 5-HT2B Receptors. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharayil, V.S.; Wouters, M.M.; Stanich, J.E.; Roeder, J.L.; Lei, S.; Beyder, A.; Gomez-Pinilla, P.J.; Gershon, M.D.; Maroteaux, L.; Gibbons, S.J.; et al. Lack of Serotonin 5-HT2B Receptor Alters Proliferation and Network Volume of Interstitial Cells of Cajal in Vivo. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. Off. J. Eur. Gastrointest. Motil. Soc. 2010, 22, 462.e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, M.M.; Roeder, J.L.; Tharayil, V.S.; Stanich, J.E.; Strege, P.R.; Lei, S.; Bardsley, M.R.; Ordog, T.; Gibbons, S.J.; Farrugia, G. Protein Kinase Cγ Mediates Regulation of Proliferation by the Serotonin 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor 2B. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 21177–21184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassil, A.K.; Taylor, C.M.; Bolton, V.J.N.; Gray, K.M.; Brown, J.D.; Cutler, L.; Summerfield, S.G.; Bruton, G.; Winchester, W.J.; Lee, K.; et al. Inhibition of Colonic Motility and Defecation by RS-127445 Suggests an Involvement of the 5-HT2B Receptor in Rodent Large Bowel Physiology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’mahony, S.M.; Bulmer, D.C.; Coelho, A.-M.; Fitzgerald, P.; Bongiovanni, C.; Lee, K.; Winchester, W.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. 5-HT2B Receptors Modulate Visceral Hypersensitivity in a Stress-Sensitive Animal Model of Brain-Gut Axis Dysfunction. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 573.e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, N.; Inagaki, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Kawamura, K. The Novel 5-HT2B Receptor Antagonist, RQ-00310941, Attenuates Visceral Hypersensitivity and Abnormal Defecation in Rat Models. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, S-607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, J.; Lin, X.; Huang, X.-P.; Wu, K.; Huang, N. Structure-Based Discovery of Novel and Selective 5-Hydroxytryptamine 2B Receptor Antagonists for the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, H.; Mochiki, E.; Takahashi, N.; Kawamura, K.; Watanabe, A.; Sutou, T.; Ogawa, A.; Yanai, M.; Ogata, K.; Fujii, T.; et al. Effects of 5-HT2B, 5-HT3 and 5-HT4 Receptor Antagonists on Gastrointestinal Motor Activity in Dogs. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2013, 19, 6604–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, M.J.; Quinlan, M.A.; Blakely, R.D. Immune System Activation and Depression: Roles of Serotonin in the Central Nervous System and Periphery. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacqué-Cazenave, J.; Bharatiya, R.; Barrière, G.; Delbecque, J.-P.; Bouguiyoud, N.; Di Giovanni, G.; Cattaert, D.; De Deurwaerdère, P. Serotonin in Animal Cognition and Behavior. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, A.K.; Piantadosi, P.T.; Uhl, G.R.; Hall, F.S.; Holmes, A. Improved Visual Discrimination Learning in Mice with Partial 5-HT2B Gene Deletion. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 738, 135378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, M.E. Role of Glycogenolysis in Memory and Learning: Regulation by Noradrenaline, Serotonin and ATP. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, A.; Nieto-Vera, R.; Anaya-Jiménez, R.M. 5-HT2A/2B/2C Receptors, Memory and Therapeutic Targets. The Receptors. In 5-HT2A Receptors in the Central Nervous System; Guiard, B.P., Di Giovanni, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 32, pp. 259–271. ISBN 978-3-319-70474-6. [Google Scholar]
- Borkowski, L.F.; Craig, T.A.; Stricklin, O.E.; Johnson, K.A.; Nichols, N.L. 5-HT2A/B Receptor Expression in the Phrenic Motor Nucleus in a Rat Model of ALS (SOD1G93A). Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2020, 279, 103471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perim, R.R.; Fields, D.P.; Mitchell, G.S. Cross-Talk Inhibition between 5-HT2B and 5-HT7 Receptors in Phrenic Motor Facilitation via NADPH Oxidase and PKA. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2018, 314, R709–R715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadjalli, A.; Mitchell, G.S. Cervical Spinal 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B Receptors Are Both Necessary for Moderate Acute Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Phrenic Long-Term Facilitation. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 127, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segelcke, D.; Messlinger, K. Putative Role of 5-HT2B Receptors in Migraine Pathophysiology. Cephalalgia Int. J. Headache 2017, 37, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalón, M.; Maassen, C.; Van Den Brink, A. The Role of 5-Hydroxytryptamine in the Pathophysiology of Migraine and Its Relevance to the Design of Novel Treatments. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Yao, X.X.; Gao, S.H.; Li, R.; Li, B.J.; Yang, W.; Cui, R.J. Role of 5-HT Receptors in Neuropathic Pain: Potential Therapeutic Implications. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fozard, J.R.; Gray, J.A. 5-HT1C Receptor Activation: A Key Step in the Initiation of Migraine? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1989, 10, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, B.; Ullmer, C.; Segelcke, D.; Gwarek, M.; Zhu, X.-R.; Lübbert, H. BF-1—A Novel Selective 5-HT2B Receptor Antagonist Blocking Neurogenic Dural Plasma Protein Extravasation in Guinea Pigs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 751, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunfeld, A.; Segelcke, D.; Bäcker, I.; Mecheri, B.; Hemmer, K.; Dlugosch, E.; Andriske, M.; Paris, F.; Zhu, X.; Lübbert, H. Hypoxia Facilitates Neurogenic Dural Plasma Protein Extravasation in Mice: A Novel Animal Model for Migraine Pathophysiology. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-Y.; Chang, W.-J.; Lin, C.-S.; Huang, C.-Y.; Wang, H.-F.; Sun, W.-H. Serotonin Receptor 5-HT2B Mediates Serotonin-Induced Mechanical Hyperalgesia. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.-H. Commentary: Serotonin Receptor 2B Mediates Mechanical Hyperalgesia by Regulating Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1. J. Neurol. Neuromedicine 2016, 1, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Durán, C.; Vidal-Cantú, G.C.; Barragán-Iglesias, P.; Pineda-Farias, J.B.; Bravo-Hernández, M.; Murbartián, J.; Granados-Soto, V. Role of Peripheral and Spinal 5-HT2B Receptors in Formalin-Induced Nociception. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 102, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes-Durán, C.; Pineda-Farias, J.B.; Bravo-Hernández, M.; Quiñonez-Bastidas, G.N.; Vidal-Cantú, G.C.; Barragán-Iglesias, P.; Granados-Soto, V. Evidence for the Participation of Peripheral 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C Receptors in Formalin-Induced Secondary Mechanical Allodynia and Hyperalgesia. Neuroscience 2013, 232, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes-Durán, C.; Vidal-Cantú, G.C.; Godínez-Chaparro, B.; Granados-Soto, V. Role of Spinal 5-HT2 Receptors Subtypes in Formalin-Induced Long-Lasting Hypersensitivity. Pharmacol. Rep. 2016, 68, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineda-Farias, J.B.; Velázquez-Lagunas, I.; Barragán-Iglesias, P.; Cervantes-Durán, C.; Granados-Soto, V. 5-HT2B Receptor Antagonists Reduce Nerve Injury-Induced Tactile Allodynia and Expression of 5-HT2B Receptors. Drug Dev. Res. 2015, 76, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Bo, J.; Lei, Y.; Hu, F.; Xia, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lu, C.; Sun, Y.; Hou, B.; Ni, K.; et al. Anxiety-Induced Hyperalgesia in Female Rats Is Mediated by Cholecystokinin 2 Receptor in Rostral Ventromedial Medulla and Spinal 5-Hydroxytryptamine 2B Receptor. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 2009–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urtikova, N.; Berson, N.; Van Steenwinckel, J.; Doly, S.; Truchetto, J.; Maroteaux, L.; Pohl, M.; Conrath, M. Antinociceptive Effect of Peripheral Serotonin 5-HT2B Receptor Activation on Neuropathic Pain. Pain 2012, 153, 1320–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Andrea, I.; Béchade, C.; Maroteaux, L. Serotonin and 5-HT2B receptors in microglia control of behavior. In Handbook of Behavioral Neuroscience; Müller, C.P., Cunningham, K.A., Eds.; Handbook of the Behavioral Neurobiology of Serotonin; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Chapter 34; Volume 31, pp. 589–599. [Google Scholar]
- Kolodziejczak, M.; Béchade, C.; Gervasi, N.; Irinopoulou, T.; Banas, S.M.; Cordier, C.; Rebsam, A.; Roumier, A.; Maroteaux, L. Serotonin Modulates Developmental Microglia via 5-HT2B Receptors: Potential Implication during Synaptic Refinement of Retinogeniculate Projections. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béchade, C.; D’Andrea, I.; Etienne, F.; Verdonk, F.; Moutkine, I.; Banas, S.M.; Kolodziejczak, M.; Diaz, S.L.; Parkhurst, C.N.; Gan, W.B.; et al. The Serotonin 2B Receptor Is Required in Neonatal Microglia to Limit Neuroinflammation and Sickness Behavior in Adulthood. Glia 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, B.; Lovatt, D.; Xu, J.; Song, D.; Goldman, S.A.; Nedergaard, M.; Hertz, L.; Peng, L. 5-HT2B Receptors Are Expressed on Astrocytes from Brain and in Culture and Are a Chronic Target for All Five Conventional “Serotonin-Specific Reuptake Inhibitors”. Neuron Glia Biol. 2010, 6, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, S.L.; Doly, S.; Narboux-Nême, N.; Fernández, S.; Mazot, P.; Banas, S.M.; Boutourlinsky, K.; Moutkine, I.; Belmer, A.; Roumier, A.; et al. 5-HT 2B Receptors Are Required for Serotonin-Selective Antidepressant Actions. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 17, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Nu, W.; Cai, L.; Hertz, L.; Peng, L. Fluoxetine-Mediated 5-HT2B Receptor Stimulation in Astrocytes Causes EGF Receptor Transactivation and ERK Phosphorylation. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2008, 201, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Hertz, L.; Peng, L. Serotonin Increases ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in Astrocytes by Stimulation of 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C Receptors. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 57, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Song, D.; Li, B.; Verkhratsky, A. Astroglial 5-HT2B Receptor in Mood Disorders. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2018, 18, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Song, D.; Gu, L.; Ren, Y.; Verkhratsky, A.; Peng, L. Decrease of Gene Expression of Astrocytic 5-HT2B Receptors Parallels Development of Depressive Phenotype in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Ma, K.; Verkhratsky, A.; Peng, L. L-Dopa and Fluoxetine Upregulate Astroglial 5-HT2B Receptors and Ameliorate Depression in Parkinson’s Disease Mice. Neuroglia 2018, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Chen, B.; Zhang, M.; Dong, C.; Verkhratsky, A.; Guan, D.; et al. Sleep Deprivation Selectively Down-Regulates Astrocytic 5-HT2B Receptors and Triggers Depressive-Like Behaviors via Stimulating P2X7 Receptors in Mice. Neurosci. Bull. 2020, 36, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liang, S.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Xia, M.; Verkhratsky, A.; Li, B. Leptin Increases Expression of 5-HT2B Receptors in Astrocytes Thus Enhancing Action of Fluoxetine on the Depressive Behavior Induced by Sleep Deprivation. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spampinato, U.; Cathala, A.; Devroye, C. The serotonin2B receptor and neurochemical regulation in the brain. In Handbook of Behavioral Neuroscience; Müller, C.P., Cunningham, K.A., Eds.; Handbook of the Behavioral Neurobiology of Serotonin; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Chapter 7; Volume 31, pp. 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Devroye, C.; Haddjeri, N.; Cathala, A.; Rovera, R.; Drago, F.; Piazza, P.V.; Artigas, F.; Spampinato, U. Opposite Control of Mesocortical and Mesoaccumbal Dopamine Pathways by Serotonin2B Receptor Blockade: Involvement of Medial Prefrontal Cortex Serotonin1A Receptors. Neuropharmacology 2017, 119, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auclair, A.L.; Cathala, A.; Sarrazin, F.; Depoortère, R.; Piazza, P.V.; Newman-Tancredi, A.; Spampinato, U. The Central Serotonin2B Receptor: A New Pharmacological Target to Modulate the Mesoaccumbens Dopaminergic Pathway Activity. J. Neurochem. 2010, 114, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devroye, C.; Cathala, A.; Di Marco, B.; Caraci, F.; Drago, F.; Piazza, P.V.; Spampinato, U. Central Serotonin2B Receptor Blockade Inhibits Cocaine-Induced Hyperlocomotion Independently of Changes of Subcortical Dopamine Outflow. Neuropharmacology 2015, 97, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devroye, C.; Cathala, A.; Haddjeri, N.; Rovera, R.; Vallée, M.; Drago, F.; Piazza, P.V.; Spampinato, U. Differential Control of Dopamine Ascending Pathways by Serotonin2B Receptor Antagonists: New Opportunities for the Treatment of Schizophrenia. Neuropharmacology 2016, 109, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitychoutis, P.M.; Belmer, A.; Moutkine, I.; Adrien, J.; Maroteaux, L. Mice Lacking the Serotonin Htr 2B Receptor Gene Present an Antipsychotic-Sensitive Schizophrenic-Like Phenotype. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 2764–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doly, S.; Valjent, E.; Setola, V.; Callebert, J.; Hervé, D.; Launay, J.-M.; Maroteaux, L. Serotonin 5-HT2B Receptors Are Required for 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine-Induced Hyperlocomotion and 5-HT Release In Vivo and In Vitro. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 2933–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cathala, A.; Devroye, C.; Robert, É.; Vallée, M.; Revest, J.-M.; Artigas, F.; Spampinato, U. Serotonin2B Receptor Blockade in the Rat Dorsal Raphe Nucleus Suppresses Cocaine-Induced Hyperlocomotion through an Opposite Control of Mesocortical and Mesoaccumbens Dopamine Pathways. Neuropharmacology 2020, 180, 108309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, X.; Topin, J.; Golebiowski, J. Class A GPCRs: Structure, Function, Modeling and Structure-Based Ligand Design. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 4390–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, D.; Wang, C.; Katritch, V.; Han, G.W.; Huang, X.-P.; Vardy, E.; McCorvy, J.D.; Jiang, Y.; Chu, M.; Siu, F.Y.; et al. Structural Features for Functional Selectivity at Serotonin Receptors. Science 2013, 340, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wacker, D.; Gati, C.; Han, G.W.; James, D.; Wang, D.; Nelson, G.; Weierstall, U.; Katritch, V.; Barty, A.; et al. Serial Femtosecond Crystallography of G Protein–Coupled Receptors. Science 2013, 342, 1521–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, D.; Wang, S.; McCorvy, J.D.; Betz, R.M.; Venkatakrishnan, A.J.; Levit, A.; Lansu, K.; Schools, Z.L.; Che, T.; Nichols, D.E.; et al. Crystal Structure of an LSD-Bound Human Serotonin Receptor. Cell 2017, 168, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishchenko, A.; Wacker, D.; Kapoor, M.; Zhang, A.; Han, G.W.; Basu, S.; Patel, N.; Messerschmidt, M.; Weierstall, U.; Liu, W.; et al. Structural Insights into the Extracellular Recognition of the Human Serotonin 2B Receptor by an Antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8223–8228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCorvy, J.D.; Wacker, D.; Wang, S.; Agegnehu, B.; Liu, J.; Lansu, K.; Tribo, A.R.; Olsen, R.H.J.; Che, T.; Jin, J.; et al. Structural Determinants of 5-HT 2B Receptor Activation and Biased Agonism. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A Visualization System for Exploratory Research and Analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, S.G.F.; DeVree, B.T.; Zou, Y.; Kruse, A.C.; Chung, K.Y.; Kobilka, T.S.; Thian, F.S.; Chae, P.S.; Pardon, E.; Calinski, D.; et al. Crystal Structure of the β 2 Adrenergic Receptor–Gs Protein Complex. Nature 2011, 477, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherezov, V.; Rosenbaum, D.M.; Hanson, M.A.; Rasmussen, S.G.F.; Thian, F.S.; Kobilka, T.S.; Choi, H.-J.; Kuhn, P.; Weis, W.I.; Kobilka, B.K.; et al. High-Resolution Crystal Structure of an Engineered Human Β2-Adrenergic G Protein–Coupled Receptor. Science 2007, 318, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, D.; Wu, M.; Guo, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhong, L.; Cai, X.; Dai, A.; Jang, W.; Shakhnovich, E.I.; et al. Common Activation Mechanism of Class A GPCRs. eLife 2019, 8, e50279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manglik, A.; Kruse, A.C. Structural Basis for G Protein-Coupled Receptor Activation. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 5628–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, H.; Wacker, D.; Katritch, V.; Han, G.W.; Liu, W.; Huang, X.-P.; Vardy, E.; et al. Structural Basis for Molecular Recognition at Serotonin Receptors. Science 2013, 340, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez, M.; Nguyen, T.N.; Omieczynski, C.; Wolber, G. Strategies for the Discovery of Biased GPCR Ligands. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weïwer, M.; Xu, Q.; Gale, J.P.; Lewis, M.; Campbell, A.J.; Schroeder, F.A.; Van de Bittner, G.C.; Walk, M.; Amaya, A.; Su, P.; et al. Functionally Biased D2R Antagonists: Targeting the β-Arrestin Pathway to Improve Antipsychotic Treatment. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poissonnet, G.; Parmentier, J.G.; Boutin, J.A.; Goldstein, S. The Emergence of Selective 5-HT 2B Antagonists Structures, Activities and Potential Therapeutic Applications. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brea, J.; Castro-Palomino, J.; Yeste, S.; Cubero, E.; Parraga, A.; Dominguez, E.; Loza, M.I. Emerging Opportunities and Concerns for Drug Discovery at Serotonin 5-5-HT2B Receptors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonhaus, D.W.; Flippin, L.A.; Greenhouse, R.J.; Jaime, S.; Rocha, C.; Dawson, M.; Natta, K.V.; Chang, L.K.; Pulido-Rios, T.; Webber, A.; et al. RS-127445: A Selective, High Affinity, Orally Bioavailable 5-HT2B Receptor Antagonist. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 127, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porvasnik, S.L.; Germain, S.; Embury, J.; Gannon, K.S.; Jacques, V.; Murray, J.; Byrne, B.J.; Shacham, S.; Al-Mousily, F. PRX-08066, a Novel 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor 2B Antagonist, Reduces Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Right Ventricular Hypertrophy in Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 334, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurilia, C.; Siller, M.; Arozenius, H.; Palmqvist, N.; Ryde, A.-C.; Klint, C.; Sjödin, A.; Wenglén, C.; Ekström, G.; Seifert, E.; et al. AMAP102: AN ORALLY AVAILABLE SMALL MOLECULAR DRUG WITH BENEFICIAL EFFECTS ON ARTHRITIS AND INFLAMMATORY PAIN. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 585. [Google Scholar]
- Palmqvist, N.; Siller, M.; Klint, C.; Sjödin, A. A Human and Animal Model-Based Approach to Investigating the Anti-Inflammatory Profile and Potential of the 5-HT2B Receptor Antagonist AM1030. J. Inflamm. 2016, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zai, H.; Ando, A.; Sato, N. Sa1762—First-In-Human Study of the Novel 5-HT2B Receptor Antagonist, Rq-00310941, Demonstrated Safety and Tolerability Both in Healthy Subjects and Ulcerative Colitis Patients, with Improvement of a Sense of Abnormal Bowel Movement. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, S-385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, L. Novel 5-Ht2 Antagonists. WO2016207231, 29 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Löfdahl, A.; Wenglén, C.; Rydell-Törmänen, K.; Westergren-Thorsson, G.; Larsson-Callerfelt, A.-K. Effects of 5-Hydroxytryptamine Class 2 Receptor Antagonists on Bronchoconstriction and Pulmonary Remodeling Processes. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenglén, C.; Pettersson, L.; Arozenius, H.; Ekström, G. P012 A Novel Highly Selective 5-HT2B Receptor Antagonist Reduces Myofibroblast Differentiation and Extracellular Matrix Deposition in Models of Lung Fibrosis. QJM Int. J. Med. 2016, 109, S25–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Kalyanaraman, C.; Irwin, J.J.; Jacobson, M.P. Physics-Based Scoring of Protein−Ligand Complexes: Enrichment of Known Inhibitors in Large-Scale Virtual Screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2006, 46, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Huang, X.-P.; Qi, X.; Du, Y.; Huang, N. Exploring Halogen Bonds in 5-Hydroxytryptamine 2B Receptor–Ligand Interactions. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritomo, A.; Yamada, H.; Watanabe, T.; Itahana, H.; Akuzawa, S.; Okada, M.; Ohta, M. Synthesis and Structure–Activity Relationships of New Carbonyl Guanidine Derivatives as Novel Dual 5-HT2B and 5-HT7 Receptor Antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 7841–7852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritomo, A.; Yamada, H.; Watanabe, T.; Itahana, H.; Koga, Y.; Akuzawa, S.; Okada, M. Synthesis and Structure–Activity Relationships of New Carbonyl Guanidine Derivatives as Novel Dual 5-HT2B and 5-HT7 Receptor Antagonists. Part 2. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 4323–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moritomo, A.; Yamada, H.; Matsuzawa-Nomura, T.; Watanabe, T.; Itahana, H.; Oku, M.; Akuzawa, S.; Okada, M. Synthesis and Pharmacological Evaluation of Optically Pure, Novel Carbonyl Guanidine Derivatives as Dual 5-HT2B and 5-HT7 Receptor Antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 6026–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.A.; Zaidi, S.A.; Zhang, Y. 5-Hydroxy-2-(2-Phenylethyl)Chromone (5-HPEC): A Novel Non-Nitrogenous Ligand for 5-HT2B Receptor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1489–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.A.; Zaidi, S.A.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis and Characterization of 5-Hydroxy-2-(2-Phenylethyl)Chromone (5-HPEC) and Its Analogues as Non-Nitrogenous 5-HT2B Ligands. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Truss, M.; Pagare, P.P.; Essandoh, M.A.; Zhang, Y.; Williams, D.A. Structure Activity Relationship Exploration of 5-Hydroxy-2-(3-Phenylpropyl)Chromones as a Unique 5-HT2B Receptor Antagonist Scaffold. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapadia, N.; Harding, W. Aporphine Alkaloids as Ligands for Serotonin Receptors. Med. Chem. 2016, 6, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, N.; Harding, W.W. C4 Phenyl Aporphines with Selective H5-HT2B Receptor Affinity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3451–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnala, S.; Kapadia, N.; Harding, W.W. Identification of Tris-(Phenylalkyl)Amines as New Selective H5-HT2B Receptor Antagonists. MedChemComm 2015, 6, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, M.T.; Abdel-Raziq, M.S. Pharmacophore-Based Tailoring of Biphenyl Amide Derivatives as Selective 5-Hydroxytryptamine 2B Receptor Antagonists. MedChemComm 2018, 9, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, N.; Choi, Y.; Cogan, D.; Flegg, A.; Kahrs, A.; Loke, P.; Meyn, O.; Nagaraja, R.; Napier, S.; Parker, A.; et al. A New Class of 5-HT2B Antagonists Possesses Favorable Potency, Selectivity, and Rat Pharmacokinetic Properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2206–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.R.; Xiao, H.; Wang, J.; Smith, S.B.; Topczewski, J.J. 3-Amino-Chromanes and Tetrahydroquinolines as Selective 5-HT2B, 5-HT7, or Σ1 Receptor Ligands. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.J.; Saubern, S.; Macdonald, J.M.; Huang, X.-P.; Setola, V.; Roth, B.L. N-Tetrahydrothiochromenoisoxazole-1-Carboxamides as Selective Antagonists of Cloned Human 5-HT2B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 5488–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zopf, D.A.; das Neves, L.A.A.; Nikula, K.J.; Huang, J.; Senese, P.B.; Gralinski, M.R. C-122, a Novel Antagonist of Serotonin Receptor 5-HT2B, Prevents Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, T.; Hauser, N.; Reker, D.; Reutlinger, M.; Wunderlin, T.; Hamon, J.; Koch, G.; Schneider, G. Multidimensional De Novo Design Reveals 5-HT2B Receptor-Selective Ligands. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 1571–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosh, D.K.; Ciancetta, A.; Warnick, E.; Crane, S.; Gao, Z.-G.; Jacobson, K.A. Structure-Based Scaffold Repurposing for G Protein-Coupled Receptors: Transformation of Adenosine Derivatives into 5HT2B/5HT2C Serotonin Receptor Antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 11006–11026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rataj, K.; Kelemen, Á.A.; Brea, J.; Loza, M.I.; Bojarski, A.J.; Keserű, G.M. Fingerprint-Based Machine Learning Approach to Identify Potent and Selective 5-HT2BR Ligands. Molecules 2018, 23, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, S.; Hu, Q.; Gao, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Chen, F.; Lai, L.; Pei, J. CavityPlus: A Web Server for Protein Cavity Detection with Pharmacophore Modelling, Allosteric Site Identification and Covalent Ligand Binding Ability Prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W374–W379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Che, T.; Panova, O.; DiBerto, J.F.; Lyu, J.; Krumm, B.E.; Wacker, D.; Robertson, M.J.; Seven, A.B.; Nichols, D.E.; et al. Structure of a Hallucinogen-Activated Gq-Coupled 5-HT2A Serotonin Receptor. Cell 2020, 182, 1574–1588.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.T.; Asada, H.; Inoue, A.; Kadji, F.M.N.; Im, D.; Mori, C.; Arakawa, T.; Hirata, K.; Nomura, Y.; Nomura, N.; et al. Structures of the 5-HT 2A Receptor in Complex with the Antipsychotics Risperidone and Zotepine. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; McCorvy, J.D.; Harpsøe, K.; Lansu, K.; Yuan, S.; Popov, P.; Qu, L.; Pu, M.; Che, T.; Nikolajsen, L.F.; et al. 5-HT2C Receptor Structures Reveal the Structural Basis of GPCR Polypharmacology. Cell 2018, 172, 719–730.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).