Biofabricated Fatty Acids-Capped Silver Nanoparticles as Potential Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antibiofilm and Anticancer Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physico-Chemical Characterization of LIV-AgNPs
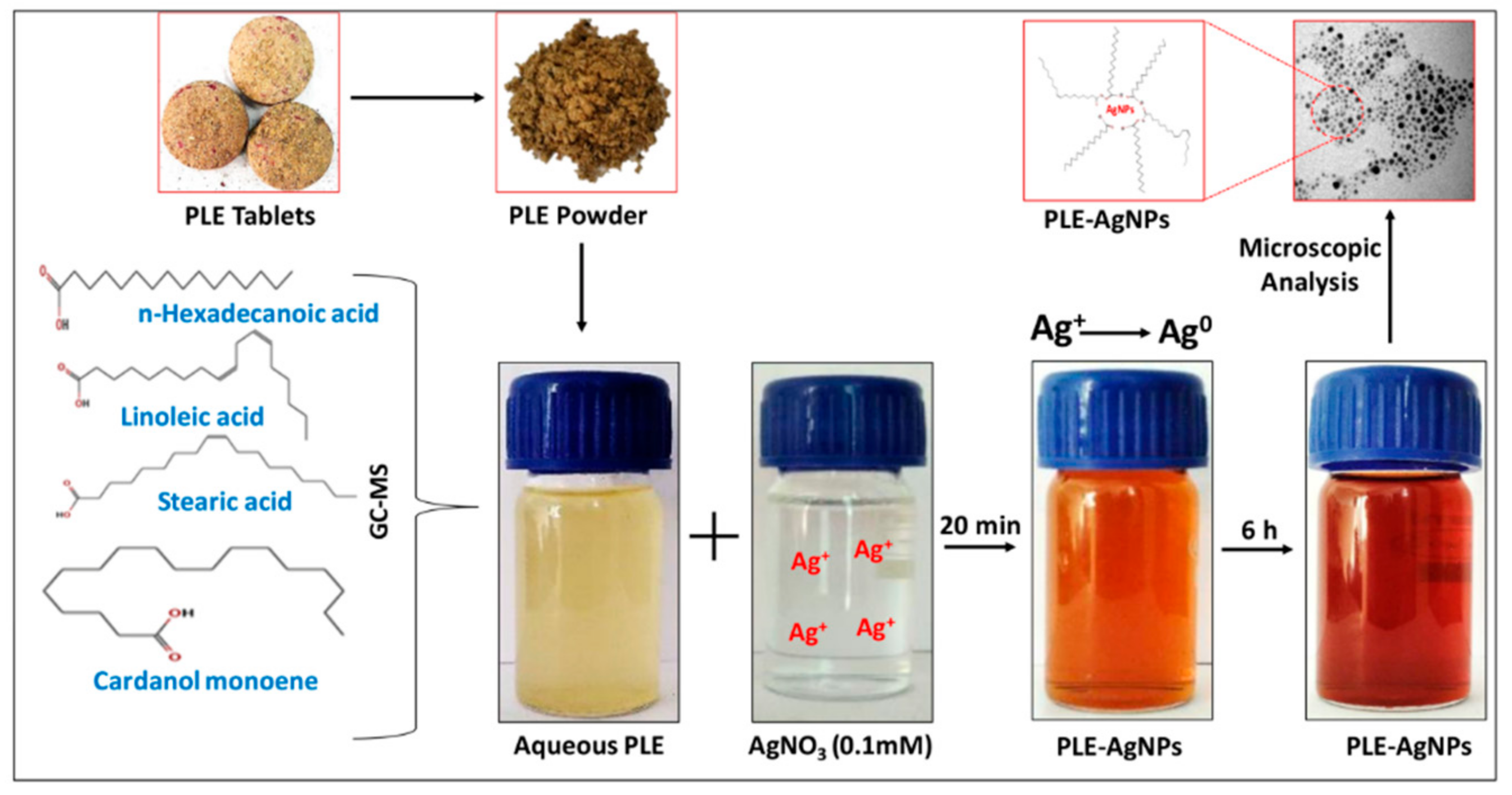
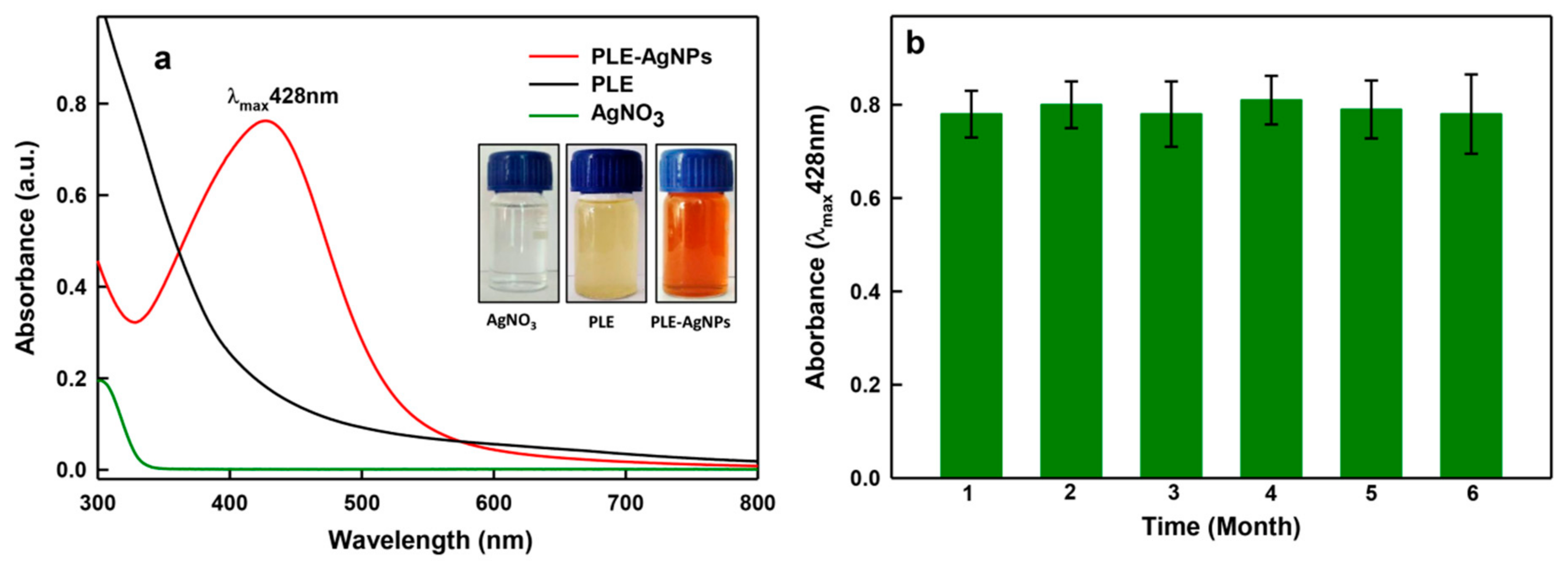
2.1.1. Synthesis and UV-Vis Analysis of LIV-AgNPs
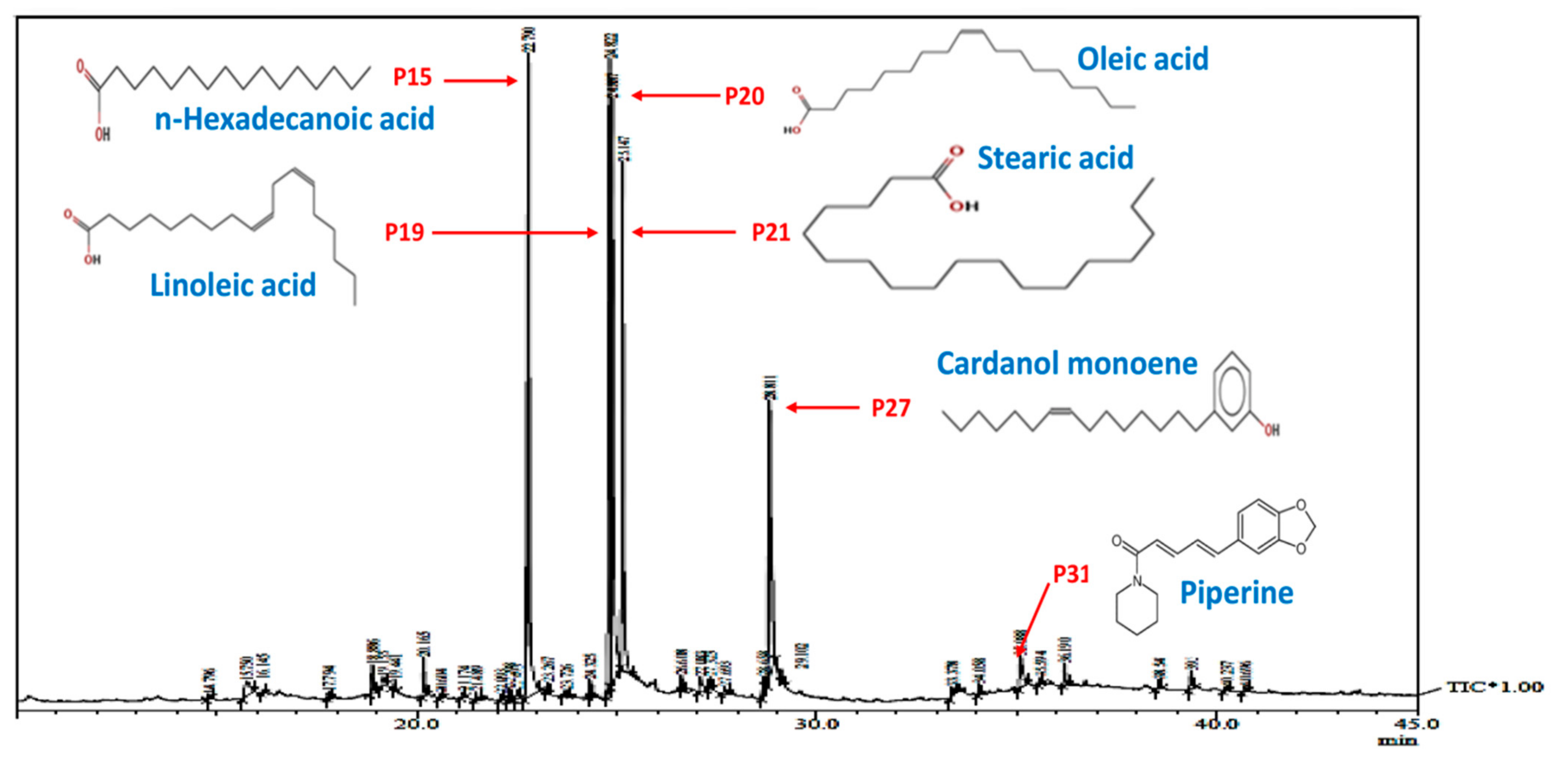
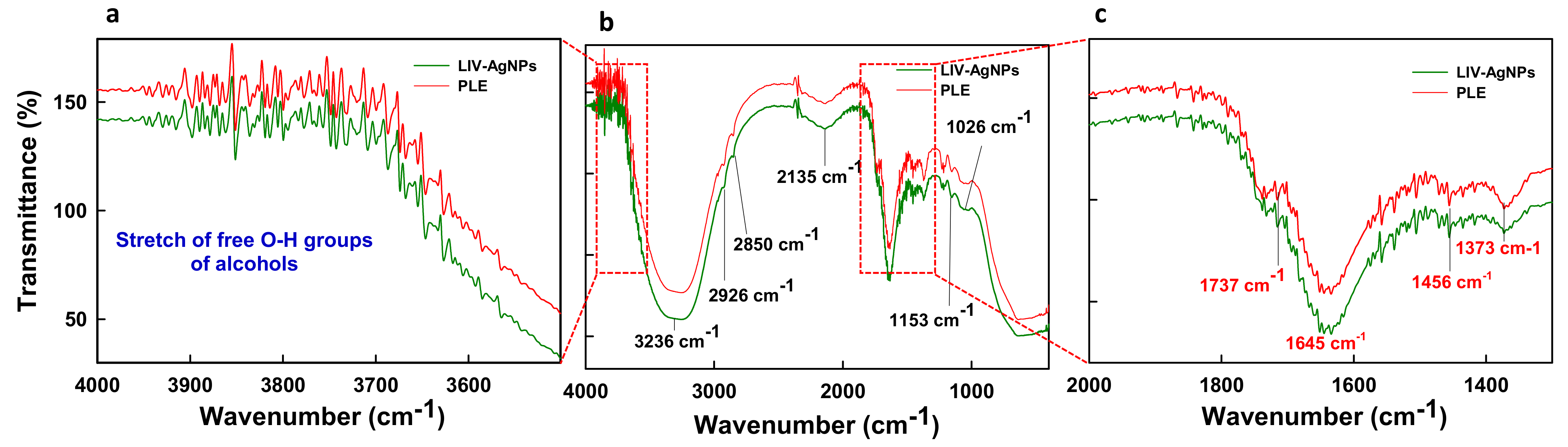
2.1.2. Assessment of Bio-Actives in Pristine PLE and LIV-AgNPs by GC-MS and FTIR
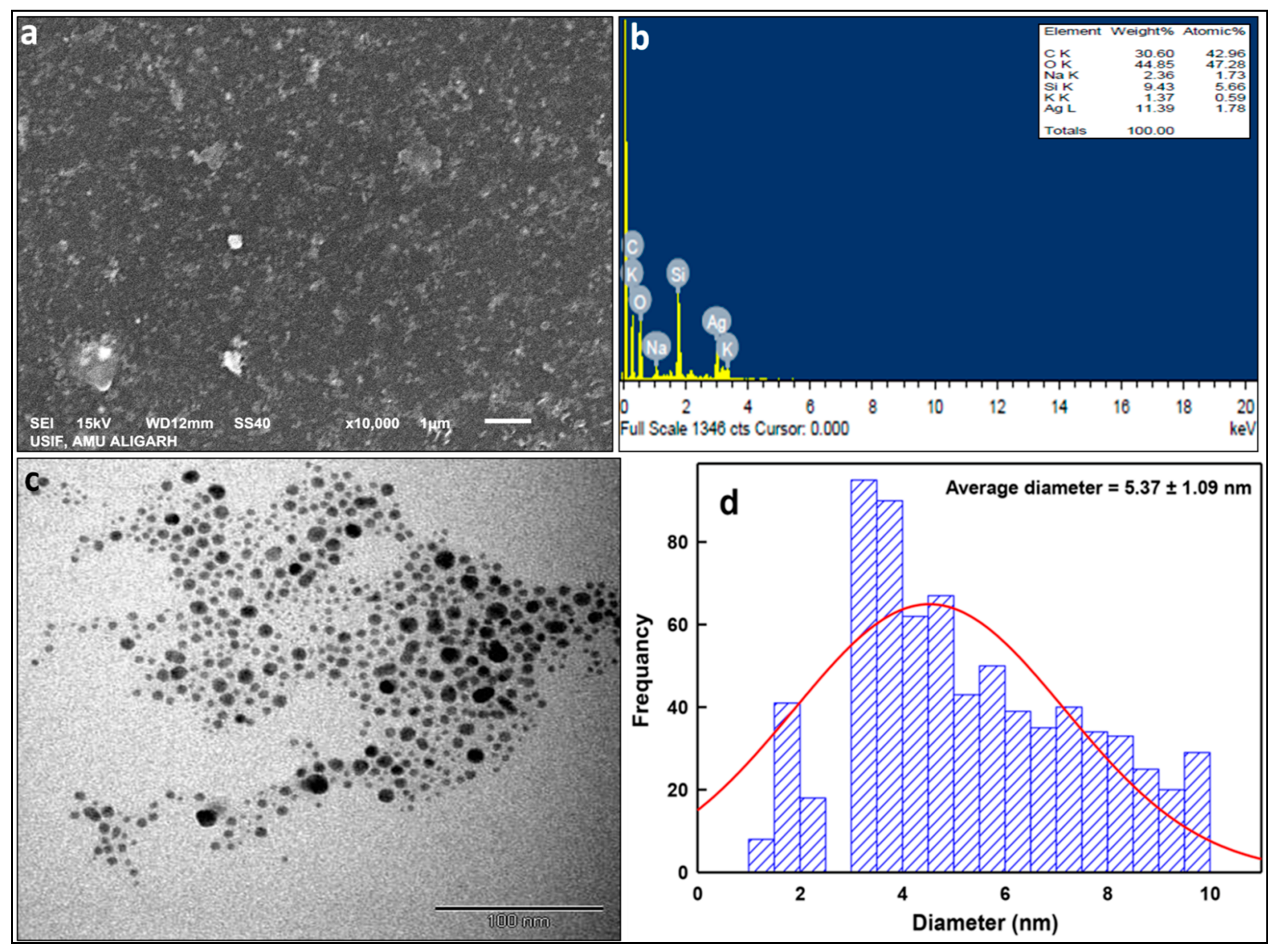
2.1.3. Electron Microscopic Properties of LIV-AgNPs
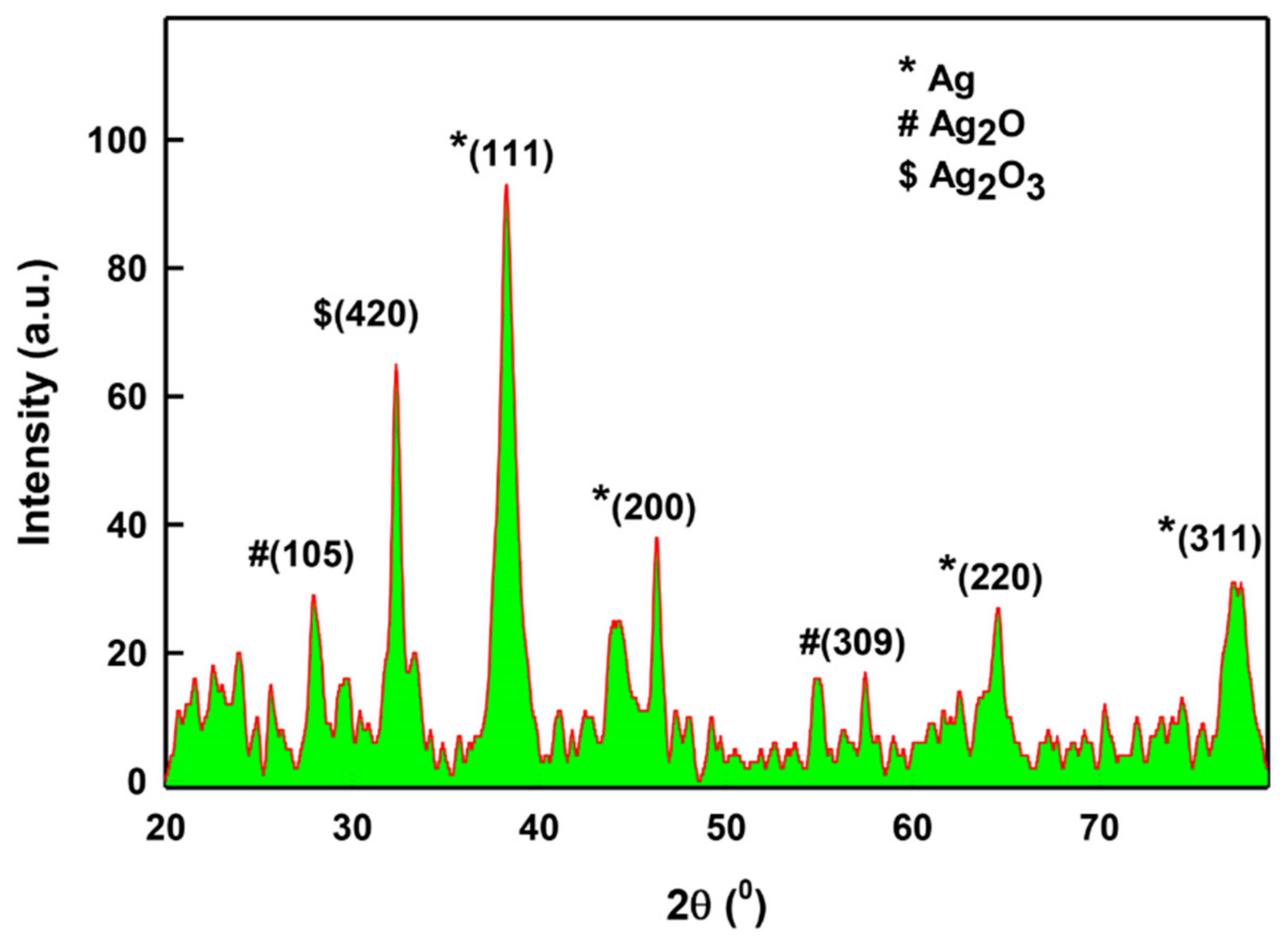
2.1.4. XRD Analysis of LIV-AgNPs
2.1.5. Antibacterial and Anticandidal Activity of LIV-AgNPs
Growth Inhibition Activity Assessment and Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC), Minimal Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) and Minimal Fungicidal Concentration (MFC) Values Determination
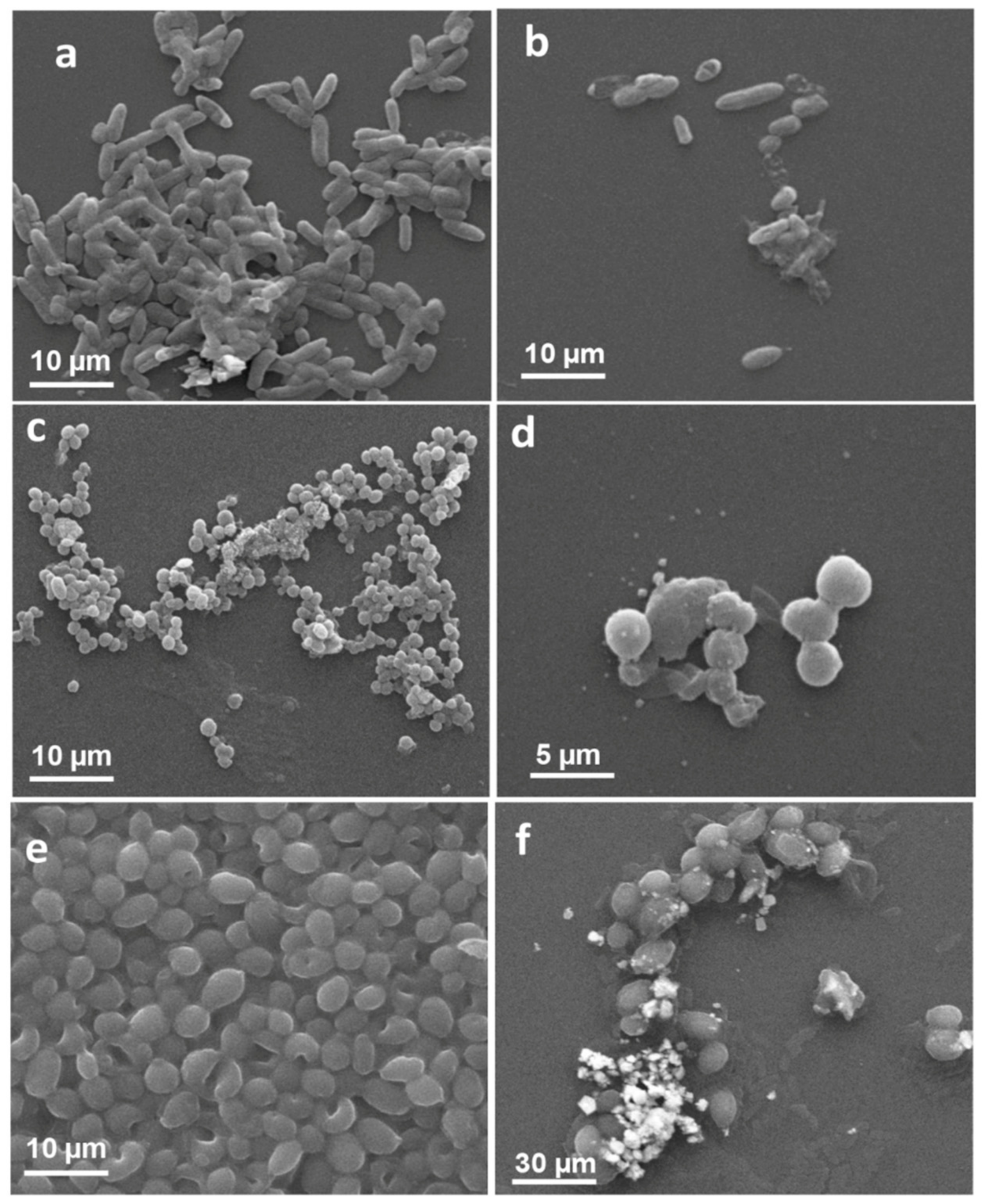
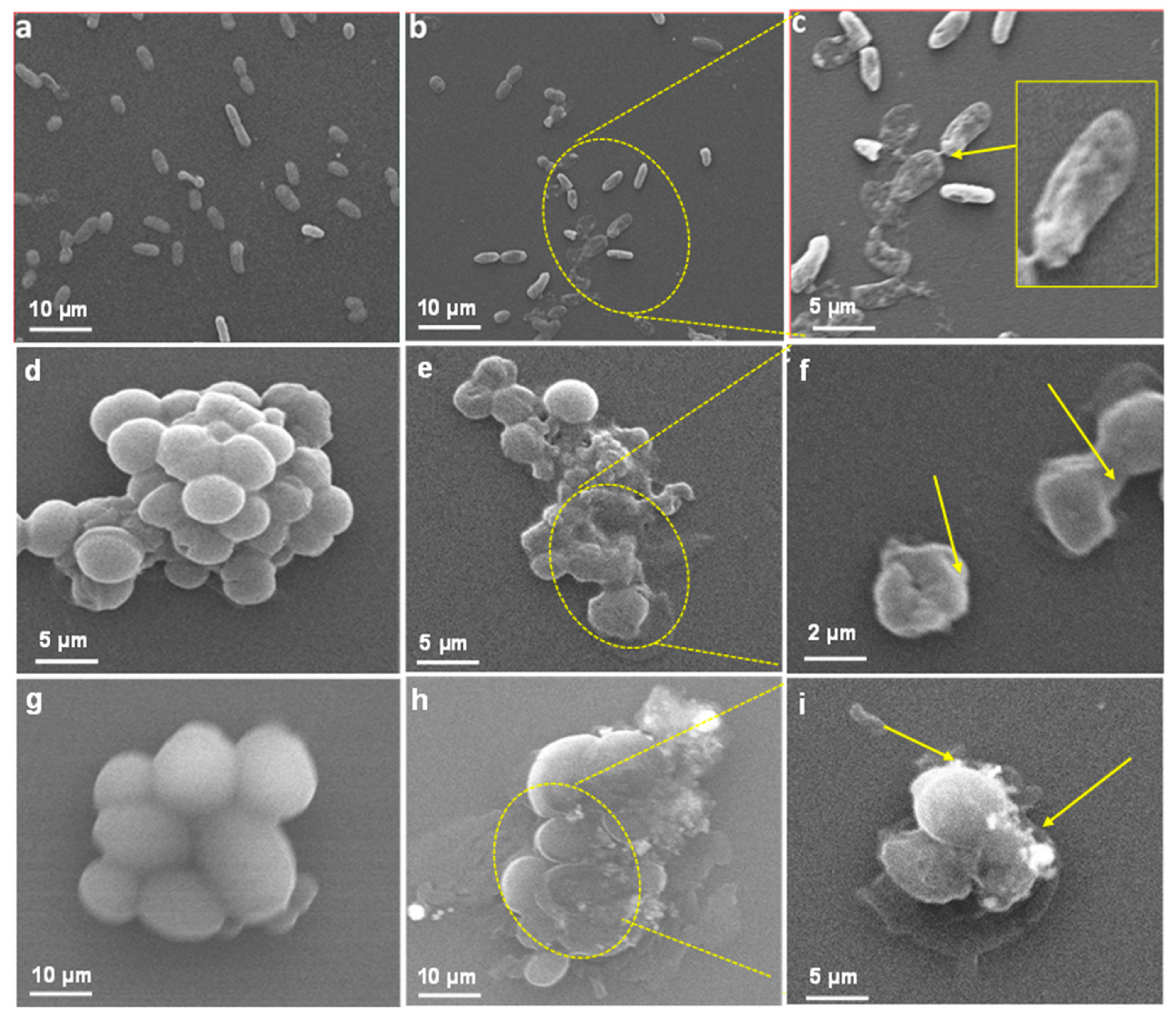
SEM Based Analysis of LIV-AgNPs Interaction and Cellular Damage
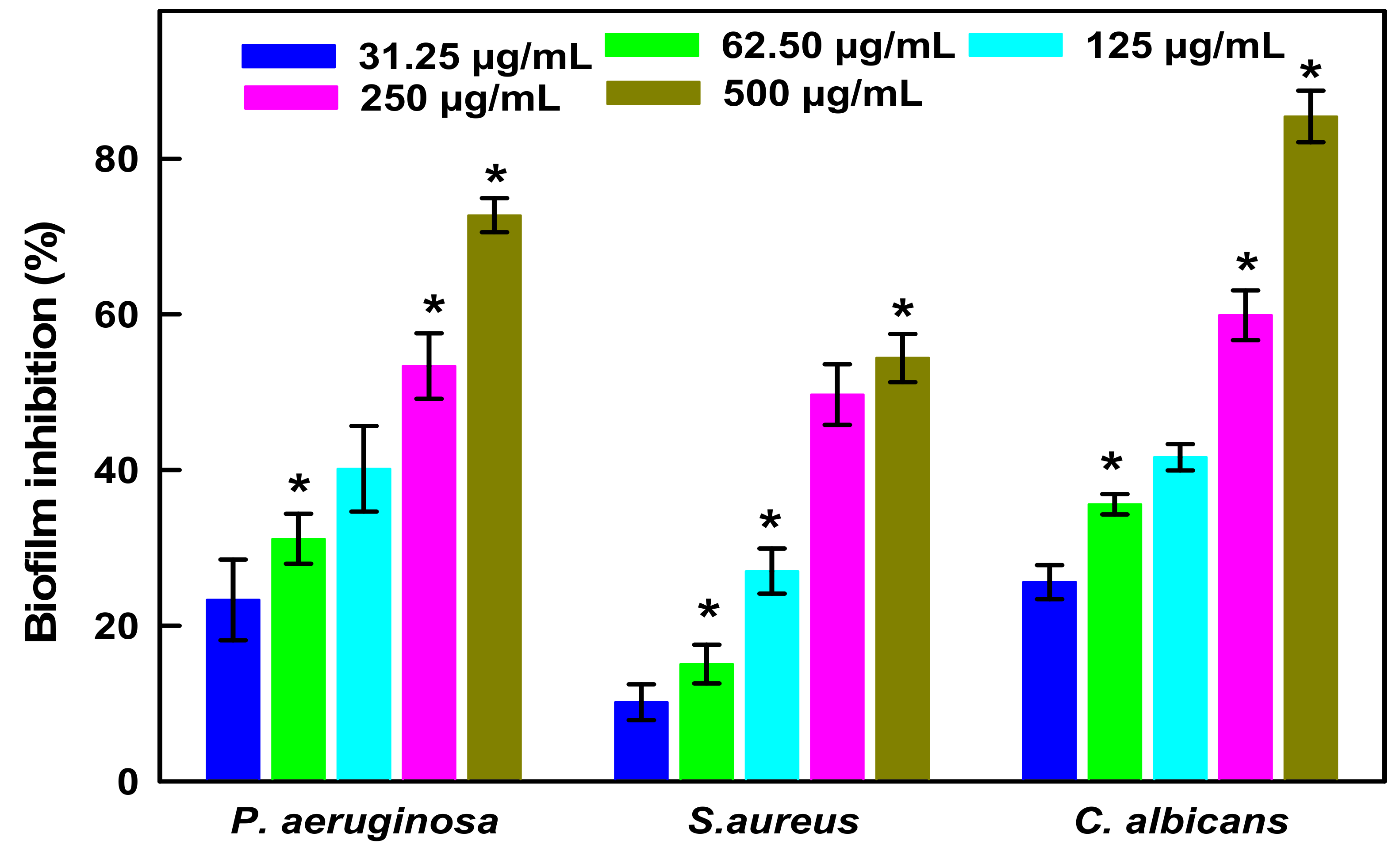
Antibiofilm Studies of LIV-AgNPs
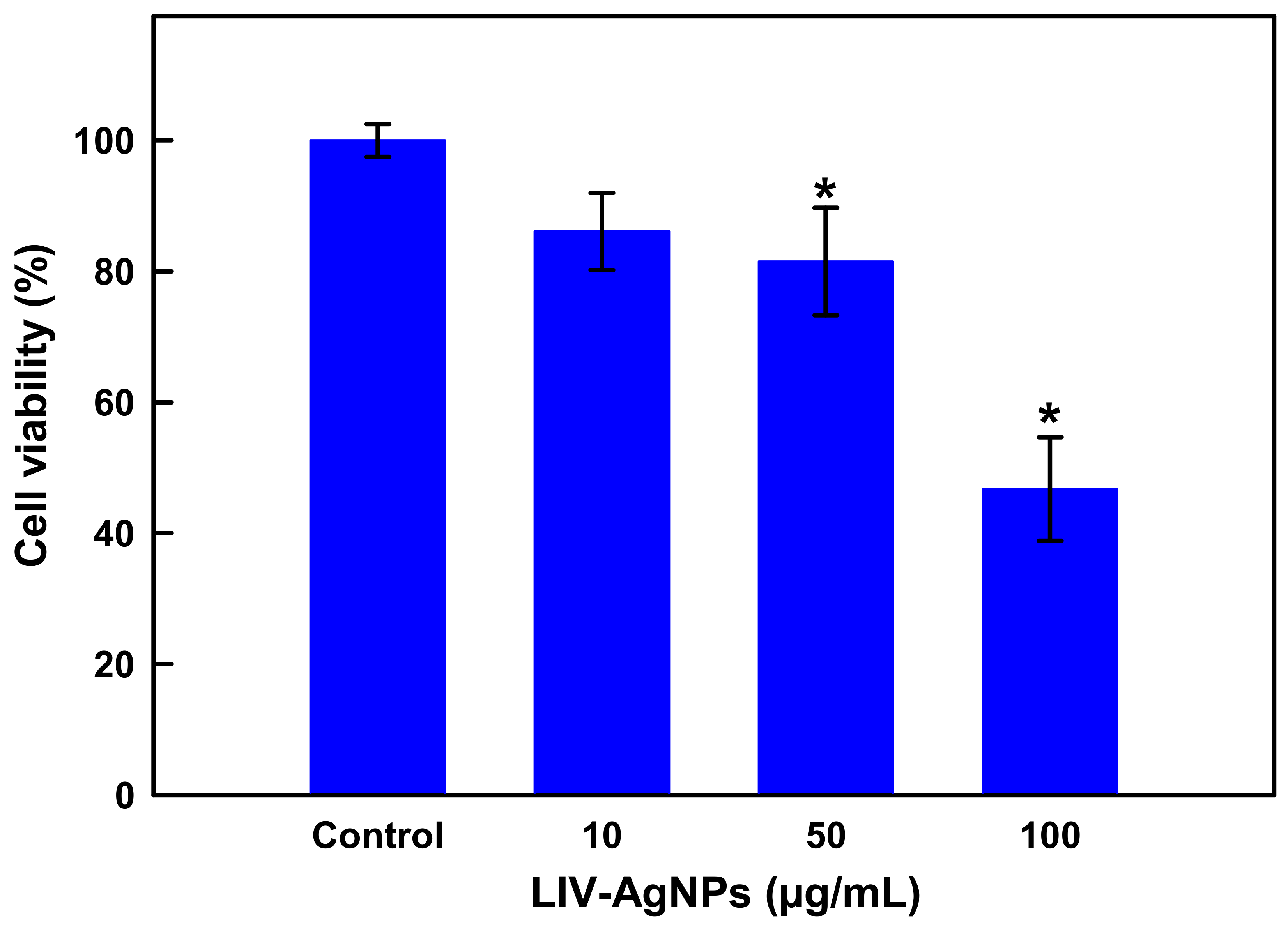
2.2. Antiproliferative Properties of LIV-AgNPs on Human Colon Cancer Cells (HCT-116)
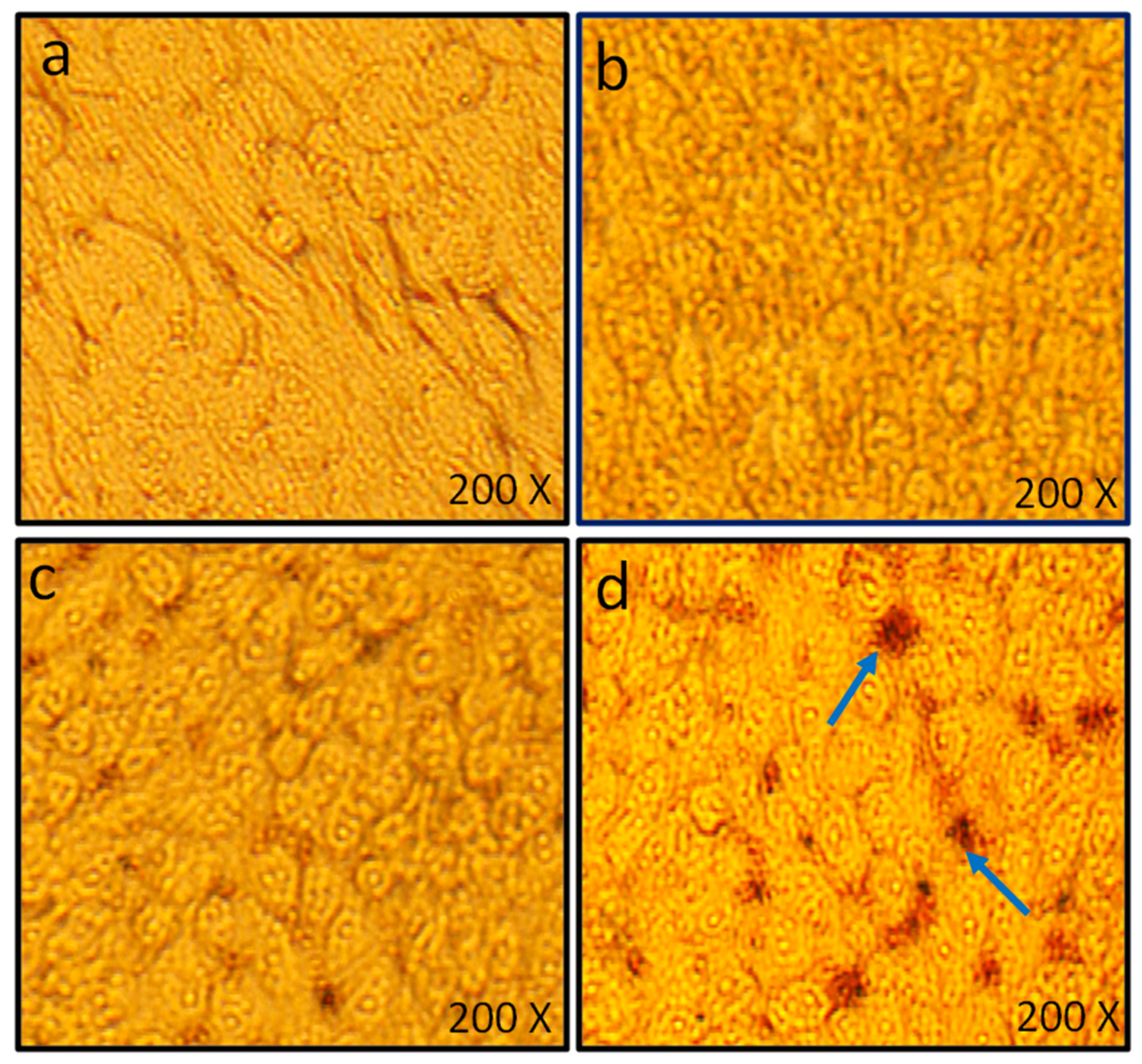
Cell Viability Assay by MTT and Microscopic Analysis of HCT-116 Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparations of Aqueous Extract of Liv52 Drug
3.2. GC-MS Based Assessment of Bio-Actives in Poly-Herbal Liv52 Drug Extract (PLE)
3.3. Nanofabrication of Poly-Herbal liv52 Drug Extract Capped AgNPs (LIV-AgNPs)
3.4. Characterization of Synthesized LIV-AgNPs
3.4.1. UV–Vis Spectroscopy and FTIR Analysis
3.4.2. Electron Microscopic and EDS Analysis of LIV-AgNPs
3.4.3. XRD Analysis of LIV-AgNPs
3.5. Microbial and Human Carcinoma Cell Cultures
3.6. Assessment of Antimicrobial Efficacy of LIV-AgNPs
3.6.1. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration, Minimal Bactericidal Concentration, Minimal Fungicidal Concentration and Zone of Inhibition Determination
3.6.2. Ultrastructural Alteration Caused by LIV-AgNPs in Bacterial and Candidal Cells
3.6.3. Inhibition of Biofilm Forming Abilities of MDR-PA, MRSA and C. albicans
3.6.4. Visualization of Biofilm Architecture by SEM
3.7. Evaluation of Anticancer Potential of LIV-AgNPs
3.7.1. MTT Assay
3.7.2. Effects of LIV-AgNPs on Morphology of HCT-116 Cells
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, N.; Kaushik, S. Synthesis of bio nano particles with special reference to gold and silver metal. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 29, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, M.; Abdallah, H.; Chetty, R.; Kumar, M.; Shaban, A. Silver nano-rods: Simple synthesis and optimization by experimental design methodology. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2019, 19, 100342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, M.; Ansari, M.A.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Ali, S.G.; Khan, H.M.; Almatroudi, A.; Siddiqui, M.I. Anticandidal activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles: Effect on growth, cell morphology, and key virulence attributes of Candida species. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4667–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomary, M.N.; Ansari, M.A. Proanthocyanins-capped biogenic TiO2 nanoparticles with enhanced penetration, antibacterial and ROS mediated inhibition of bacteria proliferation and biofilm formation: A comparative approach. Chem. A Eur. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, K.; Ahmad, B.; Ansari, S.M.; Saquib, Q.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Dwivedi, S.; Alshaeri, M.; Khan, M.S.; Musarrat, J. Comparative in situ ROS mediated killing of bacteria with bulk analogue, Eucalyptus leaf extract (ELE)-capped and bare surface copper oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 100, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Alzohairy, M.A. One-Pot Facile Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Seed Extract of Phoenix dactylifera and Their Bactericidal Potential against MRSA. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 1860280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, J.M.; Ansari, M.A.; Khan, H.M.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Choi, I. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and characterization of their inhibitory effects on AGEs formation using biophysical techniques. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, M.; Ansari, M.A.; Ali, S.G.; Khan, H.M.; Eldaif, W.A.; Alrumman, S.A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Cinnamomum tamala and its antimicrobial activity against clinical isolates of bacteria and fungi. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 4, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Saquib, Q.; Ahmed, B.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Ahmad, J.; Al-Shaeri, M.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Musarrat, J. Bio-functionalized CuO nanoparticles induced apoptotic activities in human breast carcinoma cells and toxicity against Aspergillus flavus: An in vitro approach. Process. Biochem. 2020, 91, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibrov, P.; Dzioba, J.; Gosink, K.K.; Häse, C.C. Chemiosmotic Mechanism of Antimicrobial Activity of Ag+ in Vibrio cholerae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2668–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, L.; Mustapha, A.; Li, H.; Hu, Z.Q.; Lin, M. Antibacterial activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Lin, Z.; Gua, B.; Panga, C.; Wang, X. Green synthesis and immobilization of AgNPs by lumpy corn stalk as interlayer filling material for durable antibacterial. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 158, 112987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, S.; Li, W.; Chen, M.; Li, Z. One-step in situ synthesis of nano silver-hydrotalcite coating for enhanced antibacterial and degradation property of magnesium alloys. Mater. Lett. 2020, 265, 127349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, W.; Li, Q.; Li, Q. In situ-synthesis of calcium alginate nano-silver phosphate hybrid material with high flame retardant and antibacterial properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labanni, A.; Zulhadjri; Handayani, D.; Ohya, Y.; Arief, S. Size controlled synthesis of well-distributed nano-silver on hydroxyapatite using alkanolamine compounds. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 5850–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovais, M.; Zia, N.; Khalil, A.T.; Ayaz, M.; Khalil, A.; Ahmad, I. Nanoantibiotics: Recent developments and future prospects. In Frontiers in Clinical Drug Research Anti-Infectives; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2019; Volume 5, pp. 158–182. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Moure, J.S.; Evangelopoulos, M.; Colvill, K.; Van Eps, J.L.; Tasciotti, E. Nanoantibiotics: A new paradigm for the treatment of surgical infection. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1319–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, F.; Feng, X.; Jin, Y.; Liu, D.; Yang, X.; Zhou, G.; Liu, D.; Li, Z.; Liang, X.-J.; Zhang, J. Metal–carbenicillin framework-based nanoantibiotics with enhanced penetration and highly efficient inhibition of MRSA. Biomaterials 2017, 144, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talat, I.; Arshad, A.; Mansoor, Q. Graphene nanoplatelets/Cr2O3 nanocomposites as novel nanoantibiotics: Towards control of multiple drug resistant bacteria. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, C.; Huang, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Ren, C.; Chu, L.; Liu, B.; Liu, J. Triclosan-based supramolecular hydrogels as nanoantibiotics for enhanced antibacterial activity. J. Control. Release 2020, 324, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemer, S.; Westmeier, D.; Barz, M.; Eckrich, J.; Wünsch, D.; Seckert, C.; Thyssen, C.; Schilling, O.; Hasenberg, M.; Pang, C.; et al. Biomolecule-corona formation confers resistance of bacteria to nanoparticle-induced killing: Implications for the design of improved nanoantibiotics. Biomaterials 2019, 192, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Ahmed, B.; Khan, M.S.; Musarrat, J. Differential surface contact killing of pristine and low EPS Pseudomonas aeruginosa with Aloe vera capped hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 188, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseini, H.F.; Alavian, S.; Heshmat, R.; Heydari, M.; Abolmaali, K. The efficacy of Liv-52 on liver cirrhotic patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled first approach. Phytomedicine 2005, 12, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Asiri, S.M.M. Green synthesis, antimicrobial, antibiofilm and antitumor activities of superparamagnetic γ-Fe2O3 NPs and their molecular docking study with cell wall mannoproteins and peptidoglycan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 171, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, K.; Dwivedi, S.; Azam, A.; Saquib, Q.; Al-Said, M.S.; Alkhedhairy, A.A.; Musarrat, J. Aloe vera extract functionalized zinc oxide nanoparticles as nanoantibiotics against multi-drug resistant clinical bacterial isolates. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 472, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanakani, P.E.; Santhanam, P.; Premkumar, K.; Kumar, K.E.; Dhanaraju, M.D. Nannochloropsis Extract–Mediated Synthesis of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles, Characterization and In Vitro Assessment of Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activities. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 2353–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, C.R.; Trivedi, D. Synthesis and characterization of fatty acids passivated silver nanoparticles—Their interaction with PPy. Synth. Met. 2005, 155, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Khan, H.M.; Khan, A.A.; Cameotra, S.S.; Saquib, Q.; Musarrat, J. Gum arabic capped-silver nanoparticles inhibit biofilm formation by multi-drug resistant strains ofPseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Basic Microbiol. 2014, 54, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, Z.; Razmjoue, D.; Karimi, J. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Caralluma tuberculata Extract and its Antibacterial Activity. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 4606–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopathi, S.; Gopinath, S.; Boopathi, T.; Balamurugan, V.; RajeshKumar, R.; Sundararaman, M. Characterization and Antimicrobial Properties of Silver and Silver Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized by Cell-Free Extract of a Mangrove-Associated Pseudomonas aeruginosa M6 Using Two Different Thermal Treatments. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 5976–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.G.; Ansari, M.A.; Khan, H.M.; Jalal, M.; Mahdi, A.A.; Cameotra, S.S. Crataeva nurvala nanoparticles inhibit virulence factors and biofilm formation in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Basic Microbiol. 2017, 57, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.G.; Ansari, M.A.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; Alyahya, S.; Jalal, M.; Khan, H.M.; Asiri, S.M.M.; Ahmad, W.; Mahdi, A.A.; et al. Biogenic Gold Nanoparticles as Potent Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Nano-Antibiotics against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anuj, S.A.; Gajera, H.P.; Hirpara, D.G.; Golakiya, B.A. Bacterial membrane destabilization with cationic particles of nano-silver to combat efflux-mediated antibiotic resistance in Gram-negative bacteria. Life Sci. 2019, 230, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kadmy, I.M. Manufacturing silver nano-coating currencies to prevent the bacteria growing on the surface of currency. Gene Rep. 2020, 19, 100648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, A.K.; Hogan, D.A. Candida albicans: Molecular interactions with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2014, 28, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, S.; Das, S.R.; Padhy, R.N. Surveillance of bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa and MRSA associated with chronic suppurative otitis media. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 83, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Karankar, V.S. New avenues of controlling microbial infections through anti-microbial and anti-biofilm potentials of green mono-and multi-metallic nanoparticles: A review. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 167, 105766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, R.G.; Bhusari, G.S.; Tiple, A.; Rai, A.R.; Somkuvar, S.R.; Potbhare, A.K.; Lambat, T.L.; Ingle, P.P.; Abdala, A.A. Metal/Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: Toxicity, Applications, and Future Prospects. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 4013–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasath, K.G.; Sethupathy, S.; Pandian, S.K. Proteomic analysis uncovers the modulation of ergosterol, sphingolipid and oxidative stress pathway by myristic acid impeding biofilm and virulence in Candida albicans. J. Proteom. 2019, 208, 103503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, M.; Alexandre, S.; Luizet, J.-B.; Skogman, M.; Jouenne, T.; Salcedo, S.P.; Dé, E. Unsaturated Fatty Acids Affect Quorum Sensing Communication System and Inhibit Motility and Biofilm Formation of Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murzyn, A.; Krasowska, A.; Stefanowicz, P.; Dziadkowiec, D.; Łukaszewicz, M. Capric Acid Secreted by S. boulardii Inhibits C. albicans Filamentous Growth, Adhesion and Biofilm Formation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-G.; Lee, J.-H.; Raorane, C.J.; Oh, S.T.; Park, J.G.; Lee, J. Herring Oil and Omega Fatty Acids Inhibit Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation and Virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenderska, I.B.; Chong, M.; McNulty, J.; Wright, G.D.; Burrows, L.L. Palmitoyl-dl-Carnitine is a Multitarget Inhibitor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Development. ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 2759–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthamil, S.; Balasubramaniam, B.; Balamurugan, K.; Pandian, S.K. Synergistic Effect of Quinic Acid Derived from Syzygium cumini and Undecanoic Acid Against Candida spp. Biofilm and Virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Batal, A.I.; Elkodous, M.A.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Al-Hazmi, N.E.; Gobara, M.; Baraka, A. Gum Arabic polymer-stabilized and Gamma rays-assisted synthesis of bimetallic silver-gold nanoparticles: Powerful antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities against pathogenic microbes isolated from diabetic foot patients. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo-Tayo, B.C.; Salaam, A.; Ajibade, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle using Oscillatoria sp. extract, its antibacterial, antibiofilm potential and cytotoxicity activity. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, N.; Ceylan, Y.; Hamid, A.; Karadağ, A.; Bülbül, A.S.; Aftab, M.N.; Çevik, Ö.; Şen, F. Biogenic silver nanoparticles synthesized via Mimusops elengi fruit extract, a study on antibiofilm, antibacterial, and anticancer activities. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhakumari, S.; Nilofernisha, N.M.; Ponraj, J.G.; Pandian, S.K.; Ravi, A.V. In vitro and in vivo exploration of palmitic acid from Synechococcus elongatus as an antibiofilm agent on the survival of Artemia franciscana against virulent vibrios. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 150, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, K.A.; Jesudhasan, P.; Cepeda, M.; Widmer, K.; Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Patil, B.S.; Hume, M.E.; Pillai, S.D. Identification of Ground Beef–Derived Fatty Acid Inhibitors of Autoinducer-2—Based Cell Signaling. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Ichwan, S.J.A.; Al-Zikri, P.N.H.; Suriyah, W.H.; Soundharrajan, I.; Govindan, N.; Maniam, G.P.; Yusoff, M. In Vitro Anticancer Activity of Au, Ag Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Commelina nudiflora L. Aqueous Extract Against HCT-116 Colon Cancer Cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 173, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Long, Y.; Liang, Q.; Purushotham, B.; Swamy, M.K.; Duan, Y. Safed Musli (Chlorophytum borivilianum L.) Callus-Mediated Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Evaluation of their Antimicrobial Activity and Cytotoxicity against Human Colon Cancer Cells. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 2418785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Shi, L.-H.; Yu, X.-H.; Wang, C.-F.; Wang, H.-J. Conjugated linolenic acid polymer dressings impregnated with silver nano-crystals: Fabrication and dual inhibition functions assessment on tumor cells and microorganisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 245, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Prasad, K. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its activity on SiHa cervical cancer cell line. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2014, 5, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Shang, M.; Niu, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Gan, J.; Li, W.; et al. Silver nanoparticles induced cytotoxicity in HT22 cells through autophagy and apoptosis via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almatroudi, A.; Khadri, H.; Azam, M.; Rahmani, A.H.; Al Khaleefah, F.K.; Khateef, R.; Ansari, M.A.; Allemailem, K.S. Antibacterial, Antibiofilm and Anticancer Activity of Biologically Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Seed Extract of Nigella sativa. Processes 2020, 8, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, F.; Abdelmageed, M.; Ansari, M.A.; Azzazy, H.M.E.-S. Synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles using pulp and seed aqueous extract of Citrullus colocynth and evaluation of their antimicrobial activity. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollur, S.P.; Prasad, S.K.; Ansari, M.A.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; Alyahya, S.; Srinivasa, C.; Murali, M.; Ankegowda, V.M.; Shivamallu, C. Tumoricidal and Bactericidal Properties of ZnONPs Synthesized Using Cassia auriculata Leaf Extract. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.; Jermy, B.R.; Asiri, S.M.; Shah, M.A.; Farooq, R.; Ravinayagam, V.; Ansari, M.A.; AlSalem, Z.; Al Jindan, R.; Reshi, Z.; et al. Using Fomitopsis pinicola for bioinspired synthesis of titanium dioxide and silver nanoparticles, targeting biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 32137–32147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Khan, H.M.; Khan, A.A.; Pal, R.; Cameotra, S.S. Antibacterial potential of Al2O3 nanoparticles against multidrug resistance strains of Staphylococcusaureus isolated from skin exudates. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Alam, J.; Ansari, M.A.; Alhoshan, M.; Ali, F.A.A. Antimicrobial and antifouling properties of versatile PPSU/carboxylated GO nanocomposite membrane against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and protein. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34103–34113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Albetran, H.M.; Alheshibri, M.H.; Timoumi, A.; Algarou, N.A.; Akhtar, S.; Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.; AlAhmari, F.; Baykal, A.; et al. Synthesis of Electrospun TiO2 Nanofibers and Characterization of Their Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Potential against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, U.; Ansari, M.A.; Gondal, M.A.; Akhtar, S.; Khan, F.A.; Falath, W.S. Single step production of high-purity copper oxide-titanium dioxide nanocomposites and their effective antibacterial and anti-biofilm activity against drug-resistant bacteria. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 22, 110992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

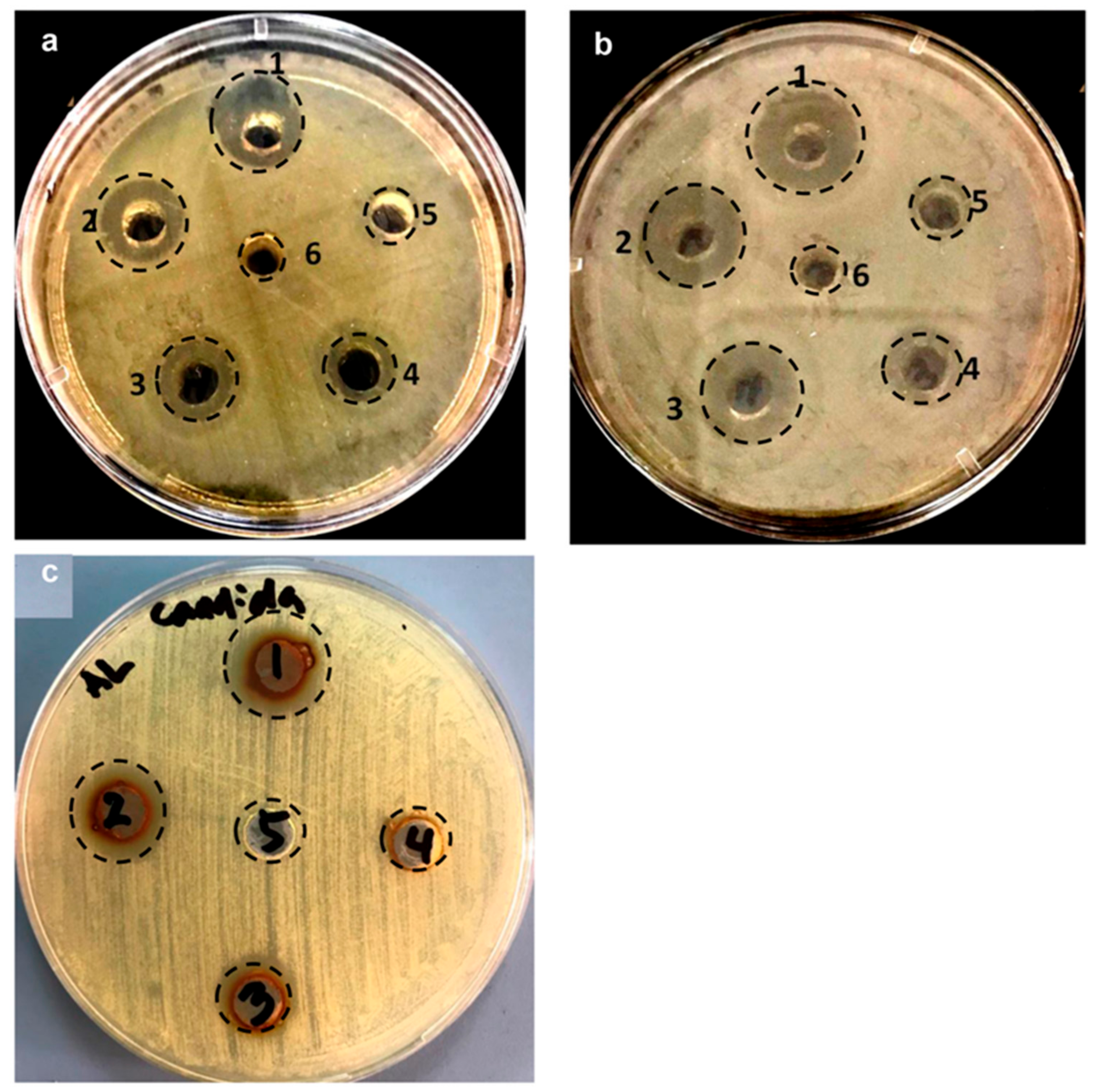

| Well No. | LIV-AgNPs (µg/mL) | Diameter of Growth Inhibition Zone (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDR-PA | MRSA | C. albicans | ||
| 1 | 200 | 18.5 ± 1.0 | 22.5 ± 1.5 | 16.5 ± 1.2 |
| 2 | 100 | 16.0 ± 2.0 | 19.5 ± 4.5 | 15.0 ± 2.2 |
| 3 | 50 | 13.5 ± 1.5 | 16.5 ± 1.5 | 13.7 ± 1.0 |
| 4 | 25 | 13.0 ± 2.0 | 12.0 ± 0.5 | ND |
| 5 | 12.5 | 10.0 ± 2.2 | 10.5 ± 2.5 | ND |
| 6 | Control (PLE) | ND | ND | ND |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ansari, M.A.; Asiri, S.M.M.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; Almatroudi, A.; Khan, F.A. Biofabricated Fatty Acids-Capped Silver Nanoparticles as Potential Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antibiofilm and Anticancer Agents. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020139
Ansari MA, Asiri SMM, Alzohairy MA, Alomary MN, Almatroudi A, Khan FA. Biofabricated Fatty Acids-Capped Silver Nanoparticles as Potential Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antibiofilm and Anticancer Agents. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(2):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020139
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnsari, Mohammad Azam, Sarah Mousa Maadi Asiri, Mohammad A. Alzohairy, Mohammad N. Alomary, Ahmad Almatroudi, and Firdos Alam Khan. 2021. "Biofabricated Fatty Acids-Capped Silver Nanoparticles as Potential Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antibiofilm and Anticancer Agents" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 2: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020139
APA StyleAnsari, M. A., Asiri, S. M. M., Alzohairy, M. A., Alomary, M. N., Almatroudi, A., & Khan, F. A. (2021). Biofabricated Fatty Acids-Capped Silver Nanoparticles as Potential Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antibiofilm and Anticancer Agents. Pharmaceuticals, 14(2), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020139








