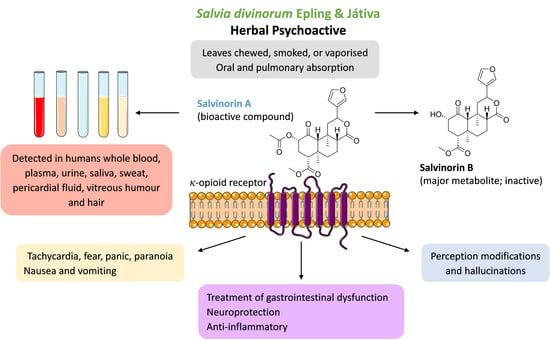
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Salvinorin A and Salvia divinorum: Clinical and Forensic Aspects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Plant Botany and Chemical Characterisation of S. divinorum
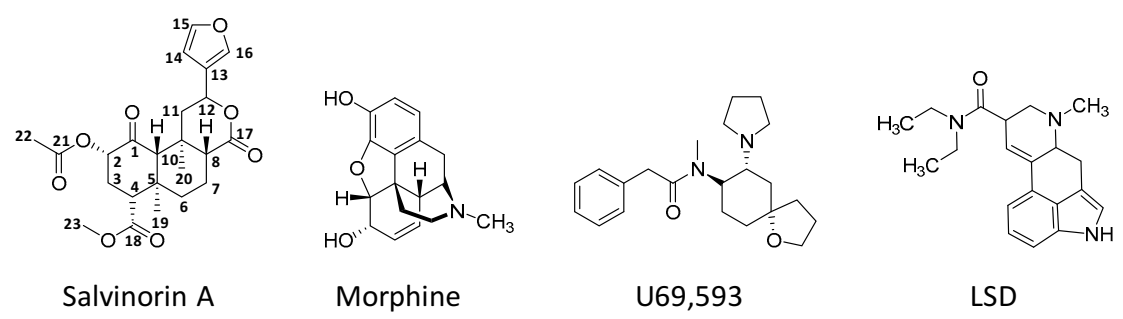
4. Biosynthesis, Structure, and Physicochemical Properties of Salvinorin A
5. Prevalence and Patterns of Use
6. Legal Status
7. Pharmacokinetics
7.1. Routes of Administration and Absorption
7.2. Distribution
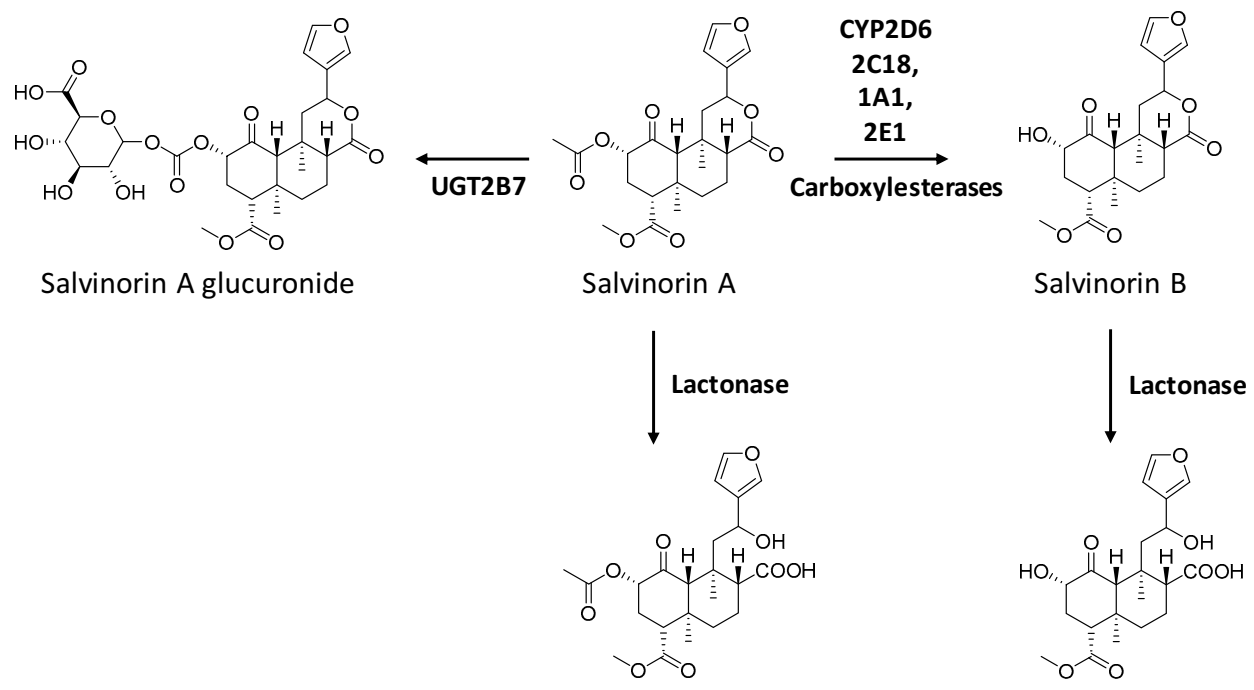
7.3. Metabolism
7.4. Excretion
8. Drug Analysis and Forensic Relevance
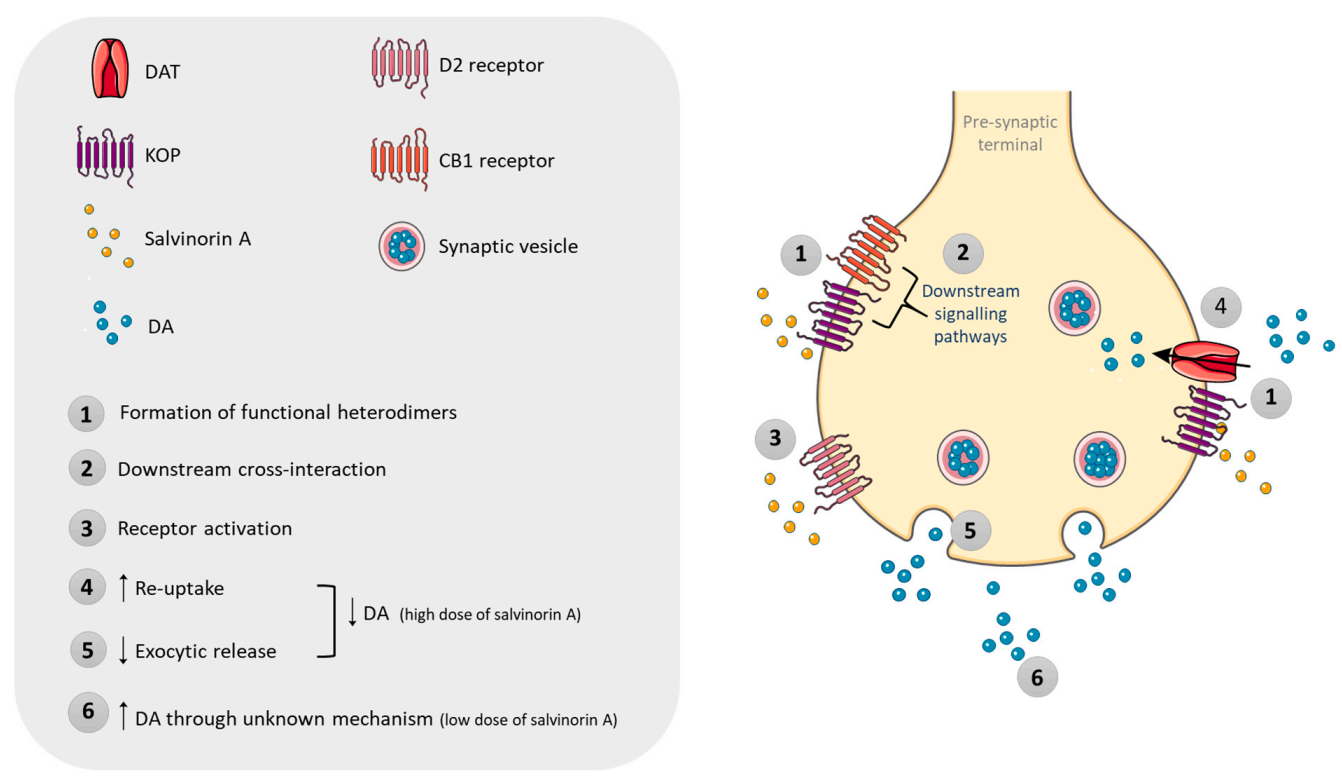
9. Pharmacodynamics
10. Psychological and Physiological Effects
10.1. Effects in Humans
10.2. Effects in Animal Models
11. Toxicity and Adverse Effects
11.1. Effects in Humans
11.2. Effects in Animal and In Vitro Models
12. Abuse Potential, Dependence, and Tolerance
12.1. Effects in Humans
12.2. Animal Testing
13. Potential Therapeutic Benefits
13.1. Remediation and Prevention of Gastrointestinal Dysfunction
13.2. Antidepressant/Pro-Depressant and Anxiolytic Properties
13.3. Neuroprotection
13.4. Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Properties
13.5. Treatment of Drug Dependence
14. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valdés, L.J., 3rd; Díaz, J.L.; Paul, A.G. Ethnopharmacology of ska María Pastora (Salvia divinorum, Epling and Játiva-M.). J. Ethnopharmacol. 1983, 7, 287–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, D.J. Salvia divinorum and salvinorin A: New pharmacologic findings. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1994, 43, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, N.R.; Greenberg, C.S. Psychoactive herb use and youth: A closer look at salvia divinorum. J. Psychosoc. Nurs. Ment. Health Serv. 2011, 49, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.M.; McCurdy, C.R.; Boyer, E.W. Opioid receptors and legal highs: Salvia divinorum and Kratom. Clin. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisfield, S.A. The botany of Salvia divinorum (Labiatae). SIDA 1993, 15, 349–366. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, A.; Blount, J.F.; Manchand, P.S. Salvinorin, a new trans-neoclerodane diterpene from Salvia divinorum. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. I 1982, 1, 2505–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, L.J. 3rd. Salvia divinorum and the unique diterpene hallucinogen, Salvinorin (divinorin) A. J. Psychoact. Drugs 1994, 26, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffler, D.J.; Roth, B.L. Salvinorin A: The “magic mint” hallucinogen finds a molecular target in the kappa opioid receptor. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2003, 24, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Roth, B.L. Salvinorin A: A novel and highly selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 2615–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, B.L.; Baner, K.; Westkaemper, R.; Siebert, D.; Rice, K.C.; Steinberg, S.; Ernsberger, P.; Rothman, R.B. Salvinorin A: A potent naturally occurring nonnitrogenous kappa opioid selective agonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11934–11939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavkin, C.; Sud, S.; Jin, W.; Stewart, J.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Siebert, D.J.; Toth, B.A.; Hufeisen, S.J.; Roth, B.L. Salvinorin A, an active component of the hallucinogenic sage salvia divinorum is a highly efficacious kappa-opioid receptor agonist: Structural and functional considerations. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Metabolism of psilocybin and psilocin: Clinical and forensic toxicological relevance. Drug Metab. Rev. 2017, 49, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Pereira, C.L.; Da Silva, D.D. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Aspects of Peyote and Mescaline: Clinical and Forensic Repercussions. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-da-Costa, A.M.; Dias-da-Silva, D.; Gomes, N.G.M.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Madureira-Carvalho, Á. Toxicokinetics and Toxicodynamics of Ayahuasca Alkaloids N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT), Harmine, Harmaline and Tetrahydroharmine: Clinical and Forensic Impact. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggott, M.J.; Erowid, E.; Erowid, F.; Galloway, G.P.; Mendelson, J. Use patterns and self-reported effects of Salvia divinorum: An internet-based survey. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010, 111, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.T.; Woody, G.E.; Yang, C.; Li, J.H.; Blazer, D.G. Recent national trends in Salvia divinorum use and substance-use disorders among recent and former Salvia divinorum users compared with nonusers. Subst. Abuse Rehabil. 2011, 2011, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Barnes, B.B.; Snow, N.H. Analysis of Salvinorin A in plants, water, and urine using solid-phase microextraction-comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1226, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casselman, I.; Heinrich, M. Novel use patterns of Salvia divinorum: Unobtrusive observation using YouTube™. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, L.E.; Panos, J.J.; Killinger, B.A.; Peet, M.M.; Bell, L.M.; Haliw, L.A.; Walker, S.L. Comparison of the discriminative stimulus effects of salvinorin A and its derivatives to U69,593 and U50,488 in rats. Psychopharmacology 2009, 203, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prisinzano, T.E. Psychopharmacology of the hallucinogenic sage Salvia divinorum. Life Sci. 2005, 78, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.W.; MacLean, K.A.; Reissig, C.J.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Griffiths, R.R. Human psychopharmacology and dose-effects of salvinorin A, a kappa opioid agonist hallucinogen present in the plant Salvia divinorum. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011, 115, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujikawa, K.; Kuwayama, K.; Miyaguchi, H.; Kanamori, T.; Iwata, Y.T.; Yoshida, T.; Inoue, H. Determination of salvinorin A and salvinorin B in Salvia divinorum-related products circulated in Japan. Forensic Sci. Int. 2008, 180, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumnall, H.R.; Measham, F.; Brandt, S.D.; Cole, J.C. Salvia divinorum use and phenomenology: Results from an online survey. J. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 25, 1496–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, B.; Crean, C.; Levissianos, S.; Mermerci, D.; Tun Nay, S.; Otani, T.; Park, M.; Pazos, D.; Piñeros, K.; Umapornsakula, A.; et al. The Challenge of New Psychoactive Substances; UNODC Global SMART Programme: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vortherms, T.A.; Roth, B.L. Salvinorin A: From natural product to human therapeutics. Mol. Interv. 2006, 6, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqueda, A.E. The use of Salvia divinorum from a Mazatec perspective. In Plant Medicines, Healing and Psychedelic Science; Labate, B.C., Cavnar, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 55–70. [Google Scholar]
- Akaberi, M.; Iranshahi, M.; Mehri, S. Molecular Signaling Pathways behind the Biological Effects of Salvia Species Diterpenes in Neuropharmacology and Cardiology. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 878–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braida, D.; Donzelli, A.; Martucci, R.; Capurro, V.; Sala, M. Learning and memory impairment induced by salvinorin A, the principal ingredient of Salvia divinorum, in wistar rats. Int. J. Toxicol. 2011, 30, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.B.; Ni, Z.Y.; Shi, Q.W.; Dong, M.; Kiyota, H.; Gu, Y.C.; Cong, B. Constituents from Salvia species and their biological activities. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5967–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, C.W.; Rothman, R.B.; Prisinzano, T.E. Neuropharmacology of the naturally occurring kappa-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 316–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, T.A.; Rizzacasa, M.A. Salvinorins D-F, new neoclerodane diterpenoids from Salvia divinorum, and an improved method for the isolation of salvinorin A. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 703–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigham, A.K.; Munro, T.A.; Rizzacasa, M.A.; Robins-Browne, R.M. Divinatorins A-C, new neoclerodane diterpenoids from the controlled sage Salvia divinorum. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1242–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, W.W.; Tidgewell, K.; Schmidt, M.; Shah, K.; Dersch, C.M.; Snyder, J.; Parrish, D.; Deschamps, J.R.; Rothman, R.B.; Prisinzano, T.E. Salvinicins A and B, new neoclerodane diterpenes from Salvia divinorum. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 3017–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lee, D.Y.; Ma, Z.; Liu-Chen, L.Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr.; Cohen, B. New neoclerodane diterpenoids isolated from the leaves of Salvia divinorum and their binding affinities for human kappa opioid receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 5635–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casselman, I.; Nock, C.J.; Wohlmuth, H.; Weatherby, R.P.; Heinrich, M. From local to global-fifty years of research on Salvia divinorum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 768–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, D.J. Localization of salvinorin A and related compounds in glandular trichomes of the psychoactive sage, Salvia divinorum. Ann. Bot. 2004, 93, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertea, C.M.; Luciano, P.; Bossi, S.; Leoni, F.; Baiocchi, C.; Medana, C.; Azzolin, C.M.; Temporale, G.; Lombardozzi, M.A.; Maffei, M.E. PCR and PCR-RFLP of the 5S-rRNA-NTS region and salvinorin A analyses for the rapid and unequivocal determination of Salvia divinorum. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, O.; Phipps, S.M.; Zadezensky, I.; Butterweck, V. Salvia divinorum and salvinorin A: An update on pharmacology and analytical methodology. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medana, C.; Massolino, C.; Pazzi, M.; Baiocchi, C. Determination of salvinorins and divinatorins in Salvia divinorum leaves by liquid chromatography/multistage mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolowich, W.R.; Perkins, A.M.; Cienki, J.J. Analysis of the psychoactive terpenoid salvinorin A content in five Salvia divinorum herbal products. Pharmacotherapy 2006, 26, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, J.W.; Siebert, D.J.; Der Marderosian, A.H.; Hock, R.S. High performance liquid chromatographic quantification of salvinorin A from tissues of Salvia divinorum Epling & Játiva-M. Phytochem. Anal. 1999, 10, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Pelot, K.A.; Mitchell, R.; Kwon, M.; Hagelthorn, L.M.; Wardman, J.F.; Chiang, A.; Bohlmann, J.; Ro, D.K.; Zerbe, P. Biosynthesis of the psychotropic plant diterpene salvinorin A: Discovery and characterization of the Salvia divinorum clerodienyl diphosphate synthase. Plant J. 2017, 89, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheerer, J.R.; Lawrence, J.F.; Wang, G.C.; Evans, D.A. Asymmetric synthesis of salvinorin A, a potent kappa opioid receptor agonist. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8968–8969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Metz, P. Total Synthesis of the Neoclerodane Diterpene Salvinorin A via an Intramolecular Diels-Alder Strategy. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 3418–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.J.; Brion, A.; Shenvi, R.A. Chemical syntheses of the salvinorin chemotype of KOR agonist. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 128563, Salvinorin A. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Salvinorin-A (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Orton, E.; Liu, R. Salvinorin A: A Mini Review of Physical and Chemical Properties Affecting Its Translation from Research to Clinical Applications in Humans. Transl. Perioper Pain Med. 2014, 1, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ansonoff, M.A.; Zhang, J.; Czyzyk, T.; Rothman, R.B.; Stewart, J.; Xu, H.; Zjwiony, J.; Siebert, D.J.; Yang, F.; Roth, B.L.; et al. Antinociceptive and hypothermic effects of Salvinorin A are abolished in a novel strain of kappa-opioid receptor-1 knockout mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 318, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teksin, Z.S.; Lee, I.J.; Nemieboka, N.N.; Othman, A.A.; Upreti, V.V.; Hassan, H.E.; Syed, S.S.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Eddington, N.D. Evaluation of the transport, in vitro metabolism and pharmacokinetics of Salvinorin A, a potent hallucinogen. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faudree, P. “Making Medicine” with Salvia divinorum: Competing Approaches and Their Implications. Med. Anthropol. 2020, 39, 582–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulenberg, J.E.; Johnston, L.D.; O’Malley, P.M.; Bachman, J.G.; Miech, R.A.; Patrick, M.E. Monitoring the Future National Survey Results on Drug Use, 1975–2019; College Students and Adults Ages 19–60; Institute for Social Research, The University of Michigan: Michigan, Germany, 2020; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, J.E.; Reed, M.B.; Croff, J.M.; Clapp, J.D. College student use of Salvia divinorum. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008, 94, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Khey, D.N.; Miller, B.L.; Griffin, O.H. Salvia divinorum use among a college student sample. J. Drug Educ. 2008, 38, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertson, D.N.; Grubbs, L.E. Subjective effects of Salvia divinorum: LSD- or marijuana-like? J. Psychoactive Drugs 2009, 41, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyi, P.P.; Lai, E.P.; Lee, D.Y.; Biglete, S.A.; Torrecer, G.I.; Anderson, I.B. Influence of age on Salvia divinorum use: Results of an Internet survey. J. Psychoactive Drugs 2010, 42, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, C.L. Epidemiology of adolescent Salvia divinorum use in Canada. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013, 128, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMCDDA. Salvia Divinorum Drug Profile. Available online: https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/publications/drug-profiles/salvia (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- González, D.; Riba, J.; Bouso, J.C.; Gómez-Jarabo, G.; Barbanoj, M.J. Pattern of use and subjective effects of Salvia divinorum among recreational users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2006, 85, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.; Guerreiro, C.; Dias, L.; Costa, J.L. Consumos, Representações e Perceções das Novas Substâncias Psicoativas Entre Estudantes Universitários; SICAD: Portugal, Lisbon, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.G.S. Da Mediatização do Fenómeno das Smart Drugs ao Perfil dos Consumidores: Um Estudo Exploratório; Instituto Universitário de Ciências Psicológicas, Sociais e da Vida: Lisboa, Portugal, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Perron, B.E.; Ahmedani, B.K.; Vaughn, M.G.; Glass, J.E.; Abdon, A.; Wu, L.T. Use of Salvia divinorum in a nationally representative sample. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 2012, 38, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- US Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). Salvia Divinorum and Salvinorin A; Diversion Control Division D.C.E.S., Ed.; US Department of Justice: Springfield, VA, USA, 2020.
- Griffin, O.H.; Miller, B.L.; Khey, D.N. Legally high? Legal considerations of Salvia divinorum. J. Psychoactive Drugs 2008, 40, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State of Michigan Ninety-fifth Legislature. Enrolled House Bill 6038. Public Act 171 of 2010. Available online: http://legislature.mi.gov/doc.aspx?2010-HB-6038 (accessed on 6 November 2020).
- Ford, J.A.; Watkins, W.C.; Blumenstein, L. Correlates of Salvia divinorum use in a national sample: Findings from the 2009 National Survey on Drug Use and Health. Addict. Behav. 2011, 36, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebert, D. The Legal Status of Salvia Divinorum. Available online: http://www.sagewisdom.org/legalstatus.html (accessed on 6 November 2020).
- Bücheler, R.; Gleiter, C.H.; Schwoerer, P.; Gaertner, I. Use of nonprohibited hallucinogenic plants: Increasing relevance for public health? A case report and literature review on the consumption of Salvia divinorum (Diviner’s Sage). Pharmacopsychiatry 2005, 38, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichini, S.; Abanades, S.; Farré, M.; Pellegrini, M.; Marchei, E.; Pacifici, R.; Torre Rde, L.; Zuccaro, P. Quantification of the plant-derived hallucinogen Salvinorin A in conventional and non-conventional biological fluids by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry after Salvia divinorum smoking. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.X.; Li, J.H.; Chen, S.H.; Chang, H.C.; McKetin, R. Quantitative determination of salvinorin A, a natural hallucinogen with abuse liability, in Internet-available Salvia divinorum and endemic species of Salvia in Taiwan. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listos, J.; Merska, A.; Fidecka, S. Pharmacological activity of salvinorin A, the major component of Salvia divinorum. Pharmacol. Rep. 2011, 63, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalho, C.; Corte-Real, F.; López-Rivadulla, M.; Gallardo, E. Salvia divinorum: Toxicological aspects and analysis in human biological specimens. Bioanalysis 2016, 8, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, F.; Kivell, B.; Boyle, O. “Quite a Profoundly Strange Experience”: An Analysis of the Experiences of Salvia divinorum Users. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2016, 48, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Bello, R.; García-Rodríguez, R.V.; García-Sosa, K.; Peña-Rodríguez, L.M.; Vázquez-Hernández, M.; Ramos-Morales, F.R.; Corcoran, O.; Sánchez-Medina, A. Salvinorin A content in legal high products of Salvia divinorum sold in Mexico. Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 249, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Alvarado, R.B.; Madariaga-Mazón, A.; Ortega, A.; Martinez-Mayorga, K. DARK Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Salvinorin A. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvinorin Nasal Dosage. Available online: https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&t=94938 (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Salvinorin-a Nasal Spary? Available online: https://www.reddit.com/r/Salvia/comments/at9lma/salvinorin%CE%B1_nasal_spray/ (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Dalgarno, P. Subjective effects of Salvia divinorum. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2007, 39, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keasling, A.W.; Pandey, P.; Doerksen, R.J.; Pedrino, G.R.; Costa, E.A.; Da Cunha, L.C.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Fajemiroye, J.O. Salvindolin elicits opioid system-mediated antinociceptive and antidepressant-like activities. J. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 33, 865–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelson, J.E.; Coyle, J.R.; Lopez, J.C.; Baggott, M.J.; Flower, K.; Everhart, E.T.; Munro, T.A.; Galloway, G.P.; Cohen, B.M. Lack of effect of sublingual salvinorin A, a naturally occurring kappa opioid, in humans: A placebo-controlled trial. Psychopharmacology 2011, 214, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqueda, A.E.; Valle, M.; Addy, P.H.; Antonijoan, R.M.; Puntes, M.; Coimbra, J.; Ballester, M.R.; Garrido, M.; González, M.; Claramunt, J.; et al. Naltrexone but Not Ketanserin Antagonizes the Subjective, Cardiovascular, and Neuroendocrine Effects of Salvinorin-A in Humans. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.W.; MacLean, K.A.; Caspers, M.J.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Griffiths, R.R. Time course of pharmacokinetic and hormonal effects of inhaled high-dose salvinorin A in humans. J. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 30, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, M.; Schnakenberg, A.; Skosnik, P.D.; Cohen, B.M.; Pittman, B.; Sewell, R.A.; D’Souza, D.C. Dose-related behavioral, subjective, endocrine, and psychophysiological effects of the κ opioid agonist Salvinorin A in humans. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 72, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.D.; Schmidt, M.S.; Butelman, E.R.; Harding, W.W.; Tidgewell, K.; Murry, D.J.; Kreek, M.J.; Prisinzano, T.E. Pharmacokinetics of the plant-derived kappa-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A in nonhuman primates. Synapse 2005, 58, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooker, J.M.; Xu, Y.; Schiffer, W.; Shea, C.; Carter, P.; Fowler, J.S. Pharmacokinetics of the potent hallucinogen, salvinorin A in primates parallels the rapid onset and short duration of effects in humans. Neuroimage 2008, 41, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béguin, C.; Richards, M.R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu-Chen, L.Y.; Ma, Z.; Lee, D.Y.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr.; Cohen, B.M. Synthesis and in vitro pharmacological evaluation of salvinorin A analogues modified at C(2). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 2761–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butelman, E.R.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Deng, H.; Rus, S.; Kreek, M.J. Unconditioned behavioral effects of the powerful kappa-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A in nonhuman primates: Fast onset and entry into cerebrospinal fluid. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 328, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooker, J.M.; Patel, V.; Kothari, S.; Schiffer, W.K. Metabolic changes in the rodent brain after acute administration of salvinorin A. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2009, 11, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butelman, E.R.; Caspers, M.; Lovell, K.M.; Kreek, M.J.; Prisinzano, T.E. Behavioral effects and central nervous system levels of the broadly available κ-agonist hallucinogen salvinorin A are affected by P-glycoprotein modulation in vivo. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.S.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Tidgewell, K.; Harding, W.; Butelman, E.R.; Kreek, M.J.; Murry, D.J. Determination of Salvinorin A in body fluids by high performance liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure chemical ionization. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2005, 818, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujikawa, K.; Kuwayama, K.; Miyaguchi, H.; Kanamori, T.; Iwata, Y.T.; Inoue, H. In vitro stability and metabolism of salvinorin A in rat plasma. Xenobiotica 2009, 39, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés, L.J., 3rd; Chang, H.M.; Visger, D.C.; Koreeda, M. Salvinorin C, a new neoclerodane diterpene from a bioactive fraction of the hallucinogenic Mexican mint Salvia divinorum. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 3935–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurdy, C.R.; Sufka, K.J.; Smith, G.H.; Warnick, J.E.; Nieto, M.J. Antinociceptive profile of salvinorin A, a structurally unique kappa opioid receptor agonist. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 83, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Khoury, J.; Sahakian, N. The Association of Salvia divinorum and Psychotic Disorders: A Review of the Literature and Case Series. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2015, 47, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, M.K.; Shirota, O.; Sasaki-Tabata, K.; Tanaka, H.; Sekita, S.; Morimoto, S. Development of an enzyme immunoassay using a monoclonal antibody against the psychoactive diterpenoid salvinorin A. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, M.K.; Shirota, O.; Sakamoto, S.; Morimoto, S.; Tanaka, H. An immunochromatographic assay for rapid etection of salvinorin A. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2017, 38, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, I.; Da Fonseca, B.; Oppolzer, D.; Martinho, A.; Barroso, M.; Cruz, A.; Queiroz, J.A.; Gallardo, E. Analysis of Salvinorin A in urine using microextraction in packed syringe and GC-MS/MS. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margalho, C.; Gallardo, E.; Castanheira, A.; Vieira, D.N.; López-Rivadulla, M.; Real, F.C. A validated procedure for detection and quantitation of salvinorin a in pericardial fluid, vitreous humor, whole blood and plasma using solid phase extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1304, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspers, M.J.; Williams, T.D.; Lovell, K.M.; Lozama, A.; Butelman, E.R.; Kreek, M.J.; Johnson, M.; Griffiths, R.; Maclean, K.; Prisinzano, T.E. LC-MS/MS quantification of salvinorin A from biological fluids. Anal. Methods 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, P.C.; Holler, J.M.; Vorce, S.P.; Bosy, T.Z.; Magluilo, J., Jr.; Past, M.R. The detection and quantitative analysis of the psychoactive component of Salvia divinorum, salvinorin A, in human biological fluids using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2008, 32, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichini, S.; Marchei, E.; García-Algar, O.; Gomez, A.; Di Giovannandrea, R.; Pacifici, R. Ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry determination of hallucinogenic drugs in hair of psychedelic plants and mushrooms consumers. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 100, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appley, M.G.; Beyramysoltan, S.; Musah, R.A. Random Forest Processing of Direct Analysis in Real-Time Mass Spectrometric Data Enables Species Identification of Psychoactive Plants from Their Headspace Chemical Signatures. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15636–15644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.H.; Wiseman, J.M. Direct analysis of Salvia divinorum leaves for salvinorin A by thin layer chromatography and desorption electrospray ionization multi-stage tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczuk, A.P.; Raman, V.; Galal, A.M.; Khan, I.A.; Siebert, D.J.; Zjawiony, J.K. Vegetative anatomy and micromorphology of Salvia divinorum (Lamiaceae) from Mexico, combined with chromatographic analysis of salvinorin A. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 68, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier Moreira, F.; Carvalho, F.; De Lourdes Bastos, M.; Guedes de Pinho, P. Analytical investigation of legal high products containing Salvia divinorum traded in smartshops and internet. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 242, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.M.; Bola, G. DNA identification of Salvia divinorum samples. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2013, 7, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Mosier, P.D.; Westkaemper, R.B.; Stewart, J.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Vortherms, T.A.; Sheffler, D.J.; Roth, B.L. Identification of the molecular mechanisms by which the diterpenoid salvinorin A binds to kappa-opioid receptors. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 8643–8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vortherms, T.A.; Mosier, P.D.; Westkaemper, R.B.; Roth, B.L. Differential helical orientations among related G protein-coupled receptors provide a novel mechanism for selectivity. Studies with salvinorin A and the kappa-opioid receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 3146–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichna, J.; Schicho, R.; Andrews, C.N.; Bashashati, M.; Klompus, M.; McKay, D.M.; Sharkey, K.A.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Janecka, A.; Storr, M.A. Salvinorin A inhibits colonic transit and neurogenic ion transport in mice by activating kappa-opioid and cannabinoid receptors. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2009, 21, 1326-e1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, G.; Savona, G.; Rodríguez, B.; Dersch, C.M.; Rothman, R.B.; Prisinzano, T.E. Synthetic studies of neoclerodane diterpenoids from Salvia splendens and evaluation of Opioid Receptor affinity. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 10041–10048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butelman, E.R.; Mandau, M.; Tidgewell, K.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Yuferov, V.; Kreek, M.J. Effects of salvinorin A, a kappa-opioid hallucinogen, on a neuroendocrine biomarker assay in nonhuman primates with high kappa-receptor homology to humans. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 320, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spetea, M.; Asim, M.F.; Noha, S.; Wolber, G.; Schmidhammer, H. Current κ opioid receptor ligands and discovery of a new molecular scaffold as a κ opioid receptor antagonist using pharmacophore-based virtual screening. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 7362–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beerepoot, P.; Lam, V.; Luu, A.; Tsoi, B.; Siebert, D.; Szechtman, H. Effects of salvinorin A on locomotor sensitization to D2/D3 dopamine agonist quinpirole. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 446, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, B.E.; McCurdy, C.R.; Ferguson, D.M. Toward a structure-based model of salvinorin A recognition of the kappa-opioid receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1824–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruchas, M.R.; Chavkin, C. Kinase cascades and ligand-directed signaling at the kappa opioid receptor. Psychopharmacology 2010, 210, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Lovell, K.M.; Frankowski, K.J.; Slauson, S.R.; Phillips, A.M.; Streicher, J.M.; Stahl, E.; Schmid, C.L.; Hodder, P.; Madoux, F.; et al. Development of functionally selective, small molecule agonists at kappa opioid receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 36703–36716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, B.L.; Willins, D.L.; Kristiansen, K.; Kroeze, W.K. 5-Hydroxytryptamine2-family receptors (5-hydroxytryptamine2A, 5-hydroxytryptamine2B, 5-hydroxytryptamine2C): Where structure meets function. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 79, 231–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butelman, E.R.; Harris, T.J.; Kreek, M.J. The plant-derived hallucinogen, salvinorin A, produces kappa-opioid agonist-like discriminative effects in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 2004, 172, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmore-Fordham, C.B.; Krall, D.M.; McCurdy, C.R.; Kinder, D.H. The hallucinogen derived from Salvia divinorum, salvinorin A, has kappa-opioid agonist discriminative stimulus effects in rats. Neuropharmacology 2007, 53, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, B.A.; Devi, L.A. G-protein-coupled receptor heterodimerization modulates receptor function. Nature 1999, 399, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, A.D.; Reed, B.; Erazo, J.; Ben-Ezra, A.; Kreek, M.J. Signaling Properties of Structurally Diverse Kappa Opioid Receptor Ligands: Toward in Vitro Models of in Vivo Responses. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 3590–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, K.; Inan, S.; Siebert, D.; Holzgrabe, U.; Lee, D.Y.; Huang, P.; Li, J.G.; Cowan, A.; Liu-Chen, L.Y. Comparison of pharmacological activities of three distinct kappa ligands (Salvinorin A, TRK-820 and 3FLB) on kappa opioid receptors in vitro and their antipruritic and antinociceptive activities in vivo. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 312, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, F.; Wang, S.; Akins, N.S.; Hossain, M.I.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, J.; Ji, J.; Xi, J.; Lin, W.; et al. Kappa opioid receptors internalization is protective against oxygen-glucose deprivation through β-arrestin activation and Akt-mediated signaling pathway. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 137, 104748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, D.N.; Damez-Werno, D.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr.; Cohen, B.M.; Chartoff, E.H. Repeated exposure to the κ-opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A modulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase and reward sensitivity. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Rice, K.C.; France, C.P. Discriminative stimulus effects of 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)-2-aminopropane in rhesus monkeys. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 324, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killinger, B.A.; Peet, M.M.; Baker, L.E. Salvinorin A fails to substitute for the discriminative stimulus effects of LSD or ketamine in Sprague-Dawley rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2010, 96, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffeen, U.; Canseco-Alba, A.; Simón-Arceo, K.; Almanza, A.; Mercado, F.; León-Olea, M.; Pellicer, F. Salvinorin A reduces neuropathic nociception in the insular cortex of the rat. Eur. J. Pain 2018, 22, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, R.; Borrelli, F.; Cascio, M.G.; Aviello, G.; Huben, K.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Marini, P.; Romano, B.; Di Marzo, V.; Capasso, F.; et al. Inhibitory effect of salvinorin A, from Salvia divinorum, on ileitis-induced hypermotility: Cross-talk between kappa-opioid and cannabinoid CB(1) receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 155, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braida, D.; Limonta, V.; Pegorini, S.; Zani, A.; Guerini-Rocco, C.; Gori, E.; Sala, M. Hallucinatory and rewarding effect of salvinorin A in zebrafish: Kappa-opioid and CB1-cannabinoid receptor involvement. Psychopharmacology 2007, 190, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braida, D.; Limonta, V.; Capurro, V.; Fadda, P.; Rubino, T.; Mascia, P.; Zani, A.; Gori, E.; Fratta, W.; Parolaro, D.; et al. Involvement of kappa-opioid and endocannabinoid system on Salvinorin A-induced reward. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walentiny, D.M.; Vann, R.E.; Warner, J.A.; King, L.S.; Seltzman, H.H.; Navarro, H.A.; Twine, C.E., Jr.; Thomas, B.F.; Gilliam, A.F.; Gilmour, B.P.; et al. Kappa opioid mediation of cannabinoid effects of the potent hallucinogen, salvinorin A, in rodents. Psychopharmacology 2010, 210, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeman, P.; Guan, H.C.; Hirbec, H. Dopamine D2High receptors stimulated by phencyclidines, lysergic acid diethylamide, salvinorin A, and modafinil. Synapse 2009, 63, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Butelman, E.R.; Schlussman, S.D.; Ho, A.; Kreek, M.J. Effects of the plant-derived hallucinogen salvinorin A on basal dopamine levels in the caudate putamen and in a conditioned place aversion assay in mice: Agonist actions at kappa opioid receptors. Psychopharmacology 2005, 179, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlezon, W.A., Jr.; Béguin, C.; DiNieri, J.A.; Baumann, M.H.; Richards, M.R.; Todtenkopf, M.S.; Rothman, R.B.; Ma, Z.; Lee, D.Y.; Cohen, B.M. Depressive-like effects of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A on behavior and neurochemistry in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 316, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrke, B.J.; Chefer, V.I.; Shippenberg, T.S. Effects of acute and repeated administration of salvinorin A on dopamine function in the rat dorsal striatum. Psychopharmacology 2008, 197, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivell, B.; Uzelac, Z.; Sundaramurthy, S.; Rajamanickam, J.; Ewald, A.; Chefer, V.; Jaligam, V.; Bolan, E.; Simonson, B.; Annamalai, B.; et al. Salvinorin A regulates dopamine transporter function via a kappa opioid receptor and ERK1/2-dependent mechanism. Neuropharmacology 2014, 86, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, V.; Fattore, L.; Scherma, M.; Collu, R.; Spano, M.S.; Fratta, W.; Fadda, P. Behavioural and neurochemical assessment of salvinorin A abuse potential in the rat. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, M.; Neri, E.; Zappettini, S.; Massa, F.; Bisio, A.; Romussi, G.; Marchi, M.; Pittaluga, A. Salvinorin A exerts opposite presynaptic controls on neurotransmitter exocytosis from mouse brain nerve terminals. Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, B.L.; Lopez, E.; Beischel, S.; Westkaemper, R.B.; Evans, J.M. Screening the receptorome to discover the molecular targets for plant-derived psychoactive compounds: A novel approach for CNS drug discovery. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 102, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothman, R.B.; Murphy, D.L.; Xu, H.; Godin, J.A.; Dersch, C.M.; Partilla, J.S.; Tidgewell, K.; Schmidt, M.; Prisinzano, T.E. Salvinorin A: Allosteric interactions at the mu-opioid receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 320, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, J.L. Salvia divinorum: A psychopharmacological riddle and a mind-body prospect. Curr. Drug Abuse Rev. 2013, 6, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, J.E.; Daniel, J.; Homer, K.; Reed, M.B.; Clapp, J.D. Salvia divinorum: Effects and use among YouTube users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010, 108, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqueda, A.E.; Valle, M.; Addy, P.H.; Antonijoan, R.M.; Puntes, M.; Coimbra, J.; Ballester, M.R.; Garrido, M.; González, M.; Claramunt, J.; et al. Salvinorin-A Induces Intense Dissociative Effects, Blocking External Sensory Perception and Modulating Interoception and Sense of Body Ownership in Humans. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addy, P.H. Acute and post-acute behavioral and psychological effects of salvinorin A in humans. Psychopharmacology 2012, 220, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addy, P.H.; Garcia-Romeu, A.; Metzger, M.; Wade, J. The subjective experience of acute, experimentally-induced Salvia divinorum inebriation. J. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 29, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, A.; Said, A.; Assaad, C.; Hallit, S.; Haddad, G.; Hachem, D.; Kazour, F. Abuse and Effects of Salvia divinorum in a Sample of Patients Hospitalized for Substance Dependence. Community Ment. Health J. 2019, 55, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, K.A.; Johnson, M.W.; Reissig, C.J.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Griffiths, R.R. Dose-related effects of salvinorin A in humans: Dissociative, hallucinogenic, and memory effects. Psychopharmacology 2013, 226, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, C.L.; Paine, T.A.; Rittiner, J.E.; Béguin, C.; Carroll, F.I.; Roth, B.L.; Cohen, B.M.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr. Role of kappa-opioid receptors in the effects of salvinorin A and ketamine on attention in rats. Psychopharmacology 2010, 210, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chartoff, E.H.; Potter, D.; Damez-Werno, D.; Cohen, B.M.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr. Exposure to the selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A modulates the behavioral and molecular effects of cocaine in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 2676–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantegrossi, W.E.; Kugle, K.M.; Valdes, L.J., 3rd; Koreeda, M.; Woods, J.H. Kappa-opioid receptor-mediated effects of the plant-derived hallucinogen, salvinorin A, on inverted screen performance in the mouse. Behav. Pharmacol. 2005, 16, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braida, D.; Capurro, V.; Zani, A.; Rubino, T.; Viganò, D.; Parolaro, D.; Sala, M. Potential anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects of salvinorin A, the main active ingredient of Salvia divinorum, in rodents. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Trujano, M.E.; Brindis, F.; López-Ruiz, E.; Ramírez-Salado, I.; Martínez, A.; Pellicer, F. Depressant Effects of Salvia divinorum Involve Disruption of Physiological Sleep. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, M.T.; Smith, S.E.; Niehoff, J.A.; McCurdy, C.R.; Taylor, G.T. Antidepressive effects of the κ-opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A in a rat model of anhedonia. Behav. Pharmacol. 2012, 23, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, T.F.; French, L.G.; Erlichman, J.S. The antinociceptive effect of salvinorin A in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 545, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butelman, E.R.; McElroy, B.D.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Kreek, M.J. Impact of Pharmacological Manipulation of the κ-Opioid Receptor System on Self-grooming and Anhedonic-like Behaviors in Male Mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichna, J.; Dicay, M.; Hirota, S.A.; Traboulsi, D.; Macdonald, J.A.; Janecka, A.; Beck, P.L.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Macnaughton, W.K.; Storr, M.A. Differential effects of salvinorin A on endotoxin-induced hypermotility and neurogenic ion transport in mouse ileum. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 583-e212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichna, J.; Dicay, M.; Lewellyn, K.; Janecka, A.; Zjawiony, J.K.; MacNaughton, W.K.; Storr, M.A. Salvinorin A has antiinflammatory and antinociceptive effects in experimental models of colitis in mice mediated by KOR and CB1 receptors. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2012, 18, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, R.; Borrelli, F.; Capasso, F.; Siebert, D.J.; Stewart, D.J.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Izzo, A.A. The hallucinogenic herb Salvia divinorum and its active ingredient salvinorin A inhibit enteric cholinergic transmission in the guinea-pig ileum. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2006, 18, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capasso, R.; Borrelli, F.; Zjawiony, J.; Kutrzeba, L.; Aviello, G.; Sarnelli, G.; Capasso, F.; Izzo, A.A. The hallucinogenic herb Salvia divinorum and its active ingredient salvinorin A reduce inflammation-induced hypermotility in mice. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2008, 20, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviello, G.; Borrelli, F.; Guida, F.; Romano, B.; Lewellyn, K.; De Chiaro, M.; Luongo, L.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Maione, S.; Izzo, A.A.; et al. Ultrapotent effects of salvinorin A, a hallucinogenic compound from Salvia divinorum, on LPS-stimulated murine macrophages and its anti-inflammatory action in vivo. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 89, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morani, A.S.; Schenk, S.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Kivell, B.M. A single injection of a novel κ opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A attenuates the expression of cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in rats. Behav. Pharmacol. 2012, 23, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivell, B.M.; Ewald, A.W.; Prisinzano, T.E. Salvinorin A analogs and other κ-opioid receptor compounds as treatments for cocaine abuse. Adv. Pharmacol. 2014, 69, 481–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, J.H. Hallucinogens and dissociative agents naturally growing in the United States. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 102, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggs, J.M.; Morgan, J.A.; Lardieri, A.B.; Kishk, O.A.; Klein-Schwartz, W. Abuse and Misuse of Selected Dietary Supplements among Adolescents: A Look at Poison Center Data. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 22, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, C.R.; Ray, G.A.; Marlowe, K.F. A Report of Nausea and Vomiting with Discontinuation of Chronic Use of Salvia divinorum. Case Rep. Med. 2012, 2012, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vohra, R.; Seefeld, A.; Cantrell, F.L.; Clark, R.F. Salvia divinorum: Exposures reported to a statewide poison control system over 10 years. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 40, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, C.D.; Carreiro, S.P.; Babu, K.M. Here today, gone tomorrow…and back again? A review of herbal marijuana alternatives (K2, Spice), synthetic cathinones (bath salts), kratom, Salvia divinorum, methoxetamine, and piperazines. J. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winslow, M.; Mahendran, R. From divination to madness: Features of acute intoxication with Salvia use. Singap. Med. J. 2014, 55, e52–e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulzen, M.; Gründer, G. Toxic psychosis after intake of the hallucinogen salvinorin A. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2008, 69, 1501–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Adolescent salvia substance abuse. Addiction 2007, 102, 823–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przekop, P.; Lee, T. Persistent psychosis associated with salvia divinorum use. Am. J. Psychiatry 2009, 166, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, E.G.; Writer, B.W. Salvia divinorum. Psychosomatics 2012, 53, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowry, M.; Mosher, M.; Briner, W. Acute physiologic and chronic histologic changes in rats and mice exposed to the unique hallucinogen salvinorin A. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2003, 35, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socała, K.; Doboszewska, U.; Wlaź, P. Salvinorin A Does Not Affect Seizure Threshold in Mice. Molecules 2020, 25, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinho, A.; Silva, S.M.; Gallardo, E. Cytotoxic Effects of Salvinorin A, A Major Constituent of Salvia divinorum. Med. Chem. 2016, 12, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Khoury, J.; Baroud, E. Case series: Salvia divinorum as a potential addictive hallucinogen. Am. J. Addict. 2018, 27, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butelman, E.R.; Kreek, M.J. Salvinorin A, a kappa-opioid receptor agonist hallucinogen: Pharmacology and potential template for novel pharmacotherapeutic agents in neuropsychiatric disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón-Arceo, K.; González-Trujano, M.E.; Coffeen, U.; Fernández-Mas, R.; Mercado, F.; Almanza, A.; Contreras, B.; Jaimes, O.; Pellicer, F. Neuropathic and inflammatory antinociceptive effects and electrocortical changes produced by Salvia divinorum in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 206, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanes, K.R. Antidepressant effects of the herb Salvia divinorum: A case report. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2001, 21, 634–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebner, S.R.; Roitman, M.F.; Potter, D.N.; Rachlin, A.B.; Chartoff, E.H. Depressive-like effects of the kappa opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A are associated with decreased phasic dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. Psychopharmacology 2010, 210, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béguin, C.; Potter, D.N.; Dinieri, J.A.; Munro, T.A.; Richards, M.R.; Paine, T.A.; Berry, L.; Zhao, Z.; Roth, B.L.; Xu, W.; et al. N-methylacetamide analog of salvinorin A: A highly potent and selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist with oral efficacy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 324, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cui, X.; Matsunaga, F.; Ma, J.; Ma, N.; Abel, T.; Liu, R. Salvinorin A decreases mortality and improves neurological outcome in a neonatal mouse hypoxia model. Transl. Perioper. Pain Med. 2014, 1, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Su, D.; Riley, J.; Armstead, W.M.; Liu, R. Salvinorin A pretreatment preserves cerebrovascular autoregulation after brain hypoxic/ischemic injury via extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase in piglets. Anesth. Analg. 2012, 114, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, N.; Riley, J.; Armstead, W.M.; Liu, R. Salvinorin A administration after global cerebral hypoxia/ischemia preserves cerebrovascular autoregulation via kappa opioid receptor in piglets. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, D.; Riley, J.; Kiessling, W.J.; Armstead, W.M.; Liu, R. Salvinorin A produces cerebrovasodilation through activation of nitric oxide synthase, κ receptor, and adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channel. Anesthesiology 2011, 114, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Xi, C.; Liang, X.; Ma, J.; Su, D.; Abel, T.; Liu, R. The Role of κ Opioid Receptor in Brain Ischemia. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, e1219–e1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.P.; Zhou, W.; Ma, X.X.; He, Z.Z.; Wang, Z.H. Salvinorin A preserves cerebral pial artery autoregulation after forebrain ischemia via the PI3K/AKT/cGMP pathway. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, e6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhou, W.; Xin, J.; Shi, H.; Yao, X.; He, Z.; Wang, Z. Salvinorin A moderates postischemic brain injury by preserving endothelial mitochondrial function via AMPK/Mfn2 activation. Exp. Neurol. 2019, 322, 113045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, W.; Yan, J.; Yang, L.; Zhou, C.; Liu, R.; Chen, C. Salvinorin A ameliorates cerebral vasospasm through activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in a rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Microcirculation 2018, 25, e12442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lu, J.; Hu, Q.; Liu, R.; Zhou, C.; Chen, C. Salvinorin A attenuates early brain injury through PI3K/Akt pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rat. Brain Res. 2019, 1719, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, Z. Highly selective non-opioid kappa opioid receptor (KOR) agonist salvinorin A protects against forebrain ischemia-induced brain injury in rats. Brain Res. 2016, 1637, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wu, D.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.; Yao, T.; He, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhi, X.; Liu, R.; Ji, X. Intranasal salvinorin A improves neurological outcome in rhesus monkey ischemic stroke model using autologous blood clot. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2020, 271678x20938137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, A.; Pace, S.; Tedesco, F.; Pagano, E.; Guerra, G.; Troisi, F.; Werner, M.; Roviezzo, F.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Werz, O.; et al. The hallucinogenic diterpene salvinorin A inhibits leukotriene synthesis in experimental models of inflammation. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 106, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Caiazzo, E.; Bilancia, R.; Riemma, M.A.; Pagano, E.; Cicala, C.; Ialenti, A.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Izzo, A.A.; Capasso, R.; et al. Salvinorin A Inhibits Airway Hyperreactivity Induced by Ovalbumin Sensitization. Front. Pharmacol 2016, 7, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, C.J.; Liu, R.; Barr, G.A. Effects of plant-derived analgesic compounds sinomenine and salvinorin A in infant rats. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 18, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, F.; Luongo, L.; Aviello, G.; Palazzo, E.; De Chiaro, M.; Gatta, L.; Boccella, S.; Marabese, I.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Capasso, R.; et al. Salvinorin A reduces mechanical allodynia and spinal neuronal hyperexcitability induced by peripheral formalin injection. Mol. Pain 2012, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paton, K.F.; Kumar, N.; Crowley, R.S.; Harper, J.L.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Kivell, B.M. The analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of Salvinorin A analogue β-tetrahydropyran Salvinorin B in mice. Eur. J. Pain 2017, 21, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, K.B.; Naylor, J.E.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Woolverton, W.L. Assessment of the kappa opioid agonist, salvinorin A, as a punisher of drug self-administration in monkeys. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 2751–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello, N.K.; Negus, S.S. Effects of d-amphetamine and buprenorphine combinations on speedball (cocaine+heroin) self-administration by rhesus monkeys. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivell, B.; Prisinzano, T.E. Kappa opioids and the modulation of pain. Psychopharmacology 2010, 210, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejeda, H.A.; Chefer, V.I.; Zapata, A.; Shippenberg, T.S. The effects of kappa-opioid receptor ligands on prepulse inhibition and CRF-induced prepulse inhibition deficits in the rat. Psychopharmacology 2010, 210, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, J.J.; Shenvi, R.A. A review of salvinorin analogs and their kappa-opioid receptor activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Lee, D.Y.; Ma, Z.; Rawls, S.M.; Cowan, A.; Liu-Chen, L.Y. 2-Methoxymethyl-salvinorin B is a potent kappa opioid receptor agonist with longer lasting action in vivo than salvinorin A. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 324, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morani, A.S.; Ewald, A.; Prevatt-Smith, K.M.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Kivell, B.M. The 2-methoxy methyl analogue of salvinorin A attenuates cocaine-induced drug seeking and sucrose reinforcements in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 720, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, W.W.; Tidgewell, K.; Byrd, N.; Cobb, H.; Dersch, C.M.; Butelman, E.R.; Rothman, R.B.; Prisinzano, T.E. Neoclerodane diterpenes as a novel scaffold for mu opioid receptor ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 4765–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groer, C.E.; Tidgewell, K.; Moyer, R.A.; Harding, W.W.; Rothman, R.B.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Bohn, L.M. An opioid agonist that does not induce mu-opioid receptor--arrestin interactions or receptor internalization. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, D.; Wilson, N.; Chatenet, F.T.; LaCroix, C.; Gerona, R. Non-targeted screening for novel psychoactive substances among agitated emergency department patients. Clin. Toxicol. 2016, 54, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | Salvinorin A (mg/g) | Salvinorin B (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves from private collections 1 and endemic populations of Oaxaca 2 | 0.89–3.70 | - | [41] |
| Leaves from plants endemic to Sierra Mazatecan | 7.6 | 4.20 | [39] |
| Leaves from Hawaiian plants | 7.8 | 10.4 | [39] |
| Leaves and extracts purchased on the Internet (1–20×) | 0.126–1.137 | - | [40] |
| Dried leaves and concentrated extract products purchased on Japanese drug market (1×) | 3.2–5.0 | 0.10–0.17 | [22] |
| Ground young leaves of plants purchased from the Vancouver Seed Bank | 0.9 | [42] |
| Constituent | Matrices | Sample Preparation and/or Methodology | Linearity (R2) | Intra-Day Assay | Inter-Day Assay | LOD (μg/mL) | LOQ (μg/mL) | Recovery (%) | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision (%CV) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%CV) | Accuracy (%) | ||||||||
| Salvinorin A | Methanol extract of S. divinorum | icELISA | - | <3.19 | - | 2.78–9.65 | - | 0.0195 | - | 96.15–104.10 | [94] |
| Salvinorin A | Plasma; urine; saliva; sweat | LLE; GC-MS | >0.99 | <13.0 | - | <15.0 | - | 0.05 for plasma, urine, saliva; 0.03 for sweat | 0.015 for plasma, urine, saliva; 0.010 for sweat | 77–94 | [68] |
| Salvinorin A | Human plasma; rhesus monkey CSF | LC-MS/MS-ESI | - | <2.85 for plasma; <1.3 for CSF | <7.08 for plasma; <4.94 for CSF | <3.47 for plasma; <1.7 for CSF | <2.37 for plasma; <9.42 for CSF | - | 0.00005 for plasma; 0.0000125 for CSF | 93–114 for plasma | [98] |
| Salvinorin A | Urine | LC-MS-ESI | 0.997 | <7.5 | <9.5 | <8.5 | <6.2% | 0.0025 | 0.005 | - | [99] |
| Salvinorin A | Hair | UHPLC-MS/MS | 0.0997 | <12.0 | - | <7.0 | - | 0.00002 μg/mg | 0.00005 μg/mg | 76.6–97.4 | [100] |
| Salvinorin A | Urine | MEPS; GC-MS/MS | >0.99 | <11.0 | <9.0 | <8.0 | <8.0 | 0.005 | 0.02 | 71–80 | [96] |
| Salvinorin A | Human plasma | SPE; HPLC-APCI-MS | 0.999 | <11.2 | 96.4–104.0 | <10.3 | 98.7–101.1 | 0.002 | 0.002 | - | [89] |
| Salvinorin A | Pericardial fluid; vitreous humour; whole blood; plasma | SPE; GC-MS-EI | >0.99 | <12.0 | 9.0 | - | - | 0.005 | 0.005 | 79.65–99.09 | [97] |
| Salvinorin A | S. divinorum products sold throughout Mexico | HPLC | >0.999 | <5.0 | - | <2.0 | - | 0.44 | 1.34 | - | [73] |
| Salvinorin A Salvinorin B Salvinorin C | S. divinorum products obtained online and in Portuguese smartshops | GC-MS | >0.99 | 3.6–8.6 | - | 6.6–14.9 | - | 1.25 μg/mg | 2.5 μg/mg | - | [104] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brito-da-Costa, A.M.; Dias-da-Silva, D.; Gomes, N.G.M.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Madureira-Carvalho, Á. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Salvinorin A and Salvia divinorum: Clinical and Forensic Aspects. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020116
Brito-da-Costa AM, Dias-da-Silva D, Gomes NGM, Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Madureira-Carvalho Á. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Salvinorin A and Salvia divinorum: Clinical and Forensic Aspects. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(2):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020116
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrito-da-Costa, Andreia Machado, Diana Dias-da-Silva, Nelson G. M. Gomes, Ricardo Jorge Dinis-Oliveira, and Áurea Madureira-Carvalho. 2021. "Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Salvinorin A and Salvia divinorum: Clinical and Forensic Aspects" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 2: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020116
APA StyleBrito-da-Costa, A. M., Dias-da-Silva, D., Gomes, N. G. M., Dinis-Oliveira, R. J., & Madureira-Carvalho, Á. (2021). Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Salvinorin A and Salvia divinorum: Clinical and Forensic Aspects. Pharmaceuticals, 14(2), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020116