Evaluation of Amebicidal and Cysticidal Activities of Antifungal Drug Isavuconazonium Sulfate against Acanthamoeba T4 Strains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
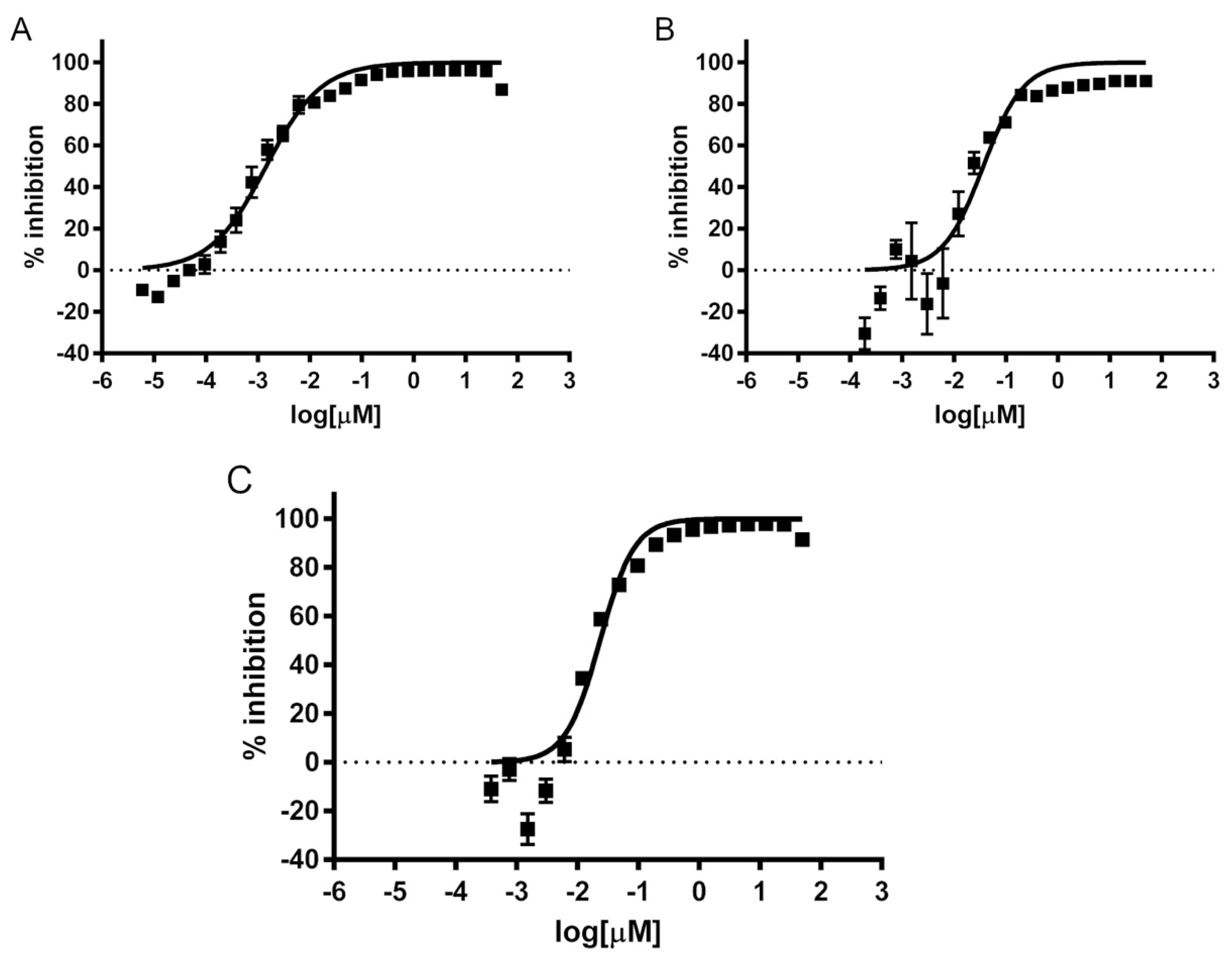
2.1. Determination of Amebicidal Activity
2.2. Determination of Cysticidal Activity
2.3. Effect of Combination of Isavuconazonium and PHMB on Cysts
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Determination of Amebicidal Activity
4.3. Cyst Generation
4.4. Determination of Cysticidal Activity
4.5. Effect of Combination of Isavuconazonium and PHMB on Cysts
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siddiqui, R.; Aqeel, Y.; Khan, N.A. The Development of Drugs against Acanthamoeba Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6441–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, D.; Panda, G.S.; Bakhshi, S. Successful treatment of acanthamoeba meningoencephalitis during induction therapy of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2008, 50, 1292–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, T.; Bajpai, A.; Kalra, V.; Kabra, S.K.; Samantaray, J.C.; Satpathy, G.; Gupta, A.K. Successful treatment of Acanthamoeba meningitis with combination oral antimicrobials. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2001, 20, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvesvara, G.S. Amebic meningoencephalitides and keratitis: Challenges in diagnosis and treatment. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 23, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, F.L.; Visvesvara, G.S. Free-living amoebae as opportunistic and non-opportunistic pathogens of humans and animals. Int. J. Parasitol 2004, 34, 1001–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledee, D.R.; Iovieno, A.; Miller, D.; Mandal, N.; Diaz, M.; Fell, J.; Fini, M.E.; Alfonso, E.C. Molecular identification of t4 and t5 genotypes in isolates from acanthamoeba keratitis patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 1458–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shing, B.; Singh, S.; Podust, L.M.; McKerrow, J.H.; Debnath, A. The Antifungal Drug Isavuconazole Is both Amebicidal and Cysticidal against Acanthamoeba castellanii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e02223-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrell, D.; Bossaer, J.B.; Carico, R.; Harirforoosh, S.; Cluck, D. Isavuconazonium sulfate: A triazole prodrug for invasive fungal infections. Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2017, 25, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaselgrave, W.; Hamad, A.; Coles, S.; Hau, S. In Vitro Evaluation of the Inhibitory Effect of Topical Ophthalmic Agents on Acanthamoeba Viability. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iovieno, A.; Miller, D.; Ledee, D.R.; Alfonso, E.C. Cysticidal activity of antifungals against different genotypes of Acanthamoeba. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5626–5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lamy, R.; Chan, E.; Good, S.D.; Cevallos, V.; Porco, T.C.; Stewart, J.M. Riboflavin and ultraviolet A as adjuvant treatment against Acanthamoeba cysts. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 44, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.E.; Oum, B.S.; Choi, H.Y.; Yu, H.S.; Lee, J.S. Cysticidal effect on acanthamoeba and toxicity on human keratocytes by polyhexamethylene biguanide and chlorhexidine. Cornea 2007, 26, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbott, M.; Cevallos, V.; Chen, M.C.; Chin, S.A.; Lalitha, P.; Seitzman, G.D.; Lietman, T.M.; Keenan, J.D. Synergy Testing of Antiamoebic Agents for Acanthamoeba: Antagonistic Effect of Voriconazole. Cornea 2019, 38, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, C.A.; Troth, E.V.; Russell, A.C.; Kyle, D.E. Discovery of Anti-Amoebic Inhibitors from Screening the MMV Pandemic Response Box on Balamuthia mandrillaris, Naegleria fowleri, and Acanthamoeba castellanii. Pathogens 2020, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldenburg, C.E.; Acharya, N.R.; Tu, E.Y.; Zegans, M.E.; Mannis, M.J.; Gaynor, B.D.; Whitcher, J.P.; Lietman, T.M.; Keenan, J.D. Practice patterns and opinions in the treatment of acanthamoeba keratitis. Cornea 2011, 30, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shing, B.; Balen, M.; McKerrow, J.H.; Debnath, A. Acanthamoeba Keratitis: An update on amebicidal and cysticidal drug screening methodologies and potential treatment with azole drugs. Expert. Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, 1427–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt-Hoffmann, A.H.; Kato, K.; Townsend, R.; Potchoiba, M.J.; Hope, W.W.; Andes, D.; Spickermann, J.; Schneidkraut, M.J. Tissue Distribution and Elimination of Isavuconazole following Single and Repeat Oral-Dose Administration of Isavuconazonium Sulfate to Rats. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01292-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Natesan, S.K.; Chandrasekar, P.H. Isavuconazole for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis and mucormycosis: Current evidence, safety, efficacy, and clinical recommendations. Infect. Drug Resist. 2016, 9, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sohn, H.J.; Kang, H.; Seo, G.E.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, S.Y.; Shin, H.J. Efficient Liquid Media for Encystation of Pathogenic Free-Living Amoebae. Korean J. Parasitol. 2017, 55, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Inhibitor | Strain | Mean (µM) | 95% Lower CL (µM) a | 95% Upper CL (µM) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isavuconazonium sulfate | Ma | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| CDC:V240 | 0.037 | 0.027 | 0.049 | |
| MEEI 0184 | 0.024 | 0.021 | 0.027 | |
| Standards of care | ||||
| Chlorhexidine [7] | Ma | 1.7 | 1.4 | 1.9 |
| CDC:V240 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 1.2 | |
| MEEI 0184 | 1 | 0.9 | 1.1 | |
| PHMB [7] | Ma | 7.2 | 6.6 | 8.0 |
| CDC:V240 | 11.8 | 10.5 | 13.4 | |
| MEEI 0184 | 4.6 | 3.0 | 7.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shing, B.; Balen, M.; Debnath, A. Evaluation of Amebicidal and Cysticidal Activities of Antifungal Drug Isavuconazonium Sulfate against Acanthamoeba T4 Strains. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121294
Shing B, Balen M, Debnath A. Evaluation of Amebicidal and Cysticidal Activities of Antifungal Drug Isavuconazonium Sulfate against Acanthamoeba T4 Strains. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(12):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121294
Chicago/Turabian StyleShing, Brian, Mina Balen, and Anjan Debnath. 2021. "Evaluation of Amebicidal and Cysticidal Activities of Antifungal Drug Isavuconazonium Sulfate against Acanthamoeba T4 Strains" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 12: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121294
APA StyleShing, B., Balen, M., & Debnath, A. (2021). Evaluation of Amebicidal and Cysticidal Activities of Antifungal Drug Isavuconazonium Sulfate against Acanthamoeba T4 Strains. Pharmaceuticals, 14(12), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121294







