Role of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)-Derived Exosomes in Tumor Progression and Survival
Abstract
1. Introduction
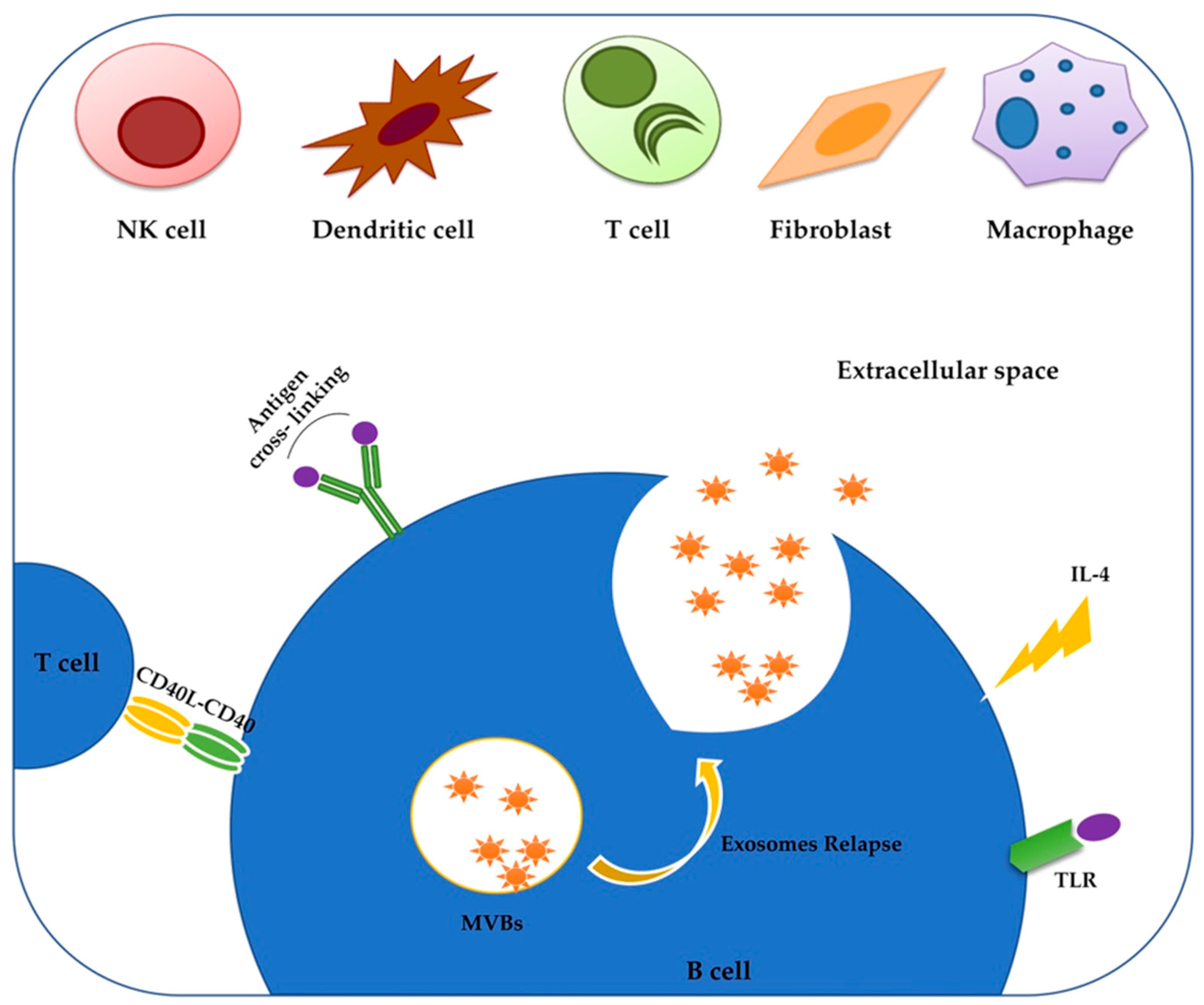
2. Exosomes: The Low-Cost Carriers
3. miRNAs of CLL-Derived Exosomes Modify the Tumor Microenvironment
4. Proteins Delivered by CLL Exosomes Modulate Intracellular Pathways in Favor of CLL Progression
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mertens, D.; Stilgenbauer, S. Prognostic and predictive factors in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Relevant in the era of novel treatment approaches? J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacopelli, B.; Ruppert, A.S.; Wu, Y.Z.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Wierda, W.G.; Rai, K.R.; Kay, N.E.; Brown, J.E.; Kipps, T.J.; Byrd, J.C.; et al. Comparative evaluation of prognostic factors that assess the natural history of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2016, 128, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Muñoz, R.; Roldan Galiacho, V.; Llorente, L. Immunological aspects in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) development. Ann. Hematol. 2012, 91, 981–996. [Google Scholar]
- Witkowska, M.; Nowak, W.; Cebula-Obrzut, B.; Majchrzak, A.; Medra, A.; Robak, T.; Smolewski, P. Spontaneous in vitro apoptosis of de novo chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells correlates with risk of the disease progression. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2014, 86, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamberale, R.; Geffner, J.; Arrosagaray, G.; Scolnik, M.; Salamone, G.; Trevani, A.; Vermeulen, M.; Giordano, M. Non-malignant leukocytes delay spontaneous B-CLL cell apoptosis. Leukemia 2001, 15, 1860–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Herishanu, Y.; Katz, B.Z.; Lipsky, A.; Wiestner, A. Biology of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in different microenvironments: Clinical and therapeutic implications. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 27, 173–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Gribben, J.G. The microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and other B cell malignancies: Insight into disease biology and new targeted therapies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 24, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Coussens, L.M. Accessories to the crime: Functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2012, 21, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartz, M.A.; Iida, N.; Roberts, E.W.; Sangaletti, S.; Wong, M.H.; Yull, F.E.; Coussens, L.M.; DeClerck, Y.A. Tumor microenvironment complexity: Emerging roles in cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2473–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleiss, C.; Ilias, W.; Tahar, O.; Güler, Y.; Miguet, L.; Mayer-Rousse, C.; Mauvieux, L.; Forneker, L.M.; Touissant, E.; Herbrecht, R.; et al. BCR-associated factors driving chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells proliferation ex vivo. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissard, F.; Tosolini, M.; Ligat, L.; Quillet-Mary, A.; Lopez, F.; Fournié, J.J.; Ysebaert, L.; Poupot, M. Nurse-like cells promote CLL survival through LFA-3/CD2 interactions. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 52225–52236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boissard, F.; Fournié, J.J.; Laurent, C.; Poupot, M.; Ysebaert, L. Nurse like cells: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia associated macrophages. Leuk Lymphoma 2015, 56, 1570–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polk, A.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Seymour, E.; Bailey, N.G.; Singer, J.W.; Boonstra, P.S.; Lim, M.S.; Malek, S.; Wilcox, R.A. Colony-Stimulating Factor-1 Receptor Is Required for Nurse-like Cell Survival in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 6118–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, A.A.; Ciseł, B.; Wąsik-Szczepanek, E. Guilty bystanders: Nurse-like cells as a model of microenvironmental support for leukemic lymphocytes. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 15, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Théry, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Ann. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loria, A.D.; Dattilo, V.; Santoro, D.; Santoro, D.; Guccione, J.; De Luca, A.; Ciaramella, P.; Pirozzi, M.; Iaccino, E. Expression of Serum Exosomal miRNA 122 and Lipoprotein Levels in Dogs Naturally Infected by Leishmania infantum: A Preliminary Study. Animals 2020, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldolesi, J. Exosomes and Ectosomes in Intercellular Communication. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R435–R444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortzel, I.; Dror, S.; Kenific, C.M.; Lyden, D. Exosome-Mediated Metastasis: Communication from a Distance. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuno, Y.; Kanke, T.; Maruyama, N.; Fujii, W.; Naito, K.; Sugiura, K. Characterization of mRNA profiles of the exosome-like vesicles in porcine follicular fluid. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, M. Exosomes: Revisiting their role as “garbage bags”. Traffic 2019, 20, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, Y.L.; Chen, K.C.; Hsieh, J.T.; Shen, T.L. Exosomes in cancer development and clinical applications. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2364–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatun, Z.; Bhat, A.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, A. Elucidating diversity of exosomes: Biophysical and molecular characterization methods. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 2359–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, M.; Goodarzi, M.; Jaafari, M.R.; Mirzaei, H.R.; Mirzaei, H. Circulating microRNA: A new candidate for diagnostic biomarker in neuroblastoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, H.; Khataminfar, S.; Mohammadparast, S.; Shahid Sales, S.; Maftouh, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Avan, A. Circulating microRNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets in gastric cancer: Current status and future perspectives. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 4135–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatpour, L.; Fadaee, E.; Fadaei, S.; Mansour, R.N.; Mohammadi, M.; Mousavi, S.; Mirzaei, H. Glioblastoma: Exosome and microRNA as novel diagnosis biomarkers. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonian, M.; Mosallayi, M.; Mirzaei, H. Circulating miR-21 as novel biomarker in gastric cancer: Diagnostic and prognostic biomarker. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 14, 475. [Google Scholar]
- Trams, E.G.; Lauter, C.J.; Salem, N., Jr.; Heine, U. Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1981, 645, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.T.; Johnstone, R.M. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: Selective externalization of the receptor. Cell 1983, 33, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, G.; Kay, N.E.; Ghosh, A.K. Microvesicles in CLL: Predictor of disease progression/relapse. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 90632–90633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, J.; Tkach, M.; Thery, C. Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 29, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babst, M. MVB vesicle formation: ESCRT-dependent, ESCRT-independent and everything in between. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wemmer, M.; Azmi, I.; West, M.; Davies, B.; Katzmann, D.; Odorizzi, G. Bro1 binding to Snf7 regulates ESCRT-III membrane scission activity in yeast. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 192, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, E.; Sandrin, V.; Chung, H.Y.; Morham, S.G.; Gygi, S.P.; Rodesch, C.K.; Sundquist, W.I. Human ESCRT and ALIX proteins interact with proteins of the midbody and function in cytokinesis. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cheng, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Dong, M.; Zhan, F.H.; Liu, J. The ceramide pathway is involved in the survival, apoptosis and exosome functions of human multiple myeloma cells in vitro. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2018, 39, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajkovic, K.; Hsu, C.; Chiantia, S.; Rajendran, L.; Wenzel, D.; Wieland, F.; Schwille, P.; Brügger, B.; Simons, M. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 2008, 319, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Meng, J.; Zhu, L.; Peng, Y. Exosomal noncoding RNAs in Glioma: Biological functions and potential clinical applications. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccaro, A.M.; Sacco, A.; Maiso, P.; Azab, A.K.; Tai, Y.T.; Reagan, M.; Azab, F.; Flores, L.M.; Campigotto, F.; Weller, E.; et al. BM mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes facilitate multiple myeloma progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1542–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutzeit, C.; Nagy, N.; Gentile, M.; Lyberg, K.; Gumz, J.; Vallhov, H.; Puga, I.; Klein, E.; Gabrielsson, S.; Cerutti, A.; et al. Exosomes derived from Burkitt’s lymphoma cell lines induce proliferation, differentiation, and class-switch recombination in B cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 5852–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitan, E.; Suire, C.; Zhang, S.; Mattson, M.P. Impact of lysosome status on extracellular vesicle content and release. Ageing Res Rev. 2016, 32, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhao, H.P.; Dai, K.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, L. Circulating exosomal miRNAs as potential biomarkers for Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 2889–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, P.; Almeida, F. Role of Exosomal miRNAs and the Tumor Microenvironment in Drug Resistance. Cells 2020, 9, E1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghikhani, A.; Farzaneh, F.; Sharifzad, F.; Mardpour, S.; Ebrahimi, M.; Hassan, Z.M. Engineered Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Potentials in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, Y.; Yashiro, M.; Okuno, T.; Kuroda, K.; Togano, S.; Hirakawa, K.; Ohira, M. Clinico-pathological significance of exosome marker CD63 expression on cancer cells and stromal cells in gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf Malik, M.; Ishtiyaq Ali Mirza, J.; Umar, M.; Manzoor, S. CD81+ Exosomes Play a Pivotal Role in the Establishment of Hepatitis C Persistent Infection and Contribute Toward the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Viral. Immunol. 2019, 32, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friand, V.; David, G.; Zimmermann, P. Syntenin and syndecan in the biogenesis of exosomes. Biol. Cell. 2015, 107, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, S.I.; van Balkom, B.W.; Aalberts, M.; Heck, A.J.; Wauben, M.; Stoorvogel, W. MHC class II-associated proteins in B-cell exosomes and potential functional implications for exosome biogenesis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2010, 88, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaccino, E.; Mimmi, S.; Dattilo, V.; Marino, F.; Candeloro, P.; Di Loria, A.; Marimpietri, D.; Pisano, A.; Albano, F.; Vecchio, E.; et al. Monitoring multiple myeloma by idiotype-specific peptide binders of tumor-derived exosomes. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, I.; Iaccino, E.; Dattilo, V.; Barone, S.; Vecchio, E.; Mimmi, S.; Filippelli, E.; Demonte, G.; Polidoro, S.; Granata, A.; et al. Exosome-associated miRNA profile as a prognostic tool for therapy response monitoring in multiple sclerosis patients. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 4241–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głuszko, A.; Szczepański, M.J.; Ludwig, N.; Mirza, S.M.; Olejarz, W. Exosomes in Cancer: Circulating Immune-Related Biomarkers. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1628029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoraki, M.N.; Yerneni, S.S.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Gooding, W.E.; Whiteside, T.L. Clinical Significance of PD-L1+ Exosomes in Plasma of Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, M.; Rubbi, C.; Liu, L.; Slupsky, J.R.; Kalakonda, N. CLL Exosomes Modulate the Transcriptome and Behaviour of Recipient Stromal Cells and Are Selectively Enriched in miR-202-3p. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLellan, A.D. Exosome release by primary B cells. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 29, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunderson, S.C.; Schuberth, P.C.; Dunn, A.C.; Miller, L.; Hock, B.D.; MacKay, P.A.; Koch, N.; Jack, R.A.; McLellan, A.D. Induction of exosome release in primary B cells stimulated via CD40 and the IL-4 receptor. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 8146–8152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.Y.; Ozer, H.C.; Lehman, A.M.; Maddocks, K.; Yu, L.; Johnson, A.J.; Byrd, J.C. Characterization of CLL exosomes reveals a distinct microRNA signature and enhanced secretion by activation of BCR signaling. Blood 2015, 125, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skokos, D.; Le Panse, S.; Villa, I.; Rousselle, J.C.; Peronet, R.; David, B.; Namane, A.; Mécheri, S. Mast cell-dependent B and T lymphocyte activation is mediated by the secretion of immunologically active exosomes. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paggetti, J.; Haderk, F.; Seiffert, M.; Janji, B.; Distler, U.; Ammerlaan, W.; Kim, Y.J.; Adam, J.; Lichter, P.; Solary, E.; et al. Exosomes released by chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells induce the transition of stromal cells into cancer-associated fibroblasts. Blood 2015, 126, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, A.; Toedt, G.; Zenz, T.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Lichter, P.; Seiffert, M. Inflammatory cytokines and signaling pathways are associated with survival of primary chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in vitro: A dominant role of CCL2. Haematologica 2011, 96, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, B.S.; McClanahan, F.; Yazdanparast, H.; Zaborsky, N.; Kalter, V.; Rößner, P.M.; Benner, A.; Dürr, C.; Egle, A.; Gribben, J.G.; et al. Depletion of CLL associated patrolling monocytes and macrophages controls disease development and repairs immune dysfunction in vivo. Leukemia 2016, 30, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crompot, E.; Van Damme, M.; Pieters, K.; Vermeersch, M.; Perez-Morga, D.; Mineur, O.; Maerevoet, M.; Meuleman, N.; Bron, D.; Lagneaux, L.; et al. Extracellular vesicles of bone marrow stromal cells rescue chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from apoptosis, enhance their migration and induce gene expression modifications. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1594–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, E.G. MicroRNAs: Hidden in the genome. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, R138–R140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, E.G.; Poethig, R.S. MicroRNAs: Something new under the sun. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, R688–R690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Jiang, J.; Liu, Q.; Yang, L. A high-throughput method to monitor the expression of microRNA precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, M.T.; Petersen, C.P.; Haines, B.B.; Chen, J.; Sharp, P.A. Gene silencing using micro-RNA designed hairpins. RNA 2002, 8, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.C.; Yu, D.; Lee, Y.S.; Wentzel, E.A.; Arking, D.E.; West, K.M.; Dang, C.V.; Thomas-Tikhonenko, A.; Mendell, J.T. Widespread microRNA repression by Myc contributes to tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet 2008, 40, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R.I. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, A.A.; Grenda, A.; Popek, S.; Koczkodaj, D.; Michalak-Wojnowska, M.; Budzyński, M.; Wąsik-Szczepanek, E.; Zmorzyński, S.; Karczmarczyk, A.; Giannopoulos, K. Expression of circulating miRNAs associated with lymphocyte differentiation and activation in CLL-another piece in the puzzle. Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathullahzadeh, S.; Mirzaei, H.; Honardoost, M.A.; Sahebkar, A.; Salehi, M. Circulating microRNA-192 as a diagnostic biomarker in human chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Gene 2016, 23, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, G.V.; Peterson, K.J.; Emanuel, K.; Mittal, A.K.; Joshi, A.D.; Dickinson, J.D.; Kollessery, G.J.; Bociek, R.G.; Bierman, P.; Vose, J.M.; et al. Hedgehog-induced survival of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in a stromal cell microenvironment: A potential new therapeutic target. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Daly, S.M.; Bayraktar, R.; Anfossi, S.; Calin, G.A. The Interplay between MicroRNAs and the Components of the Tumor Microenvironment in B-Cell Malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez-Ferrer, S.; Bonnet, D.; Steensma, D.P.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Ghobrial, I.M.; Gribben, J.G.; Andreeff, M.; Krause, D.S. Bone marrow niches in haematological malignancies. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2020, 20, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Jiang, X.; Chen, J. The role of miR-150 in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3887–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mraz, M.; Chen, L.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Ghia, E.M.; Li, H.; Jepsen, K.; Smith, E.N.; Messer, K.; Frazer, K.A.; Kipps, T.J. miR-150 influences B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia by regulating expression of GAB1 and FOXP1. Blood 2014, 124, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatopoulos, B.; Van Damme, M.; Crompot, E.; Dessars, B.; Housni, H.E.; Mineur, P.; Meuleman, N.; Bron, D.; Lagneaux, L. Opposite Prognostic Significance of Cellular and Serum Circulating MicroRNA-150 in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.N. Generalized Reticular Cell Sarcoma of Lymph Nodes Associated with Lymphatic Leukemia. Am. J. Pathol. 1928, 4, 285–292.7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tschautscher, M.A.; Rabe, K.G.; Call, T.G.; Leis, J.F.; Kenderian, S.S.; Kay, N.E.; Muchtar, E.; Van Dyke, D.L.; Koehler, A.B.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of Richter transformation: Experience of 204 patients from a single center. Haematologica 2020, 105, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W. Richter transformation in the era of novel agents. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2018, 2018, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzimichael, E.; Papathanasiou, K.; Zerdes, I.; Flindris, S.; Papoudou-Bai, A.; Kapsali, E. Plasmablastic Lymphoma with Coexistence of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in an Immunocompetent Patient: A Case Report and Mini-Review. Case Rep. Hematol. 2017, 2017, 2861596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurj, A.; Pop, L.; Petrushev, B.; Pasca, S.; Dima, D.; Frinc, I.; Deak, D.; Desmirean, M.; Trifa, A.; Fetica, B.; et al. Exosome-carried microRNA-based signature as a cellular trigger for the evolution of chronic lymphocytic leukemia into Richter syndrome. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2018, 55, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elton, T.S.; Selemon, H.; Elton, S.M.; Parinandi, N.L. Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes. Gene 2013, 532, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruns, H.; Böttcher, M.; Qorraj, M.; Fabri, M.; Jitschin, S.; Dindorf, J.; Busch, L.; Jitschin, R.; Mackensen, A.; Mougiakakos, D. CLL-cell-mediated MDSC induction by exosomal miR-155 transfer is disrupted by vitamin D. Leukemia 2017, 31, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollinerova, S.; Vassanelli, S.; Modriansky, M. The role of miR-29 family members in malignant hematopoiesis. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc. Czech Repub. 2014, 158, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatopoulos, B.; Meuleman, N.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Saussoy, P.; Van Den Neste, E.; Michaux, L.; Heimann, P.; Martiat, P.; Bron, D.; Lagneaux, L. microRNA-29c and microRNA-223 down-regulation has in vivo significance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and improves disease risk stratification. Blood 2009, 113, 5237–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christov, C.P.; Trivier, E.; Krude, T. Noncoding human Y RNAs are overexpressed in tumours and required for cell proliferation. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosar, J.P.; Gámbaro, F.; Sanguinetti, J.; Bonilla, B.; Witwer, K.W.; Cayota, A. Assessment of small RNA sorting into different extracellular fractions revealed by high-throughput sequencing of breast cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 5601–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haderk, F.; Schulz, R.; Iskar, M.; Cid, L.L.; Worst, T.; Willmund, K.V.; Seiffert, M. Tumor-derived exosomes modulate PD-L1 expression in monocytes. Sci. Immunol. 2017, 2, eaah5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zeng, X.; Ding, T.; Guo, L.; Li, Y.; Ou, S.; Yuan, H. Microarray profile of circular RNAs identifies hsa_circ_0014130 as a new circular RNA biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, K.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Gupta, S.K.; Chang, N.; Yen, L.; Sun, H.S.; Tsai, S.J. Noncoding effects of circular RNA CCDC66 promote colon cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2339–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Sun, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Liu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, W.; Jin, H.; Li, J. Mitochondrial Genome-Derived circRNA mc-COX2 Functions as an Oncogene in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Mol. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Corzo, C.A.; Luetteke, N.; Yu, B.; Nagaraj, S.; Bui, M.M.; Ortiz, M.; Nacken, W.; Sorg, C.; Vogl, T.; et al. Inhibition of dendritic cell differentiation and accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer is regulated by S100A9 protein. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2235–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, D.; Sotelo, N.; Seija, N.; Sernbo, S.; Abreu, C.; Durán, R.; Gil, M.; Sicco, E.; Irigoin, V.; Oliver, C.; et al. S100-A9 protein in exosomes from chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells promotes NF-κB activity during disease progression. Blood 2017, 130, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanier, L.L. Up on the tightrope: Natural killer cell activation and inhibition. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veuillen, C.; Aurran-Schleinitz, T.; Castellano, R.; Rey, J.; Mallet, F.; Orlanducci, F.; Pouyet, L.; Just-Landi, S.; Coso, D.; Ivanov, V.; et al. Primary B-CLL resistance to NK cell cytotoxicity can be overcome in vitro and in vivo by priming NK cells and monoclonal antibody therapy. J. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 32, 632–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiners, K.S.; Topolar, D.; Henke, A.; Simhadri, V.R.; Kessler, J.; Sauer, M.; Bessler, M.; Hansen, H.P.; Tawadros, S.; Herling, M.; et al. Soluble ligands for NK cell receptors promote evasion of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells from NK cell anti-tumor activity. Blood 2013, 121, 3658–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten Hacken, E.; Gounari, M.; Ghia, P.; Burger, J.A. The importance of B cell receptor isotypes and stereotypes in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimmi, S.; Vecchio, E.; Iaccino, E.; Rossi, M.; Lupia, A.; Albano, F.; Chiurazzi, F.; Fiume, G.; Pisano, A.; Ceglia, S.; et al. Evidence of shared epitopic reactivity among independent B-cell clones in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. Leukemia 2016, 30, 2419–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimmi, S.; Maisano, D.; Nisticò, N.; Vecchio, E.; Chiurazzi, F.; Ferrara, K.; Iannalfo, M.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Fiume, G.; Iaccino, E.; et al. Detection of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia subpopulations in peripheral blood by phage ligand of tumor immunoglobulin B-Cell receptors. Leukemia 2020. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarfò, L.; Ferreri, A.J.; Ghia, P. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 104, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2020 update on diagnosis, risk stratification and treatment. Am J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1266–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertault-Daneshpouy, M.; Noguera, M.E.; Gisselbrecht, C.; Haddad, A.; Brice, P.; Marolleau, J.P.; Soulier, J.; Mounier, N. ZAP-70 protein expression and CD38 positivity in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2008, 6, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Quinto, I.; Chen, X.; Palmieri, C.; Rabin, R.L.; Scwartz, O.M.; Nelson, D.L.; Scala, G. Direct inhibition of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase by IBtk, a Btk-binding protein. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiume, G.; Scialdone, A.; Rizzo, F.; De Filippo, M.R.; Laudanna, C.; Albano, F.; Golino, G.; Vecchio, E.; Pontoriero, M.; Mimmi, S.; et al. IBTK Differently Modulates Gene Expression and RNA Splicing in HeLa and K562 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albano, F.; Chiurazzi, F.; Mimmi, S.; Vecchio, E.; Pastore, A.; Cimmino, C.; Frieri, C.; Iaccino, E.; Pisano, A.; Golino, G.; et al. The expression of inhibitor of bruton’s tyrosine kinase gene is progressively up regulated in the clinical course of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia conferring resistance to apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchio, E.; Golino, G.; Pisano, A.; Albano, F.; Falcone, C.; Ceglia, S.; Iaccino, E.; Mimmi, S.; Fiume, G.; Giurato, G.; et al. IBTK contributes to B-cell lymphomagenesis in Eμ-myc transgenic mice conferring resistance to apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisano, A.; Ceglia, S.; Palmieri, C.; Vecchio, E.; Fiume, G.; de Laurentiis, A.; Mimmi, S.; Falcone, C.; Iaccino, E.; Scialdone, A.; et al. CRL3IBTK Regulates the Tumor Suppressor Pdcd4 through Ubiquitylation Coupled to Proteasomal Degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 13958–13971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, S.; Agathangelidis, A.; Schneider, C.; Bahlo, J.; Robrecht, S.; Tausch, E.; Bloehdorn, J.; Hoechstetter, M.; Fischer, K.; Eichhorst, B.; et al. Prognostic impact of prevalent chronic lymphocytic leukemia stereotyped subsets: Analysis within prospective clinical trials of the German CLL Study Group (GCLLSG). Haematologica 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.K.; Forconi, F.; Packham, G. The meaning and relevance of B-cell receptor structure and function in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Semin. Hematol. 2014, 51, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangini, M.; Iaccino, E.; Mosca, M.G.; Mimmi, S.; D’Angelo, R.; Quinto, I.; Scala, G.; Mariggiò, S. Peptide-guided targeting of GPR55 for anti-cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 5179–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, M.; Fiume, G.; Caivano, A.; de Laurentiis, A.; Falcone, C.; Masci, F.F.; Iaccino, E.; Mimmi, S.; Palmieri, C.; Pisano, A.; et al. Design and characterization of a peptide mimotope of the HIV-1 gp120 bridging sheet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 5674–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupia, A.; Mimmi, S.; Iaccino, E.; Maisano, D.; Moraca, F.; Talarico, C.; Vecchio, E.; Fiume, G.; Ortuso, F.; Scala, G.; et al. Molecular modelling of epitopes recognized by neoplastic B lymphocytes in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 185, 111838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimmi, S.; Maisano, D.; Quinto, I.; Iaccino, E. Phage Display: An Overview in Context to Drug Discovery. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2019, 40, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manier, S.; Park, J.; Capelletti, M.; Bustoros, M.; Freeman, S.S.; Ha, G.; Rhoades, J.; Liu, C.J.; Huynh, D.; Reed, S.C.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing of cell-free DNA and circulating tumor cells in multiple myeloma. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajeev Krishnan, S.; De Rubis, G.; Suen, H.; Joshua, D.; Lam Kwan, Y.; Bebawy, M. A liquid biopsy to detect multidrug resistance and disease burden in multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rubis, G.; Rajeev Krishnan, S.; Bebawy, M. Liquid Biopsies in Cancer Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Prognosis. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2019, 40, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisano, D.; Mimmi, S.; Russo, R.; Fioravanti, A.; Fiume, G.; Vecchio, E.; Nisticò, N.; Quinto, I.; Iaccino, E. Uncovering the Exosomes Diversity: A Window of Opportunity for Tumor Progression Monitoring. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, E180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontoriero, M.; Fiume, G.; Vecchio, E.; de Laurentiis, A.; Albano, F.; Iaccino, E.; Mimmi, S.; Pisano, A.; Agosti, V.; Giovannone, E.; et al. Activation of NF-κB in B cell receptor signaling through Bruton’s tyrosine kinase-dependent phosphorylation of IκB-α. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, E.; Fiume, G.; Mignogna, C.; Iaccino, E.; Mimmi, S.; Maisano, D.; Trapasso, F.; Quinto, I. IBTK Haploinsufficiency Affects the Tumor Microenvironment of Myc-Driven Lymphoma in E-myc Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xia, B.; Wang, Y.; You, M.J.; Zhang, Y. Potential Therapeutic Roles of Exosomes in Multiple Myeloma: A Systematic Review. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 6154–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyiadzis, M.; Whiteside, T.L. The emerging roles of tumor-derived exosomes in hematological malignancies. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, S.; Corrado, C.; Raimondi, L.; De Leo, G.; Alessandro, R. Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Hematological Malignancies. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 821613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| miRNA | Expression Level in CLL-Derived Exosomes | Target | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-202-3p | ↑ | Sufu gene | Hegde G.V. et al., MCR 2008 [70] |
| miR-146a/miR-451 | ↑ | Kinases in Stromal cells | Paggetti J. et al., Blood 2015 [57] |
| miR-150 | ↑ | Hematopoiesis | Stamatopoulos B. et al., Mol Med 2015 [75] |
| miR-19b | ↑ | TP53 and MKI67 | Jurj A. et al., Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2018 [80] |
| miR-155 | ↑ | MDSCs induction | Bruns H. et al., Leukemia 2017 [82] |
| miR-29 | ↑ | TCL1 | Yeh YY. et al., Blood 2015 [55] |
| miR-223 | ↓ | HSP90B1 | Yeh YY. et al., Blood 2015 [55] |
| Y RNA | ↑ | Proliferation | Haderk F. et al., Sci Immunol. 2017 [87] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nisticò, N.; Maisano, D.; Iaccino, E.; Vecchio, E.; Fiume, G.; Rotundo, S.; Quinto, I.; Mimmi, S. Role of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)-Derived Exosomes in Tumor Progression and Survival. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13090244
Nisticò N, Maisano D, Iaccino E, Vecchio E, Fiume G, Rotundo S, Quinto I, Mimmi S. Role of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)-Derived Exosomes in Tumor Progression and Survival. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(9):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13090244
Chicago/Turabian StyleNisticò, Nancy, Domenico Maisano, Enrico Iaccino, Eleonora Vecchio, Giuseppe Fiume, Salvatore Rotundo, Ileana Quinto, and Selena Mimmi. 2020. "Role of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)-Derived Exosomes in Tumor Progression and Survival" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 9: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13090244
APA StyleNisticò, N., Maisano, D., Iaccino, E., Vecchio, E., Fiume, G., Rotundo, S., Quinto, I., & Mimmi, S. (2020). Role of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)-Derived Exosomes in Tumor Progression and Survival. Pharmaceuticals, 13(9), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13090244







