Comparative In Vitro Toxicology of Novel Cytoprotective Short-Chain Naphthoquinones
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
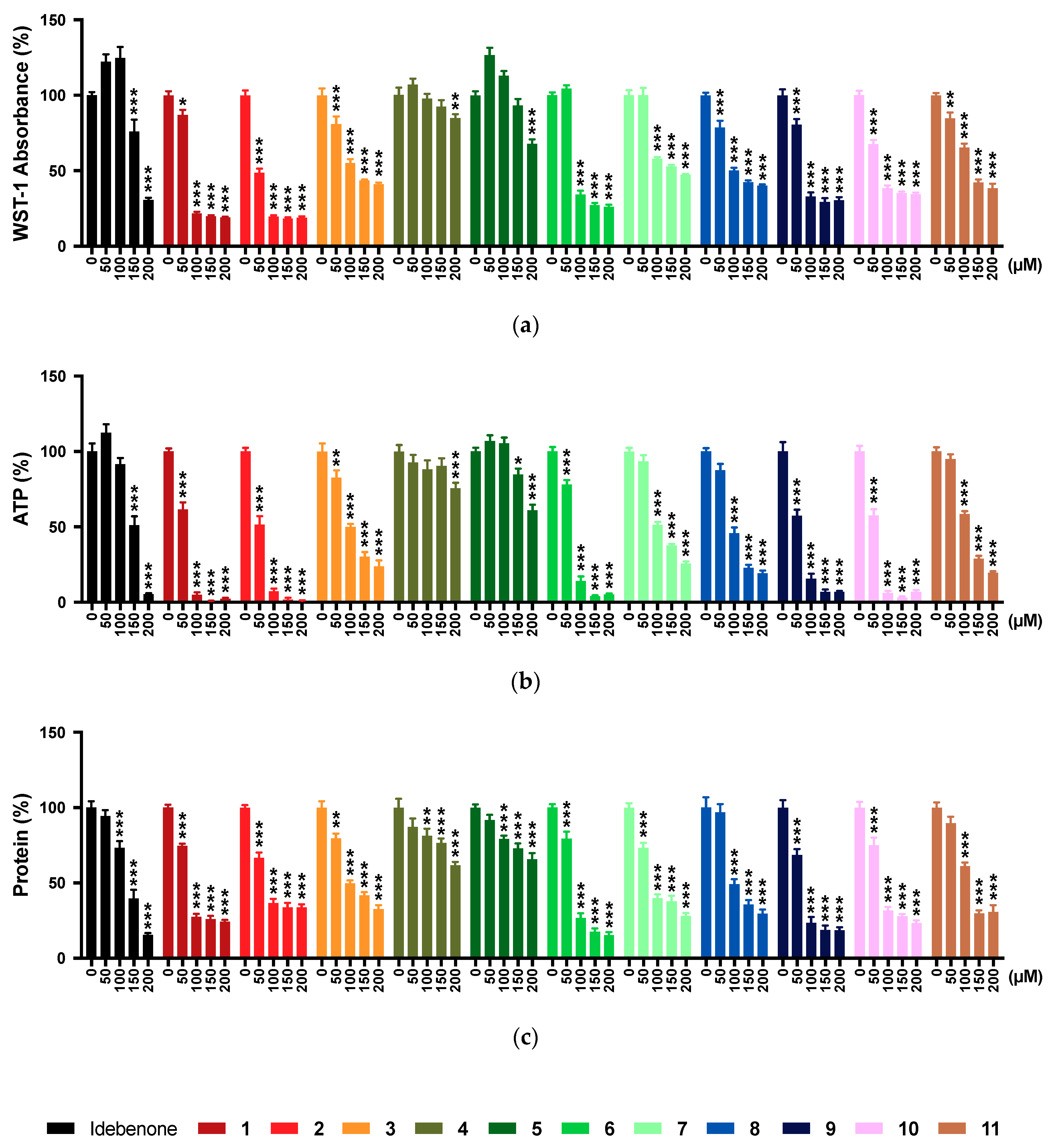
2.1. WST-1 Assay
2.2. ATP Levels
2.3. Protein Levels
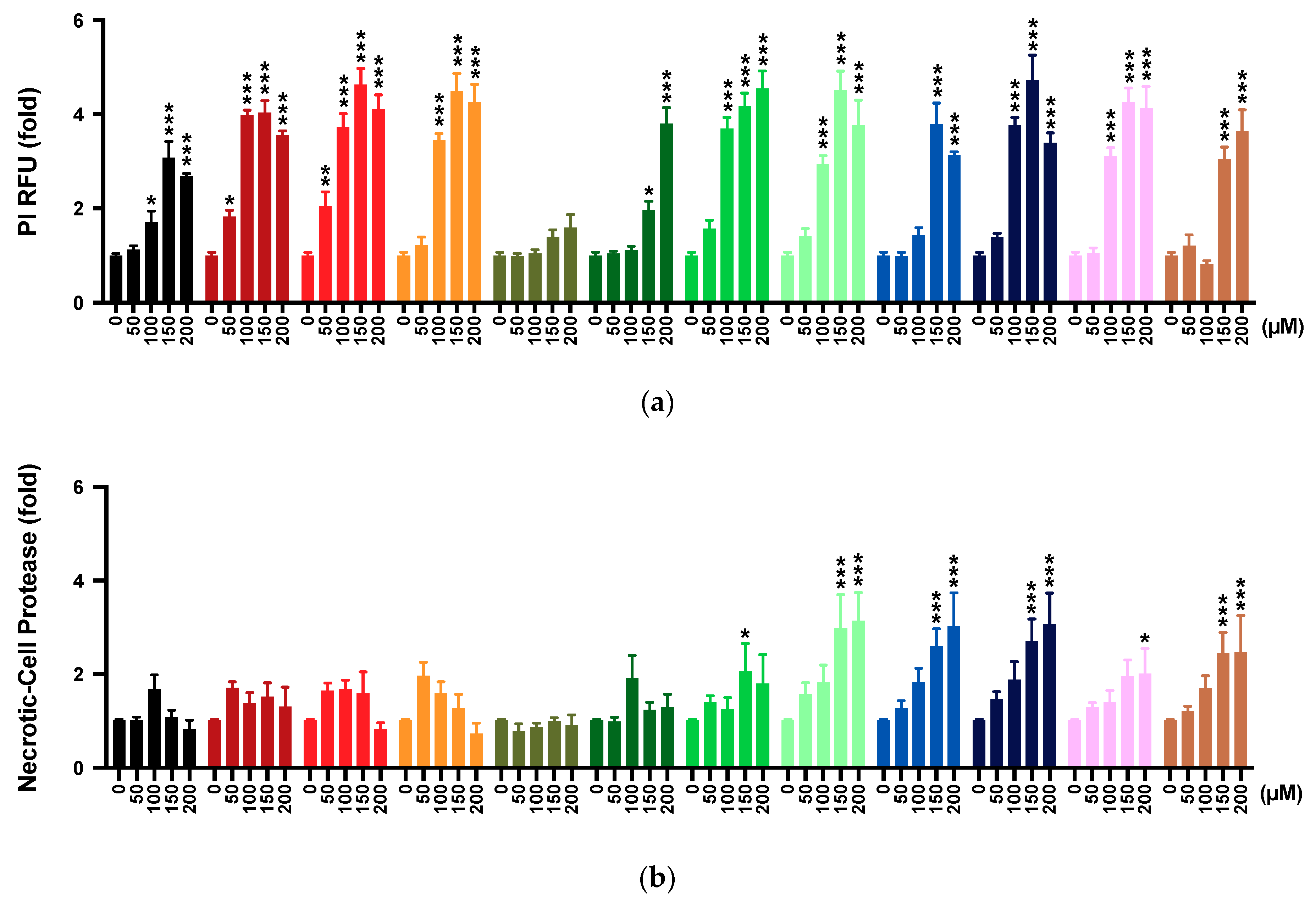
2.4. Membrane Integrity
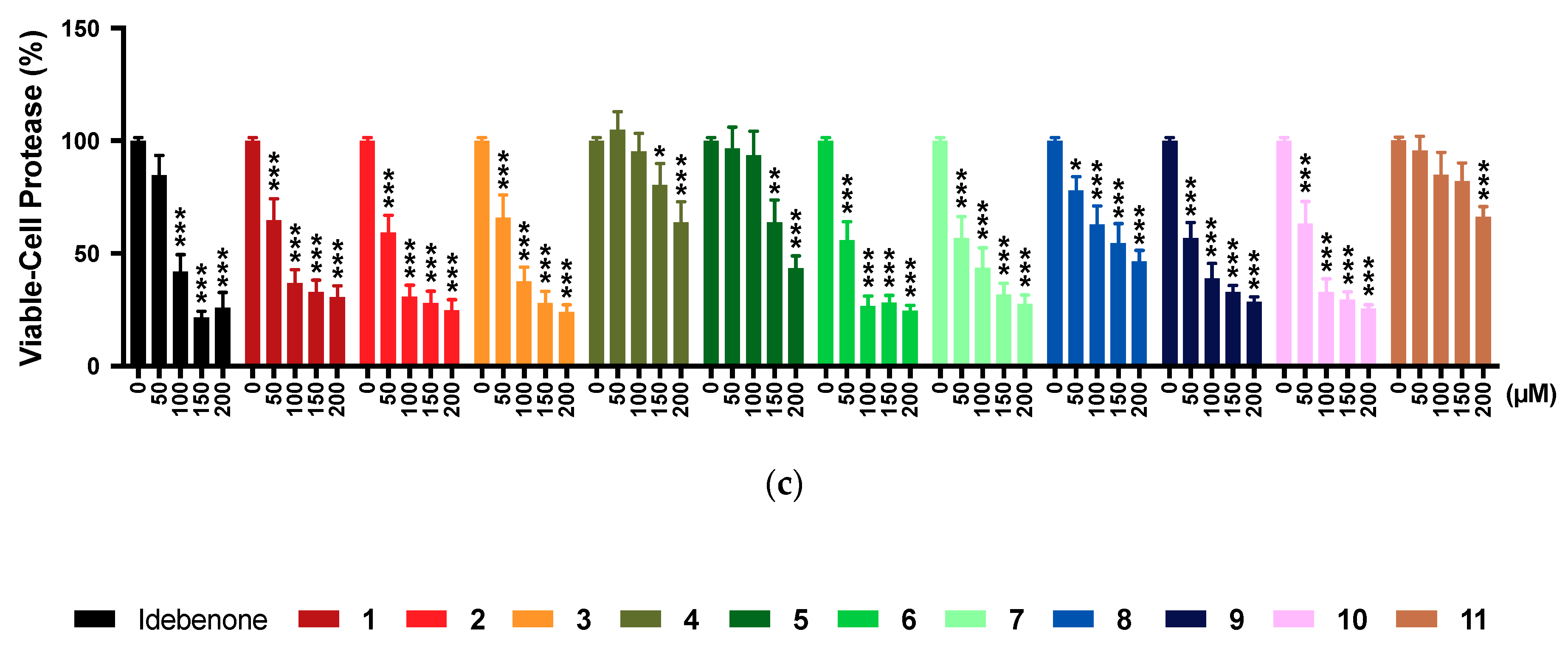
2.5. Multi-Tox Fluor Assay
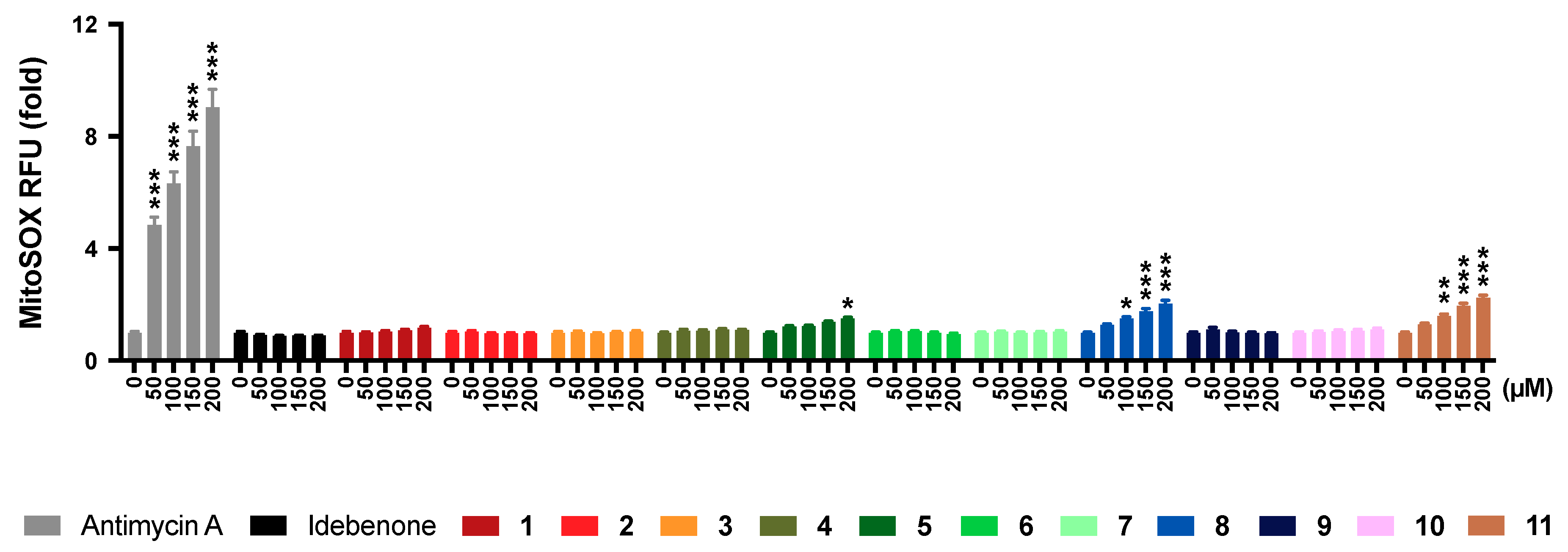
2.6. Mitochondrial Superoxide Production
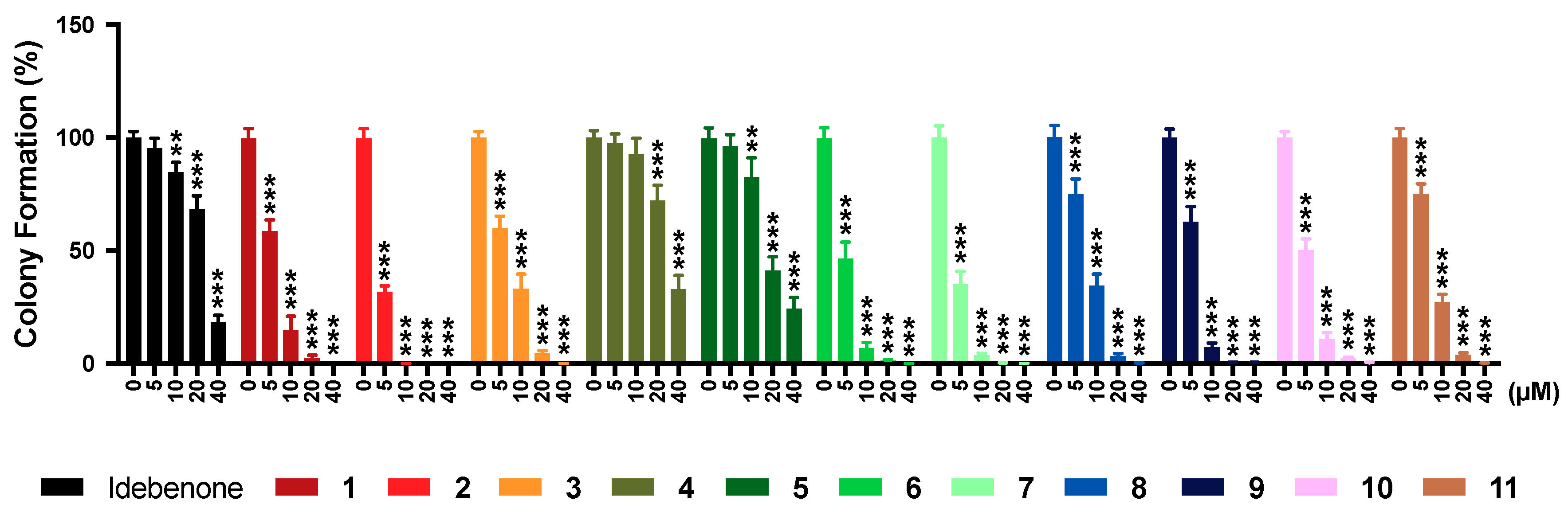
2.7. Colony Formation
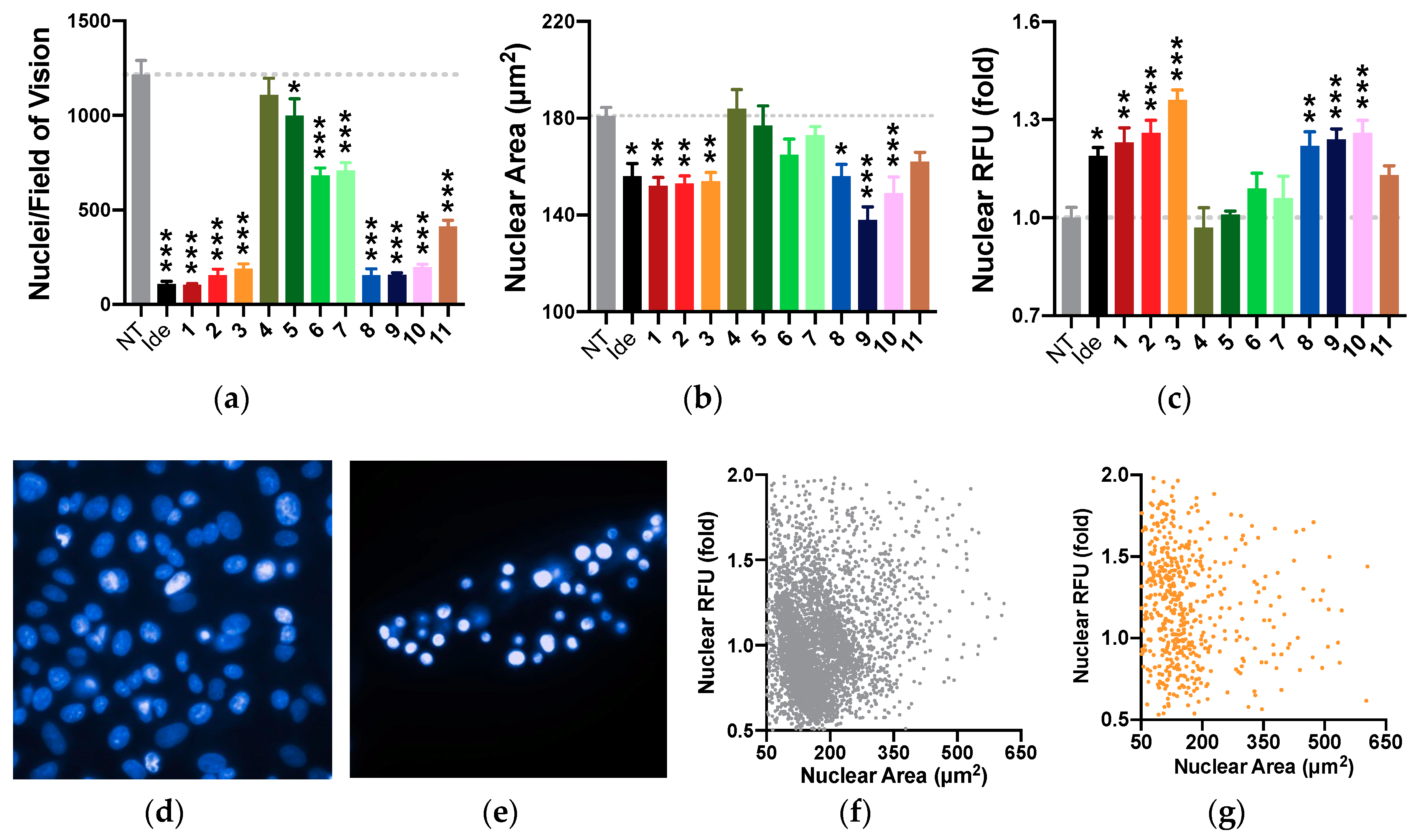
2.8. Nuclear Morphology
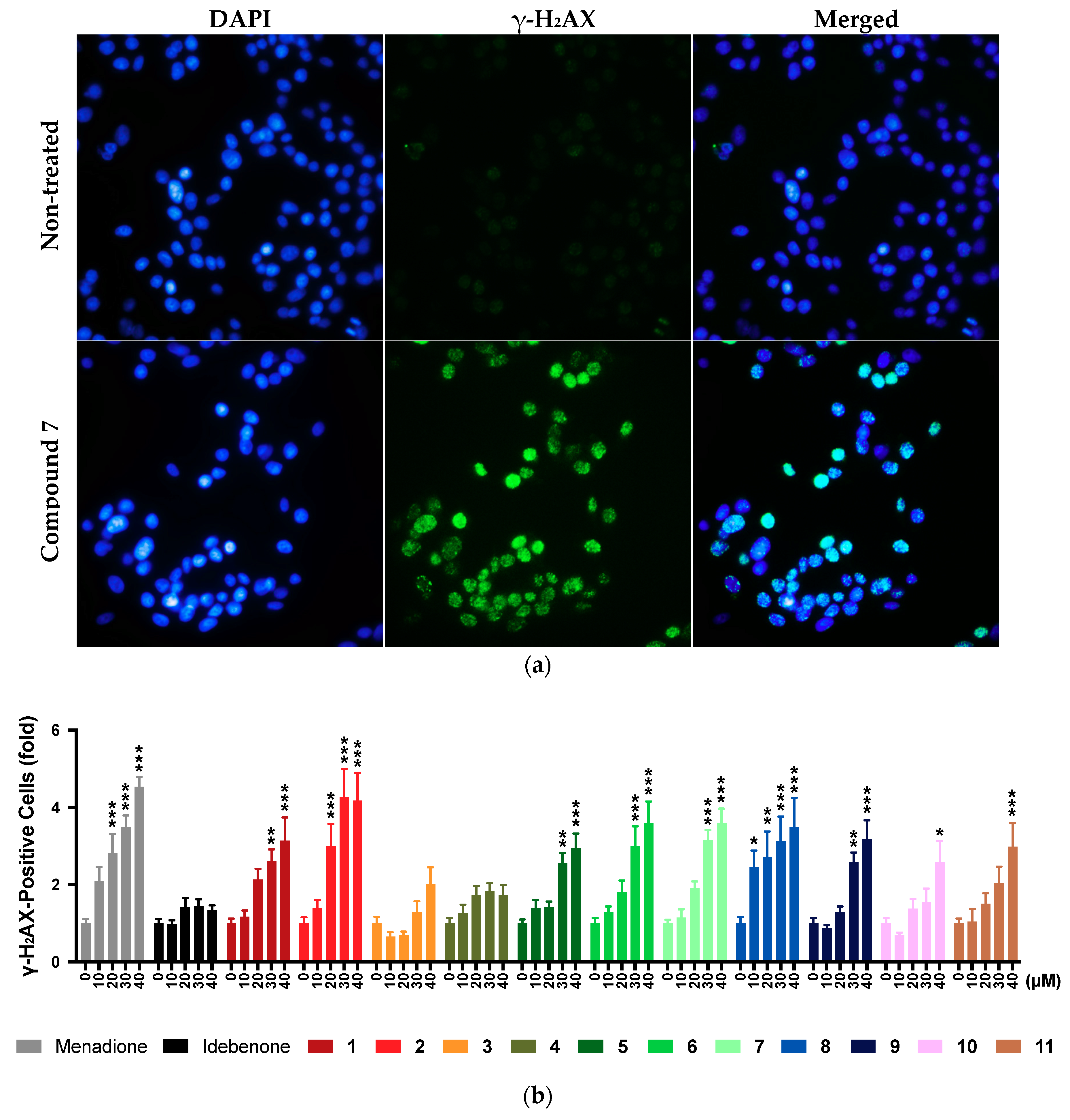
2.9. DNA Damage
2.10. Transformation Potential
2.11. Summary of Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Multiplex Detection of NAD(P)H, ATP, and Protein Levels
4.4. Propidium Iodide Incorporation
4.5. Multi-Tox Fluor Kit
4.6. MitoSOX
4.7. Colony Formation Assay
4.8. Assessment of Changes in Nuclear Morphology
4.9. Assessment of DNA Damage
4.10. Agar Invasion Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stepanova, A.; Magrané, J. Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurons in Friedreich’s ataxia. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 102, 103419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Han, X.; Yamaza, H.; Masuda, K.; Hirofuji, Y.; Sato, H.; Pham, T.T.M.; Taguchi, T.; Nonaka, K. Direct effects of mitochondrial dysfunction on poor bone health in Leigh syndrome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, S.; Geffroy, G.; Desquiret-Dumas, V.; Gueguen, N.; Bris, C.; Belal, S.; Amati-Bonneau, P.; Chevrollier, A.; Barth, M.; Henrion, D.; et al. The addition of ketone bodies alleviates mitochondrial dysfunction by restoring complex I assembly in a MELAS cellular model. Biochem. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabebi, M.; Charfi, N.; Kallabi, F.; Alila-Fersi, O.; Mahmoud, A.B.; Tlili, A.; Keskes-Ammar, L.; Kamoun, H.; Abid, M.; Mnif, M.; et al. Whole mitochondrial genome screening of a family with maternally inherited diabetes and deafness (MIDD) associated with retinopathy: A putative haplotype associated to MIDD and a novel MT-CO2 m.8241T>G mutation. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2017, 31, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, L.K.; Tiwari, M.; Rai, N.K.; Bai, Y. Mitophagy activation repairs Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy-associated mitochondrial dysfunction and improves cell survival. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagnoli, M.; La Morgia, C.; Carbonelli, M.; Di Vito, L.; Amore, G.; Zenesini, C.; Cascavilla, M.L.; Barboni, P.; Carelli, V. Idebenone increases chance of stabilization/recovery of visual acuity in OPA1-dominant optic atrophy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Ru, Q.; Chen, L.; Tian, X.; Li, C. Mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammatory response in the cytotoxicity of NR8383 macrophages induced by fine particulate matter. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 55, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, M.; Wallace, D.C.; Burelle, Y. The rise of mitochondria in medicine. Mitochondrion 2016, 30, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozin, M.S.; Kulakova, O.G.; Favorova, O.O. Involvement of Mitochondria in Neurodegeneration in Multiple Sclerosis. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2018, 83, 813–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigotto, G.; Basso, E. Mitochondrial Dysfunctions: A Thread Sewing Together Alzheimer’s Disease, Diabetes, and Obesity. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7210892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueven, N.; Woolley, K.; Smith, J. Border between natural product and drug: Comparison of the related benzoquinones idebenone and coenzyme Q10. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erb, M.; Hoffmann-Enger, B.; Deppe, H.; Soeberdt, M.; Haefeli, R.H.; Rummey, C.; Feurer, A.; Gueven, N. Features of idebenone and related short-chain quinones that rescue ATP levels under conditions of impaired mitochondrial complex I. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haefeli, R.H.; Erb, M.; Gemperli, A.C.; Robay, D.; Fruh, I.C.; Anklin, C.; Dallmann, R.; Gueven, N. NQO1-dependent redox cycling of idebenone: Effects on cellular redox potential and energy levels. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K.; Freeman, M.; Shaw, J.; Gooch, C.; Huang, Y.; Klein, M.; Miller, G.; Zesiewicz, T. EPI-743 for Friedreichs Ataxia Patients with Point Mutations (P5.388). Neurology 2016, 86, P5.388. [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli, D.; Catteruccia, M.; Piemonte, F.; Pastore, A.; Tozzi, G.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Pontrelli, G.; Corsetti, T.; Livadiotti, S.; Kheifets, V.; et al. EPI-743 reverses the progression of the pediatric mitochondrial disease--genetically defined Leigh Syndrome. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 107, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, M.C.H.; Koene, S.; de Laat, P.; Hemelaar, P.; Pickkers, P.; Spaans, E.; Beukema, R.; Beyrath, J.; Groothuis, J.; Verhaak, C.; et al. The KHENERGY Study: Safety and Efficacy of KH176 in Mitochondrial m.3243A>G Spectrum Disorders. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 105, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koene, S.; Spaans, E.; Van Bortel, L.; Van Lancker, G.; Delafontaine, B.; Badilini, F.; Beyrath, J.; Smeitink, J. KH176 under development for rare mitochondrial disease: A first in man randomized controlled clinical trial in healthy male volunteers. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopstock, T.; Yu-Wai-Man, P.; Dimitriadis, K.; Rouleau, J.; Heck, S.; Bailie, M.; Atawan, A.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Schubert, M.; Garip, A.; et al. A randomized placebo-controlled trial of idebenone in Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy. Brain 2011, 134, 2677–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, G.; Dimitriadis, K.; Buchner, B.; Heck, S.; Al-Tamami, J.; Seidensticker, F.; Rummey, C.; Leinonen, M.; Meier, T.; Klopstock, T. Effects of idebenone on color vision in patients with leber hereditary optic neuropathy. J. Neuro-ophthalmol. 2013, 33, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klopstock, T.; Metz, G.; Yu-Wai-Man, P.; Buchner, B.; Gallenmuller, C.; Bailie, M.; Nwali, N.; Griffiths, P.G.; von Livonius, B.; Reznicek, L.; et al. Persistence of the treatment effect of idebenone in Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy. Brain 2013, 136, e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboni, P.; Valentino, M.L.; La Morgia, C.; Carbonelli, M.; Savini, G.; De Negri, A.; Simonelli, F.; Sadun, F.; Caporali, L.; Maresca, A.; et al. Idebenone treatment in patients with OPA1-mutant dominant optic atrophy. Brain 2013, 136, e231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagedrost, S.J.; Sutton, M.S.; Cohen, M.S.; Satou, G.M.; Kaufman, B.D.; Perlman, S.L.; Rummey, C.; Meier, T.; Lynch, D.R. Idebenone in Friedreich ataxia cardiomyopathy-results from a 6-month phase III study (IONIA). Am. Heart J. 2011, 161, 639–645.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomilov, A.; Allen, S.; Hui, C.K.; Bettaieb, A.; Cortopassi, G. Idebenone is a cytoprotective insulin sensitizer whose mechanism is Shc inhibition. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 137, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiefenbach, J.; Magomedova, L.; Liu, J.; Reunov, A.A.; Tsai, R.; Eappen, N.S.; Jockusch, R.A.; Nislow, C.; Cummins, C.L.; Krause, H.M. Idebenone and coenzyme Q10 are novel PPARalpha/gamma ligands, with potential for treatment of fatty liver diseases. Dis. Model Mech. 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, D.; Shao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, H. Synergistic neuroprotective effect of rasagiline and idebenone against retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury via the Lin28-let-7-Dicer pathway. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 12137–12153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Becker, C.; Bray-French, K.; Drewe, J. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of idebenone. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2010, 6, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyse, G.M.; Voit, T.; Schara, U.; Straathof, C.S.; D’Angelo, M.G.; Bernert, G.; Cuisset, J.M.; Finkel, R.S.; Goemans, N.; Rummey, C.; et al. Treatment effect of idebenone on inspiratory function in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Pediat. Pulmonol. 2017, 52, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodmer, M.; Vankan, P.; Dreier, M.; Kutz, K.W.; Drewe, J. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of idebenone in healthy male subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 65, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolley, K.L.; Nadikudi, M.; Koupaei, M.N.; Corban, M.; McCartney, P.; Bissember, A.C.; Lewis, T.W.; Gueven, N.; Smith, J.A. Amide linked redox-active naphthoquinones for the treatment of mitochondrial dysfunction. MedChemComm 2019, 10, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Smith, J.A.; Gueven, N.; Quirino, J.P. Metabolic Stability of New Mito-Protective Short-Chain Naphthoquinones. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2020, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, C.L.; Gerencser, A.A.; Treberg, J.R.; Brand, M.D. The mechanism of superoxide production by the antimycin-inhibited mitochondrial Q-cycle. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 31361–31372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luukkonen, J.; Liimatainen, A.; Hoyto, A.; Juutilainen, J.; Naarala, J. Pre-exposure to 50 Hz magnetic fields modifies menadione-induced genotoxic effects in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S.N.; Towne, D.L.; Burns, D.J.; Warrior, U. A high-throughput soft agar assay for identification of anticancer compound. J. Biomol. Screen. 2007, 12, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzarski, J.S.; DiVito, M.D.; Wertheim, J.A.; Miller, W.M. Essential design considerations for the resazurin reduction assay to noninvasively quantify cell expansion within perfused extracellular matrix scaffolds. Biomaterials 2017, 129, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, W.H.; Wu, R.W.; Cebula, T.A.; Felton, J.S. Specificity of base substitution mutations induced by the dietary carcinogens 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (PhlP) and 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline (IQ) in Salmonella. Environ. Mol. Mutagenes. 1998, 31, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Shin, Y.K.; Sohn, D.S.; Lee, C.S. Menadione induces the formation of reactive oxygen species and depletion of GSH-mediated apoptosis and inhibits the FAK-mediated cell invasion. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2014, 387, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Scharf Santana, N.; Lima, N.A.; Desoti, V.C.; Bidoia, D.L.; de Souza Bonfim Mendonca, P.; Ratti, B.A.; Nakamura, T.U.; Nakamura, C.V.; Consolaro, M.E.; Ximenes, V.F.; et al. Vitamin K3 induces antiproliferative effect in cervical epithelial cells transformed by HPV 16 (SiHa cells) through the increase in reactive oxygen species production. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2016, 294, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.S.; Berridge, M.V. Differential effects of redox-cycling and arylating quinones on trans-plasma membrane electron transport. BioFactors 2008, 34, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.S.; Berridge, M.V. Evidence for NAD(P)H: Quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1)-mediated quinone-dependent redox cycling via plasma membrane electron transport: A sensitive cellular assay for NQO1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dustin, C.M.; Heppner, D.E.; Lin, M.J.; van der Vliet, A. Redox regulation of tyrosine kinase signalling: More than meets the eye. J. Biochem. 2020, 167, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, H.; Yoshida, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Tsukamoto, T.; Tanayama, S. Disposition of idebenone (CV-2619), a new cerebral metabolism improving agent, in rats and dogs. J. Pharmacobiodyn. 1985, 8, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.K.; Yang, X.N.; Zhu, X.; Xiao, X.R.; Yang, X.W.; Qin, H.B.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Li, F. Role of Metabolic Activation in Elemicin-Induced Cellular Toxicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8243–8252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sussman, N.L.; Kelly, J.H. Artificial liver: A forthcoming attraction. Hepatology 1993, 17, 1163–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Terasaki, N.; Kawataki, T.; Takekawa, K.; Iwase, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Sanoh, S.; Ohta, S. Comparison of Drug Metabolism and Its Related Hepatotoxic Effects in HepaRG, Cryopreserved Human Hepatocytes, and HepG2 Cell Cultures. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L.; Vandenabeele, P.; Abrams, J.; Alnemri, E.S.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Blagosklonny, M.V.; El-Deiry, W.S.; Golstein, P.; Green, D.R.; et al. Classification of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2009. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, B.K.; Choi, J.; Park, J.H.; Doh, K.O.; Byeon, J.H. In vitro exposure of simulated meat-cooking fumes to assess adverse biological effects. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingetti, M.; Porfido, F.A.; Ciarimboli, M.; Oliviero, U.; Cocozza, M.; Coto, V.; Policicchio, D.; Carifi, S.; Piermatteo, E.; Lombardi, R.; et al. Evaluation of the clinical efficacy of idebenone in patients affected by chronic cerebrovascular disorders. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 1992, 15, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geromel, V.; Darin, N.; Chretien, D.; Benit, P.; DeLonlay, P.; Rotig, A.; Munnich, A.; Rustin, P. Coenzyme Q (10) and idebenone in the therapy of respiratory chain diseases: Rationale and comparative benefits. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2002, 77, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisano, P.; Durand, A.; Autret, E.; Desnuelle, C.; Pinsard, N.; Serratrice, G.; Legout, V.; Joubert, M.; Blin, O. Plasma concentrations and pharmacokinetics of idebenone and its metabolites following single and repeated doses in young patients with mitochondrial encephalomyopathy. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1996, 51, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitz, F.D.; Erb, M.; Anklin, C.; Robay, D.; Pernet, V.; Gueven, N. Idebenone protects against retinal damage and loss of vision in a mouse model of Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Prospero, N.A.; Baker, A.; Jeffries, N.; Fischbeck, K.H. Neurological effects of high-dose idebenone in patients with Friedreich’s ataxia: A randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | Structure | N | R | Formula | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | LogP 1 | LogD 2 | In Vitro Cytoprotection 3 | In Vitro Metabolic Stability 4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | p-Value | % | p-Value | ||||||||
| Idebenone | 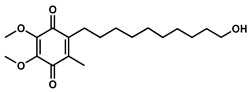 | - | - | C19H30O5 | 338.4 | 1.24 | 3.57 | 66.2 ± 12.0 | - | 27.3 ± 3.9 | - |
| 1 (UTAS#81) |  | 2 | 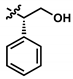 | C23H23NO4 | 377.4 | 2.24 | 2.81 | 83.8 ± 19.9 | 0.191 | 92.6 ± 16.9 | <0.001 |
| 2 (UTAS#80) |  | C23H23NO4 | 377.4 | 2.24 | 2.81 | 87.6 ± 19.7 | 0.025 | 96.6 ± 11.1 | <0.001 | ||
| 3 (UTAS#62) | 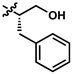 | C24H25NO4 | 391.5 | 2.52 | 3.10 | 93.1 ± 13.7 | <0.001 | 84.0 ± 15.5 | <0.001 | ||
| 4 (UTAS#37) | 2 |  | C24H23NO5 | 405.4 | 2.48 | 0.12 | 100.3 ± 17.3 | <0.001 | 96.0 ± 7.5 | <0.001 | |
| 5 (UTAS#72) | 3 | C25H25NO5 | 419.5 | 2.90 | 0.74 | 90.7 ± 15.6 | 0.146 | 91.4 ± 0.8 | <0.001 | ||
| 6 (UTAS#74) | 2 | 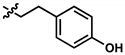 | C23H23NO4 | 377.4 | 2.67 | 3.43 | 91.7 ± 15.6 | 0.101 | 45.7 ± 2.9 | 0.034 | |
| 7 (UTAS#88) | 3 | C24H25NO4 | 391.5 | 3.09 | 3.87 | 91.8 ± 9.8 | 0.097 | 60.3 ± 1.7 | <0.001 | ||
| 8 (UTAS#54) | 2 | 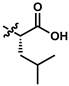 | C21H25NO5 | 371.4 | 2.04 | 0.26 | 98.7 ± 10.9 | 0.004 | 84.3 ± 9.2 | <0.001 | |
| 9 (UTAS#77) |  | C25H27NO5 | 421.5 | 2.80 | 3.41 | 95.9 ± 19.4 | 0.017 | 58.3 ± 11.0 | <0.001 | ||
| 10 (UTAS#61) | 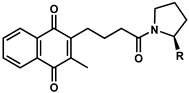 | - | 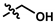 | C20H23NO4 | 341.4 | 1.06 | 1.71 | 100.7 ± 28.4 | 0.002 | 78.9 ± 7.4 | <0.001 |
| 11 (UTAS#43) | - | 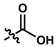 | C20H21NO5 | 355.4 | 1.02 | -1.32 | 92.7 ± 7.6 | 0.018 | 67.2 ± 2.3 | <0.001 | |
| Compound | Multiplex Detection | Membrane Integrity 2 | Multi-Tox Fluor Assay | Mitochondrial Superoxide 2 | Colony Formation 1 | Pyknosis | DNA Damage 2 | Transformation Potential | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WST-1 1 | ATP 1 | Protein 1 | Necrotic-Cell Protease 2 | Viable-Cell Protease 1 | |||||||
| Idebenone | 151.7 ± 5.9 | 146.8 ± 14.2 | 136.8 ± 4.7 | ≥100 | N | 71.1 ± 11.1 | N | 26.0 ± 5.2 | Y | N | N |
| 1 | 59.0 ± 2.2 | 59.0 ± 4.7 | 59.6 ± 0.6 | ≥50 | N | 55.8 ± 9.1 | N | 6.2 ± 1.8 | Y | ≥30 | N |
| 2 | 45.7 ± 1.3 | 45.5 ± 3.8 | 52.7 ± 7.1 | ≥50 | N | 50.7 ± 7.1 | N | 4.8 ± 0.1 | Y | ≥20 | N |
| 3 | 88.8 ± 8.8 | 95.4 ± 9.2 | 66.1 ± 7.2 | ≥75 | N | 54.9 ± 7.6 | N | 7.1 ± 3.2 | Y | N | N |
| 4 | >200 | >200 | >200 | N | N | >200 | N | 31.2 ± 10.5 | N | N | N |
| 5 | >200 | >200 | >200 | ≥150 | N | 161.5 ± 15.2 | ≥200 | 20.6 ± 5.9 | N | ≥30 | N |
| 6 | 69.6 ± 1.8 | 67.0 ± 4.7 | 66.3 ± 4.9 | ≥75 | ≥125 | 52.0 ± 9.3 | N | 4.7 ± 1.1 | N | ≥30 | N |
| 7 | 78.0 ± 5.6 | 78.2 ± 4.4 | 60.0 ± 8.3 | ≥100 | ≥125 | 56.1 ± 8.2 | N | 4.2 ± 1.0 | N | ≥30 | N |
| 8 | 83.1± 3.7 | 88.8 ± 10.5 | 80.8 ± 3.3 | ≥125 | ≥125 | 155.8 ± 15.7 | ≥100 | 8.1 ± 2.3 | Y | ≥10 | N |
| 9 | 55.4 ± 6.7 | 52.3 ± 4.8 | 57.3 ± 9.2 | ≥75 | ≥125 | 49.0 ± 11.8 | N | 5.6 ± 1.1 | Y | ≥30 | N |
| 10 | 51.5 ± 9.6 | 55.9 ± 12.0 | 61.2 ± 7.7 | ≥75 | ≥200 | 57.9 ± 7.8 | N | 4.8 ± 0.5 | Y | ≥40 | N |
| 11 | 99.7 ± 5.8 | 108.0 ± 19.2 | 91.8 ± 5.1 | ≥150 | ≥125 | >200 | ≥100 | 7.4 ± 1.4 | N | ≥40 | N |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Z.; Sedeeq, M.; Daniel, A.; Corban, M.; Woolley, K.L.; Condie, R.; Azimi, I.; Smith, J.A.; Gueven, N. Comparative In Vitro Toxicology of Novel Cytoprotective Short-Chain Naphthoquinones. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080184
Feng Z, Sedeeq M, Daniel A, Corban M, Woolley KL, Condie R, Azimi I, Smith JA, Gueven N. Comparative In Vitro Toxicology of Novel Cytoprotective Short-Chain Naphthoquinones. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(8):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080184
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Zikai, Mohammed Sedeeq, Abraham Daniel, Monika Corban, Krystel L. Woolley, Ryan Condie, Iman Azimi, Jason A. Smith, and Nuri Gueven. 2020. "Comparative In Vitro Toxicology of Novel Cytoprotective Short-Chain Naphthoquinones" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 8: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080184
APA StyleFeng, Z., Sedeeq, M., Daniel, A., Corban, M., Woolley, K. L., Condie, R., Azimi, I., Smith, J. A., & Gueven, N. (2020). Comparative In Vitro Toxicology of Novel Cytoprotective Short-Chain Naphthoquinones. Pharmaceuticals, 13(8), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080184






