Design and Development of Novel Urea, Sulfonyltriurea, and Sulfonamide Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of Sphingosine Kinase 1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemistry
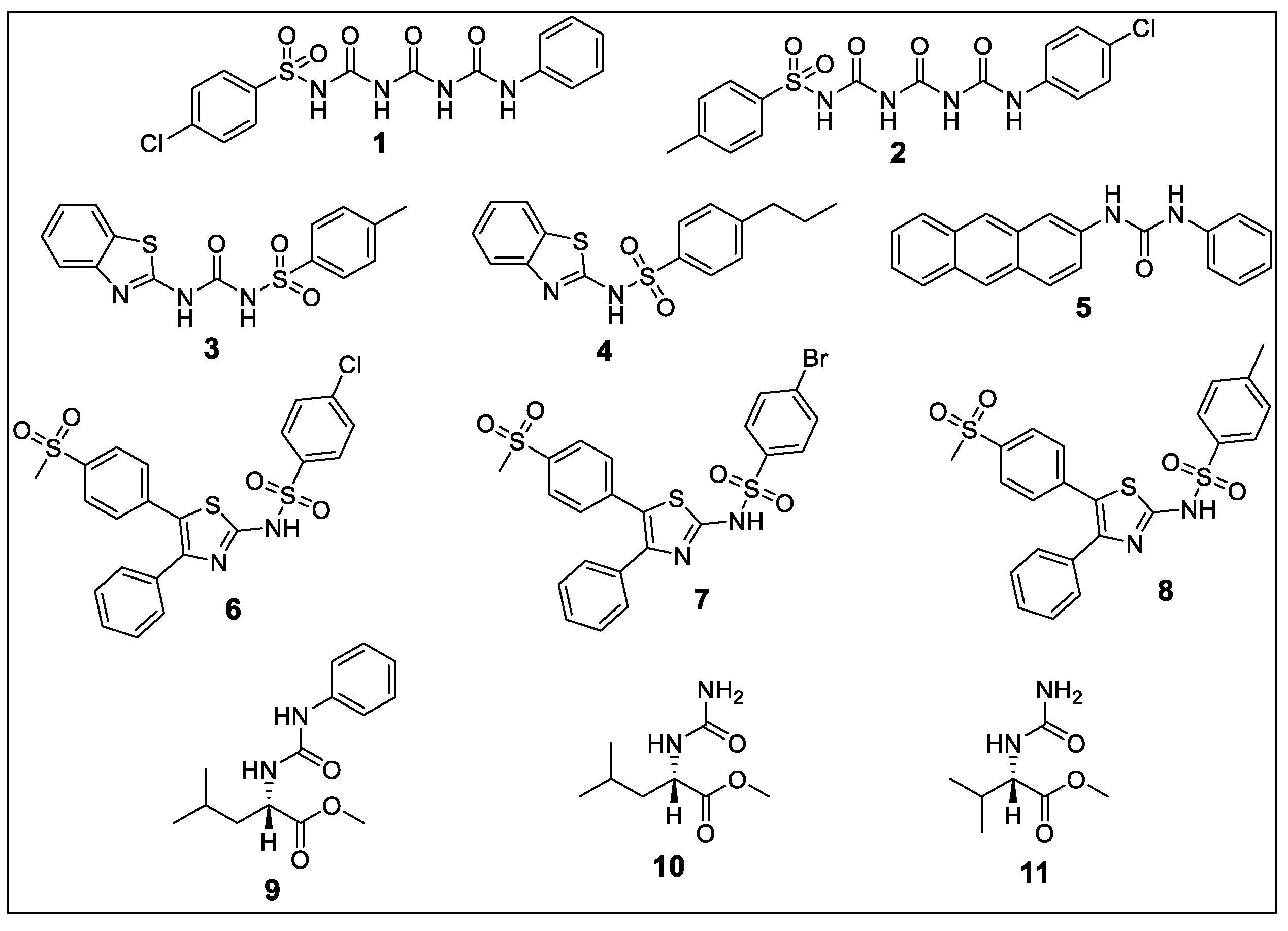
2.1.1. 4-chloro-N-(((phenylcarbamoyl)carbamoyl)carbamoyl)benzenesulfonamide (1)
2.1.2. N-((((4-chlorophenyl)carbamoyl)carbamoyl)carbamoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide (2)
2.1.3. N-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-ylcarbamoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide (3)
2.1.4. N-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-4-propylbenzenesulfonamide (4)
2.1.5. 1-(anthracen-2-yl)-3-phenylurea (5)
2.1.6. 4-chloro-N-(5-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-4-phenylthiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide (6)
2.1.7. 4-bromo-N-(5-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-4-phenylthiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide (7)
2.1.8. 4-methyl-N-(5-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-4-phenylthiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide (8)
2.1.9. Methyl (phenylcarbamoyl)-l-leucinate (9)
2.1.10. Methyl carbamoyl-l-leucinate (10)
2.1.11. Methyl carbamoyl-l-valinate (11)
2.2. Biological Evaluations
2.2.1. Fluorescence Binding Studies
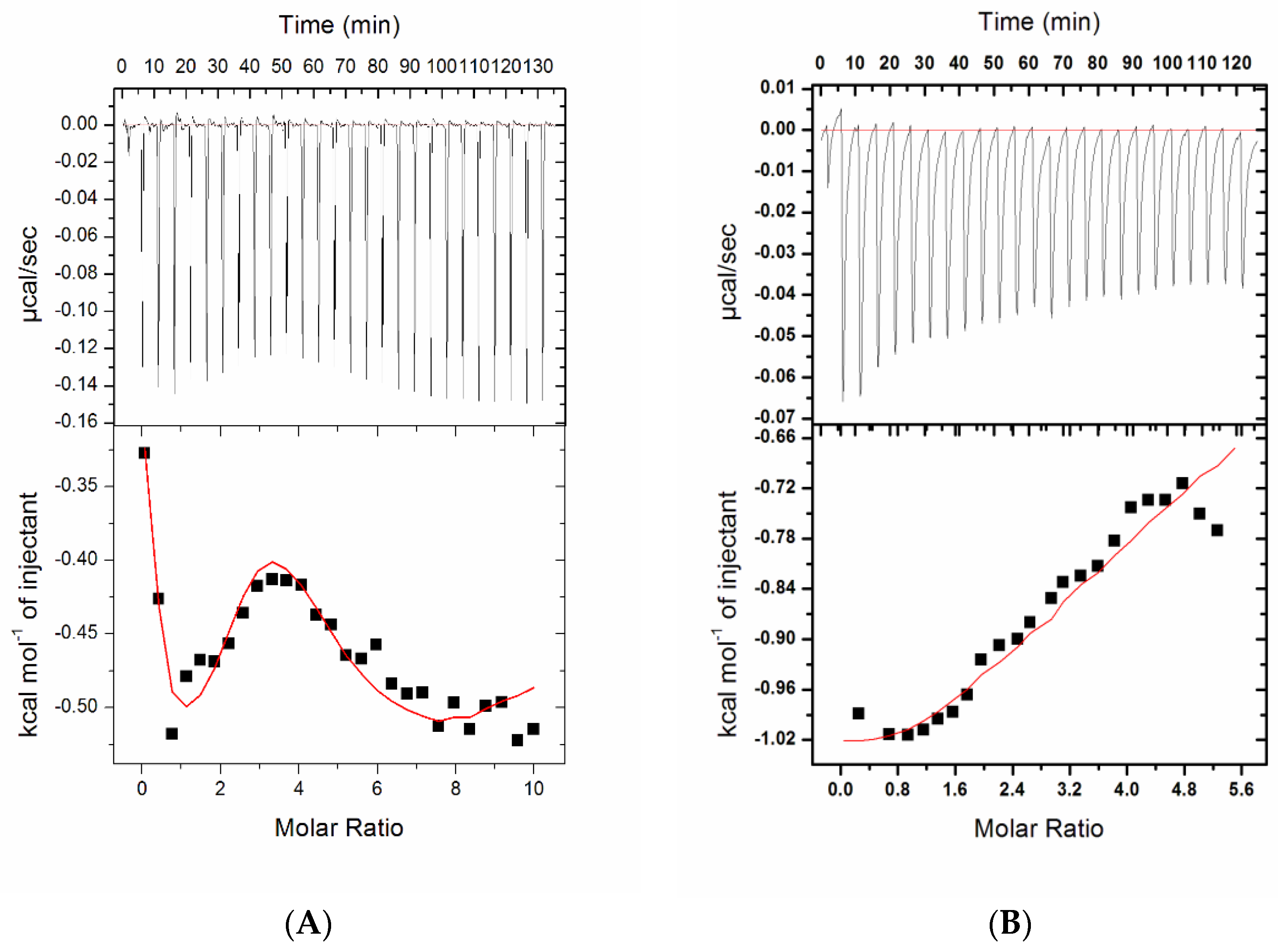
2.2.2. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
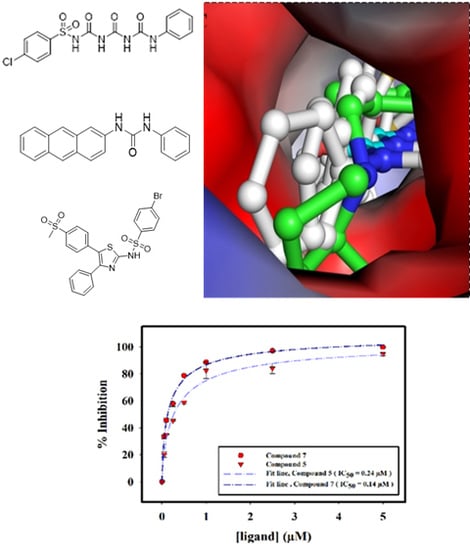
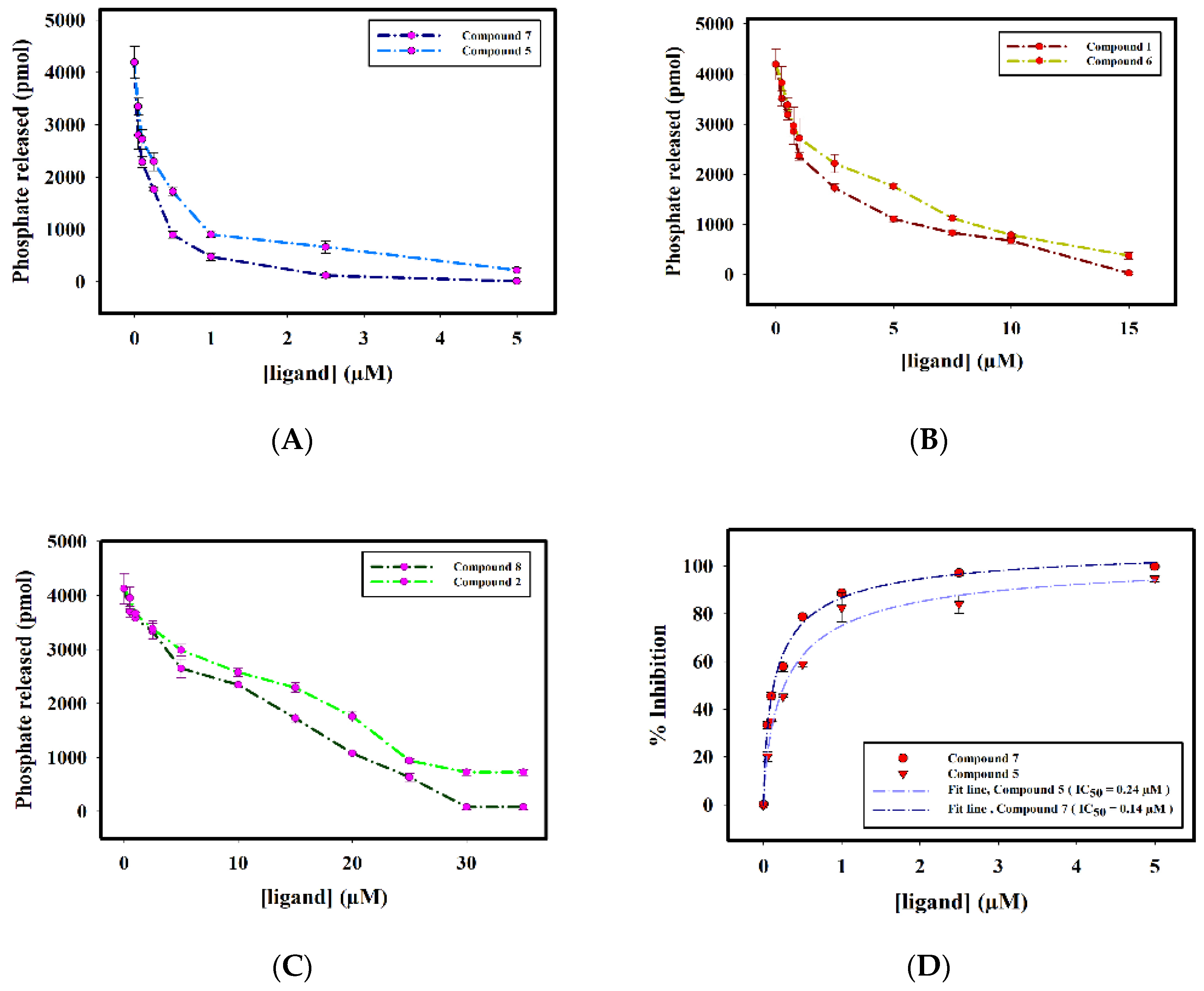
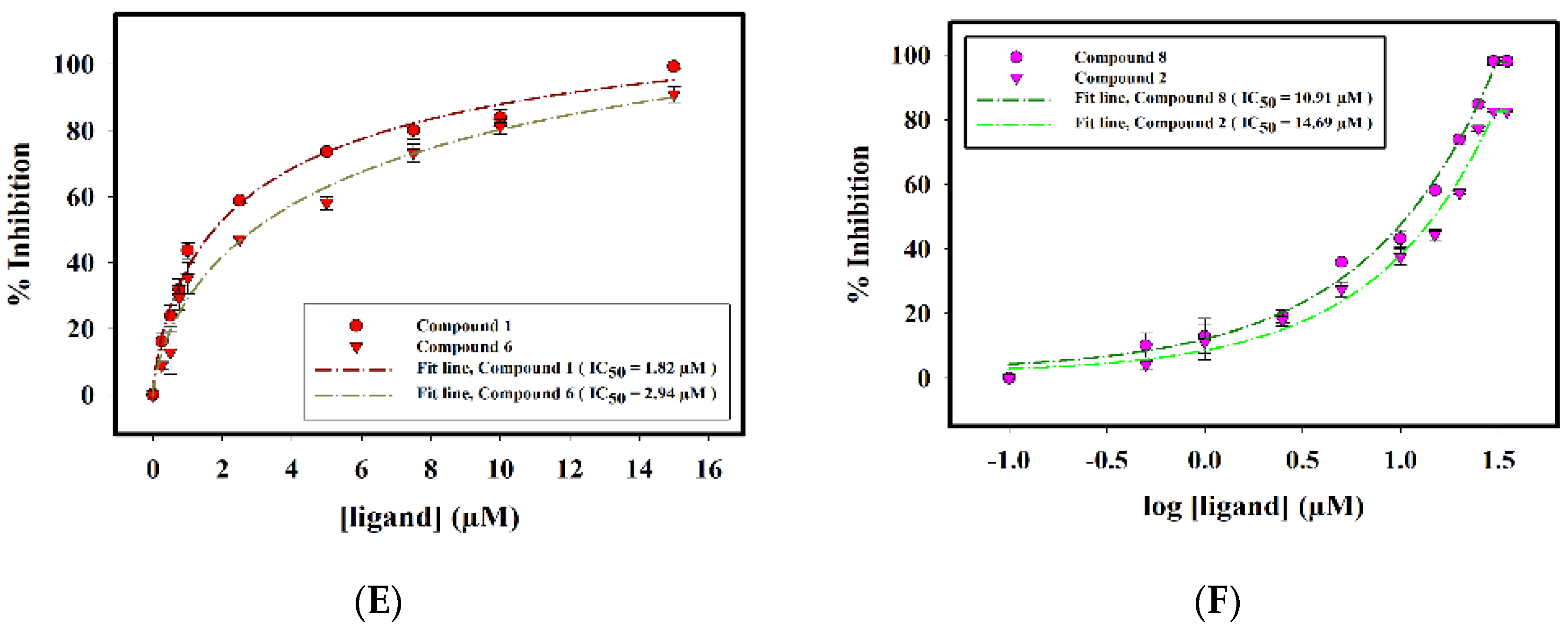
2.2.3. Enzyme Inhibition Assay
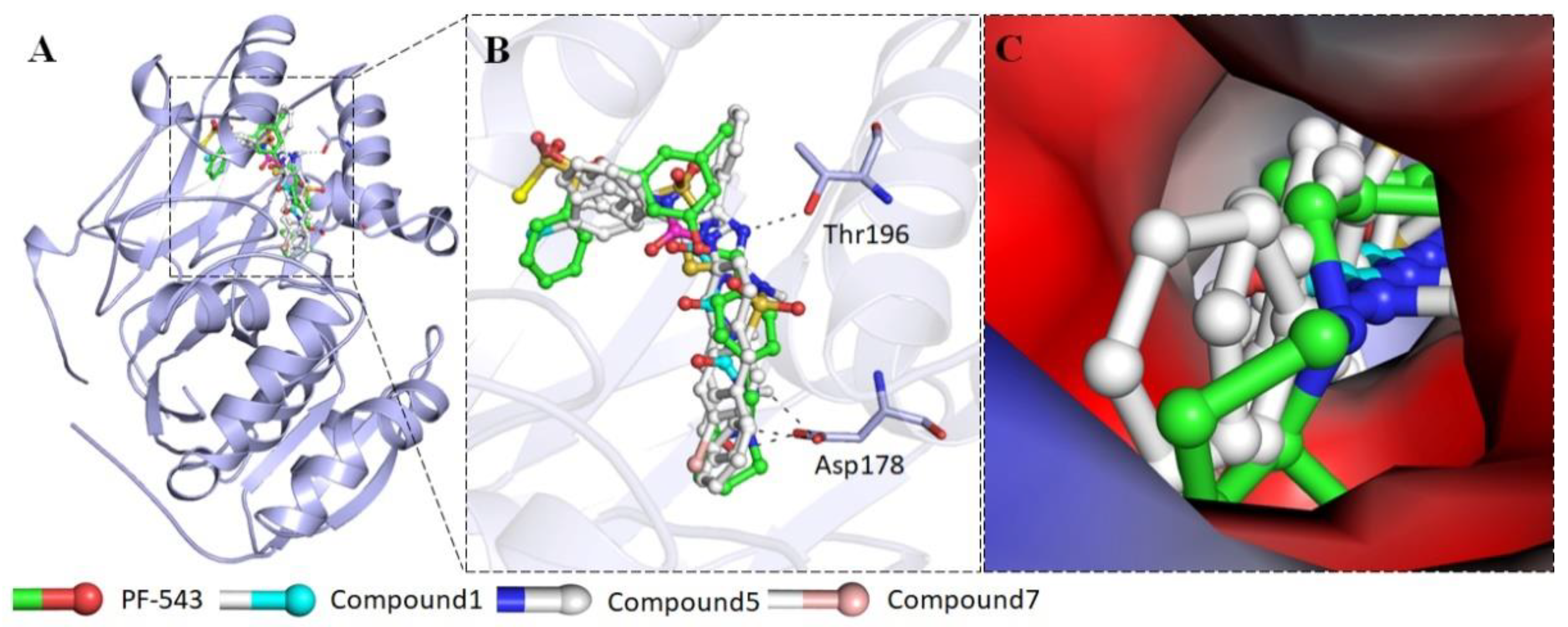
2.2.4. Interaction of Selected Inhibitors with SphK1
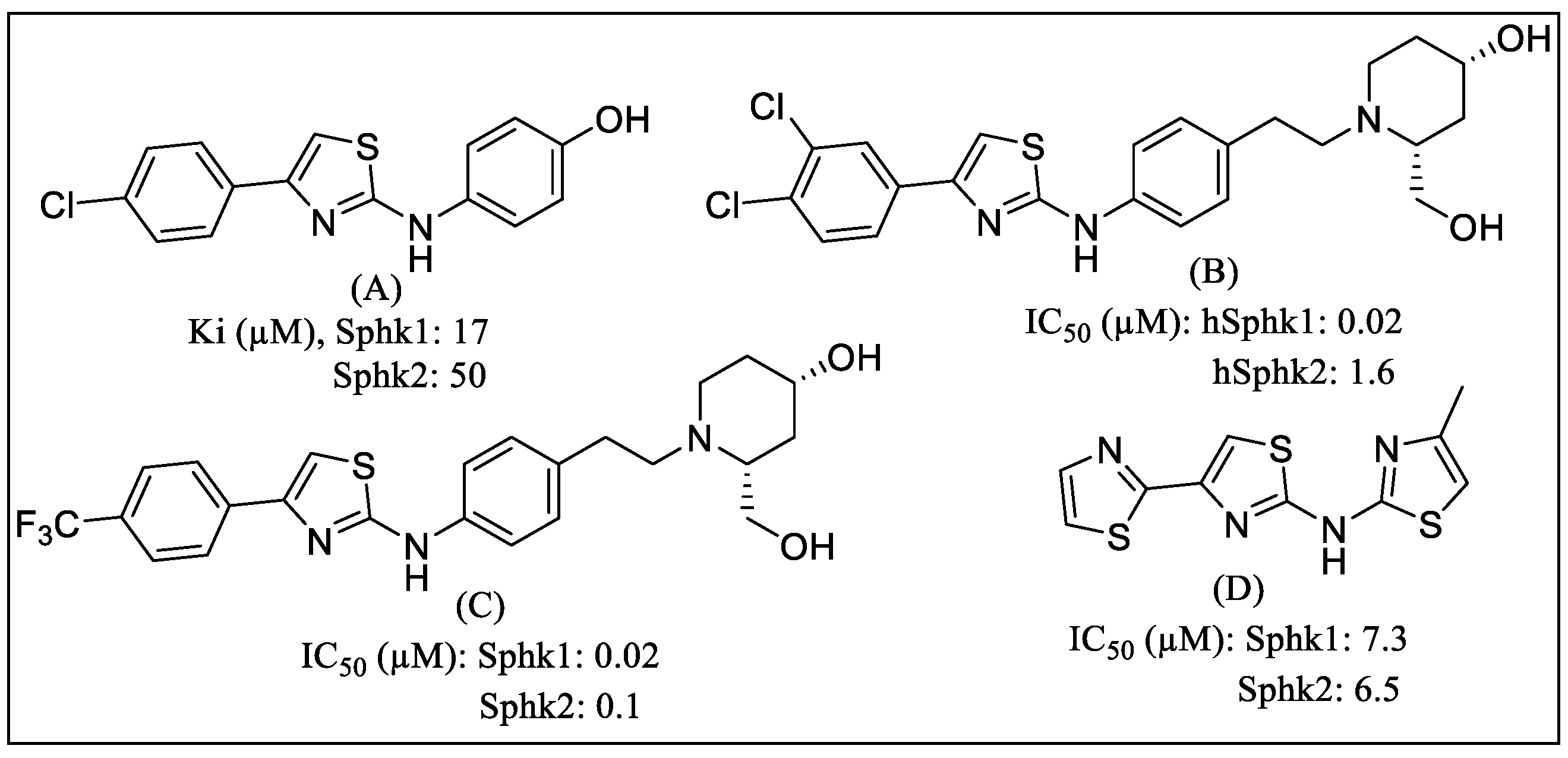
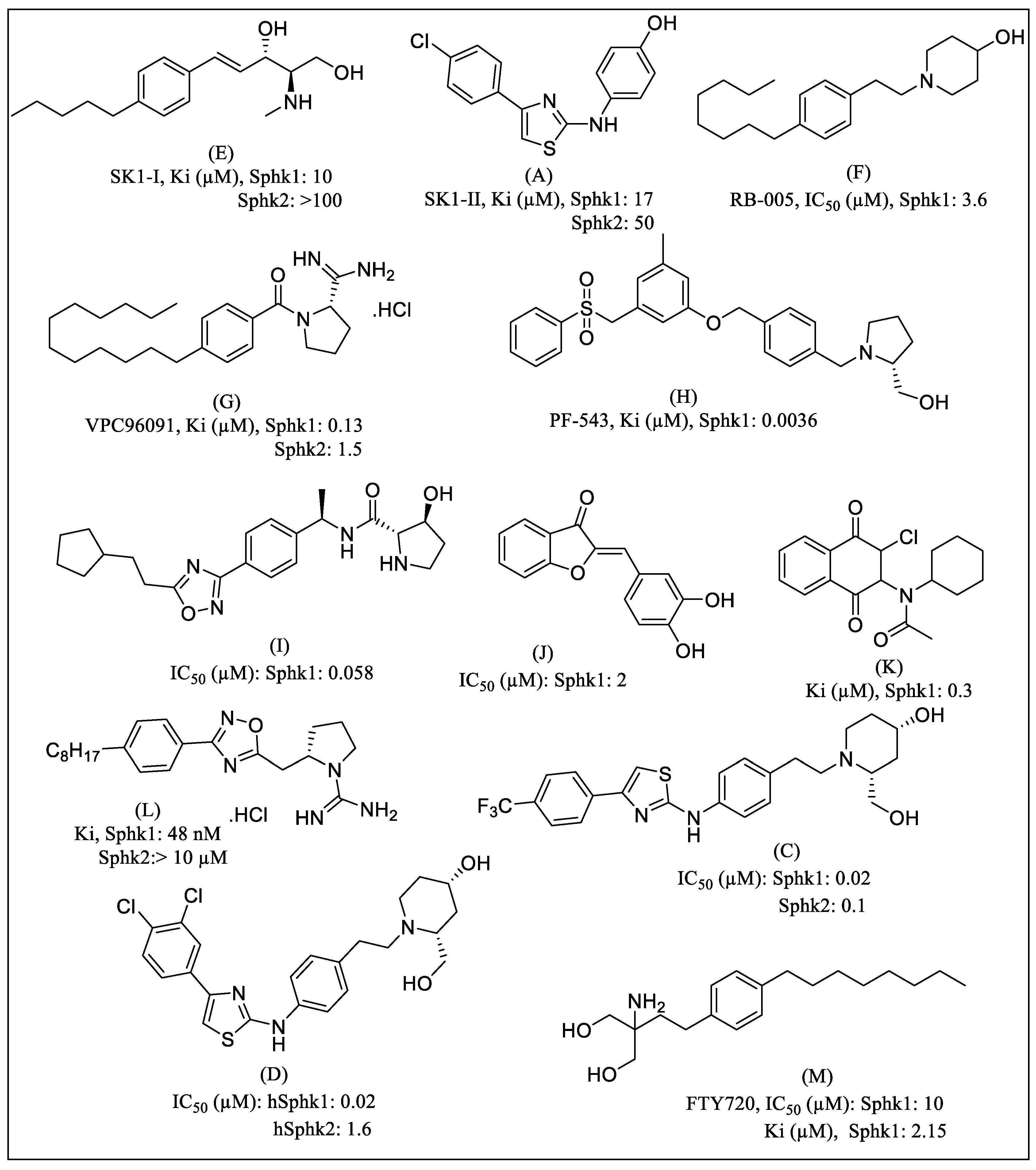
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.1.1. Materials
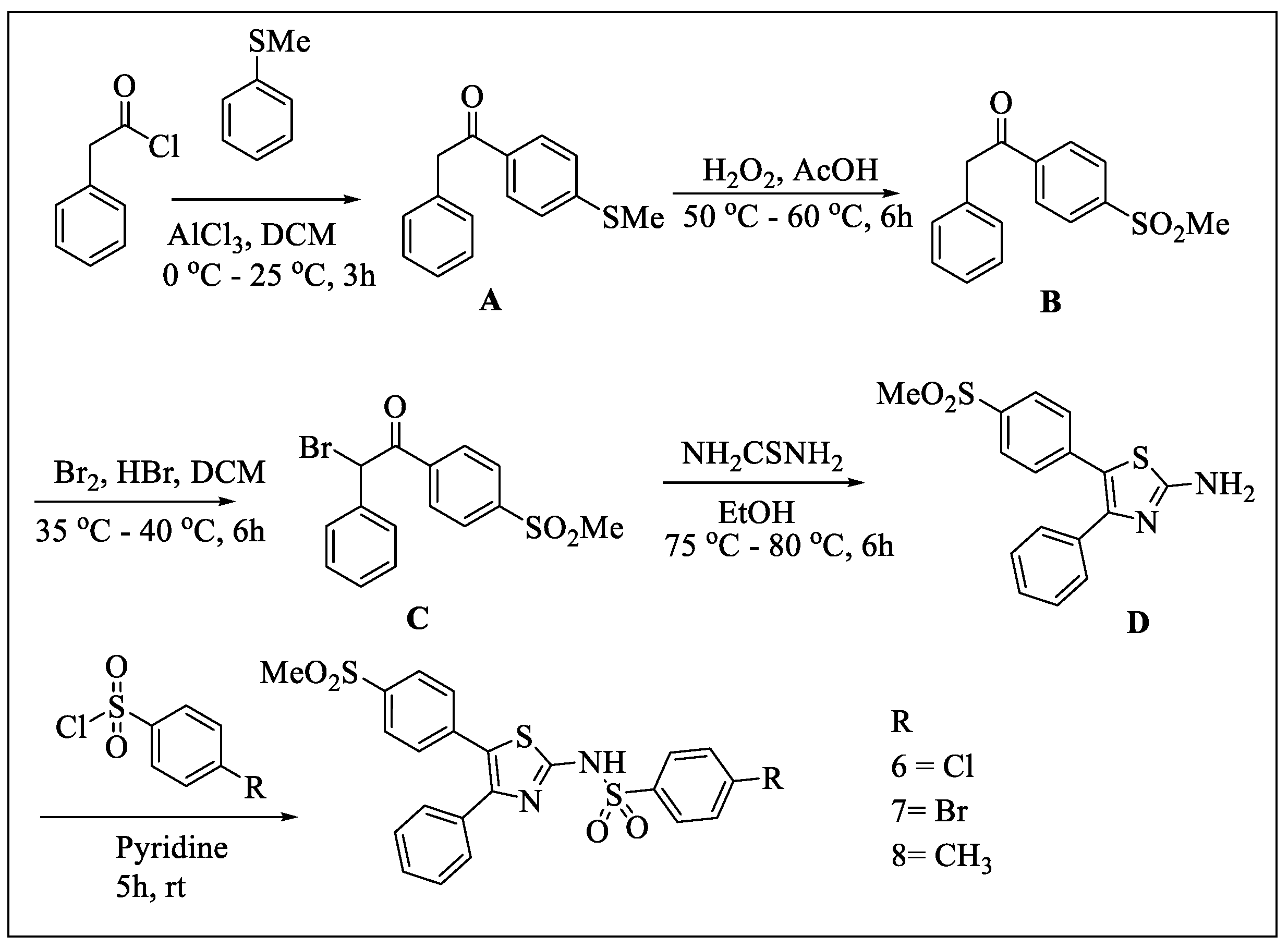
4.1.2. Synthesis
- General procedure for the synthesis of sulfonyltriurea (Compounds 1, 2, and 3)
- 2.
- General procedure for the synthesis of sulfonamide derivatives (Compound 4)
- 3.
- General procedure for the synthesis of Compound 5
- 4.
- General procedure for the synthesis of Compounds 6, 7, and 8
- 5.
- General procedure for the synthesis of Compound 9
- 6.
- General procedure for the synthesis of Compounds 10 and 11
4.2. Biological Studies
4.2.1. Materials
4.2.2. Expression and Purification of SphK1
4.2.3. Fluorescence Binding Studies
4.2.4. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
4.2.5. Enzyme Inhibition Assay
4.2.6. Molecular Docking
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nishizuka, Y. Intracellular signaling by hydrolysis of phospholipids and activation of protein kinase C. Science 1992, 258, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryland, L.K.; Fox, T.E.; Liu, X.; Loughran, T.P.; Kester, M. Dysregulation of sphingolipid metabolism in cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salh, B.; Marotta, A.; Wagey, R.; Sayed, M.; Pelech, S. Dysregulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and downstream effectors in human breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 98, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, P.; Jain, S.K. Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate and cellular signaling: Implications for obesity and diabetes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 35, 1253–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dituri, F.; Mazzocca, A.; Giannelli, G.; Antonaci, S. PI3K functions in cancer progression, anticancer immunity and immune evasion by tumours. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2011, 2011, 947858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Savill, J. Resolution of inflammation: The beginning programs the end. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyne, S.; Pyne, N.J. Sphingosine 1-phosphate signalling in mammalian cells. Biochem. J. 2000, 349, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contos, J.A.; Ishii, I.; Chun, J. Lysophosphatidic acid receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wymann, M.O.; Pirola, L. Structure and function of phosphoinositide 3-kinases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta–Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 1998, 1436, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.-D.; Schwartz, M.A. Regulation of inositol lipid kinases by Rho and Rac. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1998, 8, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauss, T.C.; Jaffer, F.E.; Abboud, H.E. Phosphatidic acid modulates DNA synthesis, phospholipase C, and platelet-derived growth factor mRNAs in cultured mesangial cells. Role of protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 14457–14463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bokoch, G.M.; Reilly, A.M.; Daniels, R.H.; King, C.C.; Olivera, A.; Spiegel, S.; Knaus, U.G. A GTPase-independent mechanism of p21-activated kinase action regulation by sphingosine and other biologically active lipids. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 8137–8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rameh, L.E.; Cantley, L.C. The role of phosphoinositide-3-kinase lipid products in cell function. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 8347–8350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Min, X.; Xiao, S.-H.; Johnstone, S.; Romanow, W.; Meininger, D.; Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Dai, J.; An, S. Molecular basis of sphingosine kinase 1 substrate recognition and catalysis. Structure 2013, 21, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakane, F.; Shin-ichi, I.; Kai, M.; Yasuda, S.; Kanoh, H. Diacylglycerol kinases as emerging potential drug targets for a variety of diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2008, 9, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohama, T.; Olivera, A.; Edsall, L.; Nagiec, M.M.; Dickson, R.; Spiegel, S. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of murine sphingosine kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 23722–23728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Sugiura, M.; Nava, V.E.; Edsall, L.C.; Kono, K.; Poulton, S.; Milstien, S.; Kohama, T.; Spiegel, S. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a novel mammalian sphingosine kinase type 2 isoform. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 19513–19520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceyka, M.; Payne, S.G.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine kinase, sphingosine-1-phosphate, and apoptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1585, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zha, R.; Huang, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, T.; Li, J.; Tu, H.; et al. Sphingosine kinase 1 promotes tumour cell migration and invasion via the S1P/EDG1 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfe, G.; Mirone, G.; Shukla, A.; Di Stefano, C. Sphingosine Kinases Signalling in Carcinogenesis. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Desai, N.N.; Olivera, A.; Seki, T.; Brooker, G.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate, a novel lipid, involved in cellular proliferation. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 114, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivera, A.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate as second messenger in cell proliferation induced by PDGF and FCS mitogens. Nature 1993, 365, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiss, U.; Oskouian, B.; Zhou, J.; Gupta, V.; Sooriyakumaran, P.; Kelly, S.; Wang, E.; Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Saba, J.D. Sphingosine-phosphate Lyase Enhances Stress-induced Ceramide Generation and Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hla, T. Physiological and pathological actions of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 15, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maceyka, M.; Harikumar, K.B.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling and its role in disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huwiler, A.; Pfeilschifter, J. Lipids as targets for novel anti-inflammatory therapies. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 124, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saddoughi, S.A.; Song, P.; Ogretmen, B. Roles of bioactive sphingolipids in cancer biology and therapeutics. Subcell Biochem. 2008, 49, 413–440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alemany, R.; van Koppen, C.J.; Danneberg, K.; Ter Braak, M.; Zu Heringdorf, D.M. Regulation and functional roles of sphingosine kinases. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2007, 374, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-D.; Zhou, Z.-S.; Qiu, J.-H.; Shen, W.-H.; Wu, Q.; Xiao, J. Increased SPHK1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in bladder cancer. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 2075–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wu, Z. Sphingosine kinase 1 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis and oxaliplatin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshaker, H.; Sauer, L.; Monteil, D.; Ottaviani, S.; Srivats, S.; Bohler, T.; Pchejetski, D. Therapeutic potential of targeting SK1 in human cancers. Adv. Cancer Res. 2013, 117, 143–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Truman, J.P.; Garcia-Barros, M.; Obeid, L.M.; Hannun, Y.A. Evolving concepts in cancer therapy through targeting sphingolipid metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 1174–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffernan-Stroud, L.A.; Obeid, L.M. Sphingosine kinase 1 in cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2013, 117, 201–235. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamori, T.; Kaneshiro, T.; Okumura, M.; Maalouf, S.; Uflacker, A.; Bielawski, J.; Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Role for sphingosine kinase 1 in colon carcinogenesis. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirai, K.; Kaneshiro, T.; Wada, M.; Furuya, H.; Bielawski, J.; Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M.; Ogretmen, B.; Kawamori, T. A role of sphingosine kinase 1 in head and neck carcinogenesis. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustin, D.J.; Li, Y.; Brown, M.L.; Min, X.; Schmitt, M.J.; Wanska, M.; Wang, X.; Connors, R.; Johnstone, S.; Cardozo, M. Structure guided design of a series of sphingosine kinase (SphK) inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4608–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Knapp, S.; Pyne, N.J.; Pyne, S.; Elkins, J.M. Crystal structure of sphingosine kinase 1 with PF-543. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Weng, W.; Sun, Z.-X.; Fu, X.-J.; Ma, J.; Zhuang, W.-F. SphK1 inhibitor II (SKI-II) inhibits acute myelogenous leukemia cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Choi, J.W.; Chun, J. Neurological S1P signaling as an emerging mechanism of action of oral FTY720 (fingolimod) in multiple sclerosis. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2010, 33, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childress, E.S.; Kharel, Y.; Brown, A.M.; Bevan, D.R.; Lynch, K.R.; Santos, W.L. Transforming Sphingosine Kinase 1 Inhibitors into Dual and Sphingosine Kinase 2 Selective Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, and in Vivo Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 3933–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.J.; Mathews, T.P.; Kharel, Y.; Field, S.D.; Moyer, M.L.; East, J.E.; Houck, J.D.; Lynch, K.R.; MacDonald, T.L. Development of Amidine-Based Sphingosine Kinase 1 Nanomolar Inhibitors and Reduction of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate in Human Leukemia Cells. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3524–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vettorazzi, M.; Gutierrez, L.; Andujar, S.; Insuasty, D.; Lima, S.; Spiegel, S.; Nogueras, M.; Marchal, A.; Abonia, R.; Cobo, J.; et al. Design of new quinolin-2-one-pyrimidine hybruds as sphingosine kinases inhibitors. Bioorganic Chem. 2020, 94, 103414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Ying, L.; Huining, C.; Takayuki, Y.; Liu, B.; Qingqiang, Y. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-epi-jasmine B analogs as selective sphingosine kinase 1 inhibitors. Bioorganic Chem. 2019, 103369. [Google Scholar]
- Corvino, A.; Rosa, R.; Incisivo, G.M.; Fiorino, F.; Frecentese, F.; Magli, E.; Perissutti, E.; Saccone, I.; Santagada, V.; Cirino, G.; et al. Development of 1,2,3-triazole-based sphingosine kinase inhibitors and their evaluation as antiproliferative agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, D.; Weber, J.; Ihlefeld, K.; Brueggerhoff, A.; Proschak, E.; Stark, H. Design, synthesis and evaluation of 2-aminothiazole derivatives as sphingosine kinase inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 5354–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengst, J.A.; Wang, X.u.; Sk, U.H.; Sharma, A.K.; Amin, S.; Yun, J.K. Development of a sphingosine kinase 1 specific small-molecule inhibitor. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 7498–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Xu, S.; Guo, Y.; Wu, J.; Luo, R.; Wang, W.; Tu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhu, W.; Zheng, P. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of phenylpicolinamide sorafenib derivatives as antitumour agents. Med. Chem. Res. 2018, 27, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettorazzi, M.; Angelina, E.; Lima, S.; Gonec, T.; Otevrel, J.; Marvanova, P.; Padrtova, T.; Mokyr, P.; Bobal, P.; Acosta, L.M.; et al. An integrative study to identify novel scaffolds for sphingosine kinase 1 inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 139, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadianawala, M.; Datta, B. Design and development of sulfonylurea derivatives as zinc metalloenzyme modulators. Rsc Adv. 2016, 6, 8923–8929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, D.; Hadianawala, M.; Das Mahapatra, A.; Datta, B.; Roy, S.; Ahamad, S.; khan, P.; Hassan, M.I. Implication of sulfonylurea derivatives as prospective inhibitors of human carbonic anhydrase II. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, K.J.; Schrecengost, R.S.; Lee, B.D.; Zhuang, Y.; Smith, S.N.; Eberly, J.L.; Yun, J.K.; Smith, C.D. Discovery and Evaluation of Inhibitors of Human Sphingosine Kinase. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5962–5969. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mathews, T.P.; Kennedy, A.J.; Kharel, Y.; Kennedy, P.C.; Nicoara, O.; Sunkara, M.; Morris, A.J.; Wamhoff, B.R.; Lynch, K.R.; Macdonald, T.L. Discovery, biological evaluation and structure-activity relationship of amidine based sphingosine kinase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2766–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, D.J.; MacRitchie, N.; Pyne, N.J.; Pyne, S.; Bittman, R. Synthesis of selective inhibitors of sphingosine kinase 1. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2136–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnute, M.E.; McReynolds, M.D.; Kasten, T.; Yates, M.; Jerome, G.; Rains, J.W.; Hall, T.; Chrencik, J.; Kraus, M.; Cronin, C.N.; et al. Modulation of cellular S1P levels with a novel, potent and specific inhibitor of sphingosine kinase-1. Biochem. J. 2012, 444, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Peterson, Y.K.; Smith, R.A.; Smith, C.D. Characterization of isoenzyme-selective inhibitors of human sphingosine kinases. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwardhan, N.N.; Morris, E.A.; Kharel, Y.; Raje, M.R.; Gao, M.; Tomsig, J.L.; Lynch, K.R.; Santos, W.L. Structure-activity relationship studies and in vivo activity of guanidine-based sphingosine kinase inhibitors: Discovery of sphK1- and sphK2-selective inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 1879–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vessey, D.A.; Kelley, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Tao, R.; Karliner, J.S. Dimethylsphingosine and FTY720 inhibit the SK1 form but activate the SK2 form of sphingosine kinase from rat heart. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2007, 21, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, F.; Lim, K.G.; Loveridge, C.; Long, J.; Pitson, S.M.; Tigyi, G.; Bittman, R.; Pyne, S.; Pyne, N.J. FTY720 and (S)-FTY720 vinylphosphonate inhibit sphingosine kinase 1 and promote its proteasomal degradation in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle, breast cancer and androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. Cell. Signal. 2010, 22, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Weert, M.; Stella, L. Fluorescence quenching and ligand binding: A critical discussion of a popular methodology. J. Mol. Struct. 2011, 998, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.-L.; Ai, S.-M.; Liang, J.; Sang, P.; Ji, X.-L.; Liu, S.-Q. Insights into protein–ligand interactions: Mechanisms, models, and methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, C.H.; Holloway, M.K. Thermodynamics of Ligand Binding and Efficiency. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Mohammad, T.; Khan, P.; Alajmi, M.F.; Hussain, A.; Rehman, M.T.; Hassan, M.I. Evaluation of ellagic acid as an inhibitor of sphingosine kinase 1: A targeted approach towards anticancer therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Mohammad, T.; Dahiya, R.; Roy, S.; Noman, O.M.A.; Alajmi, M.F.; Hussain, A.; Hassan, M.I. Evaluation of binding and inhibition mechanism of dietary phytochemicals with sphingosine kinase 1: Towards targeted anticancer therapy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, W.I.; Saba, J.D. S1P metabolism in cancer and other pathological conditions. Biochimie 2010, 92, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hatoum, D.; Haddadi, N.; Lin, Y.; Nassif, N.T.; McGowan, E.M. Mammalian sphingosine kinase (SphK) isoenzymes and isoform expression: Challenges for SphK as an oncotarget. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 36898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, W.L.; Lynch, K.R. Drugging sphingosine kinases. Acs Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, K.R.; Thorpe, S.B.; Santos, W.L. Sphingosine kinase inhibitors: A review of patent literature (2006–2015). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadianawala, M.; Shaik, A.; Hasija, N.; Vasu, A.K.; Datta, B. Sodium Cyanate Mediated Synthesis of Sulfonylurea and Sulfonyltriuret from Sulfonyl Chloride and Amine. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 2212–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luci, D.K.; Jameson, J.B.I.; Yasgar, A.; Diaz, G.; Joshi, N.; Kantz, A.; Markham, K.; Perry, S.; Kuhn, N.; Yeung, J.; et al. Synthesis and Structure-Activity Relationship Studies of 4-((2-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)amino)benzenesulfonamide Derivatives as Potent and Selective Inhibitors of 12-Lipoxygenase. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Saibaba, V.; Ravikumar, V.; Rudrawar, S.V.; Daga, P.; Rao, C.S.; Akhila, V.; Hegde, P.; Rao, Y.K. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2,3-diarylpyrazines and quinoxalines as selective COX-2 inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 1881–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelazeem, A.H.; Habash, M.; Maghrabi, I.A.; Taha, M.O. Synthesis and evaluation of novel diphenylthiazole derivatives as potential anti-inflammatory agents. Med. Chem. Res. 2015, 24, 3681–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Khan, F.I.; Roy, S.; Anwar, S.; Dahiya, R.; Alajmi, M.F.; Hussain, A.; Rehman, M.T.; Lai, D.; Hassan, M.I. Functional implications of pH-induced conformational changes in the Sphingosine kinase 1. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 225, 117453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boaz, H.; Rollefson, G. The quenching of fluorescence. Deviations from the Stern-Volmer law. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 72, 3435–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, P.; Rahman, S.; Queen, A.; Manzoor, S.; Naz, F.; Hasan, G.M.; Luqman, S.; Kim, J.; Islam, A.; Ahmad, F.; et al. Elucidation of Dietary Polyphenolics as Potential Inhibitor of Microtubule Affinity Regulating Kinase 4: In silico and in vitro Studies. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahiya, R.; Mohammad, T.; Gupta, P.; Haque, A.; Alajmi, M.F.; Hussain, A.; Hassan, M.I. Molecular interaction studies on ellagic acid for its anticancer potential targeting pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 3. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 23302–23315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, P.; Queen, A.; Mohammad, T.; Smita; Khan, N.S.; Hafeez, Z.B.; Hassan, M.I.; Ali, S. Identification of alpha-Mangostin as a Potential Inhibitor of Microtubule Affinity Regulating Kinase 4. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2252–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahiya, R.; Mohammad, T.; Roy, S.; Anwar, S.; Gupta, P.; Haque, A.; Khan, P.; Kazim, S.N.; Islam, A.; Ahmad, F.; et al. Investigation of inhibitory potential of quercetin to the pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 3: Towards implications in anticancer therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, S.; Kar, R.K.; Haque, M.A.; Dahiya, R.; Gupta, P.; Islam, A.; Ahmad, F.; Hassan, M.I. Effect of pH on the structure and function of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 3: Combined spectroscopic and MD simulation studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLano, W. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.2 r3pre; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Biovia, D.S. Discovery studio modeling environment. San Diego Dassault Systèmes 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, T.; Khan, F.I.; Lobb, K.A.; Islam, A.; Ahmad, F.; Hassan, M.I. Identification and evaluation of bioactive natural products as potential inhibitors of human microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 (MARK4). J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 37, 1813–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, A.A.; Mohammad, T.; Hasan, G.M.; Hassan, M. Advancements in docking and molecular dynamics simulations towards ligand-receptor interactions and structure-function relationships. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1755–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Khan, F.I.; Mohammad, T.; Lan, D.; Hassan, M.; Wang, Y. Identification and Evaluation of Inhibitors of Lipase from Malassezia restricta using Virtual High-Throughput Screening and Molecular Dynamics Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
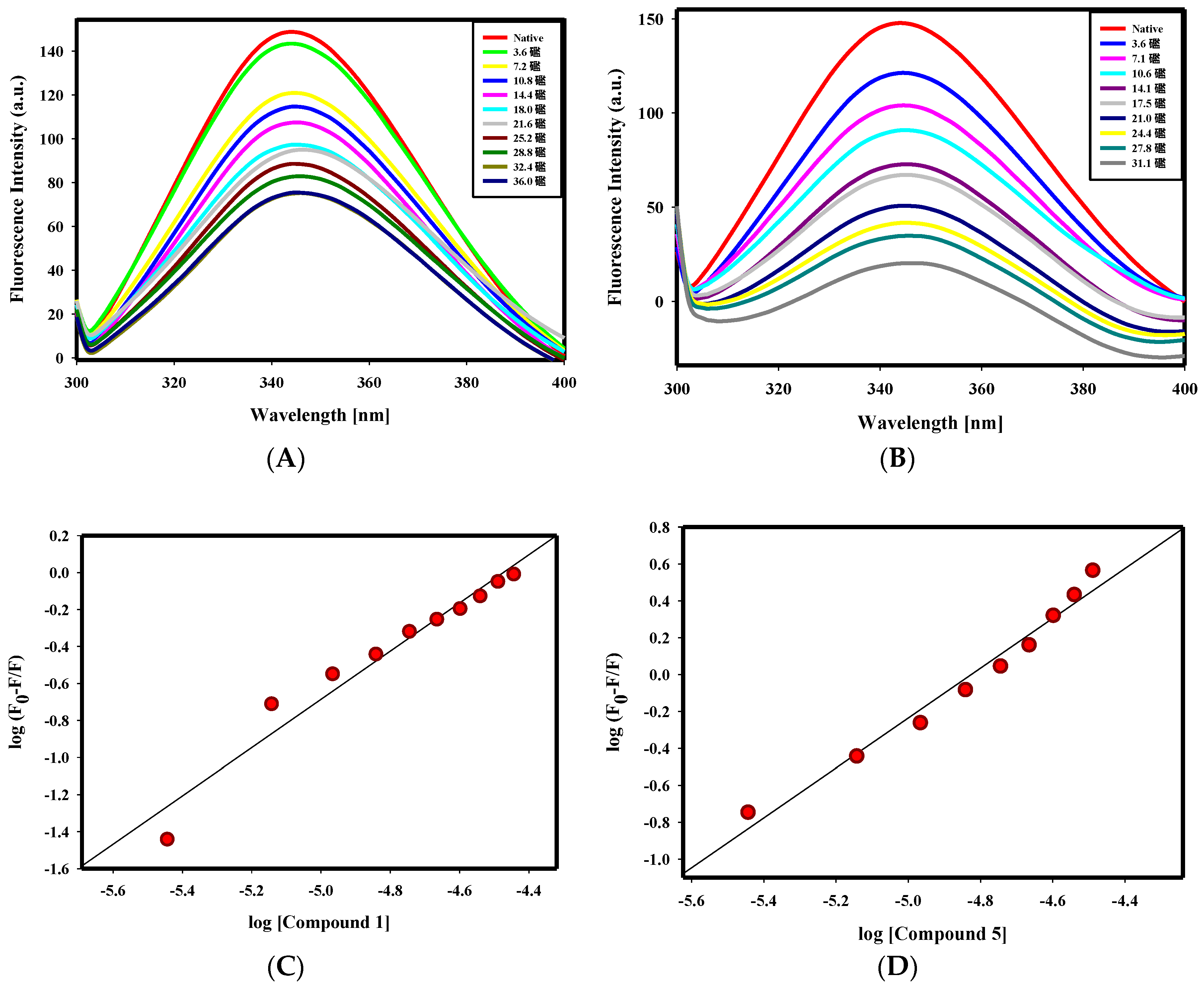
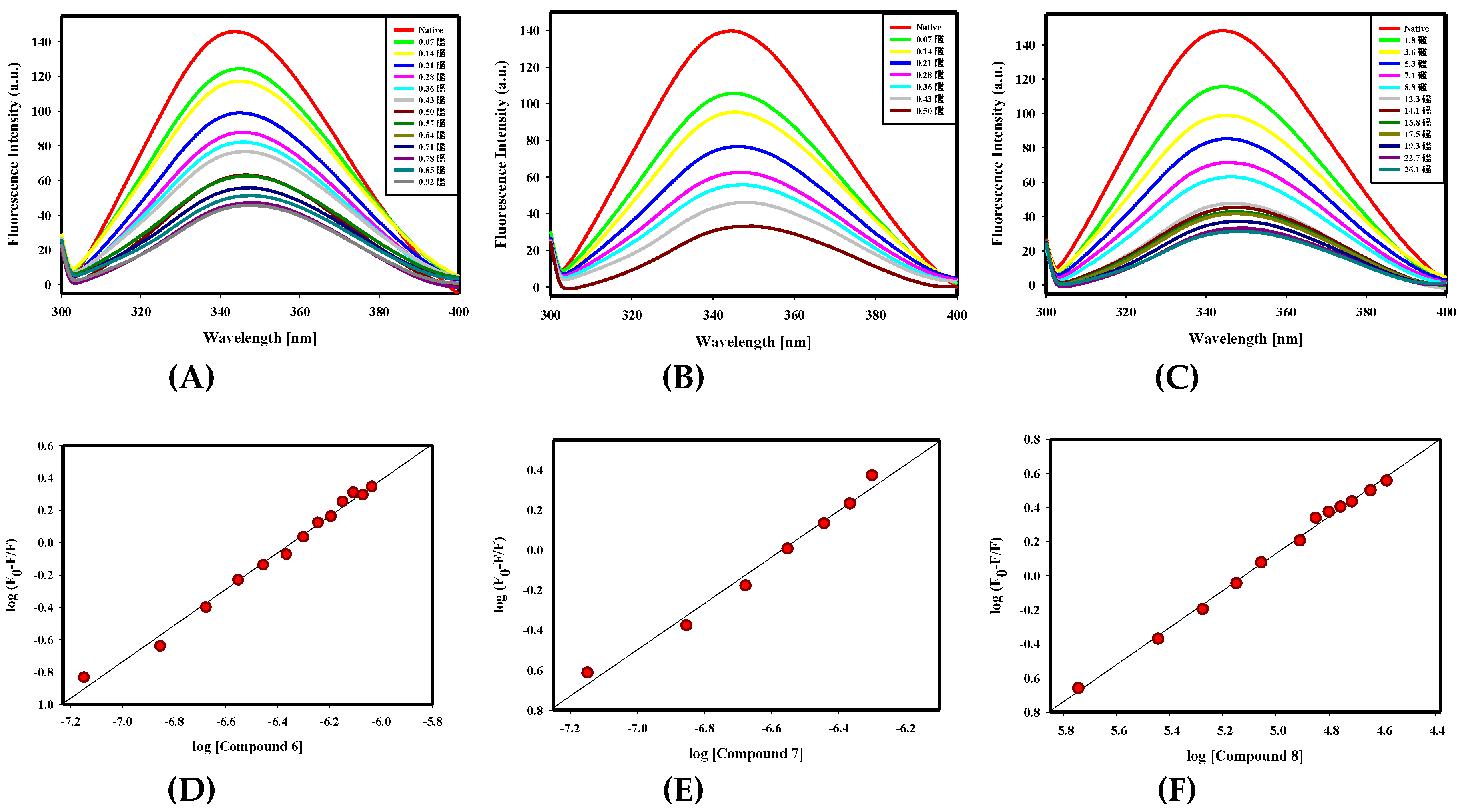

| S. No. | Compound ID | Structure | Predicted Affinity ΔG € (kcal/mol) | ¥ Binding Affinity Constant (Ka), M−1 | ¥ Number of Binding Sites (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Compound 1 | 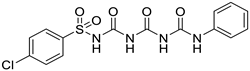 | −9.3 | 6.81 × 105 | 1.3 |
| 2. | Compound 2 | 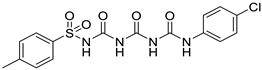 | −9.6 | 2.71 × 104 | 1 |
| 3. | Compound 3 |  | −8.9 | 3.75 × 104 | 1 |
| 4. | Compound 4 | 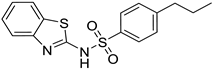 | −8.6 | 1.34 × 104 | 0.9 |
| 5. | Compound 5 | 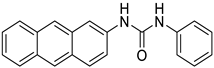 | −10.7 | 1.58 × 106 | 1.3 |
| 6. | Compound 6 | 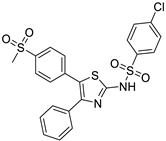 | −8.5 | 1.32 × 107 | 1.1 |
| 7. | Compound 7 | 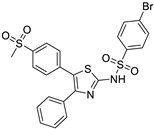 | −8.7 | 3.9 × 107 | 1.2 |
| 8. | Compound 8 | 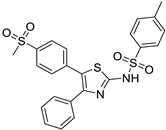 | −8.4 | 3.52 × 105 | 1 |
| 9. | Compound 9 | 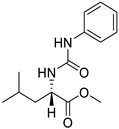 | −6.4 | 9.43 × 102 | 0.6 |
| 10. | Compound 10 | 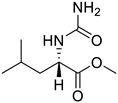 | −5.8 | NA | NA |
| 11. | Compound 11 |  | −5.2 | NA | NA |
| 12. | * PF-543 |  | −9.7 | NA | NA |
| Complex | Number of Binding Sites, N | Association Constant Ka, M−1 | Dissociation Constant KD, µM | Enthalpy Change ΔH, cal/moL | Entropy Change ΔS, cal/mol/deg | ΔG (Free Energy Change), kcal/mol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound 1 | 2 | Ka1 = 1.63 × 104 ± 9.1 × 102 | KD1 = 61.3 | ΔH1 = −5204 ± 265 | ΔS1 = 1.82 | ΔG1 = −5.75 |
| Ka2 = 3.67 × 103 ± 3.0 × 102 | KD2 = 272.4 | ΔH2 = −1.909 × 104 ± 1.73 × 103 | ΔS2 = −47.7 | ΔG2 = −4.88 | ||
| Compound 7 | 4 | Ka1 = 4.79 × 104 ± 3.8 × 103 | KD1 = 20.8 | ΔH1 = −608.7 ± 59.9 | ΔS1 = 19.4 | ΔG1 = −6.39 |
| Ka2 = 1.81 × 105 ± 6.9 × 103 | KD2 = 5.5 | ΔH2 = −934.5 ± 97 | ΔS2 = 20.9 | ΔG2 = −7.16 | ||
| Ka3 = 1.19 × 104 ± 4.6 × 102 | KD3 = 84 | ΔH3 = 277.1 ± 227 | ΔS3 = 19.6 | ΔG3 = −5.56 | ||
| Ka4 = 4.40 × 103 ± 1.2 × 102 | KD4 = 227.3 | ΔH4 = −1.898× 104 ± 569 | ΔS4 = −47.0 | ΔG4 = −4.97 |
| S. No. | Compound ID | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Compound 1 | 1.82 ± 0.06 |
| 2. | Compound 2 | 14.69 ± 0.02 |
| 3. | Compound 5 | 0.24 ± 0.02 |
| 4. | Compound 6 | 2.94 ± 0.07 |
| 5. | Compound 7 | 0.14 ± 0.01 |
| 6. | Compound 8 | 10.91 ± 0.02 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roy, S.; Mahapatra, A.D.; Mohammad, T.; Gupta, P.; Alajmi, M.F.; Hussain, A.; Rehman, M.T.; Datta, B.; Hassan, M.I. Design and Development of Novel Urea, Sulfonyltriurea, and Sulfonamide Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of Sphingosine Kinase 1. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13060118
Roy S, Mahapatra AD, Mohammad T, Gupta P, Alajmi MF, Hussain A, Rehman MT, Datta B, Hassan MI. Design and Development of Novel Urea, Sulfonyltriurea, and Sulfonamide Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of Sphingosine Kinase 1. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(6):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13060118
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoy, Sonam, Amarjyoti Das Mahapatra, Taj Mohammad, Preeti Gupta, Mohamed F. Alajmi, Afzal Hussain, Md. Tabish Rehman, Bhaskar Datta, and Md. Imtaiyaz Hassan. 2020. "Design and Development of Novel Urea, Sulfonyltriurea, and Sulfonamide Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of Sphingosine Kinase 1" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 6: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13060118
APA StyleRoy, S., Mahapatra, A. D., Mohammad, T., Gupta, P., Alajmi, M. F., Hussain, A., Rehman, M. T., Datta, B., & Hassan, M. I. (2020). Design and Development of Novel Urea, Sulfonyltriurea, and Sulfonamide Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of Sphingosine Kinase 1. Pharmaceuticals, 13(6), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13060118