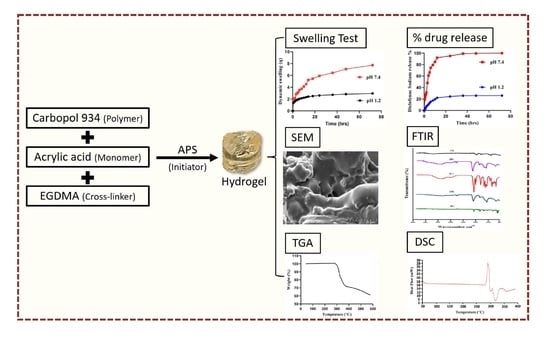
Using Carbomer-Based Hydrogels for Control the Release Rate of Diclofenac Sodium: Preparation and In Vitro Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
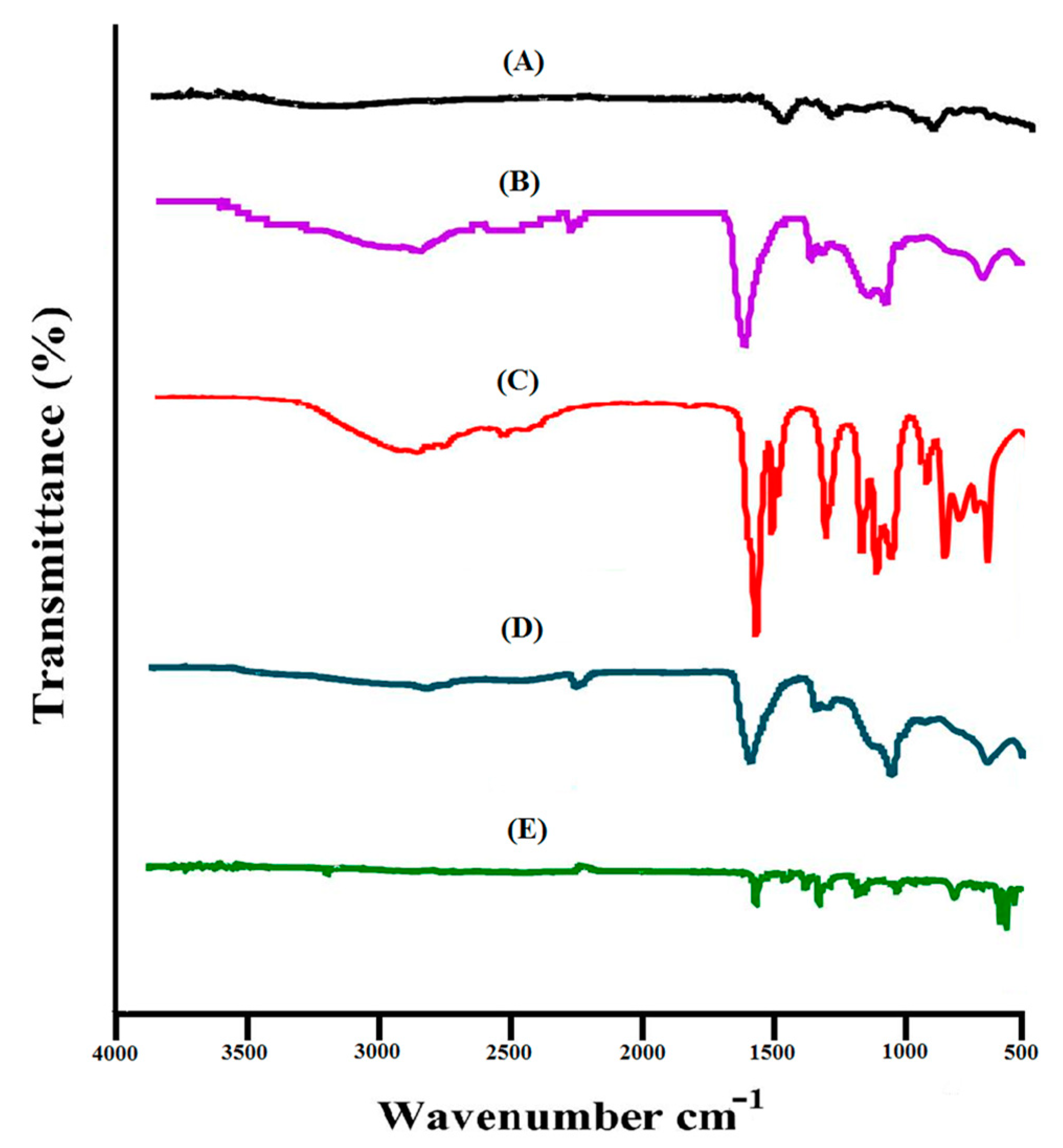
2.1. Analysis of FTIR
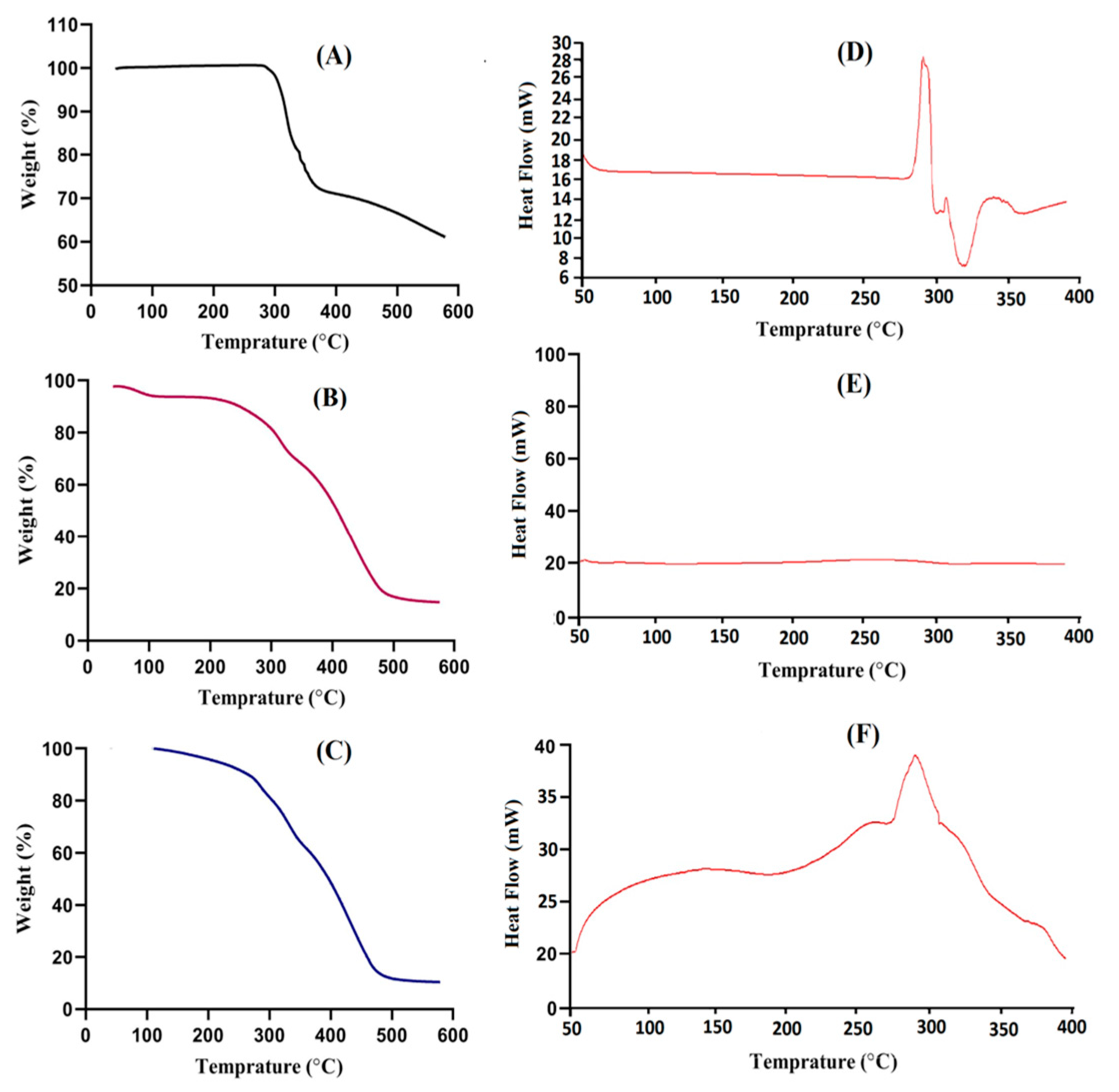
2.2. Thermal Analysis
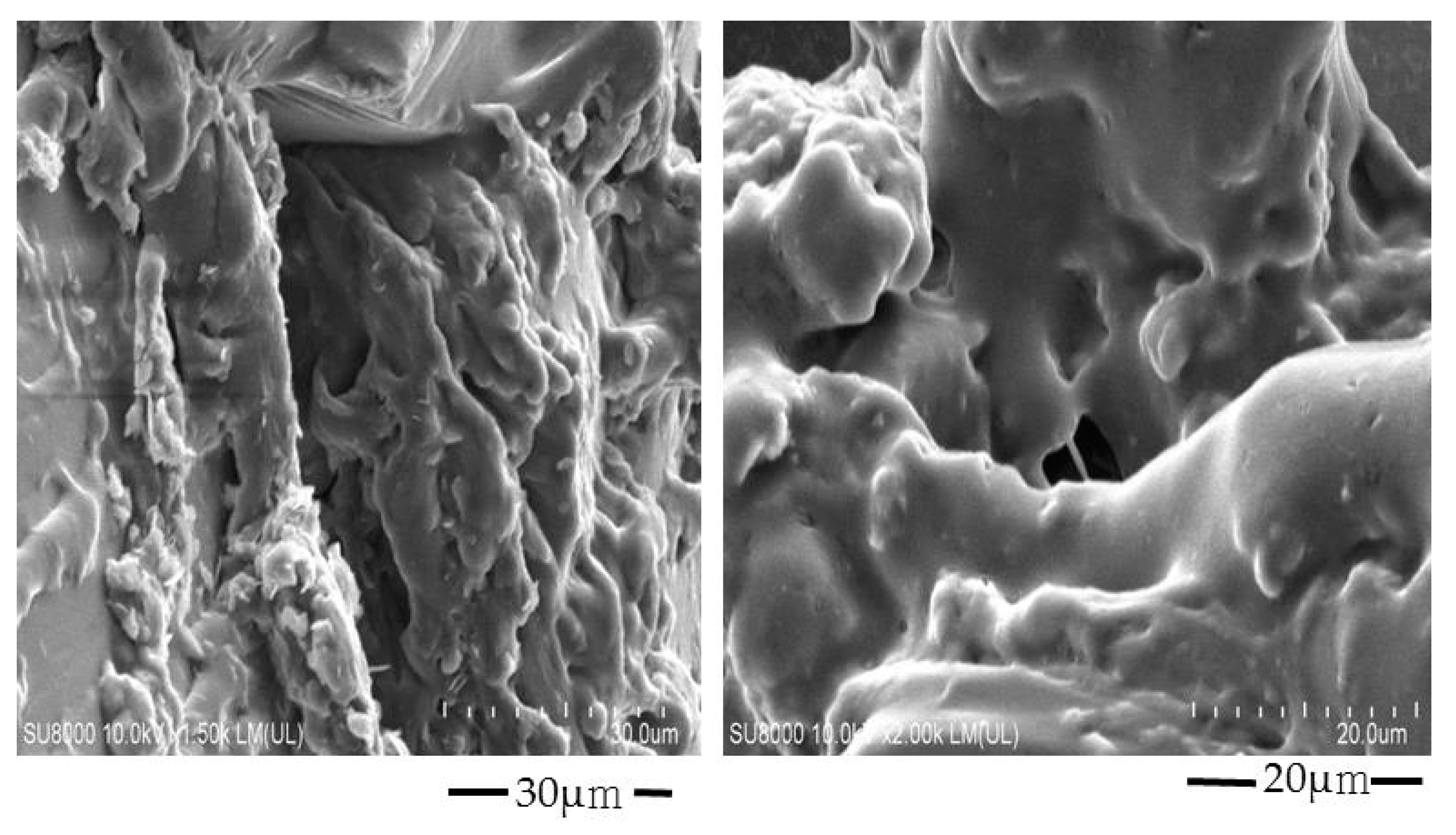
2.3. Scanning of Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
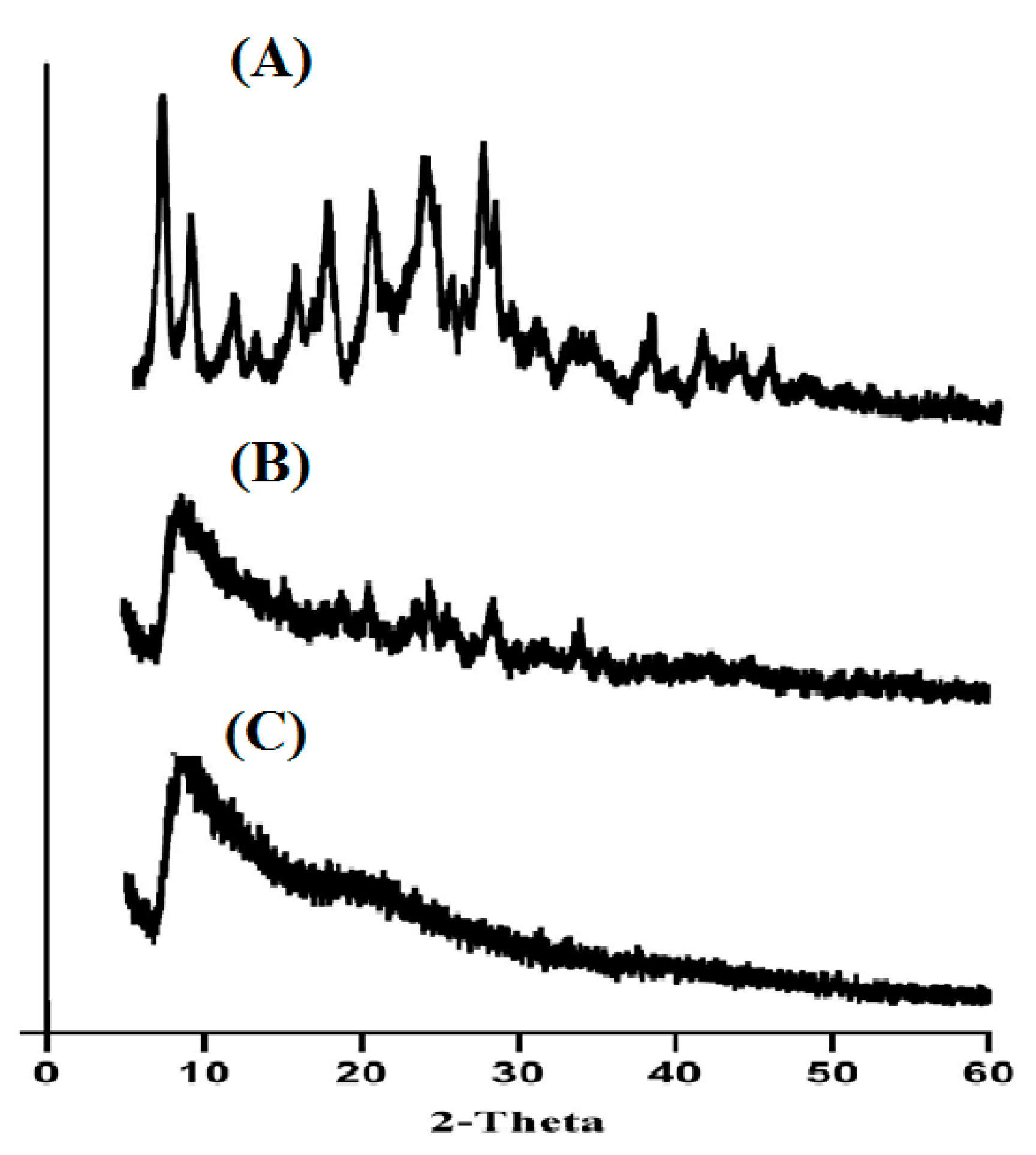
2.4. Powder X-Ray Diffractometry (PXRD) Analysis
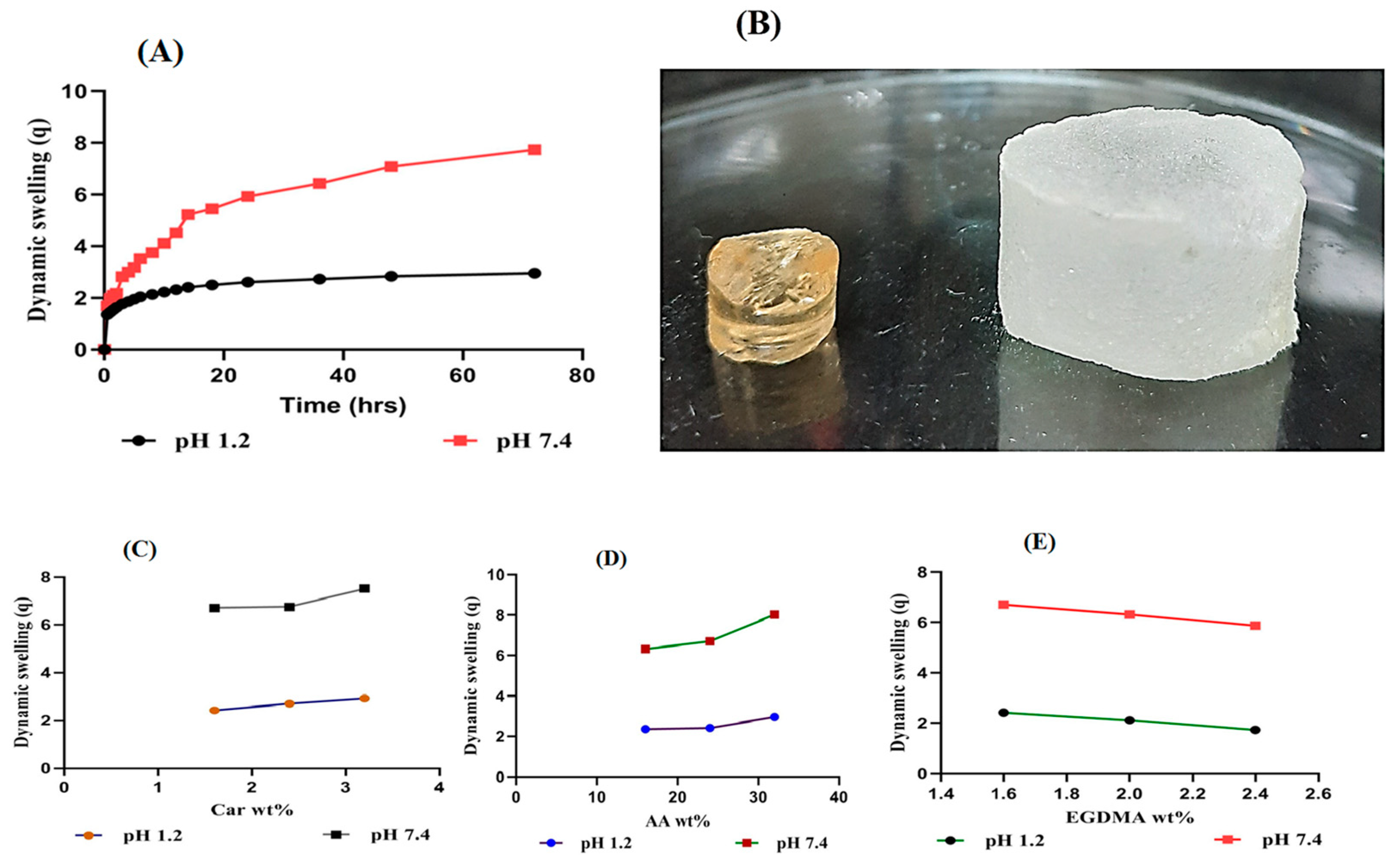
2.5. Dynamic Swelling
2.5.1. Response of pH on Dynamic Swelling
2.5.2. Influence of Carbopol/AA/and Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate (EGDMA) on Swelling
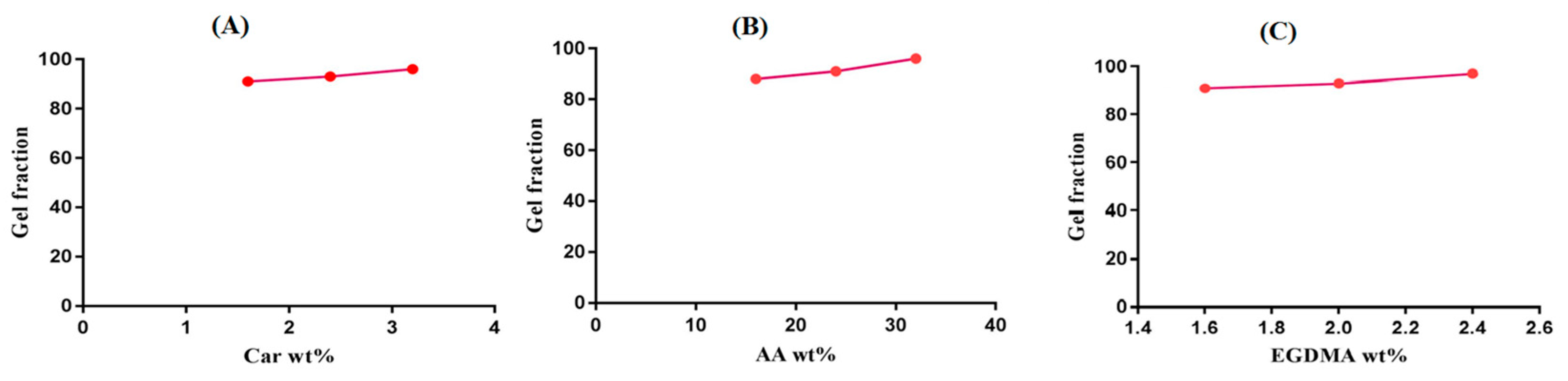
2.6. Sol–Gel Alysis
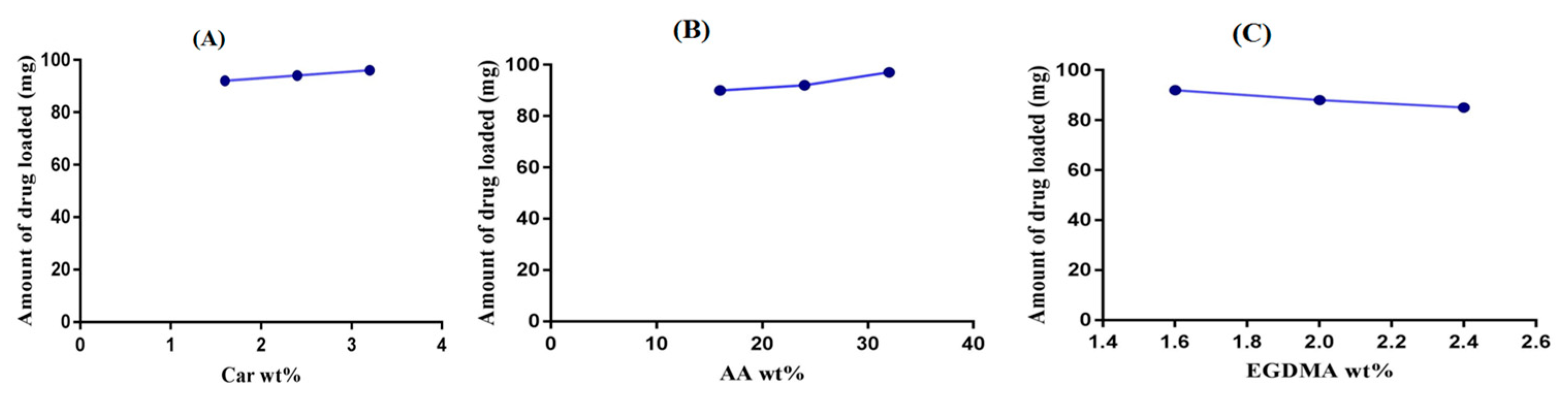
2.7. Drug Loading Analysis
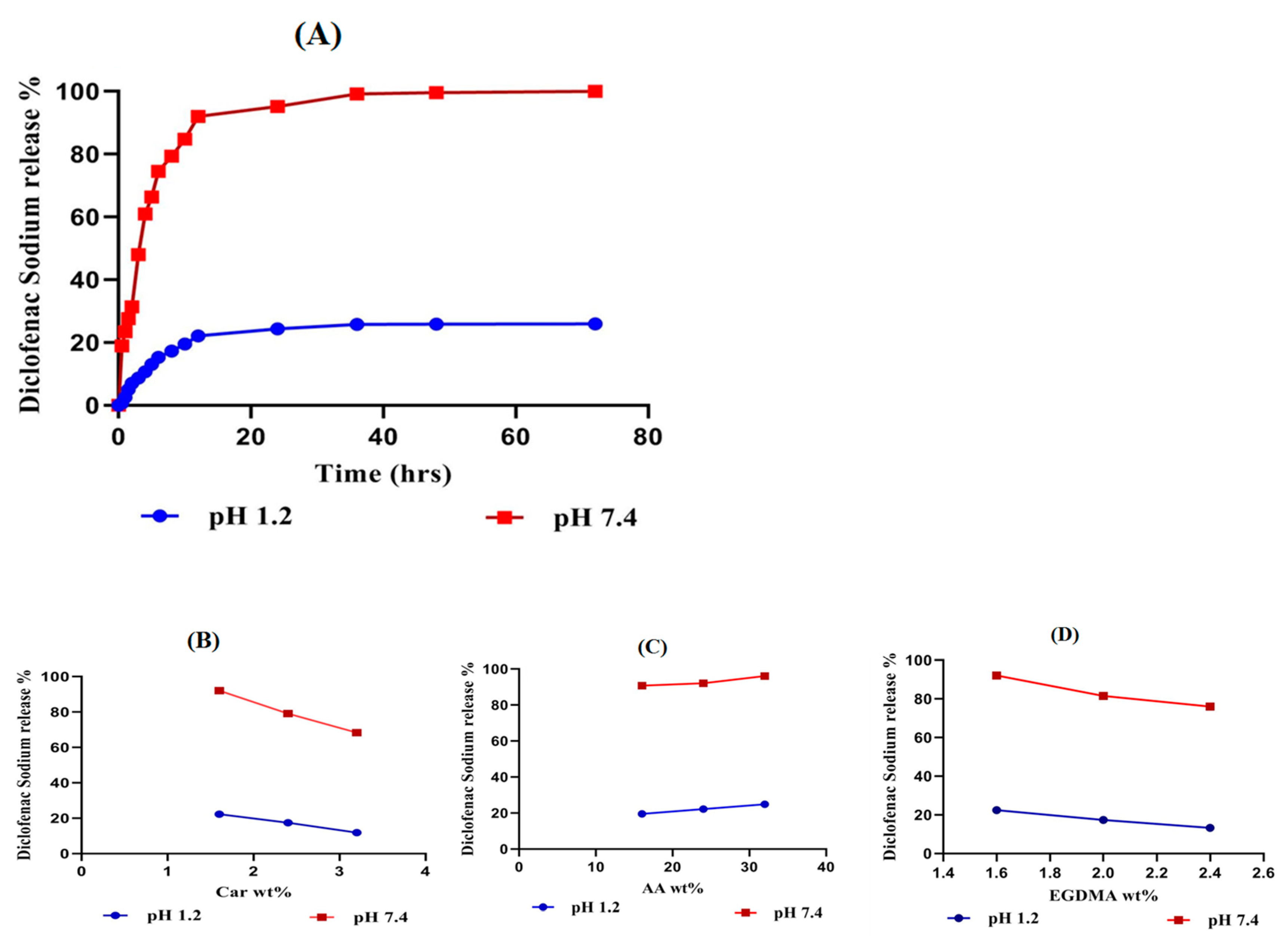
2.8. In-Vitro Drug Release Studies
2.8.1. Influence of pH on Drug Release
2.8.2. Influence of Carbopol/AA/and EGDMA on Drug Release
2.9. Release Kinetic of DS
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Fabrication of Car934-g-poly (acrylic acid) Hydrogels
3.2.2. FTIR Analysis
3.2.3. Thermal Analysis
3.2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
3.2.5. PXRD Analysis
3.2.6. Dynamic Swelling Studies
- q = dynamic swelling,
- W1 = initial weight (before swelling)
- and W2 = final weight (after swelling) at time t.
- M1 = weight of swollen hydrogels discs, while M2 = weight of dry hydrogel discs.
3.2.7. Determination of Sol–Gel Fraction
3.2.8. Drug Loading
3.2.9. In-Vitro Study
3.2.10. Release Kinetics of SD
3.2.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yar, M.; Shahzad, S.; Siddiqi, S.A.; Mahmood, N.; Rauf, A.; Anwar, M.S.; Chaudhry, A.A.; Rehman, I.U. Triethyl orthoformate mediated a novel crosslinking method for the preparation of hydrogels for tissue engineering applications: Characterization and in vitro cytocompatibility analysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 56, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, H.S.; Ray, S.K. Controlled release of tinidazole and theophylline from chitosan based composite hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 106, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, F.; Othman, M.B.H.; Javed, F.; Ahmad, Z.; Akil, H.M. Classification, processing and application of hydrogels: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 57, 414–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabaharan, M. Prospective of guar gum and its derivatives as controlled drug delivery systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.; Gunn, J.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siepmann, J.; Siegel, R.A.; Rathbone, M.J. Fundamentals and Applications of Controlled Release Drug Delivery; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 77–105. [Google Scholar]
- Miyata, T.; Uragami, T.; Nakamae, K. Biomolecule-sensitive hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulijn, R.V.; Bibi, N.; Jayawarna, V.; Thornton, P.D.; Todd, S.; Mart, R.J.; Smith, A.M.; Gough, J. Bioresponsive hydrogels. Mater. Today 2007, 10, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, S.; Khaliq, S.; Islam, A.; Javeria, I.; Jamil, T.; Athar, M.M.; Shafiq, M.I.; Ghaffar, A. Injectable biopolymer based hydrogels for drug delivery applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, O.; Panchagnula, R. Polymers in drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2001, 5, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buenger, D.; Topuz, F.; Groll, J. Hydrogels in sensing applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1678–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, L. Temperature-responsive gels and thermogelling polymer matrices for protein and peptide delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1998, 31, 197–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Park, K. Environment-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 53, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettini, R.; Colombo, P.; Peppas, N.A. Solubility Effects on Drug Transport through Ph-Sensitive, Swelling-Controlled Release Systems-Transport of Theophylline and Metoclopramide Monohydrochloride. J. Control. Release 1995, 37, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogueri, L.R.; Singh, L.R.F.A.S. Smart Polymers for Controlled Delivery of Proteins and Peptides: A Review of Patents. Recent Patents Drug Deliv. Formul. 2009, 3, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaev, I. ’Smart’ polymers and what they could do in biotechnology and medicine. Trends Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.W.; Bagley, E.B. Tailoring closely packed gel–particle systems for use as thickening agents. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1977, 21, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Food Contact Materials, Enzymes and Processing Aids (CEP); Silano, V.; Baviera, J.M.B.; Bolognesi, C.; Brüschweiler, B.J.; Chesson, A.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Crebelli, R.; Gott, D.M.; Grob, K.; et al. Safety assessment of the active substance polyacrylic acid, sodium salt, cross-linked, for use in active food contact materials. EFSA J. 2018, 16, 05448. [Google Scholar]
- Mun, E.A.; Hannell, C.; Rogers, S.E.; Hole, P.; Williams, A.C.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. On the Role of Specific Interactions in the Diffusion of Nanoparticles in Aqueous Polymer Solutions. Langmuir 2014, 30, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, I.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Barkat, K. Preparation and characterization of alginate-PVA-based semi-IPN: Controlled release pH-responsive composites. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 1075–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.X.; Omer, A.; Hu, Z.-H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, D.; Ouyang, X.-K. Efficient adsorption of diclofenac sodium from aqueous solutions using magnetic amine-functionalized chitosan. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, R.; Bosch, B.; Brune, K.; Patrignani, P.; Young, C. Advances in NSAID Development: Evolution of Diclofenac Products Using Pharmaceutical Technology. Drugs 2015, 75, 859–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnihotri, S.M.; Vavia, P.R. Diclofenac-loaded biopolymeric nanosuspensions for ophthalmic application. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2009, 5, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, R.; Nagamani, R.; Panda, S. Formulation, in vitro Characterization and Stability Studies of Fast Dispersing Tablets of Diclofenac Sodium. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 094–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Chakraborti, C.K.; Behera, P.K.; Mishra, S.C. Characterization of mucoadhesive ciprofloxacin suspensions by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2011, 11, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, R.; Dadhani, B.; Ladani, R.; Baria, A.; Patel, J. Formulation, evaluation and optimization of stomach specific in situ gel of clarithromycin and metronidazole benzoate. Int. J. Drug Deliv. 2010, 2, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharram, M.A.; Khafagi, M.G. Application of FTIR spectroscopy for structural characterization of ternary poly(acrylic acid)–metal–poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) complexes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 1888–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, I.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Barkat, K.; Sohail, M. Cross-Linked Sodium Alginate-g-poly(Acrylic Acid) Structure: A Potential Hydrogel Network for Controlled Delivery of Loxoprofen Sodium. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2016, 37, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, V.; Madhusudhana, K.; Sashidhar, R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Khar, R.K.; Ahmed, F.J.; Diwan, P.V. Polyelectrolyte complexes of gum kondagogu and chitosan, as diclofenac carriers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, G.O.K.; Tan, Y.T.F.; Peh, K.K. Hydrophilic polymer solubilization on norfloxacin solubility in preparation of solid dispersion. Powder Technol. 2014, 256, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, M.-K.; Bhusal, P.; Choi, H.-K. Application of Carbopol/PVP interpolymer complex to prepare mucoadhesive floating granule. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2013, 36, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Yu, D.; Zhu, L.; Branford-White, C.; White, K.; Chatterton, N.P. Electrospun diclofenac sodium loaded Eudragit(R) L 100-55 nanofibers for colon-targeted drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 408, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.F.; Chiang, W.H. Swelling and drug-release behavior of the poly(AA-co-N-vinyl pyrrolidone)/chitosan interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 2135–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Saha, N.; Saha, P. Influence of temperature, pH and simulated biological solutions on swelling and structural properties of biomineralized (CaCO3) PVP–CMC hydrogel. Prog. Biomater. 2015, 4, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Dhiman, A. Functionalization of carbopol with NVP for designing antibiotic drug loaded hydrogel dressings for better wound management. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Res. 2019, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanum, H.; Ullah, K.; Murtaza, G.; Khan, S.A. Fabrication and in vitro characterization of HPMC-g-poly(AMPS) hydrogels loaded with loxoprofen sodium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, R.M.; Khan, M.U.; Mahmood, A.; Akram, M.R.; Minhas, M.U.; Qaisar, M.N.; Ali, M.R.; Ahmad, H.; Zaman, M. Synthesis of co-polymeric network of carbopol-g-methacrylic acid nanogels drug carrier system for gastro-protective delivery of ketoprofen and its evaluation. Polym. Technol. Mater. 2020, 59, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Ali, L.; Munir, A.; Khalid, I. Synthesis and Characterization of Graft PVA Composites for Controlled Delivery of Valsartan. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2014, 33, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar]
- Sharmin, N.; Elias-Al-Mamun, M.; Jalil, R.-U. A Novel Method to Study the Effect of pH and Excipients on Water Uptake and Swelling Behaviour of Carbopol Polymers. Bangl. Pharma. J. 2010, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sullad, A.G.; Manjeshwar, L.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Novel pH-Sensitive Hydrogels Prepared from the Blends of Poly(vinyl alcohol) with Acrylic Acid-graft-Guar Gum Matrixes for Isoniazid Delivery. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 7323–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caykara, T.; Turan, E. Effect of the amount and type of the crosslinker on the swelling behavior of temperature-sensitive poly(N-tert-butylacrylamide-co-acrylamide) hydrogels. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2006, 284, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teijón, C.; Olmo, R.; Blanco, M.D.; Teijón, J.M.; Romero, A. Effect of the crosslinking degree and the nickel salt load on the thermal decomposition of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogels and on the metal release from them. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 295, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teijón, J.; Trigo, R.; García, O.; Blanco, M. Cytarabine trapping in poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogels: Drug delivery studies. Biomaterials 1997, 18, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, B.; Gurruchaga, M.; Goni, I. Hydrogels Based on Graft-Copolymerization of Hema Bma Mixtures onto Soluble Gelatin-Swelling Behavior. Polymer 1995, 36, 2311–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, N.M.; Prabhu, P.; Charyulu, R.N.; Gulzar, M.A.; Subrahmanyam, E.V.S. Formulation and evaluation ofin situgels containing clotrimazole for oral candidiasis. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 71, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, T.; Ranjha, N.M.; Shahzad, Y. Swelling and Controlled Release of Tramadol Hydrochloride from a pH-Sensitive Hydrogel. Des. Monomers Polym. 2011, 14, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergunov, S.A.; Nam, I.K.; Mun, G.A.; Nurkeeva, Z.S.; Shaikhutdinov, E.M. Radiation synthesis and characterization of stimuli-sensitive chitosan–polyvinyl pyrrolidone hydrogels. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2005, 72, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, P.K.; Mohan, Y.M.; Sreeramulu, J.; Raju, K.M. Semi-IPNs of starch and poly(acrylamide-co-sodium methacrylate): Preparation, swelling and diffusion characteristics evaluation. React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, H.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Sohail, M.; Aamir, M.F. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid) Cross Linked Polymeric Network for the Delivery of Analgesic Agent. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2015, 37, 999–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, G.M.; Jiabi, Z. Formulation and in vitro evaluation of ibuprofen-carbopol® 974P-NF controlled release matrix tablets III: Influence of co-excipients on release rate of the drug. J. Control. Release 1998, 54, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, G.M. Studies on drug release kinetics from ibuprofen-carbomer hydrophilic matrix tablets: Influence of co-excipients on release rate of the drug. J. Control. Release 1999, 57, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanli, O.; Ay, N.; Isiklan, N. Release characteristics of diclofenac sodium from poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate and poly(vinyl alcohol)-grafted-poly(acrylamide)/sodium alginate blend beads. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 65, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.F.; Ranjha, N.M.; Hanif, M. Effect of ethylene glycol dimethacrylate on swelling and on metformin hydrochloride release behavior of chemically crosslinked pH–sensitive acrylic acid–polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 23, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maziad, N.A.; El-Hanouly, S.; Zied, E.; El Kelani, T.A.; Nasef, N.R. Radiation preparation of smart hydrogel has antimicrobial properties for controlled release of ciprofloxacin in drug delivery systems. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2015, 8, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Shoaib, M.H.; Tazeen, J.; Berardi, A.; Yousuf, R.I. Evaluation of drug release kinetics from ibuprofen matrix tablets using HPMC. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 19, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, A.; Ahmad, M.; Sarfraz, R.M.; Minhas, M.U.; Yaqoob, A. Formulation and in Vitro Evaluation of Acyclovir Loaded Polymeric Microparticles: A Solubility Enhancement Study. Acta Pol. Pharm.-Drug Res. 2016, 73, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Sarfraz, R.M.; Khan, H.U.; Mahmood, A.; Ahmad, M.; Maheen, S.; Sher, M. Formulation and Evaluation of Mouth Disintegrating Tablets of Atenolol and Atorvastatin. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 77, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Ahmad, M.; Sarfraz, R.M.; Minhas, M.U. Development of Acyclovir Loaded β-Cyclodextrin-g-Poly Methacrylic Acid Hydrogel Microparticles: An In Vitro Characterization. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2016, 37, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Sharma, N. Mechanistic Implication for Cross-Linking in Sterculia-Based Hydrogels and Their Use in GIT Drug Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2515–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Ali, L.; Khalid, I.; Rashid, H. Controlled delivery of valsartan by cross-linked polymeric matrices: Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 487, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmandnia, S.; Vasheghani-Farahani, E.; Nosrati, M.; Atyabi, F. Preparation and characterization of ketoprofen-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles made from beeswax and carnauba wax. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.M.H.; Khan, S.; Rehanullah, M.; Ranjha, N.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Chemically Cross-Linked Acrylic Acid/Gelatin Hydrogels: Effect of pH and Composition on Swelling and Drug Release. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Warnke, J.; Lyubchenko, Y.L. Nanoprobing of α-synuclein misfolding and aggregation with atomic force microscopy. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2011, 7, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppas, N.A.; Sahlin, J.J. A simple equation for the description of solute release. III. Coupling of diffusion and relaxation. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 57, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Formulation Code | Zero-Order (r2) | First-Order (r2) | Higuchi (r2) | Korsmeyer-Peppas | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (r2) | n | ||||
| CAAF-1 | 0.7149 | 0.9308 | 0.8949 | 0.9595 | 0.5306 |
| CAAF-2 | 0.8695 | 0.9631 | 0.9446 | 0.9601 | 0.5135 |
| CAAF-3 | 0.9647 | 0.9901 | 0.9842 | 0.9838 | 0.5213 |
| CAAF-4 | 0.7518 | 0.9118 | 0.9009 | 0.9604 | 0.5770 |
| CAAF-5 | 0.7149 | 0.9308 | 0.8949 | 0.9595 | 0.5306 |
| CAAF-6 | 0.6878 | 0.9522 | 0.8760 | 0.9424 | 0.5129 |
| CAAF-7 | 0.7149 | 0.9308 | 0.8949 | 0.9595 | 0.5306 |
| CAAF-8 | 0.9116 | 0.9669 | 0.9499 | 0.9818 | 0.6605 |
| CAAF-9 | 0.9151 | 0.9635 | 0.9542 | 0.9877 | 0.7413 |
| Formulation Code (100 g) | Polymer (Carbopol 934) (g) | Monomer (Acrylic Acid) (g) | Initiator (APS) (g) | Crosslinker (EGDMA) (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAAF-1 | 1.6 | 24 | 0.4 | 1.6 |
| CAAF-2 | 2.4 | 24 | 0.4 | 1.6. |
| CAAF-3 | 3.2 | 24 | 0.4 | 1.6 |
| CAAF-4 | 1.6 | 16 | 0.4 | 1.6 |
| CAAF-5 | 1.6 | 24 | 0.4 | 1.6 |
| CAAF-6 | 1.6 | 32 | 0.4 | 1.6 |
| CAAF-7 | 1.6 | 24 | 0.4 | 1.6 |
| CAAF-8 | 1.6 | 24 | 0.4 | 2.0 |
| CAAF-9 | 1.6 | 24 | 0.4 | 2.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suhail, M.; Wu, P.-C.; Minhas, M.U. Using Carbomer-Based Hydrogels for Control the Release Rate of Diclofenac Sodium: Preparation and In Vitro Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110399
Suhail M, Wu P-C, Minhas MU. Using Carbomer-Based Hydrogels for Control the Release Rate of Diclofenac Sodium: Preparation and In Vitro Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(11):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110399
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuhail, Muhammad, Pao-Chu Wu, and Muhammad Usman Minhas. 2020. "Using Carbomer-Based Hydrogels for Control the Release Rate of Diclofenac Sodium: Preparation and In Vitro Evaluation" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 11: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110399
APA StyleSuhail, M., Wu, P.-C., & Minhas, M. U. (2020). Using Carbomer-Based Hydrogels for Control the Release Rate of Diclofenac Sodium: Preparation and In Vitro Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals, 13(11), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110399