Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Taste-Masking Effect of Selected Flavors on Dental Lidocaine HCl Injection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
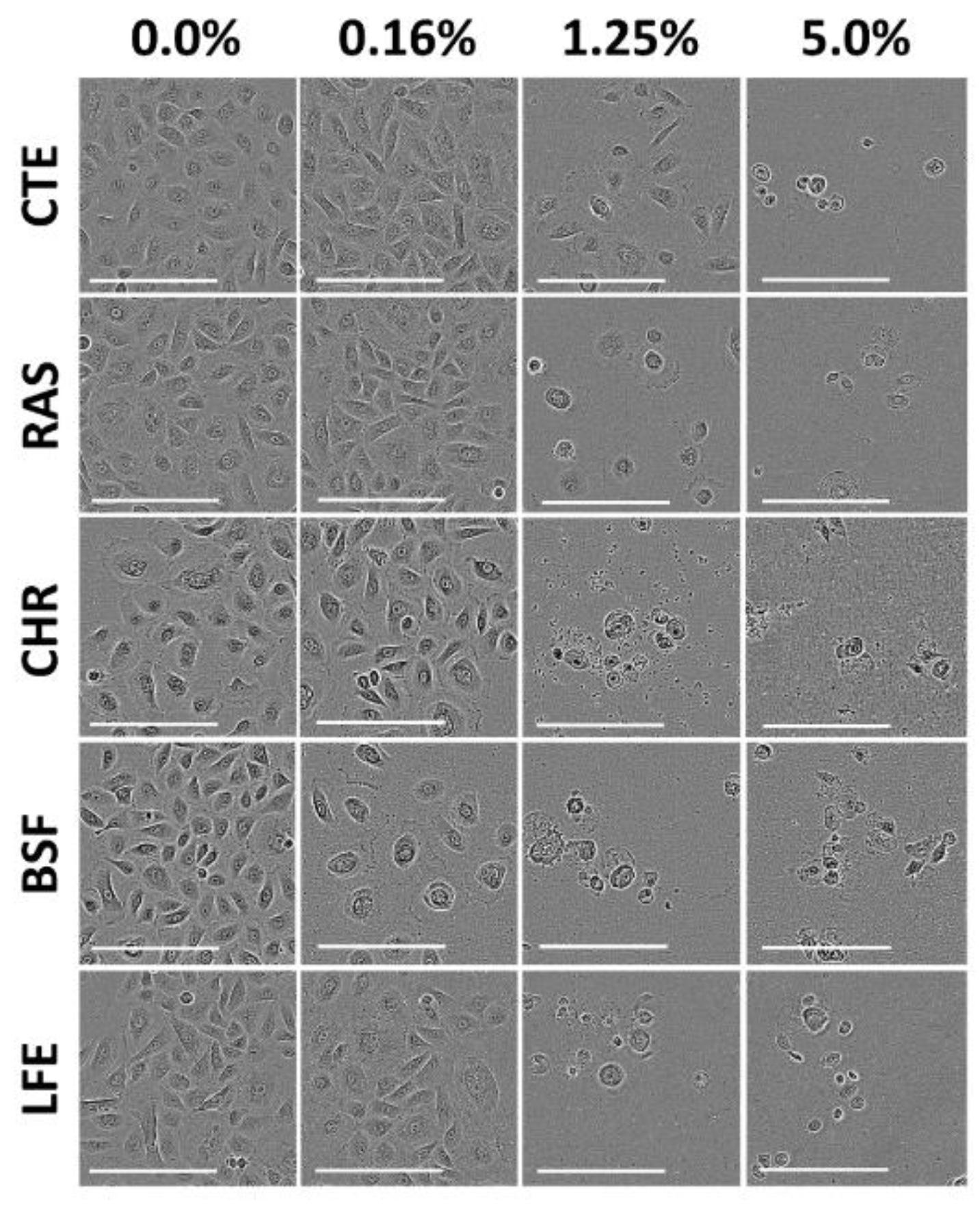
3.2. Cytotoxicity of Selected Flavors in Primary Gingival Keratinocytes (PGK)
3.3. Preparation of Samples for Taste Analysis
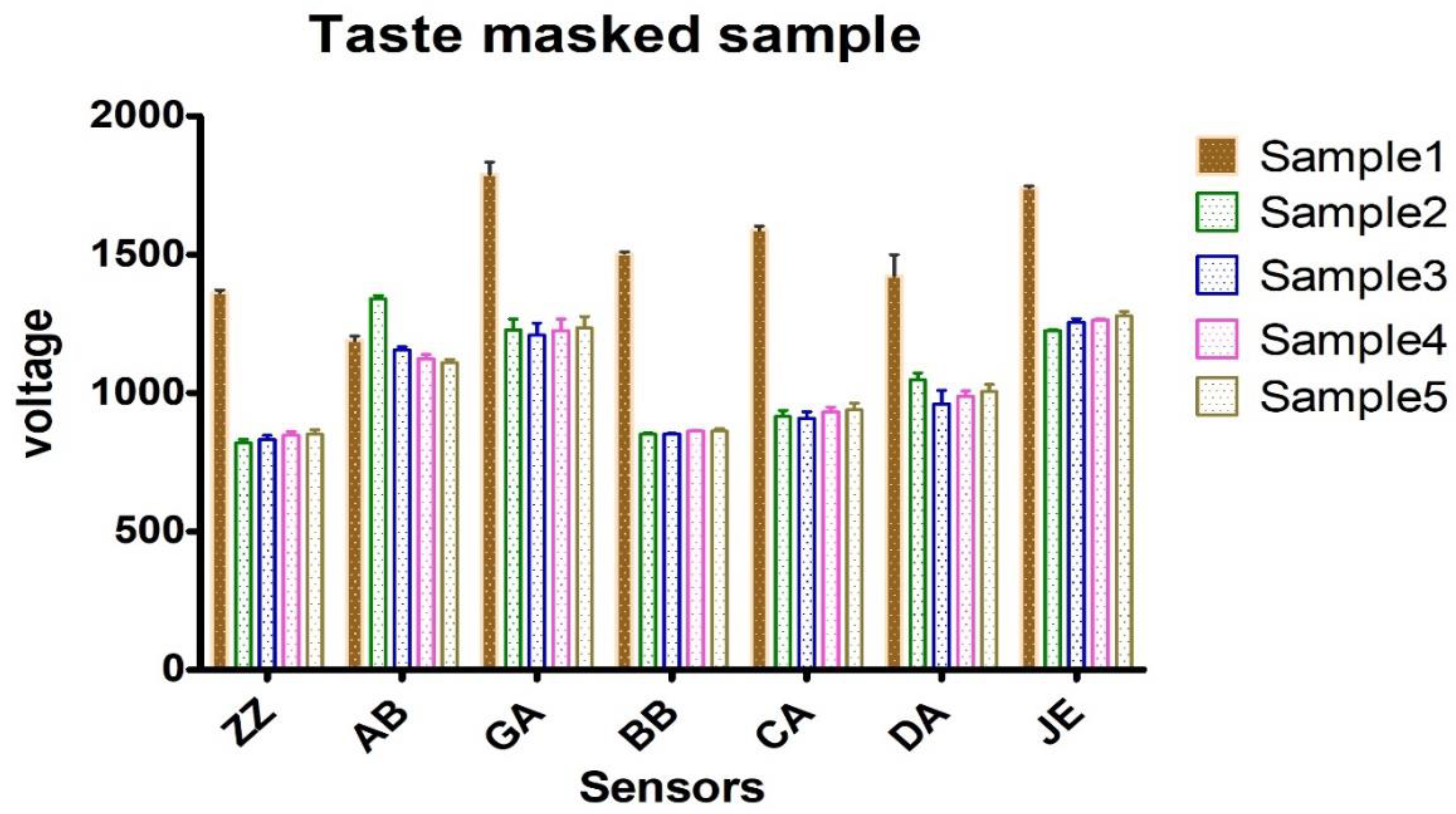
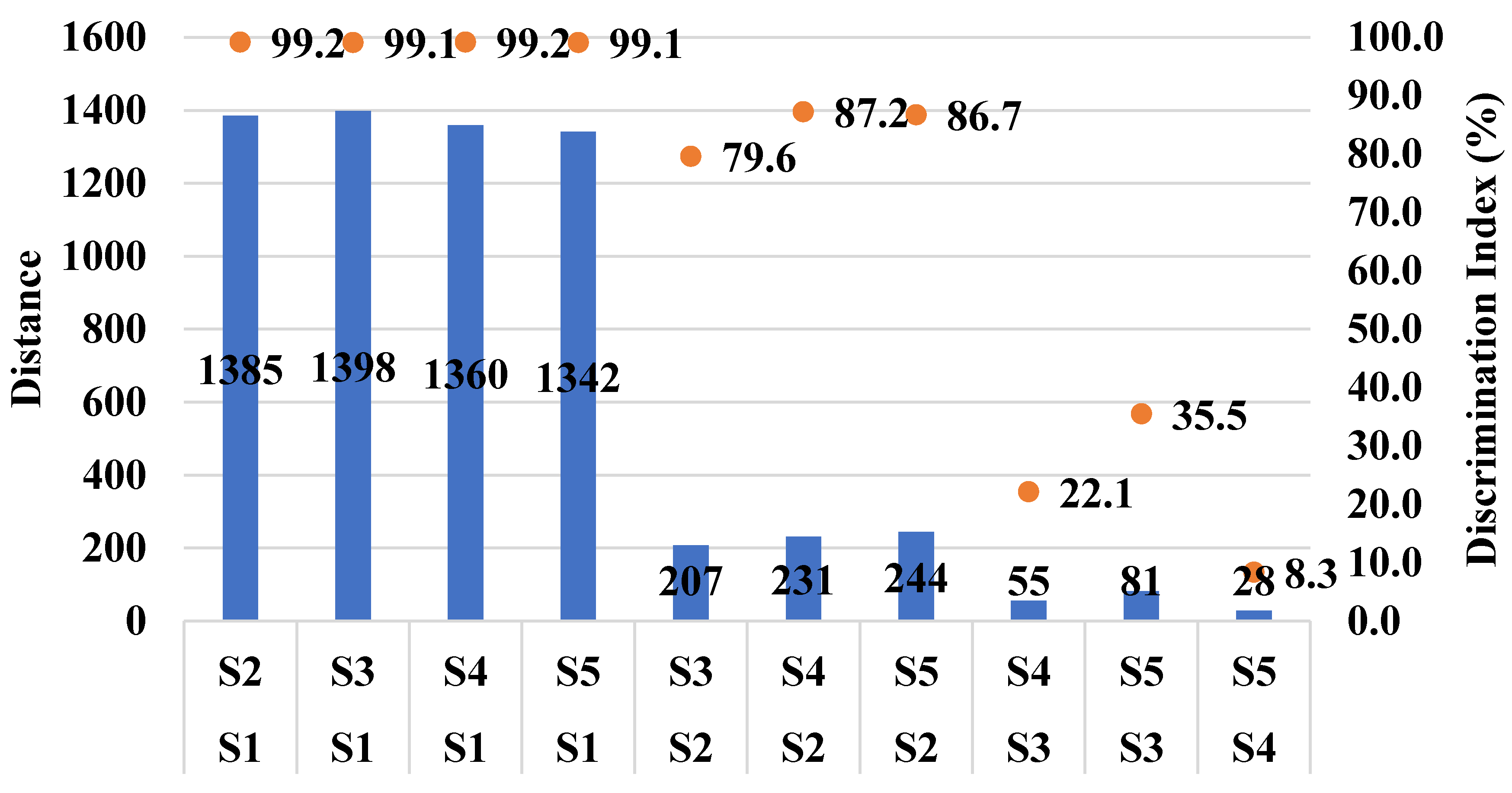
3.4. Taste Analysis Using Astree Electronic Tongue (ETongue)
3.5. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fulzele, S.; Rieschl, S. Taste-masking—Pharmaceutical taste-masking technologies. Drug Dev. Deliv. 2015, 15. Available online: https://drug-dev.com/taste-masking-pharmaceutical-taste-masking-technologies/ (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Wei, Y.; Nedley, M.P.; Bhaduri, S.B.; Bredzinski, X.; Boddu, S.H.S. Masking the bitter taste of injectable lidocaine HCl formulation for dental procedures. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, D.A. An update on local anesthetics in dentistry. J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2002, 68, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malamed, S.F. Handbook of Local Anesthesia, 4th ed.; Mosby: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1997; 327p. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Wun, E.; Stern, A. Current treatments and advances in pain and anxiety management. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 55, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.D.; Summers, A.; Williams, D.J. A nomogram to calculate the maximum dose of local anaesthetic in a paediatric dental setting. Br. Dent. J. 2015, 218, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, S.G.; Lalonde, D.H. How acidic is the lidocaine we are injecting, and how much bicarbonate should we add? Can. J. Plast. Surg. 2012, 20, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebedyeva, I.O.; Oliferenko, A.A.; Oliferenko, P.V.; Hromas, R.A.; Neubert, J.K.; Caudle, R.M.; Wickersham, J.; Castleman, W.L.; Altschuler, G.I.; Ostrov, D.A. Ionic conjugates of lidocaine and sweeteners as better tasting local anesthetics for dentistry. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 8492–8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drašković, M.; Medarević, D.; Aleksić, I.; Parojčić, J. In vitro and in vivo investigation of taste-masking effectiveness of Eudragit E PO as drug particle coating agent in orally disintegrating tablets. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panraksa, P.; Boonsermsukcharoen, K.; Hwang, K.-M.; Park, E.-S.; Jantrawut, P. Taste Masking of Nizatidine Using Ion-Exchange Resins. Processes 2019, 7, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautala, J.; Heinämäki, J.; Hietala, S.; Juppo, A.M. Development of novel flavored Eudragit® E films for feline minitablet coatings. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thawabteh, A.; Lelario, F.; Scrano, L.; Bufo, S.A.; Nowak, S.; Behrens, M.; Di Pizio, A.; Niv, M.Y.; Karaman, R. Bitterless guaifenesin prodrugs—Design, synthesis, characterization, in vitro kinetics, and bitterness studies. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 93, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faisal, W.; Farag, F.; Abdellatif, A.A.; Abbas, A. Taste masking approaches for medicines. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehleber, J.; Ross, N. Taste Masking of Anesthetics and Analgesics. U.S. Patent 14/211,000, 25 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hough, W.L.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquids then and now: from solvents to materials to active pharmaceutical ingredients. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 80, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Muthumalage, T.; Rahman, I. Mechanisms of toxicity and biomarkers of flavoring and flavor enhancing chemicals in emerging tobacco and non-tobacco products. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 288, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amawi, H.; Hussein, N.A.; Karthikeyan, C.; Manivannan, E.; Wisner, A.; Williams, F.E.; Samuel, T.; Trivedi, P.; Ashby, C.R., Jr.; Tiwari, A.K. HM015k, a Novel Silybin Derivative, Multi-Targets Metastatic Ovarian Cancer Cells and Is Safe in Zebrafish Toxicity Studies. Front. Pharm. 2017, 8, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boddu, S.H.S.; Jwala, J.; Chowdhury, M.R.; Mitra, A.K. In vitro evaluation of a targeted and sustained release system for retinoblastoma cells using Doxorubicin as a model drug. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. Off. J. Assoc. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 26, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohi, H.; Sultana, Y.; Khar, R.K. Taste Masking Technologies in Oral Pharmaceuticals: Recent Developments and Approaches. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2004, 30, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vummaneni, V.; Nagpal, D. Taste masking technologies: an overview and recent updates. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Biomed. Sci. 2012, 3, 510–524. [Google Scholar]
- Bin Rohin, M.A.K.; Ridzwan, N.; Jumli, M.N.; Abd Hadi, N.; Johari, S.A.T.T.; Latif, A.Z.A. Cytotoxicity study and morphological changes of different extraction for Bismillah leaf (Vernonia amygdalina) in human glioblastoma multiforme cell line (U-87). Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 28. Available online: https://www.biomedres.info/biomedical-research/cytotoxicity-study-and-morphological-changes-of-different-extraction-for-bismillah-leaf-vernonia-amygdalina-in-human-glioblastoma-.html (accessed on 29 October 2020).
- Wanichpakorn, S.; Kedjarune-Laggat, U. Primary cell culture from human oral tissue: gingival keratinocytes, gingival fibroblasts and periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2010, 32, 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, G.S.; de Oliveira da Silva, S.I.; de Castro e Sousa, J.M.; Ferreira, P.M.P.; Peron, A.P. Cytotoxic and genotoxic potential of liquid synthetic food flavorings evaluated alone and in combination. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 35, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pérez-Esteve, É.; Lerma-García, M.J.; Fuentes, A.; Palomares, C.; Barat, J.M. Control of undeclared flavoring of cocoa powders by the determination of vanillin and ethyl vanillin by HPLC. Food Control 2016, 67, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malowicki, S.M.; Martin, R.; Qian, M.C. Volatile composition in raspberry cultivars grown in the Pacific Northwest determined by stir bar sorptive extraction—Gas chromatography—Mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4128–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malowicki, S.M.; Martin, R.; Qian, M.C. Comparison of sugar, acids, and volatile composition in raspberry bushy dwarf virus-resistant transgenic raspberries and the wild type ‘Meeker’ (Rubus Idaeus L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6648–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kośmider, L.; Sobczak, A.; Prokopowicz, A.; Kurek, J.; Zaciera, M.; Knysak, J.; Smith, D.; Goniewicz, M. Cherry-flavoured electronic cigarettes expose users to the inhalation irritant, Benzaldehyde. Thorax 2016, 71, 376–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalzadeh, L.; Ghafoori, H.; Sariri, R.; Rabuti, H.; Nasirzade, J.; Hasani, H.; Aghamaali, M.R. Cytotoxic effects of some common organic solvents on MCF-7, RAW-264.7 and human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Avicenna J. Med. Biochem. 2016, 4, e33453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
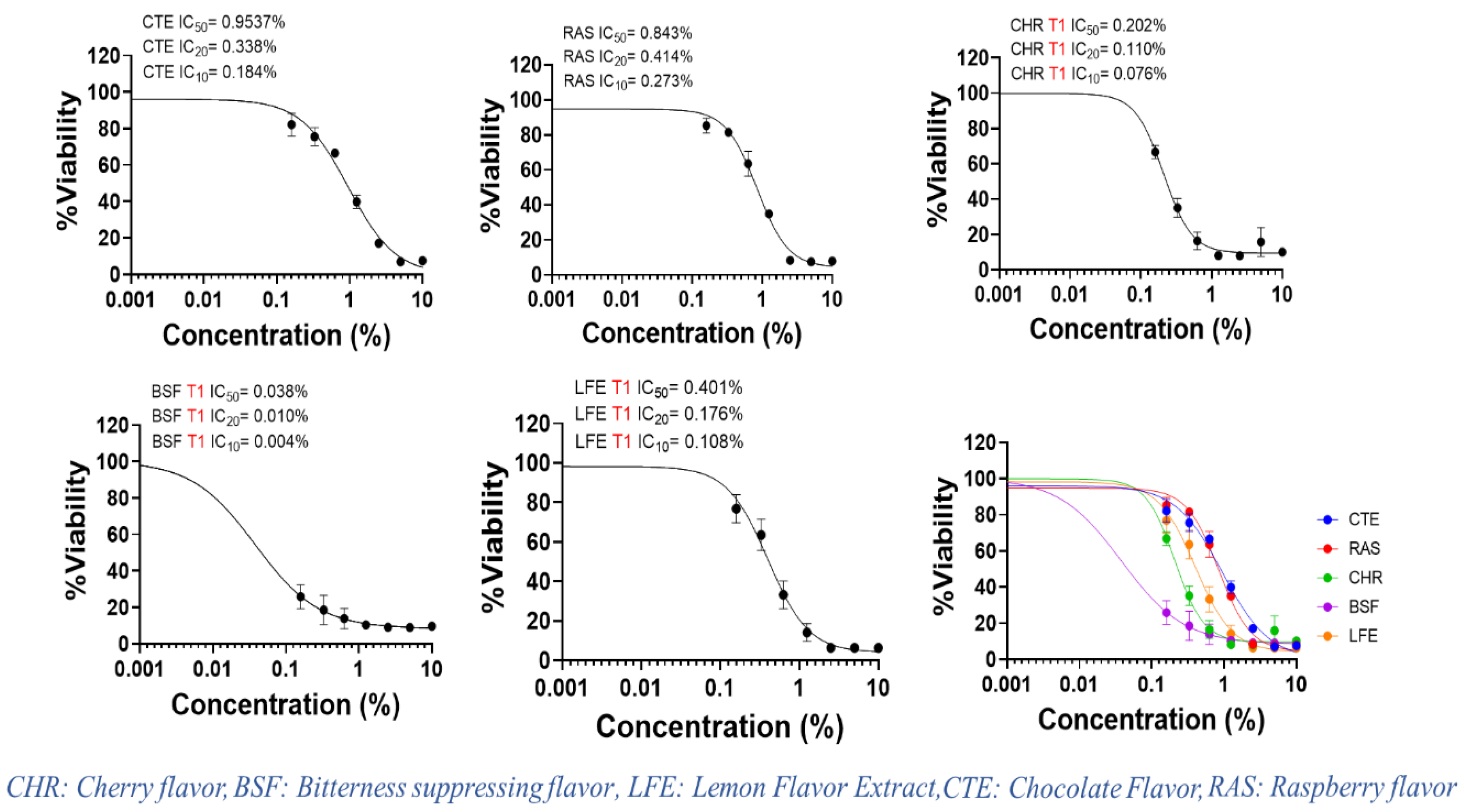


| Flavors | IC50 (mg/mL) | IC20 (mg/mL) | IC10 (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chocolate flavor (CTE) | 9.54 | 3.38 | 1.84 |
| Raspberry flavor (RAS) | 8.43 | 4.14 | 2.37 |
| Cherry flavor (CHR) | 2.21 | 0.86 | 0.49 |
| Bitter suppressing flavor (BSF) | 0.38 | 0.1 | 0.04 |
| Lemon flavor (LFE) | 4.01 | 1.76 | 1.08 |
| Sample Name | Code | SD | %RSD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 (control) | S1 | 20.1 | 1.3 |
| Sample 2 | S2 | 14.1 | 1.3 |
| Sample 3 | S3 | 17.9 | 1.7 |
| Sample 4 | S4 | 13.0 | 1.2 |
| Sample 5 | S5 | 17.0 | 1.6 |
| Sample Number | Lidocaine HCl/Epinephrine 2% | Sodium Saccharine (% w/v) | Chocolate Natural and Artificial Flavor (% v/v) | Raspberry Flavor Artificial (% v/v) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 (control) | Lidocaine/Epinephrine Injection 2% | - | - | - |
| Sample 2 | Lidocaine/Epinephrine Injection 2% | 0.09 | 0.338 | - |
| Sample 3 | Lidocaine/Epinephrine Injection 2% | 0.09 | 0.184 | |
| Sample 4 | Lidocaine/Epinephrine Injection 2% | 0.09 | - | 0.414 |
| Sample 5 | Lidocaine/Epinephrine Injection 2% | 0.09 | - | 0.237 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boddu, S.H.S.; Tukaramrao, D.B.; Al-Tabakha, M.M.; Ashames, A.; Neupane, R.; Babu, R.J.; Renukuntla, J.; Tiwari, A.K. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Taste-Masking Effect of Selected Flavors on Dental Lidocaine HCl Injection. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110353
Boddu SHS, Tukaramrao DB, Al-Tabakha MM, Ashames A, Neupane R, Babu RJ, Renukuntla J, Tiwari AK. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Taste-Masking Effect of Selected Flavors on Dental Lidocaine HCl Injection. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(11):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110353
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoddu, Sai H. S., Diwakar B. Tukaramrao, Moawia M. Al-Tabakha, Akram Ashames, Rabin Neupane, R. Jayachandra Babu, Jwala Renukuntla, and Amit K. Tiwari. 2020. "Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Taste-Masking Effect of Selected Flavors on Dental Lidocaine HCl Injection" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 11: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110353
APA StyleBoddu, S. H. S., Tukaramrao, D. B., Al-Tabakha, M. M., Ashames, A., Neupane, R., Babu, R. J., Renukuntla, J., & Tiwari, A. K. (2020). Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Taste-Masking Effect of Selected Flavors on Dental Lidocaine HCl Injection. Pharmaceuticals, 13(11), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110353








