Abstract
Ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3) has two epimers, 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 (SRg3) and 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3 (RRg3), and while Rg3 itself has been reported to have anti-cancer properties, few studies have been reported on the anti-cancer effects of the different epimers. The aim was to investigate the stereoselective effects of the Rg3 epimers on triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell lines, tested using cell-based assays for proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, migration and invasion. Molecular docking showed that Rg3 interacted with the aquaporin 1 (AQP1) water channel (binding score −9.4 kJ mol−1). The Xenopus laevis oocyte expression system was used to study the effect of Rg3 epimers on the AQP1 water permeability. The AQP1 expression in TNBC cell lines was compared with quantitative-polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The results showed that only SRg3 inhibited the AQP1 water flux and inhibited the proliferation of MDA-MB-231 (100 μM), due to cell cycle arrest at G0/G1. SRg3 inhibited the chemoattractant-induced migration of MDA-MB-231. The AQP1 expression in MDA-MB-231 was higher than in HCC1143 or DU4475 cell lines. These results suggest a role for AQP1 in the proliferation and chemoattractant-induced migration of this cell line. Compared to SRg3, RRg3 had more potency and efficacy, inhibiting the migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231. Rg3 has stereoselective anti-cancer effects in the AQP1 high-expressing cell line MDA-MB-231.
1. Introduction
Ginsenosides are a class of natural triterpenoid saponins with the general structure of an aglycone steroid backbone and a glycoside side chain. They are extracted from the plant Panax ginseng Meyer, commonly known as ginseng, and play an important role in the medicinal effects of ginseng extract [1,2]. Ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3) is one of the extensively studied members of the ginsenoside family, having a variety of biological actions and efficacies, including anti-oxidant properties [3] and protective effects in cardiovascular diseases [4,5,6], neurological disorders [7,8,9,10], diabetes [11,12,13], immune function and inflammation [14,15,16,17], and cancer [18]. Although many papers refer to Rg3 as a single molecule and report the effects of Rg3, rather than a specific epimer, it is noteworthy that Rg3, like other ginsenosides, has two epimers: 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 (SRg3) and 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3 (RRg3). Each of these epimers has distinct pharmacological actions, intracellular targets, effects and efficacies. For example, the SRg3 epimer activates caspases in the human gastric cancer cell line [19] and inhibits Ca2+, Na+ and K+ ion channels [20], while the RRg3 epimer has antioxidant properties to combat cyclophosphamide-induced cellular stress [3].
The anti-cancer properties of Rg3 have made it a notable drug candidate for many cancer models. Few studies have focused on the anti-cancer effects of Rg3 in breast cancer models, specifically in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC), a subtype of breast cancer with a poor prognosis [21]. Since this subtype of breast tumour lacks the expression or overexpression of an estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor or human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER) 2, there are as yet no targeted therapies for TNBC; chemotherapy regimens, along with their adverse effects, remain the mainstay of treatment in most TNBC patients. Thus, finding a targeted biological agent for TNBC would make a paradigm shift in the treatment of these patients. Previous reported studies have shown that Rg3-induced apoptosis [22] inhibited the activation of NF-κB [23], induced G0/G1 arrest [24] and inhibited chemoinvasion directed by CXCR4 [25] in breast cancer cell lines. However, these studies did not use a specific epimer of Rg3, nor did they specify the ratio of the two epimers.
Aquaporin 1 (AQP1) is a member of the AQP family of water transporters. Like other AQPs, AQP1 is a homo-tetramer. Each monomer, as depicted in Figure 1A, works as a single channel for water transport. The central pore of the tetramer is responsible for gas and ion transport, the latter of which is gated by cGMP. It is already shown that AQP1 plays a role in the growth, angiogenesis and metastasis of tumours [26,27,28,29]. AQP1 is highly expressed in mouse models of breast tumour [30], and AQP1 deficiency in such models decreased the number of lung metastases [31]. Furthermore, clinical studies have shown that some TNBC tumours have higher levels of AQP1 expression and an expression correlated with a poorer prognosis [32,33].
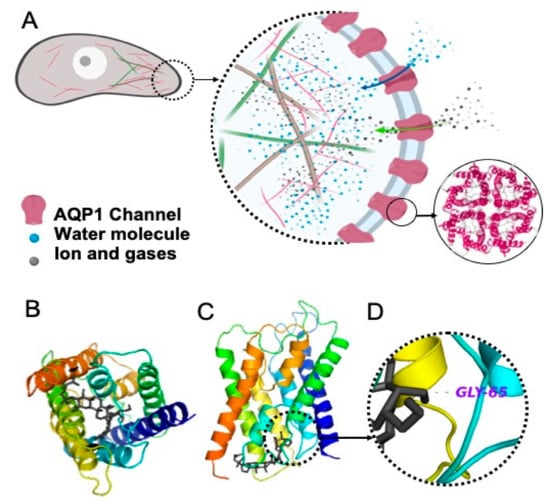
Figure 1.
(A) The role of aquaporin 1 (AQP1) in cell migration and invasion (as reviewed in [39]). AQPs are redistributed to the leading edge of the migrating cell, leading water, ions and gases inside the cell; hence, along with changes in actin polymerisation, they play a role in the forward movement of the cell. AQP1 is a tetramer. Water passes through the pore of each monomer, and ions and gases pass through the central pore of the tetramer. (B) Top view of an AQP1 monomer, being blocked with Rg3, the black structure, (C) Side view of an AQP1 monomer, blocked with Rg3, and (D) H-bonding between Rg3 and Gly 65.
To date, no studies have focused on the stereoselectivity of Rg3 epimers on TNBC cell lines, and no studies have shown the interaction between Rg3 epimers and AQP1. The aim of our study was to investigate the stereoselective effects of Rg3 on human TNBC cell lines. In particular, our aim was to investigate whether these two epimers have effects on different functions on TNBC in cell line models, including proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, migration and invasion. Furthermore, in line with our previous research focus [28,34,35,36,37], we investigated the interaction of Rg3 epimers with AQP1 in in silico models.
2. Results
2.1. Interaction of Rg3 with AQP1
2.1.1. Molecular Docking of Rg3
The in silico molecular docking studies were performed on Rg3 docked within the water channel of AQP1, AQP2, AQP4 and AQP5. The results in Table 1 are the scores based on Gibbs free energy (kJ mol−1).

Table 1.
The results of the in silico molecular docking of Rg3 with aquaporin water channels in comparison with other blockers of AQP1. The results are presented as Gibbs free energy (kJ mol−1).
The modelled binding energetically favoured AQP1 (−9.4 kJ mol−1) at a level comparable to known AQP1-inhibitors such as bacopaside I (−9.2 kJ mol−1) and bacopaside II (−9.3 kJ mol−1) [38]. Figure 1A illustrates the role of the AQP channels in migration and invasion (as reviewed in [39]). We showed that the water channel of the AQP1 monomer was blocked by Rg3 (Figure 1B,C). The H-bonding between the OH group (located on the C4’ of the second sugar molecule) with Gly65 (located in the second transmembrane helices, between loops A and B), with a distance of 3.4 Å, is shown in Figure 1D.
2.1.2. Stereoselectivity of Rg3 in Inhibiting AQP1 Water Channel
To find out if this interaction of Rg3-AQP1 is stereoselective, a Xenopus laevis oocyte expression system expressing human AQP1 was used. Native Xenopus laevis oocytes lack water channels, and hence a heterologous expression of human AQP1 on these cells makes them permeable to water. Following exposure to hypotonic media, water penetrates the cells based on osmotic driving forces. Figure 2A shows the result of the double swelling assays. The slope (± standard error) of the swelling rate for untreated, vehicle, RRg3 and SRg3 groups was 0.9 ± 0.1, 0.9 ± 0.2, 1.0 ± 0.2 and 0.4 ± 0.1, respectively. This shows that the rate of swelling in untreated, vehicle or RRg3 treated oocytes was similar, while the rate of swelling for SRg3 treated cells was reduced by almost 2.6 times, indicating the blockage of AQP1 with SRg3.
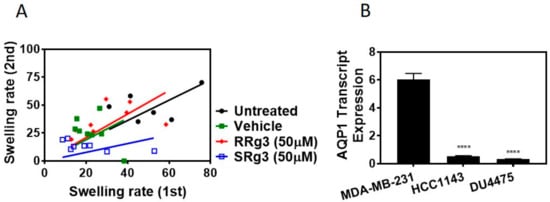
Figure 2.
(A) Double swelling assay showing the swelling rates for the first and the second swelling on a single oocyte. Eight oocytes per treatment were measured for swelling in a hypotonic medium, before and 2 h after exposure to a vehicle or epimers of Rg3. The results were analysed and presented with a linear regression. (B) The AQP1 transcript expression in MDA-MB-231, HCC1143 and DU4475 cell lines. Each data point represents a mean ± SD value of 3 replicates, and comparisons were made with the vehicle control group (**** p < 0.0001).
2.2. Rg3 Has Stereoselectivity and Cell Line-Specificity in Inhibition of Proliferation
To study the effect of Rg3 epimers on the proliferation of TNBC cell lines, MDA-MB-231, HCC1143 and the non-adherent DU4475 were tested. Within 3 days of treatment, all of the cell lines showed an increased cell proliferation. Interestingly, only SRg3 at 100 µM had an anti-proliferative effect on MDA-MB-231 in both assays (Figure 3A,B). A crystal violet assay showed that SRg3 (100 µM) inhibited the proliferation of cells by 45%. This indicates a stereoselective activity and cell line specificity of Rg3, since neither of the other cell lines showed an inhibition of proliferation with SRg3 or RRg3. A potential mechanism for the effect of SRg3 on the inhibition of proliferation in MDA-MB-231 was investigated by measuring the AQP1 transcript expression. Since the MDA-MB-231 cells had an 11 and 19 times higher expression of AQP1 compared to the HCC1143 and DU4475 cell lines, respectively (p < 0.0001) (Figure 2B), SRg3 may, in part, exert its activity through blocking AQP1.
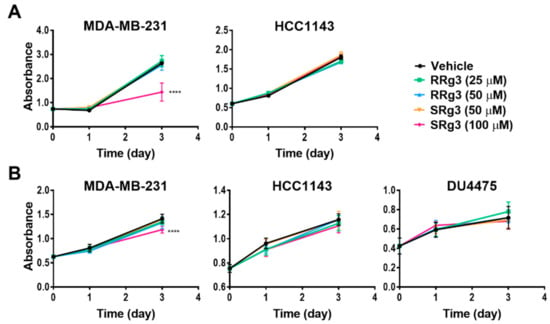
Figure 3.
Effect of SRg3 and RRg3 on the proliferation of MDA-MB-231, HCC1143 and DU4475 triple negative breast cancer cell lines, after 3 days, with (A) a crystal violet assay on the adherent cell lines and (B) an MTS assay. Only 100 µM of SRg3 showed an inhibition of proliferation of MDA-MB-231 in both assays, indicating the cell line selectivity and stereoselective effect of Rg3 for the inhibition of proliferation. Each data point represents a mean ± SD value of 6 replicates, and comparisons are made with the vehicle control group (**** p < 0.0001).
2.3. Cytostatic Effect of SRg3 Inhibits Cell Proliferation in MDA-MB-231 Cell Line without Inducing Apoptosis
The MDA-MB-231 cell line was exposed to a concentration of 100 µM SRg3 for 3 days, after which the cells were tested to see if the inhibition of proliferation was due to the induction of apoptosis. As shown in Figure 4A,B, there were no significant differences between the amount of apoptosis induced by vehicle (11.29% ± 3.22) or 100 µM of SRg3 (6.96% ± 1. 81) (p = 0.11). Since SRg3 was not inducing apoptosis, the cells were tested to determine if the inhibition of proliferation was due to cell cycle arrest. The percentages of cells in each cell cycle phase for the untreated cells were 51.3% ± 2.9 for G0/G1, 29.8% ± 1.8 for S, and 17.1% ± 1.9 for G2/M (Figure 4C,D). Vehicle-treated cells have similar values, at 52.8 ± 5.1, 27.6 ± 3.0 and 19.8 ± 1.2, respectively. The statistical analysis showed no significant differences between the untreated and vehicle control groups for each phase. However, the cells treated with 100 µM of SRg3 for 3 days showed a significant accumulation of cells in G0/G1 (65.3% ± 3.22) (p < 0.0001) and a reduction of cells in the G2/M phase (12.5% ± 1.4) (p < 0.05), compared to the vehicle group. Together, these data suggest that 100 µM SRg3 inhibited the MDA-MB-231 proliferation by inducing a G0/G1 cell cycle arrest.
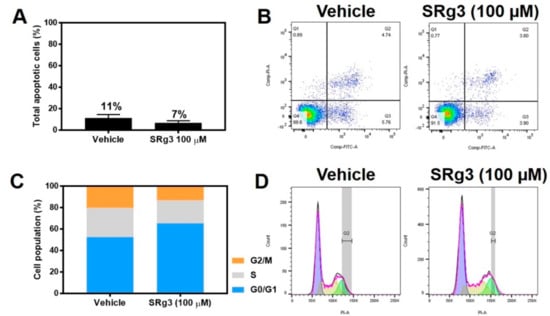
Figure 4.
The effect of SRg3 on apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in the MDA-MB-231 cell line. (A) Total apoptotic cells (%) induced by vehicle or 100 µM SRg3 after 3 days of exposure; (B) Scatter plots of untreated cells or the cells treated with vehicle or SRg3. The left lower quadrant, right lower quadrant, right upper quadrant and left upper quadrant indicate viable cells, early apoptotic cells, late apoptotic cells and necrotic cells, respectively. (C) Cell population (%) in each of the G0/G1, S and G2/M phases of the cell cycle. (D) Histograms of the untreated, vehicle and SRG3-treated cells, following staining with PI. The violet, yellow and green curves represent events in the G0/G1, S and G2/M phases, respectively. The data presented is representative of 3 repeats.
2.4. Stereoselective Inhibition of Migration of MDA-MB-231 Cell Line
To study if the epimers of Rg3 had any effect on the MDA-MB-231 migration, the cells were pre-treated with Rg3 epimers for 3 days, after which they were seeded for a circular wound closure assay. The results of this assay showed that after 24 h, the untreated and vehicle cells closed the circular wound by about 80% (Figure 5A). The wound closure in the cells treated with 100 µM of SRg3 was 76% ± 3.8, not significantly different to the vehicle (p = 0.81), while the wound closure in the cells treated with 50 µM of RRg3 was inhibited by 22 % compared to the vehicle control group (p = 0.001).
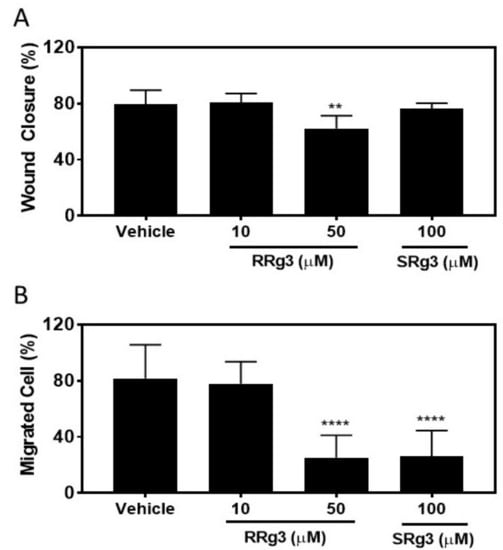
Figure 5.
Migration assays on the MDA-MB-231 cell line following exposure to RRg3 and SRg3. (A) The percentage of wound closure following exposure of the MDA-MB-231 cell line to RRg3 and SRg3. Data is presented as mean ± SD of 6 repeats, and comparisons are made with the vehicle control group (** p = 0.001). (B) The transwell migration assay on the MDA-MB-231 cell line following exposure to RRg3 and SRg3. Data are presented as mean ± SD of 3 replicates, and comparisons are made with the vehicle control group (**** p < 0.0001).
We showed, using a chemoattractant transwell migration assay, that at 50 and 100 µM of RRg3 and SRg3, the transwell migration of MDA-MB-231 cells was significantly inhibited by 69 and 68%, respectively (p < 0.0001).
2.5. Stereoselective Inhibition of Invasion
The ability of epimers of Rg3 to inhibit invasion was tested with a spheroid invasion assay. As shown in Figure 6, 50 µM of RRg3 resulted in inhibition (p = 0.0001). The inhibition of invasion was 78% for the spheroids treated with 50 µM RRg3. SRg3 did not inhibit spheroid invasion in this assay.
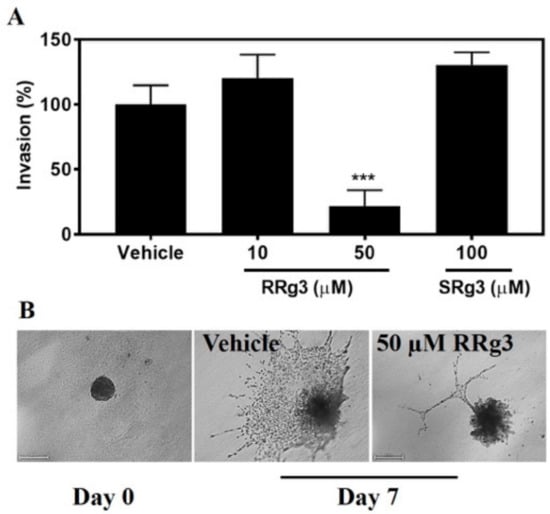
Figure 6.
Spheroid invasion assay on the MDA-MB-231 cell line following exposure to RRg3 and SRg3. (A) The percentage of increase in the area, as an indicator of invasion to the extracellular matrix, following exposure of the MDA-MB-231 spheroids to RRg3 and SRg3. Data are presented as mean ± SD of 3 replicates, and comparisons are made with the vehicle control group (***) p = 0.0001. (B) Representative images of the vehicle control and RRg3-treated spheroids after 7 days, indicating the inhibition of spheroid invasion in the RRg3-treated spheroids.
3. Discussion
This is the first study to investigate the stereoselective effects of epimers of Rg3 on TNBC cell lines. To our knowledge, the literature has no comparable studies that define the Rg3 epimers, or the specific ratio of SRg3/RRg3 in breast cancer models. Notably, we showed the stereoselectivity of Rg3 in the inhibition of proliferation in MDA-MB-231, the only cell line that showed sensitivity toward the anti-proliferative effects of SRg3. Neither of the Rg3 epimers inhibited the proliferation of the HCC1143 or DU4475 cell lines. MDA-MB-231 is a basal-like B [40,41] but with claudin-low [42] or mesenchymal-like [41] features, representative of tumours with a worse prognosis and more aggressive nature. Higher levels of AQP1 expression in breast tumours have been correlated with a triple negativity, poorer prognosis of the disease and higher tumour grade [33,43]. We showed that the AQP1 expression in MDA-MB-231 is much higher than in the HCC1143 and DU4475 cell lines. Molecular docking studies showed that Rg3 had a promising binding score with AQP1, comparable with some other blockers of AQP1 such as AqB013 [44], bacopaside I and bacopaside II [38]. Furthermore, for the first time, we showed that SRg3 was the only epimer that inhibited the AQP1 water flux. This stereoselective inhibition of the AQP1 water flux and inhibition of proliferation in the cell line with a higher expression of AQP1 by SRg3 suggests that AQP1 might be one of the important proteins involved in the proliferation of MDA-MB-231. Importantly, it is already reported that the over-expression of AQP1 in MDA-MB-231 significantly increased the proliferation and chemotactic invasion [45].
We also showed that the inhibition of proliferation of MDA-MB-231 by SRg3 was not due to the induction of apoptosis, but rather due to cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle. This G0/G1-arrest mechanism was comparable with similar studies in prostate [45], melanoma [46] and breast cell lines [24]. None of them, however, have defined a specific epimer in their studies. For example, the study on the breast cancer cell line exposed MCF7 (an estrogen and progesterone receptor positive cell line) to Rg3 and the heated extract of ginseng, containing about 5% Rg3 [24]. We have shown that it is SRg3 that causes G0/G1-arrest in MDA-MB-231. In fact, it has been shown that the over-expression of AQP1 causes a higher level of cyclin D and E, which are crucial for phase transition [47]. Cyclin E is a regulator for G1-S transition, and the blockage of AQP1 or inhibiting the expression of AQP1, as suggested by Pan et al. [45], inhibits the G1-S transition and arrests the cells in G0/G1.
Migration was tested in two assays. While the scratch wound closure assay measures the rate of cells migrating on plastic to close the circular wound, the transwell migration assay measures the ability of cells in suspension to migrate toward a chemoattractant [48]. Both of the epimers inhibited the chemoattractant-induced migration of cells. Notably, SRg3, which inhibited the water transport function of AQP1 in a stereoselective manner, was only effective in the chemoattractant-induced migration of cells as opposed to adherent cells migrating on plastic. This suggests that these epimers might have different mechanisms of action for the inhibition of migration. For example, in ovarian carcinoma cell lines, SRg3 was the only epimer that inhibited migration and invasion via blocking hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), the degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and the transcriptional repression of Snail and hence E-cadherin [49]. Importantly, Rg3 decreased the expression of AQP1 in the PC-M3 prostate cancer cell line, causing the inhibition of the chemoattractant-induced migration of these tumour cells [45]. It is already known that AQP1 is involved in the chemotactic migration of the cancer cells [29,50,51]. The chemotactic movement of the cancer cells is an important driver toward metastasis. Cancer cells sense the chemotactic gradient, and polarize into the leading edge to move forward toward the chemotactic agent. AQP1 is found on the leading edge of migrating cells (Figure 1A). AQP1, via directing the water influx and interactions with the actin cytoskeleton at the protrusion site of the migrating cell, plays roles in the migration of cancer cells, as reviewed in [39]. In our studied assays of migration and invasion, the transwell migration assay was the only assay in which the chemoattractant-induced migration of cells was assessed and SRg3, as a stereoselective inhibitor of AQP1, showed inhibitory effects. This suggests that AQP1, along with other mechanisms, is involved in the chemoattractant-induced migration of highly AQP1-expressing MDA-MB-231 cells.
While SRg3 showed no efficacy in the inhibition of migration in the wound closure migration assay nor in the spheroid invasion assays, RRg3, with a higher potency, inhibited migration and invasion in all of the studied assays. This suggests that RRg3 modulates different targets and pathways. Similar to our results, studies on the lung cancer A549 cell line showed that RRg3 at concentrations < 50 µg/mL did not inhibit the proliferation of the cells, but, in a stereoselective manner, suppressed TGF-β1-induced EMT, through repressing the Snail expression and inhibiting the activation of Smad and non-Smad (p38 MAPK) signalling pathways, hence inhibiting the E-cadherin expression [52]. The RRg3 inhibition of TGF-β1-induced EMT caused the inhibition of migration, invasion and anoikis resistance. RRg3 inhibited the TGF-β1-induced MMP-2 expression and inhibited the activation of Smad2 and p38 MAPK [52]. Other suggested mechanisms for the RRg3 inhibition of EMT and invasion were through the downregulation of fucosyltransferase IV (FUT4) [53]. FUT4 is an enzyme responsible for abnormal fucosylation in cancer cells, associated with the proliferation and metastasis of breast tumour cells [54], and it is also suggested as a biomarker for the diagnosis of breast tumours [55].
This is the first paper to study the stereoselectivity of epimers of Rg3 in TNBC cell lines and demonstrates that SRg3 and RRg3 have distinct effects. Furthermore, this is the first time that the interaction between Rg3 epimers and AQP1 is demonstrated. The effect of Rg3 epimers on the inhibition of proliferation of TNBC cell lines was specific to MDA-MB-231, suggesting that basal-like claudin-low or mesenchymal type tumours, with a high AQP1 expression, might be better candidates for treatment with SRg3. SRg3 had cytostatic effects on the MDA-MB-231 cell line, leading to the inhibition of proliferation. It inhibited the chemoattractant-induced cell migration and, notably, was the only epimer that blocked the AQP1 water channel function. This suggests that the SRg3 blocking of the AQP1-mediated water flux is a potential contributor to the mechanism of inhibition of chemoattractant-induced cell migration and the inhibition of proliferation in this cell line, but may not be the only target of action. Importantly, RRg3 is not cytotoxic to the cells, yet it inhibited the cell migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231, with a higher potency. The distinct and stereoselective actions of each epimer suggest that SRg3 and RRg3 should be considered as separate drug candidates. Although this study was limited to cell lines and in vitro assays, these results will inform the doses of each epimer to be tested in a mouse model of breast cancer.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
SRg3 (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) and RRg3 (AdooQ Bioseciences Irvine, CA, USA) epimers, both with purities > 98%, were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) at 12.7 and 6.5 mM stocks and stored in aliquots at −20 °C. Due to the low water solubility, log S −4.04 (ChemAxon, Cambridge, MA, USA), and relatively high lipophilicity (logP 4) of Rg3, these stocks were found to have the highest stock concentration of Rg3, which did not precipitate out upon dilution in aqueous media. The maximum concentration of DMSO with no observable biological effects in this study was found to be 0.8%. Triple negative breast cancer cell lines; MDA-MB-231 (basal-like with mesenchymal or claudin-low phenotype), HCC1143 (basal-like), and DU4475 (basal-like) were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC; Manassas, VA, USA) and used at low passage numbers.
4.2. Molecular Docking of Rg3
The molecular docking of Rg3 on aquaporin (AQP) channels was performed as previously described [38,56]. The crystal structures of the proteins were obtained from the protein data bank of NCBI (RCSB PDB). The structure IDs were as follows: AQP1 (1FQY), AQP2 (4NEF), AQP4 (3GD8), AQP5 (3D9S). The SMILES structure of Rg3 was obtained from PubChem. The three-dimensional structure of Rg3 was prepared in the UCSF Chimera program (version 1.13.1-mac64). The Autodock Vina algorithm (version 1.1.2_Mac) and UCSF Chimera program were used for in silico molecular docking. Images were prepared in the PyMol Molecular Graphics System, The X Window System, XQuartz 2.7.11. Notably, Autodock uses a stochastic search method to explore the conformational space of the ligand molecule, and this is by the random generation of distinct conformations, leading to finding a global energy minimum, expressed by a score for the Gibbs free energy of protein-ligand binding [57]. Due to this random generation of conformations, it is not practical to study a single epimer with this algorithm.
4.3. Oocyte Expression System and Swelling Assay
The unfertilized oocytes from a native Xenopus laevis frog were prepared and maintained, as previously described [38]. Briefly, the oocytes were injected with 3 ng of AQP1 cRNA and incubated at 16–18 °C for 3 days to allow for AQP1 expression. The inhibitory effect of Rg3 epimers on the AQP1 water channel was measured with the double-swelling assay. The swelling rate in hypotonic media (50% saline) for each oocyte was recorded and measured with ImageJ software (Wayne Rashband, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA), before and after a 2 h exposure to normal saline (as the untreated group), vehicle, or 50 µM of RRg3 or SRg3. Each treatment group consisted of 8 oocytes, and the rate of swelling in each group was compared with the vehicle group, using a linear regression analysis, as previously described [38].
4.4. Cell Culture
All of the TNBC cell lines were cultured as recommended by ATCC. The cells were thawed, and cultured in their respective media supplemented with a final concentration of 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS; Corning, Corning, NY, USA), 1% penicillin-streptomycin solution (Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY, USA) and 1% GlutaMax (Life Technologies), and they were incubated at 37 °C, 5% CO2 in the air.
4.5. Quantitative PCR for Expression of AQP1
The cell lines were seeded at 5 × 105 cells/well in 6-well plates. Following an overnight incubation, RNA was extracted using the PureLink RNA mini kit (Life Technologies), followed by the reverse transcription of 200 ng RNA with the iScript cDNA Synthesis Kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). The duplex TaqMan Gene Expression Assays for aquaporin-1 (AQP1; Hs01028916_m1; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) and the reference gene serine-rich coiled-coil domain-containing protein 2 (CCSER2; HS00982799_mH, Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) were used to determine the transcript expression, as previously described [58]. Reactions were performed using the Applied Biosystems ViiA 7 Real-Time PCR System (Life Technologies) with activation for 30 s at 95 °C, followed by 40 cycles of 15 s at 95 °C and 30 s at 60 °C. The AQP1 transcript expression was calculated using the 2-ΔCt formula.
4.6. Proliferation Assay
The effect of Rg3 epimers on the proliferation of the MDA-MB-231 and HCC1143 adherent cell lines was tested with a crystal violet assay, as described previously [58]. DU4475, a non-adherent cell line, along with the two adherent ones, were also tested with the MTS assay (CellTiter 96® AQueous Non-Radioactive Cell Proliferation Assay, Promega, Madison, WI, USA), as described previously [34]. Briefly, 7 × 103 cells/well were seeded in 96-well plates, incubated overnight and treated with 0–100 µM (final concentration) Rg3 epimers (6 replicates). The absorptions at 595 nm (for the crystal violet assay) and 490 nm (for the MTS assay) were measured at 0, 24 and 72 h of treatment.
4.7. Apoptosis Assay
An apoptosis assay was performed using the Annexin-V-FLUOS staining kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany), based on the previously described method [34]. Briefly, a density of 1 × 105 cells/well of 6-well plates were seeded in triplicate and incubated overnight. MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with 100 µM SRg3 for 72 h. Paclitaxel (400 nM) was used as a positive control. A control for necrosis was prepared by heating the cells at 63 °C for 30 min. Following the staining of the samples, they were analysed in BD FACSCanto II (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) and FlowJo software, v 10.4 (FlowJo, LLC, Ashland, OR, USA).
4.8. Cell Cycle Analysis
MDA-MB-231 cells were seeded at 1 × 105 cells/well of 6-well plates, in triplicate. After an overnight incubation, 100 µM of SRg3 was added to the cells. After 3 days, propidium iodide staining and a cell cycle analysis were performed on the cells, as previously described [59,60]. The samples were analysed with BD FACSCanto II and FlowJo software, v 10.4.
4.9. Scratch Wound Closure Assay
MDA-MB-231 cells were pre-treated with Rg3 epimers for 3 days and then seeded at 8 × 104 cells/well in 96-well plates for a scratch wound closure assay. The cells were exposed to different concentrations of RRg3 and SRg3, and the assay was performed as described previously [61]. Images were taken at time 0 and 24 h using a Nikon microscope, and the wound closure (%) was measured using ImageJ software. The relative wound closure (%) at time 24 h was calculated compared to time 0, with 6 replicates.
4.10. Transwell Migration Assay
MDA-MB-231 cells were pre-treated with either vehicle or Rg3 epimers for 3 days. Then, 1 × 105 cells were suspended in 250 µL of serum-free DMEM containing vehicle or Rg3 epimers and placed in the upper chamber of the Corning® transwells (8 µm pore size). The lower chamber was filled with 750 µL DMEM supplemented with final concentrations of 10% FBS, 1% penicillin-streptomycin solution and 1% GlutaMax. The cells were incubated for 4.5 h, after which the cells on top of the membrane were removed with a cotton swab. The migrated cells on the other side of the membrane were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin for 30 min, stained in a crystal violet solution (1% crystal violet in 2% ethanol) for 10 min, and washed in distilled water. The experiment was carried out in triplicate, and the total migrated cells were counted in five fields of view per chamber, at 200× magnification using NIS-Elements (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). The migration percentage for each treatment group is presented relative to the average vehicle control group.
4.11. Spheroid Invasion Assay
A single cell suspension (3 × 103 cell/well) and 1X Spheroid Formation ECM (Cultrex®, Trevigen Inc., Gaithersburg, MD, USA) (5 µL/well) was prepared, and 50 µL of this suspension was placed in each well of the 96-well ultra-low attachment Costar® plates (Corning Inc., Corning, NY, USA). The plate was centrifuged at 200× g for 3 min and incubated in a 37 °C, 5% CO2 incubator for 72 h. Then, the plate was left on ice for 15 min, and 50 µL of Invasion Matrix (Cultrex®) was added to each well (day 0). The plate was then centrifuged at 300× g, 4 °C, 5 min, followed by a 1 h incubation. The spheres were then treated with different concentrations of Rg3. At day 0 and day 7, images were taken of the spheres using a Nikon Eclipse TE2000-U light microscope, and the area of each sphere was measured using NIS-elements software (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). The invasion (%) of each spheroid was normalized to the mean invasion area of the vehicle group.
4.12. Statistical Analysis
A one-way or two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed for the data analysis using GraphPad Prism (version 7.02). The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). p < 0.05 was considered as the level of statistical significance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.N., H.M.P., A.J.Y. and J.E.H.; Data curation, Y.T., E.S. and J.V.P.; Formal analysis, M.N., H.M.P., A.J.Y. and J.E.H.; Funding acquisition, T.J.P., A.R.T. and J.E.H.; Investigation, M.N.; Methodology, M.N., H.M.P., A.J.Y. and J.V.P.; Resources, T.J.P. and A.R.T.; Supervision, J.E.H.; Writing—original draft, M.N.; Writing—review & editing, H.M.P., Y.T., E.S., T.J.P., A.J.Y., J.V.P., A.R.T. and J.E.H.
Funding
This research was funded by the Margaret Elcombe Hospital Research Foundation Research Grant.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, M.S.; Wu, M.Y. Chinese ginseng. In Nutraceuticals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Nederlands, 2016; pp. 693–705. [Google Scholar]
- Szczuka, D.; Nowak, A.; Zakłos-Szyda, M.; Kochan, E.; Szymańska, G.; Motyl, I.; Blasiak, J.J.N. American ginseng (panax quinquefolium l.) as a source of bioactive phytochemicals with pro-health properties. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Su, F.; Su, X.; Hu, T.; Hu, S. Stereospecific antioxidant effects of ginsenoside rg3 on oxidative stress induced by cyclophosphamide in mice. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Lim, K.-M.; Kim, S.-Y.; Bae, O.-N.; Noh, J.-Y.; Chung, S.-M.; Kim, K.; Shin, Y.-S.; Lee, M.-Y.; Chung, J.-H. Vascular smooth muscle dysfunction and remodeling induced by ginsenoside rg3, a bioactive component of ginseng. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 117, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Huang, C.; Wang, C.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, P.; Xu, Y.; Chen, H.; Shen, W. Ginsenoside rg3 improves cardiac mitochondrial population quality: Mimetic exercise training. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-B.; Kwon, S.K.; Nagar, H.; Jung, S.-B.; Jeon, B.H.; Kim, C.S.; Oh, J.-H.; Song, H.-J.; Kim, C.-S. Rg3-enriched korean red ginseng improves vascular function in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 38, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tian, J.; Fu, F.; Geng, M.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, J.; Jiang, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, K. Neuroprotective effect of 20 (s)-ginsenoside rg3 on cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 374, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Hao, J.; Zhang, J.; Xia, W.; Dong, X.; Hu, X.; Kong, F.; Cui, X. Ginsenoside rg3 promotes beta-amyloid peptide degradation by enhancing gene expression of neprilysin. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Chen, P.; Yang, J.; Yun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, R.; Shen, Z. Neuroprotective effect of 20 (r)-ginsenoside rg3 against transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 526, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Anderson, G.A.; Fernandez, T.G.; Dore, S. Efficacy and mechanism of panax ginseng in experimental stroke. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, E.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, S.-D.; Park, S.-J.; Kwak, D.; Oh, J.-H.; Park, C.-K.; Rhee, M.H. Alleviation of diabetic complications by ginsenoside rg3-enriched red ginseng extract in western diet-fed ldl–/–mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.W.; Ha, J.; Chung, S.H. 20 (s)-ginsenoside rg3 enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and activates ampk. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 748–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.S.; Yamabe, N.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, J.H.; Yokozawa, T. Therapeutic potential of 20 (s)-ginsenoside rg3 against streptozotocin-induced diabetic renal damage in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 591, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kee, J.-Y.; Hong, S.-H. Ginsenoside rg3 suppresses mast cell–mediated allergic inflammation via mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Chen, J.; Su, F.; Su, X.; Hu, T.; Hu, S. Stereospecificity of ginsenoside rg3 in promotion of the immune response to ovalbumin in mice. Int. Immunol. 2012, 24, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Ru, Q.; Chen, L.; Ma, B.; Li, C. Stereospecificity of ginsenoside rg3 in the promotion of cellular immunity in hepatoma h22-bearing mice. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, H1430–H1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.-S. Roles of ginsenosides in inflammasome activation. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhjavani, M.; Hardingham, J.E.; Palethorpe, H.M.; Tomita, Y.; Smith, E.; Price, T.J.; Townsend, A.R. Ginsenoside rg3: Potential molecular targets and therapeutic indication in metastatic breast cancer. Medicines 2019, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Yamabe, N.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, H.-K.; Jang, H.-J.; Kim, J.H.; Cheon, G.J.; Ham, J.; Kang, K.S. Stereospecific anticancer effects of ginsenoside rg3 epimers isolated from heat-processed american ginseng on human gastric cancer cell. J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 38, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.M.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, B.-H.; Yoon, I.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Rhim, H.; Kim, Y.; Nah, S.-Y. Stereospecificity of ginsenoside rg 3 action on ion channels. Mol. Cells 2004, 18, 383–389. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail-Khan, R.; Bui, M.M. A review of triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Control 2010, 17, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-M.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Na, H.-K.; Surh, Y.-J. Ginsenoside rg3 induces apoptosis of human breast cancer (mda-mb-231) cells. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 18, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.-M.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Surh, Y.-J.; Na, H.-K. Ginsenoside rg3 inhibits constitutive activation of nf-κb signaling in human breast cancer (mda-mb-231) cells: Erk and akt as potential upstream targets. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Z.; Aung, H.H.; Zhang, B.; Sun, S.; Li, X.-L.; He, H.; Xie, J.-T.; He, T.-C.; Du, W.; Yuan, C.-S. Chemopreventive effects of heat-processed panax quinquefolius root on human breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 2545–2551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-P.; Qian, L.-L.; Jiang, H.; Chen, J.-H. Ginsenoside rg3 inhibits cxcr 4 expression and related migrations in a breast cancer cell line. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 16, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yool, A.J.; Brown, E.A.; Flynn, G.A. Roles for novel pharmacological blockers of aquaporins in the treatment of brain oedema and cancer. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 37, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yool, A.J. Functional domains of aquaporin-1: Keys to physiology, and targets for drug discovery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 3212–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorward, H.S.; Du, A.; Bruhn, M.A.; Wrin, J.; Pei, J.V.; Evdokiou, A.; Price, T.J.; Yool, A.J.; Hardingham, J.E. Pharmacological blockade of aquaporin-1 water channel by aqb013 restricts migration and invasiveness of colon cancer cells and prevents endothelial tube formation in vitro. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, M.; Saadoun, S.; Verkman, A. Aquaporins and cell migration. Pflug. Arch.—Eur. J. Physiol. 2008, 456, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M.; Jain, R.K.; Witwer, B.; Brown, D. Water channel (aquaporin 1) expression and distribution in mammary carcinomas and glioblastomas. Microvasc. Res. 1999, 58, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva-Font, C.; Jin, B.-J.; Verkman, A. Aquaporin-1 gene deletion reduces breast tumor growth and lung metastasis in tumor-producing mmtv-pyvt mice. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, T.; Luo, L.; Zhao, H.; Cheng, J.; Xiang, J.; Zhao, C. Aquaporins in human breast cancer: Identification and involvement in carcinogenesis of breast cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 106, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otterbach, F.; Callies, R.; Adamzik, M.; Kimmig, R.; Siffert, W.; Schmid, K.W.; Bankfalvi, A. Aquaporin 1 (aqp1) expression is a novel characteristic feature of a particularly aggressive subgroup of basal-like breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 120, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palethorpe, H.; Tomita, Y.; Smith, E.; Pei, J.; Townsend, A.; Price, T.; Young, J.; Yool, A.; Hardingham, J. The aquaporin 1 inhibitor bacopaside ii reduces endothelial cell migration and tubulogenesis and induces apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.; Tomita, Y.; Palethorpe, H.M.; Howell, S.; Nakhjavani, M.; Townsend, A.R.; Price, T.J.; Young, J.P.; Hardingham, J.E. Reduced aquaporin-1 transcript expression in colorectal carcinoma is associated with promoter hypermethylation. Epigenetics 2019, 14, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, Y.; Palethorpe, H.M.; Smith, E.; Nakhjavani, M.; Townsend, A.R.; Price, T.J.; Yool, A.J.; Hardingham, J.E. Bumetanide-derived aquaporin 1 inhibitors, aqb013 and aqb050 inhibit tube formation of endothelial cells through induction of apoptosis and impaired migration in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, Y.; Dorward, H.; Yool, A.; Smith, E.; Townsend, A.; Price, T.; Hardingham, J. Role of aquaporin 1 signalling in cancer development and progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, J.V.; Kourghi, M.; De Ieso, M.L.; Campbell, E.M.; Dorward, H.S.; Hardingham, J.E.; Yool, A.J. Differential inhibition of water and ion channel activities of mammalian aquaporin-1 by two structurally related bacopaside compounds derived from the medicinal plant bacopa monnieri. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ieso, M.L.; Yool, A.J. Mechanisms of aquaporin-facilitated cancer invasion and metastasis. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 135. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Cheng, H.; Bai, Z.; Li, J. Breast cancer cell line classification and its relevance with breast tumor subtyping. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, J.; Salari, K.; Bocanegra, M.; Choi, Y.-L.; Girard, L.; Gandhi, J.; Kwei, K.A.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; Wang, P.; Gazdar, A.F. Molecular profiling of breast cancer cell lines defines relevant tumor models and provides a resource for cancer gene discovery. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.; van Jaarsveld, M.T.; Hollestelle, A.; Prager-van der Smissen, W.J.; Heine, A.A.; Boersma, A.W.; Liu, J.; Helmijr, J.; Ozturk, B.; Smid, M. Mirna expression profiling of 51 human breast cancer cell lines reveals subtype and driver mutation-specific mirnas. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobasheri, A.; Shakibaei, M.; Marples, D. Immunohistochemical localization of aquaporin 10 in the apical membranes of the human ileum: A potential pathway for luminal water and small solute absorption. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 121, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliati, E.; Meurice, N.; DuBois, P.; Fang, J.S.; Somasekharan, S.; Beckett, E.; Flynn, G.; Yool, A.J. Inhibition of aquaporin-1 and aquaporin-4 water permeability by a derivative of the loop diuretic bumetanide acting at an internal pore-occluding binding site. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.-Y.; Guo, H.; Han, J.; Hao, F.; An, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiaokaiti, Y.; Pan, Y.; Li, X.-J. Ginsenoside rg3 attenuates cell migration via inhibition of aquaporin 1 expression in pc-3m prostate cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 683, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, X.; Fu, Y.-S.; Aziz, F.; Wang, X.-Q.; Yan, Q.; Liu, J.-W. Ginsenoside rg3 inhibits melanoma cell proliferation through down-regulation of histone deacetylase 3 (hdac3) and increase of p53 acetylation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Cobo, A.; Ramírez-Lorca, R.; Toledo-Aral, J.J.; Echevarría, M. Aquaporin-1 plays important role in proliferation by affecting cell cycle progression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justus, C.R.; Leffler, N.; Ruiz-Echevarria, M.; Yang, L.V. In vitro cell migration and invasion assays. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 752, 10–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, D.; Hou, H.; Ding, L.; Li, X. Ginsenoside 20 (s)-rg3 targets hif-1α to block hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelagalli, A.; Nardelli, A.; Fontanella, R.; Zannetti, A. Inhibition of aqp1 hampers osteosarcoma and hepatocellular carcinoma progression mediated by bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Zhang, H.; Shao, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Fu, L.; Gu, F.; Ma, Y. Expression of aquaporin1, a water channel protein, in cytoplasm is negatively correlated with prognosis of breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Choi, W.-I.; Jeon, B.-N.; Choi, K.-C.; Kim, K.; Kim, T.-J.; Ham, J.; Jang, H.J.; Kang, K.S.; Ko, H. Stereospecific effects of ginsenoside 20-rg3 inhibits tgf-β1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition and suppresses lung cancer migration, invasion and anoikis resistance. Toxicology 2014, 322, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Shen, D.; Li, X.; Shan, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, Q.; Liu, J. Ginsenoside rg3 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition (emt) and invasion of lung cancer by down-regulating fut4. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Feng, X.; Song, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, L.; Jia, L. Mir-493-5p attenuates the invasiveness and tumorigenicity in human breast cancer by targeting fut4. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Lin, Y.; Liu, S.; Yan, Q. Fucosyltransferase iv (fut4) as an effective biomarker for the diagnosis of breast cancer. BioMed Pharmacother. 2015, 70, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yool, A.J.; Morelle, J.; Cnops, Y.; Verbavatz, J.-M.; Campbell, E.M.; Beckett, E.A.; Booker, G.W.; Flynn, G.; Devuyst, O. Aqf026 is a pharmacologic agonist of the water channel aquaporin-1. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrel, A. Development of Computational Methods to Predict Protein Pocket Druggability and profile Ligands Using Structural Data. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, E.; Palethorpe, H.M.; Tomita, Y.; Pei, J.V.; Townsend, A.R.; Price, T.J.; Young, J.P.; Yool, A.J.; Hardingham, J.E. The purified extract from the medicinal plant bacopa monnieri, bacopaside ii, inhibits growth of colon cancer cells in vitro by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Cells 2018, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palethorpe, H.M.; Leach, D.A.; Need, E.F.; Drew, P.A.; Smith, E. Myofibroblast androgen receptor expression determines cell survival in co-cultures of myofibroblasts and prostate cancer cells in vitro. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 19100–19114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palethorpe, H.M.; Drew, P.A.; Smith, E. Androgen signaling in esophageal adenocarcinoma cell lines in vitro. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 3402–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourghi, M.; Pei, J.V.; De Ieso, M.L.; Flynn, G.; Yool, A.J. Bumetanide derivatives aqb007 and aqb011 selectively block the aquaporin-1 ion channel conductance and slow cancer cell migration. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 89, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).