Evaluation of Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Effect of Ursolic Acid as a Novel Toxoplasmosis Inhibitor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
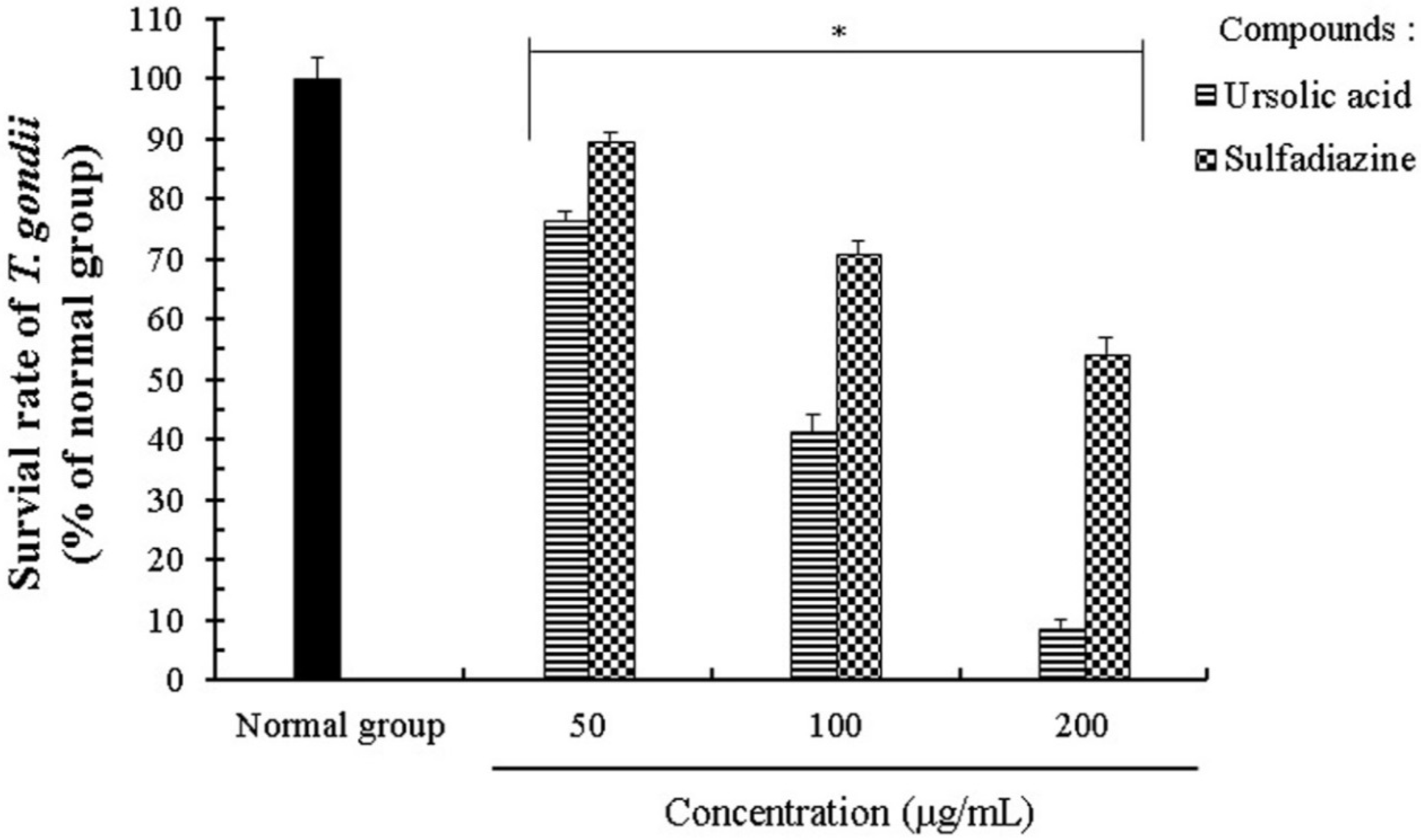
2.1. Effect of Ursolic Acid on the Proliferation and Growth of T. gondii
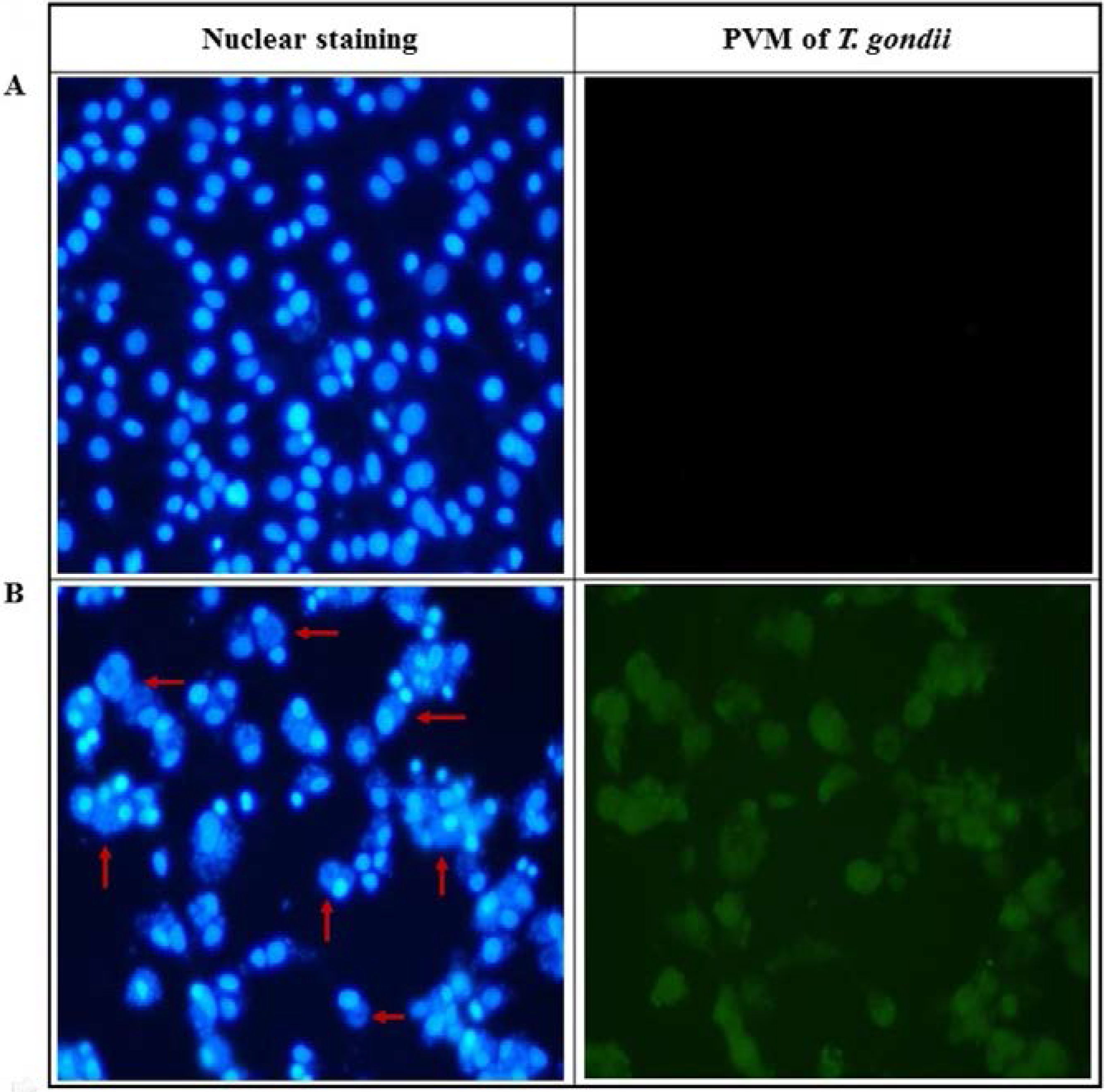
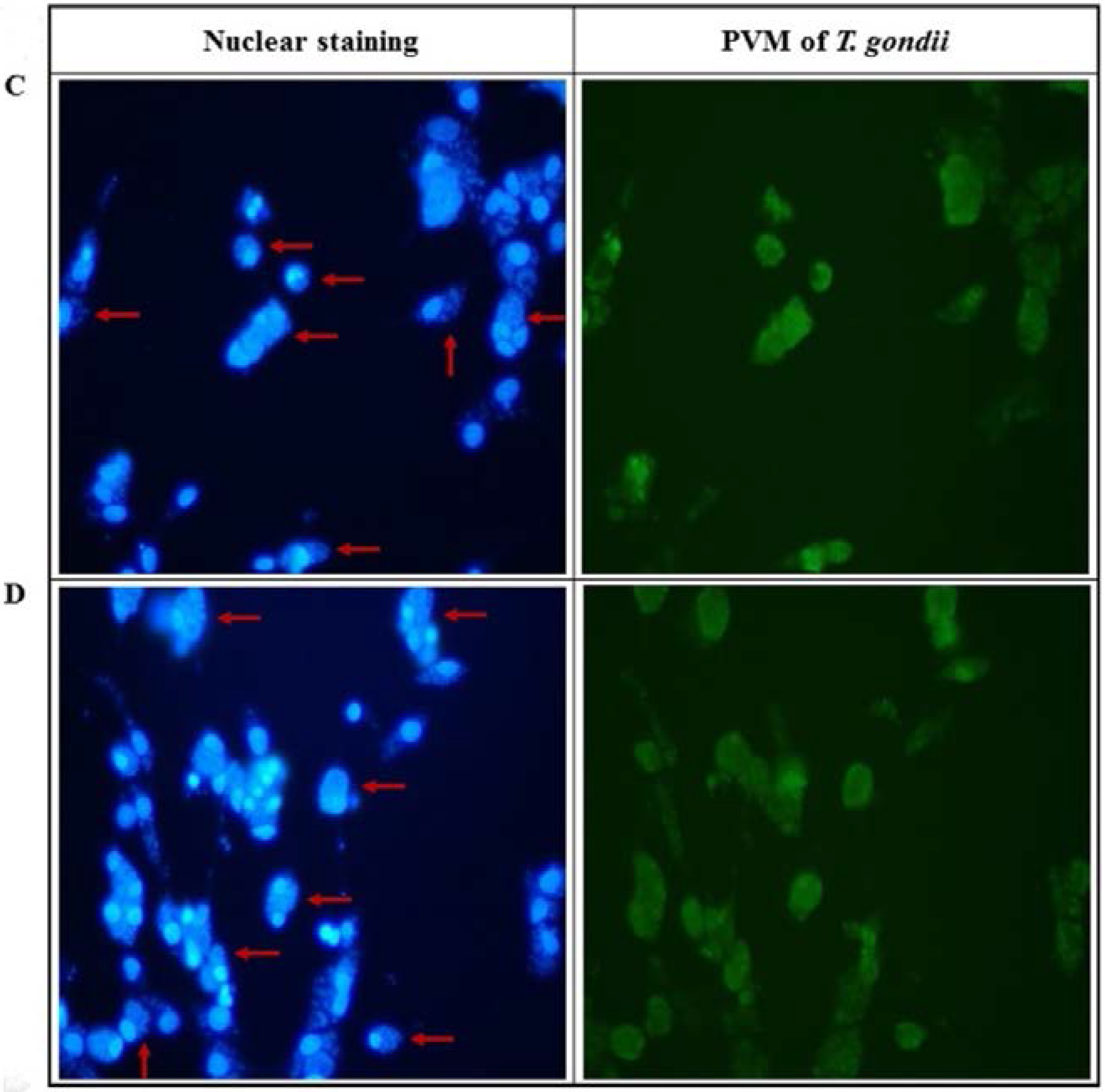
2.2. Anti-Parasitic Effect of Ursolic Acid on PVM Formed by T. gondii Proliferation
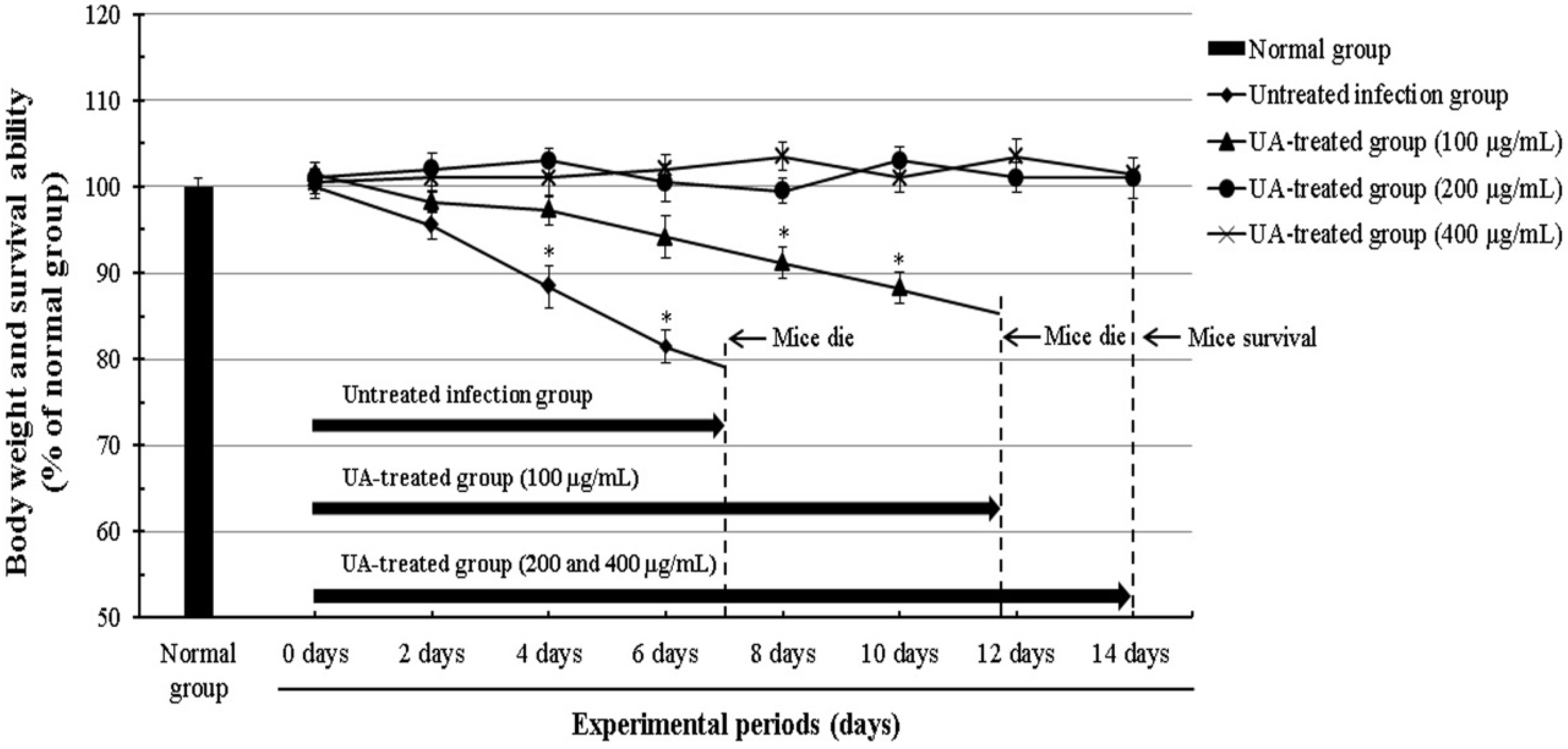
2.3. Effect of Ursolic Acid through the Inhibition of T. gondii in T. gondii-Infected Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animals
4.3. Preparation of Anti-T. gondii Drugs
4.4. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions of T. gondii
4.5. Evaluation of The Viability of T. gondii
4.6. Microscopic Observation of T. gondii in Infected Cells
4.7. Nuclear Staining of T. gondii-Infected Host Cells
4.8. PVM Formation in T. gondii-Infected Cells
4.9. The Survival Rate of T. gondii-Infected Mice
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joiner, K.A.; Roos, D.S. Secretory traffic in the eukaryotic parasite Toxoplasma gondii: Less is more. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 157, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonhomme, A.; Bouchot, A.; Pezzella, N.; Gomez, J.; Le, M.H.; Pinon, J.M. Signaling during the invasion of host cells by Toxoplasma gondii. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 23, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneceur, P.; Bouldouyre, M.A.; Aubert, D.; Villena, I.; Menotti, J.; Sauvage, V.; Garin, J.F.; Derouin, F. In vitro susceptibility of various genotypic strains of Toxoplasma gondii to pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, and atovaquone. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doliwa, C.; Xia, D.; Escotte-Binet, S.; Newsham, E.L.; Sanya, J.S.; Aubert, D.; Randle, N.; Wastling, J.M.; Villena, I. Identification of differentially expressed proteins in sulfadiazine resistant and sensitive strains of Toxoplasma gondii using difference-gel electrophoresis (DIGE). Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2013, 3, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspinall, T.V.; Joynson, D.H.; Guy, E.; Hyde, J.E.; Sims, P.F. The molecular basis of sulfonamide resistance in Toxoplasma gondii and implications for the clinical management of toxoplasmosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.H.; Lee, I.A. The anti-tubercular activity of Melia azedarach L. and Lobelia chinensis Lour. and their potential as effective anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis candidate agents. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Chen, K.P. Anti-HBV agents derived from botanical origin. Fitoterapia 2013, 84, 140–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wycoff, K.; Maclean, J.; Belle, A.; Yu, L.; Tran, Y.; Roy, C.; Hayden, F. Anti-infective immunoadhesins from plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 1078–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, L.H.G.; Silva de Sousa, P.A.P.; Hilario, F.F.; Nascimento, G.J.; Morais, J.P.S.; de Medeiros, E.P.; de Sousa, M.F.; da Cruz Nunes, F. Agave sisalana extract induces cell death in Aedes aegypti hemocytes increasing nitric oxide production. Asian. Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tao, L.; Xu, H. Chinese herbal medicines as a source of molecules with anti-enterovirus 71 activity. Chin. Med. 2016, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.H. Novel pharmacological activity of artesunate and artemisinin: Their potential as anti-tubercular agents. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavitha, N.; Noordin, R.; Chan, K.L.; Sasidharan, S. In vitro anti-Toxoplasma gondii activity of root extract/fractions of Eurycoma longifolia Jack. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomar, M.L.; Rasse-Suriani, F.O.; Ganuza, A.; Coceres, V.M.; Cabrerizo, F.M.; Angel, S.O. In vitro evaluation of b-carboline alkaloids as potential anti-Toxoplasma agents. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzitko, K.; Grzybowski, M.M.; Pawełczyk, J.; Dziadek, B.; Gatkowska, J.; Sta˛czek, P.; Długonska, H. Phytoecdysteroids as modulators of the Toxoplasma gondii growth rate in human and mouse cells. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparotto Junior, A.; Cosmo, M.L.; Reis Mde, P.; Dos Santos, P.S.; Gonçalves, D.D.; Gasparotto, F.M.; Navarro, I.T.; Lourenço, E.L. Effects of extracts from Echinacea purpurea (L.) MOENCH on mice infected with different strains of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 3999–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, L.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wu, X.; Park, H.; Quan, H.; Jin, C. Antiparasitic effects of oxymatrine and matrine against Toxoplasma gondii in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 165, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colla, A.R.; Rosa, J.M.; Cunha, M.P.; Rodrigues, A.L. Anxiolytic-like effects of ursolic acid in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 758, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanjoormana, M.; Kuttan, G. Antiangiogenic activity of ursolic acid. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazmi, I.; Afzal, M.; Gupta, G.; Anwar, F. Antiepileptic potential of ursolic acid stearoyl glucoside by GABA receptor stimulation. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2012, 18, 799–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Wu, D.M.; Zheng, Y.L.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Z.F.; Ye, Q.; Liu, C.M.; Shan, Q.; Wang, Y.J. Ursolic acid attenuates d-galactose-induced inflammatory response in mouse prefrontal cortex through inhibiting AGEs/RAGE/NF-κB pathway activation. Cereb. Cortex 2010, 20, 2540–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checker, R.; Sandur, S.K.; Sharma, D.; Patwardhan, R.S.; Jayakumar, S.; Kohli, V.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Sainis, K.B. Potent anti-inflammatory activity of ursolic acid, a triterpenoid antioxidant, is mediated through suppression of NF-κB, AP-1 and NF-AT. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Kong, C.Z.; Wang, L.H.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, X.K.; Xu, B.; Xu, C.L.; Sun, Y.H. Ursolic acid overcomes Bcl-2-mediated resistance to apoptosis in prostate cancer cells involving activation of JNK-Induced Bcl-2 phosphorylation and degradation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 109, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.H.; Chu, J.P.; Jiang, M.H.; Baek, S.H.; Park, H.D. Effects of fraction obtained from Korean Corni Fructus extracts causing anti-proliferation and p53-dependent apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Yadav, V.R.; Sung, B.; Gupta, S.C.; Tyagi, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Ursolic acid inhibits the growth of human pancreatic cancer and enhances the antitumor potential of gemcitabine in an orthotopic mouse model through suppression of the inflammatory microenvironment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13182–13196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, A.A.; Pereira-Wilson, C.; Collins, A.R. Protective effects of ursolic acid and luteolin against oxidative DNA damage include enhancement of DNA repair in Caco-2 cells. Mutat. Res. 2010, 692, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Nascimento, P.G.; Lemos, T.L.; Bizerra, A.M.; Arriaga, A.M.; Ferreira, D.A.; Santiago, G.M.; Braz-Filho, R.; Costa, J.G. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of ursolic acid and derivatives. Molecules 2014, 19, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Arellanes, A.; Luna-Herrera, J.; Cornejo-Garrido, J.; Lopez-Garcia, S.; Castro-Mussot, M.E.; Meckes-Fischer, M.; Mata-Espinosa, D.; Marquina, B.; Torres, J.; Hernández-Pando, R. Ursolic and oleanolic acids as antimicrobial and immunomodulatory compounds for tuberculosis treatment. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.Y.; Yoon, S.Y.; Roh, D.H.; Jeon, M.J.; Seo, H.S.; Uh, D.K.; Kwon, Y.B.; Kim, H.W.; Han, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; et al. The anti-arthritic effect of ursolic acid on zymosan-induced acute inflammation and adjuvant-induced chronic arthritis models. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.L.; Li, H.; Yue, L.T.; Zhang, X.X.; Wang, C.C.; Wang, S.; Duan, R.S. Low and high doses of ursolic acid ameliorate experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis through different pathways. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 281, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, I.P.; Castanheira, L.E.; Barbosa, B.F.; de Souza, D.L.; da Silva, R.J.; Mineo, J.R.; Tudini, K.A.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Ferro, E.A.; de Melo, R.V. Anti-parasitic effect on Toxoplasma gondii induced by BnSP-7, a Lys49-phospholipase A2 homologue from Bothrops pauloensis venom. Toxicon 2016, 119, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanfelice, R.A.; da Silva, S.S.; Bosqui, L.R.; Miranda-Sapla, M.M.; Barbosa, B.F.; Silva, R.J.; Ferro, E.A.V.; Panagio, L.A.; Navarro, I.T.; Bordignon, J.; et al. Pravastatin and simvastatin inhibit the adhesion, replication and proliferation of Toxoplasma gondii (RH strain) in HeLa cells. Acta Trop. 2017, 167, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmen, J.C.; Southard, R.C.; Sinai, A.P. The complexity of signaling in host-pathogen interactions revealed by the Toxoplasma gondii-dependent modulation of JNK phosphorylation. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 3724–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laliberte, J.; Carruthers, V.B. Host cell manipulation by human pathogen Toxoplasma gondii. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 1900–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubbels, M.J.; White, M.; Szatanek, T. The cell cycle and Toxoplasma gondii cell division: Tightly knit or loosely stitched. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1343–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesus, J.A.; Fragoso, T.N.; Yamamoto, E.S.; Laurenti, M.D.; Silva, M.S.; Ferreira, A.F.; Lago, J.H.; Santos-Gomes, G.; Passero, L.F. Therapeutic effect of ursolic acid in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, E.S.; Campos, B.L.; Jesus, J.A.; Laurenti, M.D.; Ribeiro, S.P.; Kallas, E.G.; Rafael-Fernandes, M.; Santos-Gomes, G.; Silva, M.S.; Sessa, D.P.; et al. The Effect of Ursolic Acid on Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis is Related to Programed Cell Death and Presents Therapeutic Potential in Experimental Cutaneous Leishmaniasis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latt, S.A.; Stetten, G. Spectral studies on 33258 Hoechst and related bisbenzimidazole dyes useful for fluorescent detection of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1976, 24, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| The Tested Compound | Structure (C30H48O3) | The IC50 (µg/mL) of Ursolic Acid against T. gondii | The IC50 (µg/mL) of Ursolic Acid against T. gondii–Infected Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ursolic acid (UA) | 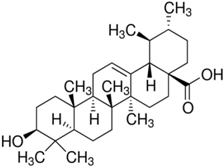 | 94.62 | 162.25 |
| Infection Ratio of T. gondii (MOI) | Incubation Time | Concentrations (µg/mL) | The Survival Rate (%) of T. gondii-Infected Cells | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ursolic Acid (UA) | Sulfadiazine (SF) | |||
| Cells:T. gondii = 1:5 | 24 h | 0 | 100.00 ± 2.28 | 100.00 ± 3.46 |
| 25 | 92.35 ± 2.74 | 94.26 ± 1.82 | ||
| 50 | 85.52 ± 1.55 | 91.35 ± 1.64 | ||
| 100 | 67.61 ± 1.87 | 77.58 ± 3.45 | ||
| 200 | 38.42 ± 3.12 | 60.45 ± 1.68 | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, W.H.; Lee, I.A. Evaluation of Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Effect of Ursolic Acid as a Novel Toxoplasmosis Inhibitor. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11020043
Choi WH, Lee IA. Evaluation of Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Effect of Ursolic Acid as a Novel Toxoplasmosis Inhibitor. Pharmaceuticals. 2018; 11(2):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11020043
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Won Hyung, and In Ah Lee. 2018. "Evaluation of Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Effect of Ursolic Acid as a Novel Toxoplasmosis Inhibitor" Pharmaceuticals 11, no. 2: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11020043
APA StyleChoi, W. H., & Lee, I. A. (2018). Evaluation of Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Effect of Ursolic Acid as a Novel Toxoplasmosis Inhibitor. Pharmaceuticals, 11(2), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11020043




