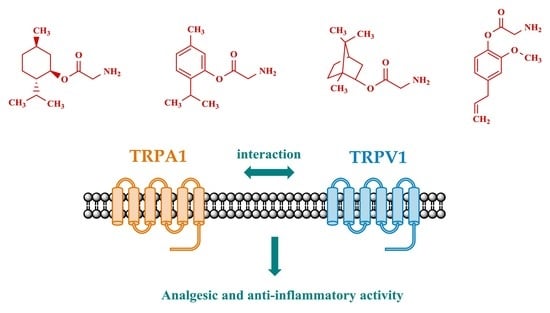
Synthesis and Pharmacological Properties of Novel Esters Based on Monoterpenoids and Glycine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
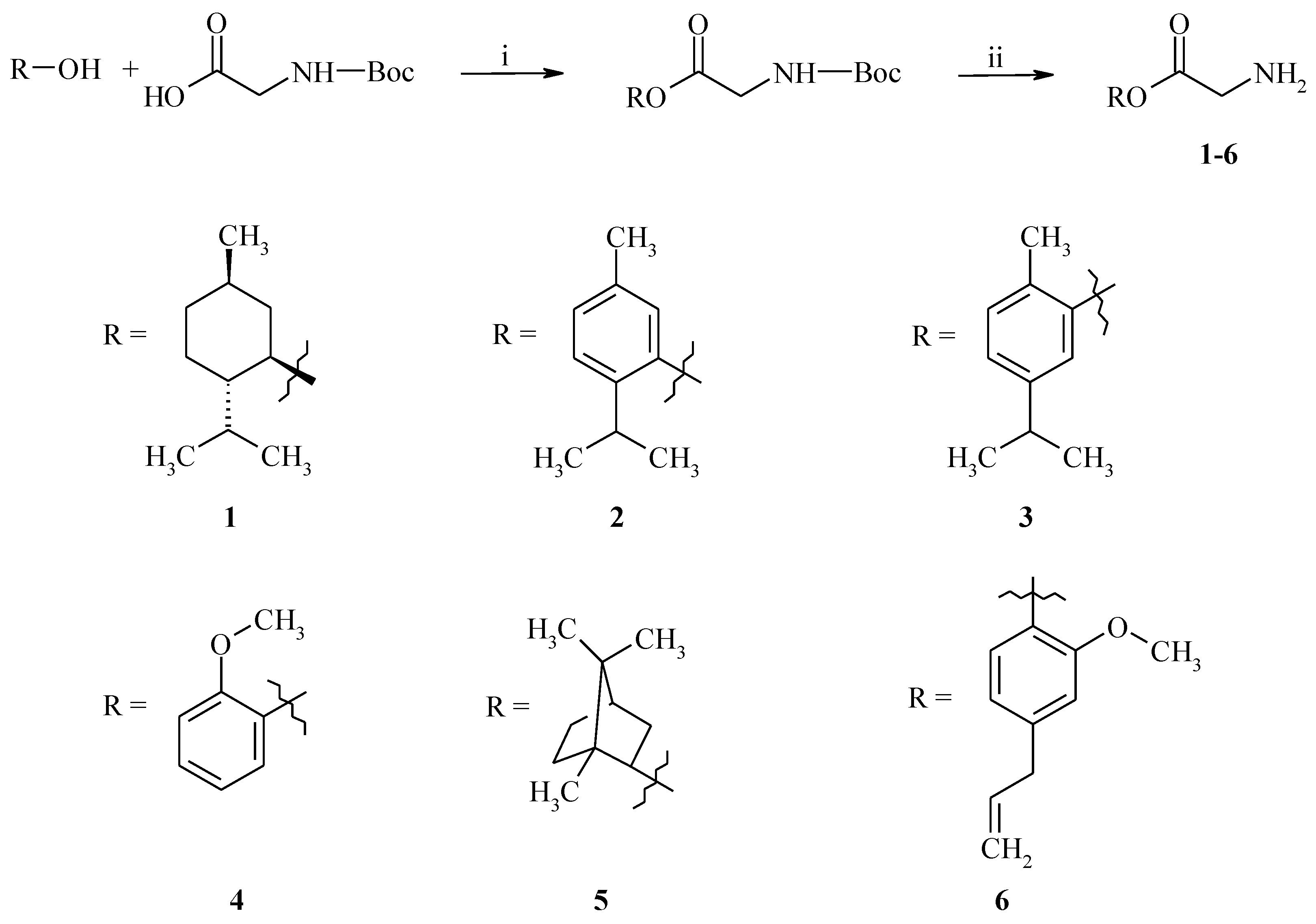
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Pharmacology
2.2.1. Antinociception Testing
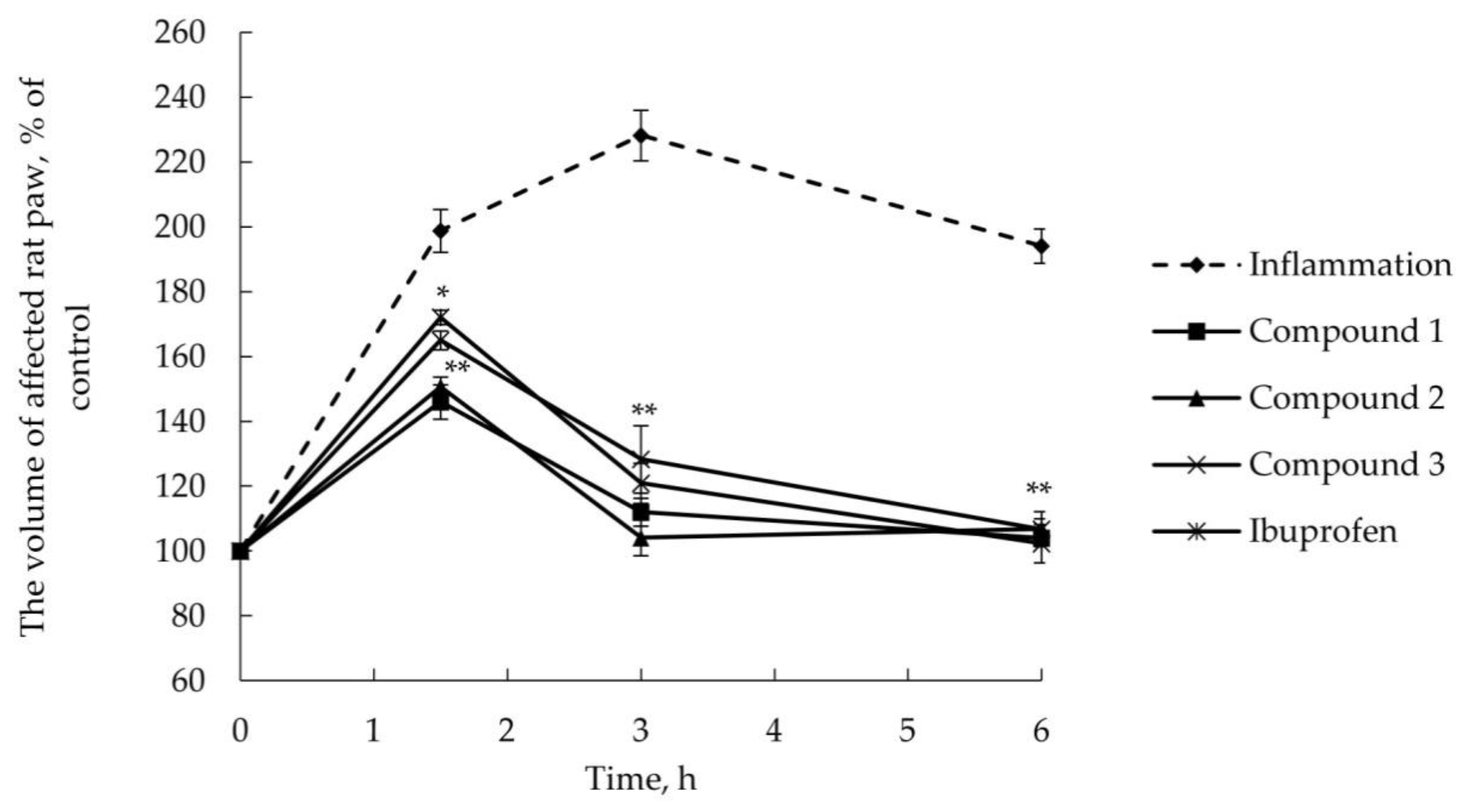
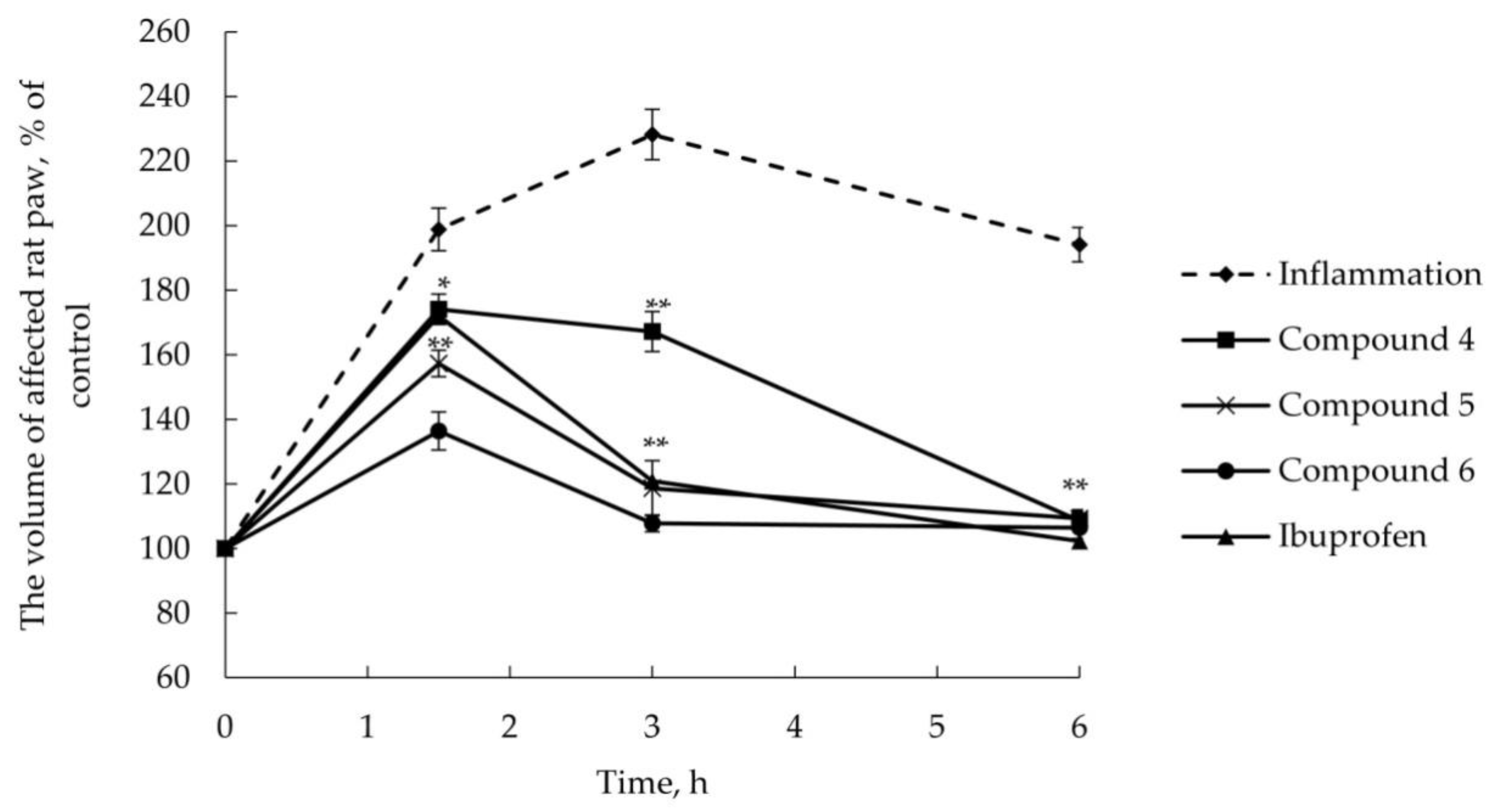
2.2.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
3.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of GABA Esters 1–6
3.3. Animals
3.4. Drug Administration
3.5. Antinociception Testing
3.6. AITC-Induced Acute Inflammatory Model
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernández-Carvajal, A.; Fernández-Ballester, G.; Devesa, I.; Manuel González-Ros, J.; Ferrer-Montiel, A. New strategies to develop novel pain therapies: addressing thermoreceptors from different points of view. Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 16–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radresa, O.; Paré, M.; Albert, J.S. Multiple roles of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels in inflammatory conditions and current status of drug development. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X. A new tr(i)p to sense pain: TRPA1 channel as a target for novel analgesics. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2008, 8, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billeter, A.T.; Hellmann, J.L.; Bhatnagar, A.; Polk, H.C. Transient receptor potential ion channels: Powerful regulators of cell function. Ann. Surg. 2014, 259, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premkumar, L.S. Transient receptor potential channels as targets for phytochemicals. ACS. Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, B.K.; Karim, S.; Goodchild, A.K.; Vaughan, C.W.; Drew, G.M. Menthol enhances phasic and tonic GABAA receptor-mediated currents in midbrain periaqueductal grey neurons. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 2803–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, H.; Mizogami, M. Comparative interactions of anesthetic alkylphenols with lipid membranes. Open J. Anesthesiol. 2014, 4, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterkina, M.; Kravchenko, I. Synthesis and pharmacological properties of novel esters based on monocyclic terpenes and GABA. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, P.; Bischofberger, J.; Sandkühler, J. Corelease of two fast neurotransmitters at a central synapse. Science 1998, 281, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, R.J.; Ryan, R.M.; Carland, J.E.; Imlach, W.L.; Christie, M.J. Glycine transport inhibitors for the treatment of pain. Trends. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, R.J.; Yee, B.K. Glycine transporters as novel therapeutic targets in schizophrenia, alcohol dependence and pain. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2013, 12, 866–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozdnev, V.F. Activation of carboxylic acids with pyrocarbonates. Esterification of N-acylamino acids with secondary alcohols using di-tret-butylpyrocarbonate—Pyridine as the condensing reagents. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 1985, 11, 725–732. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, E.L.; Meotti, F.C.; Calixto, J.B. TRPA1 antagonists as potential analgesic drugs. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 133, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.-C.; Lee, C.-H. TRP channels in skin: from physiological implications to clinical significances. Biophysics 2015, 11, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Anjos, J.L.; Alonso, A. Terpenes increase the partitioning and molecular dynamics of an amphipathic spin label in stratum corneum membranes. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 350, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leffler, A.L.; Fischer, M.J.; Rehner, D.; Kienel, S.; Kistner, K.; Sauer, S.K.; Narender, R.G.; Reeh, P.W.; Nau, C. The vanilloid receptor TRPV1 is activated and sensitized by local anesthetics in rodent sensory neurons. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannon, A.W. Current Protocols in Pharmacology; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 1–4239. [Google Scholar]
- McNamara, C.R.; Mandel-Brehm, J.; Bautista, D.M.; Siemens, J.; Deranian, K.L.; Zhao, M.; Hayward, N.J.; Chong, J.A.; Julius, D.; Moran, M.M.; et al. TRPA1 mediates formalin-induced pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13525–13530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moilanen, L.J.; Laavola, M.; Kukkonen, M.; Korhonen, R.; Leppänen, T.; Högestätt, E.D.; Zygmunt, P.M.; Nieminen, R.M.; Moilanen, E. TRPA1 contributes to the acute inflammatory response and mediates carrageenan-induced paw edema in the mouse. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheedarala, R.K.; Sunkara, V.; Park, J.W. Facile synthesis of second-generation dendrons with an orthogonal functional group at the focal point. Synth. Commun. 2009, 39, 1966–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sałat, K.; Filipek, B. Antinociceptive activity of transient receptor potential channel TRPV1, TRPA1, and TRPM8 antagonists in neurogenic and neuropathic pain models in mice. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2015, 16, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compound | Reaction Time (s) | Compound | Reaction Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 10 ± 0.6 | 6 | 32 ± 3.8 ** |
| Benzocaine | 18 ± 0.9 * | 7 | 24 ± 3.9 * |
| 1 | 29 ± 6.5 * | 8 | 15 ± 0.3 * |
| 2 | 47 ± 1.3 ** | 9 | 19 ± 1.9 * |
| 3 | 21 ± 2.5 * | 10 | 20 ± 0.5 * |
| 4 | 23 ± 2.8 * | 11 | 27 ± 2.8 * |
| 5 | 49 ± 0.9 ** | 12 | 21 ± 3.1 * |
| Compound | Licking Time (s) | Compound | Licking Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 103 ± 8.5 | 6 | 30 ± 5.6 |
| Benzocaine | 36 ± 2.4 | 7 | 24 ± 5.6 |
| 1 | 19 ± 3.7 | 8 | 50 ± 5.2 |
| 2 | 47 ± 1.3 | 9 | 38 ± 3.8 |
| 3 | 29 ± 6.9 | 10 | 54 ± 6.8 |
| 4 | 35 ± 1.9 | 11 | 26 ± 4.7 |
| 5 | 19 ± 1.5 | 12 | 40 ± 3.3 |
| Compound | Licking Time (s) | Compound | Licking Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 71 ± 1.8 | 6 | 25 ± 1.2 * |
| Benzocaine | 48 ± 2.0 * | 7 | 7 ± 1.2 ** |
| 1 | 16 ± 4.6 ** | 8 | 25 ± 3.8 * |
| 2 | 13 ± 0.9 ** | 9 | 35 ± 2.2 * |
| 3 | 15 ± 0.9 ** | 10 | 21 ± 2.8 * |
| 4 | 30 ± 8.3 * | 11 | 8 ± 3.5 ** |
| 5 | 20 ± 1.2 ** | 12 | 30 ± 2.2 * |
| Compound | Licking Time (s) | Compound | Licking Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 46 ± 1.8 | 6 | 18 ± 0.9 * |
| Benzocaine | 29 ± 6.6 * | 7 | 11 ± 2.7 ** |
| 1 | 11 ± 1.5 ** | 8 | 35 ± 4.1 |
| 2 | 16 ± 3.2 * | 9 | 23 ± 6.4 * |
| 3 | 14 ± 0.8 * | 10 | 23 ± 2.7 * |
| 4 | 20 ± 3.6 * | 11 | 12 ± 5.0 * |
| 5 | 15 ± 1.3 * | 12 | 20 ± 3.4 * |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nesterkina, M.; Kravchenko, I. Synthesis and Pharmacological Properties of Novel Esters Based on Monoterpenoids and Glycine. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10020047
Nesterkina M, Kravchenko I. Synthesis and Pharmacological Properties of Novel Esters Based on Monoterpenoids and Glycine. Pharmaceuticals. 2017; 10(2):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10020047
Chicago/Turabian StyleNesterkina, Mariia, and Iryna Kravchenko. 2017. "Synthesis and Pharmacological Properties of Novel Esters Based on Monoterpenoids and Glycine" Pharmaceuticals 10, no. 2: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10020047
APA StyleNesterkina, M., & Kravchenko, I. (2017). Synthesis and Pharmacological Properties of Novel Esters Based on Monoterpenoids and Glycine. Pharmaceuticals, 10(2), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10020047