RNA-Eluting Surfaces for the Modulation of Gene Expression as A Novel Stent Concept
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
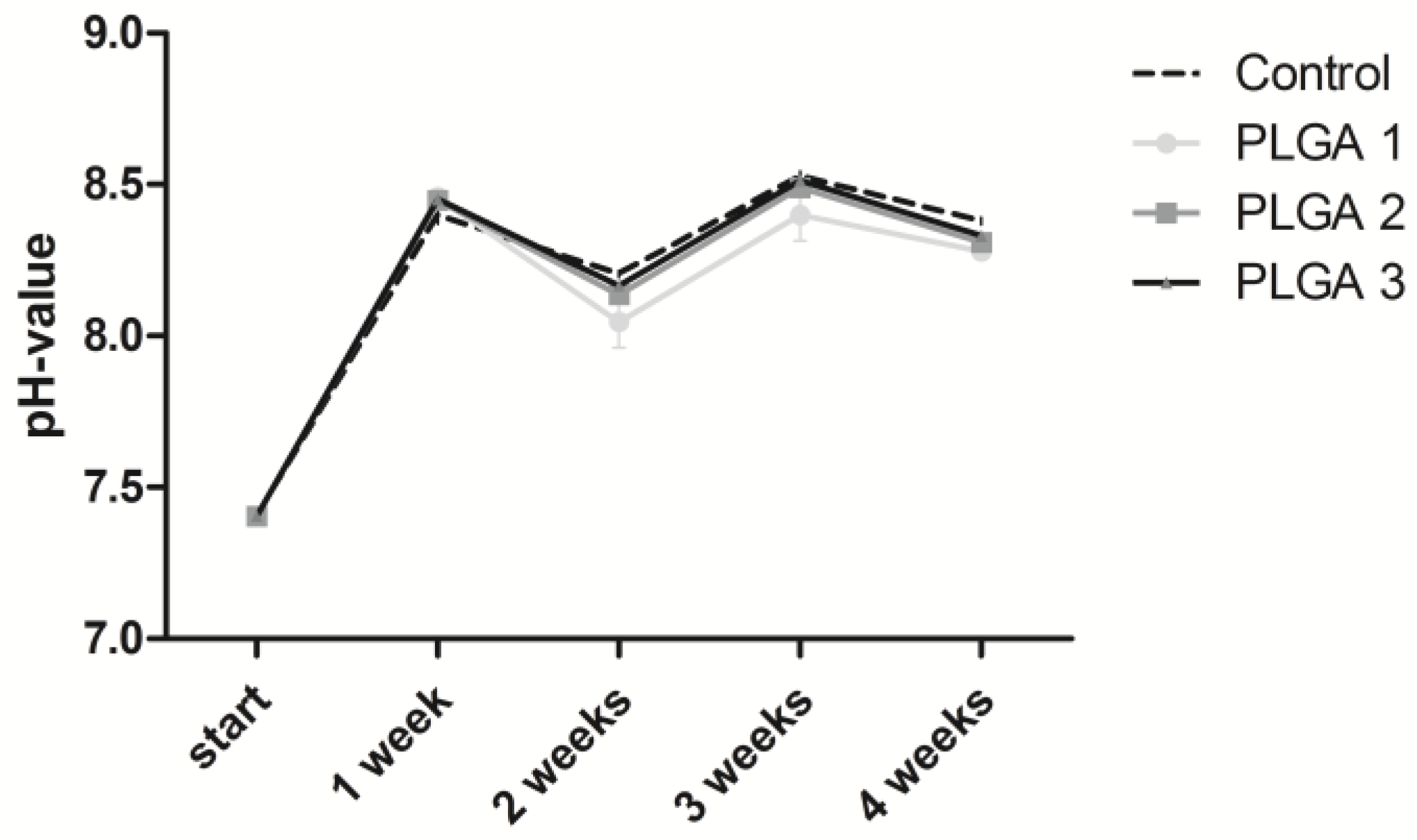
2.1. Stability of the pH Value
2.2. Influence of PLGA on Cell Viability
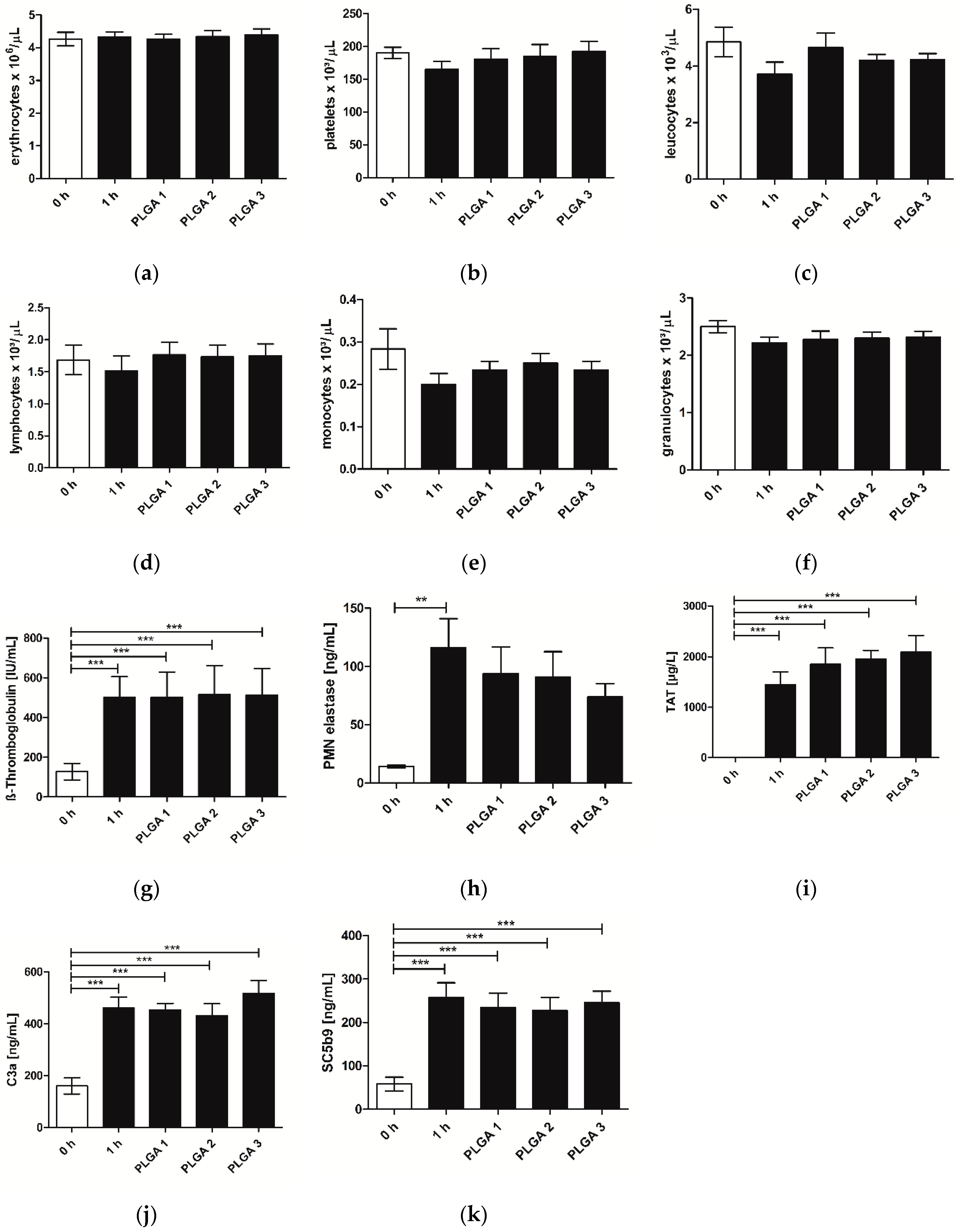
2.3. Hemocompatibility
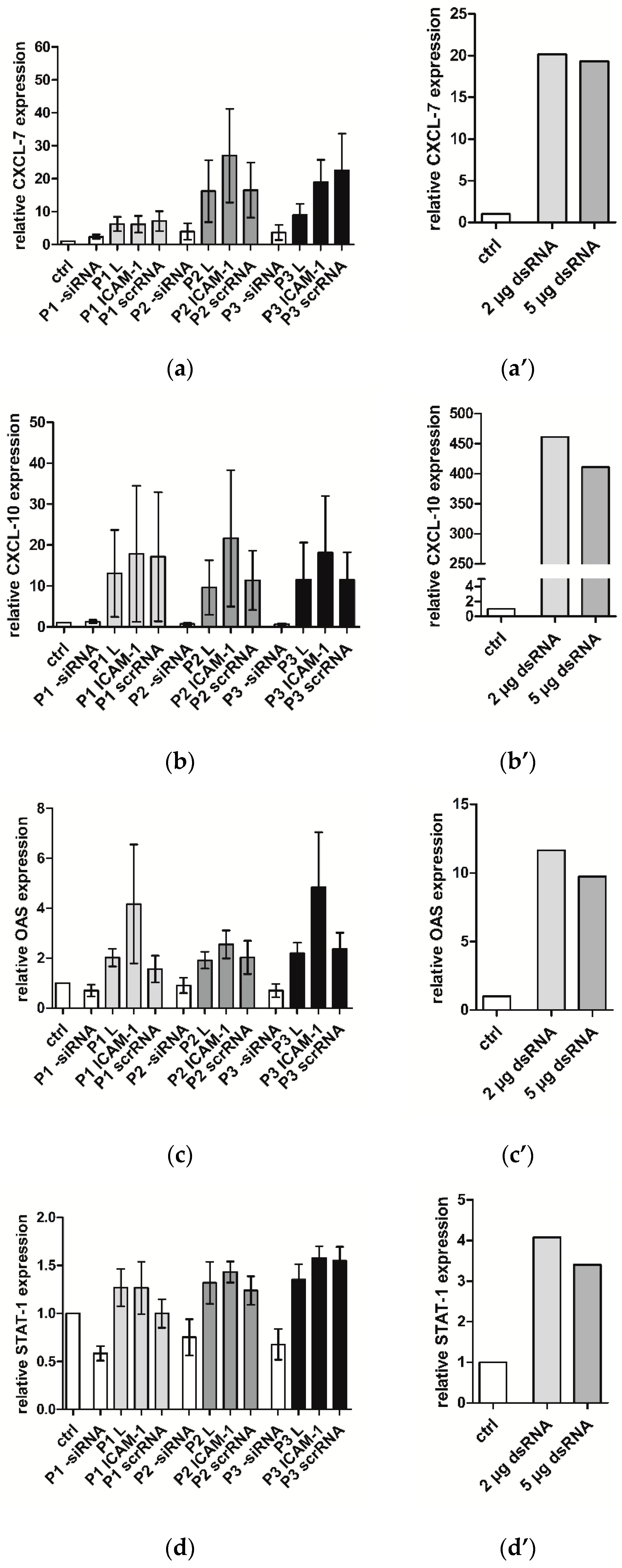
2.4. Immune Response of hVECs to Different PLGAs
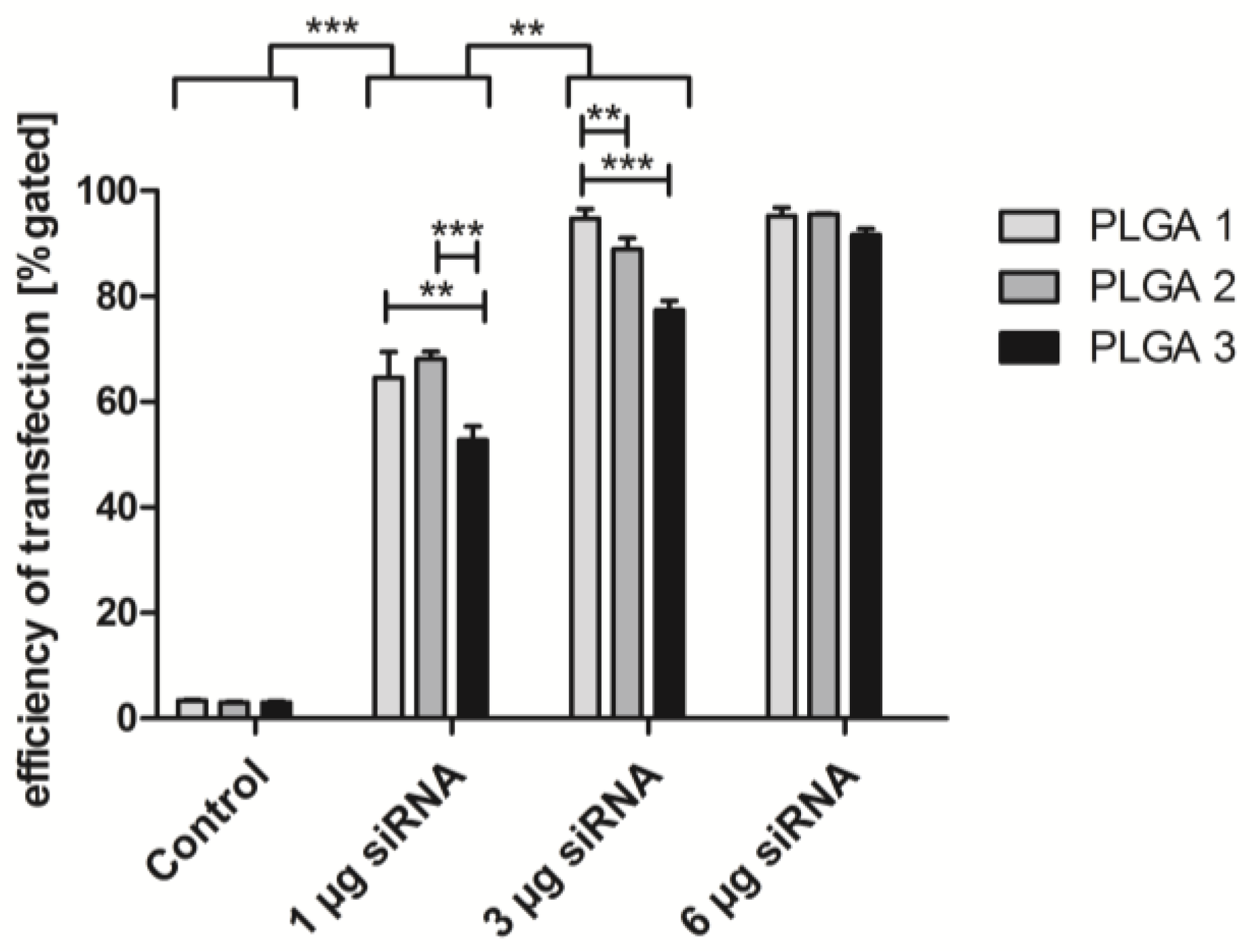
2.5. Short-Term Uptake of siRNA AF488
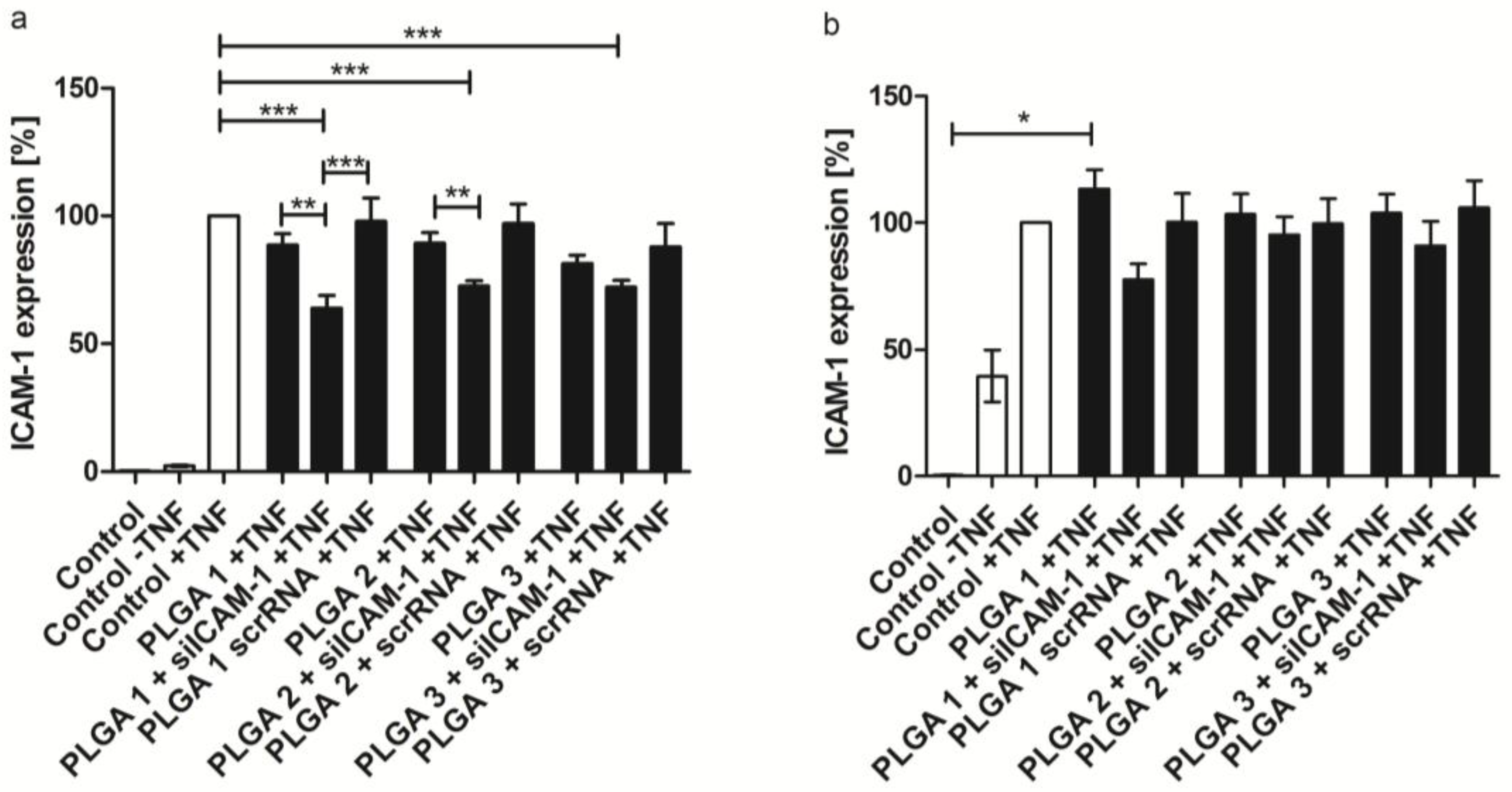
2.6. ICAM-1 Knockdown and mRNA Levels of EA.hy926 and hVECs
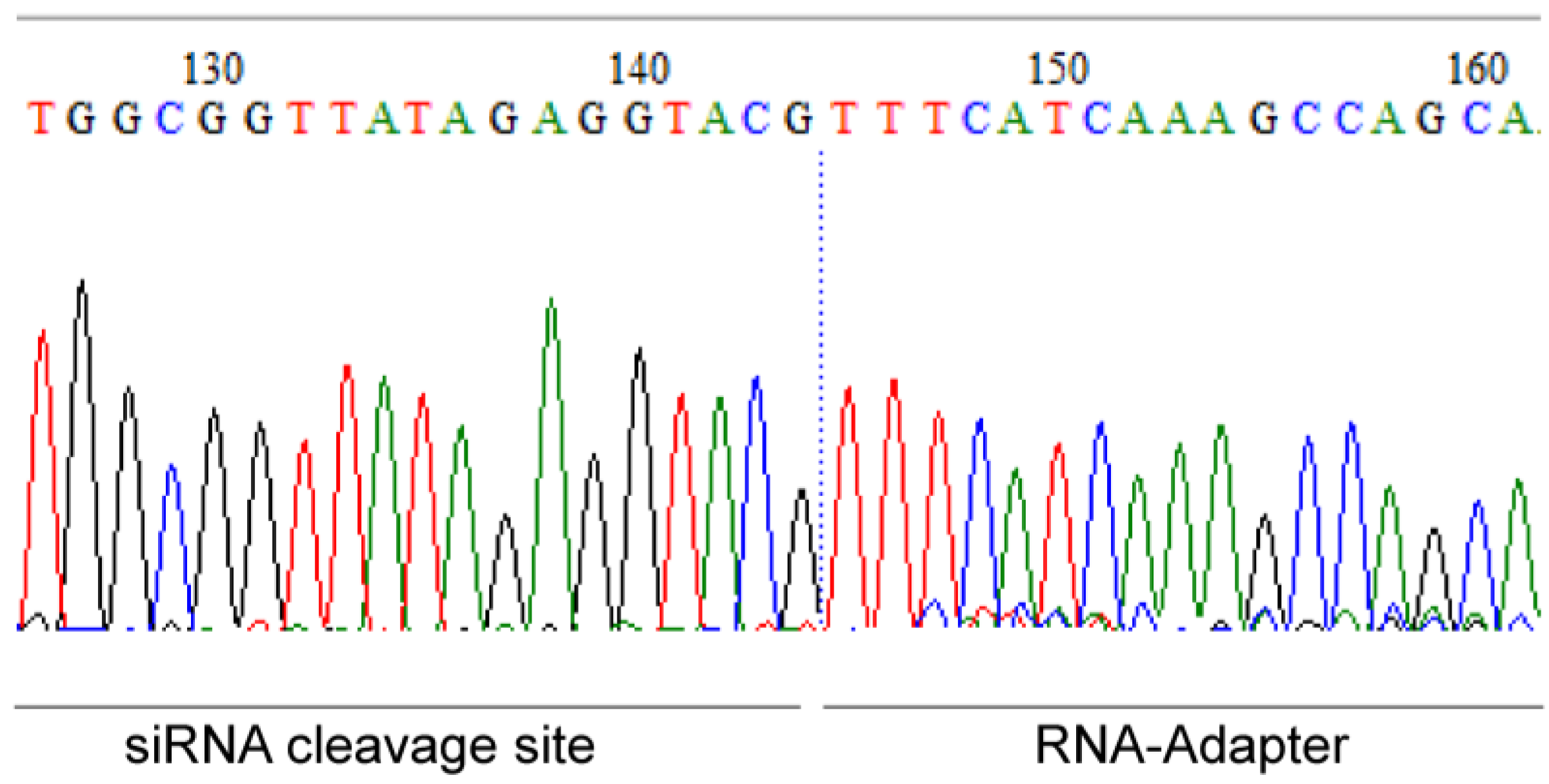
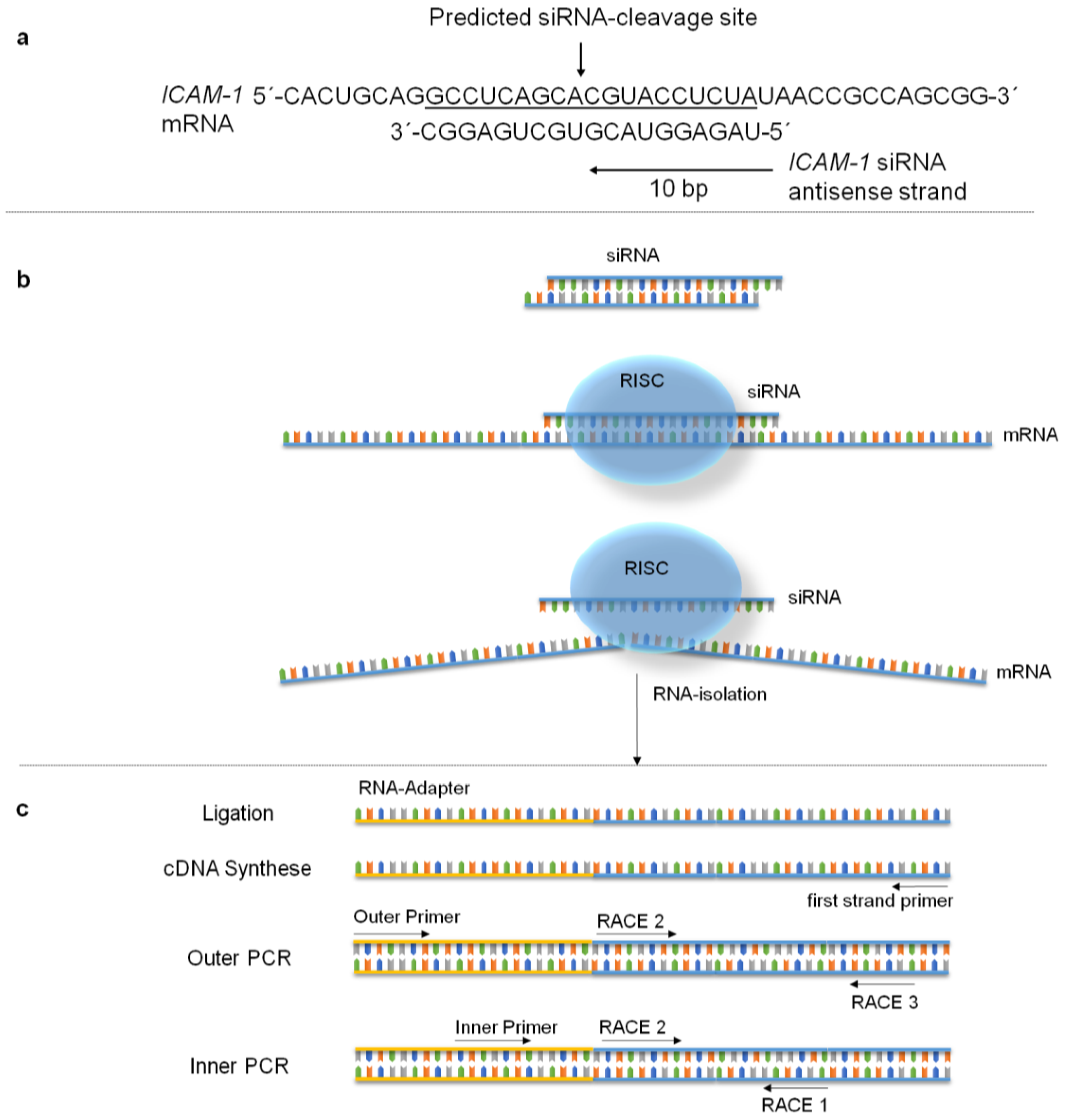
2.7. Specific mRNA Degradation Analyzed by 5′-RLM-RACE-PCR
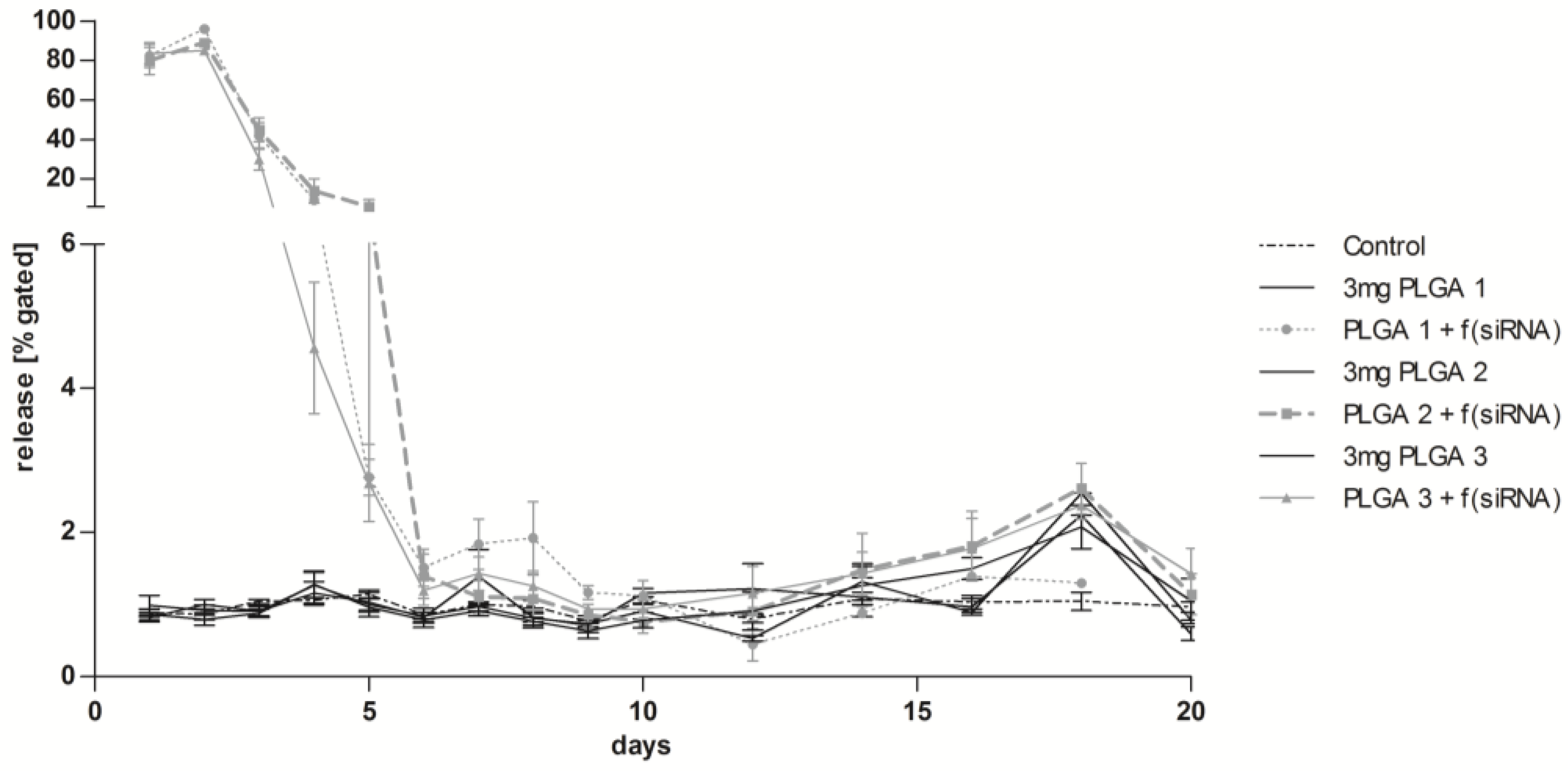
2.8. Long-Term Release of siRNA Complexes
2.9. Co-Transfection of eGFPmRNA and siRNA AF 555 in EA.hy926
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals for PLGA Coating
4.2. SiRNAs
4.3. Synthesis of eGFPmRNA
4.4. Substrate for PLGA Coatings
4.5. Build-Up of PLGA/RNA Coatings
4.6. Cultivation of EA.hy926 and Human Primary Endothelial Cells (hVECs)
4.7. Measurement of pH Value
4.8. PLGA/RNA Mediated Transfection of EA.hy926 and hVECs
4.9. Cell Viability Assay
4.10. Hemocompatibility Testing
4.11. Flow Cytometry
4.12. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.13. 5′-RNA Ligase–Mediated Rapid Amplification of cDNA-Ends PCR (5′-RLM-RACE-PCR)
4.14. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mendis, S.; Puska, P.; Norrving, B. Global atlas on cardiovascular disease prevention and control. World Health Organization, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Espinola-Klein, C.; Rupprecht, H.J.; Bickel, C.; Lackner, K.; Schnabel, R.; Munzel, T.; Blankenberg, S. Inflammation, atherosclerotic burden and cardiovascular prognosis. Atherosclerosis 2007, 195, e126–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R. Atherosclerosis—An inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüntzig, A. Transluminal dilatation of coronary-artery stenosis. The Lancet 1978, 311, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, R.A.; Joner, M.; Kastrati, A. Stent thrombosis and restenosis: What have we learned and where are we going? The Andreas Grüntzig Lecture ESC 2014. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 3320–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, H.; Bona-Casas, C.; Hoekstra, A.G. Modelling the effect of a functional endothelium on the development of in-stent restenosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, F.; Finn, A.V.; Yazdani, S.K.; Nakano, M.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Virmani, R. The importance of the endothelium in atherothrombosis and coronary stenting. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2012, 9, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sluiter, W.; Pietersma, A.; Lamers, J.M.; Koster, J.F. Leukocyte adhesion molecules on the vascular endothelium: Their role in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease and the mechanisms underlying their expression. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1993, 22, S37–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Node, K. Molecular basis of restenosis and novel issues of drug-eluting stents. Circ. J. 2009, 73, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnerts, M.E.; van Kooyk, Y.; Simmons, D.L.; Figdor, C.G. Distinct binding of T lymphocytes to ICAM-1, -2 or -3 upon activation of LFA-1. Eur. J. Immunol. 1994, 24, 2155–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koedam, J.A.; Cramer, E.M.; Briend, E.; Furie, B.; Furie, B.C.; Wagner, D.D. P-selectin, a granule membrane protein of platelets and endothelial cells, follows the regulated secretory pathway in ATT-20 cells. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 116, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welt, F.G.; Rogers, C. Inflammation and restenosis in the stent era. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, K.; Laudanna, C.; Cybulsky, M.I.; Nourshargh, S. Getting to the site of inflammation: The leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat. Rev. Immun. 2007, 7, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Croce, K.; Morooka, T.; Sakuma, M.; Node, K.; Simon, D.I. Vascular inflammation and repair: Implications for re-endothelialization, restenosis, and stent thrombosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2011, 4, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, W.; Farah, S.; Domb, A.J. Drug eluting stents: Developments and current status. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.M.; Boyle, F.J. Drug-eluting stents for coronary artery disease: A review. Med. Eng. Phys. 2011, 33, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendel, H.P.; Avci-Adali, M.; Ziemer, G. Endothelial progenitor cell capture stents--hype or hope? Int. J. Cardiol. 2010, 145, 115–117, author reply 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, G.; Granada, J.F.; Alviar, C.L.; Tellez, A.; Kaluza, G.L.; Guilhermier, M.Y.; Parker, S.; Rowland, S.M.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Leon, M.B.; et al. Anti-CD34 antibodies immobilized on the surface of sirolimus-eluting stents enhance stent endothelialization. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2010, 3, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Feng, S.-C.; Pang, X.-J.; Li, W.-X.; Bi, Y.-H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, S.-X.; Wang, Y.; Feng, B. Combination coating of chitosan and anti-CD34 antibody applied on sirolimus-eluting stents can promote endothelialization while reducing neointimal formation. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2012, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.; Goh, D.; Farhatnia, Y.; G, N.; Lim, J.; Teoh, S.H.; Rajadas, J.; Alavijeh, M.S.; Seifalian, A.M. An anti-CD34 antibody-functionalized clinical-grade poss-PCU nanocomposite polymer for cardiovascular stent coating applications: A preliminary assessment of endothelial progenitor cell capture and hemocompatibility. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danhier, F.; Ansorena, E.; Silva, J.M.; Coco, R.; Le Breton, A.; Preat, V. PLGA-based nanoparticles: An overview of biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, S.C. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloid. Surface B 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredenberg, S.; Wahlgren, M.; Reslow, M.; Axelsson, A. The mechanisms of drug release in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-based drug delivery systems—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 415, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vert, M.; Mauduit, J.; Li, S. Biodegradation of PLA/GA polymers: Increasing complexity. Biomaterials 1994, 15, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, N.; Abbadessa, A.; Di Stefano, A.; van Nostrum, C.F.; Vermonden, T.; Rahimian, S.; Teunissen, E.A.; van Steenbergen, M.J.; Amidi, M.; Hennink, W.E. The effect of lauryl capping group on protein release and degradation of poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) particles. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houchin, M.L.; Topp, E.M. Chemical degradation of peptides and proteins in PLGA: A review of reactions and mechanisms. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2395–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolnik, B.S.; Burgess, D.J. Evaluation of in vivo-in vitro release of dexamethasone from PLGA microspheres. J. Control. Release 2008, 127, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenjob, R.; Taranamai, P.; Na, K.; Yang, S.-G. Recent trend in applications of polymer materials to stents. Gastrointest. Interv. 2015, 4, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Park, S. Local delivery of antiproliferative agents via stents. Polymers 2014, 6, 755–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klugherz, B.D.; Jones, P.L.; Cui, X.; Chen, W.; Meneveau, N.F.; DeFelice, S.; Connolly, J.; Wilensky, R.L.; Levy, R.J. Gene delivery from a DNA controlled-release stent in porcine coronary arteries. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brito, L.A.; Chandrasekhar, S.; Little, S.R.; Amiji, M.M. Non-viral enos gene delivery and transfection with stents for the treatment of restenosis. Biomed. Eng. Online 2010, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.S.; Wang, N. Synthesis, characterization, biodegradation, and drug delivery application of biodegradable lactic/glycolic acid polymers. Part II: Biodegradation. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2001, 12, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.Y.; Chen, M.; Zheng, B.; Wang, X.G.; Huo, Y. Long-term effects of novel biodegradable, polymer-coated, sirolimus-eluting stents on neointimal formation in a porcine coronary model. Int. Heart J. 2009, 50, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte, A.; Raabe, C.; Walker, T.; Simon, P.; Ziemer, G.; Wendel, H.P. Optimized basic conditions are essential for successful siRNA transfection into primary endothelial cells. Oligonucleotides 2009, 19, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Juan, A.; Bala, M.; Hlawaty, H.; Portes, P.; Vranckx, R.; Feldman, L.J.; Letourneur, D. Development of a functionalized polymer for stent coating in the arterial delivery of small interfering RNA. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 3074–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, H.; Sun, W.; Han, S.; Yu, C.; Li, J. VCAM-1 siRNA reduces neointimal formation after surgical mechanical injury of the rat carotid artery. J. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 50, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluvinet, R.; Petriz, J.; Torras, J.; Herrero-Fresneda, I.; Cruzado, J.M.; Grinyo, J.M.; Aran, J.M. RNAi-mediated silencing of CD40 prevents leukocyte adhesion on CD154-activated endothelial cells. Blood 2004, 104, 3642–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Qian, H.; Yang, H.; Xu, L.; Xu, W.; Yan, J. Regression of atherosclerosis plaques in apolipoprotein e−/− mice after lentivirus-mediated RNA interference of cd40. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 163, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, T.; Wendel, H.P.; Tetzloff, L.; Heidenreich, O.; Ziemer, G. Suppression of ICAM-1 in human venous endothelial cells by small interfering RNAS. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2005, 28, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, T.; Wendel, H.P.; Tetzloff, L.; Raabe, C.; Heidenreich, O.; Simon, P.; Scheule, A.M.; Ziemer, G. Inhibition of adhesion molecule expression on human venous endothelial cells by non-viral siRNA transfection. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2007, 11, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossfeld, S.; Nolte, A.; Hartmann, H.; Recke, M.; Schaller, M.; Walker, T.; Kjems, J.; Schlosshauer, B.; Stoll, D.; Wendel, H.P.; et al. Bioactive coronary stent coating based on layer-by-layer technology for siRNA release. Acta Biomater 2013, 9, 6741–6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte, A.; Walker, T.; Schneider, M.; Kray, O.; Avci-Adali, M.; Ziemer, G.; Wendel, H.P. Small-interfering RNA-eluting surfaces as a novel concept for intravascular local gene silencing. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.A. The manufacturing techniques of various drug loaded biodegradable poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) devices. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2475–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Braatz, R.D. A mechanistic model for drug release in PLGA biodegradable stent coatings coupled with polymer degradation and erosion. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 2269–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Shi, G.; Bei, J.; Wang, S. Enzymatic degradation behavior and mechanism of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) foams by trypsin. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Cai, Q.; Yan, N.; Deng, X.; Yang, X. In vitro hydrolytic and enzymatic degradation of nestlike-patterned electrospun poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 95A, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gresch, O.; Altrogge, L. Transfection of difficult-to-transfect primary mammalian cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 801, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hamm, A.; Krott, N.; Breibach, I.; Blindt, R.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Efficient transfection method for primary cells. Tissue Eng. 2002, 8, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avci-Adali, M.; Behring, A.; Keller, T.; Krajewski, S.; Schlensak, C.; Wendel, H.P. Optimized conditions for successful transfection of human endothelial cells with in vitro synthesized and modified mRNA for induction of protein expression. J. Biol. Eng. 2014, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, T.; Wendel, H.P.; Raabe, C.; Wiechnik, P.; Spranger, L.; Heidenreich, O.; Scheule, A.M.; Nordheim, A.; Ziemer, G. Graft protection in bypass surgery: siRNA-mediated silencing of adhesion molecules. Oligonucleotides 2009, 19, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minuth, W.W.; Schumacher, K.; Strehl, R.; de Vries, U. Mikroreaktortechnik für Tissue Engineering. In Medizintechnik mit biokompatiblen werkstoffen und verfahren, 3rd ed.; Wintermantel, E., Ha, S.-W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Soutschek, J.; Akinc, A.; Bramlage, B.; Charisse, K.; Constien, R.; Donoghue, M.; Elbashir, S.; Geick, A.; Hadwiger, P.; Harborth, J.; et al. Therapeutic silencing of an endogenous gene by systemic administration of modified siRNAs. Nature 2004, 432, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.E.; Zuckerman, J.E.; Choi, C.H.; Seligson, D.; Tolcher, A.; Alabi, C.A.; Yen, Y.; Heidel, J.D.; Ribas, A. Evidence of RNAi in humans from systemically administered siRNA via targeted nanoparticles. Nature 2010, 464, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozen, S.; Skaletsky, H. Primer3 on the www for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 132, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Positive Cells (%) | Ctrl (++) | *mRNA* siRNA (+) | *mRNA* siRNA | *-mRNA +siRNA | +mRNA *siRNA | +mRNA +siRNA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| siRNA positive | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 26.03 | 0.01 | 6.25 |
| mRNA positive | 0.94 | 2.19 | 2.86 | 0.26 | 10.91 | 7.90 |
| siRNA + mRNA positive | 1.02 | 1.72 | 3.18 | 4.33 | 2.84 | 11.01 |
| qRT-PCR Primer | Sequence |
| OAS | forward: 5’-GGAGACAGCTGGAAGCCTGTC-3’ reverse: 5’-TGACCCAGGGCATCAAAGG-3’ |
| STAT-1 | forward: 5’-TGGAAGCGGAGACAGCAGAG-3’ reverse: 5’-AGGTGTATTTCTGTTCCAATTCCTC-3’ |
| CXCL-10 | forward: 5’-AAGTGGCATTCAAGGAGTACC-3’ reverse: 5’-ACGTGGACAAAATTGGCTTGC-3’ |
| ICAM-1 | forward: 5’-CTTGAGGGCACCTACCTCTGTC-3’ reverse: 5’-CGGCTGCTACCACAGTGATG-3’ |
| ß-Actin | forward: 5’-GAGCACAGAGCCTCGCCTTT-3’ reverse: 5’-TCATCATCCATGGTGAGCTGG-3’ |
| 5′-RLM-RACE PCR | sequence |
| ICAM-1 first strand | 5´-AGGTACCATGGCCCCAAATG-3´ |
| ICAM-1 RACE 1 | 5´-ACTCTGTTCAGTGTGGCACC-3´ |
| ICAM-1 RACE 2 | 5´-TCTTCCTCGGCCTTCCCATA-3´ |
| ICAM-1 RACE 3 | 5´-TGGCCCCAAATGCTGTTGTA-3´ |
| RNA-Adapter (universally) | 5´-GCUGAUGGCGAUGAAUGAACACUGCGUUUGCUGGCUUUGAUGAAA-3´ |
| Outer Primer (universally) | 5´-GCTGATGGCGATGAATGAACACTG-3´ |
| Inner Primer (universally) | 5´-CGCGGATCCGAACACTGCGTTTGCTGGCTTTGATG-3´ |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koenig, O.; Zengerle, D.; Perle, N.; Hossfeld, S.; Neumann, B.; Behring, A.; Avci-Adali, M.; Walker, T.; Schlensak, C.; Wendel, H.P.; et al. RNA-Eluting Surfaces for the Modulation of Gene Expression as A Novel Stent Concept. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10010023
Koenig O, Zengerle D, Perle N, Hossfeld S, Neumann B, Behring A, Avci-Adali M, Walker T, Schlensak C, Wendel HP, et al. RNA-Eluting Surfaces for the Modulation of Gene Expression as A Novel Stent Concept. Pharmaceuticals. 2017; 10(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoenig, Olivia, Diane Zengerle, Nadja Perle, Susanne Hossfeld, Bernd Neumann, Andreas Behring, Meltem Avci-Adali, Tobias Walker, Christian Schlensak, Hans Peter Wendel, and et al. 2017. "RNA-Eluting Surfaces for the Modulation of Gene Expression as A Novel Stent Concept" Pharmaceuticals 10, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10010023
APA StyleKoenig, O., Zengerle, D., Perle, N., Hossfeld, S., Neumann, B., Behring, A., Avci-Adali, M., Walker, T., Schlensak, C., Wendel, H. P., & Nolte, A. (2017). RNA-Eluting Surfaces for the Modulation of Gene Expression as A Novel Stent Concept. Pharmaceuticals, 10(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10010023




