A Community-Based Event Delivery Protocol in Publish/Subscribe Systems for Delay Tolerant Sensor Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Routing Strategies in Pub/Sub Systems for Traditional Mobile Networks
2.2. Routing Strategies in Pub/Sub Systems for MANET
2.3. Routing Strategies in Pub/Sub Systems for DTN
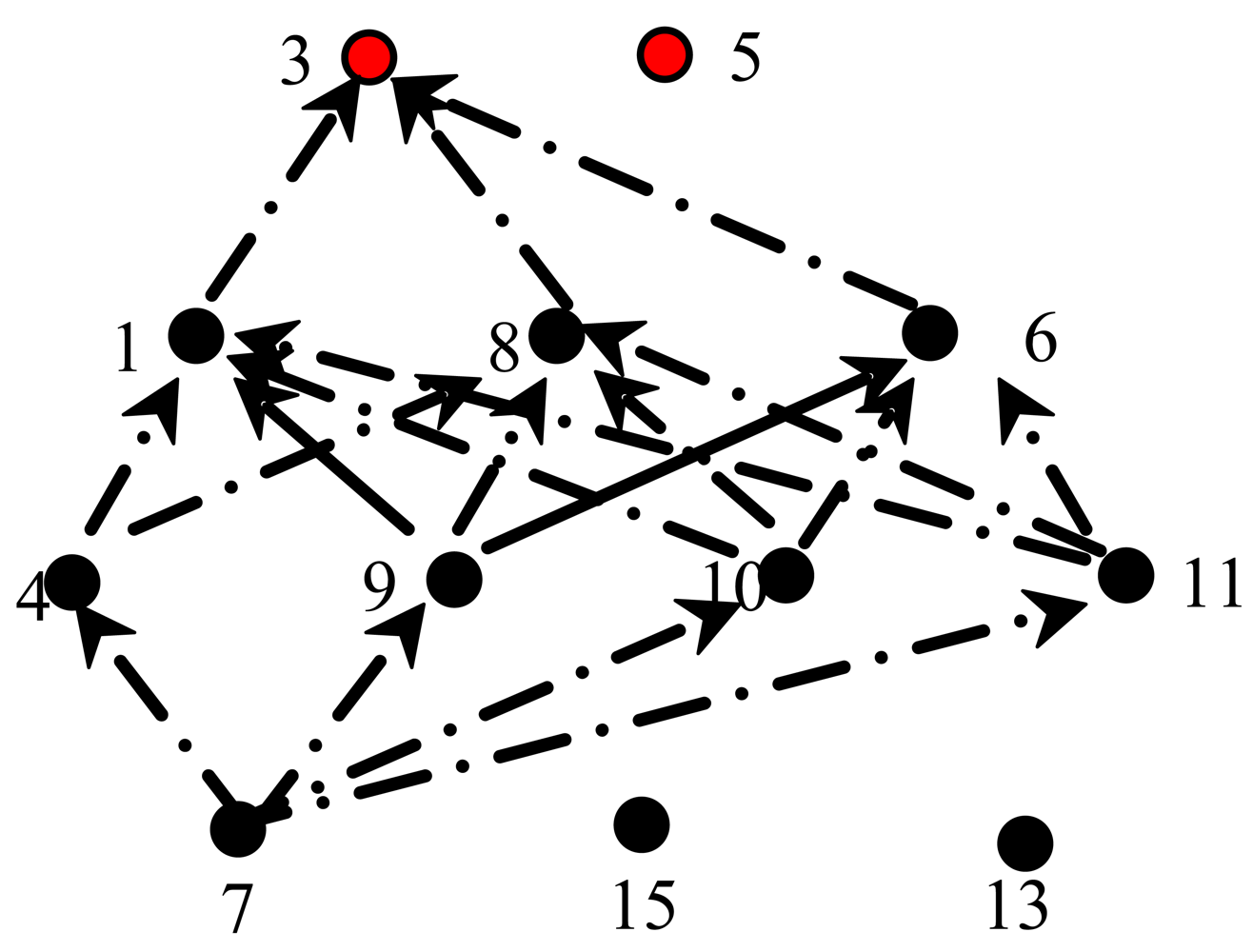
3. Network Model
- Each of the sensor nodes has a unique ID number.
- The mobility of all the mobile subscriber nodes in the given area is assumed to follow the Random Waypoint Model (RWP) [19].
- Since the energy of mobile subscribers can be complemented timely, we assume both the energy and the memory queue of the mobile subscribers are adequate.
- Every node can directly communicate only with the nodes in the same gird or the nodes located in the neighboring grids sharing at least one side or one corner with the grid of this node.
- The mobile subscriber nodes cannot directly communicate with each other.
- All sensor nodes are aware of their locations.
4. The Proposed Community-Based Event Delivery Protocol
4.1. Routing Strategies in Pub/Sub Systems for DTN
- Initially, if the subscriber i, while moving, comes within one grid, it will broadcast Hello messages to all its neighboring sensor nodes. The neighboring sensor nodes send back their information, including community numbers, grid numbers and their ID numbers to subscriber i thereafter.
- Then, once subscriber node i finds out that it connects to community N for the first time, it sends out PATH messages including its current mobility path to its neighboring sensor nodes which belong to community N. After that, these PATH messages are broadcasted among nodes in community N.
- When subscriber i changes its moving path after connecting to community N, its current moving path should also be reported using the method mentioned in phase b.
- After receiving the PATH messages, each sensor node in community N would compare its location with each grid that the node i passes, to learn whether it could communicate directly with node i or not. Let set Z denote sensors that could communicate directly with subscriber i in community N.
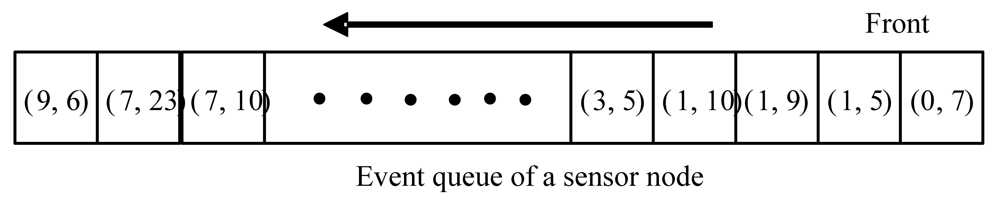
4.2. Queue Management
A. Event's survival time
B. Event's successful delivery time
C. The implementation of queue management scheme
- After the sensor acquires data from its sensing unit, it creates an event record and inserts the record into the data queue.
- When the sensor receives an event record from other sensors, it may insert the record into its data queue.
- After the sensor sends out an event record, it may insert the record again if this record is created by the source sensor node, because this record is not guaranteed to be delivered to all subscribers that have interest in it.
5. Simulation Study
5.1. Simulation Parameters
5.2. Performance Comparison
5.3. Impact of Varying Node Speed
5.4. Impact of Varying Sensor Node Density
5.5. Analysis of Network Life
6. Conclusions
- We divide the network into several communities according to the connectivity of sensor nodes.
- A dynamic routing mechanism was proposed, where events in a community are delivered to relevant mobile subscribers.
- An effective queue management scheme was proposed. According to this scheme, events with too large successful delivery time or too long survival time should be dropped to make the full use of network bandwidth and to reduce network energy consumption.
Acknowledgments
- Fall, K. A Delay-tolerant Network Architecture for Challenged Internets. Proceedings of ACM Special Internet Groupon Data Communications, Karlsruhe, Germany; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Eugster, P.; Felber, P.; Guerraoui, R.; Kermarrec, A.-M. The many faces of publish/subscribe. ACM Comput. Surv. 2001, 35, 114–131. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Cao, J.N.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.L. Efficient Event Delivery in Publish/SubscribeSystems for Wireless Mesh Networks. Proceedings of Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Hong Kong, China; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bhola, S.; Strom, R.; Bagchi, S.; Zhao, Y.; Auerbach, J. Exactly-Once Delivery in a Content-Based Publish-subscribe System. Proceedings of Dependable Systems and Networks, Bethesda, MA, USA; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, C.P.; Arkins, R.; Segall, B. Supporting Disconnectedness–Transparent Information Delivery for Mobile and Invisible Computing. Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Cluster Computing and the Grid (CCGrid), Brisbane, Australia; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Podnar, I.; Lovrek, I. Supporting Mobility with Persistent Notifications in Publish/Subscribe Systems. Proceedings of International Workshop on Distributed Event-Based Systems (DEBS), Edinburgh, UK; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Burcea, I.; Jacobsen, H.-A.; DeLara, E.; Muthusam, V.; Petrovic, M. Disconnected Operation in Publish/Subscribe Middleware. Proceedings of IEEE International on Mobile Data Management (MDM), Berkeley, CA, USA; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Muthusamy, V.; Petrovic, M.; Jacobsen, H. Effects of Routing Computations in Content-Based Routing Networks with Mobile Data Sources. Proceedings of ACM International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Cologne, Germany; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Petrovic, M.; Vinod, M.; Jacobsen, H.-A. Content-Based Routing in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Networking and Services (MobiQuitous), San Diego, CA, USA; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, P.; Picco, G. Semi-Probabilistic Content-Based Publish/Subscribe. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing (ICDCS), Columbus, OH, USA; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Baldoni, R.; Beraldi, R.; Cugola, G.; Migliavacca, M.; Querzoni, L. Structure-less Content-Based Routing In Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. Proceedings of International Conference on Pervasive Services (ICPS), Santorini, Greece; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Garcia-Molina, H. Publish/Subscribe in a Mobile Enviroment. Proceedings of the Second ACM International Workshop on Data Engineering for Wireless and Mobile Access, Santa Barbara, CA, USA; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Garcia-Molina, H. Publish/Subscribe Tree Construction in Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks. Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Mobile Data Management, Melbourne, Australia; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Musolesi, M.; Mascolo, C.; Hailes, S. EMMA: Epidemic messaging middleware for ad hoc networks. Personal Ubiquitous Comput. 2005, 10, 1617–4909. [Google Scholar]
- Mottola, L.; Cugola, G.; Picco, G. Tree overlays for publish-subscribe in mobile ad hoc networks. In Technical Report; Politecnico di Milano: Milan, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Royer, E.M.; Perkins, C.E. Multicast Ad Hoc On-Demand Distance Vector (MAODV) Routing. Proceedings of the Fifth Annual ACM/IEEE international conference on Mobile Computing and Networking Table of Contents, Seattle, WA, USA; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yoneki, E.; Hui, P.; Chan, S.Y.; Jon, C. A Socio-Aware Overlay for Publish/Subscribe Communication in Delay Tolerant Networks. Proceedings of International Workshop on Modeling Analysis and Simulation of Wireless and Mobile Systems, Chania, Greece; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Greifenberg, J.; Kutscher, D. Efficient Publish/Subscribe-based Multicast for Opportunistic Networking with Self-Organized Resource Utilization. Proceedings of IEEE International Workshop on Opportunistic Networking (WON-2008), Ginowan, Okinawa, Japan; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Camp, T.; Boleng, J.; Davies, V. A survey of mobility models for ad hoc network research. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2002, 2, 483–502. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.L.; Cao, J.N.; Li, J.; Wu, J. Achieving Bounded Delay on Message Delivery in Publish/Subscribe Systems. Proceedings of International Conference on Parallel Processing (ICPP'06), Columbus, OH, USA; 2006; pp. 407–416. [Google Scholar]






| Parameter | Default Value |
|---|---|
| Network size | 200 × 200 |
| Number of Grids | 15 × 15 |
| Number of sensor node | 100 |
| Number of subscribe node | 10 |
| Initial energy of each sensor node (J) | 10 J |
| Size of each event(bite) | 250 bits |
| Number of events successfully transferred per second | 20 |
| E elec | 50 nJ/bit |
| ε_fs | 10 pJ/bit/m2 |
| ε_mp | 0.0013 pJ/bit/m4 |
| Speed of subscribe node V(m/s) | 0-5 |
| Pause time Tpause (s) | 0∼120 |
| Maximum queue size of sensor | 200 events |
| Value of α | 20 |
| Maximum delay tolerant value (s) | 2,000 s |
| Threshold valueθ(J) | 5 |
| Value of γ | 4 |
| CED | DG | |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery ratio (%) | 86.5 | 47.0 |
| Average copies of each event | 4.2 | 75.9 |
| Average delay(s) | 230.6 | 615.5 |
| CED | DG | |
|---|---|---|
| Network lifetime(day) | 3.57 | 6.04 |
| Delivery ratio(%) | 86.5 | 47.0 |
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, N.; Liu, M.; Zhu, J.; Gong, H. A Community-Based Event Delivery Protocol in Publish/Subscribe Systems for Delay Tolerant Sensor Networks. Sensors 2009, 9, 7580-7594. https://doi.org/10.3390/s91007580
Liu N, Liu M, Zhu J, Gong H. A Community-Based Event Delivery Protocol in Publish/Subscribe Systems for Delay Tolerant Sensor Networks. Sensors. 2009; 9(10):7580-7594. https://doi.org/10.3390/s91007580
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Nianbo, Ming Liu, Jinqi Zhu, and Haigang Gong. 2009. "A Community-Based Event Delivery Protocol in Publish/Subscribe Systems for Delay Tolerant Sensor Networks" Sensors 9, no. 10: 7580-7594. https://doi.org/10.3390/s91007580
APA StyleLiu, N., Liu, M., Zhu, J., & Gong, H. (2009). A Community-Based Event Delivery Protocol in Publish/Subscribe Systems for Delay Tolerant Sensor Networks. Sensors, 9(10), 7580-7594. https://doi.org/10.3390/s91007580





