Specific Dynamic Parameters: A Novel Multi-View Stereo Vision Measurement System for Vector Nozzle
Abstract
1. Introduction
- How do we use non-contact measurement methods and adapt to the dynamic changes of the nozzle at the same time? This includes the joint calibration of multiple cameras and the perception of the nozzle structure.
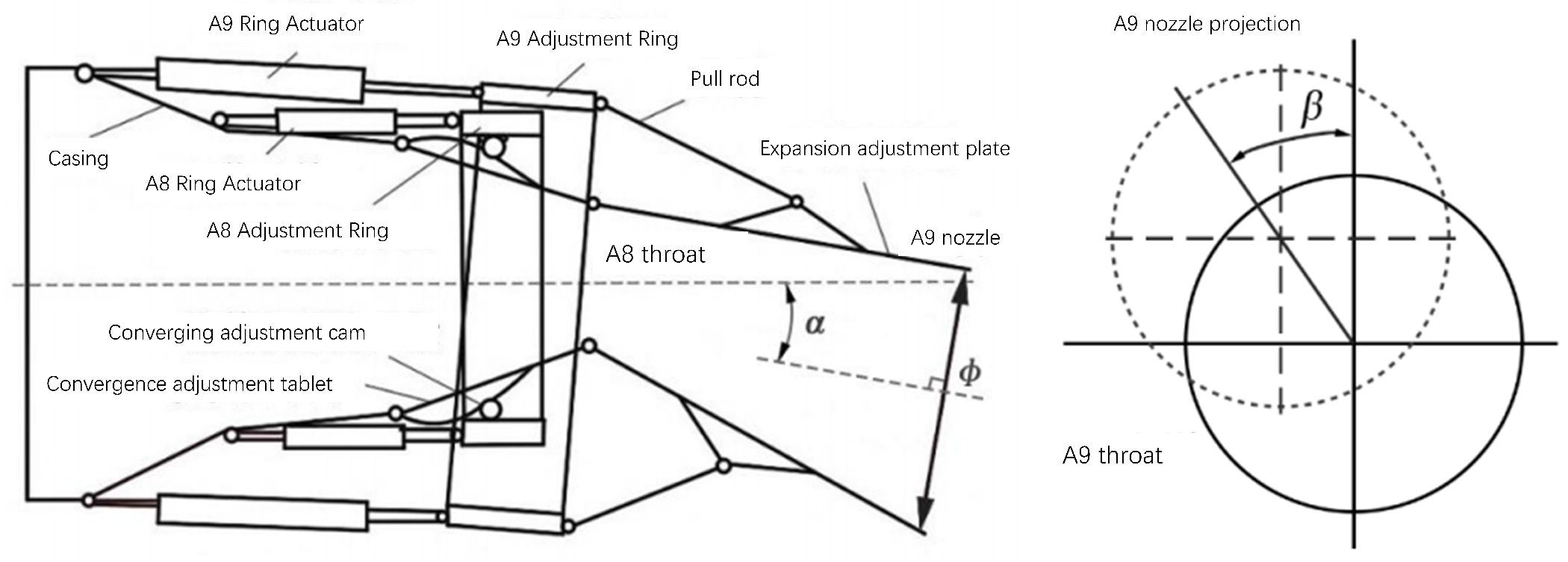
- How do we specifically extract the geometric parameters of the nozzle? These include the nozzle opening size, nozzle deflection angle, and azimuth angle.
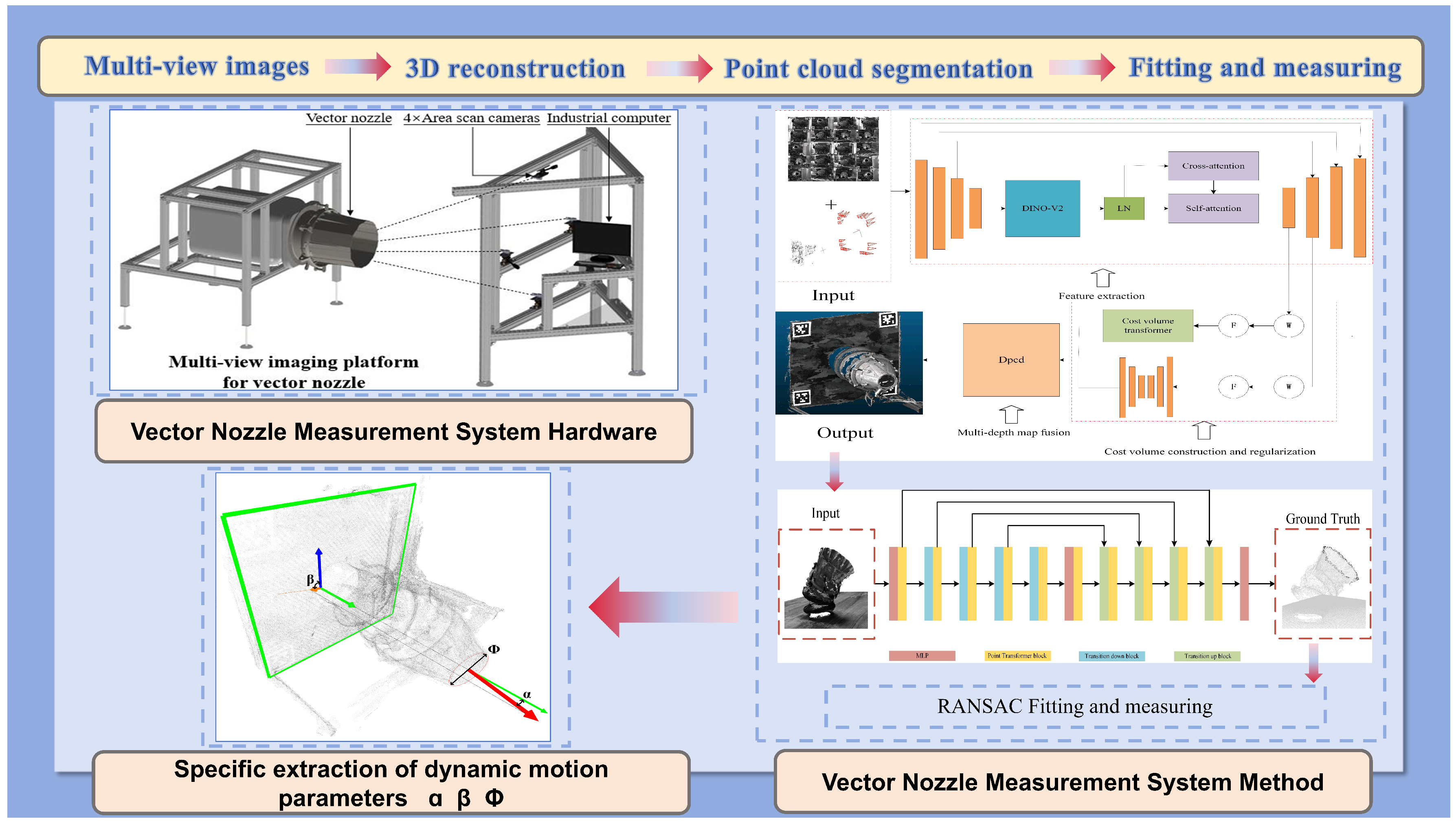
- A technical solution of “3D reconstruction–point cloud segmentation–fitting measurement” was proposed in this paper, which innovatively realizes “non-contact, no additional, and calibration-free” visual measurement of the motion geometry parameters of vector nozzles.
- An axisymmetric vector nozzle model was designed and a multi-view vision platform was built in this paper, through which the dynamic geometric parameters of the vector nozzle can be obtained by three methods: drive motor parameter calculation, laser sensor, and vision measurement, thereby achieving the measurement of the accuracy and consistency of the vision measurement method.
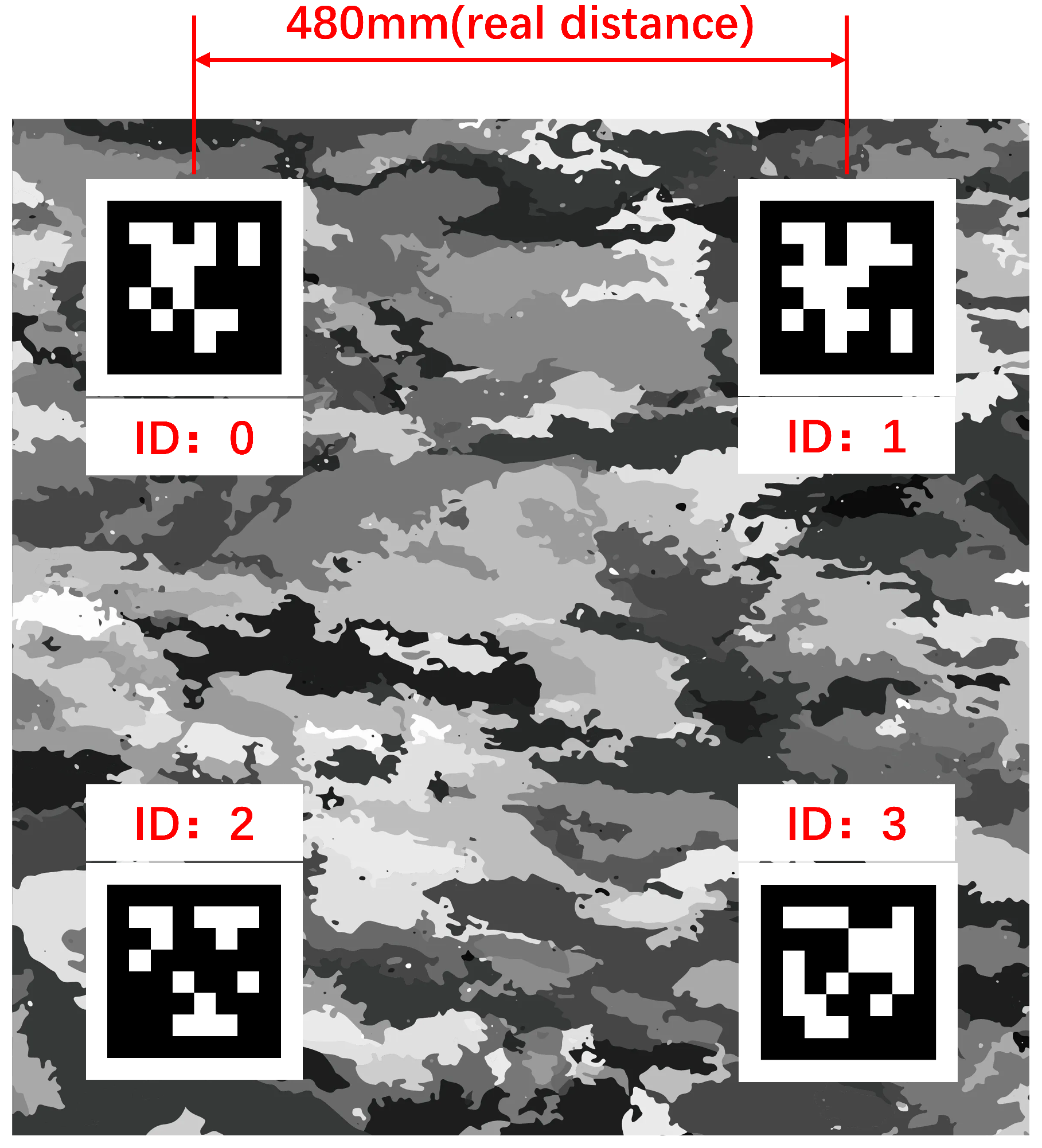
- AprilTag-encoded landmarks were used in this paper to address the lack of absolute scale information in the vector nozzle point cloud obtained using multi-camera stereo vision. The complex multi-camera joint calibration process was replaced, reducing the complexity of the visual measurement method and the requirements for the test environment.
2. Related Works
2.1. Thrust Vector Nozzle
2.2. Multi-View Stereo Vision Measurement
2.3. Point Cloud Segmentation
2.4. Fitting Measurement
3. Proposed Method
3.1. 3D Reconstruction
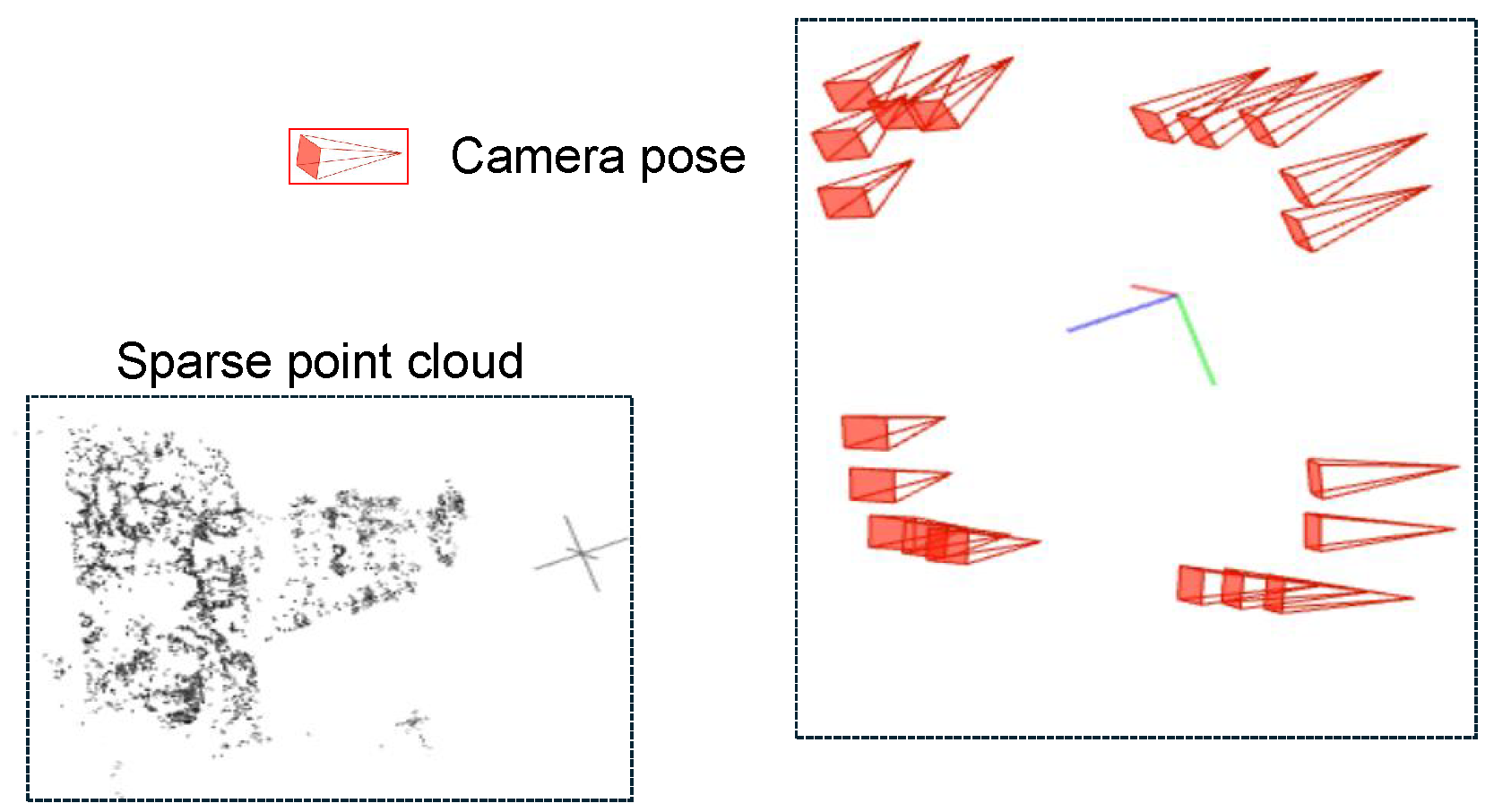
3.1.1. Structure-from-Motion
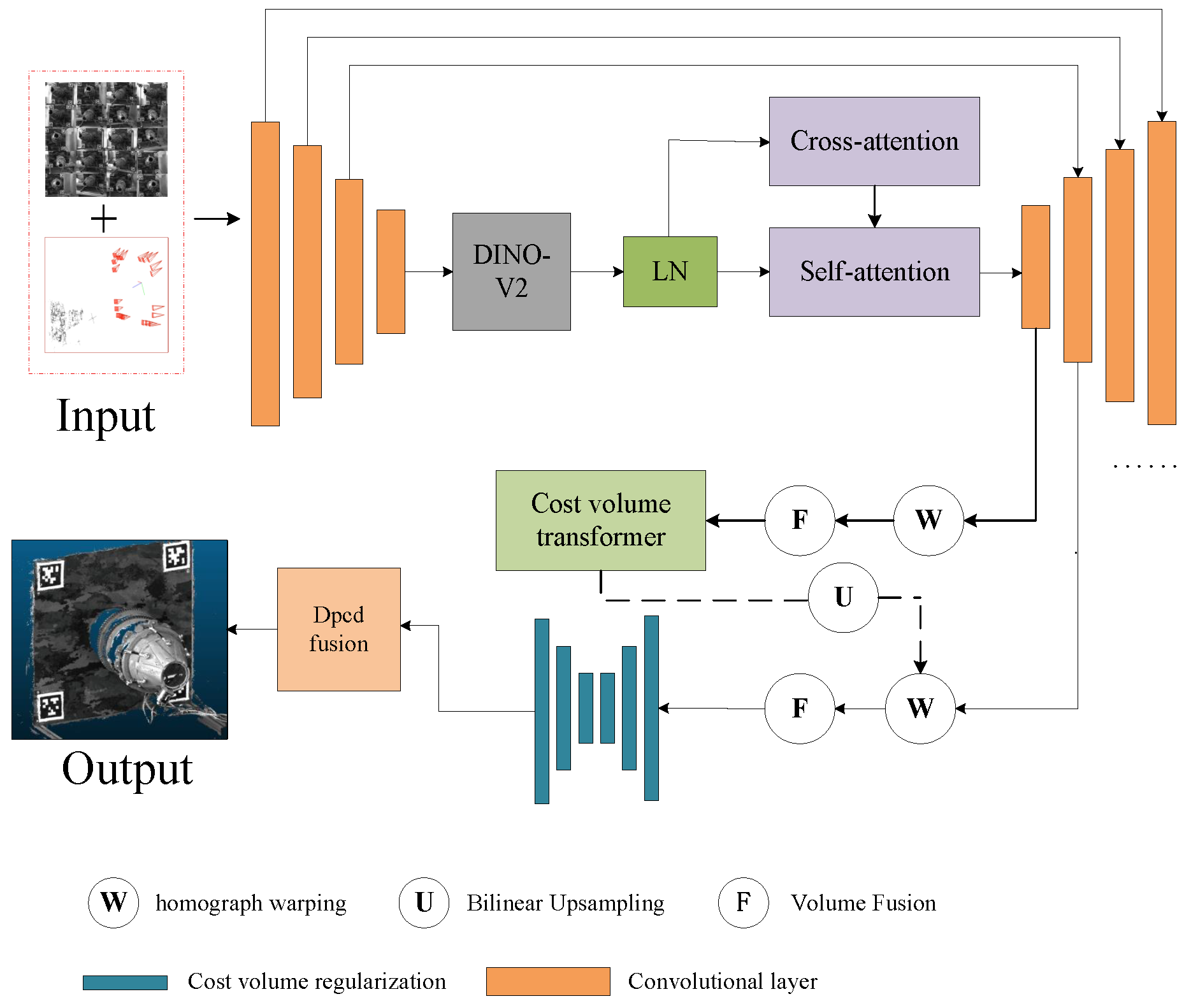
3.1.2. Multi-View Stereo Vision
3.1.3. AprilTag Scale Return
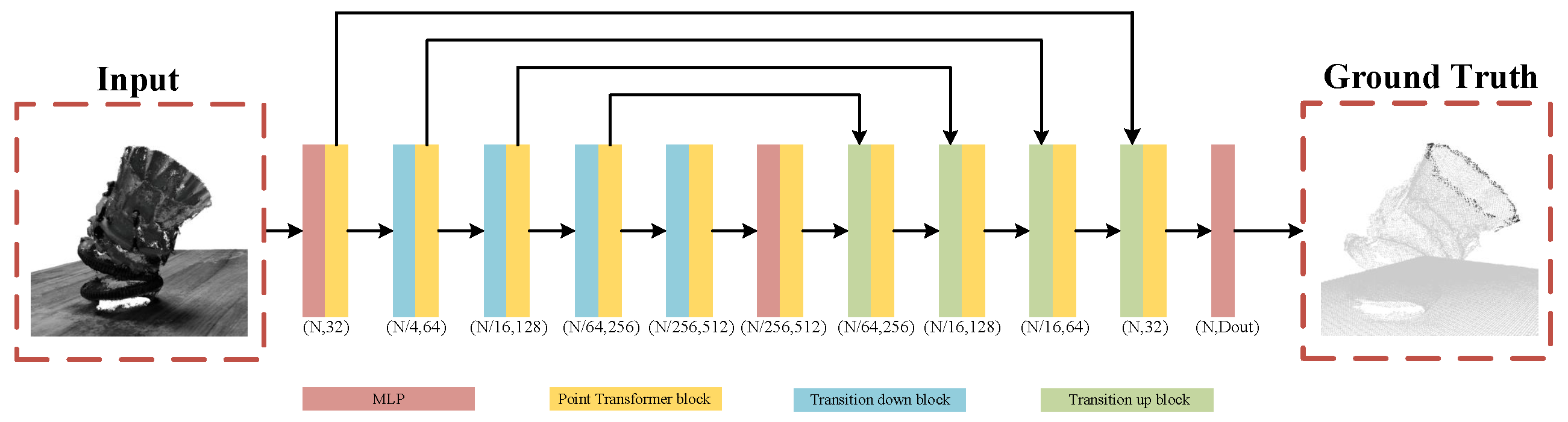
3.2. End Face Point Cloud Segmentation
3.2.1. End Face Segmentation Dataset
| Algorithm 1 Point cloud post-processing algorithm |
|
3.2.2. Point Cloud Segmentation Algorithm
3.3. Fitting Measurement
3.3.1. Geometric Fitting
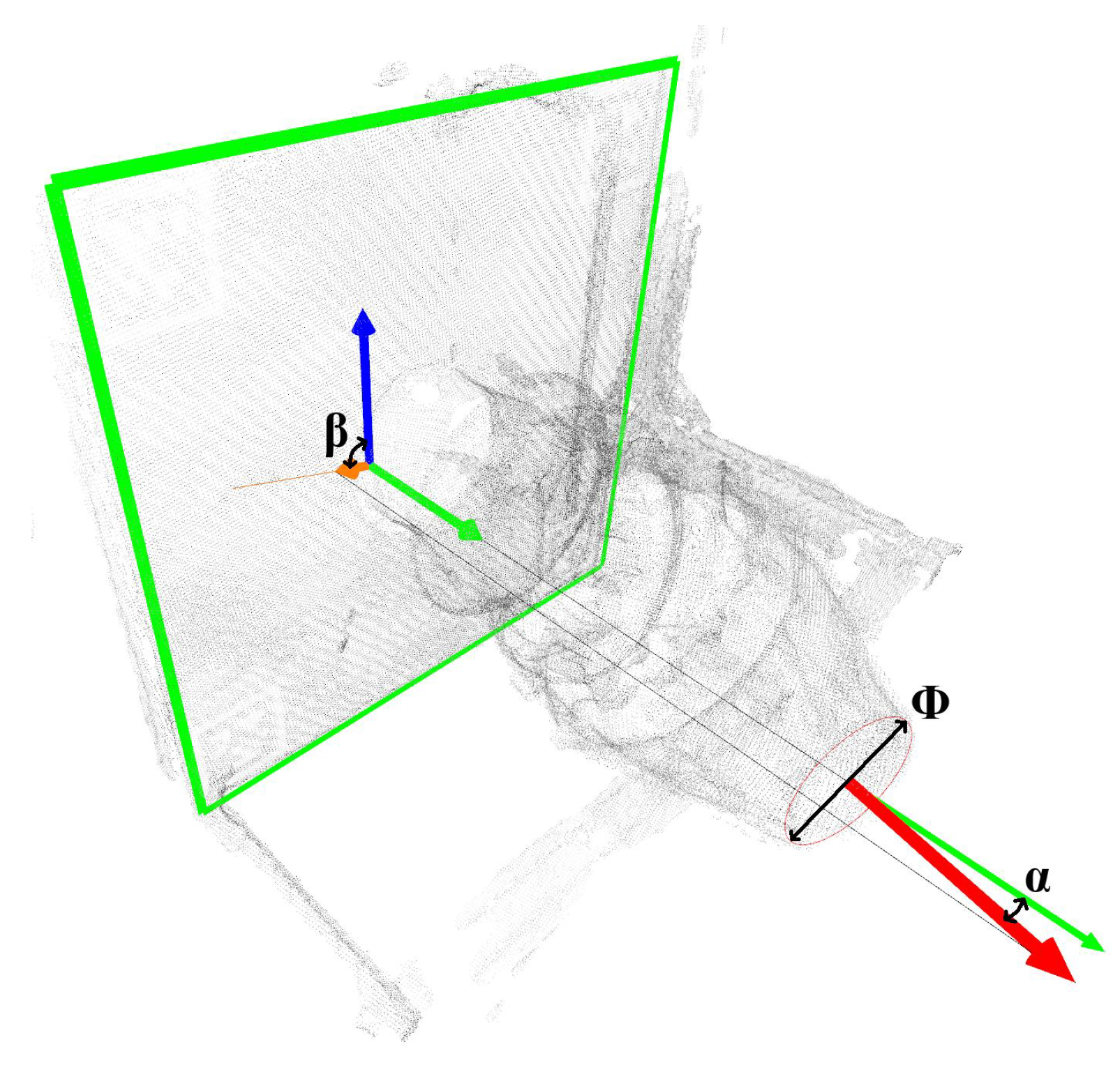
3.3.2. Motion Parameter Measurement
4. Experiment and Analysis
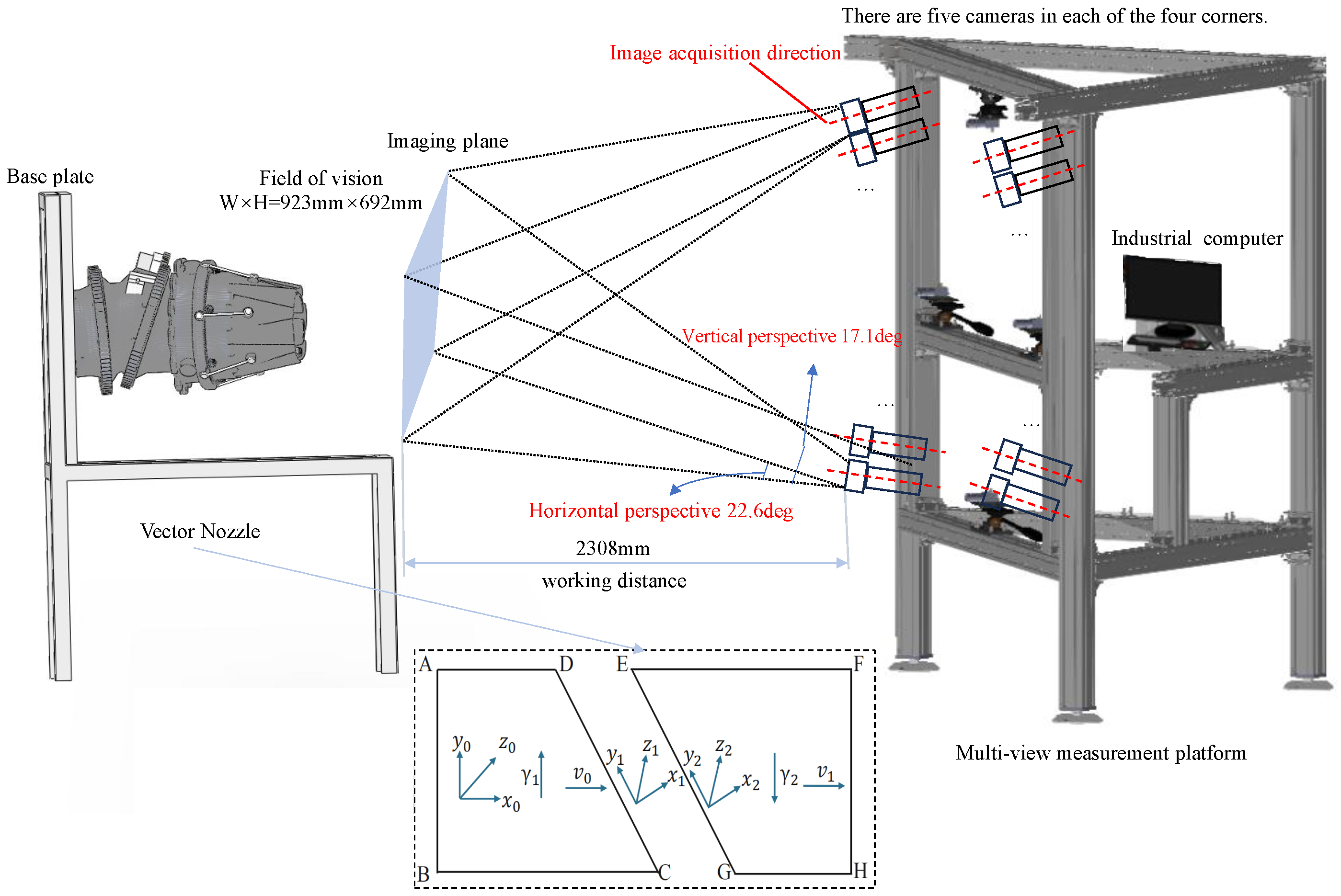
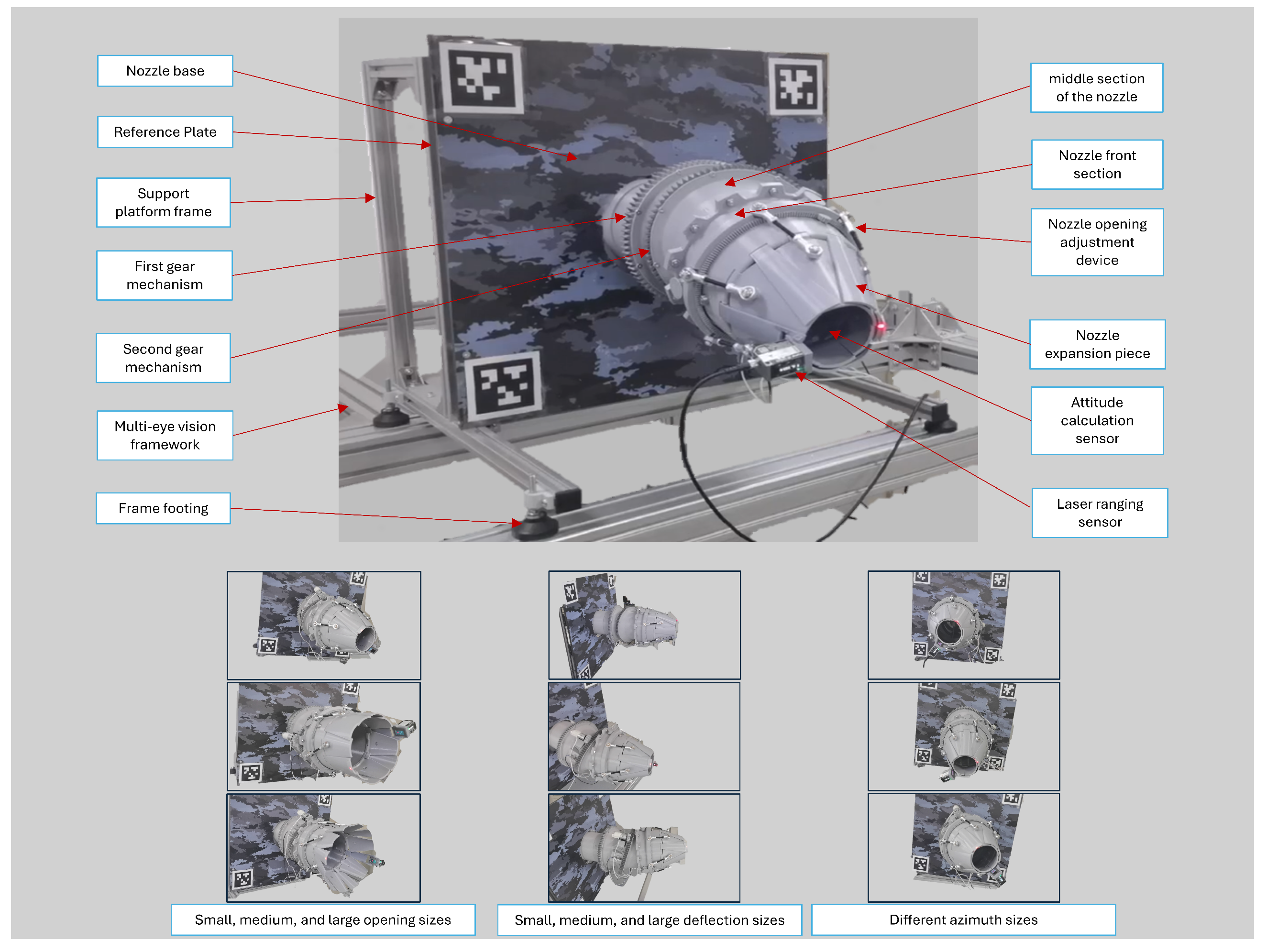
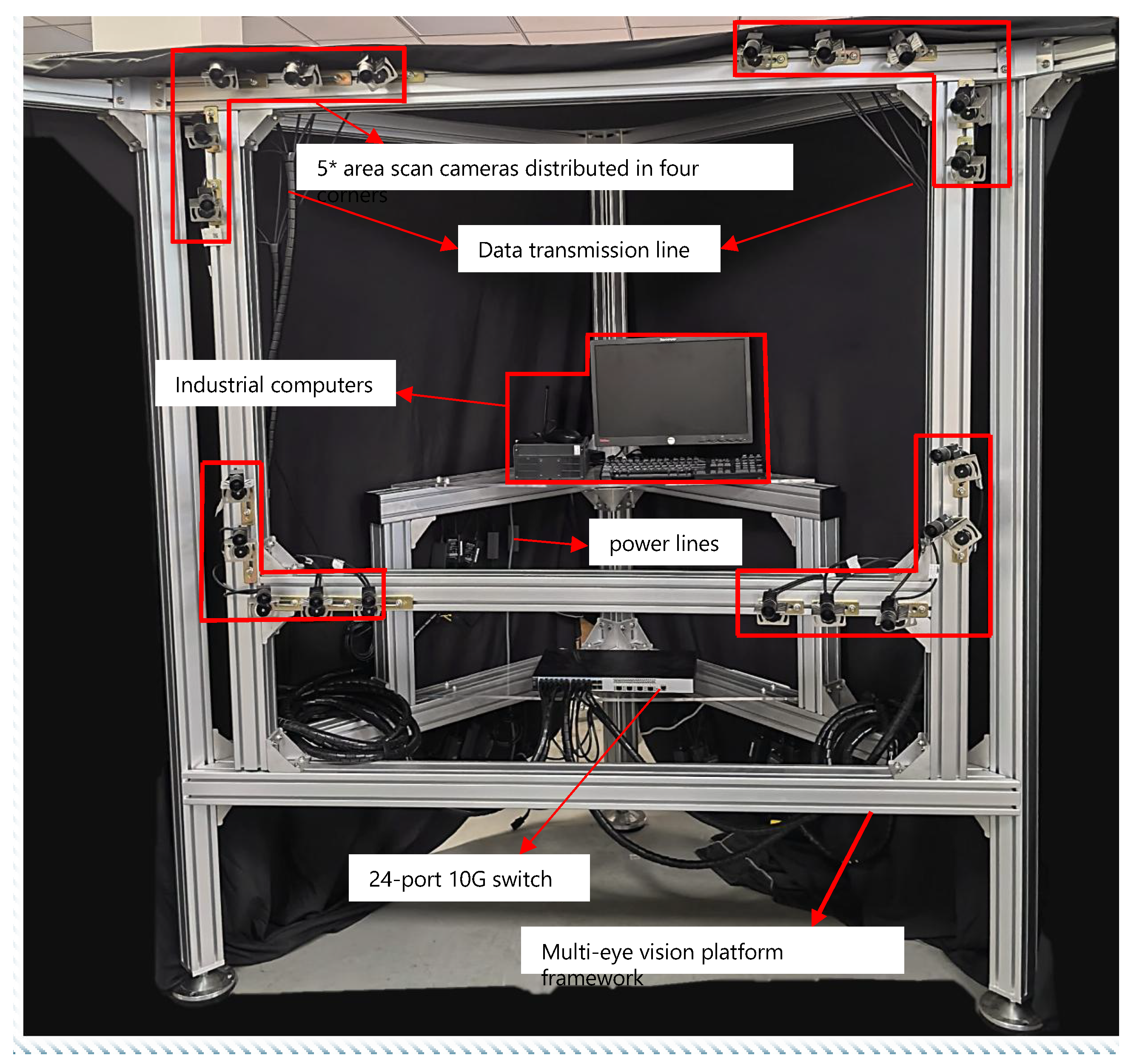
4.1. Measurement System
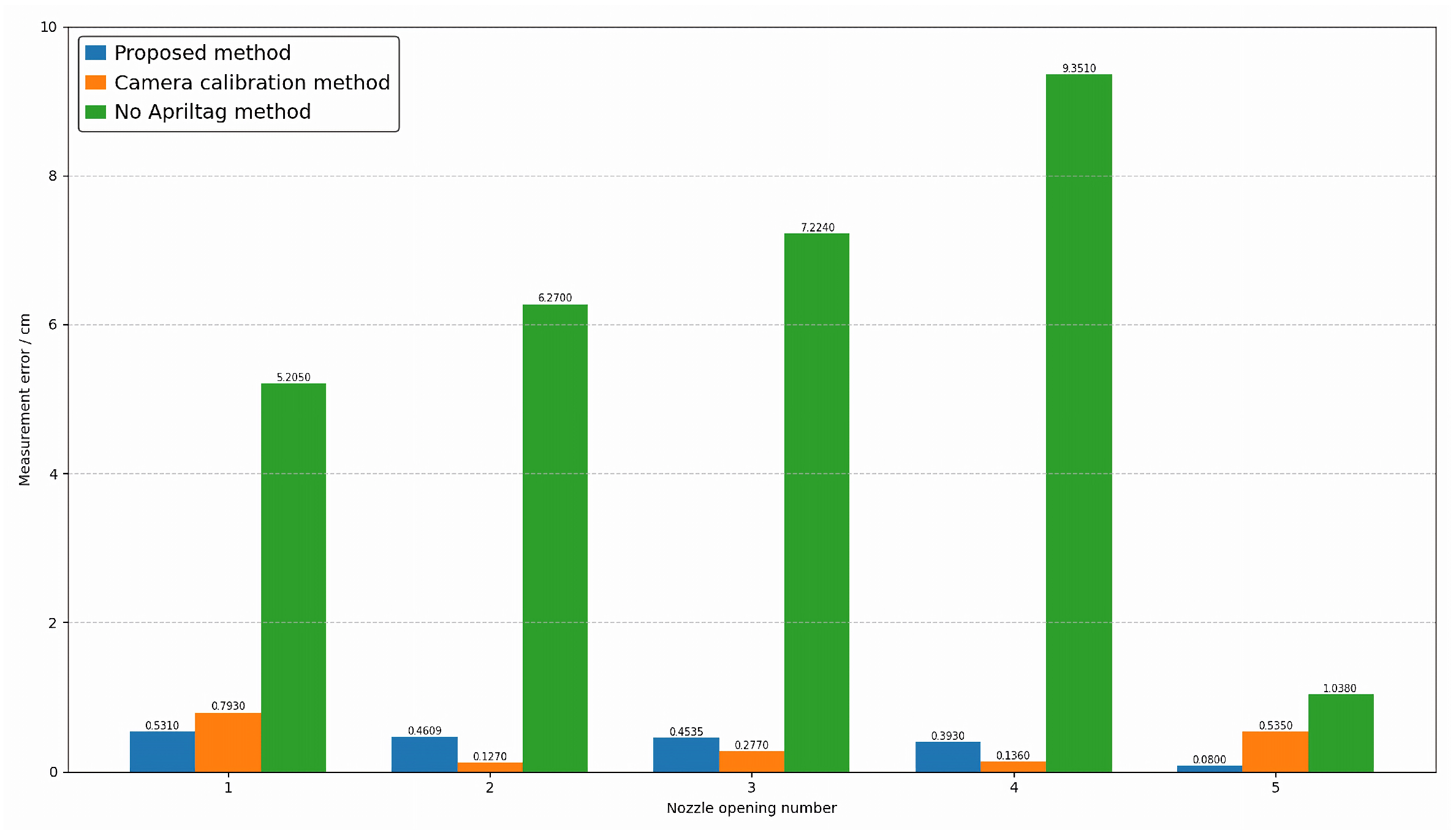
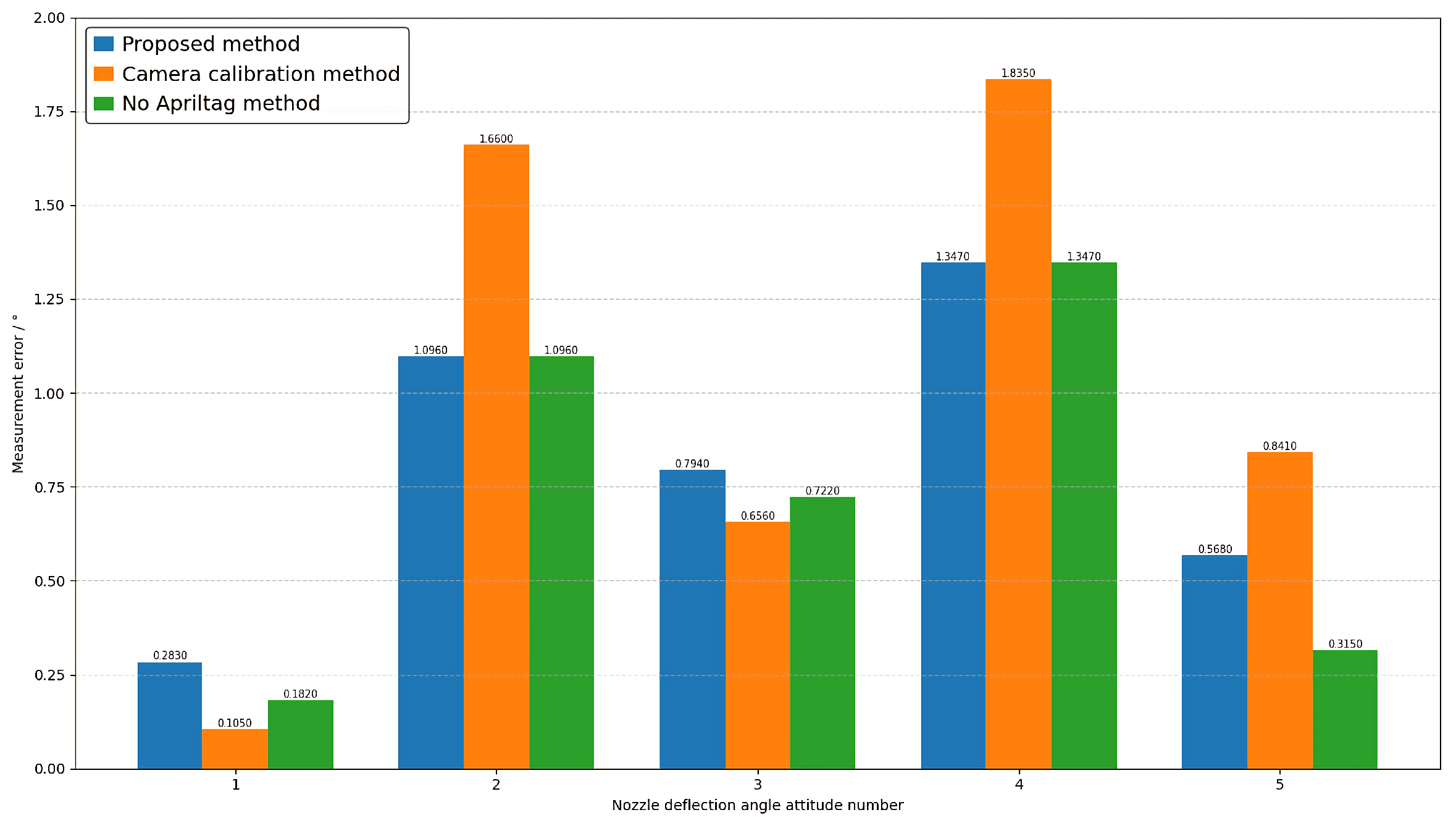
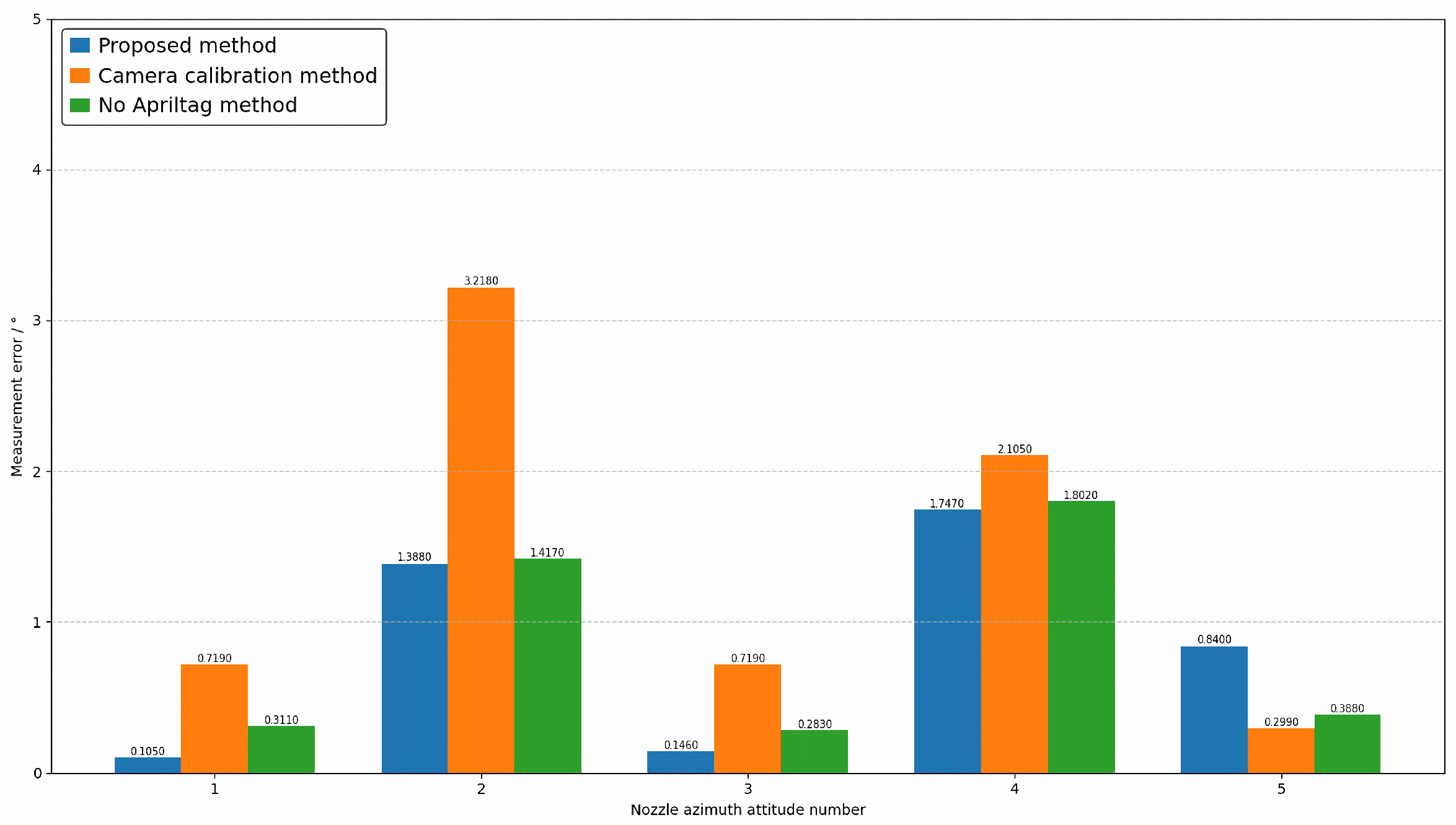
4.2. Comparative Experiment
4.3. Evaluation Indicators and Measurement Systems Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Afridi, S.; Khan, T.A.; Shah, S.I.A.; Shams, T.A.; Mohiuddin, K.; Kukulka, D.J. Techniques of Fluidic Thrust Vectoring in Jet Engine Nozzles: A Review. Energies 2023, 16, 5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catana, R.M.; Badea, G.P. Experimental Analysis on the Operating Line of Two Gas Turbine Engines by Testing with Different Exhaust Nozzle Geometries. Energies 2023, 16, 5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramraj, H.; Sundararaj, T.; Sekar, C.; Arora, R.; Kushari, A. Effect of nozzle exit area on the performance of a turbojet engine. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 106844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Rui, X.; Zhou, Q. Study on simulation and experiment of control for multiple launch rocket system by computed torque method. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 91, 1639–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.; Choia, H. Control of laminar vortex shedding behind a circular cylinder using splitter plates. Phys. Fluids 1996, 8, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlauto, M.; Marsilio, R. Numerical Investigation of the Dynamic Characteristics of a Dual-Throat-Nozzle for Fluidic Thrust-Vectoring. AIAA J. 2017, 55, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Huang, J.; Sun, Z.; Duan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y. Leakage Detection in Subway Tunnels Using 3D Point Cloud Data: Integrating Intensity and Geometric Features with XGBoost Classifier. Sensors 2025, 25, 4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakim, K.; Hamitouche, T.; Said, B. Numerical Simulation of Fluidic Thrust Vectoring in The Conical Nozzle. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2024, 73, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquah, R.; Misiulis, E.; Sandak, A.; Skarbalius, G.; Navakas, R.; Džiugys, A.; Sandak, J. Integrating LiDAR, Photogrammetry, and Computational Fluid Dynamics for Wind Flow Simulations Around Existing Buildings. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tang, W.; Li, H.P.; Wang, J.; Chen, J. Application of laser tracker to thrust line measurement of solid rocket motor. J. Solid Rocket. Technol. 2007, 30, 548–551. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, G.; Ye, D.; Yu, X.; Yuan, F. 2-DOF Angle Measurement of Rocket Nozzle with Multivision. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2013, 5, 942580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Feng, D.; Min, C.; Tian, Q. Novel method of rocket nozzle motion parameters non-contact consistency measurement based on stereo vision. Optik 2019, 195, 163049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyluoğlu, M.; Orabi, R.; Hermon, S.; Bakirtzis, N. Digitizing Challenging Heritage Sites with the Use of iPhone LiDAR and Photogrammetry: The Case-Study of Sourp Magar Monastery in Cyprus. Geomatics 2025, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.; Kochi, N.; Kodama, K.; Isobe, S.; Tanabata, T. CLCFM3: A 3D Reconstruction Algorithm Based On Photogrammetry for High-Precision Whole Plant Sensing Using All-Around Images. Sensors 2025, 25, 5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zeng, Y.; Qiu, M.; Wang, X. Construction of a High-Precision Underwater 3D Reconstruction System Based on Line Laser. Sensors 2025, 25, 5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Sun, Z.; Hu, Y.; Qiang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Numerical Investigation of the Two-Phase Flow Characteristics of an Axisymmetric Bypass Dual-Throat Nozzle. Aerospace 2025, 12, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Li, J.; Cheng, B. Key Technology of Aircraft Propulsion System—Thrust Vectoring Technology. J. Air Force Eng. Univ. 2000, 1, 86–87. [Google Scholar]
- Sieder-Katzmann, J.; Propst, M.; Stark, R.H.; Schneider, D.; General, S.; Tajmar, M.; Bach, C. Surface Pressure Measurement of Truncated, Linear Aerospike Nozzles Utilising Secondary Injection for Aerodynamic Thrust Vectoring. Aerospace 2024, 11, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, L.; Gong, Y.; Xia, Z. Numerical Analysis of Full-envelope Thrust Characteristics of Axisymmetric Convergent-divergent Nozzle with Single Actuating Ring. Aeroengine 2024, 50, 82–84. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Jin, B.; Li, Y. Development of Spherical Convergent Flap Nozzle. Aeroengine 2002, 3, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, L.; Luo, Z.; Song, H. Kinematic Modeling and Trajectory Analysis of Axisymmetric Vectoring Nozzle. Aeroengine 2024, 50, 87–89. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Ji, H.; Pang, C. Research on Axisymmetric Vectoring Exhaust Nozzle Dynamic Characteristics Considering Aerodynamic and Thermal Loads Effect. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2025, 18, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Niu, L. Three-Dimensional Morphology and Size Measurement of High-Temperature Metal Components Based on Machine Vision Technology: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Yang, D. Binocular stereo vision calibration based on alternate adjustment algorithm. Optik 2018, 173, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Luo, Z.; Li, S.; Fang, T.; Quan, L. MVSNet: Depth Inference for Unstructured Multi-view Stereo. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 767–783. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Mao, W.; Alvarez, J.M.; Liu, M. Cost Volume Pyramid Based Depth Inference for Multi-View Stereo. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 4121–4130. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Fan, Z.; Zhu, S.; Dai, Z.; Tan, F.; Tan, P. Cascade Cost Volume for High-Resolution Multi-View Stereo and Stereo Matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2495–2504. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Peng, R.; Hu, Y.; Wang, R. GeoMVSNet: Learning Multi-View Stereo with Geometry Perception. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 21508–21518. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Ren, X.; Fu, Y. MVSFormer: Multi-View Stereo by Learning Robust Image Features and Temperature-based Depth. Trans. Mach. Learn. Res. TMLR 2023, 4, 1–10. Available online: https://openreview.net/forum?id=2VWR6JfwNo (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Cao, C.; Ren, X.; Fu, Y. MVSFormer++: Revealing the Devil in Transformer’s Details for Multi-View Stereo. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Vienna, Austria, 7–11 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, E. AprilTag: A robust and flexible visual fiducial system. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 3400–3407. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5099–5108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Tuzel, O. VoxelNet: End-to-End Learning for Point Cloud Based 3D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4490–4499. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, B.; Engelcke, M.; van der Maaten, L. 3D Semantic Segmentation with Submanifold Sparse Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 9224–9232. [Google Scholar]
- Choy, C.B.; Gwak, J.; Savarese, S. 4D Spatio-Temporal ConvNets: Minkowski Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3075–3084. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Hu, Y.; Yang, X.; Dou, Z.; Kang, L. Robust multi-task learning network for complex LiDAR point cloud data preprocessing. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, L.; Jia, J.; Torr, P.H.S.; Koltun, V. Point Transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 16259–16268. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wu, M.; Lam, S.K.; Ning, X.; Yu, S.; Wang, R.; Srikanthan, T. GPSformer: A global perception and local structure fitting-based transformer for point cloud understanding. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 75–92. [Google Scholar]
- Taubin, G. Estimation of Planar Curves, Surfaces, and Nonplanar Space Curves Defined by Implicit Equations with Applications to Edge and Range Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1991, 13, 1115–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, V. Direct Least-Squares Fitting of Algebraic Surfaces. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH Conference, Anaheim, CA, USA, 27–31 July 1987; pp. 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting with Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

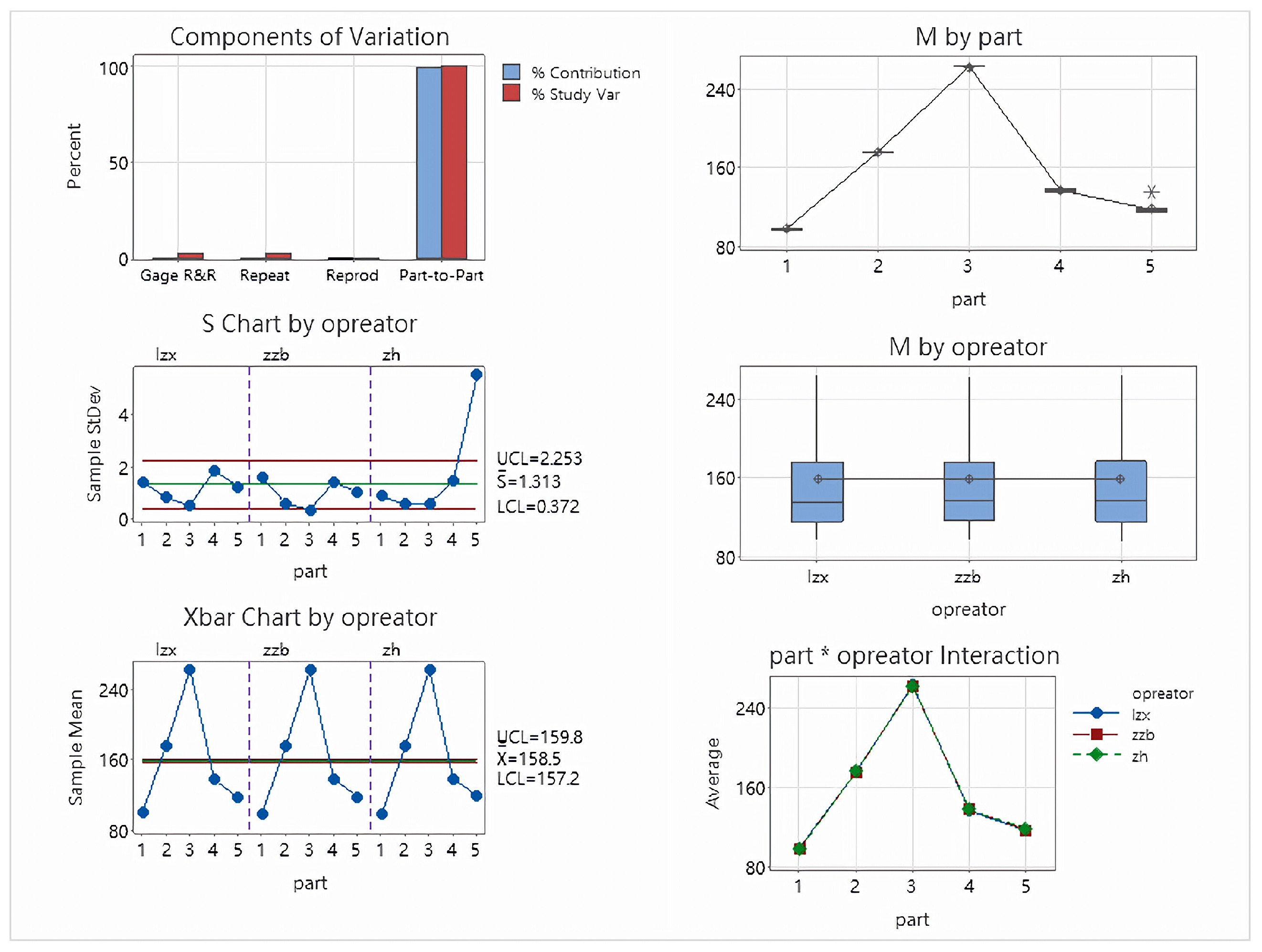
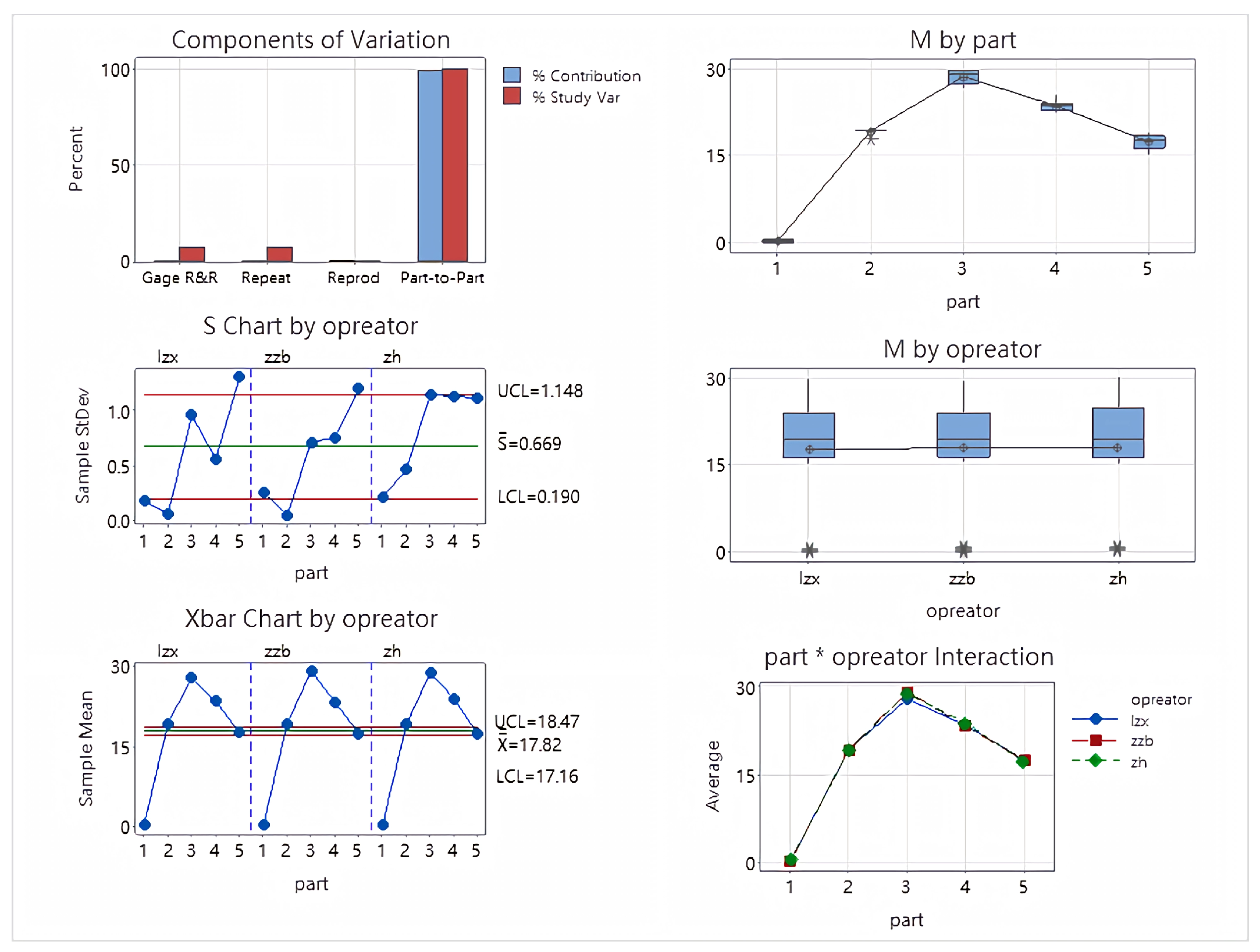
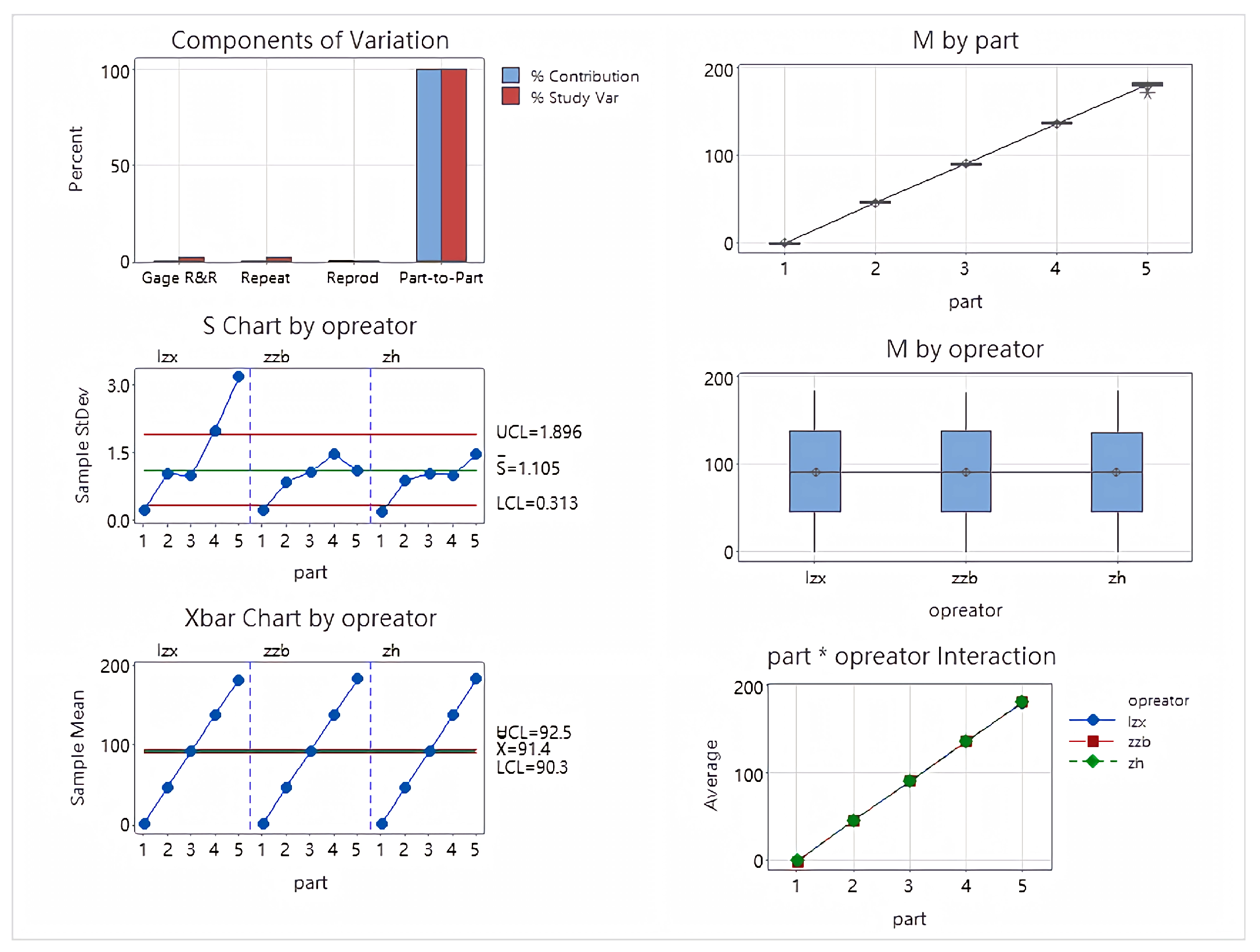
| Source | StdDev (SD) | Study Var (6 × SD) | %Study Var (%SV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Gage R&R | 1.8135 | 10.881 | 2.81 |
| Repeatablity | 1.8135 | 10.881 | 2.81 |
| Reproducibility | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Operator | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Part-To-Part | 64.4532 | 386.719 | 99.96 |
| Total Variation | 64.4787 | 386.872 | 100 |
| Source | StdDev (SD) | Study Var (6 × SD) | %Study Var (%SV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Gage R&R | 0.8190 | 4.9140 | 7.69 |
| Repeatablity | 0.8190 | 4.9140 | 7.69 |
| Reproducibility | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Operator | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Part-To-Part | 10.6154 | 63.6926 | 99.7 |
| Total Variation | 10.6470 | 63.8818 | 100 |
| Source | StdDev (SD) | Study Var (6 × SD) | %Study Var (%SV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Gage R&R | 1.3119 | 7.872 | 1.84 |
| Repeatablity | 1.3119 | 7.872 | 1.84 |
| Reproducibility | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Operator | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Part-To-Part | 71.4645 | 428.787 | 99.98 |
| Total Variation | 71.4766 | 428.859 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Lin, Z.; Song, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Yan, Y. Specific Dynamic Parameters: A Novel Multi-View Stereo Vision Measurement System for Vector Nozzle. Sensors 2026, 26, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26010093
Lin Z, Song K, Zhang H, Zhou Z, Zhang Y, Li C, Yan Y. Specific Dynamic Parameters: A Novel Multi-View Stereo Vision Measurement System for Vector Nozzle. Sensors. 2026; 26(1):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26010093
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Zhixiao, Kechen Song, Han Zhang, Zhenbo Zhou, Yansong Zhang, Chenggang Li, and Yunhui Yan. 2026. "Specific Dynamic Parameters: A Novel Multi-View Stereo Vision Measurement System for Vector Nozzle" Sensors 26, no. 1: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26010093
APA StyleLin, Z., Song, K., Zhang, H., Zhou, Z., Zhang, Y., Li, C., & Yan, Y. (2026). Specific Dynamic Parameters: A Novel Multi-View Stereo Vision Measurement System for Vector Nozzle. Sensors, 26(1), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26010093







