Validity and Reliability of Force Insoles to Measure Center of Pressure During Return-to-Sport Testing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
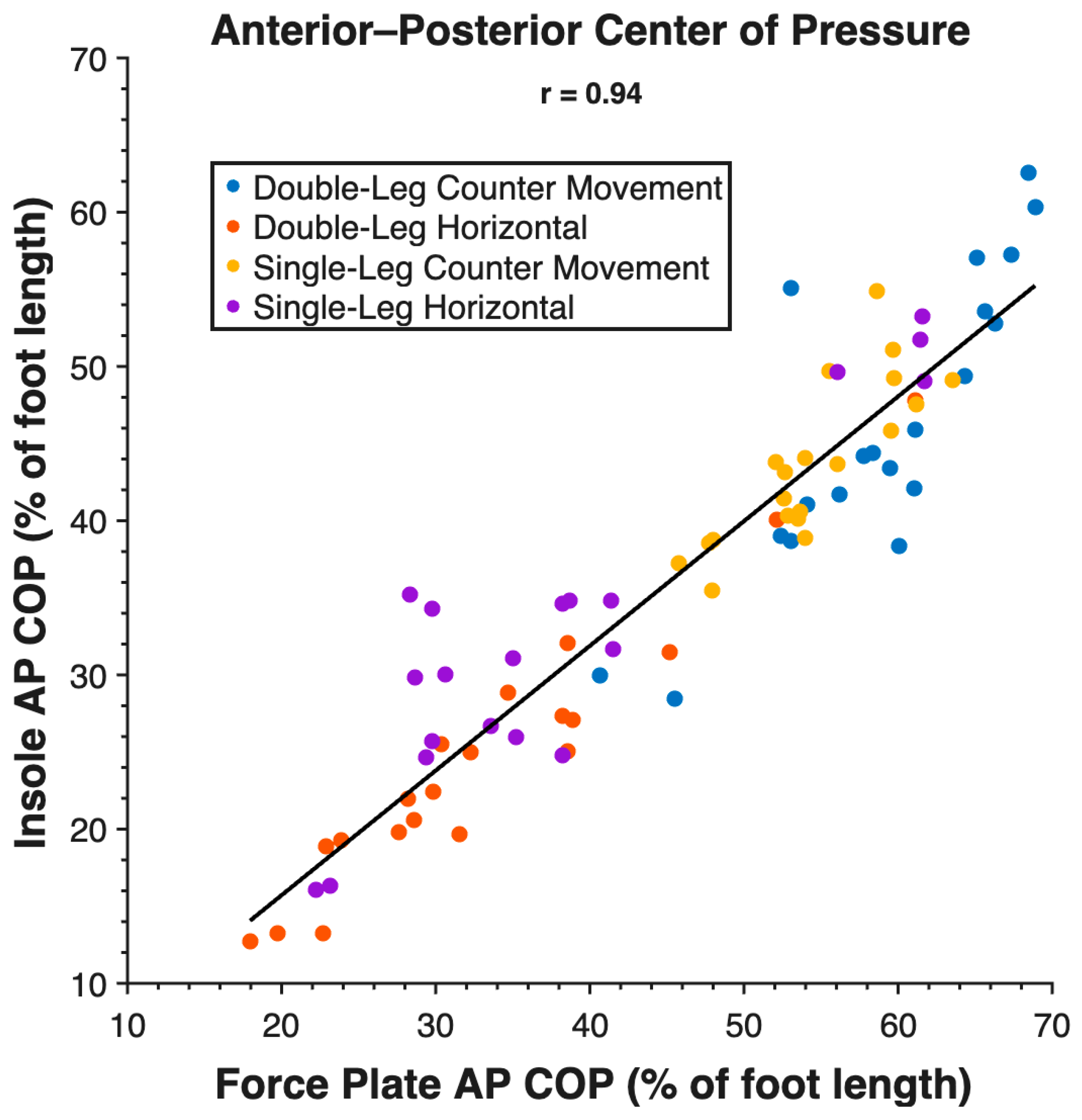
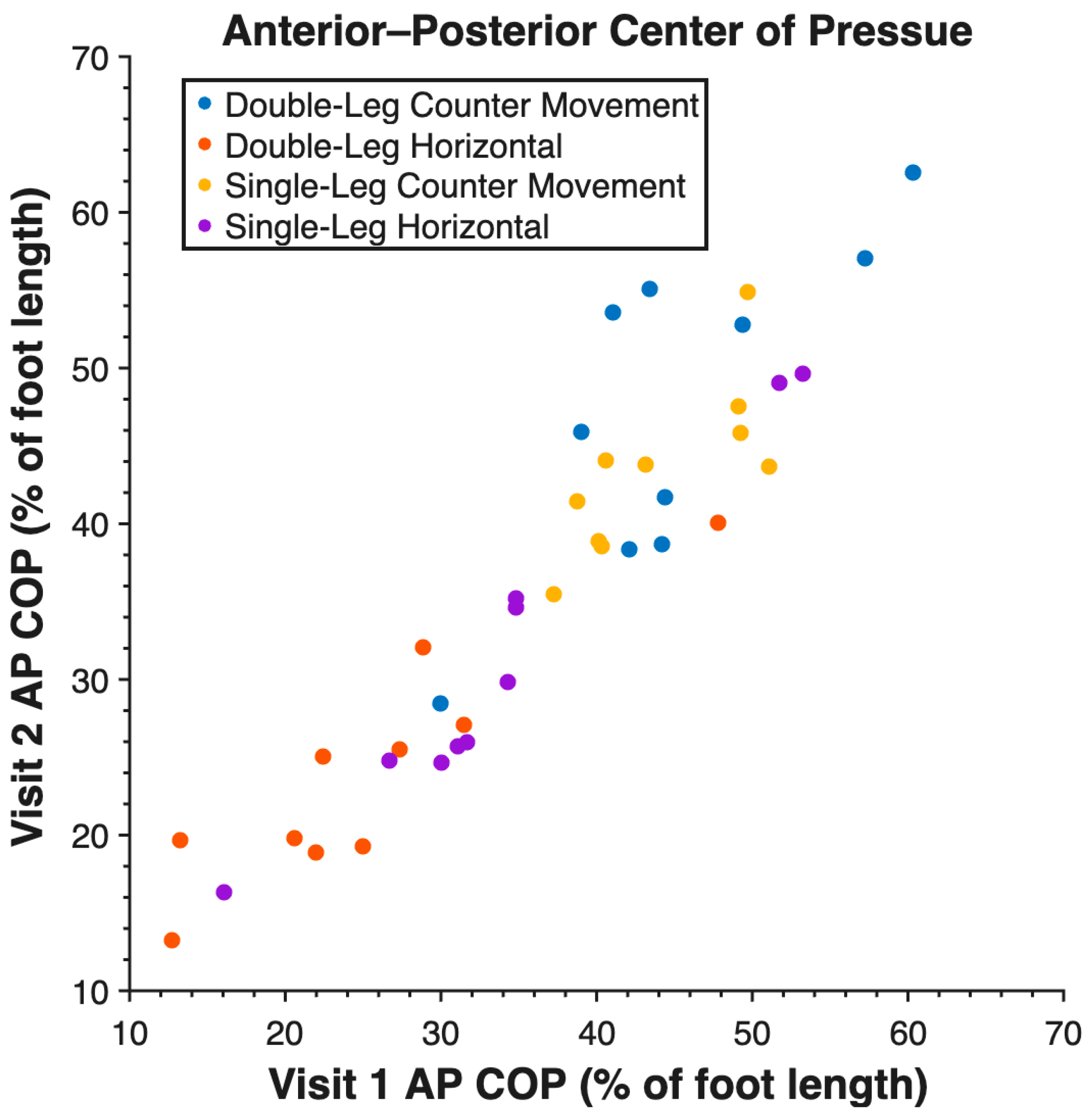
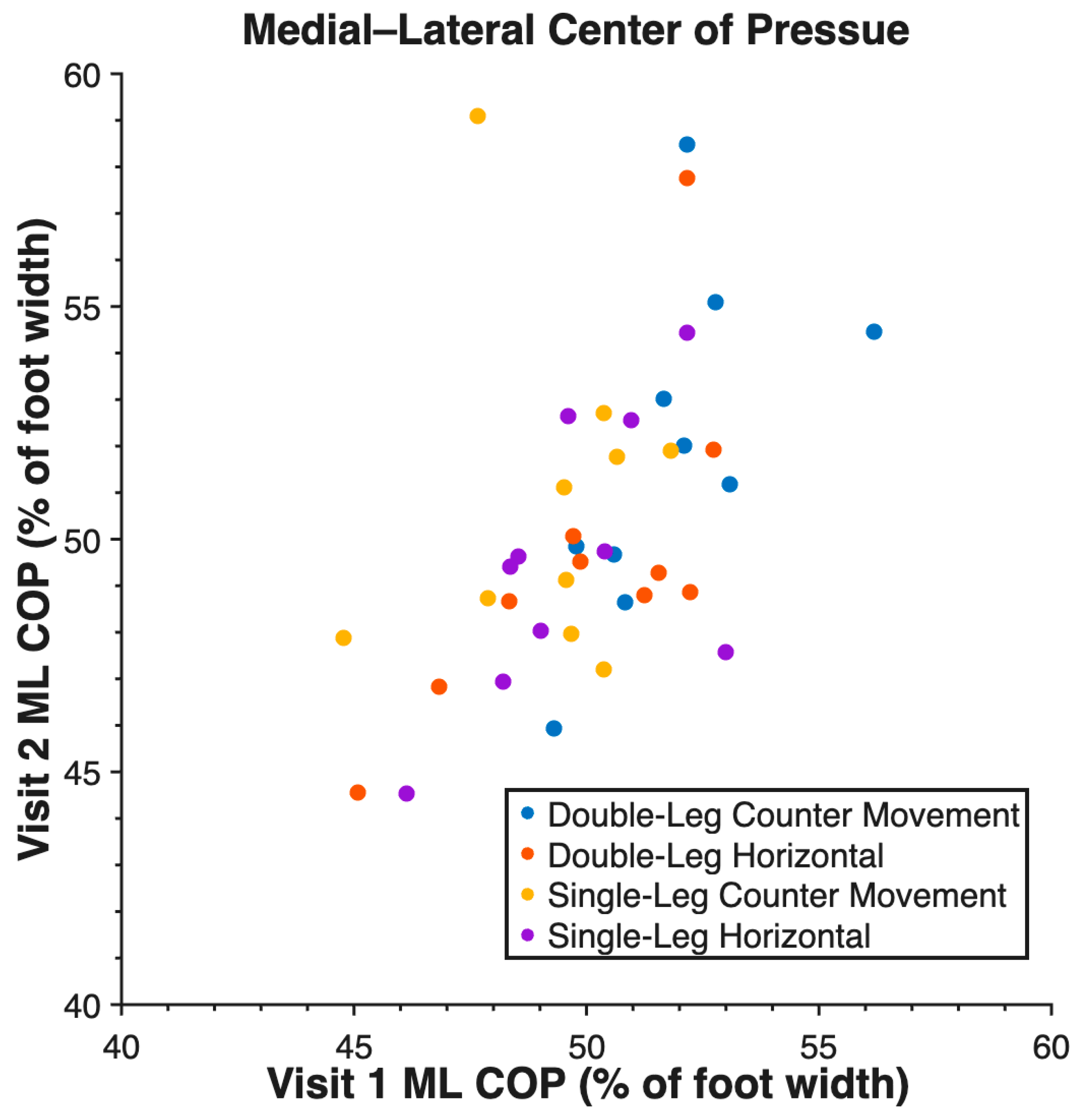
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COP | Center Of Pressure |
| AP COP | Anterior–Posterior Center of Pressure |
| ML COP | Medial–Lateral Center of Pressure |
| vGRF | Vertical Ground Reaction Force |
| DL CMJ | Double-Leg Countermovement Jump |
| SL CMJ | Single-Leg Countermovement Jump |
| DL HJ | Double-Leg Horizontal Jump |
| SL HJ | Single-Leg Horizontal Jump |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| RMSE | Root Mean Squared Error |
| MAPE | Mean Absolute Percentage Error |
| ACLR | Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction |
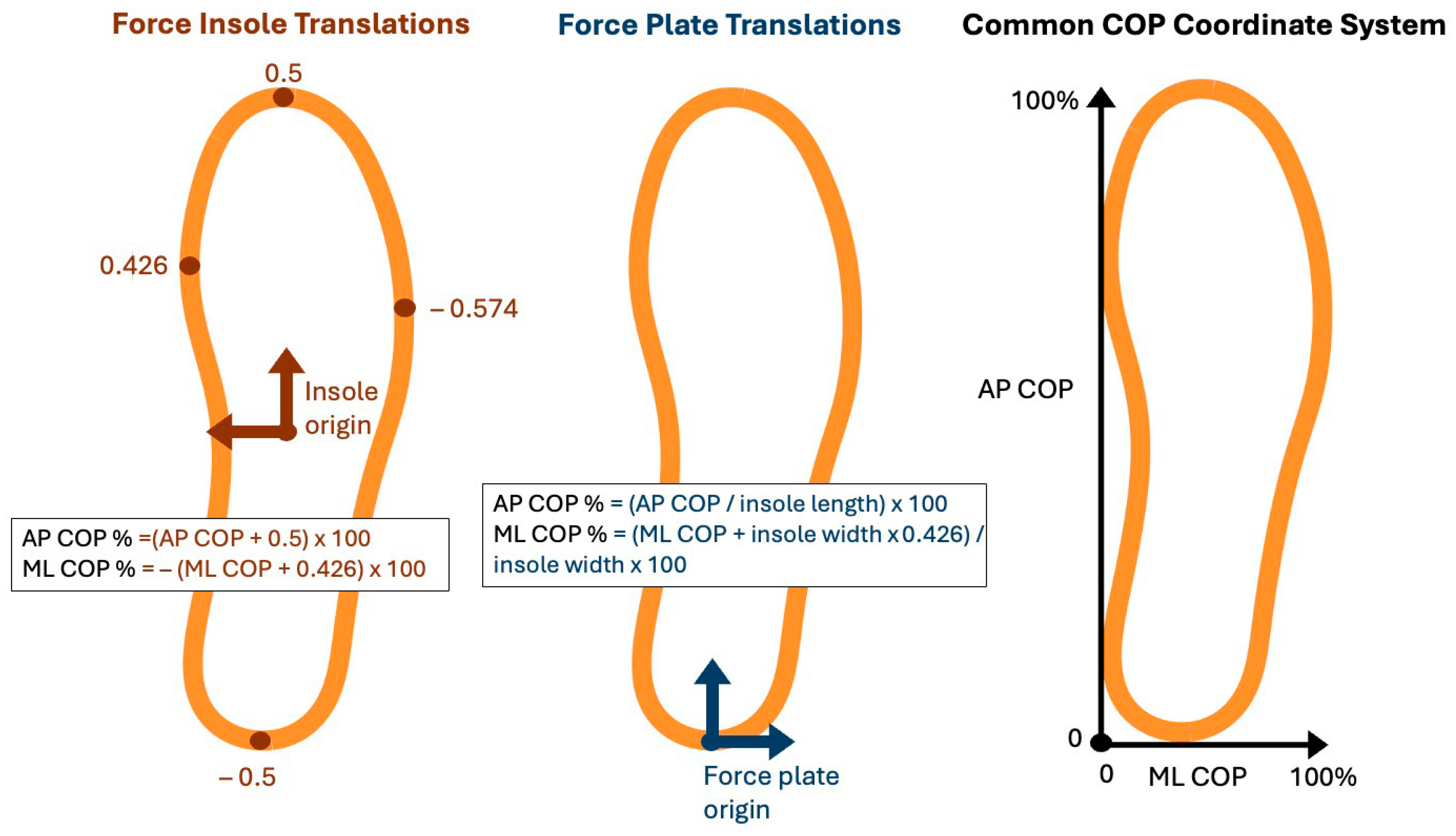
Appendix A
References
- Ishida, T.; Samukawa, M.; Kasahara, S.; Tohyama, H. The center of pressure position in combination with ankle dorsiflexion and trunk flexion is useful in predicting the contribution of the knee extensor moment during double-leg squatting. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.-S.; Sigward, S.M. Center of pressure predicts Intra-limb compensatory patterns that shift demands away from knee extensors during squatting. J. Biomech. 2020, 111, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshino, Y.; Ishida, T.; Taniguchi, S.; Samukawa, M.; Kasahara, S.; Tohyama, H. Hip and knee kinematics, center of pressure position, and ground reaction force are associated with Achilles tendon force during jump landing. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2024, 34, e14510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, T.; Ueno, R.; Kitamura, Y.; Yamakawa, Y.; Samukawa, M.; Tohyama, H. The Effect of Real-Time Feedback Regarding the Center-of-Pressure Position on Patellofemoral Joint Loading During Double-leg Squatting. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2025, 13, 23259671251319526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukaya, T.; Mutsuzaki, H.; Okubo, T.; Mori, K.; Wadano, Y. Relationships between the center of pressure and the movements of the ankle and knee joints during the stance phase in patients with severe medial knee osteoarthritis. Knee 2016, 23, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Melick, N.; van Cingel, R.E.; Brooijmans, F.; Neeter, C.; van Tienen, T.; Hullegie, W.; Nijhuis-van der Sanden, M.W. Evidence-based clinical practice update: Practice guidelines for anterior cruciate ligament rehabilitation based on a systematic review and multidisciplinary consensus. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 1506–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, E.; Campbell, A.; Wise, E.; Tidman, S.J.; Lay, B.S.; Kent, P. Physiotherapists could detect changes of 12 degrees or more in single-plane movement when observing forward bending, squat or hand-over-head: A cross-sectional experiment. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pr. 2022, 61, 102594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigward, S.M.; Chan, M.-S.M.; Lin, P.E.; Almansouri, S.Y.; Pratt, K.A. Compensatory Strategies That Reduce Knee Extensor Demand During a Bilateral Squat Change From 3 to 5 Months Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2018, 48, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Li, L.; Jensen, M.A.; Dai, B. Using trunk kinematics to predict kinetic asymmetries during double-leg jump-landings in collegiate athletes following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Gait Posture 2023, 102, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, K.; Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Bao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, K.; Teng, C.; Ushakov, N.; Kumar, S.; Li, X.; et al. AI-Assisted Insole Sensing System for Multifunctional Plantar-Healthcare Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 32662–32678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkinson, S.A.; Anderson, A.; Caiola, M.; Eguren, D.; Gonzalez, M.; Velazquez, L.M.; Dehak, N.; Motley, C.; Moukheiber, E.; Mills, K.; et al. Concurrent validity of instrumented insoles measuring gait and balance metrics in Parkinson’s disease. In Proceedings of the 2024 46th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 July 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Morin, P.; Muller, A.; Pontonnier, C.; Dumont, G. Evaluation of the Foot Center of Pressure Estimation from Pressure Insoles during Sidestep Cuts, Runs and Walks. Sensors 2022, 22, 5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarro, M.; Dickman, M.; Hulett, T.; Rowland, R.; Larkins, D.; Taylor, J.; Nelson, C. Hop to It! The Relationship Between Hop Tests and The Anterior Cruciate Ligament—Return to Sport Index After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction in NCAA Division 1 Collegiate Athletes. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2023, 18, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noehren, B.; Sanchez, Z.; Cunningham, T.; McKeon, P.O. The effect of pain on hip and knee kinematics during running in females with chronic patellofemoral pain. Gait Posture 2012, 36, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, P.W.; Morgan, K.D.; Johnson, D.L.; Ireland, M.L.; Noehren, B. Impaired Quadriceps Rate of Torque Development and Knee Mechanics After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction With Patellar Tendon Autograft. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 2553–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, L.A.; Wimmer, M.A.; Malloy, P.; O’keefe, J.A.; Knowlton, C.B.; Ferrigno, C. Validity and Reliability of the Insole3 Instrumented Shoe Insole for Ground Reaction Force Measurement during Walking and Running. Sensors 2022, 22, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, K.E.; Peebles, A.T.; Socha, J.J.; Queen, R.M. The impact of sampling frequency on ground reaction force variables. J. Biomech. 2022, 135, 111034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, V.M.; Gomes, B.B.; Neto, M.A.; Amaro, A.M. A Systematic Review of Insole Sensor Technology: Recent Studies and Future Directions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| n (M:F) | 10 (5:5) |
| Age (Average ± SD) | 25.5 ± 3.80 |
| Height (m) (Average ± SD) | 1.74 ± 0.09 |
| Mass (kg) (Average ± SD) | 74.9 ± 12.4 |
| Days between visits (Average ± SD) | 7.2 ± 4.7 |
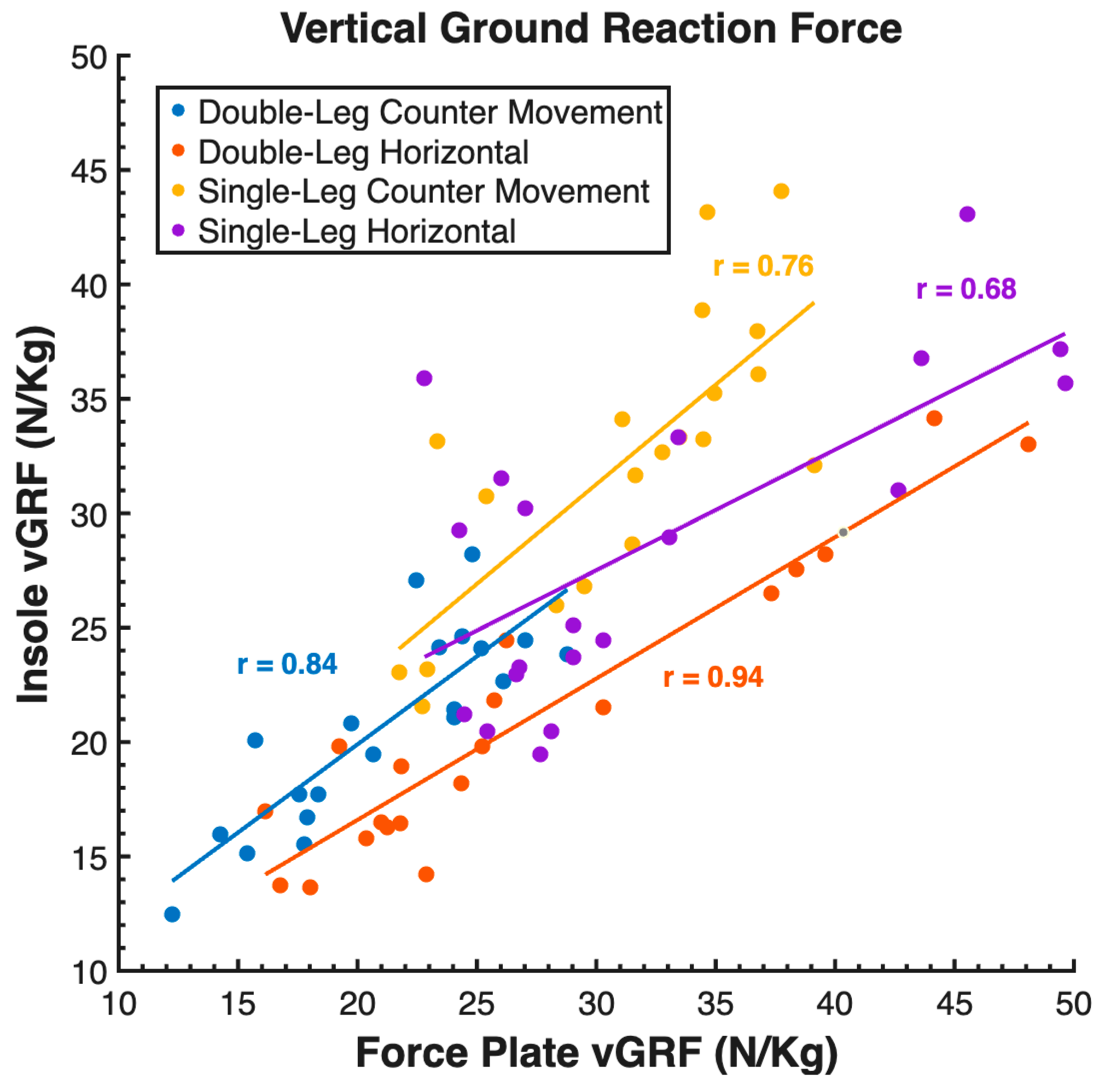
| Variable | Task | MAE (N/kg) | RMSE (N/kg) | MAPE (%) | r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRF (N/kg) | DL CMJ | 1.99 | 2.50 | 9.21 | 0.84 |
| SL CMJ | 2.94 | 4.15 | 9.72 | 0.76 | |
| DL HJ | 6.19 | 7.28 | 21.55 | 0.94 | |
| SL HJ | 6.22 | 7.25 | 19.63 | 0.68 | |
| All Tasks | 4.34 | 5.68 | 15.03 | 0.79 | |
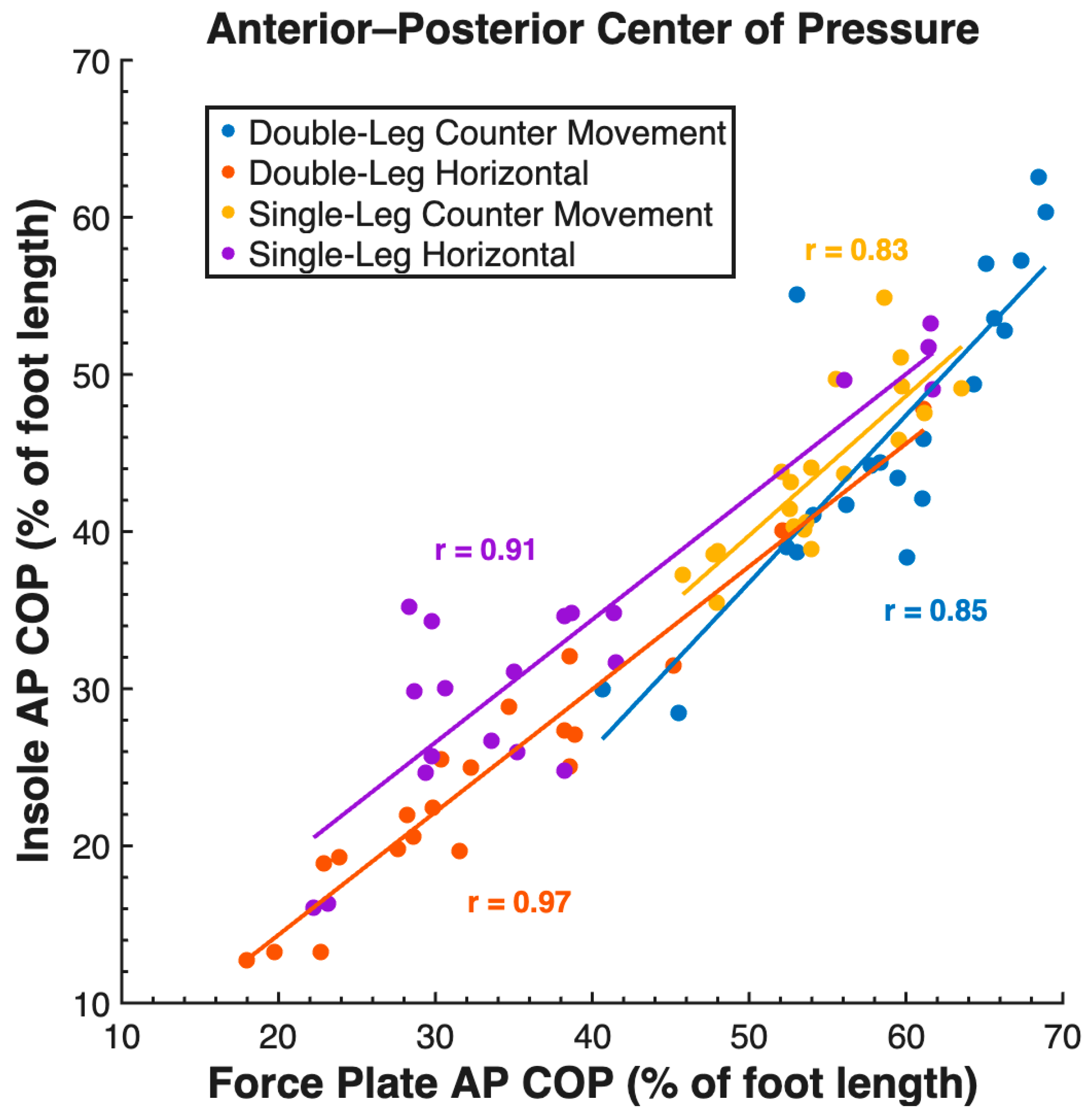
| MAE (%) | RMSE (%) | MAPE (%) | r | ||
| AP COP (%) | DL CMJ | 13 | 14 | 22.37 | 0.85 |
| SL CMJ | 11 | 11 | 19.85 | 0.83 | |
| DL HJ | 9 | 9 | 26.13 | 0.97 | |
| SL HJ | 6 | 7 | 17.29 | 0.91 | |
| All Tasks | 10 | 11 | 21.41 | 0.94 | |
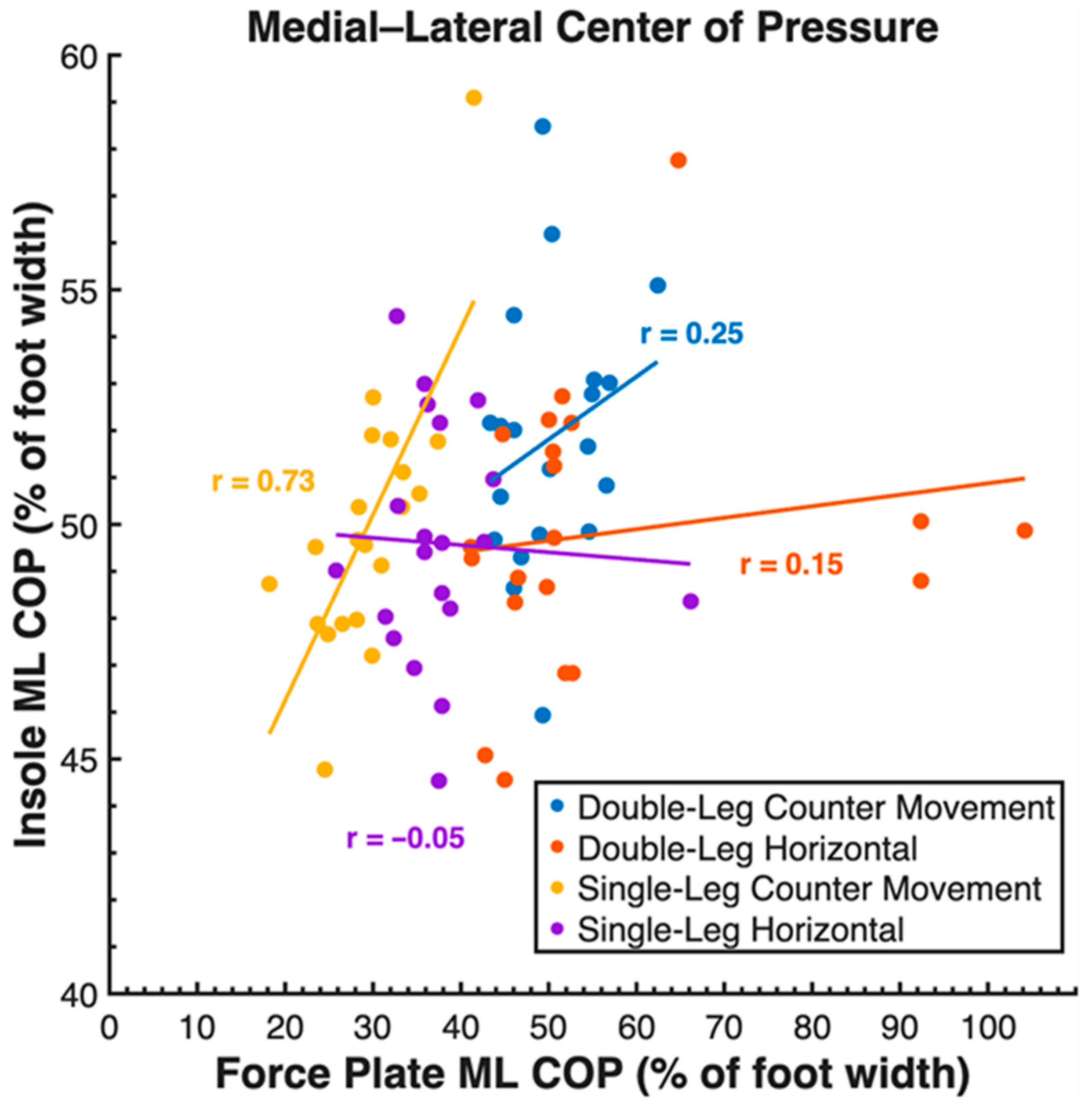
| ML COP (%) | DL CMJ | 49 | 49 | * | 0.25 |
| SL CMJ | 54 | 54 | * | 0.73 | |
| DL HJ | 45 | 46 | * | 0.15 | |
| SL HJ | 51 | 51 | * | −0.05 | |
| All Tasks | 50 | 50 | * | 0.20 |
| Variable | Task | ICC |
|---|---|---|
| GRF | DL CMJ | 0.89 |
| SL CMJ | 0.75 | |
| DL HJ | 0.89 | |
| SL HJ | 0.91 | |
| AP COP | DL CMJ | 0.88 |
| SL CMJ | 0.88 | |
| DL HJ | 0.94 | |
| SL HJ | 0.97 | |
| ML COP | DL CMJ | 0.72 |
| SL CMJ | 0.09 | |
| DL HJ | 0.82 | |
| SL HJ | 0.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
McNeese, D.; Eisner, C.; Todd, R.; Noehren, B.; Owen, M.K. Validity and Reliability of Force Insoles to Measure Center of Pressure During Return-to-Sport Testing. Sensors 2026, 26, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26010066
McNeese D, Eisner C, Todd R, Noehren B, Owen MK. Validity and Reliability of Force Insoles to Measure Center of Pressure During Return-to-Sport Testing. Sensors. 2026; 26(1):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26010066
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcNeese, Delaney, Charles Eisner, Rachel Todd, Brian Noehren, and Meredith K. Owen. 2026. "Validity and Reliability of Force Insoles to Measure Center of Pressure During Return-to-Sport Testing" Sensors 26, no. 1: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26010066
APA StyleMcNeese, D., Eisner, C., Todd, R., Noehren, B., & Owen, M. K. (2026). Validity and Reliability of Force Insoles to Measure Center of Pressure During Return-to-Sport Testing. Sensors, 26(1), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26010066






