Personalizing Seizure Detection for Individual Patients by Optimal Selection of EEG Signals
Abstract
1. Introduction
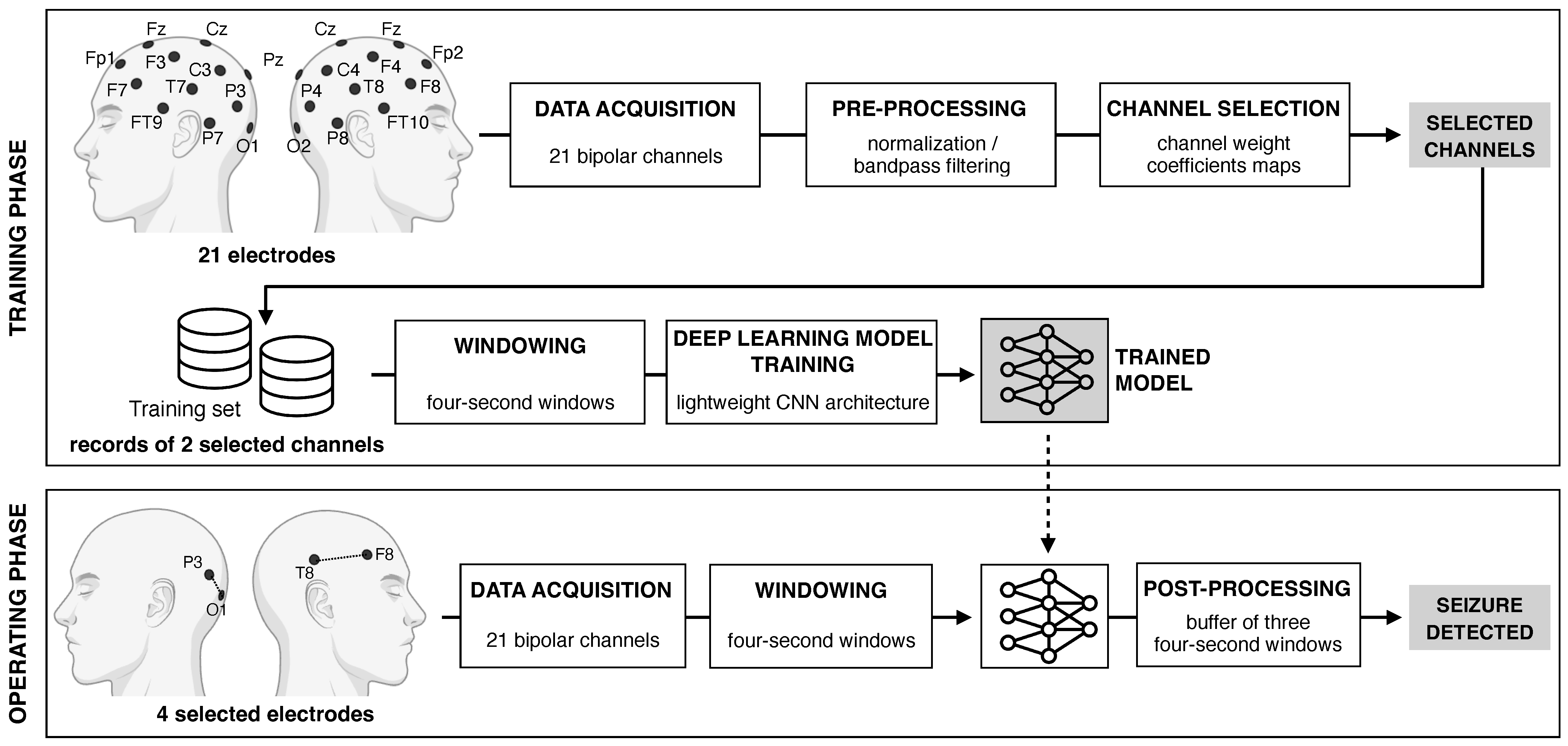
2. Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Pre-Processing
2.3. Channel Selection Procedure
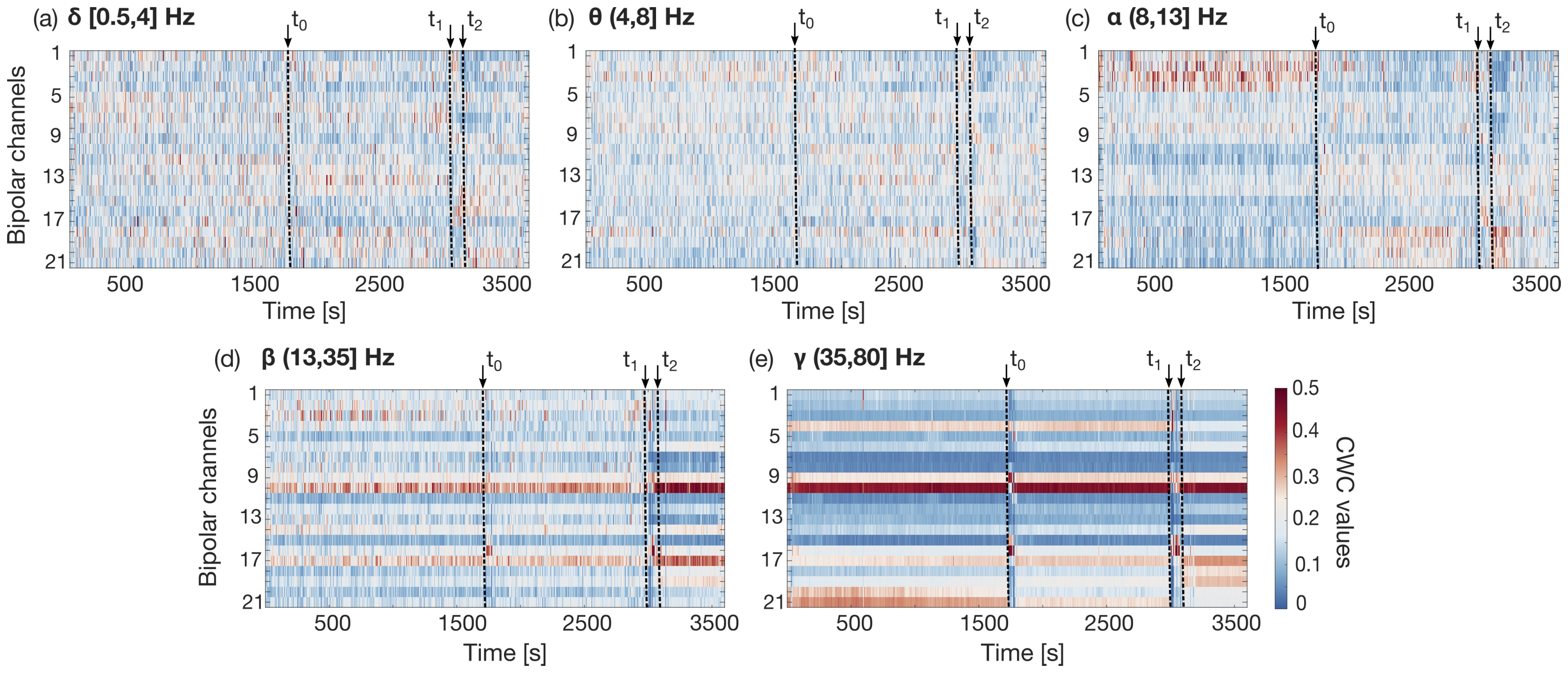
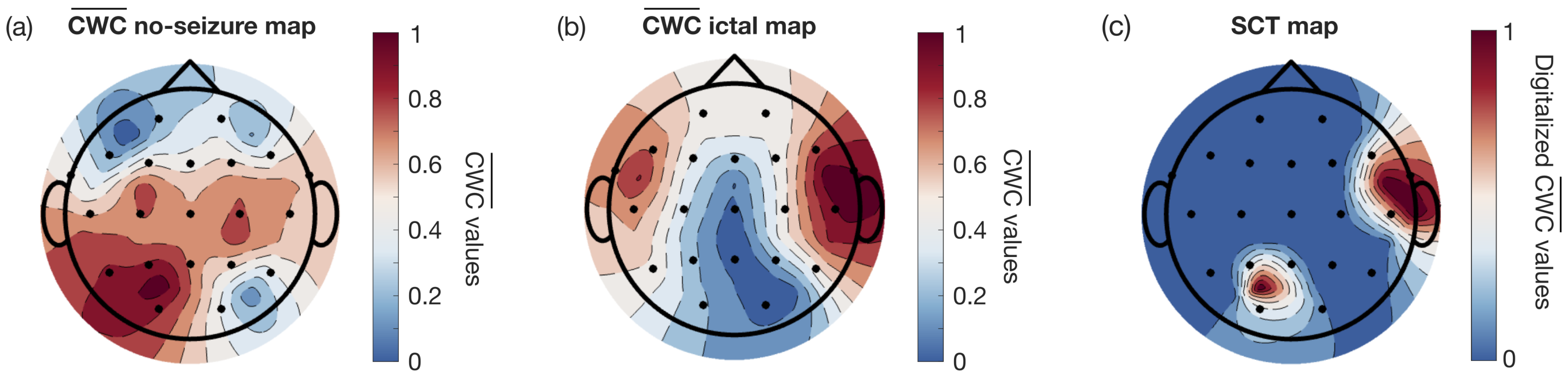
2.3.1. Channel Weight Coefficient Definition
2.3.2. Channel Weight Coefficient Evolution over Time
2.3.3. Automated Selection Algorithm
2.4. Deep Learning Model Definition and Training
2.4.1. Neural Network Architecture
2.4.2. Patient-Specific Training Strategy
2.4.3. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Patient-Specific Channel Optimization
3.2. Performance Evaluation
4. Discussion
4.1. Overall Analysis
4.2. Performance Comparison with the State-of-the-Art
4.3. Patient-Wise Analysis
| Reference | Channels | Selection Method | Classification Model | SN | Acc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qui et al. [32] | 23 | not implemented | CNN | 0.99 | N/A |
| Bahr et al. [47] | 23 | not implemented | CNN | N/A | 0.96 |
| Ke et al. [44] | 23 | not implemented | VGGNet (CNN) | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| Wang et al. [43] | 23 | not implemented | PCNN-Bi-LSTM | 0.98 | 0.99 |
| Thuwajit et al. [48] | 21 | not implemented | EEGNET-8.2 (CNN) | 0.81 | 0.96 |
| EEGWaveNet (CNN) | 0.69 | 0.98 | |||
| Chakrabarti et al. [42] | 18 | PCA | MLP | N/A | 0.87 |
| Dokare and Gupta [45] | 5-opt. | MI and RF | SVM | 0.87 | 0.98 |
| Amer et al. [20] | 4-fixed | PCC | CNN | N/A | 0.99 |
| Ingolfsson et al. [15] | 4-fixed | not implemented | EpiDeNet (CNN) | 0.69 | - |
| Gifford et al. [22] | 3-opt. | LAFS | Multi-Head Self-Attention | 0.65 | 0.85 |
| Shoka et al. [19] | 3-fixed | highest variance | SVM | N/A | 0.83 |
| Affes et al. [46] | 2-opt. | Channel Attention- | CGRNN | N/A | 0.72 |
| MLP | (CNN + GRU) | ||||
| Proposed work | 2-opt. | temporal PCA | CNN | 0.67 | 0.99 |
| 0.83 (bAcc) |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Acc | Accuracy |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| bAcc | Balanced Accuracy |
| CHB-MIT | Children’s Hospital Boston–Massachusetts Institute of Technology |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| CWC | Channel Weight Coefficient |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| FN | False Negative |
| FP | False Positive |
| FP/h | False Positive per Hour |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Neural Network |
| LAFS | Locally Adaptive Feature Selection |
| LORO | Leave-One-Record-Out |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MI | Mutual Information |
| MLP | Multi-Layer Perceptron |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PC | Principal Component |
| PCC | Pearson Correlation Coefficient |
| RF | Random Forest |
| SCT map | Selected Channels Topological Map |
| SN | Sensitivity |
| SP | Specificity |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| TN | True Negative |
| TP | True Positive |
References
- Iqbal, S.M.A.; Mahgoub, I.; Du, E.; Leavitt, M.A.; Asghar, W. Advances in healthcare wearable devices. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2021, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.A.; Li, R.; Tse, Z.T.H. Reshaping healthcare with wearable biosensors. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Bautista, J.A.; Chaparro-Cárdenas, S.L.; Esmer, C.; Huerta-Ruelas, J.A. Artificial intelligence approaches to physiological parameter analysis in the monitoring and treatment of non-communicable diseases: A review. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 87, 105463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Lim, J.; Nolan, J.K.; Lee, H.; Lee, C.H. Wearable glucose monitoring and implantable drug delivery systems for diabetes management. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teplan, M. Fundamentals of EEG measurement. Meas. Sci. Rev. 2002, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, M. Survey of emotion recognition methods using EEG information. Cogn. Robot. 2022, 2, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saegh, A.; Dawwd, S.A.; Abdul-Jabbar, J.M. Deep learning for motor imagery EEG-based classification: A review. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 63, 102172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Faust, O.; Seoni, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Barua, P.D.; Loh, H.W.; Elphick, H.; Molinari, F.; Acharya, U.R. A review of automated sleep disorder detection. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 150, 106100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averna, A.; Coelli, S.; Ferrara, R.; Cerutti, S.; Priori, A.; Bianchi, A.M. Entropy and fractal analysis of brain-related neurophysiological signals in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Eng. 2023, 20, 051001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeibi, A.; Khodatars, M.; Ghassemi, N.; Jafari, M.; Moridian, P.; Alizadehsani, R.; Acharya, U.R. Epileptic seizures detection using deep learning techniques: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopic, D.; Aminifar, A.; Atienza, D. E-Glass: A wearable system for real-time detection of epileptic seizures. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Florence, Italy, 27–30 May 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Frankel, M.A.; Lehmkuhle, M.J.; Watson, M.; Fetrow, K.; Frey, L.; Drees, C.; Spitz, M.C. Electrographic seizure monitoring with a novel, wireless, single-channel EEG sensor. Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract. 2021, 6, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, S.; Cho, B.H.; Shon, Y.-M.; Seo, D.-W.; Kim, I.Y. Semi-supervised automatic seizure detection using personalized anomaly detecting variational autoencoder with behind-the-ear EEG. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed 2022, 213, 106542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busia, P.; Cossettini, A.; Ingolfsson, T.M.; Benatti, S.; Burrello, A.; Jung, V.J.; Benini, L. Reducing false alarms in wearable seizure detection with EEGformer: A compact transformer model for MCUs. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2024, 18, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingolfsson, T.M.; Chakraborty, U.; Wang, X.; Beniczky, S.; Ducouret, P.; Benatti, S.; Benini, L. EpiDeNet: An energy-efficient approach to seizure detection for embedded systems. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Toronto, ON, Canada, 19–21 October 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Yang, J.; Sawan, M. Energy-Efficient Neural Network for Epileptic Seizure Prediction. IEEE Biomed. Eng. J. 2021, 69, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.S.; Cross, J.H.; D’souza, C.; French, J.A.; Haut, S.R.; Higurashi, N.; Zuberi, S.M. Instruction manual for the ILAE 2017 operational classification of seizure types. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaiby, T.; El-Samie, F.E.A.; Alshebeili, S.A.; Ahmad, I. A Review of Channel Selection Algorithms for EEG Signal Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 66, pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ein Shoka, A.A.; Alkinani, M.H.; El-Sherbeny, A.S.; El-Sayed, A.; Dessouky, M.M. Automated seizure diagnosis system based on feature extraction and channel selection using EEG signals. Brain Inf. 2021, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, N.S.; Belhaouari, S.B. Exploring new horizons in neuroscience disease detection through innovative visual signal analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, R.; Mukherjee, I. Efficient Seizure Prediction and EEG Channel Selection Based on Multi-Objective Optimization. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 54112–54121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifford, R.; Sollars, C.; Singh, J.; Krening, S. Locally-adaptive feature selection for nonconvulsive seizure detection. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 105, 107535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the LASSO. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Nourani, M.; Harvey, J.; Dave, H. Personalized feature selection for wearable EEG monitoring platform. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 20th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE), Cincinnati, OH, USA, 26–28 October 2020; pp. 380–386. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, Y.G.; Cho, A.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.J. Single-channel seizure detection with clinical confirmation of seizure locations using CHB-MIT dataset. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1389731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoeb, A. Application of Machine Learning to Epileptic Seizure Onset Detection and Treatment. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Homan, R.W.; Herman, J.; Purdy, P. Cerebral location of international 10–20 system electrode placement. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1987, 66, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.K. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Qiao, Y.; Duan, L.; Miao, J. Epilepsy EEG signals classification based on sparse principal component logistic regression model. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, J.; Torres, A.M.; Soria, C.; Santos, J.L. A method for removing noise from continuous brain signal recordings. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2013, 39, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K. Note on regression and inheritance in the case of two parents. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1985, 58, 240–242. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, S.; Wang, W.; Jiao, H. LightSeizureNet: A lightweight deep learning model for real-time epileptic seizure detection. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Informat. 2022, 27, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML’15), Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; Volume 37, pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Biagioni, T.; Fratello, M.; Garnier, E.; Lagarde, S.; Carron, R.; Villalon, S.M.; Pizzo, F. Interictal waking and sleep electrophysiological properties of the thalamus in focal epilepsies. Brain Commun. 2025, 7, fcaf102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingolfsson, T.M.; Benatti, S.; Wang, X.; Bernini, A.; Ducouret, P.; Ryvlin, P.; Cossettini, A. Minimizing artifact-induced false-alarms for seizure detection in wearable EEG devices with gradient-boosted tree classifiers. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.; Angelova, M.; Karmakar, C. Epileptic seizure detection using CHB-MIT dataset: The overlooked perspectives. Royal Soc. Open Sci. 2024, 11, 230601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmat, F.; Zulkafli, Z.; Ishak, A.J.; Abdul Rahman, R.Z.; De Stercke, S.; Buytaert, W.; Tahir, W.; Ab Rahman, J.; Ibrahim, S.; Ismail, S. Supervised feature selection using principal component analysis. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2024, 66, 1955–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Dayalane, S.; Mathivanan, S.K.; Rajadurai, H.; Jayagopal, P.; Dalu, G.T. Detection and classification of adult epilepsy using hybrid deep learning approach. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Wong, S.M.; Iimura, Y.; Ochi, A.; Doesburg, S.M.; Otsubo, H. Spatiotemporal changes in regularity of gamma oscillations contribute to focal ictogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabeff, V.; Teijeiro, T.; Zapater, M.; Cammoun, L.; Rheims, S.; Ryvlin, P.; Atienza, D. Interpreting deep learning models for epileptic seizure detection on EEG signals. Artif. Intell. Med. 2021, 117, 102084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Swetapadma, A.; Pattnaik, P.K. A channel selection method for epileptic EEG signals. In Emerging Technologies in Data Mining and Information Security, Proceedings of IEMIS 2018, Kolkata, India, 23–25 February 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 565–573. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Zhuo, W.; Xie, Y. An Epileptic EEG Detection Method Based on Data Augmentation and Lightweight Neural Network. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2023, 12, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, H.; Chen, D.; Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Shah, T.; Ranjan, R. Towards Brain Big Data Classification: Epileptic EEG Identification With a Lightweight VGGNet on Global MIC. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 14722–14733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokare, I.; Gupta, S. Optimized seizure detection leveraging band-specific insights from limited EEG channels. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2025, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affes, A.; Mdhaffar, A.; Triki, C.; Jmaiel, M.; Freisleben, B. Personalized attention-based EEG channel selection for epileptic seizure prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 206, 117733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, A.; Schneider, M.; Francis, M.A.; Lehmann, H.M.; Barg, I.; Buschhoff, A.S.; Faupel, F. Epileptic Seizure Detection on an Ultra-Low-Power Embedded RISC-V Processor Using a Convolutional Neural Network. Biosensors 2021, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuwajit, P.; Rangpong, P.; Sawangjai, P.; Autthasan, P.; Chaisaen, R.; Banluesombatkul, N.; Wilaiprasitporn, T. EEGWaveNet: Multiscale CNN-Based Spatiotemporal Feature Extraction for EEG Seizure Detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 5547–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Layer | Input Shape | Output Shape | Filters | Kernel Size | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conv2D | 4 | 20 | |||
| BatchNorm2D | 8 | ||||
| MaxPool | |||||
| Conv2D | 16 | 1040 | |||
| BatchNorm2D | 32 | ||||
| MaxPool | |||||
| Conv2D | 16 | 2064 | |||
| BatchNorm2D | 32 | ||||
| MaxPool | |||||
| Conv2D | 16 | 4112 | |||
| BatchNorm2D | 32 | ||||
| MaxPool | |||||
| Conv2D | 16 | 2064 | |||
| BatchNorm2D | 32 | ||||
| AverPool | |||||
| Flatten | 16 | ||||
| Dense | 16 | 2 | 34 |
| Patient | Channel A | Channel B | Patient | Channel A | Channel B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chb01 | P3-O1 | F8-T8 | 0.32 | chb13 | P4-O2 | Fp1-F7 | 0.29 |
| chb02 | T7-P7 | T8-P8 | 0.32 | chb14 | T8-P8 | Fp1-F7 | 0.24 |
| chb03 | P8-O2 | T7-P7 | 0.29 | chb15 | Cz-Pz | T7-P7 | 0.30 |
| chb04 | Cz-Pz | T8-P8 | 0.33 | chb16 | P7-O1 | C3-P3 | 0.25 |
| chb05 | Cz-Pz | P8-O2 | 0.28 | chb17 | C4-P4 | P4-O2 | 0.31 |
| chb06 | F8-T8 | T8-P8 | 0.47 | chb18 | C4-P4 | T8-P8 | 0.32 |
| chb07 | Cz-Pz | P8-O2 | 0.32 | chb19 | Cz-Pz | T8-FT10 | 0.26 |
| chb08 | P8-O2 | F4-C4 | 0.27 | chb20 | P8-O2 | T7-FT9 | 0.21 |
| chb09 | P7-O1 | T8-P8 | 0.29 | chb21 | T8-P8 | C3-P3 | 0.43 |
| chb10 | T8-P8 | T7-P7 | 0.29 | chb22 | F4-C4 | T7-P7 | 0.27 |
| chb11 | Fz-Cz | T7-P7 | 0.29 | chb23 | P8-O2 | T7-P7 | 0.23 |
| chb12 | F3-C3 | F4-C4 | 0.23 | chb24 | C4-P4 | F8-T8 | 0.31 |
| Patient | Configuration | Segment Level | Event Level | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP | SN | bAcc | Delay [s] | FP/h | Detected Seizures | |||
| chb04 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.18 ± 0.21 | 0.59 ± 0.11 | 40.0 ± 25.5 | 0.33 | 2/4 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.71 ± 0.27 | 0.85 ± 0.13 | 28.8 ± 32.9 | 0.11 | 4/4 | ||
| chb13 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 0.55 ± 0.44 | 0.77 ± 0.22 | 9.7 ± 3.0 | 0.45 | 9/10 | |
| 2-selected | 0.99 ± 0.01 | 0.65 ± 0.31 | 0.82 ± 0.16 | 9.7 ± 2.5 | 0.36 | 10/10 | ||
| chb14 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.32 ± 0.41 | 0.66 ± 0.20 | 6.5 ± 0.58 | 0.04 | 4/8 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.53 ± 0.31 | 0.76 ± 0.16 | 6.6 ± 1.0 | 0.00 | 7/8 | ||
| chb15 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.02 | 0.73 ± 0.19 | 0.87 ± 0.09 | 11.5 ± 8.2 | 0.15 | 19/20 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.02 | 0.82 ± 0.16 | 0.91 ± 0.08 | 6.7 ± 5.0 | 0.21 | 20/20 | ||
| chb17 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.28 ± 0.25 | 0.64 ± 0.13 | 39.5 ± 7.8 | 0.05 | 2/3 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.46 ± 0.10 | 0.73 ± 0.05 | 26.3 ± 6.0 | 0.00 | 3/3 | ||
| chb18 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.02 | 0.45 ± 0.38 | 0.72 ± 0.18 | 13.5 ± 6.6 | 0.46 | 4/6 | |
| 2-selected | 0.99 ± 0.04 | 0.55 ± 0.31 | 0.76 ± 0.15 | 16.2 ± 13.1 | 0.11 | 5/6 | ||
| chb01 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.86 ± 0.19 | 0.93 ± 0.10 | 9.0 ± 6.9 | 0.00 | 7/7 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.91 ± 0.10 | 0.95 ± 0.05 | 6.4 ± 3.4 | 0.00 | 7/7 | ||
| chb02 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.93 ± 0.08 | 0.96 ± 0.04 | 11.0 ± 6.6 | 0.00 | 3/3 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.93 ± 0.09 | 0.96 ± 0.04 | 8.3 ± 2.9 | 0.08 | 3/3 | ||
| chb03 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 0.77 ± 0.14 | 0.89 ± 0.07 | 17.4 ± 6.5 | 0.03 | 7/7 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 0.92 ± 0.11 | 0.96 ± 0.05 | 8.0 ± 5.8 | 0.08 | 7/7 | ||
| chb05 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.88 ± 0.12 | 0.94 ± 0.06 | 9.8 ± 4.0 | 0.08 | 5/5 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.83 ± 0.14 | 0.92 ± 0.07 | 21.8 ± 16.3 | 0.00 | 5/5 | ||
| chb07 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.57 ± 0.22 | 0.79 ± 0.11 | 14.3 ± 5.7 | 0.00 | 3/3 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.59 ± 0.31 | 0.79 ± 0.16 | 28.3 ± 12.3 | 0.03 | 3/3 | ||
| chb08 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.83 ± 0.15 | 0.91 ± 0.07 | 11.2 ± 3.27 | 0.20 | 5/5 | |
| 2-selected | 0.99 ± 0.02 | 0.85 ± 0.07 | 0.91 ± 0.05 | 15.2 ± 3.11 | 0.03 | 5/5 | ||
| chb09 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.94 ± 0.03 | 0.97 ± 0.01 | 7.3 ± 1.7 | 0.00 | 4/4 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.93 ± 0.03 | 0.97 ± 0.01 | 8.3 ± 2.5 | 0.00 | 4/4 | ||
| chb10 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.96 ± 0.07 | 0.98 ± 0.03 | 6.0 ± 2.3 | 0.00 | 7/7 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.94 ± 0.08 | 0.97 ± 0.04 | 4.9 ± 3.0 | 0.00 | 7/7 | ||
| chb11 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.83 ± 0.25 | 0.91 ± 0.12 | 3.0 ± 1.7 | 0.03 | 3/3 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.82 ± 0.08 | 0.91 ± 0.04 | 5.0 ± 5.2 | 0.17 | 3/3 | ||
| chb19 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.94 ± 0.03 | 0.97 ± 0.01 | 9.3 ± 3.8 | 0.10 | 3/3 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.83 ± 0.02 | 0.91 ± 0.00 | 16.7 ± 1.5 | 0.14 | 3/3 | ||
| chb20 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.59 ± 0.42 | 0.80 ± 0.21 | 11.9 ± 6.9 | 0.03 | 7/8 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.57 ± 0.21 | 0.78 ± 0.10 | 13.9 ± 5.0 | 0.07 | 7/8 | ||
| chb22 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.89 ± 0.17 | 0.94 ± 0.08 | 12.3 ± 11.0 | 0.00 | 3/3 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.82 ± 0.12 | 0.91 ± 0.06 | 16.3 ± 7.0 | 0.00 | 3/3 | ||
| chb23 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 0.86 ± 0.13 | 0.93 ± 0.06 | 12.0 ± 5.9 | 0.18 | 7/7 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 0.86 ± 0.05 | 0.93 ± 0.03 | 9.1 ± 2.4 | 0.18 | 7/7 | ||
| chb24 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.52 ± 0.27 | 0.76 ± 0.13 | 9.8 ± 3.2 | 0.14 | 13/16 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.50 ± 0.30 | 0.75 ± 0.15 | 9.08 ± 2.53 | 0.14 | 13/16 | ||
| chb06 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.63 ± 0.35 | 0.81 ± 0.17 | 7.9 ± 1.7 | 0.07 | 8/10 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.24 ± 0.32 | 0.62 ± 0.16 | 9.0 ± 2.16 | 0.00 | 4/10 | ||
| chb12 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 0.42 ± 0.31 | 0.71 ± 0.15 | 11.4 ± 5.9 | 0.29 | 20/27 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 0.38 ± 0.20 | 0.69 ± 0.13 | 11.6 ± 7.9 | 0.33 | 19/27 | ||
| chb21 | 4-temporal | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.65 ± 0.24 | 0.82 ± 0.12 | 14.3 ± 14.4 | 0.03 | 4/4 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.29 ± 0.28 | 0.64 ± 0.14 | 26.0 ± 18.5 | 0.03 | 3/4 | ||
| chb16 | 4-temporal | 0.99 ± 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.50 ± 0.00 | - | 0.88 | 0/8 | |
| 2-selected | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.50 ± 0.00 | - | 0.00 | 0/8 | ||
| Overall | 4-temporal | 1 ± 0.01 | 0.66 ± 0.32 | 0.83 ± 0.16 | 11.38 ± 8.02 | 0.15 ± 0.21 | 149/181 | |
| 2-selected | 1 ± 0.01 | 0.67 ± 0.31 | 0.83 ± 0.16 | 11.47 ± 9.75 | 0.10 ± 0.11 | 152/181 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrara, R.; Giaquinto, M.; Percannella, G.; Rundo, L.; Saggese, A. Personalizing Seizure Detection for Individual Patients by Optimal Selection of EEG Signals. Sensors 2025, 25, 2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092715
Ferrara R, Giaquinto M, Percannella G, Rundo L, Saggese A. Personalizing Seizure Detection for Individual Patients by Optimal Selection of EEG Signals. Sensors. 2025; 25(9):2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092715
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrara, Rosanna, Martino Giaquinto, Gennaro Percannella, Leonardo Rundo, and Alessia Saggese. 2025. "Personalizing Seizure Detection for Individual Patients by Optimal Selection of EEG Signals" Sensors 25, no. 9: 2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092715
APA StyleFerrara, R., Giaquinto, M., Percannella, G., Rundo, L., & Saggese, A. (2025). Personalizing Seizure Detection for Individual Patients by Optimal Selection of EEG Signals. Sensors, 25(9), 2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092715








