A Partial Discharge Detection Approach in Distribution Cabinets Using a Mach–Zehnder Interferometer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mach–Zehnder Detection Principle
2.1. Mach–Zehnder Fiber Interference
2.2. Hilbert–Huang Transform (HHT)
3. MZI-Based Optical Fiber Sensing Experiment Design for PD Detection
3.1. Fiber Ring Diameter and Acousto-Optic Effect
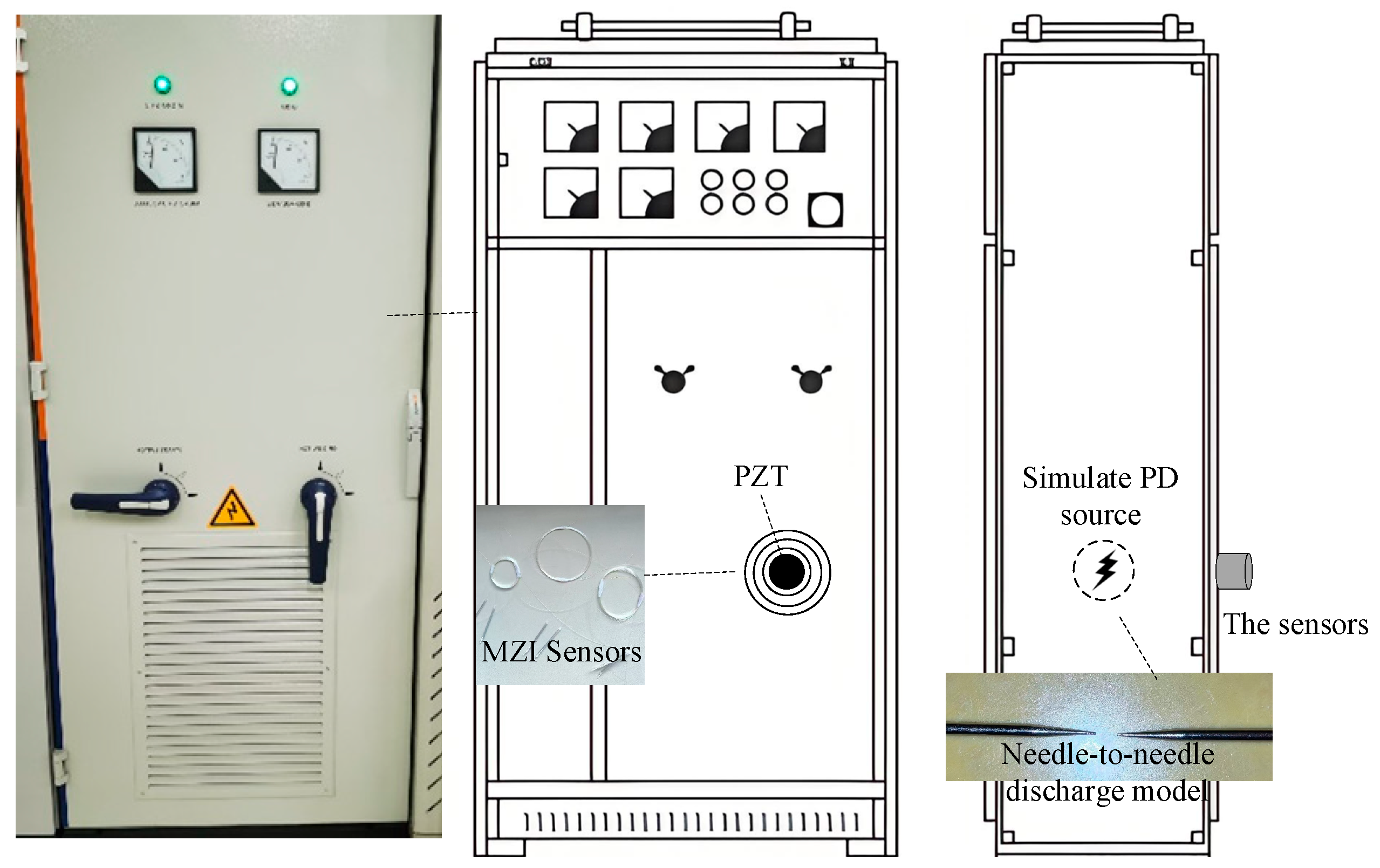
3.2. Experimental Platform Design
3.3. MZI and Its Sensor Setup
4. Experimental Analysis
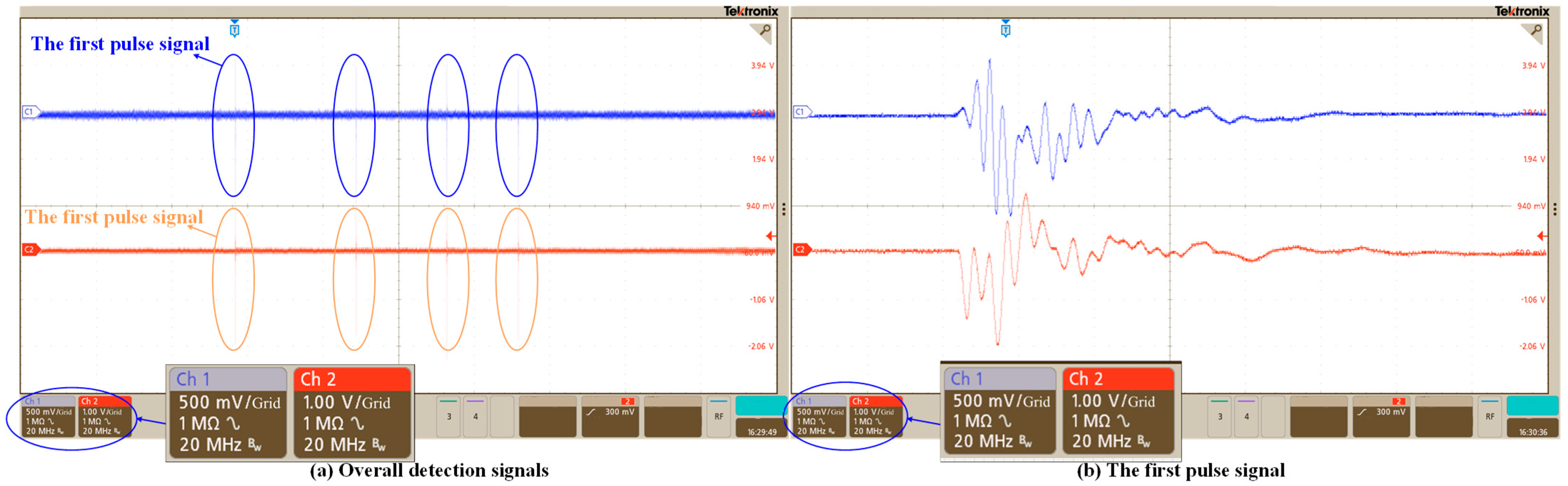
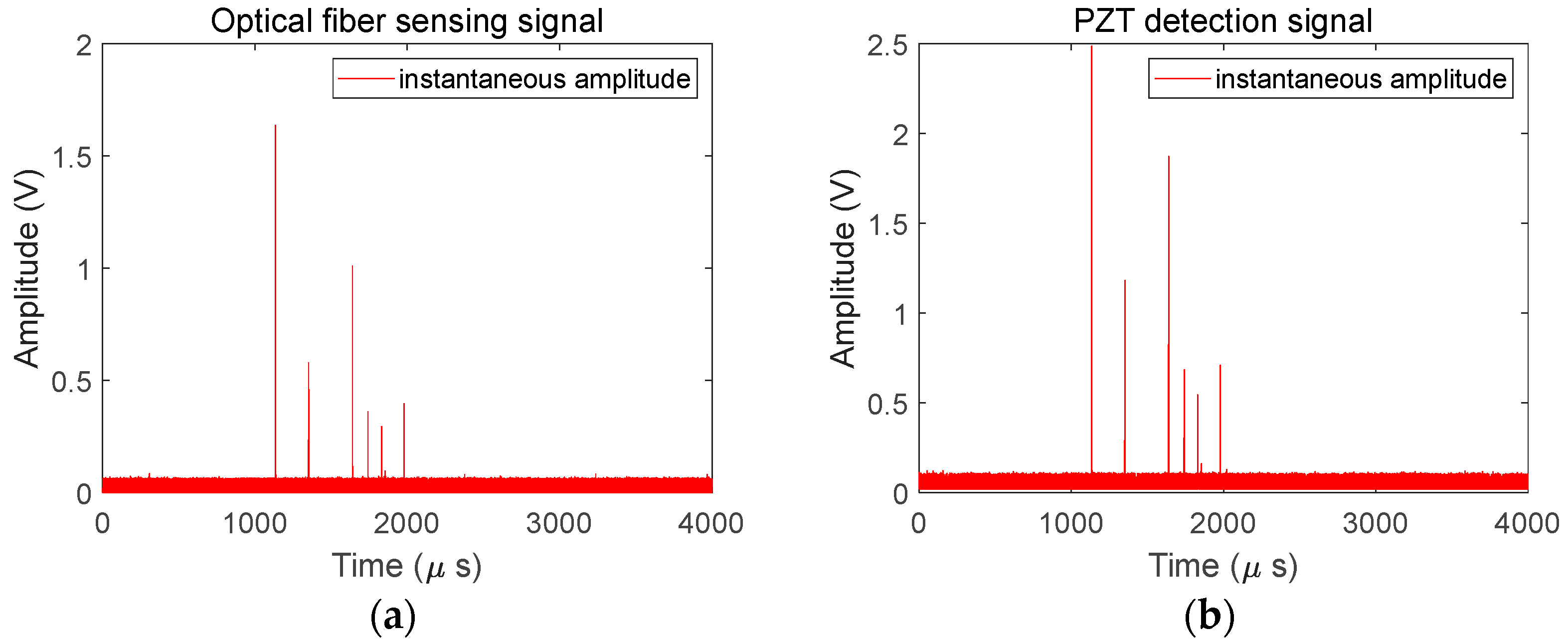
4.1. Time–Frequency-Domain Analysis of Fiber-Optic MZI Sensing
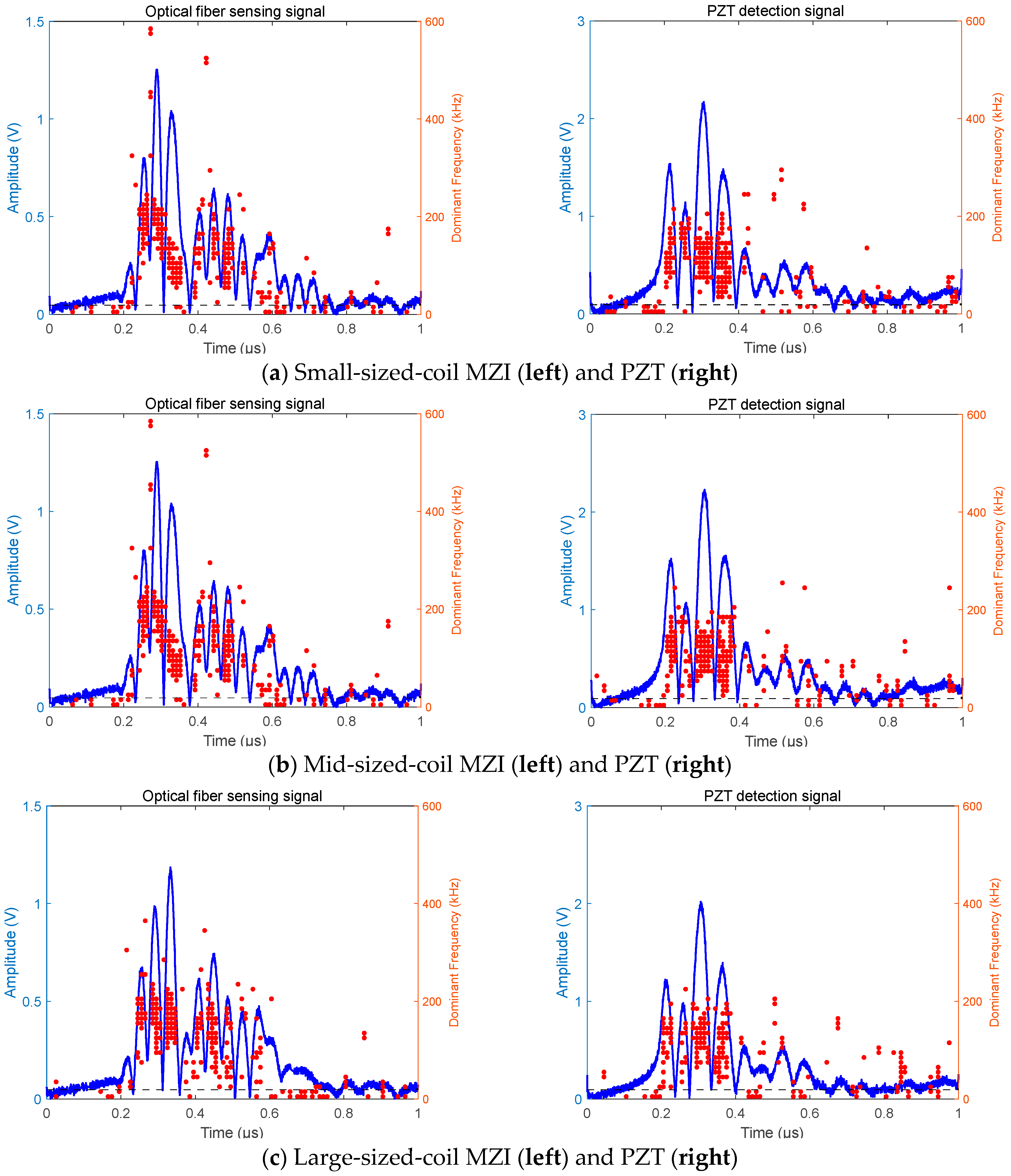
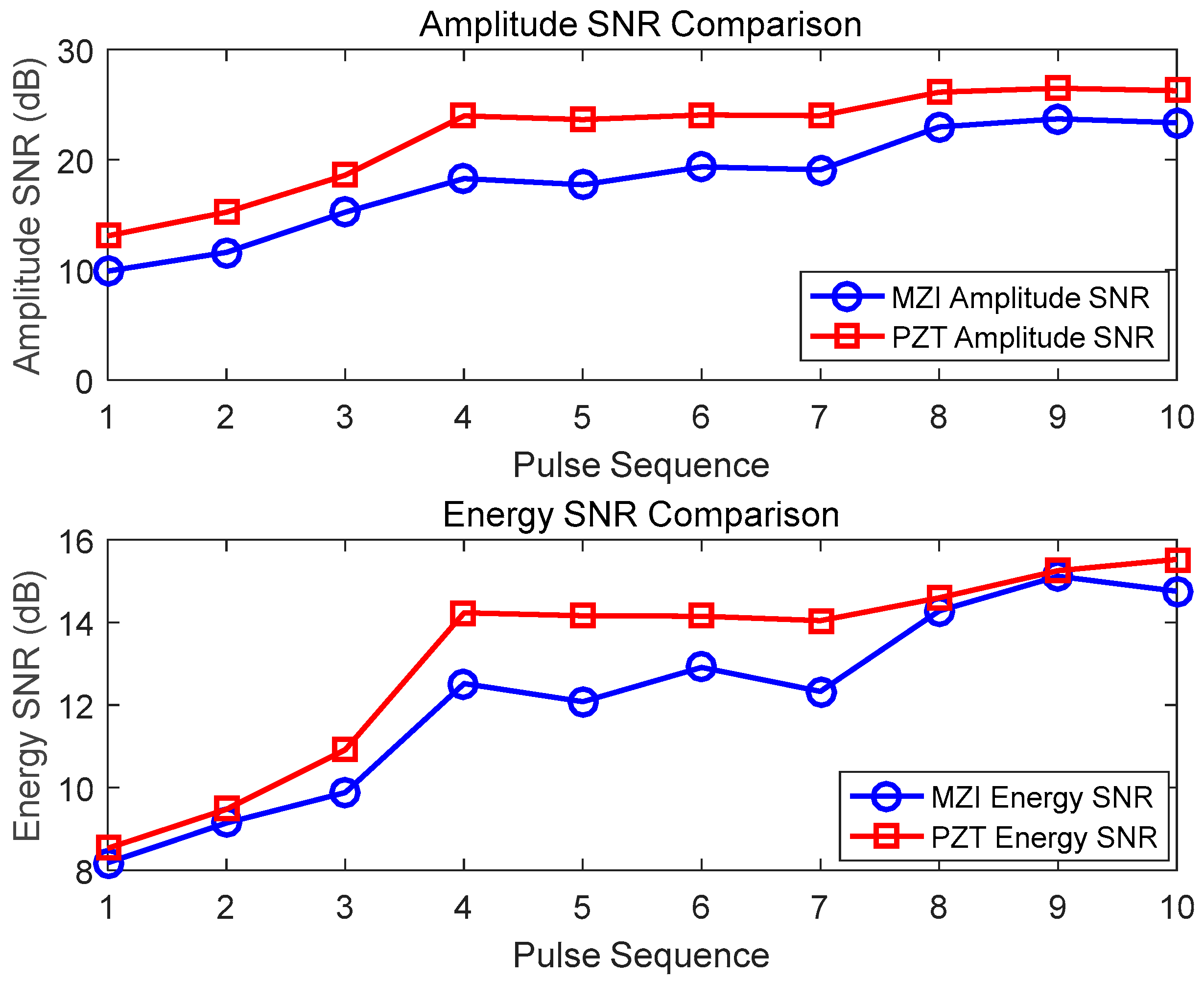
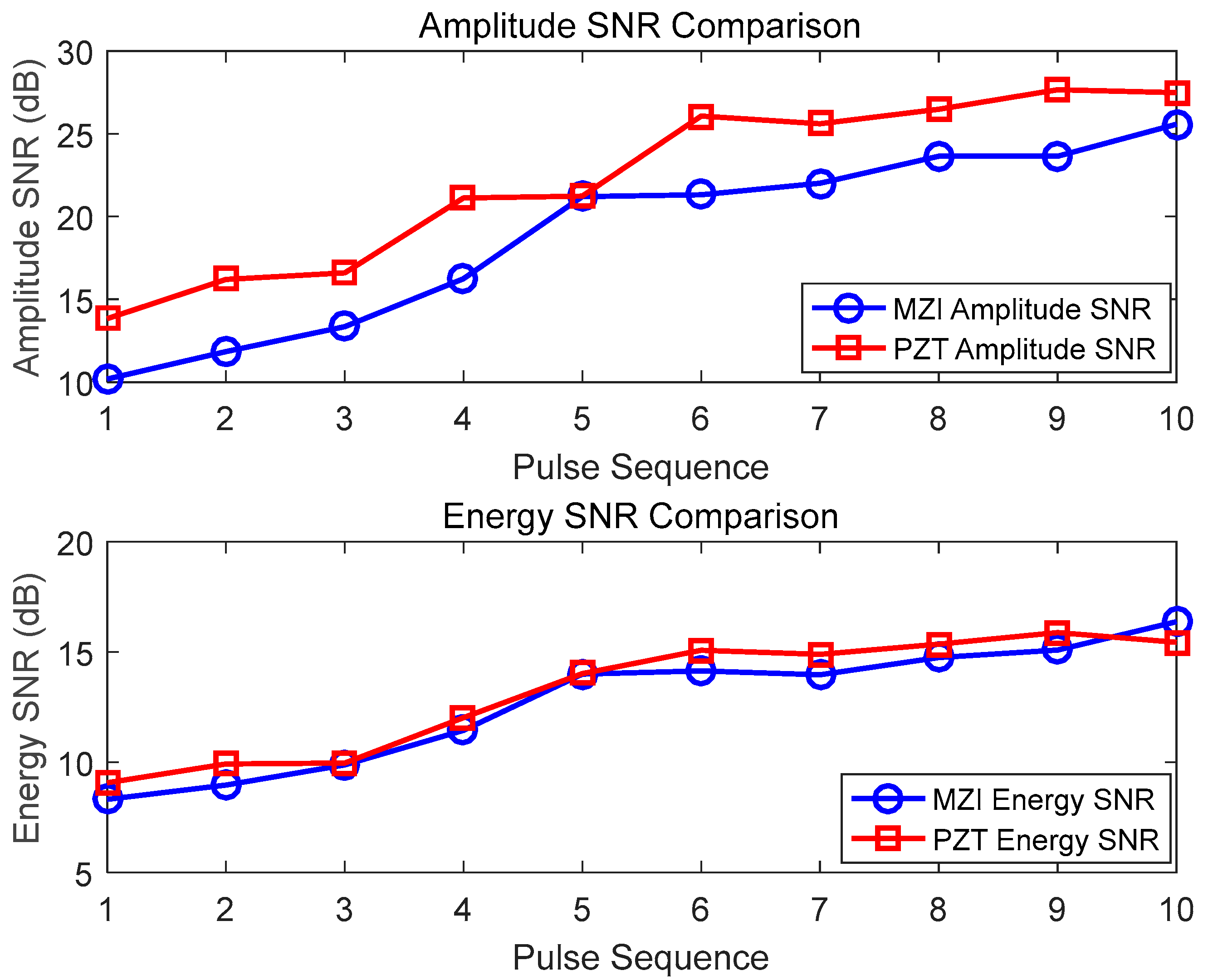
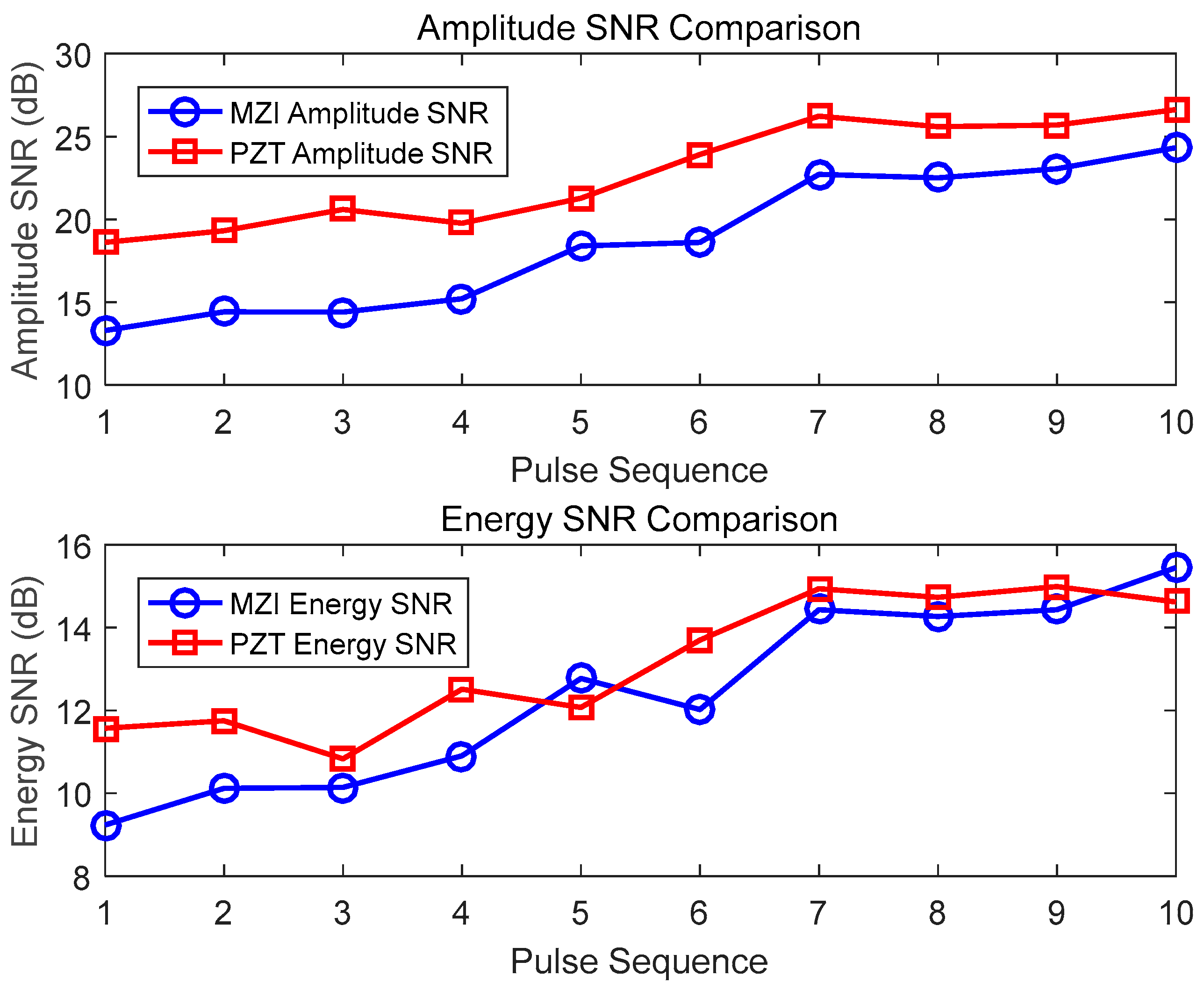
4.2. The Impact of Sensor Coil Diameter on PD Detection
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The fiber MZI technology can be used to detect the PD of the distribution cabinet, and the amplitude of the PD acoustic wave in the time domain detected by the fiber MZI is consistent with the PZT.
- (2)
- The length of the PD acoustic pulse in the distribution cabinet is 0.4 microseconds, and the main energy is concentrated in the first 0.2 microseconds of the pulse. Based on the distribution of ultrasonic signal and PD determination requirements, the effective time length of a single PD pulse detected by the fiber MZI is 0.4 microseconds, and the effective pulse length of a single PD pulse detected by the PZT is 0.2 microseconds. Thus, the frequency detection range of the fiber MZI is wider than that of the PZT.
- (3)
- The sensing characteristics of optical fiber coil sensors with diameters of 5 cm, 8 cm, and 10 cm, all with a length of 10 m, are compared. The results show that the higher the acoustic wave frequency, the more sensitive the response to the size of the coil diameter. In a comprehensive analysis of the frequency characteristics, the SNR of the pulse amplitude, and the SNR of the pulse energy, the optical fiber sensor with a diameter of 8 cm in this paper performs the best.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yadam, Y.R.; Ramanujam, S.; Arunachalam, K. An Ultrawideband Conical Monopole with Radome for Detection of Partial Discharges. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 18764–18772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Yan, J.; Zhao, D.; Lu, L.; Geng, Y. Gas-insulated switchgear partial discharge acoustic–electric joint localisation method based on the Salp Swarm Algorithm and least squares estimation. Measurement 2024, 225, 114020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; He, Y.; Farhan, A.; Wu, Y.; Tong, J. A method for the localization of partial discharge sources in transformers using TDOA and truncated singular value decomposition. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 6741–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, H.; Wang, Q.; Niu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, J. A Partial Discharge Localization Method Based on the Improved Artificial Fish Swarms Algorithm. Energies 2023, 16, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, J.; Xu, W. Active acoustic measurement of sound speed for quantifying underwater gaseous bubble emissions. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 224, 110132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Ren, M.; Chen, R.; Yu, J.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Dong, M. Multispectral optical partial discharge detection, recognition, and assessment. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 7002911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, J.; Liu, K.; Wang, R.; Sun, J.; Liu, T. Partial discharge monitoring by improved PGC-arctan algorithm. Opt. Commun. 2024, 570, 130879. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Bie, Y.; Ranjan, P.; Schwarz, H. Partial discharge detection and diagnosis of transformer bushing based on UHF method. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 16798–16806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meitei, S.N. Partial Discharge Detection Using Piezoelectric Sensors on Power Transformer: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 13730–13742. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, A.R.; Lebedev, N.; Concettoni, E.; Luna, S.; Rosignoli, F.; Cavallini, A.; Rumi, A. PD detection in inverter-fed machines using acoustic emission sensors: A preliminary investigation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference (EIC), Knoxville, TN, USA, 19–23 June 2022; pp. 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QLin, Q.; Lyu, F.; Yu, S.; Xiao, H.; Li, X. Optimized Denoising Method for Weak Acoustic Emission Signal in Partial Discharge Detection. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2022, 29, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Wu, S. Detection Study on Propagation Characteristics of Partial Discharge Optical Signal in GIS. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 7005912. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Jia, J.; Hu, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y. Research on partial discharge state detection in GIS based on Internet of Things technology. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1549, 042012. [Google Scholar]
- Ilkhechi, H.D.; Samimi, M.H. Applications of the acoustic method in partial discharge measurement: A review. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2021, 28, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, K.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Ranjan, P.; Zhang, C. Partial discharge detection and sensitivity improvement for bushing based on optical interference technique. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2021, 37, 2797–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, I.B.V.; Weber, G.H.; Gomes, D.F.; Galvão, J.R.; da Silva, M.J.; Pipa, D.R.; da Silva, J.C.C. Electric discharge detection and localization using a distributed optical fiber vibration sensor. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2020, 58, 102266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.M.; Zhou, H.Y.; Shi, C.; Li, Y.B.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.R.; Zheng, Q. Distributed Partial Discharge Detection in a Power Transformer Based on Phase-Shifted FBG. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 2788–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lv, J.; Li, D.; Xiong, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y. MEMS-on-fiber ultrasonic sensor with two resonant frequencies for partial discharges detection. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 18431–18439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z. Surface charge accumulation on a real size epoxy insulator with bouncing metal particle under DC voltage. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2021, 49, 2166–2175. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, T.; Xiao, J.; Yang, L. A Partial Discharge Detection System for XLPE Cable Terminals and Acoustic Wave Sensing Characteristics Based on Fiber Optic Mach-Zehnder Interferometer. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 21782–21790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongne, B.B.F.; Mengounou, G.M.; Nkouetcha, E.T.; Imano, A.M. Effect of sensor position on the measurement of acoustic wave produced by partial discharges. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25974. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Ma, G.M.; Qin, W.Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, Z.Q.; Jiang, J. A Multiplexing Optical Partial Discharge Sensing System for Power Transformer Using a Single Photodetector. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2021, 36, 1911–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada-Roman, J.; Garcia-Souto, J.A.; Rubio-Serrano, J. Fiber Optic Sensor for Acoustic Detection of Partial Discharges in Oil-Paper Insulated Electrical Systems. Sensors 2012, 12, 4793–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; He, H.; Wei, X. Ultrasonic Fiber Sensing Method for Partial Discharge Detection. Piezoelectrics Acoustooptics 2017, 39, 190–193. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Hao, Y.; Shen, Z.; Tan, H.; Li, L. Fiber Optic Mach–Zehnder Interferometer Sensor With Acoustic Enhancement for Partial Discharge Acoustic Emission Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 40873–40880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.M.; Zhou, H.Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.R.; Yin, Y.; Wu, Y.Y. A High Sensitivity Optical Fiber Sensor for GIS Partial Discharge Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 9235–9243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC TS 62478; High Voltage Test Techniques—Measurement of Partial Discharges by Electromagnetic and Acoustic Methods. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X. A Partial Discharge Detection Approach in Distribution Cabinets Using a Mach–Zehnder Interferometer. Sensors 2025, 25, 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072265
Wang J, Zhang Y, Gu X. A Partial Discharge Detection Approach in Distribution Cabinets Using a Mach–Zehnder Interferometer. Sensors. 2025; 25(7):2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072265
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Junliang, Ying Zhang, and Xiang Gu. 2025. "A Partial Discharge Detection Approach in Distribution Cabinets Using a Mach–Zehnder Interferometer" Sensors 25, no. 7: 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072265
APA StyleWang, J., Zhang, Y., & Gu, X. (2025). A Partial Discharge Detection Approach in Distribution Cabinets Using a Mach–Zehnder Interferometer. Sensors, 25(7), 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072265






